Goa MLAs 1980–1984 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of
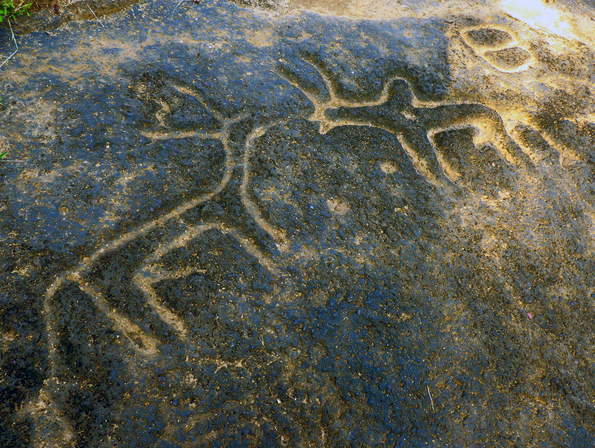 Rock art engravings found in Goa are one of the earliest known traces of human life in India. Goa, situated within the Shimoga-Goa Greenstone Belt in the Western Ghats (an area composed of metavolcanics, iron formations and ferruginous quartzite), yields evidence for Acheulean occupation.
Rock art engravings found in Goa are one of the earliest known traces of human life in India. Goa, situated within the Shimoga-Goa Greenstone Belt in the Western Ghats (an area composed of metavolcanics, iron formations and ferruginous quartzite), yields evidence for Acheulean occupation.
Mahadev Temple, Tambdi Surla (12th century).jpg, The Mahadev Temple, attributed to the Kadambas of Goa, in what is today Bhagwan Mahaveer Sanctuary and Mollem National Park
Kadamba.PNG, Gold coins issued by the Kadamba king of Goa, Shivachitta Paramadideva, 1147–1187 CE
 In 1510, the Portuguese defeated the ruling Bijapur sultan Yusuf Adil Shah with the help of a local ally, Timoji, a privateer. They set up a permanent settlement in ''Velha Goa'' (Old Goa). This was the beginning of Portuguese colonial rule in Goa that would last for four and a half centuries, until its annexation by India in 1961. The Goa Inquisition, a formal tribunal, was established in 1560, and was finally abolished in 1812.
From the latter decades of the eighteenth century, the territory of Goa was composed of two segments: the central nucleus of the '' Velhas Conquistas'' (Old Conquests)—Bardes, Ilhas de Goa, and Salcette—which territories had been under Portuguese administration since the sixteenth century; and the '' Novas Conquistas'' (New Conquests)—Bicholim, Canacona, Pernem, Quepem, Sattari, and Sanguem—territories which had been successively added through the eighteenth century.
In 1843, the Portuguese moved the capital to the ''Cidade da Nova Goa'' (City of New Goa), today known as Panaji (Panjim), from ''Velha Goa'' ( Old Goa). By the mid-18th century, Portuguese expansions lost other possessions in India until their borders stabilised and formed the Goa, Daman and Diu, which included Silvassa prior to the Annexation, it was known as ''Estado da Índia'' in Portuguese, that is the "State of Portuguese India".
In 1510, the Portuguese defeated the ruling Bijapur sultan Yusuf Adil Shah with the help of a local ally, Timoji, a privateer. They set up a permanent settlement in ''Velha Goa'' (Old Goa). This was the beginning of Portuguese colonial rule in Goa that would last for four and a half centuries, until its annexation by India in 1961. The Goa Inquisition, a formal tribunal, was established in 1560, and was finally abolished in 1812.
From the latter decades of the eighteenth century, the territory of Goa was composed of two segments: the central nucleus of the '' Velhas Conquistas'' (Old Conquests)—Bardes, Ilhas de Goa, and Salcette—which territories had been under Portuguese administration since the sixteenth century; and the '' Novas Conquistas'' (New Conquests)—Bicholim, Canacona, Pernem, Quepem, Sattari, and Sanguem—territories which had been successively added through the eighteenth century.
In 1843, the Portuguese moved the capital to the ''Cidade da Nova Goa'' (City of New Goa), today known as Panaji (Panjim), from ''Velha Goa'' ( Old Goa). By the mid-18th century, Portuguese expansions lost other possessions in India until their borders stabilised and formed the Goa, Daman and Diu, which included Silvassa prior to the Annexation, it was known as ''Estado da Índia'' in Portuguese, that is the "State of Portuguese India".
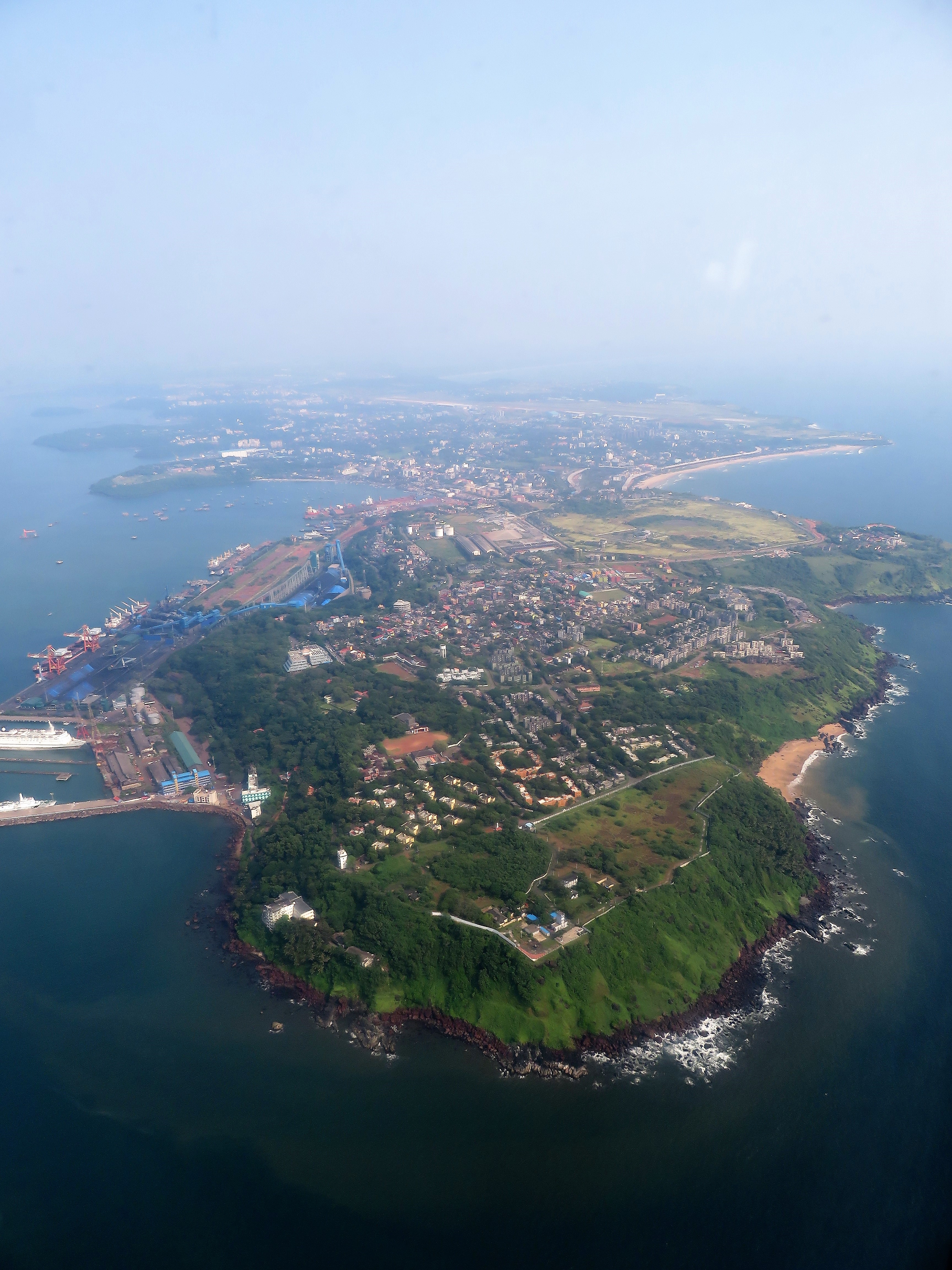
 Goa encompasses an area of . It lies between the latitudes 14°53′54″ N and 15°40′00″ N and longitudes 73°40′33″ E and 74°20′13″ E.
Goa is a part of the coastal country known as the Konkan, which is an escarpment rising up to the Western Ghats range of mountains, which separate it from the Deccan Plateau. The highest point is the
Goa encompasses an area of . It lies between the latitudes 14°53′54″ N and 15°40′00″ N and longitudes 73°40′33″ E and 74°20′13″ E.
Goa is a part of the coastal country known as the Konkan, which is an escarpment rising up to the Western Ghats range of mountains, which separate it from the Deccan Plateau. The highest point is the Dudhsagar Falls at Bhagwan Mahaveer Sanctuary and Mollem National Park" style="font-size:88%; line-height:130%; border-bottom:1px #aaa solid;" heights="150">
Doodhsagar Waterfalls.jpg, Dudhsagar Waterfalls in August
Dudhsagar Falls Triplet.jpg, Train passing next to the Dudhsagar Falls
Dudhsagar Falls triplet, 2009.JPG, Lower half of Dudhsagar Falls
 The state is divided into two civil districts—
The state is divided into two civil districts—
 The politics of Goa are a result of the uniqueness of this region due to 450 years of Portuguese rule, in comparison to three centuries of British rule experienced by the rest of India. The Indian National Congress was unable to achieve electoral success in the first two decades after the State's incorporation into India. Instead, the state was dominated by the regional political parties like Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party and the United Goans Party.
The politics of Goa are a result of the uniqueness of this region due to 450 years of Portuguese rule, in comparison to three centuries of British rule experienced by the rest of India. The Indian National Congress was unable to achieve electoral success in the first two decades after the State's incorporation into India. Instead, the state was dominated by the regional political parties like Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party and the United Goans Party.
 Equatorial forest cover in Goa stands at , most of which is owned by the government. Government-owned forest is estimated at whilst private is given as . Most of the forests in the state are located in the interior eastern regions of the state. The Western Ghats, which form most of eastern Goa, have been internationally recognised as one of the biodiversity hotspots of the world. In the February 1999 issue of ''National Geographic Magazine'', Goa was compared with the Amazon and the Congo basins for its rich tropical biodiversity.
Goa's wildlife sanctuaries boast of more than 1512 documented species of plants, over 275 species of birds, over 48 kinds of animals and over 60 genera of reptiles. Nanda Lake is the first and the only Ramsar wetland site in Goa.
Goa is also known for its coconut cultivation. The coconut tree has been reclassified by the government as a palm (like grass), enabling farmers and real estate developers to clear land with fewer restrictions.
Rice is the main food crop, and pulses (legume), ''Ragi'' (Finger Millet), and other food crops are also grown. Main cash crops are arecanut, coconut, cashew nut, sugar cane, and fruits like banana, mango, and pineapple. Goa's state animal is the ''Gaur'', the state bird is the Flame-throated bulbul, Flame-throated ''Bulbul'', and the state tree is the Terminalia elliptica, Indian Laurel.
Equatorial forest cover in Goa stands at , most of which is owned by the government. Government-owned forest is estimated at whilst private is given as . Most of the forests in the state are located in the interior eastern regions of the state. The Western Ghats, which form most of eastern Goa, have been internationally recognised as one of the biodiversity hotspots of the world. In the February 1999 issue of ''National Geographic Magazine'', Goa was compared with the Amazon and the Congo basins for its rich tropical biodiversity.
Goa's wildlife sanctuaries boast of more than 1512 documented species of plants, over 275 species of birds, over 48 kinds of animals and over 60 genera of reptiles. Nanda Lake is the first and the only Ramsar wetland site in Goa.
Goa is also known for its coconut cultivation. The coconut tree has been reclassified by the government as a palm (like grass), enabling farmers and real estate developers to clear land with fewer restrictions.
Rice is the main food crop, and pulses (legume), ''Ragi'' (Finger Millet), and other food crops are also grown. Main cash crops are arecanut, coconut, cashew nut, sugar cane, and fruits like banana, mango, and pineapple. Goa's state animal is the ''Gaur'', the state bird is the Flame-throated bulbul, Flame-throated ''Bulbul'', and the state tree is the Terminalia elliptica, Indian Laurel.
 The important forest products are bamboo canes, Maratha barks, chillar barks, and the bhirand. Coconut palm trees are common throughout Goa barring the elevated regions. A variety of deciduous trees, such as teak, Sal tree, cashew, and mango trees are present. Fruits include jackfruit, mango, pineapple, and blackberry. Goa's forests are rich in medicinal plants.
Foxes, wild boar and migratory birds are found in the jungles of Goa. The avifauna (bird species) includes kingfisher, ''myna'' and parrot. Numerous types of fish are also caught off the coast of Goa and in its rivers. Crab, lobster, shrimp, jellyfish, oysters, and catfish are the basis of the marine fishery. Goa also has a high snake population. Goa has many famous "National Parks", including the renowned Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary on the island of Chorão (Island), Chorão. Other wildlife sanctuaries include the Bondla Wildlife Sanctuary, Molem Wildlife Sanctuary, Cotigao Wildlife Sanctuary, Madei Wildlife Sanctuary, Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary, and Mahaveer Wildlife Sanctuary.
Goa has more than 33% of its geographic area under government forests (1224.38 km2) of which about 62% has been brought under Protected Areas (PA) of Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Park. Since there is a substantial area under private forests and a large tract under cashew, mango, coconut, etc. plantations, the total forest and tree cover constitutes 56.6% of the geographic area.
The important forest products are bamboo canes, Maratha barks, chillar barks, and the bhirand. Coconut palm trees are common throughout Goa barring the elevated regions. A variety of deciduous trees, such as teak, Sal tree, cashew, and mango trees are present. Fruits include jackfruit, mango, pineapple, and blackberry. Goa's forests are rich in medicinal plants.
Foxes, wild boar and migratory birds are found in the jungles of Goa. The avifauna (bird species) includes kingfisher, ''myna'' and parrot. Numerous types of fish are also caught off the coast of Goa and in its rivers. Crab, lobster, shrimp, jellyfish, oysters, and catfish are the basis of the marine fishery. Goa also has a high snake population. Goa has many famous "National Parks", including the renowned Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary on the island of Chorão (Island), Chorão. Other wildlife sanctuaries include the Bondla Wildlife Sanctuary, Molem Wildlife Sanctuary, Cotigao Wildlife Sanctuary, Madei Wildlife Sanctuary, Netravali Wildlife Sanctuary, and Mahaveer Wildlife Sanctuary.
Goa has more than 33% of its geographic area under government forests (1224.38 km2) of which about 62% has been brought under Protected Areas (PA) of Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Park. Since there is a substantial area under private forests and a large tract under cashew, mango, coconut, etc. plantations, the total forest and tree cover constitutes 56.6% of the geographic area.
Iron Ore Train Goa.jpg, Train carrying iron ore to Marmagao Port,
 According to the 2011 census, in a population of 1,458,545 people, 66.1% were Hindu, 25.1% were Christians, Christian, 8.3% were Muslim, and 0.1% were Sikh.
According to the 1909 statistics in the Catholic Encyclopedia, the total Catholic population in Portuguese controlled Goa was 293,628 out of a total population of 365,291 (80.33%). Since the 20th century, the percentage of Goan Catholics has been facing continual decline caused by a combination of permanent emigration from Goa to cosmopolitan Indian cities (e.g. Bombay, Poona, Bangalore) and foreign countries (e.g. Portugal, the United Kingdom) with the mass immigration of non-Christians from the rest of India since the 20th century.Rajesh Ghadge (2015). ''The story of Goan Migration.'' (Ethnic Goans represent less than 50% of the state's residents.)
The Catholics in Goa state and Daman and Diu union territory are served by the Metropolitan Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Goa and Daman, the Primate (bishop), primatial see of India, in which the titular Patriarchate of the East Indies is vested.
According to the 2011 census, in a population of 1,458,545 people, 66.1% were Hindu, 25.1% were Christians, Christian, 8.3% were Muslim, and 0.1% were Sikh.
According to the 1909 statistics in the Catholic Encyclopedia, the total Catholic population in Portuguese controlled Goa was 293,628 out of a total population of 365,291 (80.33%). Since the 20th century, the percentage of Goan Catholics has been facing continual decline caused by a combination of permanent emigration from Goa to cosmopolitan Indian cities (e.g. Bombay, Poona, Bangalore) and foreign countries (e.g. Portugal, the United Kingdom) with the mass immigration of non-Christians from the rest of India since the 20th century.Rajesh Ghadge (2015). ''The story of Goan Migration.'' (Ethnic Goans represent less than 50% of the state's residents.)
The Catholics in Goa state and Daman and Diu union territory are served by the Metropolitan Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Goa and Daman, the Primate (bishop), primatial see of India, in which the titular Patriarchate of the East Indies is vested.
. Retrieved 4 August 2010. Museum of Goa is a privately owned contemporary art gallery in Pilerne Industrial Estate, near Calangute.
 Having been a Portuguese India, Portuguese territory for over 450 years, Goan culture is an amalgamation of both Eastern culture, Eastern and Western culture, Western styles, with the latter having a more dominant role. The tableau of Goa showcases religious harmony by focusing on the Deepastambha, the Cross, and Ghode Modni followed by a chariot. European royal attire of kings is as much part of Goa's cultural heritage as are regional dances performed depicting a unique blend of different religions and cultures of this State. Prominent local festivals are Christmas, Easter, Carnival, Diwali, Shigmo, Ganesh Chaturthi, Chavoth, Gudi Padwa, Samvatsar Padvo, Navratri, Dasara etc. The Goan Carnival and Christmas-new year celebrations attract many tourists.
The Gomant Vibhushan Award, the highest civilian honour of the State of Goa, is given annually by Government of Goa since 2010.
Having been a Portuguese India, Portuguese territory for over 450 years, Goan culture is an amalgamation of both Eastern culture, Eastern and Western culture, Western styles, with the latter having a more dominant role. The tableau of Goa showcases religious harmony by focusing on the Deepastambha, the Cross, and Ghode Modni followed by a chariot. European royal attire of kings is as much part of Goa's cultural heritage as are regional dances performed depicting a unique blend of different religions and cultures of this State. Prominent local festivals are Christmas, Easter, Carnival, Diwali, Shigmo, Ganesh Chaturthi, Chavoth, Gudi Padwa, Samvatsar Padvo, Navratri, Dasara etc. The Goan Carnival and Christmas-new year celebrations attract many tourists.
The Gomant Vibhushan Award, the highest civilian honour of the State of Goa, is given annually by Government of Goa since 2010.
 Natak, Tiatr (most popular) and Jagor are the chief forms of Goa's traditional performance arts. Other forms are Ranmale, Dashavatari, Kalo, Goulankala, Lalit, Kala and Rathkala. Stories from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata along with more modern social subjects are narrated with song and dance.
"Jagor", the traditional folk dance-drama, is performed by the Hindu Kunbi and Christian Gauda community of Goa, to seek the Divine Grace for protection and prosperity of the crop. The literal meaning of Jagor is "jagran" or wakeful nights. The strong belief is that the night-long performance awakens the deities once a year and they continue to remain awake throughout the year guarding the village.
Perni Jagor is the ancient mask dance – drama of Goa, performed by Perni families, using well crafted and painted wooden masks, depicting various animals, birds, super natural power, deities, demons, and social characters.
Gauda Jagor is an impression of social life, that displays all the existing moods and modes of human characters. It is predominantly based on three main characters, Gharasher, Nikhandar, and Parpati wearing shining dresses and headgears. The performance is accompanied by vibrant tunes of Goan folk instruments like Nagara/Dobe, Ghumat, Madale, and Kansale.
In some places, Jagor performances are held with the participation of both Hindus and the Christian community, whereby, characters are played by Hindus and musical support is provided by Christian artistes.
''Tiatr (Teatro)'' and its artists play a major role in keeping the Konkani language and music alive. Tiatrs are conducted solely in the Roman script of Konkani as it is primarily a Christian community-based act. They are played in scenes with music at regular intervals, the scenes are portrayals of daily life and are known to depict social and cultural scenarios. Tiatrs are regularly held especially on weekends mainly at Kala Academy, Panaji, Pai Tiatrist Hall at Ravindra Bhavan, Margao and most recent shows have also started at the new Ravindra Bhavan, Baina, Vasco. Western Musical Instruments such as Drums, Bass, Keyboards, and Trumpets. are part of the show and most of them are played acoustically. It is one of Goa's few art forms that is renowned across the world with performances popular among Goans in the Middle-East, Americas and Europe.
Natak, Tiatr (most popular) and Jagor are the chief forms of Goa's traditional performance arts. Other forms are Ranmale, Dashavatari, Kalo, Goulankala, Lalit, Kala and Rathkala. Stories from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata along with more modern social subjects are narrated with song and dance.
"Jagor", the traditional folk dance-drama, is performed by the Hindu Kunbi and Christian Gauda community of Goa, to seek the Divine Grace for protection and prosperity of the crop. The literal meaning of Jagor is "jagran" or wakeful nights. The strong belief is that the night-long performance awakens the deities once a year and they continue to remain awake throughout the year guarding the village.
Perni Jagor is the ancient mask dance – drama of Goa, performed by Perni families, using well crafted and painted wooden masks, depicting various animals, birds, super natural power, deities, demons, and social characters.
Gauda Jagor is an impression of social life, that displays all the existing moods and modes of human characters. It is predominantly based on three main characters, Gharasher, Nikhandar, and Parpati wearing shining dresses and headgears. The performance is accompanied by vibrant tunes of Goan folk instruments like Nagara/Dobe, Ghumat, Madale, and Kansale.
In some places, Jagor performances are held with the participation of both Hindus and the Christian community, whereby, characters are played by Hindus and musical support is provided by Christian artistes.
''Tiatr (Teatro)'' and its artists play a major role in keeping the Konkani language and music alive. Tiatrs are conducted solely in the Roman script of Konkani as it is primarily a Christian community-based act. They are played in scenes with music at regular intervals, the scenes are portrayals of daily life and are known to depict social and cultural scenarios. Tiatrs are regularly held especially on weekends mainly at Kala Academy, Panaji, Pai Tiatrist Hall at Ravindra Bhavan, Margao and most recent shows have also started at the new Ravindra Bhavan, Baina, Vasco. Western Musical Instruments such as Drums, Bass, Keyboards, and Trumpets. are part of the show and most of them are played acoustically. It is one of Goa's few art forms that is renowned across the world with performances popular among Goans in the Middle-East, Americas and Europe.
 Konkani cinema is an Indian film industry, where films are made in the Konkani language, which is spoken mainly in the Indian states of Goa,
Konkani cinema is an Indian film industry, where films are made in the Konkani language, which is spoken mainly in the Indian states of Goa,
Goan prawn curry.jpg, Goan prawn curry, a popular dish throughout the state
Vindalho.jpg, Pork ''vindaloo'' is a popular Goan curry dish in the state and around the world
Chamuças.jpg, ''Samosa, Chamuças'', Goan samosas
Goan Fish Curry.jpg, Traditional Goan fish curry
Rice with fish curry (''xit koddi'' in Konkani language, Konkani) is the staple diet in Goa. Goan cuisine is famous for its rich variety of fish dishes cooked with elaborate recipes. Coconut and coconut oil are widely used in Goan cooking along with chili peppers, spices, and vinegar, used in the Catholic cuisine, giving the food a unique flavor. Goan cuisine is heavily influenced by Portuguese cuisine.
Goan food may be divided into Goan Catholic and Goan Hindu cuisine with each showing very distinct tastes, characteristics, and cooking styles. Pork dishes such as Vindaloo, Vindalho, Xacuti, chouriço, and Sorpotel are cooked for major occasions among the Goan Catholics. A mixed vegetable stew, known as Khatkhate, is a very popular dish during the celebrations of festivals, Hindu and Christian alike. Khatkhate contains at least five vegetables, fresh coconut, and special Goan spices that add to the aroma.
Sanna (rice cakes), Sannas, ''Hitt'', are local rice cakes and ''Polle'', ''Amboli'', and ''Kailoleo'' are rice pancakes; all are native to Goa. A rich egg (food), egg-based, multi-layered baked sweet known as bebinca is traditional at Christmas.
The most popular alcoholic beverage in Goa is Feni (liquor), feni. Cashew feni is made from the double distillation of the fermented fruit juice of the cashew tree, while coconut feni is made from the double distillation of the fermented sap of toddy palms. Urrak is another local liquor prepared from the single distillation of the fermented cashew fruit juice. In fact the bar culture is one of the unique aspects of the Goan villages where a local bar serves as a meeting point for villagers to unwind. Goa also has a rich wine culture due to Portuguese rule.
Costa Residence Margao.jpg, ''The House of the Seven Gables'' in Margao
Galeria_em_Fontainhas.jpg, ''Velha Goa Galeria'', in Panaji
The architecture of Goa is a combination of native Goan, Islamic architecture, Ottoman and Portuguese architecture, Portuguese styles. Since the Portuguese ruled and governed for four centuries, many churches and houses bear a striking element of the Portuguese style of architecture. Goan Hindu houses do not show any Portuguese influence, though the modern temple architecture is an amalgam of original Goan temple style with Dravidian architecture, Dravidian, Hemadpanthi, Islamic, and Portuguese architecture. The original Goan temple architecture fell into disuse as the temples were demolished by the Portuguese and the ''Sthapati'' known as ''Thavayi'' in Konkani were converted to Christianity though the wooden work and the ''Kaavi art, Kavi'' murals can still be seen.
 Normally other states are fond of cricket but association football is the most popular sport in Goa and is embedded in Goan culture as a result of the Portuguese influence Its origins in the state are traced back to 1883 when the visiting Irish priest Fr. William Robert Lyons established the sport as part of a "Christian education". On 22 December 1959 the ''Associação de Futebol de Goa'' was formed, which continues to administer the game in the state under the new name Goa Football Association. Goa, along with West Bengal and Kerala is the locus of football in India and is home to many football clubs in the national I-League. The state's football powerhouses include Salgaocar F.C., Salgaocar, Dempo S.C., Dempo, Churchill Brothers S.C., Churchill Brothers, Vasco S.C., Vasco, Sporting Clube de Goa and FC Goa. The first Unity World Cup was held in Goa in 2014. The state's main football stadium, Fatorda Stadium, is located at Margao and also hosts cricket matches. The state hosted few matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup in Fatorda Stadium.
A number of Goans have represented India in football and six of them, namely Samir Subash Naik, Samir Naik, Climax Lawrence, Brahmanand Sankhwalkar, Bruno Coutinho (footballer, born 1969), Bruno Coutinho, Mauricio Afonso and Roberto Fernandes have all captained the national team. Goa has its own Goa football team, state football team and league, the Goa Professional League. It is probably the only state in India where cricket is not considered the most important of all sports. Goan's are avid football fans, particularly of the football teams from Portugal (Benfica, Sporting), and Brazil especially during major football events such as the 'European Cup' and the 'World Cup' championships. The Portuguese footballer Ronaldo (Portuguese footballer), Ronaldo and Brazilian Neymar, are revered superstar football players in Goa.
Goa also has its own Goa cricket team, cricket team. Dilip Sardesai and Shikha Pandey remain the only Goans to date to play international cricket for Indian cricket team, India. Another Goan cricketer, Suyash Prabhudessai was selected by the Royal Challengers Bangalore for a base price of in Indian Premier League, IPL 2021 and for in IPL 2022.
India (Goa) is a member of the 'Lusophony Olympic Games' which are hosted every four years in one of the Portuguese CPLP member countries, with 733 athletes from 11 countries. Most of the countries competing are countries that are members of the CPLP (Community of Portuguese Language Countries), but some are countries with significant Portuguese communities or have a history with Portugal. This event is similar in concept to the Commonwealth Games (for members of the Commonwealth of Nations) and the Jeux de la Francophonie (for the Francophone community).
Normally other states are fond of cricket but association football is the most popular sport in Goa and is embedded in Goan culture as a result of the Portuguese influence Its origins in the state are traced back to 1883 when the visiting Irish priest Fr. William Robert Lyons established the sport as part of a "Christian education". On 22 December 1959 the ''Associação de Futebol de Goa'' was formed, which continues to administer the game in the state under the new name Goa Football Association. Goa, along with West Bengal and Kerala is the locus of football in India and is home to many football clubs in the national I-League. The state's football powerhouses include Salgaocar F.C., Salgaocar, Dempo S.C., Dempo, Churchill Brothers S.C., Churchill Brothers, Vasco S.C., Vasco, Sporting Clube de Goa and FC Goa. The first Unity World Cup was held in Goa in 2014. The state's main football stadium, Fatorda Stadium, is located at Margao and also hosts cricket matches. The state hosted few matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup in Fatorda Stadium.
A number of Goans have represented India in football and six of them, namely Samir Subash Naik, Samir Naik, Climax Lawrence, Brahmanand Sankhwalkar, Bruno Coutinho (footballer, born 1969), Bruno Coutinho, Mauricio Afonso and Roberto Fernandes have all captained the national team. Goa has its own Goa football team, state football team and league, the Goa Professional League. It is probably the only state in India where cricket is not considered the most important of all sports. Goan's are avid football fans, particularly of the football teams from Portugal (Benfica, Sporting), and Brazil especially during major football events such as the 'European Cup' and the 'World Cup' championships. The Portuguese footballer Ronaldo (Portuguese footballer), Ronaldo and Brazilian Neymar, are revered superstar football players in Goa.
Goa also has its own Goa cricket team, cricket team. Dilip Sardesai and Shikha Pandey remain the only Goans to date to play international cricket for Indian cricket team, India. Another Goan cricketer, Suyash Prabhudessai was selected by the Royal Challengers Bangalore for a base price of in Indian Premier League, IPL 2021 and for in IPL 2022.
India (Goa) is a member of the 'Lusophony Olympic Games' which are hosted every four years in one of the Portuguese CPLP member countries, with 733 athletes from 11 countries. Most of the countries competing are countries that are members of the CPLP (Community of Portuguese Language Countries), but some are countries with significant Portuguese communities or have a history with Portugal. This event is similar in concept to the Commonwealth Games (for members of the Commonwealth of Nations) and the Jeux de la Francophonie (for the Francophone community).
Goa University, Goa.jpg, Goa University
Carmel's College for Women, Nuvem, Goa, India.jpg, Carmel College for Women, established more than 50 years ago to address the education gender gap, is affiliated to Goa University
GMC building.jpg, Goa Medical College, previously called ''Escola Médico–Cirúrgica de Goa''
Goa had India's earliest educational institutions built with European support. The Portuguese set up seminaries for religious education and parish schools for elementary education. Founded circa 1542 by Saint Francis Xavier, Saint Paul's College, Goa was a Jesuit school in Old Goa, which later became a college. St Paul's was once the main Jesuit institution in the whole of Asia. It housed the first printing press in India and published the first books in 1556.
Medical education began in 1801 with the offering of regular medical courses at the Royal and Military Hospital in the old City of Goa. Built-in 1842 as the Escola Médico-Cirúrgica de (Nova) Goa (Medical-Surgical School of Goa), Goa Medical College is one of Asia's oldest medical colleges and has one of the oldest medical libraries (since 1845). It houses the largest hospital in Goa and continues to provide medical training to this day.
According to the 2011 census, Goa has a literacy rate of 87%, with 90% of males and 84% of females being literate. Each taluka is made up of villages, each having a school run by the government. Private schools are preferred over government-run schools. All schools come under the Goa Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary Education, whose syllabus is prescribed by the state education department. There are also a few schools that subscribe to the all-India Indian Certificate of Secondary Education, ICSE syllabus or the National Institute of Open Schooling, NIOS syllabus. Most students in Goa complete their high school with English as the medium of instruction. Most primary schools, however, use Konkani and Marathi (in private, but government-aided schools). As is the case in most of India, enrolment for vernacular media has seen a fall in numbers in favor of English medium education. Per a report published in ''The Times of India'', 84% of Goan primary schools were run without an administrative head.
Some notable schools in Goa include Sharada Mandir School in Miramar, Panaji, Miramar, Loyola High School (Goa), Loyola High School in Margao and The King's School, Goa, The King's School in São José de Areal. After ten years of schooling, students join a Higher Secondary school, which offers courses in popular streams such as Science, Liberal Arts, Arts, Law, and Commerce. A student may also opt for a course in vocational studies. Additionally, they may join three-year diploma courses. Two years of college is followed by a professional degree programme. Goa University, the sole university in Goa, is located in Taleigão and most Goan colleges are affiliated with it.
There are six engineering colleges in the state. Goa Engineering College and National Institute of Technology Goa are government-funded colleges whereas the private engineering colleges include Don Bosco College of Engineering at Fatorda, Shree Rayeshwar Institute of Engineering and Information Technology at Shiroda, Agnel Institute of Technology, and Design (AITD), Assagao, Bardez and Padre Conceicao College of Engineering at Verna. In 2004, Birla Institute of Technology and Science, BITS Pilani one of the premier institutes in India, inaugurated its second campus, the Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani – Goa Campus, BITS Pilani Goa Campus, at Zuarinagar near Dabolim. The Indian Institute of Technology Goa (IIT Goa) began functioning from its temporary campus, located in Goa Engineering College since 2016. The site for permanent campus was finalised in Cotarli, Sanguem.
There are colleges offering pharmacy, architecture and dentistry along with numerous private colleges offering law, liberal arts, arts, commerce and science. There are also two National Oceanographic Science related centres: the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research in Vasco da Gama and the National Institute of Oceanography, India, National Institute of Oceanography in Dona Paula.
Goa Institute of Management located at Sanquelim, near Panaji is one of India's premier business schools.
In addition to the engineering colleges, there are government polytechnic institutions in Government Polytechnic, Panaji, Panaji,
 Goa International Airport, is a civil enclave at INS Hansa, a Naval airfield located at Dabolim near
Goa International Airport, is a civil enclave at INS Hansa, a Naval airfield located at Dabolim near
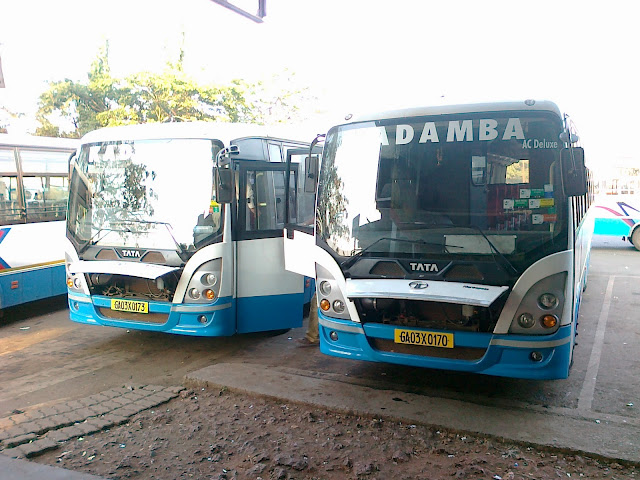
 Goa's public transport largely consists of privately operated buses linking the major towns to rural areas. Government-run buses, maintained by the Kadamba Transport Corporation, link major routes (like the Panaji–Margao route) and some remote parts of the state. The Corporation owns 15 bus stands, 4 depots and one Central workshop at Porvorim and a Head Office at Porvorim. In large towns such as Panaji and Margao, intra-city buses operate. However, public transport in Goa is less developed, and residents depend heavily on their own transportation, usually motorised two-wheelers and small family cars.
Goa's public transport largely consists of privately operated buses linking the major towns to rural areas. Government-run buses, maintained by the Kadamba Transport Corporation, link major routes (like the Panaji–Margao route) and some remote parts of the state. The Corporation owns 15 bus stands, 4 depots and one Central workshop at Porvorim and a Head Office at Porvorim. In large towns such as Panaji and Margao, intra-city buses operate. However, public transport in Goa is less developed, and residents depend heavily on their own transportation, usually motorised two-wheelers and small family cars.
 Goa has four National Highway (India), National Highways passing through it. NH-66 (ex National Highway 17 (India)(old numbering), NH-17) runs along India's west coast and links Goa to Mumbai in the north and Mangalore to the south. National Highway 4A (India), NH-4A running across the state connects the capital Panaji to Belgaum in east, linking Goa to cities in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan. The NH-366 (ex National Highway 17A (India), NH-17A) connects NH-66 to Mormugao Port from Cortalim. The new NH-566 (ex NH-17B) is a four-lane highway connecting Mormugao Port to NH-66 at Verna via Dabolim Airport, primarily built to ease pressure on the NH-366 for traffic to Dabolim Airport and Vasco da Gama. NH-768 (ex NH-4A) links Panaji and Ponda to Belgaum and NH-4. Goa has a total of of national highways, of state highway and of district highway. National Highways in Goa are among the narrowest in the country and will remain so for the foreseeable future, as the state government has received an exemption that allows narrow national highways. In Kerala, highways are wide. In other states National Highways are grade separated highways wide with a minimum of four lanes, as well as 6 or 8 lane access-controlled expressways.
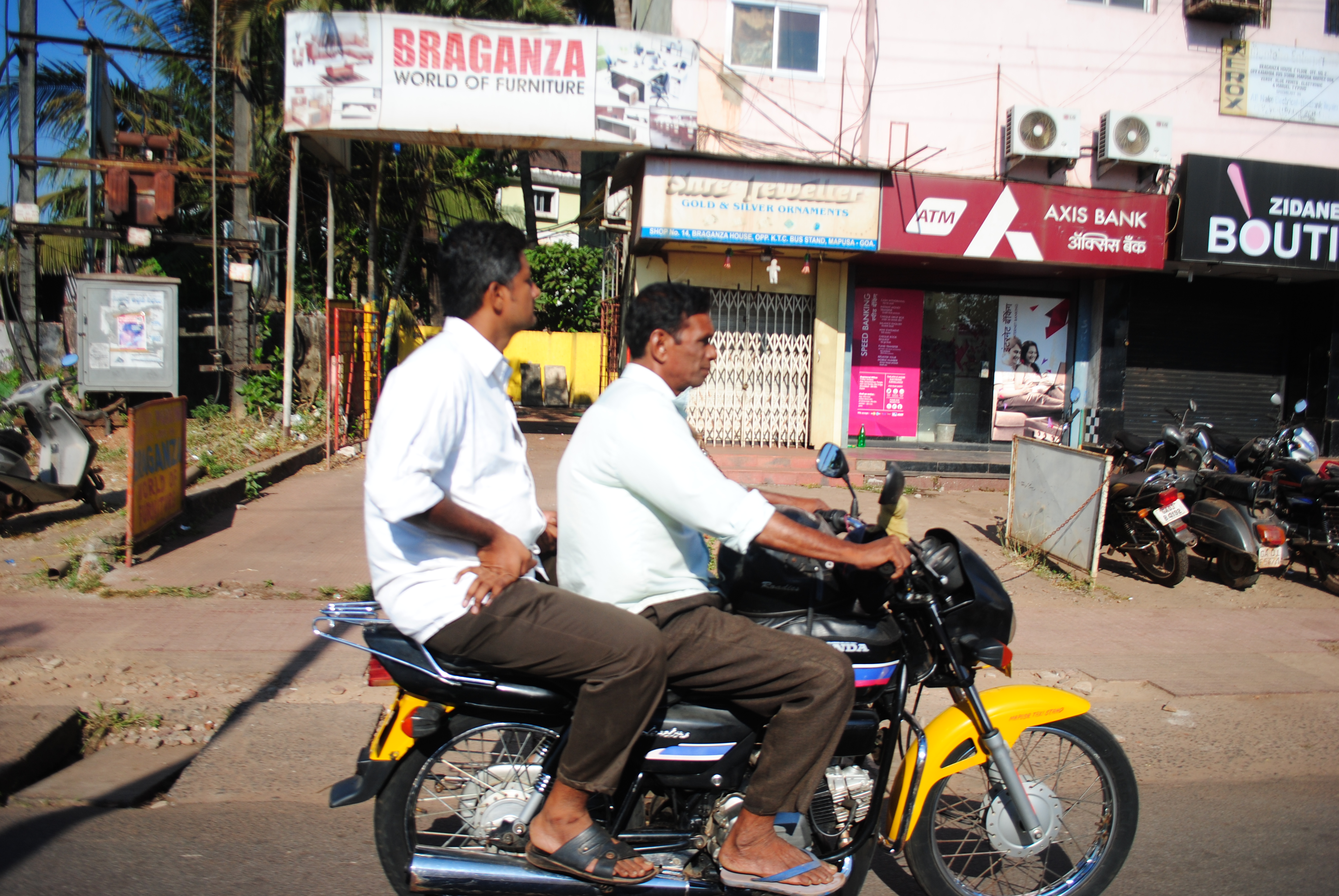
Hired forms of transport include unmetered taxis and, in urban areas, auto rickshaws. Another form of transportation in Goa is the motorcycle taxi, operated by drivers who are locally called "pilots". These vehicles transport a single pillion rider, at fares that are usually negotiated. Other than buses, "pilots" tend to be the cheapest mode of transport. River crossings in Goa are serviced by flat-bottomed ferry boats, operated by the river navigation department.
Goa has four National Highway (India), National Highways passing through it. NH-66 (ex National Highway 17 (India)(old numbering), NH-17) runs along India's west coast and links Goa to Mumbai in the north and Mangalore to the south. National Highway 4A (India), NH-4A running across the state connects the capital Panaji to Belgaum in east, linking Goa to cities in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan. The NH-366 (ex National Highway 17A (India), NH-17A) connects NH-66 to Mormugao Port from Cortalim. The new NH-566 (ex NH-17B) is a four-lane highway connecting Mormugao Port to NH-66 at Verna via Dabolim Airport, primarily built to ease pressure on the NH-366 for traffic to Dabolim Airport and Vasco da Gama. NH-768 (ex NH-4A) links Panaji and Ponda to Belgaum and NH-4. Goa has a total of of national highways, of state highway and of district highway. National Highways in Goa are among the narrowest in the country and will remain so for the foreseeable future, as the state government has received an exemption that allows narrow national highways. In Kerala, highways are wide. In other states National Highways are grade separated highways wide with a minimum of four lanes, as well as 6 or 8 lane access-controlled expressways.
Hired forms of transport include unmetered taxis and, in urban areas, auto rickshaws. Another form of transportation in Goa is the motorcycle taxi, operated by drivers who are locally called "pilots". These vehicles transport a single pillion rider, at fares that are usually negotiated. Other than buses, "pilots" tend to be the cheapest mode of transport. River crossings in Goa are serviced by flat-bottomed ferry boats, operated by the river navigation department.
 Goa has two Rail transport, rail lines – one run by the South Western Railway and the other by the Konkan Railway. The line run by the South Western Railway zone, South Western Railway was built during the colonial era linking the port town of Vasco da Gama, Goa with Belgaum, Hubli, Karnataka via Margao. The Konkan Railway line, which was built during the 1990s, runs parallel to the coast connecting major cities on the western coast.
Goa has two Rail transport, rail lines – one run by the South Western Railway and the other by the Konkan Railway. The line run by the South Western Railway zone, South Western Railway was built during the colonial era linking the port town of Vasco da Gama, Goa with Belgaum, Hubli, Karnataka via Margao. The Konkan Railway line, which was built during the 1990s, runs parallel to the coast connecting major cities on the western coast.
Government of Goa
Department of Tourism
; General information * * {{Authority control Goa, Konkan Historic Jewish communities Former Portuguese colonies Former exclaves States and territories established in 1987 1987 establishments in India City-states States and union territories of India India–Portugal relations
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
to the north and Karnataka to the east and south, with the Arabian Sea forming its western coast. It is India's smallest state by area and its fourth-smallest by population. Goa has the highest GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
among all Indian states, two and a half times as high as the GDP per capita of the country as a whole. The Eleventh Finance Commission
The Eleventh Finance Commission of India was appointed by the President on 3 July 1998 for the period 2000-2005.
Members
* Prof. A.M. Khusro, Chair
* Shri N.C Jain
* Shri J.C Jetly, IAS (retired)
* Dr. Amaresh Bagchi
* Shri T.N. Srivasta ...
of India named Goa the best-placed state because of its infrastructure, and India's National Commission on Population rated it as having the best quality of life in India (based on the commission's “12 Indicators”). It is the third-highest ranking among Indian states in the human development index.
Panaji is the state's capital, while Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link E ...
is its largest city. The historic city of Margão
Margao or Madgaon is the commercial capital of the Indian state of Goa. It stands on banks of the Sal river and is the administrative headquarters of Salcete sub-district and South Goa district. It is Goa's second largest city by population aft ...
in Goa still exhibits the cultural influence of the Portuguese, who first voyaged to the subcontinent in the early 16th century as merchants, and conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
it soon thereafter, whereupon Goa became an overseas territory of the Portuguese Empire, part of what was then known as Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
, and remained as such for about 450 years until it was annexed by India in 1961. Goa's official language, which is spoken by a majority of its inhabitants, is Konkani.
Goa is visited by large numbers of international and domestic tourists each year because of its white-sand beaches, active nightlife, places of worship, and World Heritage-listed architecture. It also has rich flora and fauna because it lies very close to the North Western Ghats rainforests, one of the rare biodiversity hotspots of the world.
Etymology
After the Bahmani-Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural ...
i city of Goa was captured by Afonso de Albuquerque in AD 1510, and made the capital of the '' Estado da Índia'', the city gave its name to the contiguous territories.
The origin of the city name "Goa" is unclear. In ancient literature, Goa was known by many names, such as ''Gomanchala'', '' Gopakapattana'', ''Gopakapattam'', ''Gopakapuri'', ''Govapuri'', ''Govem'', and ''Gomantak''. Other historical names for Goa are ''Sindapur'', ''Sandabur'', and ''Mahassapatam''.
History
Prehistory
Rock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also ...
engravings (petroglyphs) are present on laterite platforms and granite boulders in Usgalimal near the west flowing Kushavati river and in Kajur. In Kajur, the rock engravings of animals, tectiforms and other designs in granite have been associated with what is considered to be a megalithic stone circle with a round granite stone in the centre. Petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s, cones, stone-axe, and choppers dating to 10,000 years ago have been found in various locations in Goa, including Kazur, Mauxim, and the Mandovi- Zuari basin. Recently these petroglyphs have been included in the tentative list of UNESCO world heritage sites.
Evidence of Palaeolithic life is visible at Dabolim, Adkon, Shigao, Fatorpa, Arli, Maulinguinim, Diwar, Sanguem, Pilerne, and Aquem-Margaon. Difficulty in carbon dating the laterite rock compounds poses a problem for determining the exact time period.
Early Goan society underwent radical change when Indo-Aryan and Dravidian migrants amalgamated with the aboriginal locals, forming the base of early Goan culture.
Early history
In the 3rd century BC, Goa was part of theMaurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, ruled by the Buddhist emperor, Ashoka of Magadha. Buddhist monks laid the foundation of Buddhism in Goa. Between the 2nd century BC and the 6th century AD, Goa was ruled by the Bhojas of Goa. Chutus of Karwar also ruled some parts as feudatories of the Satavahanas of Kolhapur (2nd century BC to the 2nd century AD), Western Kshatrapas (around 150 AD), the Abhiras of Western Maharashtra, Bhojas of the Yadav clans of Gujarat, and the Konkan Mauryas as feudatories of the Kalachuri
The Kalachuris (IAST: Kalacuri), also known as Kalachuris of Mahishmati, were an Indian dynasty that ruled in west-central India between 6th and 7th centuries. They are also known as the Heheya Kingdom, Haihayas or as the Early Kalachuris to d ...
s. The rule later passed to the Chalukyas of Badami, who controlled it between 578 and 753, and later the Rashtrakuta
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
s of Malkhed from 753 to 963. From 765 to 1015, the Southern Silhara
The Shilahara Kingdom (IAST: Śilāhāra; also Sinhara, Shailahara, Shrilara, and Silara) was a royal dynasty that established itself in northern and southern Konkan in 8th century CE, present-day Mumbai and Southern Maharashtra (Kolhapur) du ...
s of Konkan ruled Goa as the feudatories of the Chalukyas and the Rashtrakutas. Over the next few centuries, Goa was successively ruled by the Kadambas as the feudatories of the Chalukyas of Kalyani. They patronised Jainism in Goa
Jainism flourished in Goa during the rule of Kadamba dynasty. Broken sculptures of the Jain Tirthankara Suparshvanatha, belonging to the period of the Goan Kadamba ruler Shivachitta Permadi Dev, were discovered in an old Jain temple in Jainko ...
.
In 1312, Goa came under the governance of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
. The kingdom's grip on the region was weak, and by 1370 it was forced to surrender it to Harihara I of the Vijayanagara Empire. The Vijayanagara monarchs held on to the territory until 1469 when it was appropriated by the Bahmani sultans
The Bahmani Sultanate, or Deccan, was a Persianate Sunni Muslim Indian Kingdom located in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region. It was the first independent Muslim kingdom of the Deccan,
of Gulbarga
Kalaburagi, formerly known as Gulbarga, is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kalaburagi district and is the largest city in the region of North Karnataka (Kalyana-Karnataka). Kalaburagi is 6 ...
. After that dynasty crumbled, the area fell into the hands of the Adil Shahis of Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural ...
, who established as their auxiliary capital the city known under the Portuguese as Velha Goa (or Old Goa).
Portuguese period
 In 1510, the Portuguese defeated the ruling Bijapur sultan Yusuf Adil Shah with the help of a local ally, Timoji, a privateer. They set up a permanent settlement in ''Velha Goa'' (Old Goa). This was the beginning of Portuguese colonial rule in Goa that would last for four and a half centuries, until its annexation by India in 1961. The Goa Inquisition, a formal tribunal, was established in 1560, and was finally abolished in 1812.
From the latter decades of the eighteenth century, the territory of Goa was composed of two segments: the central nucleus of the '' Velhas Conquistas'' (Old Conquests)—Bardes, Ilhas de Goa, and Salcette—which territories had been under Portuguese administration since the sixteenth century; and the '' Novas Conquistas'' (New Conquests)—Bicholim, Canacona, Pernem, Quepem, Sattari, and Sanguem—territories which had been successively added through the eighteenth century.
In 1843, the Portuguese moved the capital to the ''Cidade da Nova Goa'' (City of New Goa), today known as Panaji (Panjim), from ''Velha Goa'' ( Old Goa). By the mid-18th century, Portuguese expansions lost other possessions in India until their borders stabilised and formed the Goa, Daman and Diu, which included Silvassa prior to the Annexation, it was known as ''Estado da Índia'' in Portuguese, that is the "State of Portuguese India".
In 1510, the Portuguese defeated the ruling Bijapur sultan Yusuf Adil Shah with the help of a local ally, Timoji, a privateer. They set up a permanent settlement in ''Velha Goa'' (Old Goa). This was the beginning of Portuguese colonial rule in Goa that would last for four and a half centuries, until its annexation by India in 1961. The Goa Inquisition, a formal tribunal, was established in 1560, and was finally abolished in 1812.
From the latter decades of the eighteenth century, the territory of Goa was composed of two segments: the central nucleus of the '' Velhas Conquistas'' (Old Conquests)—Bardes, Ilhas de Goa, and Salcette—which territories had been under Portuguese administration since the sixteenth century; and the '' Novas Conquistas'' (New Conquests)—Bicholim, Canacona, Pernem, Quepem, Sattari, and Sanguem—territories which had been successively added through the eighteenth century.
In 1843, the Portuguese moved the capital to the ''Cidade da Nova Goa'' (City of New Goa), today known as Panaji (Panjim), from ''Velha Goa'' ( Old Goa). By the mid-18th century, Portuguese expansions lost other possessions in India until their borders stabilised and formed the Goa, Daman and Diu, which included Silvassa prior to the Annexation, it was known as ''Estado da Índia'' in Portuguese, that is the "State of Portuguese India".
Contemporary period
After India gained independence from British rule in 1947, India requested that Portuguese territories on the Indian subcontinent be ceded to India. Portugal refused to negotiate on the sovereignty of its Indian enclaves. On 19 December 1961, the Indian Army invaded with Operation Vijay resulting in the annexation of Goa, and of Daman and Diu islands into the Indian union. Goa, along with Daman and Diu, was organised as a centrally administered union territory of India. On 16 January 1967 a referendum was held in Goa, to decide the future of the Union Territory of Goa, Daman and Diu. It was the only referendum to have been held in independent India. The referendum offered the people of Goa a choice between continuing as a union territory or merging with the state ofMaharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
and the majority chose the former. On 30 May 1987, the union territory was split, and Goa was made India's twenty-fifth state, with Daman and Diu remaining a union territory.
Geography

 Goa encompasses an area of . It lies between the latitudes 14°53′54″ N and 15°40′00″ N and longitudes 73°40′33″ E and 74°20′13″ E.
Goa is a part of the coastal country known as the Konkan, which is an escarpment rising up to the Western Ghats range of mountains, which separate it from the Deccan Plateau. The highest point is the
Goa encompasses an area of . It lies between the latitudes 14°53′54″ N and 15°40′00″ N and longitudes 73°40′33″ E and 74°20′13″ E.
Goa is a part of the coastal country known as the Konkan, which is an escarpment rising up to the Western Ghats range of mountains, which separate it from the Deccan Plateau. The highest point is the Sonsogor
Sonsogor is the highest peak in the state of Goa, India, at an elevation of above sea level. It is located at the trijunction of Sattari taluka, North Goa district, Goa; and Khanapur taluka, Belagavi district, and Joida taluka, Uttara Kannada ...
Peak, with an altitude of . Goa has a coastline of .
Goa's seven major rivers are the Mandovi, Zuari, Terekhol, Chapora, Galgibag, Cumbarjua canal, Talpona, and the Sal
Sal, SAL, or S.A.L. may refer to:
Personal name
* Sal (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or nickname
Places
* Sal, Cape Verde, an island and municipality
* Sal, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Ca ...
. The Zuari and the Mandovi are the most important rivers, interspaced by the Cumbarjua canal, forming a major estuarine complex. These rivers are fed by the Southwest monsoon rain and their basin covers 69% of the state's geographical area. These rivers are some of the busiest in India. Goa has more than 40 estuarine, eight marine, and about 90 riverine islands. The total navigable length of Goa's rivers is . Goa has more than 300 ancient water tanks built during the rule of the Kadamba dynasty and over 100 medicinal springs.
Mormugao harbour on the mouth of the Zuari river is considered one of the best natural harbours in South Asia.
Most of Goa's soil cover is made up of laterite
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
s rich in ferric-aluminum oxides and reddish in colour. Further inland and along the riverbanks, the soil is mostly alluvial and loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–sil ...
y. The soil is rich in minerals and humus, thus conducive to agriculture. Some of the oldest rocks in the Indian subcontinent are found in Goa between Molem
Mollem (pronounced mole; the alphabet m is silent) or मोले is a small village in Goa, South India on National Highway 4 near the border with Karnataka in the foothills of the Sahyadri Mountain range at the beginning of Anmod Ghat. It co ...
and Anmod on Goa's border with Karnataka. The rocks are classified as Trondjemeitic Gneiss estimated to be 3,600 million years old, dated by rubidium isotope dating. A specimen of the rock is exhibited at Goa University.
Climate
Goa features a tropical monsoon climate under the Köppen climate classification. Goa, being in the torrid zone and near the Arabian Sea, has a hot and humid climate for most of the year. The month of May is usually the hottest, seeing daytime temperatures of over coupled with high humidity. The state's three seasons are southwest monsoon period (June–September), post-monsoon period (October–January), and pre-monsoon period (February–May). Over 90% of the average annual rainfall () is received during the monsoon season.Subdivisions
 The state is divided into two civil districts—
The state is divided into two civil districts—North Goa
North Goa district is one of the two districts that constitutes the state of Goa, India. The district has an area of , and is bounded by Kolhapur and Sindhudurg districts of Maharashtra state to the north and by Belgavi district of Karnataka t ...
and South Goa
South Goa district is one of two districts that comprises the state of Goa, India, within the region known as the Konkan. It is bounded by North Goa district to the north, the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka state to the east and south, while ...
. Each district is administered by a District Collector, appointed by the Government of India.
Panaji (Panjim) is the headquarters of North Goa district and is also the capital of Goa.
North Goa is further divided into three subdivisions—Panaji, Mapusa, and Bicholim
Bicholim, pronounced (), also known as Divchal and Dicholi, is a town and a municipal council in North Goa district in the state of Goa, India. It is the headquarters of the ''Concelho'' (district) of Bicholim, one of seven that make up the No ...
; and five '' talukas'' (subdistricts)— Tiswadi (Panaji), Bardez ( Mapusa), Pernem, Bicholim
Bicholim, pronounced (), also known as Divchal and Dicholi, is a town and a municipal council in North Goa district in the state of Goa, India. It is the headquarters of the ''Concelho'' (district) of Bicholim, one of seven that make up the No ...
, and Sattari (Valpoi
Valpoi or Valpoy (''Vallpoi'', pronounced ) is a city and a municipal council in North Goa district in the Indian state of Goa. It is the headquarters of the Sattari Taluk. The Western Ghats are to the east of the town.
According to the aut ...
).
Margao (Madgaon) is the headquarters of the South Goa district. It is also the cultural and commercial capital of Goa.
South Goa is further divided into five subdivisions— Ponda, Mormugao-Vasco Vasco may refer to:
* Basque language, called ''vasco'' in Spanish
* ''Vasco'' (album), a two-part EP by Ricardo Villalobos
* Vasco da Gama, Portuguese explorer
* Vasco da Gama, Goa, a city in India, often called simply Vasco
* Club de Regatas Va ...
, Margao, Quepem, and Dharbandora; and seven ''talukas''— Ponda, Mormugao, Salcete ( Margao), Quepem, and Canacona (Chaudi), Sanguem, and Dharbandora.
Goa's major cities are— Panaji, Margao, Vasco Vasco may refer to:
* Basque language, called ''vasco'' in Spanish
* ''Vasco'' (album), a two-part EP by Ricardo Villalobos
* Vasco da Gama, Portuguese explorer
* Vasco da Gama, Goa, a city in India, often called simply Vasco
* Club de Regatas Va ...
- Mormugao, Mapusa, Ponda, Bicholim
Bicholim, pronounced (), also known as Divchal and Dicholi, is a town and a municipal council in North Goa district in the state of Goa, India. It is the headquarters of the ''Concelho'' (district) of Bicholim, one of seven that make up the No ...
, and Valpoi
Valpoi or Valpoy (''Vallpoi'', pronounced ) is a city and a municipal council in North Goa district in the Indian state of Goa. It is the headquarters of the Sattari Taluk. The Western Ghats are to the east of the town.
According to the aut ...
.
Panaji (Panjim) has the only Municipal Corporation in Goa.
There are thirteen Municipal Councils—Margao, Mormugao (merged with Vasco), Pernem, Mapusa, Bicholim, Sanquelim, Valpoi, Ponda, Cuncolim, Quepem, Curchorem, Sanguem, and Canacona. Goa has a total number of 334 villages.
Government and politics
 The politics of Goa are a result of the uniqueness of this region due to 450 years of Portuguese rule, in comparison to three centuries of British rule experienced by the rest of India. The Indian National Congress was unable to achieve electoral success in the first two decades after the State's incorporation into India. Instead, the state was dominated by the regional political parties like Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party and the United Goans Party.
The politics of Goa are a result of the uniqueness of this region due to 450 years of Portuguese rule, in comparison to three centuries of British rule experienced by the rest of India. The Indian National Congress was unable to achieve electoral success in the first two decades after the State's incorporation into India. Instead, the state was dominated by the regional political parties like Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party and the United Goans Party.
Government
Goa has two members of parliament (MP) elected from each district representing the state in the Lok Sabha (House of the People), the lower house of the national Parliament of India. It is also has one member of parliament in the Rajya Sabha (Council of the States), the upper house of the Indian parliament. Goa's administrative capital is based in '' Panaji'', often referred as Panjim in English, Pangim in Indo-Portuguese, Portuguese & Ponjê in Konkani, the official language of the state. It lies on the left bank of the Mandovi river. The seat of the Goa Legislative Assembly is in Porvorim, across the Mandovi from Panaji. The state's highest judiciary is the Goa Bench of the Bombay High Court, a branch of the Bombay High Court permanently seated at Panjim in Goa. Unlike other states, which follow the model of personal laws framed for individual religions introduced in the days of British Raj, the Portuguese Civil Code of Goa and Damaon, a uniform code based on the Napoleonic code was retained in Goa as well as the union territory of Damaon, Diu& Silvassa. Goa has a unicameral legislature, the Goa Legislative Assembly, of 40 members, headed by a speaker. The Chief Minister heads the executive, which is made up of the party or coalition elected with a majority in the legislature. The Governor, the head of the state, is appointed by the President of India. After having stable governance for nearly thirty years up to 1990, Goa is now notorious for its political instability having seen fourteen governments in the span of the fifteen years between 1990 and 2005. In March 2005, the assembly was dissolved by the Governor and President's Rule was declared, which suspended the legislature. A by-election in June 2005 saw the Indian National Congress coming back to power after winning three of the five seats that went to polls. The Indian National Congress, Congress Party and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) are the two largest parties in the state. In the assembly poll of 2007, the INC-led coalition won and formed the government. In the 2012 Vidhan Sabha Elections, the Bharatiya Janata Party along with the Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party won a clear majority, forming the new government with Manohar Parrikar as the Chief Minister. Other parties include the United Goans Democratic Party, the Nationalist Congress Party. In the 2017 Goa Legislative Assembly election, 2017 assembly elections, the Indian National Congress gained the most seats, with the BJP coming in second. However, no party was able to gain a majority in the 40 member house. The BJP was invited to form the Government by Governor Mridula Sinha. The Congress claimed the use of money power on the part of the BJP and took the case to the Supreme Court. However, the Manohar Parikkar led Government was able to prove its majority in the Supreme Court of India, Supreme Court mandated "floor test".Flora and fauna
 Equatorial forest cover in Goa stands at , most of which is owned by the government. Government-owned forest is estimated at whilst private is given as . Most of the forests in the state are located in the interior eastern regions of the state. The Western Ghats, which form most of eastern Goa, have been internationally recognised as one of the biodiversity hotspots of the world. In the February 1999 issue of ''National Geographic Magazine'', Goa was compared with the Amazon and the Congo basins for its rich tropical biodiversity.
Goa's wildlife sanctuaries boast of more than 1512 documented species of plants, over 275 species of birds, over 48 kinds of animals and over 60 genera of reptiles. Nanda Lake is the first and the only Ramsar wetland site in Goa.
Goa is also known for its coconut cultivation. The coconut tree has been reclassified by the government as a palm (like grass), enabling farmers and real estate developers to clear land with fewer restrictions.
Rice is the main food crop, and pulses (legume), ''Ragi'' (Finger Millet), and other food crops are also grown. Main cash crops are arecanut, coconut, cashew nut, sugar cane, and fruits like banana, mango, and pineapple. Goa's state animal is the ''Gaur'', the state bird is the Flame-throated bulbul, Flame-throated ''Bulbul'', and the state tree is the Terminalia elliptica, Indian Laurel.
Equatorial forest cover in Goa stands at , most of which is owned by the government. Government-owned forest is estimated at whilst private is given as . Most of the forests in the state are located in the interior eastern regions of the state. The Western Ghats, which form most of eastern Goa, have been internationally recognised as one of the biodiversity hotspots of the world. In the February 1999 issue of ''National Geographic Magazine'', Goa was compared with the Amazon and the Congo basins for its rich tropical biodiversity.
Goa's wildlife sanctuaries boast of more than 1512 documented species of plants, over 275 species of birds, over 48 kinds of animals and over 60 genera of reptiles. Nanda Lake is the first and the only Ramsar wetland site in Goa.
Goa is also known for its coconut cultivation. The coconut tree has been reclassified by the government as a palm (like grass), enabling farmers and real estate developers to clear land with fewer restrictions.
Rice is the main food crop, and pulses (legume), ''Ragi'' (Finger Millet), and other food crops are also grown. Main cash crops are arecanut, coconut, cashew nut, sugar cane, and fruits like banana, mango, and pineapple. Goa's state animal is the ''Gaur'', the state bird is the Flame-throated bulbul, Flame-throated ''Bulbul'', and the state tree is the Terminalia elliptica, Indian Laurel.
Economy
Goa's state domestic product for 2017 is estimated at $11 billion at current prices. Goa is India's richest state with the highest GDP per capita—two and a half times that of the country—with one of its fastest growth rates: 8.23% (yearly average 1990–2000). Tourism is Goa's primary industry: it gets 12% of foreign tourist arrivals in India. Goa has two main tourist seasons: winter and summer. In winter, tourists from abroad (mainly Europe) come, and summer (which, in Goa, is the rainy season) sees tourists from across India. Goa's State Domestic Product, net state domestic product (NSDP) was around US$7.24 billion in 2015–16. The land away from the coast is rich in minerals and ores, and mining forms the second largest industry. Iron, bauxite, manganese, clays, limestone, and silica are mined. The Mormugao port handled 31.69 a million tonnes of cargo in 2007, which was 39% of India's total iron ore exports. Sesa Goa (now owned by Vedanta Resources) and Dempo are the lead miners. Rampant mining has been depleting the forest cover as well as posing a health hazard to the local population. Corporations are also mining illegally in some areas. During 2015–16, the total traffic handled by Mormugao port was recorded to be 20.78 million tonnes. Agriculture, while of shrinking importance to the economy over the past four decades, offers part-time employment to a sizeable portion of the populace. Rice is the main agricultural crop, followed by areca, cashew, and coconut. Fishing employs about 40,000 people, though recent official figures indicate a decline in the importance of this sector and also a fall in the catch, due perhaps, to traditional fishing giving way to large-scale mechanised trawling. Medium-scale industries include the manufacturing of pesticides, fertilizers, tires, tubes, footwear, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, wheat products, steel rolling, fruits and fish canning, cashew nuts, textiles, brewery products. Currently, there are 16 planned SEZs in Goa. The Goa government has recently decided to not allow any more Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in Goa after strong opposition to them by political parties and the Goa Catholic Church. Goa is also notable for its low-priced beer, wine, and spirits prices due to its very low excise duty on alcohol. Another main source of cash inflow to the state is remittance, from many of its citizens who work abroad, to their families. It is said to have some of the largest bank savings in the country. In 1976 Goa became the first state in India to legalize some types of gambling. This enabled the state to levy taxes on gambling, thereby strengthening the economy. There are several casinos available in Goa. In 2018-2019 tax revenue from casinos reached Rs 414 crore. Goa is the second state in India to achieve a 100 percent automatic telephone system with a solid network of telephone exchanges. As of September 2017, Goa had a total installed power generation capacity of 547.88 MW. Goa is also one of the few states in India to achieve 100 percent rural electrification.Vasco Vasco may refer to:
* Basque language, called ''vasco'' in Spanish
* ''Vasco'' (album), a two-part EP by Ricardo Villalobos
* Vasco da Gama, Portuguese explorer
* Vasco da Gama, Goa, a city in India, often called simply Vasco
* Club de Regatas Va ...
Panjim Downtown.JPG, Commercial area in Panaji
Demographics
Population
A native of Goa is called a Goans, Goan. Goa has a population of 1.459 million residents as of 2011, making it the fourth least populated state of India after Sikkim, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh. Population density of Goa is 394 per km2 which is higher than national average 382 per km2. Goa is the state with highest proportion of urban population with 62.17% of the population living in urban areas. The human sex ratio, sex ratio is 973 females to 1,000 males. The birth rate was 15.70 per 1,000 people in 2007. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes make up 1.74% and 10.23% of the population respectively. As of the 2011 census, over 76% of the population was born in Goa, while just over half of migrants to the state are from the neighbouring states of Karnataka and Maharashtra. Currently over 50% of the permanent resident population is of non-Goan origin, outnumbering the native ethnic Goan population.Languages
The Official Language Act, 1987, of the erstwhile Union Territory of Goa, Daman and Diu makes Konkani language, Konkani in the Devanagari script the sole official language of Goa, but provides that Marathi language, Marathi may also be used "for all or any of the official purposes". Portuguese was the sole official language during Portuguese colonial rule. The government also has a policy of replying in Marathi to correspondence received in Marathi. There have been demands for according Konkani in the Roman script official status in the state. There is widespread support for keeping Konkani as the sole official language of Goa. The entire liturgy and communication of the Catholic church in Goa is done solely in Konkani in the Roman script. Konkani is spoken as a first language by about 66.11% of the people in the state, but almost all Goans can speak and understand Konkani. A large population of people can speak and understand English as well. Other linguistic groups in the state per the 2011 census are speakers of Marathi language, Marathi (10.89%), Hindi (8.64%), Kannada (4.65%), Urdu (2.83%), and Portuguese language (1%). Historically, Konkani was neither the official nor the administrative language of the many rulers of the State. Under the Kadambas (c. 960–1310), the court language was Kannada. When under Muslim rule (1312–1370 and 1469–1510), the official and cultural language was Persian language, Persian. Various stones in the Archaeological Museum and Portrait Gallery from the period are inscribed in Kannada and Persian. During the period in between the two periods of Muslim rule, the Vijayanagara Empire, which had control of the state, mandated the use of Kannada and Telugu language, Telugu.Religion
Tourism
Tourism is generally focused on the coastal areas of Goa, with lower tourist activity inland. In 2010, there were more than 2 million tourists reported to have visited Goa, about 1.2 million of whom were from abroad. , Goa was a destination of choice for Indian and foreign tourists, particularly Britons and Russians, with limited means who wanted to party. The state was hopeful that changes could be made which would attract a more upscale demographic. Goa stands 6th in the Top 10 Nightlife cities in the world in National Geographic, National Geographic Travel. Notable nightclubs in Goa include Chronicle, Mambos and Sinq. One of the biggest tourist attractions in Goa is water sports. Beaches like Baga and Calangute offer jet-skiing, parasailing, banana boat rides, water scooter rides, and more. Patnem beach in Palolem Beach, Palolem stood third in CNN, CNN Travel's Top 20 Beaches in Asia. Over 450 years of Portuguese rule and the influence of the Portuguese culture presents to visitors to Goa a cultural environment that is not found elsewhere in India. Goa is often described as a fusion between Eastern and Western culture with Portuguese culture having a dominant position in the state be it in its architectural, cultural or social settings. The state of Goa is famous for its excellent beaches, churches, and temples. The Bom Jesus Cathedral, Fort Aguada and a new wax museum on Indian history, culture and heritage in Old Goa are other tourism destinations.Historic sites and neighbourhoods
Goa has one World Heritage Sites, World Heritage Site: the Bom Jesus Basilica with Old Goa, churches and convents of Old Goa. The basilica holds the mortal remains of St. Francis Xavier, regarded by many Catholics as the patron saint of Goa (the patron of the Archdiocese of Goa is actually Saint Joseph Vaz). These are both Portuguese-era monuments and reflect a strong European character. The relics are taken down for veneration and for public viewing, per the prerogative of the Church in Goa, not every ten or twelve years as popularly thought and propagated. The last exposition was held in 2014. Goa has the Sanctuary of Saint Joseph Vaz in Sancoale. Pilar, Goa, Pilar monastery which holds novenas of Agnelo de Souza, Venerable Padre Agnelo Gustavo de Souza from 10 to 20 November yearly. There is a claimed Marian apparition at the Church of Saints Simon and Jude at Apparition of Our Lady at Batim, Batim, Ganxim, near Pilar, Goa, Pilar, where Goans and non-resident Goans visit. There is the statue of the bleeding Jesus on the Crucifix at the Santa Monica Convent in Velha Goa. There are churches (''Igorzo''), like the baroque styled ''Nixkollounk Gorb-Sombhov Saibinnich Igorz'' (Church of the Our Lady of Immaculate Conception) in Panaji, the Gothic architecture, Gothic styled ''Mater Dei'' (''Dêv Matechi Igorz''/ Mother of God) Church (building), church in Saligao and each church having its own style and heritage, besides ''Kopelam/ Irmidi'' (chapels). The Velhas Conquistas regions are known for Goa-Portuguese style architecture. There are many forts in Goa such as Terekhol Fort, Tiracol, Chapora Fort, Chapora, Corjuem Fort, Corjuem, Fort Aguada, Aguada, Reis Magos, Fort Nanus, Nanus, Mormugao, Fort Gaspar Dias and Cabo de Rama. In many parts of Goa, mansions constructed in the Indo-Portuguese style architecture still stand, though, in some villages, most of them are in a dilapidated condition. Fontainhas (quarter), Fontainhas in Panaji has been declared a cultural quarter, showcasing the life, architecture and culture of Goa. Influences from the Portuguese era are visible in some of Goa's temples, notably the Shanta Durga Temple, the Mangueshi Temple, the Shri Damodar Temple and the Mahalasa Temple. After 1961, many of these were demolished and reconstructed in the indigenous Indian style.Museums and science centre
Goa has three important museums: the Goa State Museum, the Naval Aviation Museum (India), Naval Aviation Museum and the National Institute of Oceanography, India, National Institute of Oceanography. The aviation museum is one of three in India (the others are in Indian Air Force Museum, Palam, Delhi and HAL Aerospace Museum, Bengaluru). The Goa Science Centre is in Miramar, Panaji., Nehru Science Centre website. Retrieved 4 August 2010. The National Institute of Oceanography, India (NIO) is in Dona Paula.NIO website. Retrieved 4 August 2010. Museum of Goa is a privately owned contemporary art gallery in Pilerne Industrial Estate, near Calangute.
Beaches
Most of the beauty of Goa is present on the beaches. The coastline of about 103 km is blessed with some of the most attractive beaches flanked by the Arabian Sea. The beaches of Goa are counted among the most beautiful in the world. * Anjuna Beach * Baga beach, Baga Beach * Bambolim Beach * Betul Beach * Calangute Beach * Candolim Beach * Cavelossim Beach * Colva Beach * Majorda Beach * Miramar Beach, Goa, Miramar BeachWater Sports
Goa is one of the best destination in india for its tourism. Water sports are organized on its magnificent beach. Adventure sports like parasailing, jet skiing, banana riding, kayaking, rafting, snorkeling, surfing, and Bungee Jumping make Goa an exciting experience. Scuba diving is one of the best experiences.Culture
 Having been a Portuguese India, Portuguese territory for over 450 years, Goan culture is an amalgamation of both Eastern culture, Eastern and Western culture, Western styles, with the latter having a more dominant role. The tableau of Goa showcases religious harmony by focusing on the Deepastambha, the Cross, and Ghode Modni followed by a chariot. European royal attire of kings is as much part of Goa's cultural heritage as are regional dances performed depicting a unique blend of different religions and cultures of this State. Prominent local festivals are Christmas, Easter, Carnival, Diwali, Shigmo, Ganesh Chaturthi, Chavoth, Gudi Padwa, Samvatsar Padvo, Navratri, Dasara etc. The Goan Carnival and Christmas-new year celebrations attract many tourists.
The Gomant Vibhushan Award, the highest civilian honour of the State of Goa, is given annually by Government of Goa since 2010.
Having been a Portuguese India, Portuguese territory for over 450 years, Goan culture is an amalgamation of both Eastern culture, Eastern and Western culture, Western styles, with the latter having a more dominant role. The tableau of Goa showcases religious harmony by focusing on the Deepastambha, the Cross, and Ghode Modni followed by a chariot. European royal attire of kings is as much part of Goa's cultural heritage as are regional dances performed depicting a unique blend of different religions and cultures of this State. Prominent local festivals are Christmas, Easter, Carnival, Diwali, Shigmo, Ganesh Chaturthi, Chavoth, Gudi Padwa, Samvatsar Padvo, Navratri, Dasara etc. The Goan Carnival and Christmas-new year celebrations attract many tourists.
The Gomant Vibhushan Award, the highest civilian honour of the State of Goa, is given annually by Government of Goa since 2010.
Dance and music
Traditional Goan art forms are Dekhnni, Fugdi, Corridinho, Mando (music), Mando, Dulpod and Fado. Goan Catholics are fond of social gatherings and Tiatr (Teatro). As part of its Portuguese history, music is an integral part of Goan homes. It is often said that "Goans are born with music and sport". Western musical instruments like the piano, guitars and violins are widely used in most religious and social functions of the Catholics. Goan Hindus are very fond of Natak, Bhajan and Kirtan. Many famous Indian classical music, Indian classical singers hail from Goa, including Mogubai Kurdikar, Kishori Amonkar, Kesarbai Kerkar, Jitendra Abhisheki and Pandit Prabhakar Karekar.Theatre
Konkani cinema
 Konkani cinema is an Indian film industry, where films are made in the Konkani language, which is spoken mainly in the Indian states of Goa,
Konkani cinema is an Indian film industry, where films are made in the Konkani language, which is spoken mainly in the Indian states of Goa, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
and Karnataka and to a smaller extent in Kerala. Konkani films have been produced in Goa, Karnataka, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
and Kerala.
The first full-length Konkani film was ''Mogacho Anvddo'', released on 24 April 1950, and was produced and directed by A. L.Jerry Braganza, a native of Mapusa, under the banner of ETICA Pictures. Hence, 24 April is celebrated as Konkani Film Day.
Since 2004, starting from the 35th edition, the International Film Festival of India moved its permanent venue to Goa, it is annually held in the months of November and December.
Konkani film The Man Beyond the Bridge, Paltadcho manis has been included in the world's best films of 2009 list.
Konkani films are eligible for the National Film Award for Best Feature Film in Konkani. The most commercially successful Konkani film (as of June 2011) is O Maria directed by Rajendra Talak.
In 2012, the whole new change was adopted in Konkani Cinema by introducing Digital Theatrical Film "The Victim (2012 film), The Victim" directed by Milroy Goes.
Some old Konkani films are ''Sukhachem Sopon'', ''Amchem Noxib'', ''Nirmonn'', ''Mhoji Ghorkarn'', ''Kortubancho Sonvsar'', ''Jivit Amchem Oxem'', ''Mog ani Moipas'', ''Bhuierantlo Munis'', ''Suzanne'', ''Boglantt'', ''Padri (film), Padri'' and ''Bhogsonne''. Ujwadu is a 2011 Konkani film directed by Kasargod Chinna and produced by KJ Dhananjaya and Anuradha Padiyar.
Food
Architecture
Media and communication
Goa is served by almost all television channels available in India. Channels are received through cable in most parts of Goa. In the interior regions, channels are received via satellite dishes. Doordarshan, the national television broadcaster, has two free terrestrial channels on air. DTH (Direct To Home) TV services are available from Dish TV, Videocon D2H, Tata Sky & DD Direct Plus. The All India Radio is the only radio channel in the state that broadcasts on both Frequency Modulation, FM and Amplitude Modulation, AM bands. Two AM channels are broadcast, the primary channel at 1287 kHz and the Vividh Bharati channel at 1539 kHz. AIR's FM channel is called FM Rainbow and is broadcast at 105.4 MHz. A number of private FM radio channels are available, Big FM (Indian radio station), Big FM at 92.7 and Radio Indigo at 91.9 MHz. There is also an educational radio channel, Gyan Vani, run by IGNOU broadcast from Panaji at 107.8 MHz. In 2006, St Xavier's College, Mapusa, became the first college in the state to launch a campus community radio station "Voice of Xavier's". Major cellular service operators include Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Essar, Idea Cellular(merged with Vodafone in 2018), Telenor, Reliance Infocomm, Tata DoCoMo, BSNL CellOne and Jio. Local publications include the English language ''O Heraldo'' (Goa's oldest, once a Portuguese language paper), ''The Gomantak Times'' and ''The Navhind Times''. In addition to these, ''The Times of India'' and ''The Indian Express'' are also received from Mumbai and Bangalore in the urban areas. ''The Times of India'' has recently started publication from Goa itself, serving the local population news directly from the state capital. Among the list of officially accredited newspapers are ''O Heraldo'', ''The Navhind Times'' and ''The Gomantak Times'' in English; ''Bhaangar Bhuin'' in Konkani (Devanagari script); and ''Tarun Bharat'', ''Gomantak'', ''Navprabha'', ''Goa Times'', ''Sanatan Prabhat'', ''Govadoot'' and ''Lokmat'' (all in Marathi). All are dailies. Other publications in the state include ''Planet Goa'' (English, monthly), ''Goa Today'' (English, monthly), ''Goan Observer'' (English, weekly), ''Vauraddeancho Ixtt'' (Konkani in the Roman script, Roman-script Konkani, weekly) ''Goa Messenger'', ''Vasco Watch'', ''Gulab'' (Konkani, monthly), ''Bimb'' (Devanagari-script Konkani). One electronic mailing list that is based in Goa is Goanet.Sports
 Normally other states are fond of cricket but association football is the most popular sport in Goa and is embedded in Goan culture as a result of the Portuguese influence Its origins in the state are traced back to 1883 when the visiting Irish priest Fr. William Robert Lyons established the sport as part of a "Christian education". On 22 December 1959 the ''Associação de Futebol de Goa'' was formed, which continues to administer the game in the state under the new name Goa Football Association. Goa, along with West Bengal and Kerala is the locus of football in India and is home to many football clubs in the national I-League. The state's football powerhouses include Salgaocar F.C., Salgaocar, Dempo S.C., Dempo, Churchill Brothers S.C., Churchill Brothers, Vasco S.C., Vasco, Sporting Clube de Goa and FC Goa. The first Unity World Cup was held in Goa in 2014. The state's main football stadium, Fatorda Stadium, is located at Margao and also hosts cricket matches. The state hosted few matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup in Fatorda Stadium.
A number of Goans have represented India in football and six of them, namely Samir Subash Naik, Samir Naik, Climax Lawrence, Brahmanand Sankhwalkar, Bruno Coutinho (footballer, born 1969), Bruno Coutinho, Mauricio Afonso and Roberto Fernandes have all captained the national team. Goa has its own Goa football team, state football team and league, the Goa Professional League. It is probably the only state in India where cricket is not considered the most important of all sports. Goan's are avid football fans, particularly of the football teams from Portugal (Benfica, Sporting), and Brazil especially during major football events such as the 'European Cup' and the 'World Cup' championships. The Portuguese footballer Ronaldo (Portuguese footballer), Ronaldo and Brazilian Neymar, are revered superstar football players in Goa.
Goa also has its own Goa cricket team, cricket team. Dilip Sardesai and Shikha Pandey remain the only Goans to date to play international cricket for Indian cricket team, India. Another Goan cricketer, Suyash Prabhudessai was selected by the Royal Challengers Bangalore for a base price of in Indian Premier League, IPL 2021 and for in IPL 2022.
India (Goa) is a member of the 'Lusophony Olympic Games' which are hosted every four years in one of the Portuguese CPLP member countries, with 733 athletes from 11 countries. Most of the countries competing are countries that are members of the CPLP (Community of Portuguese Language Countries), but some are countries with significant Portuguese communities or have a history with Portugal. This event is similar in concept to the Commonwealth Games (for members of the Commonwealth of Nations) and the Jeux de la Francophonie (for the Francophone community).
Normally other states are fond of cricket but association football is the most popular sport in Goa and is embedded in Goan culture as a result of the Portuguese influence Its origins in the state are traced back to 1883 when the visiting Irish priest Fr. William Robert Lyons established the sport as part of a "Christian education". On 22 December 1959 the ''Associação de Futebol de Goa'' was formed, which continues to administer the game in the state under the new name Goa Football Association. Goa, along with West Bengal and Kerala is the locus of football in India and is home to many football clubs in the national I-League. The state's football powerhouses include Salgaocar F.C., Salgaocar, Dempo S.C., Dempo, Churchill Brothers S.C., Churchill Brothers, Vasco S.C., Vasco, Sporting Clube de Goa and FC Goa. The first Unity World Cup was held in Goa in 2014. The state's main football stadium, Fatorda Stadium, is located at Margao and also hosts cricket matches. The state hosted few matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup in Fatorda Stadium.
A number of Goans have represented India in football and six of them, namely Samir Subash Naik, Samir Naik, Climax Lawrence, Brahmanand Sankhwalkar, Bruno Coutinho (footballer, born 1969), Bruno Coutinho, Mauricio Afonso and Roberto Fernandes have all captained the national team. Goa has its own Goa football team, state football team and league, the Goa Professional League. It is probably the only state in India where cricket is not considered the most important of all sports. Goan's are avid football fans, particularly of the football teams from Portugal (Benfica, Sporting), and Brazil especially during major football events such as the 'European Cup' and the 'World Cup' championships. The Portuguese footballer Ronaldo (Portuguese footballer), Ronaldo and Brazilian Neymar, are revered superstar football players in Goa.
Goa also has its own Goa cricket team, cricket team. Dilip Sardesai and Shikha Pandey remain the only Goans to date to play international cricket for Indian cricket team, India. Another Goan cricketer, Suyash Prabhudessai was selected by the Royal Challengers Bangalore for a base price of in Indian Premier League, IPL 2021 and for in IPL 2022.
India (Goa) is a member of the 'Lusophony Olympic Games' which are hosted every four years in one of the Portuguese CPLP member countries, with 733 athletes from 11 countries. Most of the countries competing are countries that are members of the CPLP (Community of Portuguese Language Countries), but some are countries with significant Portuguese communities or have a history with Portugal. This event is similar in concept to the Commonwealth Games (for members of the Commonwealth of Nations) and the Jeux de la Francophonie (for the Francophone community).
Education
Bicholim
Bicholim, pronounced (), also known as Divchal and Dicholi, is a town and a municipal council in North Goa district in the state of Goa, India. It is the headquarters of the ''Concelho'' (district) of Bicholim, one of seven that make up the No ...
and Curchorem, and aided institutions like Father Agnel Polytechnic in Verna and the Institute of Shipbuilding Technology in Vasco da Gama which impart technical and vocational training.
Other colleges in Goa include Shri Damodar College of Commerce and Economics, V.V.M's R.M. Salgaocar Higher Secondary School in Margao, G.V.M's S.N.J.A higher secondary school, Don Bosco College, D.M.'s College of Arts, Science and Commerce, St Xavier's College, Carmel College, The Parvatibai Chowgule College, Dhempe College, Damodar College, M. E. S. College of Arts & Commerce, S. S. Samiti's Higher Secondary School of Science and Rosary College of Commerce & Arts. As the result of renewed interest in the Portuguese language and culture, Portuguese at all levels of instruction is offered in many schools in Goa, largely private ones. In some cases, Goan students do student exchange programs in Portugal.
Transportation
Air
 Goa International Airport, is a civil enclave at INS Hansa, a Naval airfield located at Dabolim near
Goa International Airport, is a civil enclave at INS Hansa, a Naval airfield located at Dabolim near Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link E ...
. The airport caters to scheduled domestic and international air services. Goa has scheduled international connections to Doha, Dubai, Muscat, Oman, Muscat, Sharjah (city), Sharjah and Kuwait in the Middle East by airlines like Air Arabia, Air India, GoAir, IndiGo, Oman Air, SpiceJet and Qatar Airways. Though night operations were not permitted till recently, the military now allows civil airlines to fly during the night.
A Mopa Airport, greenfield airport is under construction at Mopa, Goa, Mopa in Pernem taluka.
It is expected to be completed by 2022.
Road

 Goa's public transport largely consists of privately operated buses linking the major towns to rural areas. Government-run buses, maintained by the Kadamba Transport Corporation, link major routes (like the Panaji–Margao route) and some remote parts of the state. The Corporation owns 15 bus stands, 4 depots and one Central workshop at Porvorim and a Head Office at Porvorim. In large towns such as Panaji and Margao, intra-city buses operate. However, public transport in Goa is less developed, and residents depend heavily on their own transportation, usually motorised two-wheelers and small family cars.
Goa's public transport largely consists of privately operated buses linking the major towns to rural areas. Government-run buses, maintained by the Kadamba Transport Corporation, link major routes (like the Panaji–Margao route) and some remote parts of the state. The Corporation owns 15 bus stands, 4 depots and one Central workshop at Porvorim and a Head Office at Porvorim. In large towns such as Panaji and Margao, intra-city buses operate. However, public transport in Goa is less developed, and residents depend heavily on their own transportation, usually motorised two-wheelers and small family cars.
Rail
Sea
The Mormugao Port Trust near the city of Vasco handles mineral ore, petroleum, coal, and international containers. Much of the shipments consist of minerals and ores from Goa's hinterland. Panaji, which is on the banks of the Mandovi, has a minor port, which used to handle passengers Steamboat, steamers between Goa and Mumbai till the late 1980s. There was also a short-lived catamaran service linking Mumbai and Panaji operated by Damania Shipping in the 1990s.Sister states
* Hawai'i State, Hawai'i, United States of AmericaSee also
* Portuguese Civil Code of Goa and Damaon * Goa, Daman and Diu * Konkan * Outline of Goa * Portuguese Goa and DamaonReferences
Sources
* *Further reading
* * Andrada (undated). ''The Life of Dom John de Castro: The Fourth Vice Roy of India''. Jacinto Freire de Andrada. Translated into English by Peter Wyche. (1664). Henry Herrington, New Exchange, London. Facsimile edition (1994) AES Reprint, New Delhi. .External links
; GovernmentGovernment of Goa
Department of Tourism
; General information * * {{Authority control Goa, Konkan Historic Jewish communities Former Portuguese colonies Former exclaves States and territories established in 1987 1987 establishments in India City-states States and union territories of India India–Portugal relations