Geophysical Prospection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of

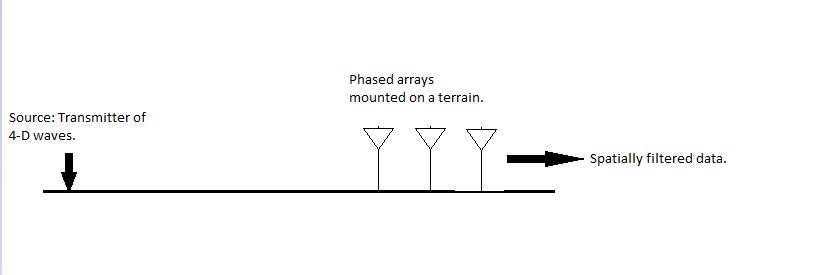 This approach is applied for filtering space-time signals. It is designed to isolate signals travelling in a particular direction. One of the simplest filters is weighted delay and sum beamformer. The output is the average of the linear combination of delayed signals. In other words, the beamformer output is formed by averaging weighted and delayed versions of receiver signals. The delay is chosen such that the passband of beamformer is directed to a specific direction in the space.
This approach is applied for filtering space-time signals. It is designed to isolate signals travelling in a particular direction. One of the simplest filters is weighted delay and sum beamformer. The output is the average of the linear combination of delayed signals. In other words, the beamformer output is formed by averaging weighted and delayed versions of receiver signals. The delay is chosen such that the passband of beamformer is directed to a specific direction in the space.
geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' so ...
data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure. Hence, detection and analysis of the electric and Magnetic fields is very crucial. As the Electromagnetic and gravitational waves are multi-dimensional signals, all the 1-D transformation techniques can be extended for the analysis of these signals as well. Hence this article also discusses multi-dimensional signal processing techniques.
Geophysical surveys may use a great variety of sensing instruments, and data may be collected from above or below the Earth's surface or from aerial, orbital, or marine platforms. Geophysical surveys have many applications in geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
, archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts ...
, mineral and energy exploration, oceanography, and engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
. Geophysical surveys are used in industry as well as for academic research.
The sensing instruments such as gravimeter
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest.
Units of measurement
G ...
, gravitational wave sensor
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong ...
and magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
s detect fluctuations in the gravitational and magnetic field. The data collected from a geophysical survey is analysed to draw meaningful conclusions out of that. Analysing the spectral density and the time-frequency localisation of any signal is important in applications such as oil exploration and seismography.
Types of geophysical survey
There are many methods and types of instruments used in geophysical surveys. Technologies used for geophysical surveys include: # Seismic methods, such asreflection seismology
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seis ...
, seismic refraction
Seismic refraction is a geophysical principle governed by Snell's Law of refraction. The seismic refraction method utilizes the refraction of seismic waves by rock or soil layers to characterize the subsurface geologic conditions and geologic str ...
, and seismic tomography
Seismic tomography or seismotomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth with seismic waves produced by earthquakes or explosions. P-, S-, and surface waves can be used for tomographic models of different resolutions based on ...
. This type of survey is carried out to discover the detailed structure of the rock formations beneath the surface of the Earth.
# Seismoelectrical method
The seismoelectrical method (which is different from the electroseismic physical principle) is based on the generation of electromagnetic fields in soils and rocks by seismic waves. This technique is still under development and in the future it may ...
# Geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), Earth rotation, orientation in space, and Earth's gravity, gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properti ...
and gravity techniques, including gravimetry
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest.
Units of measurement
Gr ...
and gravity gradiometry
Gravity gradiometry is the study and measurement of variations ( anomalies) in the Earth's gravity field. The gravity gradient tensor is the spatial rate of change of gravitational acceleration; as acceleration is a vector quantity, with magnitu ...
. This type of survey is carried out to discover the structure of rock formations beneath the surface of the Earth.
# Magnetic techniques, including aeromagnetic survey
An aeromagnetic survey is a common type of geophysical survey carried out using a magnetometer aboard or towed behind an aircraft. The principle is similar to a magnetic survey carried out with a hand-held magnetometer, but allows much larger are ...
s and magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
s.
# Electrical techniques, including electrical resistivity tomography
Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) or electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) is a geophysical technique for imaging sub-surface structures from electrical resistivity measurements made at the surface, or by electrodes in one or more boreh ...
, induced polarization
Induced polarization (IP) is a geophysical imaging technique used to identify the electrical chargeability of subsurface materials, such as ore.
The polarization effect was originally discovered by Conrad Schlumberger when measuring the resisti ...
, spontaneous potential Spontaneous potentials are often measured down boreholes for formation evaluation in the oil and gas industry, and they can also be measured along the Earth's surface for mineral exploration or groundwater investigation. The phenomenon and its appl ...
and marine control source electromagnetic (mCSEM) or EM seabed logging. This type of survey is carried out mainly to study the existence of groundwater.
# Electromagnetic methods, such as magnetotellurics
Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface.
Investigation depth ...
, ground penetrating radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a Geophysics, geophysical method that uses radar pulses to Geophysical imaging, image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, ...
and transient/time-domain electromagnetics, surface nuclear magnetic resonance
Surface nuclear magnetic resonance (SNMR), also known as magnetic resonance Sounding (MRS), is a geophysical technique specially designed for hydrogeology. It is based on the principle of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and measurements can be use ...
(also known as magnetic resonance sounding).
# Borehole geophysics, also called well logging
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record (a ''well log'') of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface ...
.
# Remote sensing techniques, including hyperspectral
Hyperspectral imaging collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifyi ...
.
Geophysical signal detection
This section deals with the principles behind measurement of geophysical waves. The magnetic and gravitational fields are important components of geophysical signals. The instrument used to measure the change in gravitational field is thegravimeter
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest.
Units of measurement
G ...
. This meter measures the variation in the gravity due to the subsurface formations and deposits. To measure the changes in magnetic field the magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
is used. There are two types of magnetometers, one that measures only vertical component of the magnetic field and the other measures total magnetic field.
With the help of these meters, either the gravity values at different locations are measured or the values of Earth's magnetic field are measured. Then these measured values are corrected for various corrections and an anomaly map is prepared. By analyzing these anomaly maps one can get an idea about the structure of rock formations in that area. For this purpose one need to use various analog or digital filters.
Measurement of Earth’s magnetic fields
Magnetometers are used to measure the magnetic fields, magnetic anomalies in the earth. The sensitivity of magnetometers depends upon the requirement. For example, the variations in the geomagnetic fields can be to the order of several aT where 1aT = 10−18T . In such cases, specialized magnetometers such as thesuperconducting quantum interference device
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting ...
(SQUID) are used.
Jim Zimmerman co-developed the rf superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) during his tenure at Ford research lab. However, events leading to the invention of the SQUID were in fact, serendipitous. John Lambe, during his experiments on nuclear magnetic resonance noticed that the electrical properties of indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 par ...
varied due to a change in the magnetic field of the order of few nT. However, Lambe was not able to fully recognize the utility of SQUID.
SQUIDs have the capability to detect magnetic fields of extremely low magnitude. This is due to the virtue of the Josephson junction
In physics, the Josephson effect is a phenomenon that occurs when two superconductors are placed in proximity, with some barrier or restriction between them. It is an example of a macroscopic quantum phenomenon, where the effects of quantum mec ...
. Jim Zimmerman pioneered the development of SQUID by proposing a new approach to making the Josephson junctions. He made use of niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it ha ...
wires and niobium ribbons to form two Josephson junctions connected in parallel. The ribbons act as the interruptions to the superconducting current flowing through the wires. The junctions are very sensitive to the magnetic fields and hence are very useful in measuring fields of the order of 10^-18T.
Seismic wave measurement using gravitational wave sensor
Gravitational wave sensors can detect even a minute change in the gravitational fields due to the influence of heavier bodies. Large seismic waves can interfere with the gravitational waves and may cause shifts in the atoms. Hence, the magnitude of seismic waves can be detected by a relative shift in the gravitational waves.Measurement of seismic waves using atom interferometer
The motion of any mass is affected by the gravitational field. The motion of planets is affected by the Sun's enormous gravitational field. Likewise, a heavier object will influence the motion of other objects of smaller mass in its vicinity. However, this change in the motion is very small compared to the motion of heavenly bodies. Hence, special instruments are required to measure such a minute change.
Atom interferometer An atom interferometer is an interferometer which uses the wave character of atoms. Similar to optical interferometers, atom interferometers measure the difference in phase between atomic matter waves along different paths. Atom interferometers h ...
s work on the principle of diffraction. The diffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural ...
s are nano fabricated materials with a separation of a quarter wavelength of light. When a beam of atoms pass through a diffraction grating, due to the inherent wave nature of atoms, they split and form interference fringes on the screen. An atom interferometer is very sensitive to the changes in the positions of atoms. As heavier objects shifts the position of the atoms nearby, displacement of the atoms can be measured by detecting a shift in the interference fringes.
Existing approaches in geophysical signal recognition
This section addresses the methods and mathematical techniques behind signal recognition and signal analysis. It considers the time domain and frequency domain analysis of signals. This section also discusses various transforms and their usefulness in the analysis of multi-dimensional waves.3D sampling
Sampling
The first step in any signal processing approach is analog to digital conversion. The geophysical signals in the analog domain has to be converted to digital domain for further processing. Most of the filters are available in 1D as well as 2D.Analog to digital conversion
As the name suggests, the gravitational and electromagnetic waves in the analog domain are detected, sampled and stored for further analysis. The signals can be sampled in both time and frequency domains. The signal component is measured at both intervals of time and space. Ex, time-domain sampling refers to measuring a signal component at several instances of time. Similarly, spatial-sampling refers to measuring the signal at different locations in space. Traditional sampling of 1D time varying signals is performed by measuring the amplitude of the signal under consideration in discrete intervals of time. Similarly sampling of space-time signals (signals which are functions of 4 variables – 3D space and time), is performed by measuring the amplitude of the signals at different time instances and different locations in the space. For example, the earth's gravitational data is measured with the help ofgravitational wave sensor
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong ...
or gradiometerE.H. Metzger, "Development Experience of Gravity Gradiometer System", IEEE Plans Meeting, 1982 by placing it in different locations at different instances of time.
Spectrum analysis
Multi-dimensional Fourier transform
The Fourier expansion of a time domain signal is the representation of the signal as a sum of its frequency components, specifically sum of sines and cosines.Joseph Fourier
Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier (; ; 21 March 1768 – 16 May 1830) was a French mathematician and physicist born in Auxerre and best known for initiating the investigation of Fourier series, which eventually developed into Fourier analysis and har ...
came up with the Fourier representation to estimate the heat distribution of a body. The same approach can be followed to analyse the multi-dimensional signals such as gravitational waves and electromagnetic waves.
The 4D Fourier representation of such signals is given by
:
* ''ω'' represents temporal frequency and ''k'' represents spatial frequency.
* ''s''(''x'',''t'') is a 4-dimensional space-time signal which can be imagined as travelling plane waves. For such plane waves, the plane of propagation is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the considered wave.
Wavelet transform
The motivation for development of the Wavelet transform was the Short-time Fourier transform. The signal to be analysed, say ''f''(''t'') is multiplied with a window function ''w''(''t'') at a particular time instant. Analysing the Fourier coefficients of this signal gives us information about the frequency components of the signal at a particular time instant. The STFT is mathematically written as: : The Wavelet transform is defined as : A variety of window functions can be used for analysis. Wavelet functions are used for both time and frequency localisation. For example, one of the windows used in calculating the Fourier coefficients is the Gaussian window which is optimally concentrated in time and frequency. This optimal nature can be explained by considering the time scaling and time shifting parameters ''a'' and ''b'' respectively. By choosing the appropriate values of ''a'' and ''b'', we can determine the frequencies and the time associated with that signal. By representing any signal as the linear combination of the wavelet functions, we can localize the signals in both time and frequency domain. Hence wavelet transforms are important in geophysical applications where spatial and temporal frequency localisation is important. Time frequency localisation using wavelets Geophysical signals are continuously varying functions of space and time. The wavelet transform techniques offer a way to decompose the signals as a linear combination of shifted and scaled version of basis functions. The amount of "shift" and "scale" can be modified to localize the signal in time and frequency.Beamforming
Simply put, space-time signal filtering problem can be thought as localizing the speed and direction of a particular signal.Dan E. Dudgeon, Russell M. Mersereau, “Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing”, Prentice-Hall Signal Processing Series, ,pp. 291-294, 1983. The design of filters for space-time signals follows a similar approach as that of 1D signals. The filters for 1-D signals are designed in such a way that if the requirement of the filter is to extract frequency components in a particular non-zero range of frequencies, abandpass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
Description
In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-po ...
with appropriate passband and stop band frequencies in determined. Similarly, in the case of multi-dimensional systems, the wavenumber-frequency response of filters is designed in such a way that it is unity in the designed region of (''k'', ''ω'') a.k.a. wavenumber – frequency and zero elsewhere.
Classical estimation theory
This section deals with the estimation of the power spectral density of the multi-dimensional signals. The spectral density function can be defined as a multidimensional Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function of the random signal.Dan E. Dudgeon, Russell M. Mersereau, “Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing”, Prentice-Hall Signal Processing Series, ,pp. 315-338, 1983 : :