|
Geophysical Prospection
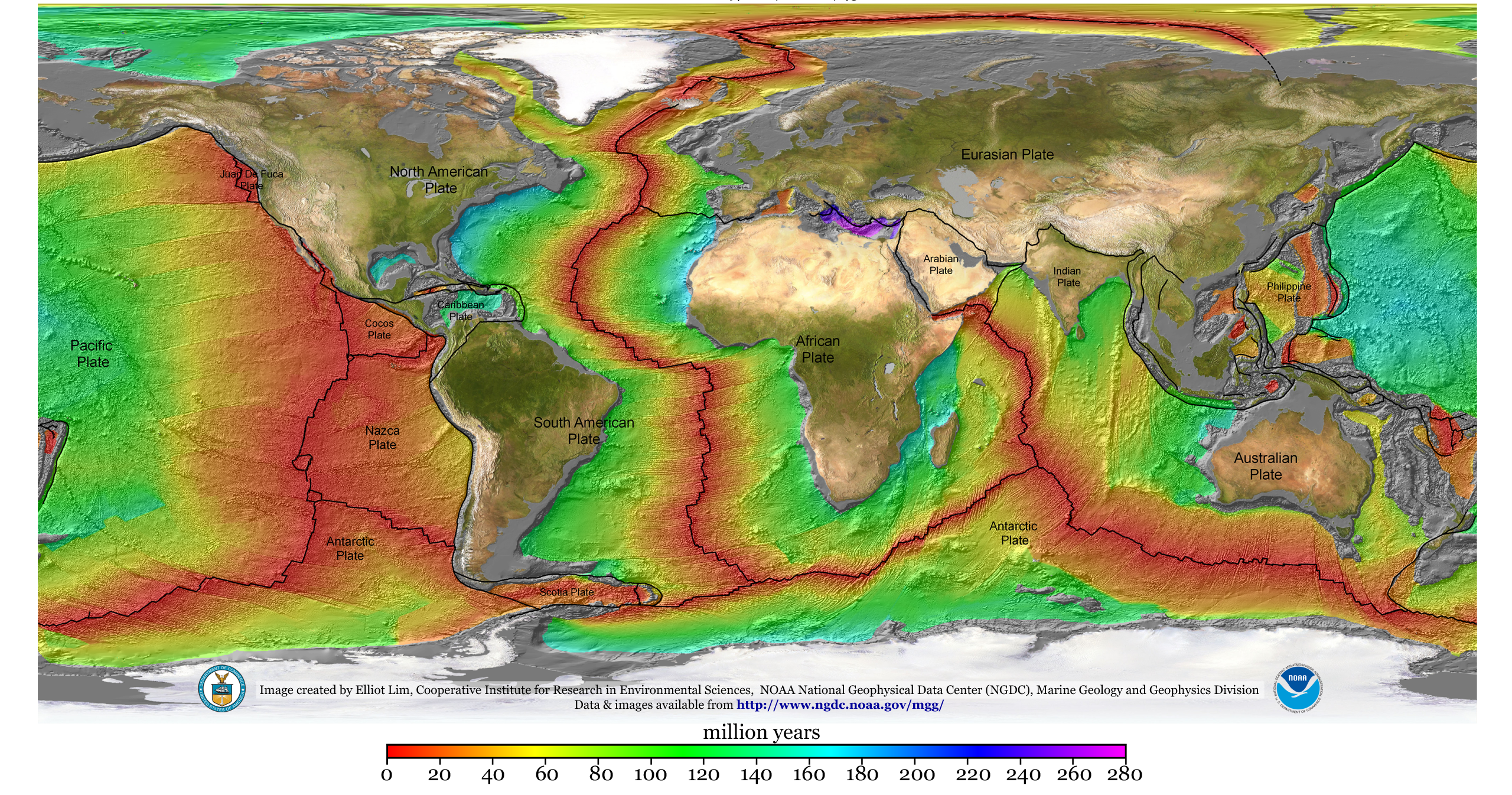
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure. Hence, detection and analysis of the electric and Magnetic fields is very crucial. As the Electromagnetic and gravitational waves are multi-dimensional signals, all the 1-D transformation techniques can be extended for the analysis of these signals as well. Hence this article also discusses multi-dimensional signal processing techniques. Geophysical surveys may use a great variety of sensing instruments, and data may be collected from above or below the Earth's surface or from aerial, orbital, or marine platforms. Geophysical surveys have many applications in geology, archaeology, mineral and energy exploration, oceanography, and engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
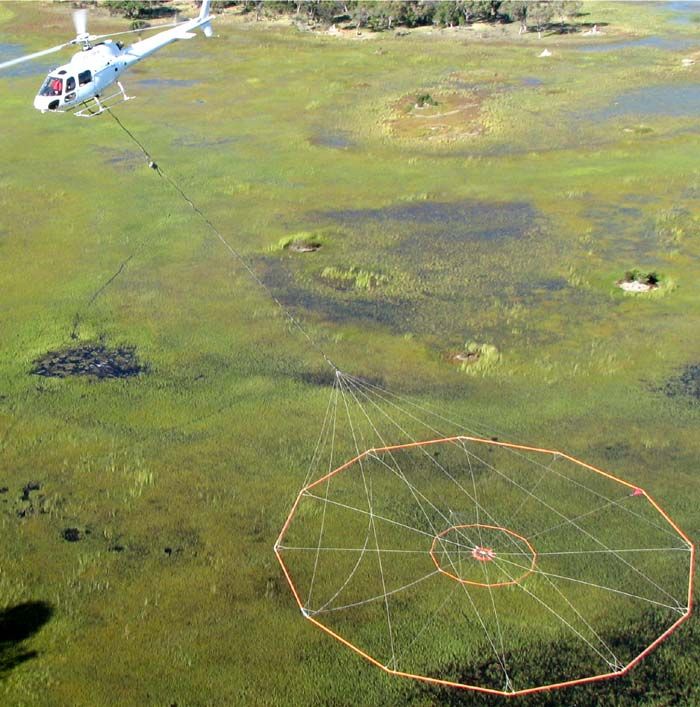
Gravity Gradiometry
Gravity gradiometry is the study and measurement of variations ( anomalies) in the Earth's gravity field. The gravity gradient tensor is the spatial rate of change of gravitational acceleration; as acceleration is a vector quantity, with magnitude and three-dimensional direction, the full gravity gradient is a 3x3 tensor. Gravity gradiometry is used by oil and mineral prospectors to measure the density of the subsurface, effectively by measuring the rate of change of gravitational acceleration due to underlying rock properties. From this information it is possible to build a picture of subsurface anomalies which can then be used to more accurately target oil, gas and mineral deposits. It is also used to image water column density, when locating submerged objects, or determining water depth (bathymetry). Physical scientists use gravimeters to determine the exact size and shape of the earth and they contribute to the gravity compensations applied to inertial navigation systems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology); it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted by a satellite or aircraft to the object and its reflection detected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well Logging
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record (a ''well log'') of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface (''geological'' logs) or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole (''geophysical'' logs). Some types of geophysical well logs can be done during any phase of a well's history: drilling, completing, producing, or abandoning. Well logging is performed in boreholes drilled for the oil and gas, groundwater, mineral and geothermal exploration, as well as part of environmental and geotechnical studies. Wireline logging The oil and gas industry uses wireline logging to obtain a continuous record of a formation's rock properties. Wireline logging can be defined as being "The acquisition and analysis of geophysical data performed as a function of well bore depth, together with the provision of related services." Note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Surface nuclear magnetic resonance (SNMR), also known as magnetic resonance Sounding (MRS), is a geophysical technique specially designed for hydrogeology. It is based on the principle of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and measurements can be used to indirectly estimate the water content of saturated and unsaturated zones in the earth's subsurface. SNMR is used to estimate aquifer properties, including the quantity of water contained in the aquifer, porosity, and hydraulic conductivity. History The MRS technique was originally conceived in the 1960s by Russell H. Varian, one of the inventors of the proton magnetometer. SNMR is a product of a joint effort by many scientists and engineers who started developing this method in the USSR under the guidance of A.G. Semenov and continued this work all over the world.Semenov AG (1987) NMR Hydroscope for water prospecting.Proceedings of a Seminar on Geotomography, Indian Geophysical Union, Hyderabad, pp 66–67 Semenov's team used nuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDEM
Transient electromagnetics, (also time-domain electromagnetics / TDEM), is a geophysical exploration technique in which electric and magnetic fields are induced by transient pulses of electric current and the subsequent decay response measured. TEM / TDEM methods are generally able to determine subsurface electrical properties, but are also sensitive to subsurface magnetic properties in applications like UXO detection and characterization. TEM/TDEM surveys are a very common surface EM technique for mineral exploration, groundwater exploration, and for environmental mapping, used throughout the world in both onshore and offshore applications. Physical principles Two fundamental electromagnetic principles are required to derive the physics behind TEM surveys: Faraday's law of induction and Lenz's Law. A loop of wire is generally energized by a direct current. At some time (''t0'') the current is cut off as quickly as possible. Faraday's law dictates that a nearly identical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Penetrating Radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a Geophysics, geophysical method that uses radar pulses to Geophysical imaging, image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables or masonry. This Nondestructive testing, nondestructive method uses electromagnetic radiation in the microwave band (radio), band (Ultra high frequency, UHF/VHF frequencies) of the radio spectrum, and detects the reflected signals from subsurface structures. GPR can have applications in a variety of media, including rock, soil, ice, fresh water, pavements and structures. In the right conditions, practitioners can use GPR to detect subsurface objects, changes in material properties, and voids and cracks. GPR uses high-frequency (usually polarized) radio waves, usually in the range 10 MHz to 2.6 GHz. A GPR transmitter and antenna emits electromagnetic energy into the ground. When the energy encounte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetotellurics
Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface. Investigation depth ranges from 300 m below ground by recording higher frequencies down to 10,000 m or deeper with long-period soundings. Proposed in Japan in the 1940s, and France and the USSR during the early 1950s, MT is now an international academic discipline and is used in exploration surveys around the world. Commercial uses include hydrocarbon (oil and gas) exploration, geothermal exploration, carbon sequestration, mining exploration, as well as hydrocarbon and groundwater monitoring. Research applications include experimentation to further develop the MT technique, long-period deep crustal exploration, deep mantle probing, sub-glacial water flow mapping, and earthquake precursor research. History The magnetotelluric technique was introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules. Electromagnetism can be thought of as a combination of electricity and magnetism, two distinct but closely intertwined phenomena. In essence, electric forces occur between any two charged particles, causing an attraction between particles with opposite charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge, while magnetism is an interaction that occurs exclusively between ''moving'' charged particles. These two effects combine to create electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of charge particles, which can exert influence on other particles via the Lorentz force. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force. The electromagnetic force is responsible for many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Potential
Spontaneous potentials are often measured down boreholes for formation evaluation in the oil and gas industry, and they can also be measured along the Earth's surface for mineral exploration or groundwater investigation. The phenomenon and its application to geology was first recognized by Conrad Schlumberger, Marcel Schlumberger, and E.G. Leonardon in 1931, and the first published examples were from Romanian oil fields. Physics Spontaneous potentials (SP) are usually caused by charge separation in clay or other minerals, due to presence of semi-permeable interface impeding the diffusion of ions through the pore space of rocks, or by natural flow of a conducting fluid through the rocks. The origin of SP across formation can be attributed to two processes involving the movement of ions: # Streaming potential (''E''k) # Electrochemical potential (''E''c) Streaming potential originates from the flow of an electrolyte (water) over naturally charged solids (i.e., surfaces that acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Polarization
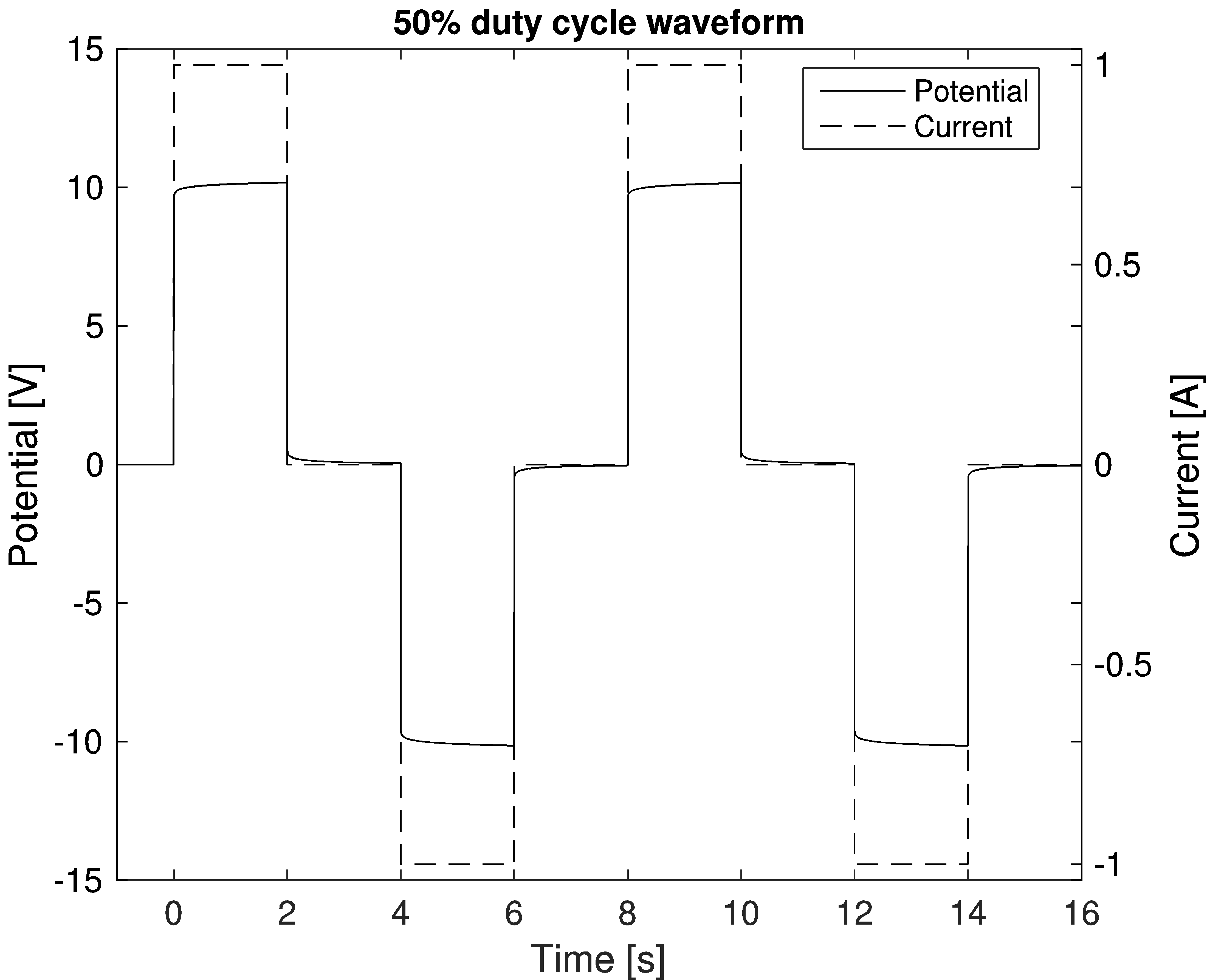
Induced polarization (IP) is a geophysical imaging technique used to identify the electrical chargeability of subsurface materials, such as ore. The polarization effect was originally discovered by Conrad Schlumberger when measuring the resistivity of rock. The survey method is similar to electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), in that an electric current is transmitted into the subsurface through two electrodes, and voltage is monitored through two other electrodes. Induced polarization is a geophysical method used extensively in mineral exploration and mine operations. Resistivity and IP methods are often applied on the ground surface using multiple four-electrode sites. In an IP survey, in addition to resistivity measurement, capacitive properties of the subsurface materials are determined as well. As a result, IP surveys provide additional information about the spatial variation in lithology and grain-surface chemistry. The IP survey can be made in time-domain and frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistivity Tomography
Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) or electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) is a geophysical technique for imaging sub-surface structures from electrical resistivity measurements made at the surface, or by electrodes in one or more boreholes. If the electrodes are suspended in the boreholes, deeper sections can be investigated. It is closely related to the medical imaging technique electrical impedance tomography (EIT), and mathematically is the same inverse problem. In contrast to medical EIT, however, ERT is essentially a direct current method. A related geophysical method, induced polarization (or spectral induced polarization), measures the transient response and aims to determine the subsurface chargeability properties. Electrical resistivity measurements can be used for identification and quantification of depth of groundwater, detection of clays, and measurement of groundwater conductivity. History The technique evolved from techniques of electrical prospecting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |