Geography of Kyrgyzstan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The mountains of Kyrgyzstan are geologically young, so that the physical terrain is marked by sharply uplifted peaks separated by deep valleys. There is also considerable glaciation, with the largest glacier being the
The mountains of Kyrgyzstan are geologically young, so that the physical terrain is marked by sharply uplifted peaks separated by deep valleys. There is also considerable glaciation, with the largest glacier being the
 The country's climate is influenced chiefly by the mountains, Kyrgyzstan's position near the middle of the Eurasian landmass, and the absence of any body of water large enough to influence weather patterns. Those factors create a distinctly continental climate that has significant local variations. Although the mountains tend to collect clouds and block sunlight (reducing some narrow valleys at certain times of year to no more than three or four hours of sunlight per day), the country is generally sunny, receiving as much as 2,900 hours of sunlight per year in some areas. The same conditions also affect temperatures, which can vary significantly from place to place. In January the warmest average temperature () occurs around the southern city of Osh, and around Ysyk-Köl. The latter, which has a volume of , does not freeze in winter. Indeed, its name means "hot lake" in Kyrgyz. The coldest temperatures are in mountain valleys. There, readings can fall to or lower; the record is . The average temperature for July similarly varies from in the Fergana Valley, where the record high is , to a low of on the highest mountain peaks. Precipitation varies from per year in the mountains above the Fergana Valley to less than per year on the west bank of Ysyk-Köl.
The country's climate is influenced chiefly by the mountains, Kyrgyzstan's position near the middle of the Eurasian landmass, and the absence of any body of water large enough to influence weather patterns. Those factors create a distinctly continental climate that has significant local variations. Although the mountains tend to collect clouds and block sunlight (reducing some narrow valleys at certain times of year to no more than three or four hours of sunlight per day), the country is generally sunny, receiving as much as 2,900 hours of sunlight per year in some areas. The same conditions also affect temperatures, which can vary significantly from place to place. In January the warmest average temperature () occurs around the southern city of Osh, and around Ysyk-Köl. The latter, which has a volume of , does not freeze in winter. Indeed, its name means "hot lake" in Kyrgyz. The coldest temperatures are in mountain valleys. There, readings can fall to or lower; the record is . The average temperature for July similarly varies from in the Fergana Valley, where the record high is , to a low of on the highest mountain peaks. Precipitation varies from per year in the mountains above the Fergana Valley to less than per year on the west bank of Ysyk-Köl.
 Although Kyrgyzstan has abundant water running through it, its water supply is determined by a post-Soviet sharing agreement among the five Central Asian republics. As in the Soviet era, Kyrgyzstan has the right to 25% of the water that originates in its territory, but the new agreement allows Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan unlimited use of the water that flows into them from Kyrgyzstan, with no compensation for the nation at the source.
Although Kyrgyzstan has abundant water running through it, its water supply is determined by a post-Soviet sharing agreement among the five Central Asian republics. As in the Soviet era, Kyrgyzstan has the right to 25% of the water that originates in its territory, but the new agreement allows Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan unlimited use of the water that flows into them from Kyrgyzstan, with no compensation for the nation at the source.
 The most important problems in land use are soil erosion and salinization in improperly irrigated farmland. An estimated 60% of Kyrgyzstan's land is affected by topsoil loss, and 6% by salinization, both problems with more serious long-term than short-term effects. In 1994 the size of livestock herds averaged twice the carrying capacity of pasturage land, continuing the serious
The most important problems in land use are soil erosion and salinization in improperly irrigated farmland. An estimated 60% of Kyrgyzstan's land is affected by topsoil loss, and 6% by salinization, both problems with more serious long-term than short-term effects. In 1994 the size of livestock herds averaged twice the carrying capacity of pasturage land, continuing the serious
''party to:''
 The NEAP, adopted in 1994, is the basic blueprint for environmental protection. The plan focuses on solving a small number of critical problems, collecting reliable information to aid in that process, and integrating environmental measures with economic and social development strategy. The initial planning period is to end in 1997. The main targets of that phase are inefficient water resource management, land degradation,
The NEAP, adopted in 1994, is the basic blueprint for environmental protection. The plan focuses on solving a small number of critical problems, collecting reliable information to aid in that process, and integrating environmental measures with economic and social development strategy. The initial planning period is to end in 1997. The main targets of that phase are inefficient water resource management, land degradation,
 Area:
Area:
''total:'' 198,951 km²
''land:'' 191,801 km²
''water:'' 8,150 km² Land boundaries:
''total:'' 5,473 km
''border countries:'' the
''lowest point:''
''highest point:''
 Terrain: peaks of
Terrain: peaks of
''arable land:'' 6.7%
''permanent crops:'' 0.4%
''permanent pasture:'' 48.3%
''forest:'' 5.1%
''other:'' 93.24% (2011)
''note:'' Kyrgyzstan has the world's largest natural growth
Kyrgyzstan
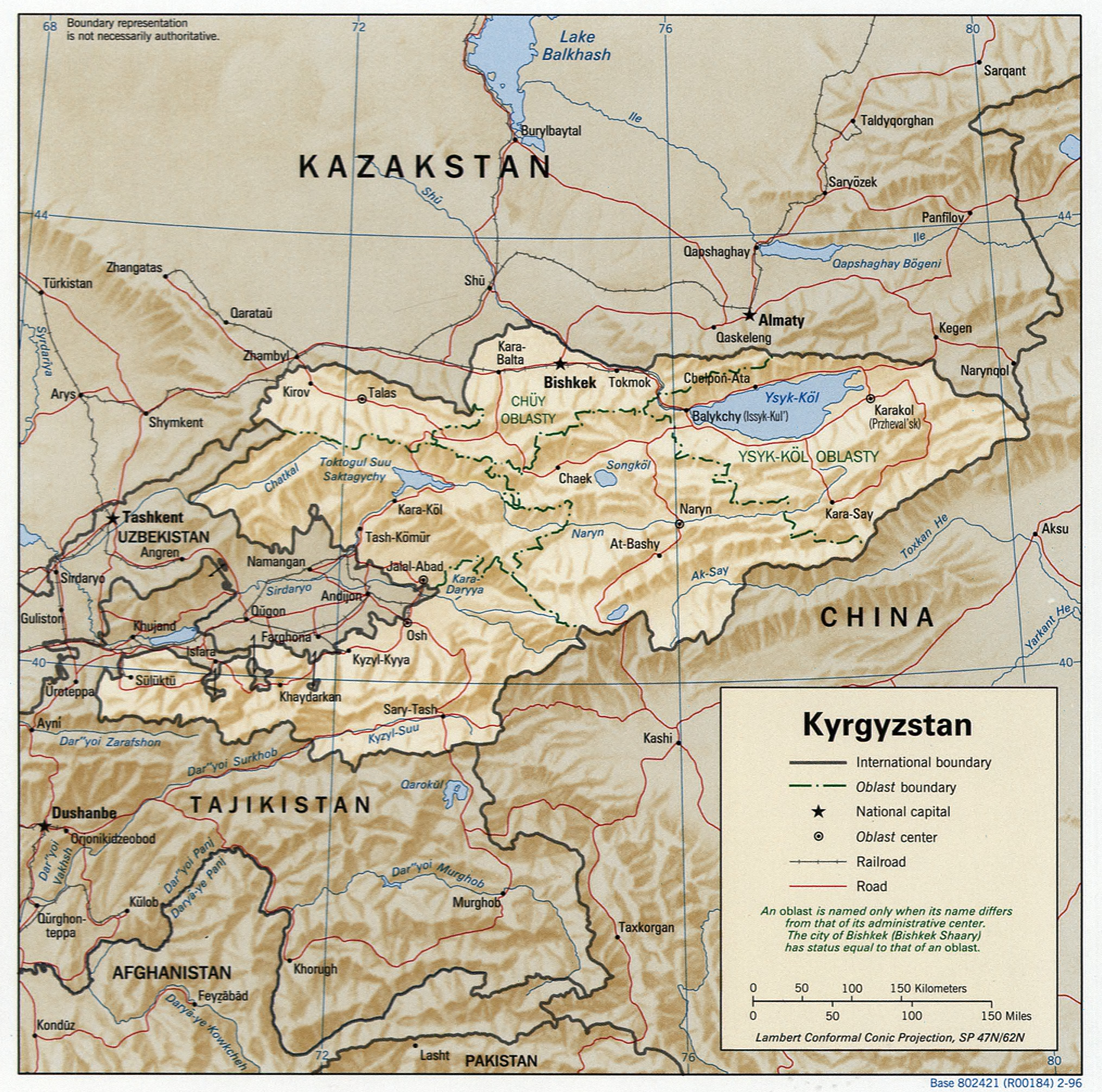
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
is a landlocked nation in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, west of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Less than a seventh the size of Mongolia, at 199,951 square kilometers, Kyrgyzstan is one of the smaller Central Asian states. The national territory extends about from east to west and from north to south.
Kyrgyzstan is bordered on the east and southeast by China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, on the north by Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, on the west by Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
and on the south by Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
. The borders with Uzbekistan and Tajikistan in the Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
are rather difficult. One consequence of the Stalinist
Stalinism is the means of governing and Marxist-Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union from 1927 to 1953 by Joseph Stalin. It included the creation of a one-party totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory o ...
division of Central Asia into five republics is that many ethnic Kyrgyz people
The Kyrgyz people (also spelled Kyrghyz, Kirgiz, and Kirghiz; ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is the nation state of the Kyrgyz people and significant diaspora can be found in China, Russia, and Uzbekistan. ...
do not live in Kyrgyzstan. Three enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
s, legally part of the territory of Kyrgyzstan but geographically removed by several kilometers, have been established, two in Uzbekistan and one in Tajikistan.
The terrain of Kyrgyzstan is dominated by the Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
and Pamir Pamir may refer to:
Geographical features
* Pamir Mountains, a mountain range in Central Asia
** Pamir-Alay, a mountain system in Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, part of the Pamir Mountains
*A pamir (valley) is a high plateau or valley surro ...
mountain systems, which together occupy about 65% of national territory. The Alay range
The Alay or Alai Range ( ky, Алай тоо кыркасы; russian: Алайский хребет) is a mountain range that extends from the Tien Shan mountain range in Kyrgyzstan west into Tajikistan. It is part of the Pamir-Alay mountain syste ...
portion of the Tian Shan system dominates the southwestern crescent of the country, and, to the east, the main Tian Shan range runs along the boundary between southern Kyrgyzstan and China before extending farther east into China's Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
. Kyrgyzstan's average elevation is , ranging from at Peak Jengish Chokusu
Jengish Chokusu ( ky, Жеңиш чокусу, , ; en, Tomur Peak, zh, s=托木尔峰, t=托木爾峰; russian: Пик Победы, ''Pik Pobedy'', ) is the highest mountain in the Tian Shan mountain system at . It lies on the Kyrgyzstan– C ...
to in the Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
near Osh
Osh (Kyrgyz: Ош, romanised Osh; uz, O‘sh/Ўш) is the second-largest city in Kyrgyzstan, located in the Fergana Valley in the south of the country and often referred to as the "capital of the south". It is the oldest city in the country (e ...
. Almost 90% of the country lies more than above sea level.
Topography and drainage

 The mountains of Kyrgyzstan are geologically young, so that the physical terrain is marked by sharply uplifted peaks separated by deep valleys. There is also considerable glaciation, with the largest glacier being the
The mountains of Kyrgyzstan are geologically young, so that the physical terrain is marked by sharply uplifted peaks separated by deep valleys. There is also considerable glaciation, with the largest glacier being the Engilchek Glacier
Engilchek Glacier ( ky, Эңилчек, russian: Энильчек - ''Enilchek'', also Иныльчек - ''Inylchek'') is a glacier in the Central Tian Shan Mountains of Issyk-Kul Region, northeastern Kyrgyzstan. Its snout is 50 km east of ...
. Kyrgyzstan's 6,500 distinct glaciers are estimated to hold about of water and cover 8,048 square kilometers (5,000 square miles) or 4.2% of Kyrgyzstan. Only around the Chüy, Talas, and Fergana
Fergana ( uz, Fargʻona/Фарғона, ), or Ferghana, is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 420 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km west of Andijan, and less than 20 km fr ...
valleys is there relatively flat land suitable for large-scale agriculture.
Because the high peaks function as moisture catchers, Kyrgyzstan is relatively well watered by the streams that descend from them. None of the rivers of Kyrgyzstan are navigable, however. The majority are small, rapid, runoff streams. Most of Kyrgyzstan's rivers are tributaries of the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
, which has its headwaters in the western Tian Shan along the Chinese border. Another large runoff system forms the Chu (Chüy), which arises in northern Kyrgyzstan, then flows northwest and disappears into the deserts of southern Kazakhstan. Ysyk-Köl is the second largest body of water in Central Asia, after the Aral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic basin, endorheic lake lyi ...
, but the saline lake has been shrinking steadily, and its mineral content has been rising gradually. Kyrgyzstan has a total of about 2,000 lakes with a total surface area of , mostly located at altitudes of 3,000 to 4,000 meters. Only the largest three, however, occupy more than each. The second- and third-largest lakes, Song-Köl
Song-Köl ( ky, Соң-Көл, , also Соңкөл ''Songköl'', literally "following lake", russian: Сон-Куль, Son-Kul', also ) is an alpine lake in northern Naryn Region, Kyrgyzstan. It lies at an altitude of 3016 m, and has an area of a ...
and Chatyr-Köl
Chatyr-Köl ( ky, Чатыр-Көл, russian: Чатыр-Куль, Chatyr-Kul') is an endorheic alpine lake in the Tian Shan mountains in At-Bashy District of Naryn Province, Kyrgyzstan; it lies in the lower part of Chatyr-Köl Depression near the ...
(the latter of which also is saline), are located in the Naryn River Basin.
Natural disasters have been frequent and varied. Overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature res ...
and deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
of steep mountain slopes have increased the occurrence of mudslide
A mudflow or mud flow is a form of mass wasting involving fast-moving flow of debris that has become liquified by the addition of water. Such flows can move at speeds ranging from 3 meters/minute to 5 meters/second. Mudflows contain a significa ...
s and avalanches, which occasionally have swallowed entire villages. In August 1992, a severe earthquake left several thousand people homeless in the southwestern city of Jalal-Abad
Jalal-Abad (also spelled Dzhalal-Abad, Djalal-Abat, Jalalabat; ky, Жалал-Aбат, ''Calal-Abat/Jalal-Abat'', جالال-ابات, ) is the administrative and economic centre of Jalal-Abad Region in southwestern Kyrgyzstan. Its area is , and ...
.
Climate
Climate change
Environmental issues
Kyrgyzstan has been spared many of the enormous environmental problems faced by its Central Asian neighbors, primarily because its designated roles in the Soviet system involved neither heavy industry nor large-scale cotton production. Also, the economic downturn of the early 1990s reduced some of the more serious effects of industrial and agricultural policy. Nevertheless, Kyrgyzstan has serious problems because of inefficient use and pollution of water resources,land degradation
Land degradation is a process in which the value of the biophysical environment is affected by a combination of human-induced processes acting upon the land.
It is viewed as any change or disturbance to the land perceived to be deleterious ...
, and improper agricultural practices. The country is prone to earthquakes, and major flooding occurs during the snow melt.
Water resources
The Kyrgyz Republic is the only Central Asian state where water resources are fully generated within its own territory. The water originates from the often glacier covered mountain ranges and its abundance is a vital component for agriculture and the production of hydro‐electric power. The mountainous Kyrgyz Republic is an essential "water tower" for irrigated arable farming on arid plain territories. In addition, the impressive glacierized mountain landscape implies a considerable potential fortourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
.
 Although Kyrgyzstan has abundant water running through it, its water supply is determined by a post-Soviet sharing agreement among the five Central Asian republics. As in the Soviet era, Kyrgyzstan has the right to 25% of the water that originates in its territory, but the new agreement allows Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan unlimited use of the water that flows into them from Kyrgyzstan, with no compensation for the nation at the source.
Although Kyrgyzstan has abundant water running through it, its water supply is determined by a post-Soviet sharing agreement among the five Central Asian republics. As in the Soviet era, Kyrgyzstan has the right to 25% of the water that originates in its territory, but the new agreement allows Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan unlimited use of the water that flows into them from Kyrgyzstan, with no compensation for the nation at the source. Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
uses the entire amount to which the agreement entitles it, but utilization is skewed heavily in favor of agricultural irrigation. During the Soviet era, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
shared their abundant water resources with Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
during summer, and these three nations shared oil and gas with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan in winter. According to the International Crisis Group
The International Crisis Group (ICG; also known as the Crisis Group) is a transnational non-profit, non-governmental organisation founded in 1995. It is a think tank, used by policymakers and academics, performing research and analysis on global ...
, the skewed system that is currently in place could cause irreversible regional destabilization, and needs to be dealt with by international actors to avoid a crisis in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. In 1994 agriculture accounted for about 88% of total water consumption, compared with 8% by industry and 4% by municipal water distribution systems. According to World Bank experts, Kyrgyzstan has an adequate supply of high-quality water for future use, provided the resource is prudently managed. However, in Central Asia water problems are on the rise. The Kyrgyz Republic exports water to irrigate the neighbouring states Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and Tajikistan. To prevent conflicts, water allocation and use, and in particular the role of agriculture as major water user, have become very important questions in the development discourse in recent years, and will continue to be in the future.
Irrigation is extremely wasteful of water because the distribution infrastructure is old and poorly maintained. In 1993 only an estimated 5% of required maintenance expenditures was allocated. , an estimated 70% of the nation's water supply network is in need of repair or replacement. The quality of drinking water from this aging system is poorly monitored—the water management staff has been cut drastically because of inadequate funds. Further, there is no money to buy new water disinfection equipment when it is needed. Some aquifers near industrial and mining centers have been contaminated by heavy metals, oils, and sanitary wastes. In addition, many localities rely on surface sources, making users vulnerable to agricultural runoff and livestock waste, which seep gradually downward from the surface. The areas of lowest water quality are the heavily populated regions of the Chui Valley and Osh
Osh (Kyrgyz: Ош, romanised Osh; uz, O‘sh/Ўш) is the second-largest city in Kyrgyzstan, located in the Fergana Valley in the south of the country and often referred to as the "capital of the south". It is the oldest city in the country (e ...
and Jalal-Abad
Jalal-Abad (also spelled Dzhalal-Abad, Djalal-Abat, Jalalabat; ky, Жалал-Aбат, ''Calal-Abat/Jalal-Abat'', جالال-ابات, ) is the administrative and economic centre of Jalal-Abad Region in southwestern Kyrgyzstan. Its area is , and ...
Regions, and areas along the rivers flowing into Ysyk-Köl.
In towns, wastewater collection provides about 70% of the water supply. Although towns have biological treatment equipment, as much as 50% of such equipment is rated as ineffective. The major sources of toxic waste in the water supply are the mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
mining combine at Haidarkan; the antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient time ...
mine at Kadamzai; the Kadzyi Sai uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
mine, which ceased extraction in 1967 but which continues to leach toxic materials into nearby Ysyk Köl; the Kara-Balta Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
Recovery Plant; the Min Kush deposit of mine tailings; and the Kyrgyz Mining and Metallurgy Plant at Orlovka.
Land management
 The most important problems in land use are soil erosion and salinization in improperly irrigated farmland. An estimated 60% of Kyrgyzstan's land is affected by topsoil loss, and 6% by salinization, both problems with more serious long-term than short-term effects. In 1994 the size of livestock herds averaged twice the carrying capacity of pasturage land, continuing the serious
The most important problems in land use are soil erosion and salinization in improperly irrigated farmland. An estimated 60% of Kyrgyzstan's land is affected by topsoil loss, and 6% by salinization, both problems with more serious long-term than short-term effects. In 1994 the size of livestock herds averaged twice the carrying capacity of pasturage land, continuing the serious overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature res ...
problem and consequent soil erosion that began when the herds were at their peak in the late 1980s. Uncertain land tenure and overall financial insecurity have caused many private farmers to concentrate their capital in the traditional form—livestock—thus subjecting new land to the overgrazing problem.
The inherent land shortage in Kyrgyzstan is exacerbated by the flooding of agricultural areas for hydroelectric projects. The creation of Toktogul
Toktogul ( ky, Toктогул, known until 31 July 1957 as ''Muztör'' ()), is a city (since 2012) in Jalal-Abad Region of Kyrgyzstan. Its population was 20,577 in 2021. It is the administrative seat of Toktogul District.
It is named after its mos ...
Reservoir on the Naryn River, for example, involved the flooding of 130 km² of fertile land. Such projects have the additional effect of constricting downstream water supply; Toktogul deprives the lower reaches of the Syr Darya in Uzbekistan and the Aral Sea Basin of substantial amounts of water. Because the Naryn Basin, where many hydroelectric projects are located, is very active seismically, flooding is also a danger should a dam be broken by an earthquake.
Environment - current issues: Nuclear waste left behind by the Soviet Union in many open-air pits in hazardous locations. Water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water ...
; many people get their water directly from contaminated streams and wells; as a result, water-borne diseases are prevalent; increasing soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the ...
from faulty irrigation practices. Illegal hunting of very rare species such as the snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia''), also known as the ounce, is a Felidae, felid in the genus ''Panthera'' native to the mountain ranges of Central Asia, Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable species, Vulnerable on the IUCN Red ...
and the Marco Polo sheep
The Marco Polo sheep (''Ovis ammon polii'') is a subspecies of argali sheep, named after Marco Polo. Their habitat are the mountainous regions of Central Asia. Marco Polo sheep are distinguishable mostly by their large size and spiraling horns. T ...
.
Environment - international agreements:
''party to:''
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
, Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, Desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
, Hazardous Wastes
Hazardous waste is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. Hazardous waste is a type of dangerous goods. They usually have one or more of the following hazardous traits: ignitability, reactivity, cor ...
, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
Aral Sea
In response to the internationally recognized environmental crisis of the rapid desiccation of theAral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic basin, endorheic lake lyi ...
, the five states sharing the Aral Sea Basin (Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan) are developing a strategy to end the crisis. The World Bank and agencies of the United Nations (UN) have developed an Aral Sea Program, the first stage of which is funded by the five countries and external donors. That stage has seven areas of focus, one of which—land and water management in the upper watersheds—is of primary concern to Kyrgyzstan. Among the conditions detrimental to the Aral Sea's environment are erosion from deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
and overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature res ...
, contamination from poorly managed irrigation systems, and uncontrolled waste from mining and municipal effluents. Kyrgyzstan's National Environmental Action Plan (NEAP) has addressed these problems as part of its first-phase priorities in cooperation with the Aral Sea Program.
Environmental policy making
 The NEAP, adopted in 1994, is the basic blueprint for environmental protection. The plan focuses on solving a small number of critical problems, collecting reliable information to aid in that process, and integrating environmental measures with economic and social development strategy. The initial planning period is to end in 1997. The main targets of that phase are inefficient water resource management, land degradation,
The NEAP, adopted in 1994, is the basic blueprint for environmental protection. The plan focuses on solving a small number of critical problems, collecting reliable information to aid in that process, and integrating environmental measures with economic and social development strategy. The initial planning period is to end in 1997. The main targets of that phase are inefficient water resource management, land degradation, overexploitation
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to replenish. The term app ...
of forest reserves, loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
, and pollution from inefficient mining and refining practices.
Because of severe budget constraints, most of the funds for NEAP operations come from international sources, including official institutions such as the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank and numerous international nongovernmental organizations. Implementation is guided by a committee of state ministers and by a NEAP Expert Working Group, both established in 1994 by executive order. A NEAP office in Bishkek was set up with funds from Switzerland.
The main environmental protection agency of the Kyrgyzstan government is the State Committee on Environmental Protection, still known by its Soviet-era acronym, Goskompriroda. Established by the old regime in 1988, the agency's post-Soviet responsibilities have been described in a series of decrees beginning in 1991. In 1994 the state committee had a central office in Bishkek, one branch in each of the seven regions, and a total staff of about 150 persons. Because of poorly defined lines of responsibility, administrative conflicts often occur between local and national authorities of Goskompriroda and between Goskompriroda and a second national agency, the Hydrometeorological Administration (Gidromet), which is the main monitoring agency for air, water, and soil quality. In general, the vertical hierarchy structure, a relic of Soviet times, has led to poor coordination and duplication of effort among environmental protection agencies.
Specially protected areas
A number of protected nature areas have been designated by the government of the republic. As of the end of 2004, they included: * Eight statenature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
s (zapovednik
Zapovednik (russian: заповедник, plural , from the Russian , 'sacred, prohibited from disturbance, committed o protect committed o heritage; ) is an established term on the territory of the former Soviet Union for a protected area whi ...
s), with the total area of 2,880 km²;
* Nine state nature national park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
s (2,760 km²);
* Ten forest, twenty-three floral, eighteen geological, and two general-purpose protected areas (zakaznik
Zakaznik (russian: зака́зник, зака́зники, transliterated: ''zakaznik, zakazniki''; uk, singular: заказни́к or зака́зник; plural: заказники́ or зака́зники, transliterated: ''zakaznyk'', ''zak ...
s), as well as fourteen game reserve
A game reserve (also known as a wildlife preserve or a game park) is a large area of land where wild animals live safely or are hunted in a controlled way for sport. If hunting is prohibited, a game reserve may be considered a nature reserve; ...
s, with the total area of 3,250 km²;
* Lake Issyk Kul
Issyk-Kul (also Ysyk-Köl, ky, Ысык-Көл, lit=warm lake, translit=Ysyk-Köl, , zh, 伊塞克湖) is an endorheic lake (i.e., without outflow) in the Northern Tian Shan mountains in Eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the seventh-deepest lake in th ...
(so designated since 1998) and Sary-Chelek biosphere reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or o ...
(since 1978), together occupying the area of 282 km².
Area and boundaries
 Area:
Area:
''total:'' 198,951 km²
''land:'' 191,801 km²
''water:'' 8,150 km² Land boundaries:
''total:'' 5,473 km
''border countries:'' the
People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
1,063 km, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
1,212 km, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
984 km, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
1,314 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Elevation extremes:
''lowest point:''
Kara-Darya
The Kara Darya ( ky, Кара-Дарыя, Kara-Daryya, قارا-دارىيا; uz, Qoradaryo, ''Қорадарё'', قارەدەريا , russian: Карадарья, Karadar'ya - literally ''black river'')''Darya'' means "river", so Kara Darya '' ...
132 m
''highest point:''
Peak Jengish Chokusu
Jengish Chokusu ( ky, Жеңиш чокусу, , ; en, Tomur Peak, zh, s=托木尔峰, t=托木爾峰; russian: Пик Победы, ''Pik Pobedy'', ) is the highest mountain in the Tian Shan mountain system at . It lies on the Kyrgyzstan– C ...
7,439 m
Resources and land use
 Terrain: peaks of
Terrain: peaks of Tien Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
and associated valleys and basins encompass entire nation
Natural resources: abundant hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
; significant deposits of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
and rare earth metals; locally exploitable coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
; other deposits of nepheline
Nepheline, also called nephelite (), is a rock-forming mineral in the feldspathoid groupa silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate, Na3 K Al4 Si4 O16, that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatites ...
, mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
.
Land use:
''arable land:'' 6.7%
''permanent crops:'' 0.4%
''permanent pasture:'' 48.3%
''forest:'' 5.1%
''other:'' 93.24% (2011)
''note:'' Kyrgyzstan has the world's largest natural growth
walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus ''Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''.
Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a true ...
forest, Arslanbob
Arslanbob ( ky, Арстанбап) is a village, sub district, valley, mountain range, and a large wild walnut (''Juglans regia'') forest in the Jalal-Abad Region of Kyrgyzstan. Kyrgyzstan's first known export to Europe was the Arslanbob walnut. ...
, located in Jalal-Abad Region
Jalal-Abad Region ( ky, Жалал-Абад облусу, Jalal-Abad oblusu; russian: Джалал-Абадская область, Dzhalal-Abadskaya oblast) is a region (''oblast'') of Kyrgyzstan. Its capital is the city of the same name, Jala ...
with an enormous variety of different genetic characteristics. It is believed that most of the world's walnut varieties derive from the original species still found here.
Irrigated land: 10,210 km² (2005)
Total renewable water resources: 23.62 km3 (2011)
References
* {{Asia topic, Climate of