|
Geography Of Kyrgyzstan
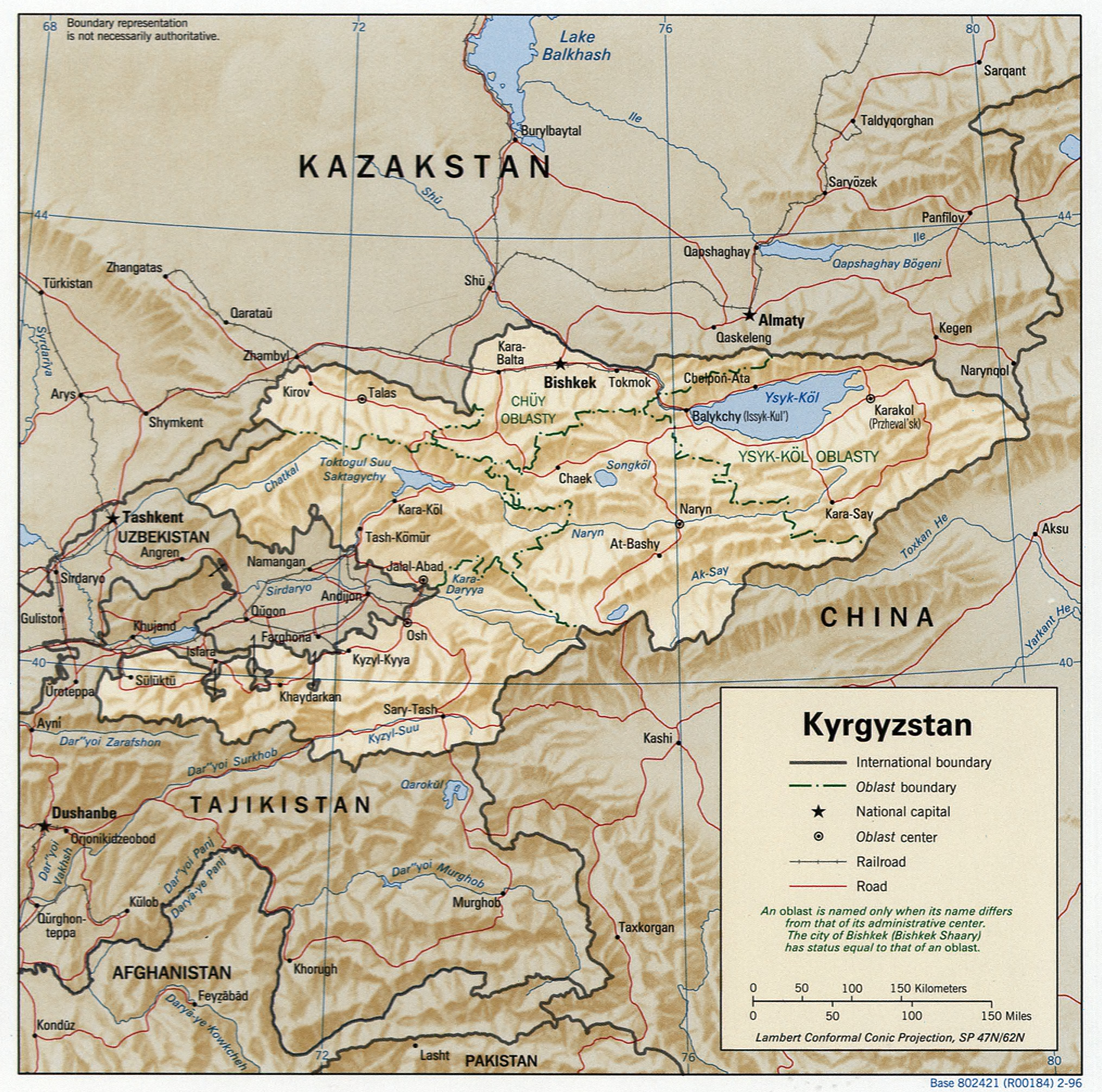
Kyrgyzstan is a landlocked nation in Central Asia, west of the People's Republic of China. Less than a seventh the size of Mongolia, at 199,951 square kilometers, Kyrgyzstan is one of the smaller Central Asian states. The national territory extends about from east to west and from north to south. Kyrgyzstan is bordered on the east and southeast by China, on the north by Kazakhstan, on the west by Uzbekistan and on the south by Tajikistan. The borders with Uzbekistan and Tajikistan in the Fergana Valley are rather difficult. One consequence of the Stalinist division of Central Asia into five republics is that many ethnic Kyrgyz people do not live in Kyrgyzstan. Three enclaves, legally part of the territory of Kyrgyzstan but geographically removed by several kilometers, have been established, two in Uzbekistan and one in Tajikistan. The terrain of Kyrgyzstan is dominated by the Tian Shan and Pamir mountain systems, which together occupy about 65% of national territory. The Alay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. Its capital and largest city is Bishkek. Ethnic Kyrgyz make up the majority of the country's seven million people, followed by significant minorities of Uzbeks and Russians. The Kyrgyz language is closely related to other Turkic languages. Kyrgyzstan's history spans a variety of cultures and empires. Although geographically isolated by its highly mountainous terrain, Kyrgyzstan has been at the crossroads of several great civilizations as part of the Silk Road along with other commercial routes. Inhabited by a succession of tribes and clans, Kyrgyzstan has periodically fallen under larger domination. Turkic nomads, who trace their ancestry to many Turkic states. It was first established as the Yenisei Kyrgyz Khaganate later in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Jengish Chokusu
Jengish Chokusu ( ky, Жеңиш чокусу, , ; en, Tomur Peak, zh, s=托木尔峰, t=托木爾峰; russian: Пик Победы, ''Pik Pobedy'', ) is the highest mountain in the Tian Shan mountain system at . It lies on the Kyrgyzstan– China border between the Ak-Suu District, in the Issyk-Kul Region of far Eastern Kyrgyzstan and Wensu County, Xinjiang, China. It is part of the Kakshaal Too, the highest part of the Tian Shan and located southeast of lake Issyk Kul. Names The mountain's official name in Kyrgyz is ''Jengish Chokusu'', which means "Victory Peak"; its Russian name is ''Pik Pobedy'' (or Pobeda Peak) meaning the same. In Uyghur, it is called ''Tömür'', which is also the official name of the mountain in China. The Chinese name ''Tuōmù'ěr Fēng'' () is a combination of the Uighur ''tomur'', meaning 'iron' and Chinese ''feng'' meaning 'peak'. Description Jengish Chokusu is a massif, with several summits along its lengthy ridge. Only its main summit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature reserves. It can also be caused by immobile, travel restricted populations of native or non-native wild animals. Overgrazing reduces the usefulness, productivity, and biodiversity of the land and is one cause of desertification and erosion. Overgrazing is also seen as a cause of the spread of invasive species of non-native plants and of weeds. Degrading land, emissions from animal agriculture and reducing the biomass in a ecosystem contribute directly to climate change. Overgrazing can be reversed or prevented by removing grazers in order to give plants time to recover between grazing events. Successful planned grazing strategies have been support in the American bison of the Great Plains, or migratory Wildebeests of the African savann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naryn (river)
The Naryn ( ky, Нарын, uz, Norin) rises in the Tian Shan mountains in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia, flowing west through the Fergana Valley into Uzbekistan. Here it merges with the Kara Darya (near Namangan) to form the Syr Darya. It is long (together with its upper course Chong-Naryn) and its basin area is . It has an annual flow of . The river contains many reservoirs which are important in the generation of hydroelectricity. The largest of these is the Toktogul Reservoir in Kyrgyzstan containing of water. Dams downstream of the Toktogul in Kyrgyzstan include: Kürpsay, Tash-Kömür, Shamaldy-Say and Üch-Korgon. Upstream of Toktogul in Kyrgyzstan is the Kambar-Ata-2 and At-Bashy Dams while the Kambar-Ata-1 Dam is in planning stages. Some places along the river: Kyrgyzstan: Kara-Say (see Barskoon), Naryn Region, Naryn, Dostuk, Jalal-Abad Region, Kazarman, Toktogul Reservoir, Kara-Köl, Tash-Kömür. Tributaries The main tributaries of the Naryn are, from source to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatyr-Köl
Chatyr-Köl ( ky, Чатыр-Көл, russian: Чатыр-Куль, Chatyr-Kul') is an endorheic alpine lake in the Tian Shan mountains in At-Bashy District of Naryn Province, Kyrgyzstan; it lies in the lower part of Chatyr-Köl Depression near the Torugart Pass border crossing into China. The name of the lake means “Celestial Lake” in Kyrgyz (literally "Roof Lake"). Climate The mean annual temperature in the lake basin is , with mean temperature of in January, and in July. The maximum temperature in summer is , and the minimum one in winter is . Some 88-90% of the lake basin's 208–269 mm of annual precipitation falls in summer. From October to end of April the lake surface freezes, the ice becoming as much as 0.25-1.5 m thick. Hydrology The water of Chatyr Kul Lake is yellowish-green with water transparency of up to . The mineralization of the lake ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 milligrams per liter (chloride, hydrocarbonate, sodium and magnesium type of mineralization). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song-Köl
Song-Köl ( ky, Соң-Көл, , also Соңкөл ''Songköl'', literally "following lake", russian: Сон-Куль, Son-Kul', also ) is an alpine lake in northern Naryn Region, Kyrgyzstan. It lies at an altitude of 3016 m, and has an area of about 270 km2 and volume of 2.64 km3. The lake's maximum length is 29 km, breadth about 18 km, and the deepest point is 13.2 m. It is the second largest lake in Kyrgyzstan after Issyk-Kul, and the largest fresh water lake in Kyrgyzstan. Geography High altitude Song-Köl belongs to the Naryn Naryn ( ky, Нарын, translit=Naryn, Mongolian : Нарийн, Nariin, Traditional Mongolian ᠨᠠᠷᠢᠨ) is the regional administrative center of Naryn Region in central Kyrgyzstan. Its area is , and its estimated population was 41,17 ... river basin. The lake sits in the central part of Song-Köl Valley surrounded by Songköl Too ridge from the north, and Borbor Alabas and Moldo Too mountains from the south. Hydrolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic basin, endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan (Aktobe Region, Aktobe and Kyzylorda Regions) in the north and Uzbekistan (Karakalpakstan autonomous region) in the south which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up by the 2010s. The name roughly translates as "Sea of Islands", referring to over 1,100 islands that had dotted its waters. In the Mongolic languages, Mongolic and Turkic languages, ''aral'' means "island, archipelago". The Aral Sea drainage basin encompasses Uzbekistan and parts of Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Afghanistan, and Iran. Formerly the fourth largest lake in the world with an area of , the Aral Sea began shrinking in the 1960s after the rivers that fed it were diverted by Soviet Union, Soviet irrigation proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
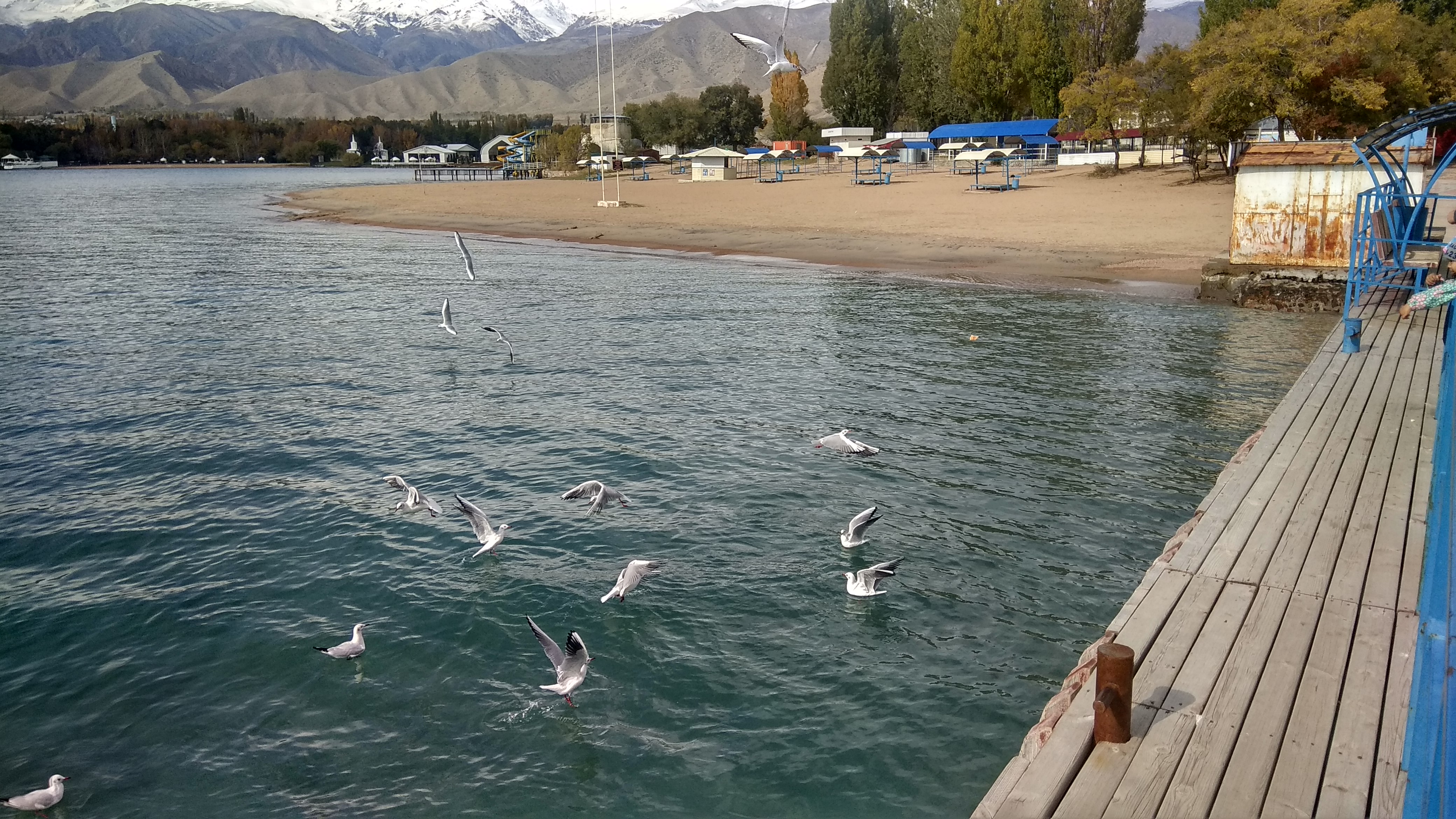
Issyk-Kul
Issyk-Kul (also Ysyk-Köl, ky, Ысык-Көл, lit=warm lake, translit=Ysyk-Köl, , zh, 伊塞克湖) is an endorheic lake (i.e., without outflow) in the Northern Tian Shan mountains in Eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the seventh-deepest lake in the world, the tenth-largest lake in the world by volume (though not in surface area) and the second-largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea. Issyk-Kul means "warm lake" in the Kyrgyz language; although it is located at a lofty elevation of and subject to severe cold during winter, it never freezes. The lake is a Ramsar site of globally significant biodiversity and forms part of the Issyk-Kul Biosphere Reserve. Geography Issyk-Kul Lake is long, up to wide and its area is . It is the second-largest mountain lake in the world behind Lake Titicaca in South America. It is at an altitude of and reaches in depth. About 118 rivers and streams flow into the lake; the largest are the Jyrgalang and Tüp. It is fed by springs, including man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu (river)
The Chu (Shu or Chüy) ( kk, Шу, Shu, شۋ; ky, Чүй, Chüy, چۉي; dng, Чў, Chwu (from , ''Chǔ''); russian: Чу, Chu) is a river in Northern Kyrgyzstan and Southern Kazakhstan. Of its total length of ,Чу (река) the first 115 kilometres are in Kyrgyzstan, then for 221 kilometres the river is the border between Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan and the last 731 kilometres are in Kazakhstan. It is one of the longest s in Kyrgyzstan and in Kazakhstan. It has a drainage basin of . The |
Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known as the Jaxartes (, grc, Ἰαξάρτης), is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian, literally means ''Syr Sea'' or ''Syr River''. It originates in the Tian Shan Mountains in Kyrgyzstan and eastern Uzbekistan and flows for west and north-west through Uzbekistan and southern Kazakhstan to the northern remnants of the Aral Sea. It is the northern and eastern of the two main rivers in the endorheic basin of the Aral Sea, the other being the Amu Darya (Jayhun). In the Soviet era, extensive irrigation projects were constructed around both rivers, diverting their water into farmland and causing, during the post-Soviet era, the virtual disappearance of the Aral Sea, once the world's fourth-largest lake. The point at which the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talas Valley
The Talas ( Kyrgyz, kk, Талас) is a river that rises in the Talas Region of Kyrgyzstan and flows west into Kazakhstan. The river is long and has a basin area of . Course It is formed from the confluence of the Karakol and Uch-Koshoy and flows roughly westwards and northwestwards. It runs through the city of Taraz in Zhambyl Province of Kazakhstan and vanishes in the Muyunkum Desert before reaching Lake Aydyn. The Ili, Chu and Talas are three steppe rivers that flow west and then north-west. The Ili rises in Xinjiang, flows west to a point north of Lake Issyk Kul and then turns north-west to reach Lake Balkash. The Chu rises west of Lake Issyk Kul, flows out into the steppe and dries up before reaching the Syr Darya. The Talas starts west and south of the Chu, flows west and north-west, but dries up before reaching the Chu. History During the Battle of Talas (named after the river) in 751, the Abbasid force defeated the Tang Chinese forces led by the General Gao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chüy Valley
The Chüy Valley ( ky, Чүй өрөөнү, Chüy Öröönü; kz, Шу аңғары, Şu añğary; russian: Чуйская долина) is a large valley located in northern Kyrgyzstan and southern Kazakhstan, in the northern part of the Tian Shan. It extends from Boom Gorge in the east to Muyunkum Desert in the west. It is long and has an area of about . It borders Kyrgyz Ala-Too in the south, and Chu-Ili mountains in the north. Through the Boom Gorge in the narrow eastern part Chüy Valley is linked with Issyk-Kul Valley. The river Chu (Chüy) is the major stream of the valley. The warm summer and availability of drinking and irrigation water makes this area one of the most fertile and most densely populated regions of Kyrgyzstan. There are deposits of zinc ore, lead, gold, and construction materials. The 2006 ''World Drug Report'' estimated that 400,000 hectares of cannabis grow wild in the Chüy Valley. Climate The climate is sharply continental. Summers are long and hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |