Genetic Deletions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency.
For
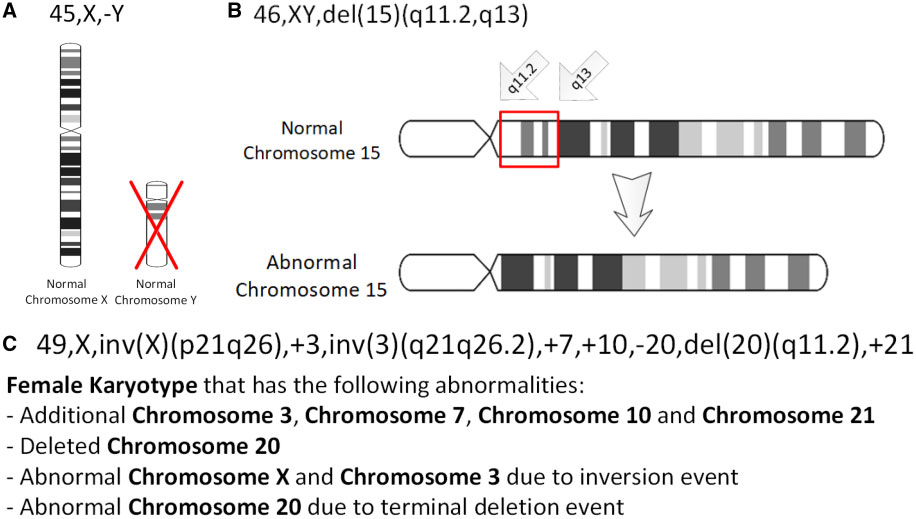 The International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (ISCN) is an international standard for human chromosome nomenclature, which includes band names, symbols and abbreviated terms used in the description of human chromosome and chromosome abnormalities. Abbreviations include a minus sign (-) for chromosome deletions, and ''del'' for deletions of parts of a chromosome.
The International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (ISCN) is an international standard for human chromosome nomenclature, which includes band names, symbols and abbreviated terms used in the description of human chromosome and chromosome abnormalities. Abbreviations include a minus sign (-) for chromosome deletions, and ''del'' for deletions of parts of a chromosome.
synapsis
Synapsis is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I of meiosis. Whe ...
to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop.
The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand slippage, within the DNA polymerase active site.
Deletions can be caused by errors in chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes' non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of geneti ...
during meiosis, which causes several serious genetic diseases. Deletions that do not occur in multiples of three bases can cause a frameshift
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process c ...
by changing the 3-nucleotide protein reading frame of the genetic sequence. Deletions are representative of eukaryotic organisms, including humans and not in prokaryotic organisms, such as bacteria.
Causes
Causes include the following: * Losses fromtranslocation
Translocation may refer to:
* Chromosomal translocation, a chromosome abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts
** Robertsonian translocation, a chromosomal rearrangement in pairs 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22
** Nonreciprocal translocation, transfer ...
* Chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes' non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of geneti ...
s within a chromosomal inversion
An inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome becomes inverted within its original position. An inversion occurs when a chromosome undergoes a two breaks within the chromosomal arm, and the segment between the two br ...
* Unequal crossing over
* Breaking without rejoining
Types
Types of deletion include the following: *Terminal deletion – a deletion that occurs towards the end of a chromosome. *Intercalary/interstitial deletion – a deletion that occurs from the interior of a chromosome. *Microdeletion – a relatively small amount of deletion (up to 5Mb that could include a dozen genes). Micro-deletion is usually found in children with physical abnormalities. A large amount of deletion would result in immediate abortion (miscarriage).Nomenclature
 The International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (ISCN) is an international standard for human chromosome nomenclature, which includes band names, symbols and abbreviated terms used in the description of human chromosome and chromosome abnormalities. Abbreviations include a minus sign (-) for chromosome deletions, and ''del'' for deletions of parts of a chromosome.
The International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (ISCN) is an international standard for human chromosome nomenclature, which includes band names, symbols and abbreviated terms used in the description of human chromosome and chromosome abnormalities. Abbreviations include a minus sign (-) for chromosome deletions, and ''del'' for deletions of parts of a chromosome.
Effects
Small deletions are less likely to be fatal; large deletions are usually fatal – there are always variations based on which genes are lost. Some medium-sized deletions lead to recognizable human disorders, e.g. Williams syndrome. Deletion of a number of pairs that is not evenly divisible by three will lead to aframeshift mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature ...
, causing all of the codon
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
s occurring after the deletion to be read incorrectly during translation, producing a severely altered and potentially nonfunctional protein. In contrast, a deletion that is evenly divisible by three is called an ''in-frame'' deletion.
Deletions are responsible for an array of genetic disorders, including some cases of male infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state ...
, two thirds of cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and two thirds of cases of cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
(those caused by ΔF508). Deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5 results in Cri du chat syndrome. Deletions in the SMN-encoding gene cause spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genetic ...
, the most common genetic cause of infant death.
Microdeletions are associated with many different conditions, including Angelman Syndrome, Prader-Willi Syndrome, and DiGeorge Syndrome. Some syndromes, including Angelman syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome, are associated with both microdeletions and genomic imprinting, meaning that same microdeletion can cause two different syndromes depending on which parent the deletion came from.
Recent work suggests that some deletions of highly conserved sequences (CONDELs) may be responsible for the evolutionary differences present among closely related species. Such deletions in humans, referred to as hCONDELs, may be responsible for the anatomical and behavioral differences between humans, chimpanzees and other varieties of mammals like ape or monkeys.
Recent comprehensive patient-level classification and quantification of driver events in TCGA cohorts revealed that there are on average 12 driver events per tumor, of which 2.1 are deletions of tumor suppressors.
Detection
The introduction of molecular techniques in conjunction with classical cytogenetic methods has in recent years greatly improved the diagnostic potential for chromosomal abnormalities. In particular, microarray-comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) based on the use of BAC clones promises a sensitive strategy for the detection of DNA copy-number changes on a genome-wide scale. The resolution of detection could be as high as >30,000 "bands" and the size of chromosomal deletion detected could as small as 5–20 kb in length. Other computation methods were selected to discover DNA sequencing deletion errors such asend-sequence profiling
End-sequence profiling (ESP) (sometimes "Paired-end mapping (PEM)") is a method based on sequence-tagged connectors developed to facilitate ''de novo'' genome sequencing to identify high-resolution copy number and structural aberrations such as ...
.
Mitochondrial DNA deletions
In the yeast '' Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', the nuclear genes ''Rad51
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 is a protein encoded by the gene ''RAD51''. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assists in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to th ...
''p, '' Rad52''p and ''Rad59p'' encode proteins that are necessary for recombinational repair and are employed in the repair of double strand breaks
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
in mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
.Stein A, Kalifa L, Sia EA. Members of the RAD52 Epistasis Group Contribute to Mitochondrial Homologous Recombination and Double-Strand Break Repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 2015 Nov 5;11(11):e1005664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005664. PMID: 26540 Loss of these proteins decreases the rate of spontaneous DNA deletion events in mitochondria. This finding implies that the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination is a step in the formation of mitochondrial DNA deletions.
See also
* Indel * Chromosome abnormalities * Null allele * List of genetic disorders * Medical genetics *Microdeletion syndrome
A microdeletion syndrome is a syndrome caused by a chromosomal deletion smaller than 5 million base pairs (5 Mb) spanning several genes that is too small to be detected by conventional cytogenetic methods or high resolution karyotyping (2–5 Mb). ...
* Chromosomal deletion syndrome Chromosomal deletion syndromes result from deletion of parts of chromosomes. Depending on the location, size, and whom the deletion is inherited from, there are a few known different variations of chromosome deletions. Chromosomal deletion syndrome ...
* Insertion (genetics)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Deletion (Genetics) Modification of genetic information Mutation