Gaia hypothesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living
The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living
 Since life started on Earth, the energy provided by the Sun has increased by 25% to 30%; however, the surface temperature of the planet has remained within the levels of habitability, reaching quite regular low and high margins. Lovelock has also hypothesised that methanogens produced elevated levels of methane in the early atmosphere, giving a view similar to that found in petrochemical smog, similar in some respects to the atmosphere on
Since life started on Earth, the energy provided by the Sun has increased by 25% to 30%; however, the surface temperature of the planet has remained within the levels of habitability, reaching quite regular low and high margins. Lovelock has also hypothesised that methanogens produced elevated levels of methane in the early atmosphere, giving a view similar to that found in petrochemical smog, similar in some respects to the atmosphere on
 In response to the criticism that the Gaia hypothesis seemingly required unrealistic group selection and cooperation between organisms, James Lovelock and Andrew Watson developed a mathematical model,
In response to the criticism that the Gaia hypothesis seemingly required unrealistic group selection and cooperation between organisms, James Lovelock and Andrew Watson developed a mathematical model,
here
by Kenneth J. Hsue, a correspondence author in 2001. Hsue suggests the " desiccation" of the Mediterranean is evidence of a functioning Gaia "kidney". In this and earlier suggested cases, it is plate movements and physics, not biology, which performs the regulation. Earlier "kidney functions" were performed during the " deposition of the
 The Gaia theorem states that the Earth's
The Gaia theorem states that the Earth's
 The idea of the Earth as an integrated whole, a living being, has a long tradition. The mythical Gaia was the primal Greek goddess personifying the
The idea of the Earth as an integrated whole, a living being, has a long tradition. The mythical Gaia was the primal Greek goddess personifying the
 Lovelock started defining the idea of a self-regulating Earth controlled by the community of living organisms in September 1965, while working at the
Lovelock started defining the idea of a self-regulating Earth controlled by the community of living organisms in September 1965, while working at the  Later, other relationships such as sea creatures producing sulfur and iodine in approximately the same quantities as required by land creatures emerged and helped bolster the hypothesis.
In 1971 microbiologist Dr. Lynn Margulis joined Lovelock in the effort of fleshing out the initial hypothesis into scientifically proven concepts, contributing her knowledge about how microbes affect the atmosphere and the different layers in the surface of the planet. The American biologist had also awakened criticism from the scientific community with her advocacy of the theory on the origin of eukaryotic
Later, other relationships such as sea creatures producing sulfur and iodine in approximately the same quantities as required by land creatures emerged and helped bolster the hypothesis.
In 1971 microbiologist Dr. Lynn Margulis joined Lovelock in the effort of fleshing out the initial hypothesis into scientifically proven concepts, contributing her knowledge about how microbes affect the atmosphere and the different layers in the surface of the planet. The American biologist had also awakened criticism from the scientific community with her advocacy of the theory on the origin of eukaryotic
PNAS April 17, 2018 115 (16)
4006-4014 proposed that differential persistence can play a similar role to differential reproduction in evolution by natural selections, thereby providing a possible reconciliation between the theory of natural selection and the Gaia hypothesis.
The Earth is about to catch a morbid fever
16 January 2006. * * * * *Lovelock, James (2006), interviewed in ''How to think about science'', CBC Ideas (radio program), broadcast January 3, 2008.
Link
* * * * * * *
Gaia as seen through the atmosphere
by James Lovelock, published in ''Biomineralization and Biological Metal Accumulation'', 1983, jameslovelock.org
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20131031191848/http://www.wildethics.org/essays/the_perceptual_implications_of_gaia.html D. Abram: The Perceptual Implications of Gaiabr>Lovelock: 'We can't save the planet'
BBC Sci Tech News
Interview: Jasper Gerard meets James Lovelock
* {{Authority control Cybernetics Ecological theories Evolution of the biosphere Superorganisms Syncretism Climate change feedbacks 1965 introductions Biogeochemistry Earth Gaia Biological hypotheses Evolution Astronomical hypotheses Meteorological hypotheses
 The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living
The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
s interact with their inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemis ...
surroundings on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
to form a synergistic and self-regulating, complex system
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communicatio ...
that helps to maintain and perpetuate the conditions for life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
on the planet.
The hypothesis was formulated by the chemist James Lovelock and co-developed by the microbiologist Lynn Margulis in the 1970s. Lovelock named the idea after Gaia
In Greek mythology, Gaia (; from Ancient Greek , a poetical form of , 'land' or 'earth'),, , . also spelled Gaea , is the personification of the Earth and one of the Greek primordial deities. Gaia is the ancestral mother—sometimes parthe ...
, the primordial goddess who personified the Earth in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of ...
. The suggestion that the theory should be called "the Gaia hypothesis" came from Lovelock's neighbour, William Golding. In 2006, the Geological Society of London awarded Lovelock the Wollaston Medal in part for his work on the Gaia hypothesis.
Topics related to the hypothesis include how the biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
and the evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
of organisms affect the stability of global temperature, salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
of seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appr ...
, atmospheric oxygen levels, the maintenance of a hydrosphere of liquid water and other environmental variables that affect the habitability of Earth.
The Gaia hypothesis was initially criticized for being teleological and against the principles of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
, but later refinements aligned the Gaia hypothesis with ideas from fields such as Earth system science, biogeochemistry and systems ecology. Even so, the Gaia hypothesis continues to attract criticism, and today many scientists consider it to be only weakly supported by, or at odds with, the available evidence.
Overview
Gaian hypotheses suggest that organisms co-evolve with their environment: that is, they "influence their abiotic environment, and that environment in turn influences thebiota
Biota may refer to:
* Biota (ecology), the plant and animal life of a region
* Biota (plant), common name for a coniferous tree, ''Platycladus orientalis''
* Biota, Cinco Villas, a municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Biota (band), a band from Color ...
by Darwinian process
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
". Lovelock (1995) gave evidence of this in his second book, ''Ages of Gaia'', showing the evolution from the world of the early thermo-acido-philic and methanogenic bacteria towards the oxygen-enriched atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. ...
today that supports more complex life
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few ...
.
A reduced version of the hypothesis has been called "influential Gaia" in "Directed Evolution of the Biosphere: Biogeochemical Selection or Gaia?" by Andrei G. Lapenis, which states the biota
Biota may refer to:
* Biota (ecology), the plant and animal life of a region
* Biota (plant), common name for a coniferous tree, ''Platycladus orientalis''
* Biota, Cinco Villas, a municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Biota (band), a band from Color ...
influence certain aspects of the abiotic world, e.g. temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
and atmosphere. This is not the work of an individual but a collective of Russian scientific research that was combined into this peer reviewed publication. It states the coevolution of life and the environment through "micro-forces" and biogeochemical processes. An example is how the activity of photosynthetic bacteria during Precambrian times completely modified the Earth atmosphere to turn it aerobic, and thus supports the evolution of life (in particular eukaryotic life).
Since barriers existed throughout the twentieth century between Russia and the rest of the world, it is only relatively recently that the early Russian scientists who introduced concepts overlapping the Gaia paradigm have become better known to the Western scientific community. These scientists include Piotr Alekseevich Kropotkin (1842–1921) (although he spent much of his professional life outside Russia), Rafail Vasil’evich Rizpolozhensky (1862 – c. 1922), Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky (1863–1945), and Vladimir Alexandrovich Kostitzin (1886–1963).
Biologists and Earth scientists usually view the factors that stabilize the characteristics of a period as an undirected emergent property or entelechy of the system; as each individual species pursues its own self-interest, for example, their combined actions may have counterbalancing effects on environmental change. Opponents of this view sometimes reference examples of events that resulted in dramatic change rather than stable equilibrium, such as the conversion of the Earth's atmosphere from a reducing environment to an oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
-rich one at the end of the Archaean and the beginning of the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
periods.
Less accepted versions of the hypothesis claim that changes in the biosphere are brought about through the coordination of living organisms and maintain those conditions through homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
. In some versions of Gaia philosophy, all lifeforms are considered part of one single living planetary being called ''Gaia''. In this view, the atmosphere, the seas and the terrestrial crust would be results of interventions carried out by Gaia through the coevolving diversity of living organisms.
The Gaia paradigm was an influence on the deep ecology movement.
Details
The Gaia hypothesis posits that the Earth is a self-regulatingcomplex system
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communicatio ...
involving the biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
, the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. ...
, the hydrospheres and the pedosphere
The pedosphere (from Greek ''pedon'' "ground" or "earth" and ''sphaira'' "sphere") is the outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, atmosphere, ...
, tightly coupled as an evolving system. The hypothesis contends that this system as a whole, called Gaia, seeks a physical and chemical environment optimal for contemporary life.Lovelock, James. ''The Vanishing Face of Gaia''. Basic Books, 2009, p. 255.
Gaia evolves through a cybernetic feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled ...
system operated unconsciously by the biota
Biota may refer to:
* Biota (ecology), the plant and animal life of a region
* Biota (plant), common name for a coniferous tree, ''Platycladus orientalis''
* Biota, Cinco Villas, a municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Biota (band), a band from Color ...
, leading to broad stabilization of the conditions of habitability in a full homeostasis. Many processes in the Earth's surface, essential for the conditions of life, depend on the interaction of living forms, especially microorganisms, with inorganic elements. These processes establish a global control system that regulates Earth's surface temperature Surface temperature is the temperature at a surface.
Specifically, it may refer to:
* Surface air temperature, the temperature of the air near the surface of the earth
* Sea surface temperature, the temperature of water close to the ocean's sur ...
, atmosphere composition and ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
, powered by the global thermodynamic disequilibrium state of the Earth system.
The existence of a planetary homeostasis influenced by living forms had been observed previously in the field of biogeochemistry, and it is being investigated also in other fields like Earth system science. The originality of the Gaia hypothesis relies on the assessment that such homeostatic balance is actively pursued with the goal of keeping the optimal conditions for life, even when terrestrial or external events menace them.
Regulation of global surface temperature
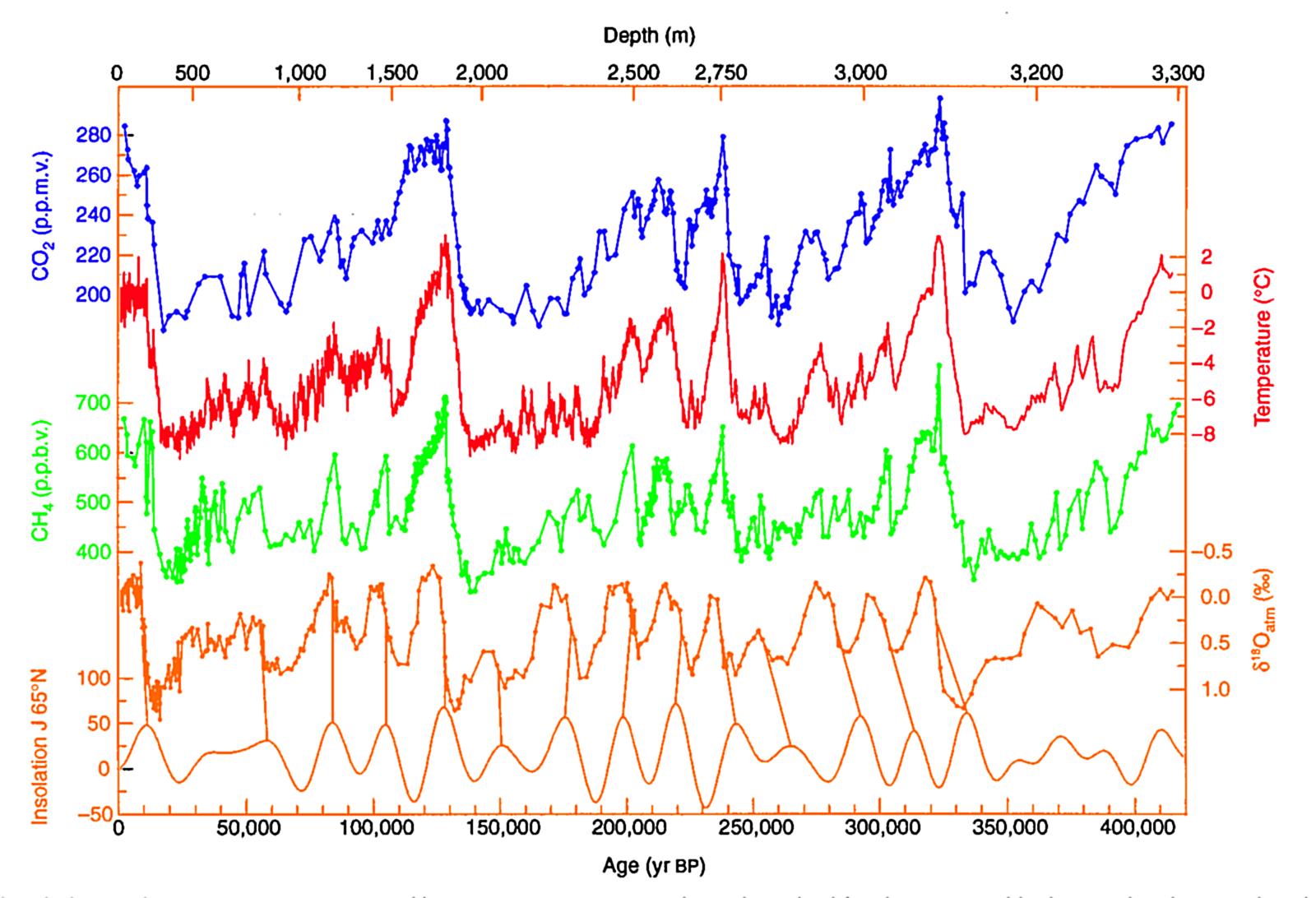
 Since life started on Earth, the energy provided by the Sun has increased by 25% to 30%; however, the surface temperature of the planet has remained within the levels of habitability, reaching quite regular low and high margins. Lovelock has also hypothesised that methanogens produced elevated levels of methane in the early atmosphere, giving a view similar to that found in petrochemical smog, similar in some respects to the atmosphere on
Since life started on Earth, the energy provided by the Sun has increased by 25% to 30%; however, the surface temperature of the planet has remained within the levels of habitability, reaching quite regular low and high margins. Lovelock has also hypothesised that methanogens produced elevated levels of methane in the early atmosphere, giving a view similar to that found in petrochemical smog, similar in some respects to the atmosphere on Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
.Lovelock, James, (1995) "The Ages of Gaia: A Biography of Our Living Earth" (W.W.Norton & Co) This, he suggests tended to screen out ultraviolet until the formation of the ozone screen, maintaining a degree of homeostasis. However, the Snowball Earth research has suggested that "oxygen shocks" and reduced methane levels led, during the Huronian
The Huronian glaciation (or Makganyene glaciation) was a period where several Ice age, ice ages occurred during the deposition of the Huronian Supergroup, rather than a single continuous event as it is commonly misrepresented to be. The depositi ...
, Sturtian and Marinoan/ Varanger Ice Ages, to a world that very nearly became a solid "snowball". These epochs are evidence against the ability of the pre Phanerozoic biosphere to fully self-regulate.
Processing of the greenhouse gas CO2, explained below, plays a critical role in the maintenance of the Earth temperature within the limits of habitability.
The CLAW hypothesis, inspired by the Gaia hypothesis, proposes a feedback loop that operates between ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s and the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
's climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologica ...
. The hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can testable, test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on prev ...
specifically proposes that particular phytoplankton that produce dimethyl sulfide are responsive to variations in climate forcing, and that these responses lead to a negative feedback loop that acts to stabilise the temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
of the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
.
Currently the increase in human population and the environmental impact of their activities, such as the multiplication of greenhouse gases may cause negative feedbacks in the environment to become positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in th ...
. Lovelock has stated that this could bring an extremely accelerated global warming, but he has since stated the effects will likely occur more slowly.
Daisyworld simulations
 In response to the criticism that the Gaia hypothesis seemingly required unrealistic group selection and cooperation between organisms, James Lovelock and Andrew Watson developed a mathematical model,
In response to the criticism that the Gaia hypothesis seemingly required unrealistic group selection and cooperation between organisms, James Lovelock and Andrew Watson developed a mathematical model, Daisyworld
Daisyworld, a computer simulation, is a hypothetical world orbiting a star whose radiant energy is slowly increasing or decreasing. It is meant to mimic important elements of the Earth-Sun system, and was introduced by James Lovelock and Andre ...
, in which ecological competition underpinned planetary temperature regulation.
Daisyworld examines the energy budget of a planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a ...
populated by two different types of plants, black daisies and white daisies, which are assumed to occupy a significant portion of the surface. The colour of the daisies influences the albedo of the planet such that black daisies absorb more light and warm the planet, while white daisies reflect more light and cool the planet. The black daisies are assumed to grow and reproduce best at a lower temperature, while the white daisies are assumed to thrive best at a higher temperature. As the temperature rises closer to the value the white daisies like, the white daisies outreproduce the black daisies, leading to a larger percentage of white surface, and more sunlight is reflected, reducing the heat input and eventually cooling the planet. Conversely, as the temperature falls, the black daisies outreproduce the white daisies, absorbing more sunlight and warming the planet. The temperature will thus converge to the value at which the reproductive rates of the plants are equal.
Lovelock and Watson showed that, over a limited range of conditions, this negative feedback due to competition can stabilize the planet's temperature at a value which supports life, if the energy output of the Sun changes, while a planet without life would show wide temperature changes. The percentage of white and black daisies will continually change to keep the temperature at the value at which the plants' reproductive rates are equal, allowing both life forms to thrive.
It has been suggested that the results were predictable because Lovelock and Watson selected examples that produced the responses they desired.
Regulation of oceanic salinity
Oceansalinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
has been constant at about 3.5% for a very long time. Salinity stability in oceanic environments is important as most cells require a rather constant salinity and do not generally tolerate values above 5%. The constant ocean salinity was a long-standing mystery, because no process counterbalancing the salt influx from rivers was known. Recently it was suggested that salinity may also be strongly influenced by seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appr ...
circulation through hot basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
ic rocks, and emerging as hot water vents on mid-ocean ridges. However, the composition of seawater is far from equilibrium, and it is difficult to explain this fact without the influence of organic processes. One suggested explanation lies in the formation of salt plains throughout Earth's history. It is hypothesized that these are created by bacterial colonies that fix ions and heavy metals during their life processes.
In the biogeochemical processes of Earth, sources and sinks are the movement of elements. The composition of salt ions within our oceans and seas is: sodium (Na+), chlorine (Cl−), sulfate (SO42−), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+) and potassium (K+). The elements that comprise salinity do not readily change and are a conservative property of seawater. There are many mechanisms that change salinity from a particulate form to a dissolved form and back. Considering the metallic composition of iron sources across a multifaceted grid of thermomagnetic design, not only would the movement of elements hypothetically help restructure the movement of ions, electrons, and the like, but would also potentially and inexplicably assist in balancing the magnetic bodies of the Earth's geomagnetic field. The known sources of sodium i.e. salts are when weathering, erosion, and dissolution of rocks are transported into rivers and deposited into the oceans.
The Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
as being Gaia's kidney is foundhere
by Kenneth J. Hsue, a correspondence author in 2001. Hsue suggests the " desiccation" of the Mediterranean is evidence of a functioning Gaia "kidney". In this and earlier suggested cases, it is plate movements and physics, not biology, which performs the regulation. Earlier "kidney functions" were performed during the " deposition of the
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
( South Atlantic), Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
(Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
), Permo-Triassic (Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
), Devonian (Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
), and Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
/Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
( Gondwana) saline giants."
Regulation of oxygen in the atmosphere
 The Gaia theorem states that the Earth's
The Gaia theorem states that the Earth's atmospheric composition
Atmospheric chemistry is a branch of atmospheric science in which the chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere and that of other planets is studied. It is a multidisciplinary approach of research and draws on environmental chemistry, physics, meteorol ...
is kept at a dynamically steady state by the presence of life. The atmospheric composition provides the conditions that contemporary life has adapted to. All the atmospheric gases other than noble gases present in the atmosphere are either made by organisms or processed by them.
The stability of the atmosphere in Earth is not a consequence of chemical equilibrium. Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
is a reactive compound, and should eventually combine with gases and minerals of the Earth's atmosphere and crust. Oxygen only began to persist in the atmosphere in small quantities about 50 million years before the start of the Great Oxygenation Event
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE), also called the Great Oxygenation Event, the Oxygen Catastrophe, the Oxygen Revolution, the Oxygen Crisis, or the Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmospher ...
. Since the start of the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
period, atmospheric oxygen concentrations have fluctuated between 15% and 35% of atmospheric volume. Traces of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
(at an amount of 100,000 tonnes produced per year) should not exist, as methane is combustible in an oxygen atmosphere.
Dry air in the atmosphere of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing ...
contains roughly (by volume) 78.09% nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seve ...
, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as a ...
, 0.039% carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, and small amounts of other gases including methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
. Lovelock originally speculated that concentrations of oxygen above about 25% would increase the frequency of wildfires and conflagration of forests. This mechanism, however, would not raise oxygen levels if they became too low. If plants can be shown to robustly over-produce O2 then perhaps only the high oxygen forest fires regulator is necessary. Recent work on the findings of fire-caused charcoal in Carboniferous and Cretaceous coal measures, in geologic periods when O2 did exceed 25%, has supported Lovelock's contention.
Processing of CO2
Gaia scientists see the participation of living organisms in the carbon cycle as one of the complex processes that maintain conditions suitable for life. The only significant natural source of atmospheric carbon dioxide ( CO2) is volcanic activity, while the only significant removal is through the precipitation of carbonate rocks. Carbon precipitation, solution and fixation are influenced by thebacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
and plant roots in soils, where they improve gaseous circulation, or in coral reefs, where calcium carbonate is deposited as a solid on the sea floor. Calcium carbonate is used by living organisms to manufacture carbonaceous tests and shells. Once dead, the living organisms' shells fall. Some arrive at the bottom of the oceans where plate tectonics and heat and/or pressure eventually convert them to deposits of chalk and limestone. Much of the falling dead shells, however, re-dissolve into the ocean below the carbon compensation depth.
One of these organisms is '' Emiliania huxleyi'', an abundant coccolithophore algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from ...
which may have a role in the formation of clouds. CO2 excess is compensated by an increase of coccolithophorid life, increasing the amount of CO2 locked in the ocean floor. Coccolithophorids, if the CLAW Hypothesis turns out to be supported (see "Regulation of Global Surface Temperature" above), could help increase the cloud cover, hence control the surface temperature, help cool the whole planet and favor precipitation necessary for terrestrial plants. Lately the atmospheric CO2 concentration has increased and there is some evidence that concentrations of ocean algal blooms are also increasing.
Lichen and other organisms accelerate the weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs '' in situ'' (on site, with little or no movemen ...
of rocks in the surface, while the decomposition of rocks also happens faster in the soil, thanks to the activity of roots, fungi, bacteria and subterranean animals. The flow of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to the soil is therefore regulated with the help of living beings. When CO2 levels rise in the atmosphere the temperature increases and plants grow. This growth brings higher consumption of CO2 by the plants, who process it into the soil, removing it from the atmosphere.
History
Precedents
 The idea of the Earth as an integrated whole, a living being, has a long tradition. The mythical Gaia was the primal Greek goddess personifying the
The idea of the Earth as an integrated whole, a living being, has a long tradition. The mythical Gaia was the primal Greek goddess personifying the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
, the Greek version of " Mother Nature" (from Ge = Earth, and Aia =
PIE grandmother), or the Earth Mother. James Lovelock gave this name to his hypothesis after a suggestion from the novelist William Golding, who was living in the same village as Lovelock at the time ( Bowerchalke, Wiltshire, UK). Golding's advice was based on Gea, an alternative spelling for the name of the Greek goddess, which is used as prefix in geology, geophysics and geochemistry. Golding later made reference to Gaia in his Nobel prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfre ...
acceptance speech.
In the eighteenth century, as geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
consolidated as a modern science, James Hutton maintained that geological and biological processes are interlinked. Later, the naturalist and explorer Alexander von Humboldt recognized the coevolution of living organisms, climate, and Earth's crust. In the twentieth century, Vladimir Vernadsky formulated a theory of Earth's development that is now one of the foundations of ecology. Vernadsky was a Ukrainian geochemist and was one of the first scientists to recognize that the oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere result from biological processes. During the 1920s he published works arguing that living organisms could reshape the planet as surely as any physical force. Vernadsky was a pioneer of the scientific bases for the environmental sciences. His visionary pronouncements were not widely accepted in the West, and some decades later the Gaia hypothesis received the same type of initial resistance from the scientific community.
Also in the turn to the 20th century Aldo Leopold, pioneer in the development of modern environmental ethics and in the movement for wilderness conservation, suggested a living Earth in his biocentric or holistic ethics regarding land.
Another influence for the Gaia hypothesis and the environmental movement in general came as a side effect of the Space Race between the Soviet Union and the United States of America. During the 1960s, the first humans in space could see how the Earth looked as a whole. The photograph '' Earthrise'' taken by astronaut William Anders in 1968 during the Apollo 8 mission became, through the Overview Effect an early symbol for the global ecology movement.
Formulation of the hypothesis
 Lovelock started defining the idea of a self-regulating Earth controlled by the community of living organisms in September 1965, while working at the
Lovelock started defining the idea of a self-regulating Earth controlled by the community of living organisms in September 1965, while working at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA ...
in California on methods of detecting life on Mars. The first paper to mention it was ''Planetary Atmospheres: Compositional and other Changes Associated with the Presence of Life'', co-authored with C.E. Giffin. A main concept was that life could be detected in a planetary scale by the chemical composition of the atmosphere. According to the data gathered by the Pic du Midi observatory, planets like Mars or Venus had atmospheres in chemical equilibrium. This difference with the Earth atmosphere was considered to be a proof that there was no life in these planets.
Lovelock formulated the ''Gaia Hypothesis'' in journal articles in 1972 and 1974, followed by a popularizing 1979 book ''Gaia: A new look at life on Earth''. An article in the ''New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publish ...
'' of February 6, 1975, and a popular book length version of the hypothesis, published in 1979 as ''The Quest for Gaia'', began to attract scientific and critical attention.
Lovelock called it first the Earth feedback hypothesis, and it was a way to explain the fact that combinations of chemicals including oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
persist in stable concentrations in the atmosphere of the Earth. Lovelock suggested detecting such combinations in other planets' atmospheres as a relatively reliable and cheap way to detect life.
 Later, other relationships such as sea creatures producing sulfur and iodine in approximately the same quantities as required by land creatures emerged and helped bolster the hypothesis.
In 1971 microbiologist Dr. Lynn Margulis joined Lovelock in the effort of fleshing out the initial hypothesis into scientifically proven concepts, contributing her knowledge about how microbes affect the atmosphere and the different layers in the surface of the planet. The American biologist had also awakened criticism from the scientific community with her advocacy of the theory on the origin of eukaryotic
Later, other relationships such as sea creatures producing sulfur and iodine in approximately the same quantities as required by land creatures emerged and helped bolster the hypothesis.
In 1971 microbiologist Dr. Lynn Margulis joined Lovelock in the effort of fleshing out the initial hypothesis into scientifically proven concepts, contributing her knowledge about how microbes affect the atmosphere and the different layers in the surface of the planet. The American biologist had also awakened criticism from the scientific community with her advocacy of the theory on the origin of eukaryotic organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' t ...
s and her contributions to the endosymbiotic theory
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory,) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and pos ...
, nowadays accepted. Margulis dedicated the last of eight chapters in her book, ''The Symbiotic Planet'', to Gaia. However, she objected to the widespread personification of Gaia and stressed that Gaia is "not an organism", but "an emergent property of interaction among organisms". She defined Gaia as "the series of interacting ecosystems that compose a single huge ecosystem at the Earth's surface. Period". The book's most memorable "slogan" was actually quipped by a student of Margulis'.
James Lovelock called his first proposal the ''Gaia hypothesis'' but has also used the term ''Gaia theory''. Lovelock states that the initial formulation was based on observation, but still lacked a scientific explanation. The Gaia hypothesis has since been supported by a number of scientific experiments and provided a number of useful predictions.
First Gaia conference
In 1985, the first public symposium on the Gaia hypothesis, ''Is The Earth A Living Organism?'' was held at University of Massachusetts Amherst, August 1–6. The principal sponsor was the National Audubon Society. Speakers included James Lovelock,George Wald
George Wald (November 18, 1906 – April 12, 1997) was an American scientist who studied pigments in the retina. He won a share of the 1967 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Haldan Keffer Hartline and Ragnar Granit.
In 1970, Wald pr ...
, Mary Catherine Bateson, Lewis Thomas, John Todd John Todd or Tod may refer to:
Clergy
*John Todd (abolitionist) (1818–1894), preacher and 'conductor' on the Underground Railroad
* John Todd (author) (1800–1873), American minister and author
* John Todd (bishop), Anglican bishop in the early ...
, Donald Michael, Christopher Bird, Thomas Berry, David Abram, Michael Cohen, and William Fields. Some 500 people attended.
Second Gaia conference
In 1988, climatologist Stephen Schneider organised a conference of theAmerican Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, atmospheric, ocean, hydrologic, space, and planetary scientists and enthusiasts that according to their website includes 130,000 people (not members). AGU's ...
. The first Chapman Conference on Gaia, was held in San Diego, California on March 7, 1988.
During the "philosophical foundations" session of the conference, David Abram spoke on the influence of metaphor in science, and of the Gaia hypothesis as offering a new and potentially game-changing metaphorics, while James Kirchner James W. Kirchner is professor of Earth and Planetary Science at University of California, Berkeley. His current research spans the fields of geomorphology, hydrology, environmental geochemistry, evolutionary ecology, and paleobiology. He curren ...
criticised the Gaia hypothesis for its imprecision. Kirchner claimed that Lovelock and Margulis had not presented one Gaia hypothesis, but four:
* CoEvolutionary Gaia: that life and the environment had evolved in a coupled way. Kirchner claimed that this was already accepted scientifically and was not new.
* Homeostatic Gaia: that life maintained the stability of the natural environment, and that this stability enabled life to continue to exist.
* Geophysical Gaia: that the Gaia hypothesis generated interest in geophysical cycles and therefore led to interesting new research in terrestrial geophysical dynamics.
* Optimising Gaia: that Gaia shaped the planet in a way that made it an optimal environment for life as a whole. Kirchner claimed that this was not testable and therefore was not scientific.
Of Homeostatic Gaia, Kirchner recognised two alternatives. "Weak Gaia" asserted that life tends to make the environment stable for the flourishing of all life. "Strong Gaia" according to Kirchner, asserted that life tends to make the environment stable, ''to enable'' the flourishing of all life. Strong Gaia, Kirchner claimed, was untestable and therefore not scientific.
Lovelock and other Gaia-supporting scientists, however, did attempt to disprove the claim that the hypothesis is not scientific because it is impossible to test it by controlled experiment. For example, against the charge that Gaia was teleological, Lovelock and Andrew Watson offered the Daisyworld
Daisyworld, a computer simulation, is a hypothetical world orbiting a star whose radiant energy is slowly increasing or decreasing. It is meant to mimic important elements of the Earth-Sun system, and was introduced by James Lovelock and Andre ...
Model (and its modifications, above) as evidence against most of these criticisms. Lovelock said that the Daisyworld model "demonstrates that self-regulation of the global environment can emerge from competition amongst types of life altering their local environment in different ways".
Lovelock was careful to present a version of the Gaia hypothesis that had no claim that Gaia intentionally or consciously maintained the complex balance in her environment that life needed to survive. It would appear that the claim that Gaia acts "intentionally" was a statement in his popular initial book and was not meant to be taken literally. This new statement of the Gaia hypothesis was more acceptable to the scientific community. Most accusations of teleologism ceased, following this conference.
Third Gaia conference
By the time of the 2nd Chapman Conference on the Gaia Hypothesis, held at Valencia, Spain, on 23 June 2000, the situation had changed significantly. Rather than a discussion of the Gaian teleological views, or "types" of Gaia hypotheses, the focus was upon the specific mechanisms by which basic short term homeostasis was maintained within a framework of significant evolutionary long term structural change. The major questions were: # "How has the global biogeochemical/climate system called Gaia changed in time? What is its history? Can Gaia maintain stability of the system at one time scale but still undergo vectorial change at longer time scales? How can the geologic record be used to examine these questions?" # "What is the structure of Gaia? Are the feedbacks sufficiently strong to influence the evolution of climate? Are there parts of the system determined pragmatically by whatever disciplinary study is being undertaken at any given time or are there a set of parts that should be taken as most true for understanding Gaia as containing evolving organisms over time? What are the feedbacks among these different parts of the Gaian system, and what does the near closure of matter mean for the structure of Gaia as a global ecosystem and for the productivity of life?" # "How do models of Gaian processes and phenomena relate to reality and how do they help address and understand Gaia? How do results from Daisyworld transfer to the real world? What are the main candidates for "daisies"? Does it matter for Gaia theory whether we find daisies or not? How should we be searching for daisies, and should we intensify the search? How can Gaian mechanisms be ''collaborated'' with using process models or global models of the climate system that include the biota and allow for chemical cycling?" In 1997, Tyler Volk argued that a Gaian system is almost inevitably produced as a result of an evolution towards far-from-equilibrium homeostatic states that maximiseentropy production
Entropy production (or generation) is the amount of entropy which is produced in any irreversible processes such as heat and mass transfer processes including motion of bodies, heat exchange, fluid flow, substances expanding or mixing, anelastic ...
, and Kleidon (2004) agreed stating: "...homeostatic behavior can emerge from a state of MEP associated with the planetary albedo"; "...the resulting behavior of a symbiotic Earth at a state of MEP may well lead to near-homeostatic behavior of the Earth system on long time scales, as stated by the Gaia hypothesis". Staley (2002) has similarly proposed "...an alternative form of Gaia theory based on more traditional Darwinian principles... In hisnew approach, environmental regulation is a consequence of population dynamics. The role of selection is to favor organisms that are best adapted to prevailing environmental conditions. However, the environment is not a static backdrop for evolution, but is heavily influenced by the presence of living and vibration-based beings and organisms. The resulting co-evolving dynamical process eventually leads to the convergence of equilibrium and optimal conditions", but would also require progress of truth and understanding in a lens that could be argued was put on hiatus while the species was proliferating the needs of Economic manipulation and environmental degradation while losing sight of the maturing nature of the needs of many. (12:22 10.29.2020)
Fourth Gaia conference
A fourth international conference on the Gaia hypothesis, sponsored by the Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority and others, was held in October 2006 at the Arlington, VA campus of George Mason University. Martin Ogle, Chief Naturalist, for NVRPA, and long-time Gaia hypothesis proponent, organized the event. Lynn Margulis, Distinguished University Professor in the Department of Geosciences, University of Massachusetts-Amherst, and long-time advocate of the Gaia hypothesis, was a keynote speaker. Among many other speakers: Tyler Volk, co-director of the Program in Earth and Environmental Science at New York University; Dr. Donald Aitken, Principal of Donald Aitken Associates; Dr. Thomas Lovejoy, President of the Heinz Center for Science, Economics and the Environment; Robert Correll, Senior Fellow, Atmospheric Policy Program, American Meteorological Society and noted environmental ethicist, J. Baird Callicott.Criticism
After initially receiving little attention from scientists (from 1969 until 1977), thereafter for a period the initial Gaia hypothesis was criticized by a number of scientists, including Ford Doolittle, Richard Dawkins and Stephen Jay Gould.Turney, Jon. "Lovelock and Gaia: Signs of Life" (Revolutions in Science) Lovelock has said that because his hypothesis is named after a Greek goddess, and championed by many non-scientists, the Gaia hypothesis was interpreted as a neo-Paganreligion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural ...
. Many scientists in particular also criticized the approach taken in his popular book ''Gaia, a New Look at Life on Earth'' for being teleological—a belief that things are purposeful and aimed towards a goal. Responding to this critique in 1990, Lovelock stated, "Nowhere in our writings do we express the idea that planetary self-regulation is purposeful, or involves foresight or planning by the biota
Biota may refer to:
* Biota (ecology), the plant and animal life of a region
* Biota (plant), common name for a coniferous tree, ''Platycladus orientalis''
* Biota, Cinco Villas, a municipality in Aragon, Spain
* Biota (band), a band from Color ...
".
Stephen Jay Gould criticized Gaia as being "a metaphor, not a mechanism." He wanted to know the actual mechanisms by which self-regulating homeostasis was achieved. In his defense of Gaia, David Abram argues that Gould overlooked the fact that "mechanism", itself, is a metaphor — albeit an exceedingly common and often unrecognized metaphor — one which leads us to consider natural and living systems as though they were machines organized and built from outside (rather than as autopoietic or self-organizing phenomena). Mechanical metaphors, according to Abram, lead us to overlook the active or agent quality of living entities, while the organismic metaphors of the Gaia hypothesis accentuate the active agency of both the biota and the biosphere as a whole. With regard to causality in Gaia, Lovelock argues that no single mechanism is responsible, that the connections between the various known mechanisms may never be known, that this is accepted in other fields of biology and ecology as a matter of course, and that specific hostility is reserved for his own hypothesis for other reasons.Lovelock, James (2001), ''Homage to Gaia: The Life of an Independent Scientist'' (Oxford University Press)
Aside from clarifying his language and understanding of what is meant by a life form, Lovelock himself ascribes most of the criticism to a lack of understanding of non-linear mathematics by his critics, and a linearizing form of greedy reductionism in which all events have to be immediately ascribed to specific causes before the fact. He also states that most of his critics are biologists but that his hypothesis includes experiments in fields outside biology, and that some self-regulating phenomena may not be mathematically explainable.
Natural selection and evolution
Lovelock has suggested that global biological feedback mechanisms could evolve bynatural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
, stating that organisms that improve their environment for their survival do better than those that damage their environment. However, in the early 1980s, W. Ford Doolittle
W. Ford Doolittle (born February 21, 1942, in Urbana, Illinois) is an evolutionary and molecular biologist. He is a member of the US National Academy of Sciences and a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada and the Norwegian Academy of Science and ...
and Richard Dawkins separately argued against this aspect of Gaia. Doolittle argued that nothing in the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
of individual organisms could provide the feedback mechanisms proposed by Lovelock, and therefore the Gaia hypothesis proposed no plausible mechanism and was unscientific. Dawkins meanwhile stated that for organisms to act in concert would require foresight and planning, which is contrary to the current scientific understanding of evolution. Like Doolittle, he also rejected the possibility that feedback loops could stabilize the system.
Lynn Margulis, a microbiologist who collaborated with Lovelock in supporting the Gaia hypothesis, argued in 1999 that "Darwin
Darwin may refer to:
Common meanings
* Charles Darwin (1809–1882), English naturalist and writer, best known as the originator of the theory of biological evolution by natural selection
* Darwin, Northern Territory, a territorial capital city i ...
's grand vision was not wrong, ''only incomplete.'' In accentuating the direct competition between individuals for resources as the primary selection mechanism, Darwin (and especially his followers) created the impression that the environment was simply a static arena". She wrote that the composition of the Earth's atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere are regulated around "set points" as in homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
, but those set points change with time.Margulis, Lynn. Symbiotic Planet: A New Look At Evolution. Houston: Basic Book 1999
Evolutionary biologist W. D. Hamilton called the concept of Gaia Copernican, adding that it would take another Newton to explain how Gaian self-regulation takes place through Darwinian natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
.Lovelock, James. ''The Vanishing Face of Gaia''. Basic Books, 2009, pp. 195-197. More recently Ford Doolittle building on his and Inkpen's ITSNTS (It's The Song Not The Singer) proposalDoolittle WF, Inkpen SA. Processes and patterns of interaction as units of selection: An introduction to ITSNTS thinkingPNAS April 17, 2018 115 (16)
4006-4014 proposed that differential persistence can play a similar role to differential reproduction in evolution by natural selections, thereby providing a possible reconciliation between the theory of natural selection and the Gaia hypothesis.
Criticism in the 21st century
The Gaia hypothesis continues to be broadly skeptically received by the scientific community. For instance, arguments both for and against it were laid out in the journal ''Climatic Change'' in 2002 and 2003. A significant argument raised against it are the many examples where life has had a detrimental or destabilising effect on the environment rather than acting to regulate it. Several recent books have criticised the Gaia hypothesis, expressing views ranging from "... the Gaia hypothesis lacks unambiguous observational support and has significant theoretical difficulties" to "Suspended uncomfortably between tainted metaphor, fact, and false science, I prefer to leave Gaia firmly in the background" to "The Gaia hypothesis is supported neither by evolutionary theory nor by the empirical evidence of the geological record". The CLAW hypothesis, initially suggested as a potential example of direct Gaian feedback, has subsequently been found to be less credible as understanding of cloud condensation nuclei has improved. In 2009 theMedea hypothesis
The Medea hypothesis is a term coined by paleontologist Peter Ward for a hypothesis that contests the Gaian hypothesis and proposes that multicellular life, understood as a superorganism, may be self-destructive or suicidal.
The metaphor refers ...
was proposed: that life has highly detrimental (biocidal) impacts on planetary conditions, in direct opposition to the Gaia hypothesis.
In a 2013 book-length evaluation of the Gaia hypothesis considering modern evidence from across the various relevant disciplines, Toby Tyrrell concluded that: "I believe Gaia is a dead end. Its study has, however, generated many new and thought provoking questions. While rejecting Gaia, we can at the same time appreciate Lovelock's originality and breadth of vision, and recognize that his audacious concept has helped to stimulate many new ideas about the Earth, and to champion a holistic approach to studying it". Elsewhere he presents his conclusion "The Gaia hypothesis is not an accurate picture of how our world works". This statement needs to be understood as referring to the "strong" and "moderate" forms of Gaia—that the biota obeys a principle that works to make Earth optimal (strength 5) or favourable for life (strength 4) or that it works as a homeostatic mechanism (strength 3). The latter is the "weakest" form of Gaia that Lovelock has advocated. Tyrrell rejects it. However, he finds that the two weaker forms of Gaia—Coeveolutionary Gaia and Influential Gaia, which assert that there are close links between the evolution of life and the environment and that biology affects the physical and chemical environment—are both credible, but that it is not useful to use the term "Gaia" in this sense and that those two forms were already accepted and explained by the processes of natural selection and adaptation.
See also
* * * * * * * * * * *References
Sources
* * * *Lovelock, James. ''The Independent''The Earth is about to catch a morbid fever
16 January 2006. * * * * *Lovelock, James (2006), interviewed in ''How to think about science'', CBC Ideas (radio program), broadcast January 3, 2008.
Link
* * * * * * *
Further reading
*External links
Gaia as seen through the atmosphere
by James Lovelock, published in ''Biomineralization and Biological Metal Accumulation'', 1983, jameslovelock.org
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20131031191848/http://www.wildethics.org/essays/the_perceptual_implications_of_gaia.html D. Abram: The Perceptual Implications of Gaiabr>Lovelock: 'We can't save the planet'
BBC Sci Tech News
Interview: Jasper Gerard meets James Lovelock
* {{Authority control Cybernetics Ecological theories Evolution of the biosphere Superorganisms Syncretism Climate change feedbacks 1965 introductions Biogeochemistry Earth Gaia Biological hypotheses Evolution Astronomical hypotheses Meteorological hypotheses