Fresnel Integral on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
250px,
Plots of and . The maximum of is about . If the integrands of and were defined using instead of , then the image would be scaled vertically and horizontally (see below).
The Fresnel integrals and are two
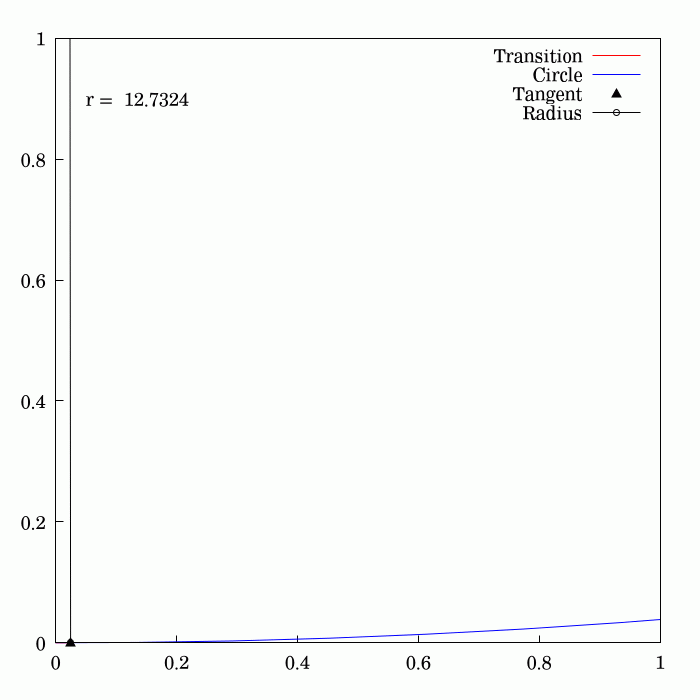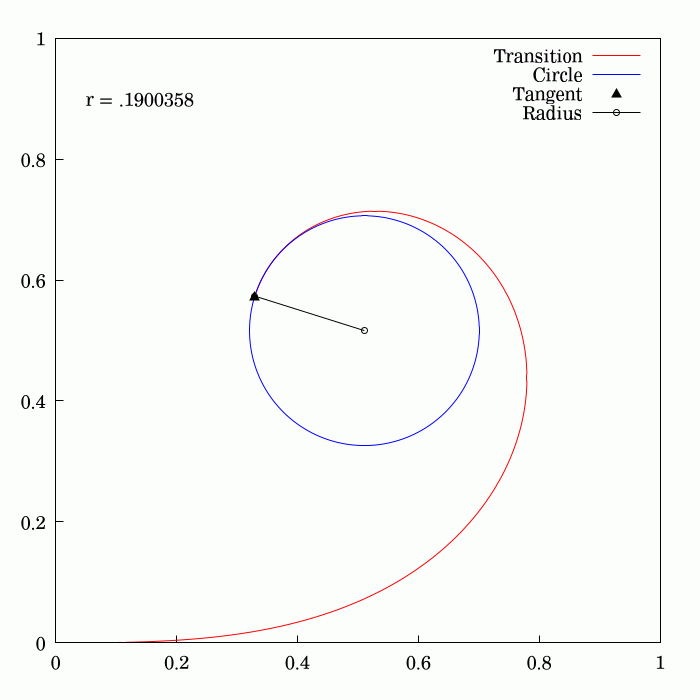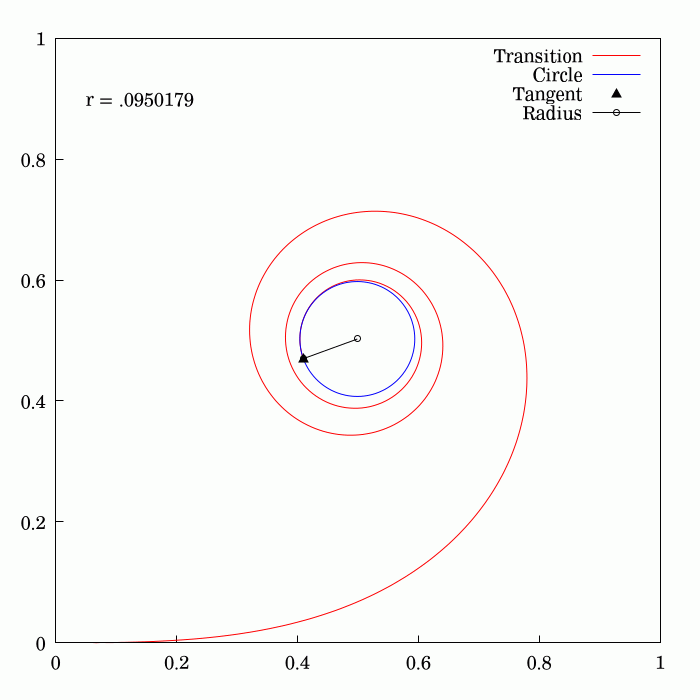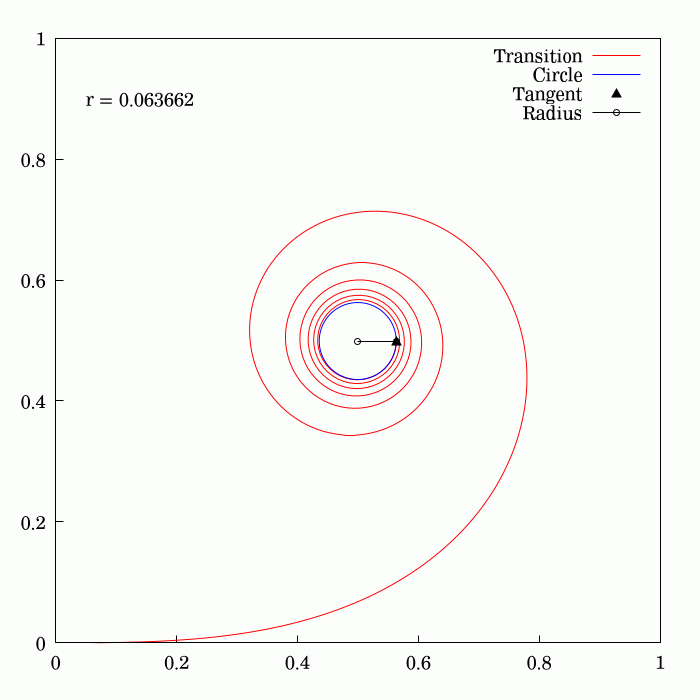 The Euler
The Euler
 Using the power series expansions above, the Fresnel integrals can be extended to the domain of
Using the power series expansions above, the Fresnel integrals can be extended to the domain of  or
or
File:Plot of the Fresnel integral function S(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D.svg, Plot of the Fresnel integral function S(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D
File:Plot of the Fresnel integral function C(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D.svg, Plot of the Fresnel integral function C(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D
File:Plot of the Fresnel auxillary function G(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D.svg, Plot of the Fresnel auxillary function G(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D
File:Plot of the Fresnel auxillary function F(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D.svg, Plot of the Fresnel auxillary function F(z) in the complex plane from -2-2i to 2+2i with colors created with Mathematica 13.1 function ComplexPlot3D
Cephes
free/open-source C++/C code to compute Fresnel integrals among other special functions. Used in
Faddeeva Package
free/open-source C++/C code to compute complex error functions (from which the Fresnel integrals can be obtained), with wrappers for Matlab, Python, and other languages. * * * * {{Nonelementary Integral Integral calculus Spirals Physical optics Special functions Special hypergeometric functions Analytic functions Diffraction
transcendental function
In mathematics, a transcendental function is an analytic function that does not satisfy a polynomial equation, in contrast to an algebraic function.
In other words, a transcendental function "transcends" algebra in that it cannot be expressed alge ...
s named after Augustin-Jean Fresnel
Augustin-Jean Fresnel (10 May 1788 – 14 July 1827) was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Isaac Newton, Newton's co ...
that are used in optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviole ...
and are closely related to the error function
In mathematics, the error function (also called the Gauss error function), often denoted by , is a complex function of a complex variable defined as:
:\operatorname z = \frac\int_0^z e^\,\mathrm dt.
This integral is a special (non-elementary ...
(). They arise in the description of near-field Fresnel diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction is an approximation of the Kirchhoff–Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field. It is used to calculate the diffraction pattern ...
phenomena and are defined through the following integral
In mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented i ...
representations:
The simultaneous parametric plot
In mathematics, a parametric equation defines a group of quantities as functions of one or more independent variables called parameters. Parametric equations are commonly used to express the coordinates of the points that make up a geometric ...
of and is the Euler spiral
An Euler spiral is a curve whose curvature changes linearly with its curve length (the curvature of a circular curve is equal to the reciprocal of the radius). Euler spirals are also commonly referred to as spiros, clothoids, or Cornu spirals.
E ...
(also known as the Cornu spiral or clothoid).
Definition
250px, Fresnel integrals with arguments instead of converge to instead of . The Fresnel integrals admit the followingpower series expansion
In mathematics, a power series (in one variable) is an infinite series of the form
\sum_^\infty a_n \left(x - c\right)^n = a_0 + a_1 (x - c) + a_2 (x - c)^2 + \dots
where ''an'' represents the coefficient of the ''n''th term and ''c'' is a cons ...
s that converge for all :
Some widely used tables use instead of for the argument of the integrals defining and . This changes their limits at infinity from to and the arc length for the first spiral turn from to 2 (at ). These alternative functions are usually known as normalized Fresnel integrals.
Euler spiral
 The Euler
The Euler spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:parametric plot
In mathematics, a parametric equation defines a group of quantities as functions of one or more independent variables called parameters. Parametric equations are commonly used to express the coordinates of the points that make up a geometric ...
of against . The Cornu spiral was created by Marie Alfred Cornu
Marie Alfred Cornu (; 6 March 1841 – 12 April 1902) was a French physicist. The French generally refer to him as Alfred Cornu.
Life
Cornu was born at Orléans to François Cornu and Sophie Poinsellier. He was educated at the École polytechni ...
as a nomogram
A nomogram (from Greek , "law" and , "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart, or abac, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function. ...
for diffraction computations in science and engineering.
From the definitions of Fresnel integrals, the infinitesimal
In mathematics, an infinitesimal number is a quantity that is closer to zero than any standard real number, but that is not zero. The word ''infinitesimal'' comes from a 17th-century Modern Latin coinage ''infinitesimus'', which originally referr ...
s and are thus:
Thus the length of the spiral measured from the origin
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Comics and manga
* Origin (comics), ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002
* The Origin (Buffy comic), ''The Origin'' (Bu ...
can be expressed as
That is, the parameter is the curve length measured from the origin , and the Euler spiral has infinite
Infinite may refer to:
Mathematics
*Infinite set, a set that is not a finite set
*Infinity, an abstract concept describing something without any limit
Music
* Infinite (group), a South Korean boy band
*''Infinite'' (EP), debut EP of American m ...
length. The vector also expresses the unit
Unit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* UNIT, a fictional military organization in the science fiction television series ''Doctor Who''
* Unit of action, a discrete piece of action (or beat) in a theatrical presentation
Music
* ''Unit'' (alb ...
tangent vector
In mathematics, a tangent vector is a vector that is tangent to a curve or surface at a given point. Tangent vectors are described in the differential geometry of curves in the context of curves in R''n''. More generally, tangent vectors are eleme ...
along the spiral, giving . Since is the curve length, the curvature can be expressed as
Thus the rate of change of curvature with respect to the curve length is
An Euler spiral has the property that its curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane.
For curves, the canonic ...
at any point is proportional to the distance along the spiral, measured from the origin. This property makes it useful as a transition curve
Transition or transitional may refer to:
Mathematics, science, and technology Biology
* Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ ...
in highway and railway engineering: if a vehicle follows the spiral at unit speed, the parameter in the above derivatives also represents the time. Consequently, a vehicle following the spiral at constant speed will have a constant rate of angular acceleration
In physics, angular acceleration refers to the time rate of change of angular velocity. As there are two types of angular velocity, namely spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity, there are naturally also two types of angular acceler ...
.
Sections from Euler spirals are commonly incorporated into the shape of rollercoaster
A roller coaster, or rollercoaster, is a type of amusement ride that employs a form of elevated railroad track designed with tight turns, steep slopes, and sometimes inversions. Passengers ride along the track in open cars, and the rides are o ...
loops to make what are known as clothoid loop
The generic roller coaster vertical loop, where a section of track causes the riders to complete a 360 degree turn, is the most basic of roller coaster inversions. At the top of the loop, riders are completely inverted.
History
The vertical ...
s.
Properties
and areodd function
In mathematics, even functions and odd functions are functions which satisfy particular symmetry relations, with respect to taking additive inverses. They are important in many areas of mathematical analysis, especially the theory of power seri ...
s of ,
Asymptotics of the Fresnel integrals as are given by the formulas:
complex number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form ...
s, where they become analytic function
In mathematics, an analytic function is a function that is locally given by a convergent power series. There exist both real analytic functions and complex analytic functions. Functions of each type are infinitely differentiable, but complex an ...
s of a complex variable.
and are entire function
In complex analysis, an entire function, also called an integral function, is a complex-valued function that is holomorphic on the whole complex plane. Typical examples of entire functions are polynomials and the exponential function, and any fin ...
s of the complex variable .
The Fresnel integrals can be expressed using the error function
In mathematics, the error function (also called the Gauss error function), often denoted by , is a complex function of a complex variable defined as:
:\operatorname z = \frac\int_0^z e^\,\mathrm dt.
This integral is a special (non-elementary ...
as follows: Limits as approaches infinity
The integrals defining and cannot be evaluated in the closed form in terms ofelementary function
In mathematics, an elementary function is a function of a single variable (typically real or complex) that is defined as taking sums, products, roots and compositions of finitely many polynomial, rational, trigonometric, hyperbolic, and exponen ...
s, except in special cases. The limits
Limit or Limits may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Limit'' (manga), a manga by Keiko Suenobu
* ''Limit'' (film), a South Korean film
* Limit (music), a way to characterize harmony
* "Limit" (song), a 2016 single by Luna Sea
* "Limits", a 2019 ...
of these functions as goes to infinity are known:
This can be derived with any one of several methods. One of themAnother method based on parametric integration is described for example in . uses a contour integral
In the mathematical field of complex analysis, contour integration is a method of evaluating certain integrals along paths in the complex plane.
Contour integration is closely related to the calculus of residues, a method of complex analysis.
...
of the function around the boundary of the sector
Sector may refer to:
Places
* Sector, West Virginia, U.S.
Geometry
* Circular sector, the portion of a disc enclosed by two radii and a circular arc
* Hyperbolic sector, a region enclosed by two radii and a hyperbolic arc
* Spherical sector, a po ...
-shaped region in the complex plane
In mathematics, the complex plane is the plane formed by the complex numbers, with a Cartesian coordinate system such that the -axis, called the real axis, is formed by the real numbers, and the -axis, called the imaginary axis, is formed by the ...
formed by the positive -axis, the bisector of the first quadrant with , and a circular arc of radius centered at the origin.
As goes to infinity, the integral along the circular arc tends to
where polar coordinates were used and Jordan's inequality was utilised for the second inequality. The integral along the real axis tends to the half Gaussian integral
The Gaussian integral, also known as the Euler–Poisson integral, is the integral of the Gaussian function f(x) = e^ over the entire real line. Named after the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss, the integral is
\int_^\infty e^\,dx = \s ...
Note too that because the integrand is an entire function
In complex analysis, an entire function, also called an integral function, is a complex-valued function that is holomorphic on the whole complex plane. Typical examples of entire functions are polynomials and the exponential function, and any fin ...
on the complex plane, its integral along the whole contour is zero. Overall, we must have
where denotes the bisector of the first quadrant, as in the diagram. To evaluate the left hand side, parametrize the bisector as
where ranges from 0 to . Note that the square of this expression is just . Therefore, substitution gives the left hand side as
Using Euler's formula
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that for an ...
to take real and imaginary parts of gives this as
where we have written to emphasize that the original Gaussian integral's value is completely real with zero imaginary part. Letting
and then equating real and imaginary parts produces the following system of two equations in the two unknowns and :
Solving this for and gives the desired result.
Generalization
The integral is aconfluent hypergeometric function
In mathematics, a confluent hypergeometric function is a solution of a confluent hypergeometric equation, which is a degenerate form of a hypergeometric differential equation where two of the three regular singularities merge into an irregular ...
and also an incomplete gamma function
In mathematics, the upper and lower incomplete gamma functions are types of special functions which arise as solutions to various mathematical problems such as certain integrals.
Their respective names stem from their integral definitions, which ...
which reduces to Fresnel integrals if real or imaginary parts are taken:
The leading term in the asymptotic expansion is
and therefore
For , the imaginary part of this equation in particular is
with the left-hand side converging for and the right-hand side being its analytical extension to the whole plane less where lie the poles of .
The Kummer transformation of the confluent hypergeometric function is
with
Numerical approximation
For computation to arbitrary precision, the power series is suitable for small argument. For large argument, asymptotic expansions converge faster. Continued fraction methods may also be used. For computation to particular target precision, other approximations have been developed. Cody developed a set of efficient approximations based on rational functions that give relative errors down to . A FORTRAN implementation of the Cody approximation that includes the values of the coefficients needed for implementation in other languages was published by van Snyder. Boersma developed an approximation with error less than .Applications
The Fresnel integrals were originally used in the calculation of the electromagnetic field intensity in an environment where light bends around opaque objects. More recently, they have been used in the design of highways and railways, specifically their curvature transition zones, seetrack transition curve
A track transition curve, or spiral easement, is a mathematically-calculated curve on a section of highway, or railroad track, in which a straight section changes into a curve. It is designed to prevent sudden changes in lateral (or centripetal ...
. Other applications are rollercoaster
A roller coaster, or rollercoaster, is a type of amusement ride that employs a form of elevated railroad track designed with tight turns, steep slopes, and sometimes inversions. Passengers ride along the track in open cars, and the rides are o ...
s or calculating the transitions on a velodrome
A velodrome is an arena for track cycling. Modern velodromes feature steeply banked oval tracks, consisting of two 180-degree circular bends connected by two straights. The straights transition to the circular turn through a moderate Track tran ...
track to allow rapid entry to the bends and gradual exit.
Gallery
See also
*Böhmer integral In mathematics, a Böhmer integral is an integral introduced by generalizing the Fresnel integrals.
There are two versions, given by
\begin
\operatorname(x,\alpha) &= \int_x^\infty t^ \cos(t) \, dt \\ ex\operatorname(x,\alpha) &= \int_x^\infty t ...
* Fresnel zone
A Fresnel zone ( ), named after physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, is one of a series of confocal prolate ellipsoidal regions of space between and around a transmitter and a receiver. The primary wave will travel in a relative straight line fro ...
* Track transition curve
A track transition curve, or spiral easement, is a mathematically-calculated curve on a section of highway, or railroad track, in which a straight section changes into a curve. It is designed to prevent sudden changes in lateral (or centripetal ...
* Euler spiral
An Euler spiral is a curve whose curvature changes linearly with its curve length (the curvature of a circular curve is equal to the reciprocal of the radius). Euler spirals are also commonly referred to as spiros, clothoids, or Cornu spirals.
E ...
* Zone plate
A zone plate is a device used to focus light or other things exhibiting wave character.G. W. Webb, I. V. Minin and O. V. Minin, “Variable Reference Phase in Diffractive Antennas”, ''IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine'', vol. 53, no. 2, ...
* Dirichlet integral
In mathematics, there are several integrals known as the Dirichlet integral, after the German mathematician Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet, one of which is the improper integral of the sinc function over the positive real line:
: \int_0^\in ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * (Uses instead of .) * * * * * *External links
Cephes
free/open-source C++/C code to compute Fresnel integrals among other special functions. Used in
SciPy
SciPy (pronounced "sigh pie") is a free and open-source Python library used for scientific computing and technical computing.
SciPy contains modules for optimization, linear algebra, integration, interpolation, special functions, FFT, signal ...
and ALGLIB
ALGLIB is a cross-platform open source numerical analysis and data processing library. It can be used from several programming languages (C++, C#, VB.NET, Python, Delphi).
ALGLIB started in 1999 and has a long history of steady development with r ...
.Faddeeva Package
free/open-source C++/C code to compute complex error functions (from which the Fresnel integrals can be obtained), with wrappers for Matlab, Python, and other languages. * * * * {{Nonelementary Integral Integral calculus Spirals Physical optics Special functions Special hypergeometric functions Analytic functions Diffraction