Five Barbarians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Five Barbarians, or Wu Hu (), is a Chinese historical
p. 120-21Peter Van Der Veer, "III. Contexts of Cosmopolitanism" in Steven Vertovec, Robin Cohen eds., ''Conceiving Cosmopolitanism: Theory, Context and Practice'' Oxford University Press 2002
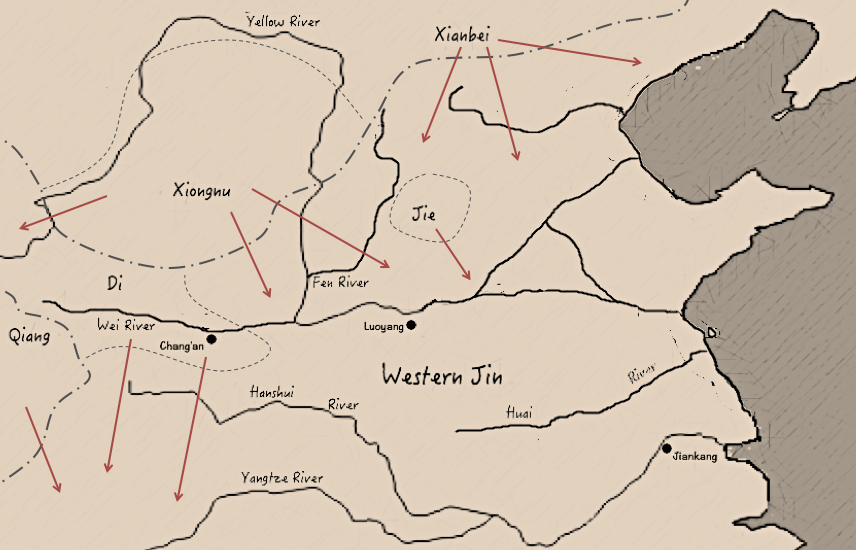
p. 200-01 The peoples categorized as the Five Barbarians were: *
段渝, 先秦巴蜀地区百濮和氐羌的来源
2006-11-30 or
 The term "Five Hu" was first used in the ''
The term "Five Hu" was first used in the ''
exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
for five ancient non-Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
peoples who immigrated to northern China in the Eastern Han dynasty, and then overthrew the Western Jin dynasty
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that i ...
and established their own kingdoms in the 4th–5th centuries.''A History of Chinese Civilization''Jacques Gernet
Jacques Gernet (; ; 22 December 1921, Algiers, French Algeria – 3 March 2018, Vannes) was an eminent French sinologist of the second half of the 20th century. His best-known work is ''The Chinese Civilization'', a 900-page summary of Chinese h ...
, Cambridge University Press 1996 P.186-87Michio Tanigawa & Joshua Fogel, ''Medieval Chinese Society and the Local "community"'' University of California Press 1985p. 120-21Peter Van Der Veer, "III. Contexts of Cosmopolitanism" in Steven Vertovec, Robin Cohen eds., ''Conceiving Cosmopolitanism: Theory, Context and Practice'' Oxford University Press 2002
p. 200-01 The peoples categorized as the Five Barbarians were: *
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
,
* Jie,
* Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
,
* Qiang,
* Di.
Of these five tribal ethnic groups, the Xiongnu and Xianbei were nomadic people
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
s from the northern steppes. The ethnic identity of the Xiongnu is uncertain, but the Xianbei appear to have been Mongolic. The Jie, another pastoral people, may have been a branch of the Xiongnu, who may have been Yeniseian
The Yeniseian languages (sometimes known as Yeniseic or Yenisei-Ostyak;"Ostyak" is a concept of areal rather than genetic linguistics. In addition to the Yeniseian languages it also includes the Uralic languages Khanty and Selkup. occasionally ...
. The Di and Qiang were from the highlands of western China. The Qiang were predominantly herdsmen and spoke Sino-Tibetan (Tibeto-Burman) languages, while the Di were farmers who may have spoken a Sino-Tibetan(Chinese段渝, 先秦巴蜀地区百濮和氐羌的来源
2006-11-30 or
Turkic language
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
.
Definition
 The term "Five Hu" was first used in the ''
The term "Five Hu" was first used in the ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Sixteen Kingdoms
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Sixteen Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese title ''Shiliuguo Chunqiu'' () is a Chinese biographical historical work of the Sixteen Kingdoms compiled by the Northern Wei official Cui Hong between 501 and 52 ...
'' (501–522), which recorded the history of the late Western Jin dynasty and the Sixteen Kingdoms during which rebellions and warfare by and among non-Han Chinese ethnic minorities ravaged Northern China. The term ''Hu'' in earlier texts had been used to describe the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
, but became a collective term for ethnic minorities who had settled in North China and took up arms during Uprising of the Five Barbarians
The Upheaval of the Five Barbarians also translated as the Rebellion, the Revolt, or the Invasion of the Five Barbarians () is a Chinese expression which refers to a series of rebellions and invasions between 304 and 316 by non- Han peoples, comm ...
. This term included the Xiongnu, Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
, Di, Qiang and Jie.
Later historians determined that more than five nomadic tribes took part, and the Five Barbarians has become a collective term for all nomadic people residing in northern parts of the previous empires of China.
They were a mix of tribes from various stocks, such as proto-Mongolic, Turkic, Tibetan and Yeniseian
The Yeniseian languages (sometimes known as Yeniseic or Yenisei-Ostyak;"Ostyak" is a concept of areal rather than genetic linguistics. In addition to the Yeniseian languages it also includes the Uralic languages Khanty and Selkup. occasionally ...
. Others divide them into two Turkic tribes, one Tungusic tribe, and two Tibetan tribes, and yet others into Tibetan and Altaic
Altaic (; also called Transeurasian) is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are ...
(proto-Mongolian and early Turkic).
The Southern Xiongnu
The Xiongnu were a people who had migrated in and out ofChina proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
, especially during times of turmoil, apparently at least since the days of the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
. the Chanyu Huhanye (呼韓邪; 58–31 BCE) signed a heqin
''Heqin'', also known as marriage alliance, refers to the historical practice of Chinese monarchs marrying princesses—usually members of minor branches of the ruling family—to rulers of neighboring states. It was often adopted as an appeaseme ...
agreement with Han China
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a war ...
in 53 BCE.
In 48 CE, after a dynastic conflict within the Xiongnu confederacy, an unnamed Shanyu (Shanyu or Chanyu meaning 'Son of Eternal Sky' and equating with the title of King) (48–56 CE) brought eight tribes of the Western Wing to China under a renewed heqin treaty, creating a polity of Southern Xiongnu in vassalage to China and a polity of Northern Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomads, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, ...
who maintained their independence.
As the Northern Xiongnu declined under internal and external conflicts, the Southern Xiongnu received waves of new migrants, and by the end of the first century CE a majority of the Xiongnu resided in China proper and along its northern borders.
In the 190s CE the Southern Xiongnu revolted against attempts of the Chinese Court to appoint a puppet Southern Shanyu against their will:
The Southern Xiongnu then elected a Shanyu from the Xubu The Xubu (; LHC: *''sio-pok'') was a tribe of the Xiongnu tribe that flourished between 3rd century BCE to 4th century CE. Chinese annals noted that the Xubu tribe replaced the Huyan tribe, which was an earlier maternal dynastic tribe of the dynast ...
in 188 CE and Chizhishizhuhou Chanyu
Chizhi Shizhu Hou (; 150–196; r. 188–195 AD), personal name Yufuluo (於夫羅), was a puppet chanyu of the Southern Xiongnu during the late Han Dynasty. In 188, he was appointed chanyu by the Han court following the murder of his father Qia ...
(188–195 CE) fled back to the Chinese court. After the death of the new Shanyu in 196 CE, most of the Southern Xiongnu left to join the Northern Xiongnu and only five tribes remained in China.and in Bichurin N.A., Collection of information on peoples in Central Asia in ancient times", vol. 1, Sankt Petersburg, 1851, pp. 146-147 (''In Russian'')
The War of the Eight Princes
The War of the Eight Princes, Rebellion of the Eight Kings, or Rebellion of the Eight Princes () was a series of civil wars among kings/princes (Chinese: ''wáng'' 王) of the Chinese Jin dynasty from 291 to 306 AD. The key point of contention in ...
during the Jin dynasty (266–420)
The Jin dynasty (; ) or the Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the (司馬晉) or the (兩晉), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Sima Yan (Emperor Wu), eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had pr ...
triggered a large-scale Southern Xiongnu uprising after 304, which resulted in the sacking of the Chinese capitals at Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang ...
(311) and Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin S ...
. The Xiongnu Kingdom of Han Zhao
The Han Zhao (; 304–329 AD), or Former Zhao (), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xiongnu people during the Sixteen Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In Chinese historiography, it was given two conditional state titles, the Northern ...
captured and executed the last two Jin emperors as the Western Jin dynasty collapsed in 317. Many Chinese fled south of the Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
as numerous tribesmen of the Xiongnu and remnants of the Jin wreaked havoc in the north. Fu Jian (337–385)
Fu Jian (; 337–385), courtesy name Yonggu () or Wenyu (), formally Emperor Xuanzhao of (Former) Qin (), was an emperor (who, however, used the title "Heavenly King" (''Tian Wang'') during his reign) of the Di-led Chinese Former Qin dynasty, u ...
temporarily unified the north but his achievement was destroyed after the Battle of Fei River. The Northern Wei unified North China again in 439 and ushered in the period of the Northern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as ...
.
The Five Barbarians after the fall of Northern Xiongnu
In the first century the EasternHan dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
brought the Northern Xiongnu into submission by military measures. Hordes of herdsmen and the Southern Xiongnu, originally subdued by the Northern Xiongnu, began trading without having heavy tribute imposed on them. Horses and animal products were traded mainly for agricultural tools, such as the harrow and the plough, and clothing of which silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
was most popular. In return those herdsmen helped defend the Han dynasty against any remaining Xiongnu. The more they engaged in commerce with the Chinese, the more they preferred to stay near China's border, to facilitate trade, instead of residing on the steppes of Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
.
Some groups of non-Xiongnu herdsmen even settled permanently within the Chinese borders, first of which was the Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', < (烏桓), who migrated to the area of today's Province of Liaoning during the era of Jiangwu (25–56). Note that the Southern Xiongnu migrated before the Wuhuan but not for commercial reasons.
Liaison among the dynasty and groups of herdsmen relied on mutual economic and military benefits. As the Northern Xiongnu, the masters of the Mongolian steppes and mortal enemy of the
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
, were still potent enough during the reigns of Emperor Ming, Emperor Zhang and Emperor He (58–105) to keep the volatile alliance intact, the Eastern Han dynasty enjoyed the most prosperous years of its almost 200 years of existence. Even fragments of the Northern Xiongnu migrated well within the border to the Xihe plain, west of the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
and south of the Ordos Desert
The Ordos Desert () is a desert/steppe region in Northwest China, administrated under the prefecture of Ordos City in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region (centered ca. ). It extends over an area of approximately , and comprises two sub-des ...
).
The picture drastically changed in the later years of Emperor He's reign, son of Emperor Zhang. Dou Xian (50s–92), brother-in-law of Emperor Zhang through his sister Empress Duo, utterly defeated the Northern Xiongnu in a series of campaigns during the ''Yongyuan'' era (89–105). The remnants just escaped annihilation, conceded defeat, began migrating out of the Mongolian steppes and disappeared as a distinct group of herdsmen once and for all. Others were assimilated into other tribes by intermarriage: the Yuwen
The Yuwen ( < Eastern Han Chinese: *''waB-mun'' < Ol ...
tribe being a good example.
In their wake a power vacuum was left on the Mongolian steppes. The main contenders were the Southern Xiongnu, who inhabited a region to the south of the steppe and had now grown into a group of more than a hundred thousand herdsmen on the Xihe plain; the Xianbei, who lived in the east of the steppe residing on the plains of Manchuria; the Dingling
The Dingling ( (174 BCE); (200 BCE); Eastern Han Chinese: *''teŋ-leŋ'' < : *''têŋ-rêŋ'') were ancient peopl ...
, who originally dwelt on the banks of Lake Baikal and had already commenced trekking south into the steppes before Duo Xian destroyed the Northern Xiongnu; and the Wuhuan, who lived south of the Xianbei and were the weakest of the four.
Instead of constantly trading for provisions, tools and luxuries, these four powerful groups of herdsmen, though still allies of the Han dynasty, often cooperated to plunder areas of the northern border. The dynasty could not muster an all-out campaign to wipe them out, but often attempted, through diplomatic and monetary measures to split one or more groups from the alliance of herdsmen.
On the other hand, the dynasty was constantly declining as clans of consorts and eunuchs engaged in a continuous struggle for power. Wealthy merchants and aristocrats were acquiring lands from peasants who had been cultivating their own land for years. "Landless" peasants had to come under the protection of the rich and so pay rent to these new landowners rather than pay taxes to the government. Coupled with bureaucratic corruption, tax revenues dropped dramatically. Large landholding families also took advantages of the weakness of central government and established their own armies. Increasingly governors of regions (the highest level) administered their territories as independent rulers. The recruitment of troops and tax collection could be carried out at the discretion of the regional governors, contributing to the disunity that led to the inevitable crumbling of China into the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the West ...
.
The dynasty also had to deal with the Qiang and Di on the western border, who had constantly been involved in skirmishes against the dynasty since the middle of Western Han dynasty (around mid-first century BCE). As the Eastern Han dynasty declined, the Qiang, nominal ancestors of modern Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans liv ...
, began planning major invasions. Through spies and collaborators, the Han court knew about the situation and had to deploy soldiers near the border to fend off Qiang skirmishes and small-scale invasions.
Although few major Qiang invasions were carried out, never successfully, such a military deployment constantly drained the treasury and was a cradle for ambitious militarists, the most famous of whom was Dong Zhuo
Dong Zhuo () (died 22 May 192), courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minist ...
(130s–192), the pretender to the Han court from 189-192. The more the Han court weakened through domestic problems, the more the herdsmen craved the dynasty's wealth. The Wuhuan were a frequent ally with the Han court against Xianbei and the Southern Xiongnu, although they also sometimes allied with the Xiongnu to fend off joint attacks by the Han and Xianbei.
The Han court also deployed mercenaries from the Xianbei and Wuhuan for campaigns against the rebels and to quell peasant insurgents. These mercenaries were often sympathetic to the peasant uprising and hence not trusted by the Han military authorities. However they were the best available option for suppressing the insurgents and consequently these soldiers were poorly treated by being deployed far away from their homeland, or in the most dangerous positions on the battlefield or by starving them of provisions and weapons. Thus military who could earn the trust of the Xianbei or Wuhuan would collaborate with the tribes for the sake of their own careers.
For instance a unit of about 5,000 Wuhuan cavalry that usually resided in You Province (part of modern northeastern Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0 ...
and western Liaoning Province) was deployed in Southern Jing Province (in Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
Province) for three consecutive years. The rebellions (187-189) of Zhang Chun (張純; died 189) and Zhang Ju (張舉; died 189) in You Province in alliance with this Wuhuan cavalry unit marked the first of many such collaborations. Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred t ...
(140s–202) and Gongsun Zan
Gongsun Zan () (before 161 - April or May 199), courtesy name Bogui, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty.
Life
Little is known of Gongsun Zan's early life. He and Liu Bei stu ...
(140s–199), two warlords of the end of the Han dynasty, also exploited Wuhuan and Xianbei respectively in their own quests for predominance. Ironically Gongsun Zan
Gongsun Zan () (before 161 - April or May 199), courtesy name Bogui, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty.
Life
Little is known of Gongsun Zan's early life. He and Liu Bei stu ...
was the commander tasked with suppressing the rebellion of Zhang Chun and Zhang Ju.
Xianbei confederacy of Tanshihuai
The difficult relationship between the Han court and various nomadic groups lasted from the start of the second century to the early 160s and the appearance of Tanshihuai (檀石槐 b. 120s - d. 181), an illegitimate son of a low ranking military officer of Xianbei mercenaries deployed against the Southern Xiongnu. Despite his low social status among Xianbei herdsmen, he managed to unify all the Xianbei tribes under his rule in a confederacy against the Han court. Each Xianbei tribe was led by a chieftain and were grouped under the confederacy into three smaller federations, the Western, the Central and the Eastern. Notable chieftains under Tanshihuai were Murong (see Sixteen Kingdoms), Huitou (see Sixteen Kingdoms) and Tuiyin (seeTuoba
The Tuoba (reconstructed Middle Chinese pronunciation: *''tʰak-bɛt''), also known as the Taugast or Tabgach ( otk, 𐱃𐰉𐰍𐰲 ''Tabγač''), was a Xianbei clan in Imperial China.Wei Shou. ''Book of Wei''. Vol. 1
During the Sixteen Kingdo ...
).
The confederacy was a rudimentary centralized government. All tribes had to share all trade profits, military duties and a unified stance against the Han court. Slavery was also important as captives were forced to work to provide provisions and weapons.
Supported by this confederacy, Tanshihuai brought the Southern Xiongnu into a close alliance. The Wuhuan, Dingling, Qiang and Di were at times aiding the confederacy which now included all the major tribes on the steppes stretching from today Jilin
Jilin (; alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea ( Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, Ryanggang and Chagang) and Russia (Prim ...
province to central Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
.
Uneasiness at the Han court about this development of a new power on the steppes finally ushered in a campaign on the northern border to annihilate the confederacy once and for all. In 177 A.D., 30,000 Han cavalry attacked the confederacy, commanded by Xia Yu (夏育), Tian Yan (田晏) and Zang Min (臧旻), each of whom was the commander of units sent respectively against the Wuhuan, the Qiang, and the Southern Xiongnu before the campaign.
Each military officer commanded 10,000 cavalrymen and advanced north on three different routes, aiming at each of the three federations. Cavalry units commanded by chieftains of each of the three federations almost annihilated the invading forces. Eighty percent of the troops were killed and the three officers, who only brought tens of men safely back, were relieved from their posts.
Tanshihuai found a temporary solution when he sacked the area of modern Jilin
Jilin (; alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea ( Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, Ryanggang and Chagang) and Russia (Prim ...
province. To make the matters worse, the successors of Tanshihuai (his sons and nephews) after his death in 181 never earned the respect from the chieftains of the three federations. They were also less ambitious and constantly fought among themselves for the increasingly powerless lord of confederacy.
On the other hand, tribes began to emigrate from the steppe, mainly to the southwest and southeast for better pasture. The weakness of the Han court also encouraged tribes to move further into China. For example, the Tufa (禿髮) tribe, an offshoot of the Tuiyin (Northern Wei Dynasty
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during t ...
), settled in the eastern mountainous area of today's Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
province. Thus, the effective border of the Han dynasty was pushed further south and east. The confederacy was virtually dissolved in the early third century, allowing the warlords of the Han dynasty to play their own game of fighting for supremacy without much interference from tribes outside of China.
Barbarian immigration during the Three Kingdoms
As the Eastern Han dynasty slowly disintegrated into an era of warlords, battles for predominance eventually ushered in theThree Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the West ...
. However years of war had generated a severe shortage of labor, a solution to which was the immigration of foreigners. Thus the Wei court, controlling Northern China at the time, allowed weaker tribes to settle in areas depopulated by war. Several large-scale forced relocations of Di to southwestern Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
and northern Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
took place in the 220s.
Surprising to some historians, the immigration went smoothly since no powerful confederacy of any tribes was established. The Wuhuan, partisans of Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred t ...
and his sons, had already been squashed when Cao Cao sent an expedition into You Province. Its herdsmen were dispersed all over Northern China and were no longer a major threat.
The later years saw only border skirmishes as the three governments concentrated on reclaiming the loss of productivity. Thus after the unification under the Western Jin dynasty an era of prosperity began as the relocated tribes adopted agriculture and contributed to the revival of the economy. Other tribes, still residing in the areas that they had occupied since the Eastern Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
, frequently served as mercenaries against minor rebellious chieftains such as Kebineng
Kebineng (died 235) was a Xianbei chieftain who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. He rose to power during the late Eastern Han dynasty after the warlord Cao Cao defeated the Wuhuan tribes in northern C ...
and Tufa Shujineng
Tufa Shujineng (died 279) was a Qiang-Xianbei chieftain who lived during the Three Kingdoms period of China. As the leader of the Tufa tribe in Hexi, he led a rebellion against the ruling Western Jin dynasty between 270 and 279. Shujineng kil ...
.
However the Jin bureaucracy forgot an underlying threat: Living in areas well south of the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups ...
and closer than ever before to the capital of China at Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang ...
, any widespread uprising by the Wu Hu would be impossible to halt.
Jin dynasty and the Uprising of the Five Barbarians
An era of relative prosperity had existed since Jin Wudi unified China in 280. The so-called barbarians residing inside and near China regularly paid taxes to the Jin court. They traded horses and animal products for agricultural goods and silk and could be paid to fight as mercenaries. Some officials foresaw a crisis. ''Discussion of the God of Money'' (錢神論 ''Qián Shén Lùn'') and ''Discussion on Tribe Relocation'' (徒戎論 ''Tú Róng Lùn'') condemned the decadence of the aristocracy and warned of an uprising by ethnic minorities living in northern China. The latter work provides accurate locations of the region where the ethnic minorities resided. Southern Xiongnu now dominated Bingzhou (in modern Shanxi province) and their horsemen could arrive at Jinyang ( Taiyuan) in half-a-day's ride andLuoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang ...
, the capital, in a few days.
The accession of the Jin Emperor Hui in 290 marked the beginning of the crumbling of the Jin dynasty. Possibly developmentally disabled, he was a puppet of powerful parties which sought to control the Jin court. During the Rebellion of the Eight Kings
The War of the Eight Princes, Rebellion of the Eight Kings, or Rebellion of the Eight Princes () was a series of civil wars among kings/princes (Chinese: ''wáng'' 王) of the Chinese Jin dynasty from 291 to 306 AD. The key point of contention in ...
, all parties in power attempted to wipe out the former rulers by murder, mass executions or battles. Each struggle grew more violent and bloodier than the one before. Not surprisingly, Wu Hu mercenaries were often called upon. Wu Hu chieftains and herdsmen clearly comprehended the selfishness of the nobility and the destruction of the country through their struggle for power and wealth. Coupled with famine, epidemic and floods, cannibalism was observed in some parts of the country only a few years after Emperor Hui's accession. Wu Hu herdsmen saw no reason to obey orders from the Jin court and widespread uprisings soon followed.
The revolt by Qi Wannian
Qi Wannian (died 299), or Qiwannian, was an ethnic Di chieftain and rebel leader during the Western Jin dynasty of China. In 296, he became leader of a tribal uprising against Jin in Qinzhou and Yongzhou that lasted until 299. The rebellion ...
(齊萬年), a Di chieftain residing in the border region of today's Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
and Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
provinces, marked the first such uprising. His group of insurgents, which was mainly made up of Di and Qiang tribesmen, numbered around fifty thousand. Although his revolt was suppressed after six years of destructive battles, waves of refugees and remnants wreaked havoc in neighboring territories. The first of the Sixteen Kingdoms was founded by a group of Di refugees who fled into Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
.
See also
*History of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapt ...
**Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
**Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the West ...
**Jin dynasty (266–420)
The Jin dynasty (; ) or the Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the (司馬晉) or the (兩晉), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Sima Yan (Emperor Wu), eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had pr ...
** Sixteen Kingdoms
**Southern and Northern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as ...
**Northern Wei Dynasty
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during t ...
*Shiliuguo Chunqiu
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Sixteen Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese title ''Shiliuguo Chunqiu'' () is a Chinese biographical historical work of the Sixteen Kingdoms compiled by the Northern Wei official Cui Hong between 501 and ...
*Chinese sovereign
The Chinese sovereign was the ruler of a particular monarchical regime in the historical periods of ancient China and imperial China. Sovereigns ruling the same regime, and descended from the same paternal line, constituted a dynasty. Several t ...
**Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
**Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
** Di (Wu Hu)
** Qiang
** Jie
*Donghu people
Donghu (; IPA: ; ) or Hu (; IPA: ) Pulleyblank E. G. (1994) “Ji Hu: Indigenous Inhabitants of Shaanbei and Western Shanxi,” in Edward H. Kaplan, ed.,'' Opuscula Altaica: Essays presented in honor of Henry Schwarz''. ed. by. Bellingham: Western ...
*Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', <
*
Dingling
The Dingling ( (174 BCE); (200 BCE); Eastern Han Chinese: *''teŋ-leŋ'' < : *''têŋ-rêŋ'') were ancient peopl ...
* Tiele
* Manchu
* Jurchen
* Khitan
*Heishui Mohe
The Heishui Mohe (; mnc, Sahaliyan i Aiman or ), also known as the , rendered in English as Blackriver Mohe or Blackwater Mohe, were a tribe of Mohe people in Outer Manchuria along the Amur River () in what is now Russia's Khabarovsk Krai, Amur Ob ...
*Sushen
Sushen is the modern Chinese name for an ancient ethnic group of people who lived in the northeastern part of China (in the area of modern Jilin and Heilongjiang) and what is in modern times the Russian Maritime Province and some other Siberi ...
*List of past Chinese ethnic groups
Ethnic groups in Chinese history refer to various or presumed ethnicities of significance to the history of China, gathered through the study of Classical Chinese literature, Chinese and non-Chinese literary sources and inscriptions, histor ...
References