Finnish Karelia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Karelia ( fi, Karjala) is a historical province of Finland which Finland partly
Karelia ( fi, Karjala) is a historical province of Finland which Finland partly

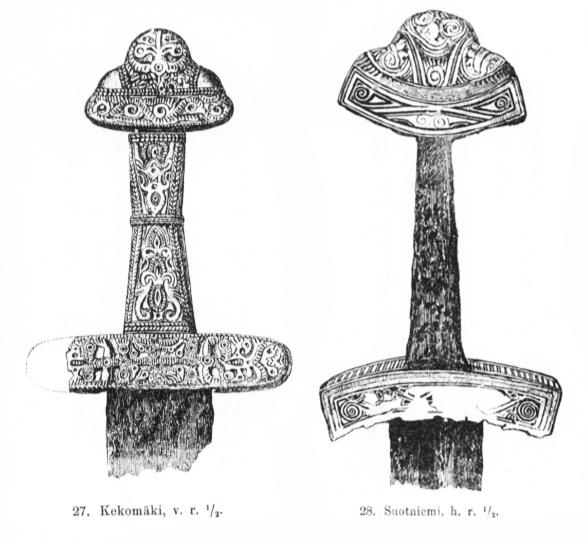 First indications of human settlement in Karelia are from the
First indications of human settlement in Karelia are from the

 The inhabitants of Karelian provinces historically belonging to
The inhabitants of Karelian provinces historically belonging to
Saimaa Canal links two Karelias
– ThisisFINLAND
– Heninen
– Flags of the World
The Karelians
ProKarelia
* ttp://visitkarelia.fi Visitkarelia.fi – Information about travel, tourism and other fields in North Karelia
Pielis.ru – travel information about North Karelia region and City of Joensuu
{{coord, 61.8792, N, 30.1136, E, source:wikidata, display=title
ceded
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdictio ...
to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
after the Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
of 1939–40. The Finnish Karelians include the present-day inhabitants of North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South Karelia
South Karelia ( fi, Etelä-Karjala; sv, Södra Karelen) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Obla ...
and the still-surviving evacuees from the ceded territories. Present-day Finnish Karelia has 315,000 inhabitants. The more than 400,000 evacuees from the ceded territories re-settled in various parts of Finland.
Finnish Karelia historically came under western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
influence, religiously and politically, and was separate from East Karelia, which was dominated by the Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of m ...
and its many successor states from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
onwards.
History
 First indications of human settlement in Karelia are from the
First indications of human settlement in Karelia are from the Mesolithic period
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously ...
. The oldest find from the area is the over 9000 years old Antrea Net which is a fishing net of willow bast. The number of finds from the area is lower towards the end of the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
. Archeological finds from Karelia are relatively rare between the years 400–800. From the Merovingian period onwards finds from Karelia display a distinct features of West Finnish influences which has been interpreted to result at least partly from a colonisation.
At least 50 sites of Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
settlements and 40 hillfort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
s are known from Karelia. According to archeological record and historical data most of the hillforts in Karelia were erected between 1100 and 1323. Particular ''Karelian culture'' including axes, brooches and ornamental culture flourished approximately between the years 1000–1400.
The River Kymi formed a boundary between the eastern and western cultural spheres by the beginning of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
at the latest and is also said to be the boundary between the Häme Finns and the Karelians during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. The 15th and 16th centuries saw the River Kymi become a more official border between the Häme Finns and the Karelians, with Naulasaari (located in Mäntyharju
Mäntyharju (, literally 'Pine Ridge') is a municipality of Finland.
It is located in the Southern Savonia region. The municipality has a population of
() and covers an area of of
which
is water. The coastline is almost . The population density ...
) serving as the meeting point of the borders between the Häme Finns, Savonians
Savonians ( fi, Savolaiset, Savonian: ''Savolaaset'', ''Savolaeset'') are a subgroup ( ''heimo'') of the Finnish people who live in the areas of the historical province of Savonia.
History
Savonians are descendants of Tavastian and Kareli ...
, and Karelians.
During the 12th and 13th century, Karelians fought against Swedes and other Finnic tribes situated in western Finland, such as Tavastians
Tavastians ( fi, Hämäläiset, sv, Tavaster, russian: Емь, Yem, Yam) are a historic people and a modern subgroup (heimo) of the Finnish people. They live in areas of the historical province of Tavastia (historical province), Tavastia (Häme) ...
and Finns proper
Finns proper ( fi, Varsinaissuomalaiset, sv, Egentliga Finnar) are a historic people and a modern subgroup (heimo) of the Finnish people. They live in the areas of the historical province of Finland Proper (Varsinais-Suomi) and Satakunta, and ...
. Karelians were listed as Novgorodian allies in the mid-12th century in Russian Chronicles. Historical records describe Karelians pillaging Sigtuna in Sweden in 1187 and making another expedition in 1257 which lead Pope Alexander IV
Pope Alexander IV (1199 or 1185 – 25 May 1261) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 December 1254 to his death in 1261.
Early career
He was born as Rinaldo di Jenne in Jenne (now in the Province of Rome), he ...
to call out a crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
against Karelians at the request of Valdemar, the king of Sweden. The Third Swedish crusade, led by the marshal
Marshal is a term used in several official titles in various branches of society. As marshals became trusted members of the courts of Medieval Europe, the title grew in reputation. During the last few centuries, it has been used for elevated o ...
Torgils Knutsson
Torkel (Tyrgils or Torgils) Knutsson (d. 1306) was Lord High Constable of Sweden, member of the Privy Council of Sweden (''Riksråd''), and virtual ruler of Sweden during the early reign of King Birger Magnusson (1280–1321).
Biography
To ...
took place between 1293 and 1295. As a result of the crusade the western parts of Karelia fell under Swedish rule and the building of the Castle of Viborg on the site of destroyed Karelian fort started. According to the Eric Chronicles
The ''Eric Chronicle'' (Swedish: ''Erikskrönikan'') is the oldest surviving Swedish chronicle. It was written by an unknown author (or, less probably, several authors) between about 1320 and 1335.
It is the oldest in a group of medieval rhymed ch ...
invading Swedes conquered 14 hundreds from Karelians during the crusade.
Hostilities between Novgorod and the kingdom of Sweden continued in 1300 when a Swedish force attacked the mouth of the River Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it i ...
and built a fort near the current location of Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. The fort was destroyed the following year by the Novgorodians. Indecisive fighting in 1321 and 1322 led to negotiations and peace by the Treaty of Nöteborg
The Treaty of Nöteborg, also known as the ''Treaty of Oreshek'' ( sv, Freden i Nöteborg, Russian: ''Ореховский мир,'' fi, Pähkinäsaaren rauha), is a conventional name for the peace treaty signed at Oreshek ( sv, Nöteborg, fi, ...
which for the first time decided the border between Sweden and Novgorod. Sweden got territory around Viborg, the western Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (russian: Карельский перешеек, Karelsky peresheyek; fi, Karjalankannas; sv, Karelska näset) is the approximately stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern ...
and South Karelia
South Karelia ( fi, Etelä-Karjala; sv, Södra Karelen) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Obla ...
; and Novgorod got the eastern Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (russian: Карельский перешеек, Karelsky peresheyek; fi, Karjalankannas; sv, Karelska näset) is the approximately stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern ...
, Ingria
Ingria is a historical region in what is now northwestern European Russia. It lies along the southeastern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordered by Lake Ladoga on the Karelian Isthmus in the north and by the River Narva on the border with Est ...
, Ladoga Karelia
Ladoga Karelia ( fi, Laatokan Karjala, russian: Ладожская Карелия, Ladožskaja Karelija, Карельское Приладожье, ''Karelskoje Priladožje'' or Северное Приладожье, ''Severnoje Priladožje'') is a ...
, North Karelia
North Karelia ( fi, Pohjois-Karjala; sv, Norra Karelen) is a region in eastern Finland. It borders the regions of Kainuu, North Savo, South Savo and South Karelia, as well as Russia's Republic of Karelia. It is the easternmost region of Fin ...
and East Karelia.
In 1617, Sweden seized Kexholm County
Kexholm County (, ) was a county of the Swedish Empire from 1634 to 1721, when the southern part was ceded to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Nystad. The capital of the county was Kexholm (), which today is Priozersk.
History
The county ...
(eastern Karelian Isthmus, Ladoga Karelia, and North Karelia) from Russia. In 1634 Savonia and old Swedish Karelia were incorporated in the Viborg and Nyslott County
Viborg and Nyslott County ( sv, Viborgs och Nyslotts län, fi, Viipurin ja Savonlinnan lääni) was a county of the Swedish Empire from 1634 to 1721. The county was named after the castle towns of Viborg ( fi, Viipuri) and Nyslott ( fi, Savonl ...
. After the Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad (russian: Ништадтский мир; fi, Uudenkaupungin rauha; sv, Freden i Nystad; et, Uusikaupunki rahu) was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War of 1700–1721. It was concluded between the Tsardom of ...
in 1721 eastern parts of the Viborg and Nyslott County
Viborg and Nyslott County ( sv, Viborgs och Nyslotts län, fi, Viipurin ja Savonlinnan lääni) was a county of the Swedish Empire from 1634 to 1721. The county was named after the castle towns of Viborg ( fi, Viipuri) and Nyslott ( fi, Savonl ...
and the Kexholm County
Kexholm County (, ) was a county of the Swedish Empire from 1634 to 1721, when the southern part was ceded to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Nystad. The capital of the county was Kexholm (), which today is Priozersk.
History
The county ...
were ceded to Russia. The rest of these counties were incorporated into the Kymmenegård and Nyslott County
Kymmenegård and Nyslott County ( sv, Kymmenegårds och Nyslotts län, fi, Savonlinnan ja Kymenkartanon lääni) was a county of Sweden from 1721 to 1747.
In 1721, following the Great Northern War, the southern parts of the counties of Viborg ...
. The southeastern part of this county was also ceded to Russia in the Treaty of Åbo
The Treaty of Åbo or the Treaty of Turku was a peace treaty signed between the Russian Empire and Sweden in Åbo ( fi, Turku) on in the end of the Russo-Swedish War of 1741–1743.
History
By the end of the war, the Imperial Russian Army had ...
of 1743. After the conquest in 1809 of the rest of Finland, Russia's 18th century gains, called "Old Finland
Old Finland ( fi, Vanha Suomi; rus, Ста́рая Финля́ндия, r=Staraya Finlyandiya; sv, Gamla Finland) is a name used for the areas that Russia gained from Sweden in the Great Northern War (1700–1721) and in the Russo-Swedis ...
", were in 1812 joined to the Grand Duchy of Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland ( fi, Suomen suuriruhtinaskunta; sv, Storfurstendömet Finland; russian: Великое княжество Финляндское, , all of which literally translate as Grand Principality of Finland) was the predecessor ...
as a gesture of good will (see Viipuri Province
Viipuri Province ( fi, Viipurin lääni'', commonly abbreviated'' Vpl, sv, Viborgs län or Wiborgs län, russian: Выборгская губерния) was a historical province of Finland from 1812 to 1945.
History
The predecessor of the ...
).
A large part of Finnish Karelia was ceded by Finland to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in 1940 after the Soviet aggression known as the Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
, when the new border was established close to that of 1721. During the Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet-Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1944, as part of World War II.; sv, fortsättningskriget; german: Fortsetzungskrieg. A ...
of 1941–44, most of the ceded area was liberated by Finnish troops, but in 1944 was occupied again by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
. After the war, the remains of the Province of Viipuri were made into the Province of Kymi. In 1997 the province was incorporated within the province of Southern Finland
Southern Finland ( fi, Etelä-Suomen lääni, sv, Södra Finlands län) was a province of Finland from 1997 to 2009. It bordered the provinces of Western Finland and Eastern Finland. It also bordered the Gulf of Finland and Russia.
History
O ...
. The Karelian question
The Karelian question or Karelian issue ( fi, Karjala-kysymys, ) is a dispute in Finnish politics over whether to try to regain control over eastern Finnish Karelia and other territories ceded to the Soviet Union in the Winter War and the Conti ...
refers to the debate regarding the return of the ceded territory to Finland.
Western Karelia, as a historical Province of Sweden, was religiously and politically distinct from the eastern parts that were under the Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
.
Regions within Finnish Karelia
Some notable regions within the Region of Finnish Karelia are:Viipuri Province
Viipuri Province ( fi, Viipurin lääni'', commonly abbreviated'' Vpl, sv, Viborgs län or Wiborgs län, russian: Выборгская губерния) was a historical province of Finland from 1812 to 1945.
History
The predecessor of the ...
(1812–1945)
Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso ( sv, Kymmenedalen; " Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means literally ''The Valley of River Kymi'' ...
(1917–)
South Karelia
South Karelia ( fi, Etelä-Karjala; sv, Södra Karelen) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Obla ...
(1917–)
North Karelia
North Karelia ( fi, Pohjois-Karjala; sv, Norra Karelen) is a region in eastern Finland. It borders the regions of Kainuu, North Savo, South Savo and South Karelia, as well as Russia's Republic of Karelia. It is the easternmost region of Fin ...
(1917–)
Culture

 The inhabitants of Karelian provinces historically belonging to
The inhabitants of Karelian provinces historically belonging to Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
are known as Karelians
Karelians ( krl, karjalaižet, karjalazet, karjalaiset, Finnish: , sv, kareler, karelare, russian: Карелы) are a Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russi ...
. Confusingly, the same name is used also of a closely related but distinct ethnic group living mostly in East Karelia, earlier also in some of the territories Finland ceded to the Soviet Union in 1944.
The traditional culture of "Ladoga-Karelia", or Finnish Karelia according to the pre-Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
borders, was by and large similar to that of Eastern Karelia, or Russian Karelia. Karelians live, and did even more so before Stalinism
Stalinism is the means of governing and Marxist-Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union from 1927 to 1953 by Joseph Stalin. It included the creation of a one-party totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory ...
and the Great Purges
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secreta ...
, also in vast areas east of Finland (in Eastern Karelia, not marked on the map above), where folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
, language and architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
during the 19th century was in the center of the Finns' interest (see Karelianism
Karelianism was a late 19th-century cultural phenomenon in the Grand Duchy of Finland and involved writers, painters, poets and sculptors. Since the publishing of the Finnish national epic Kalevala in 1835, compiled from Finnish and Karelian folk ...
), representing a "purer" Finnish culture than that of Southern and Western Finland, which had been for thousands of years in more contact with (or "contaminated by") Germanic and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
n culture, of which the Kalevala
The ''Kalevala'' ( fi, Kalevala, ) is a 19th-century work of epic poetry compiled by Elias Lönnrot from Karelian and Finnish oral folklore and mythology, telling an epic story about the Creation of the Earth, describing the controversies and r ...
and Finnish Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
are expressions.
People
*Martti Ahtisaari
Martti Oiva Kalevi Ahtisaari (; born 23 June 1937) is a Finnish politician, the tenth president of Finland (1994–2000), a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, and a United Nations diplomat and mediator noted for his international peace work.
Ahtisa ...
* Anna Easteden
Anna Easteden (born 29 November 1976) is a Finnish-American actress. Her film appearances include ''The House of Branching Love'' (2009) and ''Sideways'' (2009). She is known for her performance as "Bee Sting" in ''Who Wants to Be a Superher ...
* Ansa Ikonen
* Aarne Juutilainen
Aarne Edward Juutilainen (; 18 October 1904 – 28 October 1976), nicknamed "The Terror of Morocco", was a Finnish army captain who served in the French Foreign Legion in Morocco between 1930 and 1935. After returning to Finland, he served ...
* Eino Luukkanen
Eino Luukkanen (4 June 1909 – 9 April 1964) was a Finnish fighter ace in World War II. He scored 56 confirmed victories, becoming Finland's third highest ranking ace. He flew the Fokker D-21, Brewster B-239 Buffalo, and Bf 109G.Keskinen 1978 ...
* Veijo Meri
Veijo Väinö Valvo Meri (31 December 1928 – 21 June 2015) was a Finnish writer. Much of his work focuses on war and its absurdity. The work is anti-war and has dark humor.
Born in Viipuri (today Vyborg, Russia), Meri graduated from secondary ...
* Masa Niemi
Martti "Masa" Elis Niemi (20 July 1914 – 3 May 1960) was a Finnish actor.
Career
Niemi started his career as a drummer, but became popular as a comedian. He is most famous for his role as "Pätkä" (in English: Stub) in all thirteen ori ...
* Aaro Pajari
* Lauri Törni
Lauri Allan Törni (28 May 1919 – 18 October 1965), later known as Larry Alan Thorne, was a Finnish-born soldier who fought under three flags: as a Finnish Army officer in the Winter War and the Continuation War ultimately gaining a rank of ca ...
, born in Viipuri, Törni was a soldier and winner of the Mannerheim Cross
The Mannerheim Cross ( fi, Mannerheim-risti, sv, Mannerheimkorset), officially Mannerheim Cross of the Cross of Liberty ( fi, Vapaudenristin Mannerheim-risti, link=no, sv, Frihetskorsets Mannerheimkors, link=no) is the most distinguished Finnis ...
during the Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet-Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1944, as part of World War II.; sv, fortsättningskriget; german: Fortsetzungskrieg. A ...
, who later served with the German and American armies.
* Riitta Uosukainen
Riitta Maria Uosukainen (née Vainikka; 18 June 1942, Jääski, Viipuri Province, Finland (now Svetogorsk, Leningrad Oblast, Russia)) is a Finnish politician and former Member of Parliament. She is one of the eight people to gain the highest ho ...
* Tatu Vanhanen
Tatu Vanhanen (17 April 1929 – 22 August 2015) was a Finnish political scientist, sociologist, and writer. He was a professor of political science at the University of Tampere in Tampere, Finland. Vanhanen was a coauthor with Richard Lynn of ''I ...
* Johannes Virolainen
Johannes Virolainen (; 31 January 1914 – 11 December 2000) was a Finnish politician and who served as 30th Prime Minister of Finland.
Virolainen was born near Viipuri. After the Continuation War Virolainen moved to Lohja, but he remained one ...
See also List of Karelians
Names
Other than Finns, the historical province of Karelia also had Russian speakers living on the territory. The Russian name for the province is Карелия.Heraldry
The arms is crowned by a ducal coronet, though by Finnish tradition this more resembles a Swedish count's coronet. The symbolism of the coat of arms is supposed to represent how the region was fought over by Sweden and Russia for centuries. Blazon: "Gules, in center chief a crown or above two duelling arms, the dexter armored holding a sword and the sinister chain-mail armored with a scimitar, all argent except for hafts and gauntlet joint or."References
External links
*Saimaa Canal links two Karelias
– ThisisFINLAND
– Heninen
– Flags of the World
The Karelians
ProKarelia
* ttp://visitkarelia.fi Visitkarelia.fi – Information about travel, tourism and other fields in North Karelia
Pielis.ru – travel information about North Karelia region and City of Joensuu
{{coord, 61.8792, N, 30.1136, E, source:wikidata, display=title
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
Historical provinces of Finland
Winter War
Divided regions