|
Antrea Net
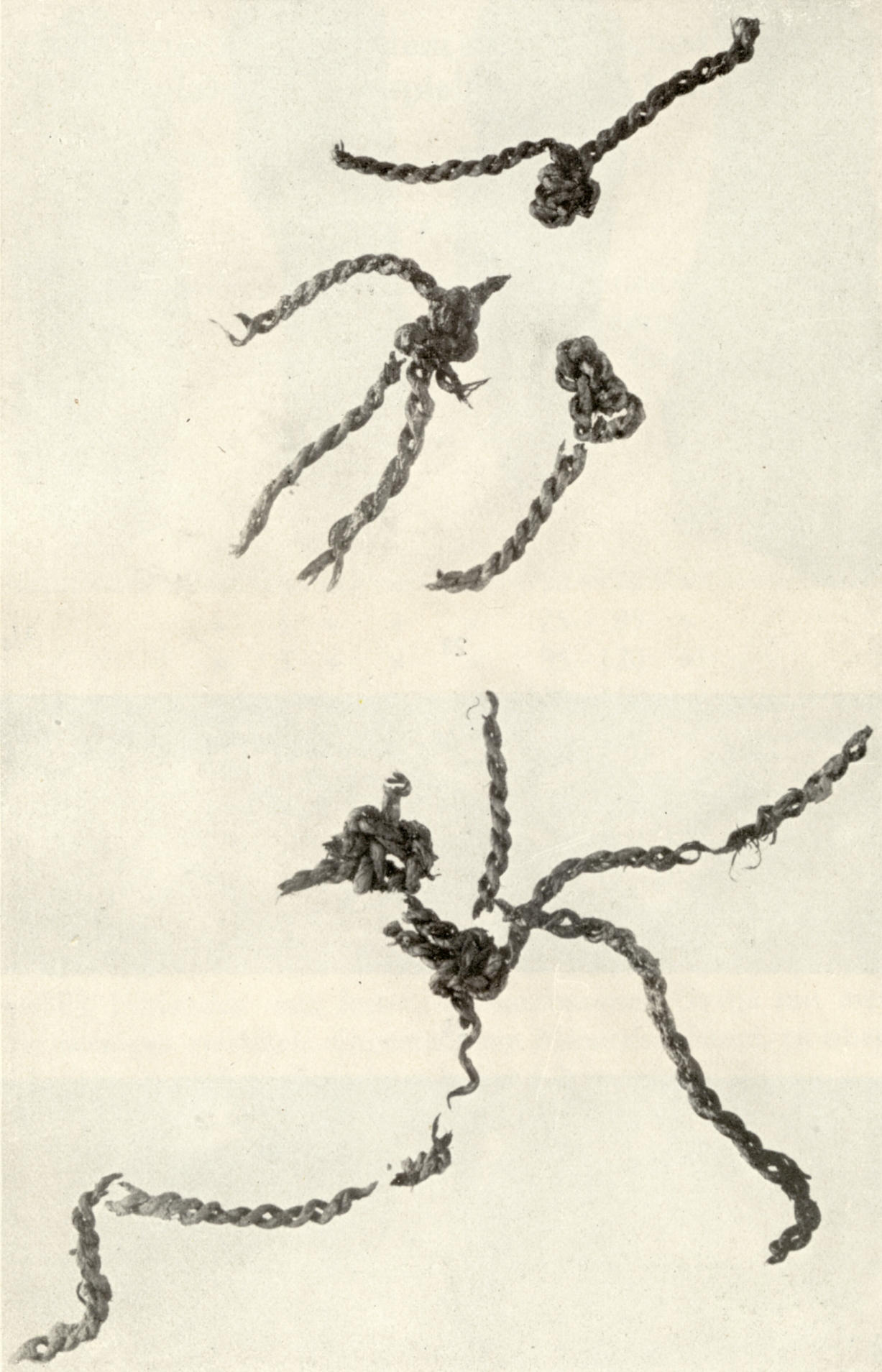
The Antrea Net is one of the oldest known fishing nets in the world, found from Karelian isthmus in Antrea, in Korpilahti village in 1913. It is dated to 8540 BCE. The net was found by farmer Antti Virolainen in Antrea, Finland (today Kamennogorsk, Russia) in autumn of 1913 at his home farm Ämmä-Mattila. While he was ditching a swamp meadow, he found several stone and bone objects which got his attention. The site was excavated by the Finnish archaeologist Sakari Pälsi in July 1914. In his excavation, Pälsi found 18 bobbers and 31 net weights and parts of the net. He also found several stone and bone objects, some birchbark and pieces of tinder fungus. All the items where found in a relatively small area, and they had likely come to the scene at the same time in one piece. The items were sunk to the bottom clay of the Ancylus Lake that existed during that period, most likely in an accident that made the fisherman's boat capsize and caused him to lose all his equipment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Karelian Isthmus
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Discoveries In Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Discoveries In Finland
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1913 Archaeological Discoveries
Events January * January 5 – First Balkan War: Battle of Lemnos (1913), Battle of Lemnos – Greek admiral Pavlos Kountouriotis forces the Turkish fleet to retreat to its base within the Dardanelles, from which it will not venture for the rest of the war. * January 13 – Edward Carson founds the (first) Ulster Volunteers, Ulster Volunteer Force, by unifying several existing Ulster loyalism, loyalist militias to resist home rule for Ireland. * January 23 – 1913 Ottoman coup d'état: Ismail Enver comes to power. * January – Stalin (whose first article using this name is published this month) travels to Vienna to carry out research. Until he leaves on February 16 the city is home simultaneously to him, Hitler, Trotsky and Josip Broz Tito, Tito alongside Alban Berg, Berg, Freud and Jung and Ludwig Wittgenstein, Ludwig and Paul Wittgenstein. February * February 1 – New York City's Grand Central Terminal, having been rebuilt, reopens as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Finns
The Baltic Finnic or Balto-Finnic peoples, also referred to as the Baltic Sea Finns, Baltic Finns, sometimes Western Finnic and often simply as the Finnic peoples, are the peoples inhabiting the Baltic Sea region in Northern and Eastern Europe who speak Finnic languages. They include the Finns, Estonians (including Võros and Setos), Karelians (including Ludes and Livvi), Veps, Izhorians, Votes, and Livonians. In some cases the Kvens, Ingrians, Tornedalians and speakers of Meänkieli are considered separate from the Finns. The bulk of the Finnic peoples (more than 98%) are ethnic Finns and Estonians, who reside in the only two independent Finnic nation states—Finland and Estonia. Finnic peoples are also significant minority groups in neighbouring countries of Sweden, Norway and especially Russia. Theories of origin According to the "Migration Theory" that was based primarily on comparative linguistics, the proto-Finns migrated from an ancient homeland somewhere in nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of . The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language. The land of what is now modern Estonia has been inhabited by '' Homo sapiens'' since at least 9,000 BC. The medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bream
The common bream, freshwater bream, bream, bronze bream, carp bream or sweaty bream (''Abramis brama''), is a European species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is now considered to be the only species in the genus ''Abramis''. Range and habitat The common bream's home range is Europe north of the Alps and Pyrenees, as well as the Balkans. They are found as far east as the Caspian Sea, the Black Sea, and the Aral Sea. The common bream lives in ponds, lakes, canals, and slow-flowing rivers. Description The bream is usually long, though some specimens of have been recorded; it usually weighs . Its maximum length is 90 cm (35.5 in),the recorded weight is around 9.1 kg (20 lb). The common bream has a laterally flattened and high-backed body and a slightly undershot mouth. It is a silvery grey colour, though older fish can be bronze-coloured, especially in clear waters. The fins are greyish to black, but never reddish. Similar-looking fish Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus'') basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the gravel stream bed, beds of shallow fresh water streams, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea fish, then return to fresh water to reproduce. However, populations of several species are restricted to fresh water throughout their lives. Folklore has it that the fish return to the exact spot where they hatched to spawn (biology), spawn, and tracking studies have shown this to be mostly true. A portion of a returning salmon run ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)


