Fruits originating in Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened
Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened
 The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
File:Nectarine Fruit Development.jpg, The development sequence of a typical
 Consistent with the three modes of fruit development plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant
Consistent with the three modes of fruit development plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant


 Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term "true berry" includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term —such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples here and in the table below:
*
Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term "true berry" includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term —such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples here and in the table below:
*
 In
In botany
Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "bot ...
, a fruit is the seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
-bearing structure in flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of ...
s that is formed from the ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the bod ...
after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of br ...
s) disseminate their seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and animals in a symbiotic relationship
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasi ...
that is the means for seed dispersal
In Spermatophyte plants, seed dispersal is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant.
Plants have limited mobility and rely upon a variety of dispersal vectors to transport their seeds, including both abiotic vecto ...
for the one group and nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficien ...
for the other; in fact, humans and many animals have become dependent on fruits as a source of food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ...
. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
output, and some (such as the apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
and the pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall.
The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean re ...
) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings.
In common language usage, "fruit" normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet or sour and edible in the raw state, such as apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
s, banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry (botany), berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa''. In some countries, Cooking banana, bananas used for ...
s, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry (botany), berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non-Climacteric (botany), climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of ...
s, lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
s, oranges, and strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid species of the genus ''Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The f ...
. In botanical usage, the term "fruit" also includes many structures that are not commonly called "fruits" in everyday language, such as nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
, bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes t ...
pods, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
kernels, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , ...
es, and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeolog ...
grains.
Botanical vs. culinary
 Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened
Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the bod ...
or carpel
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pistils' ...
that contains seeds; e.g., an apple, pomegranate, tomato or a pumpkin. A '' nut'' is a type of fruit (and not a seed), and a ''seed'' is a ripened ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the '' integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the f ...
.
In culinary language, a ''fruit'' is the sweet- or not sweet- (even sour-) tasting produce of a specific plant (e.g., a peach, pear or lemon); ''nuts'' are hard, oily, non-sweet plant produce in shells (hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species '' Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts accordi ...
, acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and bo ...
). ''Vegetables
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the edible flower, flowers, ...
'', so called, typically are savory
Savory or Savoury may refer to:
Common usage
* Herbs of the genus ''Satureja'', particularly:
** Summer savory (''Satureja hortensis''), an annual herb, used to flavor food
** Winter savory (''Satureja montana''), a perennial herb, also used to ...
or non-sweet produce (zucchini
The zucchini (; plural: zucchini or zucchinis), courgette (; plural: courgettes) or baby marrow ('' Cucurbita pepo'') is a summer squash, a vining herbaceous plant whose fruit are harvested when their immature seeds and epicarp (rind) are s ...
, lettuce, broccoli, and tomato); but some may be sweet-tasting (sweet potato).
Examples of botanically classified fruit that typically are called vegetables include: cucumber
Cucumber (''Cucumis sativus'') is a widely-cultivated creeping vine plant in the Cucurbitaceae family that bears usually cylindrical fruits, which are used as culinary vegetables.pumpkin
A pumpkin is a vernacular term for mature winter squash of species and varieties in the genus '' Cucurbita'' that has culinary and cultural significance but no agreed upon botanical or scientific meaning. The term ''pumpkin'' is sometimes u ...
, and squash ( all are cucurbits); bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes t ...
s, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
s, and peas ( all legumes); corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
, eggplant
Eggplant ( US, Canada), aubergine ( UK, Ireland) or brinjal (Indian subcontinent, Singapore, Malaysia, South Africa) is a plant species in the nightshade family Solanaceae. ''Solanum melongena'' is grown worldwide for its edible fruit.
Mo ...
, bell pepper (or sweet pepper), and tomato (see image). The spices chili pepper
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus '' Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for ...
and allspice
Allspice, also known as Jamaica pepper, myrtle pepper, pimenta, or pimento, is the dried unripe berry of ''Pimenta dioica'', a midcanopy tree native to the Greater Antilles, southern Mexico, and Central America, now cultivated in many warm par ...
are fruits, botanically speaking. In contrast, rhubarb
Rhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks ( petioles) of species and hybrids (culinary rhubarb) of '' Rheum'' in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The whole plant – a herbaceous perennial growing from short, thick r ...
is often called a fruit when used in making pies, but the edible produce of rhubarb is actually the leaf stalk or petiole of the plant. Edible gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
seeds are often given fruit names, e.g., ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus withi ...
nuts and pine nuts.
Botanically, a cereal
A cereal is any grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more foo ...
grain, such as corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domestica ...
, or wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeolog ...
is a kind of fruit (termed a caryopsis
In botany, a caryopsis (plural caryopses) is a type of simple fruit—one that is monocarpellate (formed from a single carpel) and indehiscent (not opening at maturity) and resembles an achene, except that in a caryopsis the pericarp is f ...
). However, the fruit wall is thin and fused to the seed coat, so almost all the edible grain-fruit is actually a seed.
Structure
 The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
Development
A fruit results from the fertilizing and maturing of one or more flowers. Thegynoecium
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pistil ...
, which contains the '' stigma-style-ovary'' system, is centered in the flower-head, and it forms all or part of the fruit —(see graphic: 'the parts of a flower'). Inside the ovary(ies) are one or more ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the '' integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the f ...
s. Here begins a complex sequence called '' double fertilization'': a female gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has on ...
produces an egg cell for the purpose of fertilization. (A female gametophyte is called a megagametophyte, and also called the embryo sac.) After double fertilization, the ovules will become seeds.
Ovules are fertilized in a process that starts with pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds ...
, which is the movement of pollen from the stamens to the stigma-style-ovary system within the flower-head, (see graphic). After pollination, a pollen tube
A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of seed plants when it germinates. Pollen tube elongation is an integral stage in the plant life cycle. The pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells fr ...
grows from the (deposited) pollen through the stigma down the style into the ovary to the ovule. Two sperm are transferred from the pollen to a megagametophyte. Within the megagametophyte one sperm unites with the egg, forming a zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
, while the second sperm enters the central cell forming the endosperm mother cell, which completes the double fertilization process. Later the zygote will give rise to the embryo of the seed, and the endosperm mother cell will give rise to endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the embryo an ...
, a nutritive tissue used by the embryo.
As the ovules develop into seeds, the ovary begins to ripen and the ovary wall, the ''pericarp'', may become fleshy (as in berries or drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part ( exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pit'', ''stone'', or '' pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed (''kerne ...
s), or it may form a hard outer covering (as in nuts). In some multiseeded fruits, the extent to which a fleshy structure develops is proportional to the number of fertilized ovules. The pericarp typically is differentiated into two or three distinct layers; these are called the ''exocarp'' (outer layer, also called epicarp), ''mesocarp'' (middle layer), and ''endocarp'' (inner layer) —(see image of apple-section).
In some fruits the sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 The term ''sepalum'' was coined ...
s, petal
Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corolla''. Petals are usuall ...
s, stamen
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filam ...
s and/or the style
''De Stijl'' (; ), Dutch for "The Style", also known as Neoplasticism, was a Dutch art movement founded in 1917 in Leiden. De Stijl consisted of artists and architects. In a more narrow sense, the term ''De Stijl'' is used to refer to a body ...
of the flower fall away as the fleshy fruit ripens. However, for simple fruits derived from an '' inferior ovary'' —i.e., one that lies ''below'' the attachment of other floral parts, (see graphic re 'insertion point')— there are parts (including petals, sepals, and stamens) that fuse with the ovary and ripen with it. For such a case, when floral parts other than the ovary form a significant part of the fruit that develops, it is called an accessory fruit
An accessory fruit is a fruit in which some of the flesh is derived not from the floral ovary but from some adjacent tissue exterior to the carpel.Esau, K. 1977. ''Anatomy of seed plants''. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Accessory fruits are ...
. Examples of accessory fruits include apple, rose hip, strawberry, pineapple; see below, and "Table of fleshy fruit examples".
Because several parts of the flower besides the ovary may contribute to the structure of a fruit, it is important to study flower structure to understand how a particular fruit forms. There are three general modes of fruit development:
* Apocarpous
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or m ...
fruits develop from a ''single flower'' (while having one or more separate, unfused, carpels); they are the simple fruits.
* Syncarpous fruits develop from a ''single gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pistil ...
'' (having two or more carpels fused together).
* Multiple fruits form from many flowers —i.e., an inflorescence of flowers.
drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part ( exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pit'', ''stone'', or '' pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed (''kerne ...
, the nectarine (''Prunus persica'') over a 7.5 month period, from bud formation in early winter to fruit ripening
Ripening is a process in fruits that causes them to become more palatable. In general, fruit becomes sweeter, less green, and softer as it ripens. Even though the acidity of fruit increases as it ripens, the higher acidity level does not make th ...
in midsummer (see image page for further information)
File:Mature flower diagram.svg, The parts of a flower, showing the stigma-style-ovary system.
File:Pome apples text.jpg, An apple is a simple fleshy fruit. Key parts are the epicarp, or exocarp, or outer skin, (not labelled); and the mezocarp and endocarp (labelled).
image:Ovary position.svg, upright 1.5, Insertion point: There are three positions of insertion of the ovary at the base of a flower: I superior; II half-inferior; III inferior. The 'insertion point' is where the androecium
The stamen ( plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the fila ...
parts ''(a)'', the petals ''(p)'', and the sepals ''(s)'' all converge and attach to the receptacle ''(r)''. (Ovary= gynoecium ''(g)''.)
File:Noni fruit dev.jpg, upright 1.5, In the noni, flowers are produced in time-sequence along the stem. It is possible to see a progression of flowering, fruit development, and fruit ripening.
Classification of fruits
 Consistent with the three modes of fruit development plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant
Consistent with the three modes of fruit development plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant taxa
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular n ...
may be in the same group.
While the section of a fungus
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
that produces spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
s is called a ''fruiting'' body, fungi are members of the fungi kingdom
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
and not of the plant kingdom.
Simple fruits
Simple fruits are the result of the ripening-to-fruit of a simple or compound ovary in a ''single flower'' with a ''singlepistil
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pis ...
''. In contrast, a single flower with numerous pistils typically produces an aggregate fruit A raspberry_beetle.html" ;"title="raspberry fruit (shown with a raspberry beetle">raspberry fruit (shown with a raspberry beetle larva) is an aggregate fruit, an aggregate of drupelets
image:Aquilegia vulgaris 004.JPG, The fruit of an ''Aquilegia' ...
; and the merging of several flowers, or a 'multiple' of flowers, results in a 'multiple' fruit. A simple fruit is further classified as to whether it is dry or fleshy.
To distribute their seeds, dry fruits may split open and discharge their seeds to the winds, which is called dehiscence. Or the distribution process may rely upon the decay and degradation of the fruit to expose the seeds; or it may rely upon the eating of fruit and excreting of seeds by frugivores —both are called indehiscence. Fleshy fruits do not split open, but they also are indehiscent and they may also rely on frugivores for distribution of their seeds. Typically, the entire outer layer of the ovary wall ripens into a potentially edible pericarp
Fruit anatomy is the plant anatomy of the internal structure of fruit. Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits. Ag ...
.
Types of dry simple fruits, (with examples) include:
* achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and indehiscent (they do not op ...
– most commonly seen in aggregate fruits (e.g., strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely a ...
, see below).
* capsule – (Brazil nut
The Brazil nut (''Bertholletia excelsa'') is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and it is also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds. It is one of the largest and longest-lived trees in the Amazon rainforest ...
: botanically, it is not a nut).
* caryopsis
In botany, a caryopsis (plural caryopses) is a type of simple fruit—one that is monocarpellate (formed from a single carpel) and indehiscent (not opening at maturity) and resembles an achene, except that in a caryopsis the pericarp is f ...
– (cereal grains, including wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeolog ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domestica ...
, oats
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human co ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley ...
).
* cypsela – an achene-like fruit derived from the individual florets in a capitulum: (dandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and Nor ...
).
* fibrous drupe – (coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or ...
, walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''.
Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a tru ...
: botanically, neither is a true nut.).
* follicle – follicles are formed from a single carpel, and opens by one suture: ( milkweed); also commonly seen in aggregate fruits: (magnolia
''Magnolia'' is a large genus of about 210 to 340The number of species in the genus ''Magnolia'' depends on the taxonomic view that one takes up. Recent molecular and morphological research shows that former genera ''Talauma'', ''Dugandiodendro ...
, peony
The peony or paeony is a flowering plant in the genus ''Paeonia'' , the only genus in the family Paeoniaceae . Peonies are native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. Scientists differ on the number of species that can be distinguished ...
).
* legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ...
– (bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes t ...
, pea, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
: botanically, the peanut is the seed of a legume, not a nut).
* loment
A loment (or lomentum) is a type of dehiscent legume fruit that breaks apart at constrictions occurring between segments, so that each segment contains one seed. It is a type of schizocarp.
Tick trefoil (''Desmodium'') and sweet vetch (''Hedysarum ...
– a type of indehiscent legume: ( sweet vetch or wild potato).
* nut – ( beechnut, hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species '' Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts accordi ...
, acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and bo ...
(of the oak): botanically, these are true nuts).
* samara
Samara ( rus, Сама́ра, p=sɐˈmarə), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara rivers, with a population ...
– (ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
, elm, maple key).
* schizocarp, see below – ( carrot seed).
* silique
A silique or siliqua (plural ''siliques'' or ''siliquae'') is a type of fruit (seed capsule) having two fused carpels with the length being more than three times the width. When the length is less than three times the width of the dried fruit ...
– (radish
The radish ('' Raphanus raphanistrum'' subsp. ''sativus'') is an edible root vegetable of the family Brassicaceae that was domesticated in Asia prior to Roman times.
Radishes are grown and consumed throughout the world, being mostly eaten ra ...
seed).
* silicle – ( shepherd's purse).
* utricle – ( beet, ''Rumex
The docks and sorrels, genus ''Rumex'', are a genus of about 200 species of annual, biennial, and perennial herbs in the buckwheat family, Polygonaceae.
Members of this genus are very common perennial herbs with a native almost worldwide dist ...
'').
Fruits in which part or all of the ''pericarp'' (fruit wall) is fleshy at maturity are termed ''fleshy simple fruits''.
Types of fleshy simple fruits, (with examples) include:
* berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, rasp ...
– The berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit. The entire outer layer of the ovary wall ripens into a potentially edible "pericarp", (see below).
* stone fruit
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part ( exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pit'', ''stone'', or '' pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed (''kernel ...
or drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part ( exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pit'', ''stone'', or '' pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed (''kerne ...
– The definitive characteristic of a drupe is the hard, "lignified" stone (sometimes called the "pit"). It is derived from the ovary wall of the flower: apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are al ...
, cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus '' Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet '' Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The ...
, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non- ...
, plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found ...
, mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in Sout ...
.
* pome
In botany, a pome is a type of fruit produced by flowering plants in the subtribe Malinae of the family Rosaceae. Well-known pomes include the apple, pear, and quince.
Etymology
The word ''pome'' entered English in the late 14th century, an ...
– The pome
In botany, a pome is a type of fruit produced by flowering plants in the subtribe Malinae of the family Rosaceae. Well-known pomes include the apple, pear, and quince.
Etymology
The word ''pome'' entered English in the late 14th century, an ...
fruits: apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
s, pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the p ...
s, rosehips, saskatoon berry, et al., are a syncarpous (fused) fleshy fruit, a simple fruit, developing from a half-inferior ovary, see graphic re 'Insertion point'. Pomes are of the family Rosaceae
Rosaceae (), the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera.
The name is derived from the type genus ''Rosa''. Among the most species-rich genera are '' Alchemilla'' (270), '' Sorbu ...
,
Berries


 Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term "true berry" includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term —such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples here and in the table below:
*
Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term "true berry" includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term —such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples here and in the table below:
* tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , ...
– In culinary terms, the tomato is regarded as a vegetable, but it is botanically classified as a fruit and a berry.
* banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry (botany), berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa''. In some countries, Cooking banana, bananas used for ...
– The fruit has been described as a "leathery berry". In cultivated varieties, the seeds are diminished nearly to non-existence.
* pepo – Berries with skin that is hardened: cucurbits
The Cucurbitaceae, also called cucurbits or the gourd family, are a plant family consisting of about 965 species in around 95 genera, of which the most important to humans are:
*'' Cucurbita'' – squash, pumpkin, zucchini, some gourds
*'' La ...
, including gourds, squash, melons.
* hesperidium
A hesperidium (plural hesperidia) is a modified berry with a tough, leathery rind.
Etymology
Carl Linnaeus gave the name Hesperideæ to an order containing the genus ''Citrus'', in allusion to the golden apples of the Hesperides.
Development ...
– Berries with a rind and a juicy interior: most citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is nati ...
fruit.
* cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus '' Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranber ...
, gooseberry
Gooseberry ( or (American and northern British) or (southern British)) is a common name for many species of ''Ribes'' (which also includes Ribes, currants), as well as a large number of plants of similar appearance. The berries of those in th ...
, redcurrant, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry (botany), berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non-Climacteric (botany), climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of ...
.
The ''strawberry'', regardless of its appearance, is classified as a dry, not a fleshy fruit. Botanically, it is ''not'' a berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, rasp ...
; it is an aggregate-accessory fruit, the latter term meaning the fleshy part is derived not from the plant's ovaries but from the receptacle
Receptacle may refer to:
Biology
* Receptacle (botany), a plant anatomical part
* Seminal receptacle, a sperm storage site in some insects
Electrical engineering
* Automobile auxiliary power outlet, formerly known as ''cigarette lighter recep ...
that holds the ovaries.Esau, K. (1977). ''Anatomy of seed plants''. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Numerous dry achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and indehiscent (they do not op ...
s are attached to the outside of the fruit-flesh, (see image); they appear to be seeds but each is actually an ovary of a flower, with a seed inside.
Schizocarps are dry fruits, though some appear to be fleshy. They originate from syncarpous ovaries but do not actually dehisce; rather, they split into segments with one or more seeds. They include a number of different forms from a wide range of families, including carrot, parsnip, parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley ('' Petroselinum crispum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region (Sardinia, Lebanon, Israel, Cyprus, Turkey, southern Italy, Greece, ...
, cumin
Cumin ( or , or Article title
) (''Cuminum cyminum'') is a
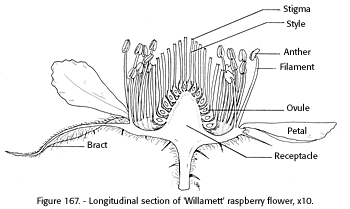 An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple
An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple
 Seedlessness is an important feature of some fruits of commerce. Commercial
Seedlessness is an important feature of some fruits of commerce. Commercial
 A
A
 Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of
Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of
 * Bayberry fruits provide a wax often used to make candles;
* Many dry fruits are used as decorations or in dried flower arrangements (e.g.,
* Bayberry fruits provide a wax often used to make candles;
* Many dry fruits are used as decorations or in dried flower arrangements (e.g.,
Images of fruit development from flowers
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu
from California Rare Fruit Growers, Inc.
Photo ID of Fruits
by Capt. Pawanexh Kohli * {{Authority control Fruit Pollination Types of food
) (''Cuminum cyminum'') is a
Aggregate fruits
 An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple
An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple pistil
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pis ...
s (see graphic of raspberry pistils). Each pistil contains one carpel
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pistils' ...
; together they form a fruitlet. The ultimate (fruiting) development of the aggregation of pistils is called an aggregate fruit, etaerio fruit, or simply an etaerio.
Different types of aggregate fruits can produce different etaerios, such as achenes, drupelets, follicles, and berries.
For example, the Ranunculaceae species, including ''Clematis
''Clematis'' is a genus of about 300 species within the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae. Their garden hybrids have been popular among gardeners, beginning with ''Clematis'' × ''jackmanii'', a garden standby since 1862; more hybrid cultiva ...
'' and '' Ranunculus'', produces an etaerio of achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and indehiscent (they do not op ...
s;
''Rubus
''Rubus'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, subfamily Rosoideae, with over 1,350 species.
Raspberries, blackberries, and dewberries are common, widely distributed members of the genus. Most of t ...
'' species, including raspberry: an etaerio of drupelets;
'' Calotropis'' species: an etaerio of follicles fruit;
''Annona
''Annona'' (from Taíno ''annon'') is a genus of flowering plants in the pawpaw/ sugar apple family, Annonaceae. It is the second largest genus in the family after '' Guatteria'', containing approximately 166
'' species: an etaerio of berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, rasp ...
.
Some other broadly recognized species and their etaerios (or aggregations) are:
* Teasel
''Dipsacus'' is a genus of flowering plant in the family Caprifoliaceae. The members of this genus are known as teasel, teazel or teazle. The genus includes about 15 species of tall herbaceous biennial plants (rarely short-lived perennial plants ...
; fruit is an aggregation of cypselas.
* Tuliptree; fruit is an aggregation of samaras.
* Magnolia
''Magnolia'' is a large genus of about 210 to 340The number of species in the genus ''Magnolia'' depends on the taxonomic view that one takes up. Recent molecular and morphological research shows that former genera ''Talauma'', ''Dugandiodendro ...
and peony
The peony or paeony is a flowering plant in the genus ''Paeonia'' , the only genus in the family Paeoniaceae . Peonies are native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. Scientists differ on the number of species that can be distinguished ...
; fruit is an aggregation of follicles.
* American sweet gum; fruit is an aggregation of capsules.
* Sycamore
Sycamore is a name which has been applied to several types of trees, but with somewhat similar leaf forms. The name derives from the ancient Greek ' (''sūkomoros'') meaning "fig-mulberry".
Species of trees known as sycamore:
* '' Acer pseudoplat ...
; fruit is an aggregation of achenes.
The ''raspberry
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with ...
''; its pistils are called ''drupelets'' because each pistil is like a small drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part ( exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pit'', ''stone'', or '' pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed (''kerne ...
attached to the receptacle. In some bramble fruits such as blackberry
The blackberry is an edible fruit produced by many species in the genus ''Rubus'' in the family Rosaceae, hybrids among these species within the subgenus ''Rubus'', and hybrids between the subgenera ''Rubus'' and ''Idaeobatus''. The taxonomy of ...
the receptacle, an accessory part, elongates and then develops as part of the fruit, making the blackberry an '' aggregate-accessory'' fruit. The strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely a ...
is also an aggregate-accessory fruit, of which the seeds are contained in the achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and indehiscent (they do not op ...
s. Notably in all these examples, the fruit develops from a single flower, with numerous pistils.
Multiple fruits
A multiple fruit is formed from a cluster of flowers, (a 'multiple' of flowers) —also called an ''inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed ...
''. Each ('smallish') flower produces a single fruitlet, which, as all develop, all merge into one mass of fruit. Examples include pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centurie ...
, fig, mulberry, Osage orange, breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family (Moraceae) believed to be a domesticated descendant of '' Artocarpus camansi'' originating in New Guinea, the Maluku Islands, and the Phil ...
. An inflorescence (a cluster) of white flowers, called a head, is produced first. After fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
, each flower in the cluster develops into a drupe; as the drupes expand, they develop as a '' connate'' organ, merging into a multiple fleshy fruit called a ''syncarp''.
Progressive stages of multiple flowering and fruit development can be observed on a single branch of the Indian mulberry, or '' noni'', (see image). During the sequence of development, a progression of second, third, and more inflorescences are initiated in turn at the head of the branch or stem.
Accessory fruit forms
Fruits may incorporate tissues derived from other floral parts besides the ovary, including the receptacle, hypanthium, petals, or sepals. Accessory fruits occur in all three classes of fruit development—simple, aggregate, and multiple. Accessory fruits are frequently designated by the hyphenated term showing both characters. For example, a pineapple is a multiple-accessory fruit. a blackberry is an aggregate-accessory fruit, and an apple is a simple-accessory fruit.Table of fleshy fruit examples
Seedless fruits
 Seedlessness is an important feature of some fruits of commerce. Commercial
Seedlessness is an important feature of some fruits of commerce. Commercial cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture ...
s of banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry (botany), berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa''. In some countries, Cooking banana, bananas used for ...
s and pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centurie ...
s are examples of seedless fruits. Some cultivars of citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is nati ...
fruits (especially grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink.
Grapefruit i ...
, mandarin orange
The mandarin orange (''Citrus reticulata''), also known as the mandarin or mandarine, is a small citrus tree fruit. Treated as a distinct species of Orange (fruit), orange, it is usually eaten plain or in fruit salads. Tangerines are a group of ...
s, navel oranges), satsumas, table grape
Table grapes are grapes intended for consumption while fresh, as opposed to grapes grown for wine production, juice production, or for drying into raisins.
''Vitis vinifera'' table grapes can be in the form of either seeded or non-seeded varieta ...
s, and of watermelon
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 var ...
s are valued for their seedlessness. In some species, seedlessness is the result of '' parthenocarpy'', where fruits set without fertilization. Parthenocarpic fruit-set may (or may not) require pollination, but most seedless citrus fruits require a stimulus from pollination to produce fruit.
Seedless bananas and grapes are triploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than one pair of (homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, where each set contains ...
s, and seedlessness results from the abortion of the embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
nic plant that is produced by fertilization, a phenomenon known as '' stenospermocarpy'', which requires normal pollination and fertilization.
Seed dissemination
Variations in fruit structures largely depend on the modes of dispersal applied to their seeds. Dispersal is achieved by wind or water, byexplosive dehiscence
Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part; structures that ...
, and by interactions with animals.
Some fruits present their outer skins or shells coated with spikes or hooked burrs; these evolved either to deter would-be foragers from feeding on them, or to serve to attach themselves to the hair, feathers, legs, or clothing of animals, thereby using them as dispersal agents. These plants are termed zoochorous; common examples include cocklebur, unicorn plant, and beggarticks (or Spanish needle).
By developments of mutual evolution the fleshy produce of fruits typically appeals to hungry animals, such that the seeds contained within are taken in, carried away and later deposited (i.e., defecated) at a distance from the parent plant. Likewise, the nutritious, oily kernels of nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
typically motivate birds and squirrels to hoard
A hoard or "wealth deposit" is an archaeological term for a collection of valuable objects or artifacts, sometimes purposely buried in the ground, in which case it is sometimes also known as a cache. This would usually be with the intention of ...
them, burying them in soil to retrieve later during the winter of scarcity; thereby, uneaten seeds are sown effectively under natural conditions to germinate
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, fer ...
and grow a new plant some distance away from the parent.
Other fruits have evolved flattened and elongated wings or helicopter-like blades, e.g., elm, maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since ht ...
, and tuliptree. This mechanism increases dispersal distance away from the parent via wind. Other wind-dispersed fruit have tiny " parachutes", e.g., dandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and Nor ...
, milkweed, salsify.
Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or ...
fruits can float thousands of miles in the ocean, thereby spreading their seeds. Other fruits that can disperse via water are nipa palm and screw pine
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with some 750 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. The greatest number of species are found in Madagascar and Malaysia. Common n ...
.
Some fruits have evolved propulsive mechanisms that fling seeds substantial distances —(perhaps up to 100 m in the case of the sandbox tree)— via explosive dehiscence
Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part; structures that ...
or other such mechanisms, (see impatiens
''Impatiens'' is a genus of more than 1,000 species of flowering plants, widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere and the tropics. Together with the genus '' Hydrocera'' (one species), ''Impatiens'' make up the family Balsaminace ...
and squirting cucumber
''Ecballium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cucurbitaceae containing a single species, ''Ecballium elaterium'', also called the squirting cucumber or exploding cucumber (not the same plant as ''Cyclanthera brachystachya''). Its u ...
.
Food uses
 A
A cornucopia
In classical antiquity, the cornucopia (), from Latin ''cornu'' (horn) and ''copia'' (abundance), also called the horn of plenty, was a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers ...
of fruits —fleshy (simple) fruits from apples to berries to watermelon; dry (simple) fruits including beans and rice, coconuts and carrots; aggregate fruits including strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, pawpaw; multiple fruits such as pineapple, fig, mulberries; (see above re all)— are commercially valuable as human food. They are eaten both fresh and as jams, marmalade and other fruit preserves
Fruit preserves are preparations of fruits whose main preserving agent is sugar and sometimes acid, often stored in glass jars and used as a condiment or spread.
There are many varieties of fruit preserves globally, distinguished by the met ...
. They are used extensively in manufactured and processed foods (cakes, cookies, baked goods, flavorings, ice cream, yogurt, canned vegetables, frozen vegetables and meals) and beverages such as fruit juices and alcoholic beverages
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The c ...
(brandy, fruit beer, wine). Spices like vanilla, black pepper, paprika, and allspice
Allspice, also known as Jamaica pepper, myrtle pepper, pimenta, or pimento, is the dried unripe berry of ''Pimenta dioica'', a midcanopy tree native to the Greater Antilles, southern Mexico, and Central America, now cultivated in many warm par ...
are derived from berries. Olive fruit is pressed for olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: ...
and similar processing is applied to other oil bearing fruits/vegetables.
Fruits are also used for socializing and gift-giving in the form of fruit baskets and fruit bouquets.
Typically, many botanical fruits —"vegetables" in culinary ''parlance''— (including tomato, green beans, leaf greens, bell pepper, cucumber, eggplant, okra, pumpkin, squash, zucchini) are bought and sold daily in fresh produce markets and greengrocer
A greengrocer is a person who owns or operates a shop selling primarily fruit and vegetables. The term may also be used to refer to a shop selling primarily produce. It is used predominantly in the United Kingdom and Australia.
In the Unite ...
ies and carried back to kitchens, at home or restaurant, for preparation of meals.
Storage
All fruits benefit from proper post harvest care, and in many fruits, the plant hormoneethylene
Ethylene ( IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene ...
causes ripening
Ripening is a process in fruits that causes them to become more palatable. In general, fruit becomes sweeter, less green, and softer as it ripens. Even though the acidity of fruit increases as it ripens, the higher acidity level does not make th ...
. Therefore, maintaining most fruits in an efficient cold chain
A cold chain is a low temperature-controlled supply chain network. An unbroken cold chain is an uninterrupted series of refrigerated production, storage and distribution activities, along with associated equipment and logistics, which maintain q ...
is optimal for post harvest storage, with the aim of extending and ensuring shelf life.Why Cold Chain for Fruits:
Nutritional value
 Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of
Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorpora ...
and water, and many are generally high in vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) a ...
. An overview of numerous studies showed that fruits (e.g., whole apples or whole oranges) are satisfying (filling) by simply eating and chewing them.
The dietary fiber
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by th ...
consumed in eating fruit promotes satiety
Satiety ( ) is a state or condition of fullness gratified beyond the point of satisfaction, the opposite of hunger. It is a state which induces meal termination.Hetherington, M.Sensory-specific satiety and its importance in meal termination ''Neuro ...
, and may help to control body weight and aid reduction of blood cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membr ...
, a risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often us ...
for cardiovascular diseases. Fruit consumption is under preliminary research for the potential to improve nutrition and affect chronic diseases. Regular consumption of fruit is generally associated with reduced risks of several diseases and functional declines associated with aging.
Food safety
Forfood safety
Food safety (or food hygiene) is used as a scientific method/discipline describing handling, food processing, preparation, and food storage, storage of food in ways that prevent foodborne illness, food-borne illness. The occurrence of two or ...
, the CDC recommends proper fruit handling and preparation to reduce the risk of food contamination and foodborne illness
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow ...
. Fresh fruits and vegetables should be carefully selected; at the store, they should not be damaged or bruised; and precut pieces should be refrigerated or surrounded by ice.
All fruits and vegetables should be rinsed before eating. This recommendation also applies to produce with rinds or skins that are not eaten. It should be done just before preparing or eating to avoid premature spoilage.
Fruits and vegetables should be kept separate from raw foods like meat, poultry, and seafood, as well as from utensils that have come in contact with raw foods. Fruits and vegetables that are not going to be cooked should be thrown away if they have touched raw meat, poultry, seafood, or eggs.
All cut, peeled, or cooked fruits and vegetables should be refrigerated within two hours. After a certain time, harmful bacteria may grow on them and increase the risk of foodborne illness.
Allergies
Fruit allergies make up about 10 percent of all food related allergies.Nonfood uses
Because fruits have been such a major part of the human diet, various cultures have developed many different uses for fruits they do not depend on for food. For example:annual honesty
''Lunaria annua'', called honesty or annual honesty in English, is a species of flowering plant in the cabbage and mustard family Brassicaceae. It is native to the Balkans and south west Asia, and cultivated throughout the temperate world.
Desc ...
, cotoneaster, lotus
Lotus may refer to:
Plants
*Lotus (plant), various botanical taxa commonly known as lotus, particularly:
** ''Lotus'' (genus), a genus of terrestrial plants in the family Fabaceae
**Lotus flower, a symbolically important aquatic Asian plant also ...
, milkweed, unicorn plant, and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeolog ...
). Ornamental tree
Ornamental plants or garden plants are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars that ...
s and shrubs are often cultivated for their colorful fruits, including beautyberry
''Callicarpa'' (beautyberry) is a genus of shrubs and small trees in the family Lamiaceae.Heywood, V.H., Brummitt, R.K., Culham, A. & Seberg, O. 2007: Flowering Plant Families of the World. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. They are native to east a ...
, cotoneaster, holly, pyracantha, skimmia, and viburnum
''Viburnum'' is a genus of about 150–175 species of flowering plants in the moschatel family Adoxaceae. Its current classification is based on molecular phylogeny. It was previously included in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae.
The mem ...
.
* Fruits of opium poppy are the source of opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
, which contains the drugs codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
and morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. Ther ...
, as well as the biologically inactive chemical theabaine from which the drug oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
is synthesized.
* Osage orange fruits are used to repel cockroach
Cockroaches (or roaches) are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of insects belonging to Blattodea, containing all members of the group except termites. About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. Some species are we ...
es.
* Many fruits provide natural dye
Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.
Archae ...
s (e.g., cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus '' Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet '' Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The ...
, mulberry, sumac, and walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''.
Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a tru ...
).
* Dried gourd
Gourds include the fruits of some flowering plant species in the family Cucurbitaceae, particularly '' Cucurbita'' and '' Lagenaria''. The term refers to a number of species and subspecies, many with hard shells, and some without. One of the e ...
s are used as bird houses, cups, decorations, dishes, musical instruments, and water jugs.
* Pumpkin
A pumpkin is a vernacular term for mature winter squash of species and varieties in the genus '' Cucurbita'' that has culinary and cultural significance but no agreed upon botanical or scientific meaning. The term ''pumpkin'' is sometimes u ...
s are carved into Jack-o'-lantern
A jack-o'-lantern (or jack o'lantern) is a carved lantern, most commonly made from a pumpkin or a root vegetable such as a rutabaga or turnip. Jack-o'-lanterns are associated with the Halloween holiday. Its name comes from the reported phenomen ...
s for Halloween
Halloween or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve) is a celebration geography of Halloween, observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Saints' Day. ...
.
* The fibrous core of the mature and dry Luffa
''Luffa'' is a genus of tropical and subtropical vines in the cucumber family (Cucurbitaceae).
In everyday non-technical usage, the luffa, also spelled loofah, usually refers to the fruits of the species '' Luffa aegyptiaca'' and '' Luffa acuta ...
fruit is used as a sponge.
* The spiny fruit of burdock or cocklebur inspired the invention of Velcro
Velcro, officially known as Velcro IP Holdings LLC and trading as Velcro Companies, is a British privately held company, founded by Swiss electrical engineer George de Mestral in the 1950s. It is the original manufacturer of hook-and-loop fast ...
.
* Coir
Coir (), also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell an ...
fiber from coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or ...
shells is used for brushes, doormats, floor tiles, insulation, mattresses, sacking, and as a growing medium for container plants. The shell of the coconut fruit is used to make bird houses, bowls, cups, musical instruments, and souvenir heads.
* The hard and colorful grain fruits of Job's tears are used as decorative beads for jewelry, garments, and ritual objects.
* Fruit is often a subject of still life
A still life (plural: still lifes) is a work of art depicting mostly wikt:inanimate, inanimate subject matter, typically commonplace objects which are either natural (food, flowers, dead animals, plants, rocks, shells, etc.) or artificiality, m ...
paintings.
See also
*Fruit tree
A fruit tree is a tree which bears fruit that is consumed or used by animals and humans — all trees that are flowering plants produce fruit, which are the ripened ovary (plants), ovaries of flowers containing one or more seeds. In hortic ...
* Fruitarianism
Fruitarianism () is a diet related to veganism that consists primarily of consuming fruits and possibly nuts and seeds, but without any animal products. Fruitarian diets are subject to criticism and health concerns.
Fruitarianism may be adopted ...
* List of countries by fruit production
* List of culinary fruits
This list contains the names of fruits that are considered edible either raw or in some cuisines. The word "fruit" is used in several different ways. The definition of fruit for this list is a culinary fruit, that is, "Any sweet, edible part o ...
* List of foods
* List of fruit dishes
This is a list of notable fruit dishes. Fruit dishes are those that use fruit as a primary ingredient. Condiments prepared with fruit as a primary ingredient are also included in this list.
Fruit dishes
*
* '
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* ...
References
Further reading
* Gollner, Adam J. (2010). ''The Fruit Hunters: A Story of Nature, Adventure, Commerce, and Obsession''. Scribner. * Watson, R. R., and Preedy, V.R. (2010, eds.). ''Bioactive Foods in Promoting Health: Fruits and Vegetables''. Academic Press.External links
Images of fruit development from flowers
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu
from California Rare Fruit Growers, Inc.
Photo ID of Fruits
by Capt. Pawanexh Kohli * {{Authority control Fruit Pollination Types of food