Fountains In Ohio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A fountain, from the
A fountain, from the


 Ancient civilizations built stone basins to capture and hold precious drinking water. A carved stone basin, dating to around 2000 BC, was discovered in the ruins of the ancient
Ancient civilizations built stone basins to capture and hold precious drinking water. A carved stone basin, dating to around 2000 BC, was discovered in the ruins of the ancient
 In
In


 Shortly after the spread of Islam, the Arabs incorporated into their city planning the famous Islamic gardens. Islamic gardens after the 7th century were traditionally enclosed by walls and were designed to represent paradise. The paradise gardens, were laid out in the form of a cross, with four channels representing the rivers of Paradise, dividing the four parts of the world. Water sometimes spouted from a fountain in the center of the cross, representing the spring or fountain, Salsabil, described in the Qur'an as the source of the rivers of Paradise.
In the 9th century, the
Shortly after the spread of Islam, the Arabs incorporated into their city planning the famous Islamic gardens. Islamic gardens after the 7th century were traditionally enclosed by walls and were designed to represent paradise. The paradise gardens, were laid out in the form of a cross, with four channels representing the rivers of Paradise, dividing the four parts of the world. Water sometimes spouted from a fountain in the center of the cross, representing the spring or fountain, Salsabil, described in the Qur'an as the source of the rivers of Paradise.
In the 9th century, the
The Crank-Connecting Rod System in a Continuously Rotating Machine
.
 The palaces of Moorish Spain, particularly the
The palaces of Moorish Spain, particularly the
 The 17th and 18th centuries were a golden age for fountains in Rome, which began with the reconstruction of ruined Roman aqueducts and the construction by the Popes of ''mostra'', or display fountains, to mark their termini. The new fountains were expressions of the new
The 17th and 18th centuries were a golden age for fountains in Rome, which began with the reconstruction of ruined Roman aqueducts and the construction by the Popes of ''mostra'', or display fountains, to mark their termini. The new fountains were expressions of the new
File:Lazio Roma Navona2 tango7174.jpg, Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi by
File:Le chateau de versailles le jardin 121.JPG
File:Fountain in the Parc de Versailles (2519408544).jpg,
File:Versailles with fountain.JPG
File:Fountain in the Parc de Versailles (2519388110).jpg
File:Samson and Lion Fountain.jpg, Samson and the Lion fountain at Peterhof Palace, Russia (1800–1802)
File:Petergof canal.JPG, Sea Canal
File:RimskyFountains Peterhof.jpg, Roman Fountains (1763–80)
File:Danaida fountain of Peterhof-3.jpg, Danaida Fountain
File:3911ParigiFontanaChatelet.JPG,
In the early 19th century, London and Paris built aqueducts and new fountains to supply clean drinking water to their exploding populations.
File:Expo 1931 Pont eau.jpg, The "Pont d'eau' from the 1931 Paris Colonial Exhibit, created a "bridge" of water forty meters long and six meters wide.
File:BuckinghamFountain ChicagoIL.jpg, Buckingham Fountain in Chicago (1933)
File:Statue at Rockefeller Centre.jpg, Fountain of Prometheus at the Rockefeller Center in New York City (1933)
File:Paris expo 1937.jpg, The battery of water cannon at the Palais de Chaillot at the World Expo in Paris (1937). The water cannon still function.
File:Kissing Students.jpg, The " Kissing Students" fountain at the Raekoja plats square near Tartu Town Hall in
Paris fountains in the 20th century no longer had to supply drinking water - they were purely decorative; and, since their water usually came from the river and not from the city aqueducts, their water was no longer drinkable. Twenty-eight new fountains were built in Paris between 1900 and 1940; nine new fountains between 1900 and 1910; four between 1920 and 1930; and fifteen between 1930 and 1940.
The biggest fountains of the period were those built for the International Expositions of 1900, 1925 and 1937, and for the Colonial Exposition of 1931. Of those, only the fountains from the 1937 exposition at the Palais de Chaillot still exist. (See
 The fountain called Bit.Fall by German artist Julius Popp (2005) uses digital technologies to spell out words with water. The fountain is run by a statistical program which selects words at random from news stories on the Internet. It then recodes these words into pictures. Then 320 nozzles inject the water into electromagnetic valves. The program uses rasterization and bitmap technologies to synchronize the valves so drops of water form an image of the words as they fall. According to Popp, the sheet of water is "a metaphor for the constant flow of information from which we cannot escape."
Crown Fountain is an interactive fountain and
The fountain called Bit.Fall by German artist Julius Popp (2005) uses digital technologies to spell out words with water. The fountain is run by a statistical program which selects words at random from news stories on the Internet. It then recodes these words into pictures. Then 320 nozzles inject the water into electromagnetic valves. The program uses rasterization and bitmap technologies to synchronize the valves so drops of water form an image of the words as they fall. According to Popp, the sheet of water is "a metaphor for the constant flow of information from which we cannot escape."
Crown Fountain is an interactive fountain and
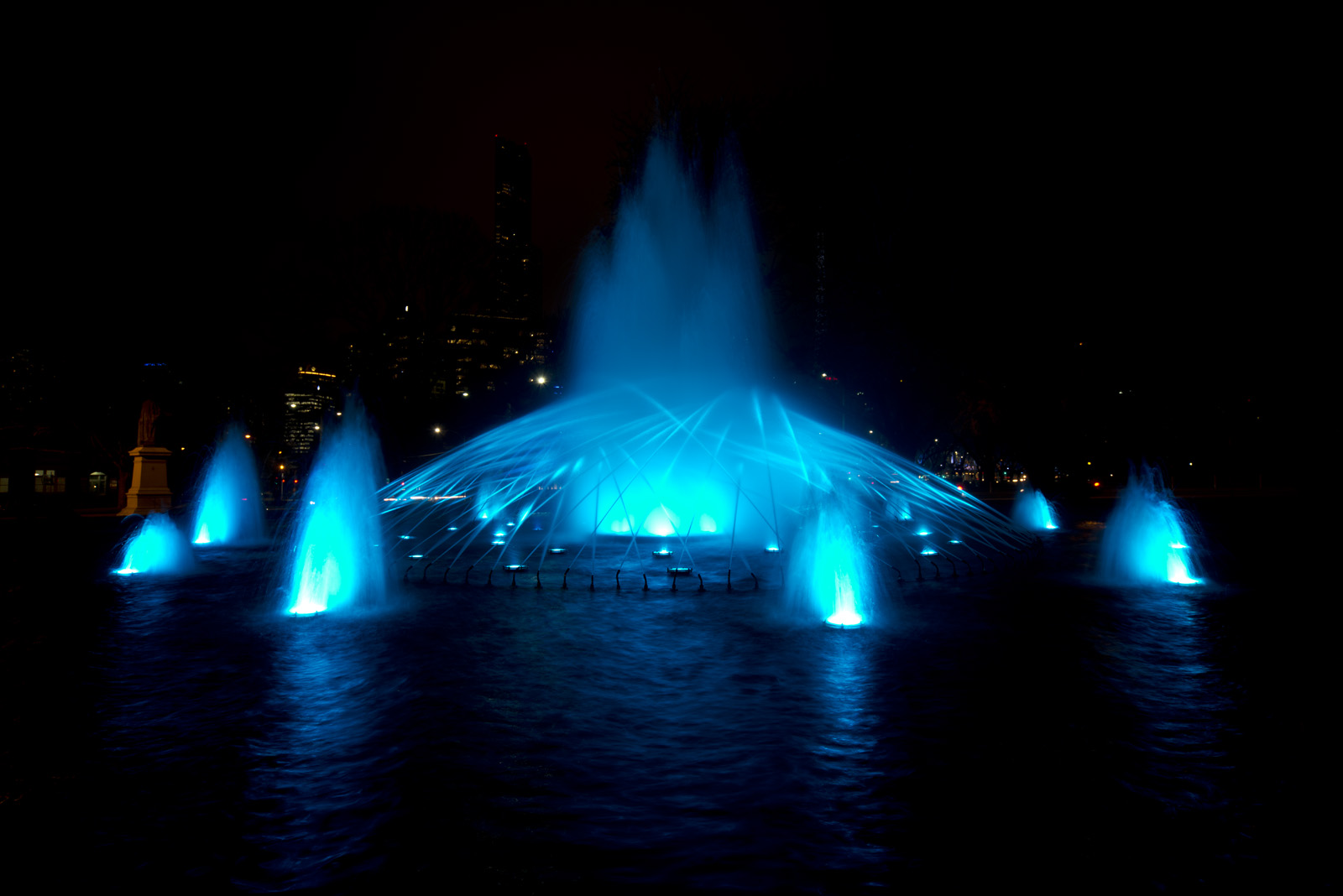
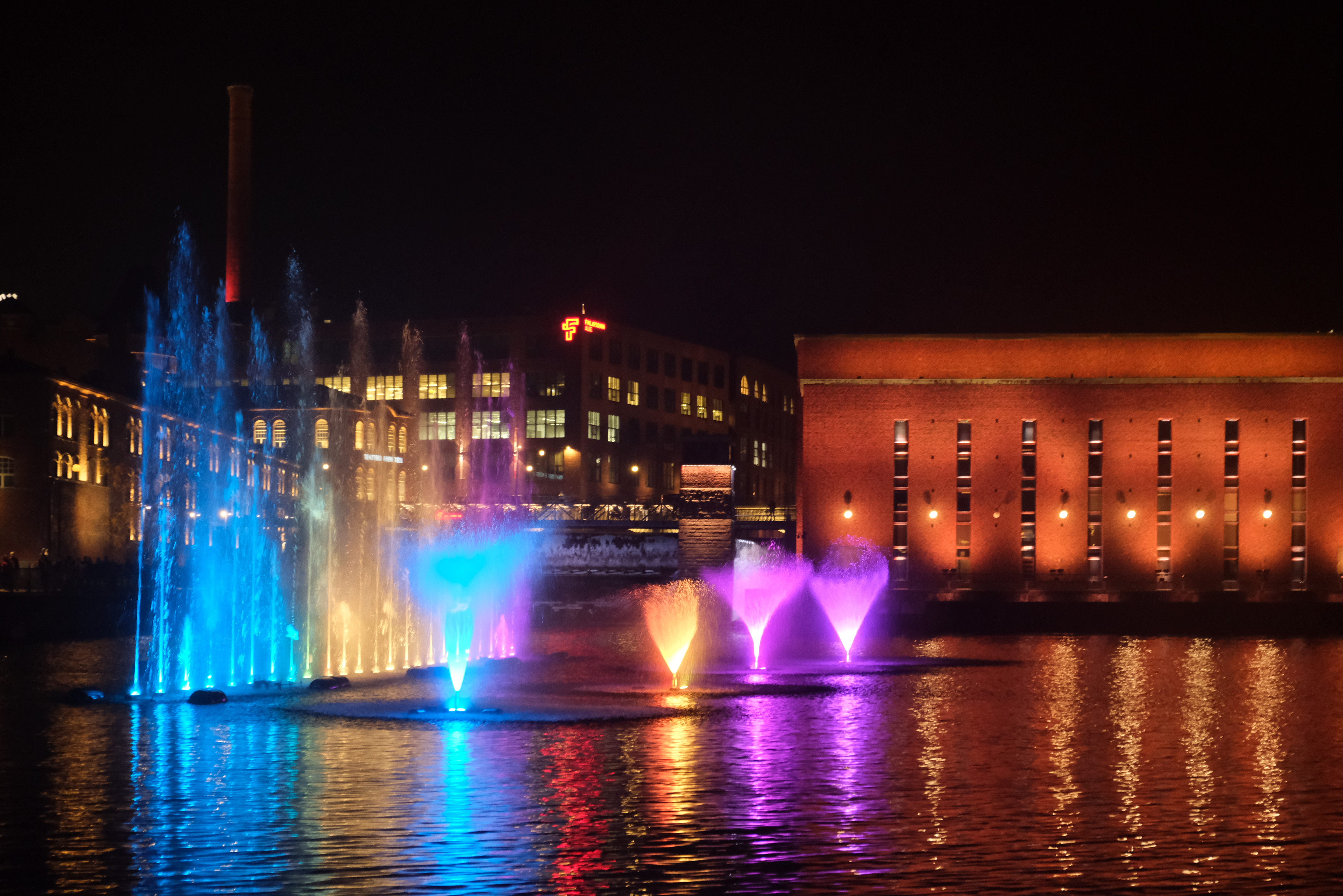 Musical fountains create a theatrical spectacle with music, light and water, usually employing a variety of programmable spouts and water jets controlled by a computer.
Musical fountains were first described in the 1st century AD by the Greek scientist and engineer Hero of Alexandria in his book ''Pneumatics''. Hero described and provided drawings of "A bird made to whistle by flowing water," "A Trumpet sounded by flowing water," and "Birds made to sing and be silent alternately by flowing water." In Hero's descriptions, water pushed air through musical instruments to make sounds. It is not known if Hero made working models of any of his designs.
During the Italian Renaissance, the most famous musical fountains were located in the gardens of the Villa d'Este, in
Musical fountains create a theatrical spectacle with music, light and water, usually employing a variety of programmable spouts and water jets controlled by a computer.
Musical fountains were first described in the 1st century AD by the Greek scientist and engineer Hero of Alexandria in his book ''Pneumatics''. Hero described and provided drawings of "A bird made to whistle by flowing water," "A Trumpet sounded by flowing water," and "Birds made to sing and be silent alternately by flowing water." In Hero's descriptions, water pushed air through musical instruments to make sounds. It is not known if Hero made working models of any of his designs.
During the Italian Renaissance, the most famous musical fountains were located in the gardens of the Villa d'Este, in
File:Villa d'Este 01.jpg, The Organ Fountain at the Villa d'Este, Tivoli (1550–1572)
File:Le Chateau d'eau and plaza, Exposition Universal, 1900, Paris, France.jpg, The Château d'eau and plaza of the Paris Universal Exposition of 1900. The fountains were illuminated with different colors at night.
File:Bellagio fountains night.jpg, The

 A splash fountain or bathing fountain is intended for people to come in and cool off on hot summer days. These fountains are also referred to as interactive fountains. These fountains are designed to allow easy access, and feature nonslip surfaces, and have no standing water, to eliminate possible drowning hazards, so that no lifeguards or supervision is required. These splash pads are often located in public pools, public parks, or public playgrounds (known as "spraygrounds"). In some splash fountains, such as Dundas Square in Toronto, Canada, the water is heated by solar energy captured by the special dark-colored granite slabs. The fountain at Dundas Square features 600 ground nozzles arranged in groups of 30 (3 rows of 10 nozzles). Each group of 30 nozzles is located beneath a stainless steel grille. Twenty such grilles are arranged in two rows of 10, in the middle of the main walkway through Dundas Square.
A splash fountain or bathing fountain is intended for people to come in and cool off on hot summer days. These fountains are also referred to as interactive fountains. These fountains are designed to allow easy access, and feature nonslip surfaces, and have no standing water, to eliminate possible drowning hazards, so that no lifeguards or supervision is required. These splash pads are often located in public pools, public parks, or public playgrounds (known as "spraygrounds"). In some splash fountains, such as Dundas Square in Toronto, Canada, the water is heated by solar energy captured by the special dark-colored granite slabs. The fountain at Dundas Square features 600 ground nozzles arranged in groups of 30 (3 rows of 10 nozzles). Each group of 30 nozzles is located beneath a stainless steel grille. Twenty such grilles are arranged in two rows of 10, in the middle of the main walkway through Dundas Square.

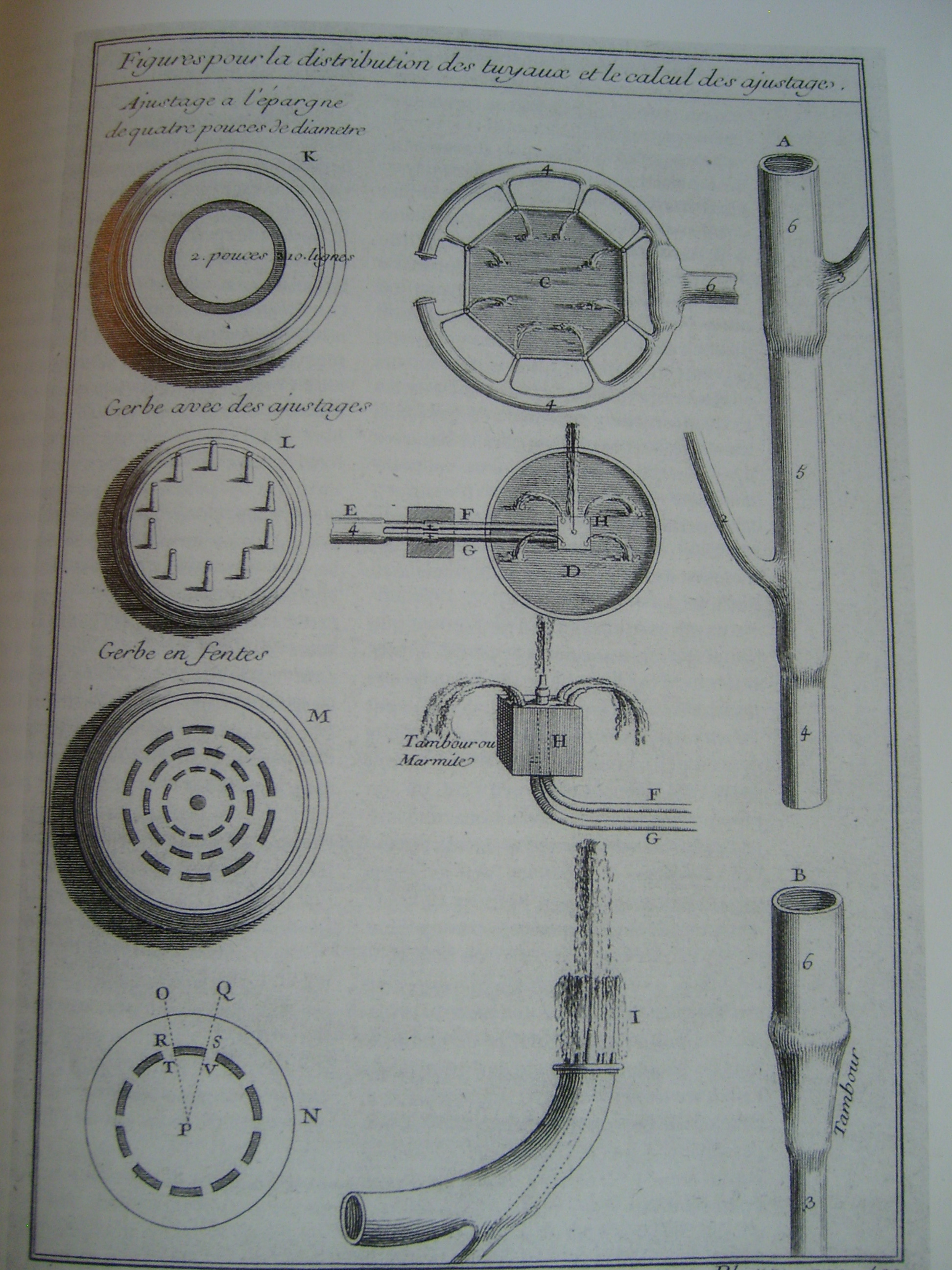 From Roman times until the end of the 19th century, fountains operated by gravity, requiring a source of water higher than the fountain itself to make the water flow. The greater the difference between the elevation of the source of water and the fountain, the higher the water would go upwards from the fountain.
In Roman cities, water for fountains came from lakes and rivers and springs in the hills, brought into city in aqueducts and then distributed to fountains through a system of lead pipes.
From the Middle Ages onwards, fountains in villages or towns were connected to springs, or to channels which brought water from lakes or rivers. In Provence, a typical village fountain consisted of a pipe or underground duct from a spring at a higher elevation than the fountain. The water from the spring flowed down to the fountain, then up a tube into a bulb-shaped stone vessel, like a large vase with a cover on top. The inside of the vase, called the ''bassin de répartition'', was filled with water up to a level just above the mouths of the canons, or spouts, which slanted downwards. The water poured down through the canons, creating a siphon, so that the fountain ran continually.
In cities and towns, residents filled vessels or jars of water jets from the canons of the fountain or paid a water porter to bring the water to their home. Horses and domestic animals could drink the water in the basin below the fountain. The water not used often flowed into a separate series of basins, a lavoir, used for washing and rinsing clothes. After being used for washing, the same water then ran through a channel to the town's kitchen garden. In Provence, since clothes were washed with ashes, the water that flowed into the garden contained potassium, and was valuable as fertilizer.
The most famous fountains of the Renaissance, at the Villa d'Este in Tivoli, were located on a steep slope near a river; the builders ran a channel from the river to a large fountain at top of the garden, which then fed other fountains and basins on the levels below. The fountains of Rome, built from the Renaissance through the 18th century, took their water from rebuilt Roman aqueducts which brought water from lakes and rivers at a higher elevation than the fountains. Those fountains with a high source of water, such as the Triton Fountain, could shoot water in air. Fountains with a lower source, such as the Trevi Fountain, could only have water pour downwards. The architect of the Trevi Fountain placed it below street level to make the flow of water seem more dramatic.
The fountains of Versailles depended upon water from reservoirs just above the fountains. As King
From Roman times until the end of the 19th century, fountains operated by gravity, requiring a source of water higher than the fountain itself to make the water flow. The greater the difference between the elevation of the source of water and the fountain, the higher the water would go upwards from the fountain.
In Roman cities, water for fountains came from lakes and rivers and springs in the hills, brought into city in aqueducts and then distributed to fountains through a system of lead pipes.
From the Middle Ages onwards, fountains in villages or towns were connected to springs, or to channels which brought water from lakes or rivers. In Provence, a typical village fountain consisted of a pipe or underground duct from a spring at a higher elevation than the fountain. The water from the spring flowed down to the fountain, then up a tube into a bulb-shaped stone vessel, like a large vase with a cover on top. The inside of the vase, called the ''bassin de répartition'', was filled with water up to a level just above the mouths of the canons, or spouts, which slanted downwards. The water poured down through the canons, creating a siphon, so that the fountain ran continually.
In cities and towns, residents filled vessels or jars of water jets from the canons of the fountain or paid a water porter to bring the water to their home. Horses and domestic animals could drink the water in the basin below the fountain. The water not used often flowed into a separate series of basins, a lavoir, used for washing and rinsing clothes. After being used for washing, the same water then ran through a channel to the town's kitchen garden. In Provence, since clothes were washed with ashes, the water that flowed into the garden contained potassium, and was valuable as fertilizer.
The most famous fountains of the Renaissance, at the Villa d'Este in Tivoli, were located on a steep slope near a river; the builders ran a channel from the river to a large fountain at top of the garden, which then fed other fountains and basins on the levels below. The fountains of Rome, built from the Renaissance through the 18th century, took their water from rebuilt Roman aqueducts which brought water from lakes and rivers at a higher elevation than the fountains. Those fountains with a high source of water, such as the Triton Fountain, could shoot water in air. Fountains with a lower source, such as the Trevi Fountain, could only have water pour downwards. The architect of the Trevi Fountain placed it below street level to make the flow of water seem more dramatic.
The fountains of Versailles depended upon water from reservoirs just above the fountains. As King
 *
*
File:Fuente Gaia de Siena.JPG, The Fonte Gaia, Piazza del Campo, Siena, Italy by Jacopo della Quercia (1419) (replaced by a copy in 1868)
File:Fontein Paleistuin.jpg, Fountain at Het Loo Palace in Apeldoorn, Netherlands
File:Jet-d'eau-Genève.jpg, The
Tallest fountain
{{Authority control Water Landscape architecture Landscape garden features Architectural elements Outdoor sculptures Public art
 A fountain, from the
A fountain, from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
"fons" (genitive
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can al ...
"fontis"), meaning source or spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a ...
, is a decorative reservoir used for discharging water. It is also a structure that jets water into the air for a decorative or dramatic effect.
Fountains were originally purely functional, connected to springs or aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
and used to provide drinking water and water for bathing and washing to the residents of cities, towns and villages. Until the late 19th century most fountains operated by gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
, and needed a source of water higher than the fountain, such as a reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contro ...
or aqueduct, to make the water flow or jet into the air.
In addition to providing drinking water, fountains were used for decoration and to celebrate their builders. Roman fountains were decorated with bronze or stone masks of animals or heroes. In the Middle Ages, Moorish and Muslim garden designers used fountains to create miniature versions of the gardens of paradise. King Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
of France used fountains in the Gardens of Versailles
The Gardens of Versailles (french: Jardins du château de Versailles ) occupy part of what was once the ''Domaine royal de Versailles'', the royal demesne of the château of Versailles. Situated to the west of the palace, the gardens cover som ...
to illustrate his power over nature. The baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
decorative fountains of Rome in the 17th and 18th centuries marked the arrival point of restored Roman aqueducts and glorified the Popes who built them.
By the end of the 19th century, as indoor plumbing became the main source of drinking water, urban fountains became purely decorative. Mechanical pumps replaced gravity and allowed fountains to recycle water and to force it high into the air. The Jet d'Eau
The Jet d'Eau (, ''Water-Jet'') is a large fountain in Geneva, Switzerland and is one of the city's most famous landmarks, being featured on the city's official tourism web site and on the official logo for Geneva's hosting of group stage matches ...
in Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial lak ...
, built in 1951, shoots water in the air. The highest such fountain in the world is King Fahd's Fountain
King Fahd's Fountain ( ar, نافورة الملك فهد), also known as the Jeddah Fountain, is in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. It is the tallest fountain of its type in the world.
Overview
The fountain was donated to the city of Jeddah by King Fahd, ...
in Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), also spelled Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; ar, , Jidda, ), is a city in the Hejaz region of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and the country's commercial center. Established in the 6th century BC as a fishing village, Jeddah's pro ...
, Saudi Arabia, which spouts water above the Red Sea.SAMIRAD (Saudi Arabia Market Information Resource Directory)
Fountains are used today to decorate city parks and squares; to honor individuals or events; for recreation and for entertainment. A splash pad
A splash pad or spray pool is a recreation area, often in a public park, for water play that has little or no standing water. This is said to eliminate the need for lifeguards or other supervision, as there is little risk of drowning.
Typicall ...
or spray pool
A splash pad or spray pool is a recreation area, often in a public park, for water play that has little or no standing water. This is said to eliminate the need for lifeguards or other supervision, as there is little risk of drowning.
Typicall ...
allows city residents to enter, get wet and cool off in summer. The musical fountain
A musical fountain, also known as a fairy fountain, prismatic fountain or dancing fountain, is a type of choreographed fountain that creates aesthetic designs as a form of entertainment. The displays are commonly synchronised to music and also ...
combines moving jets of water, colored lights and recorded music, controlled by a computer, for dramatic effects. Fountains can themselves also be musical instruments played by obstruction of one or more of their water jets.
Drinking fountains
A drinking fountain, also called a water fountain or water bubbler, is a fountain designed to provide drinking water. It consists of a basin with either continuously running water or a tap. The drinker bends down to the stream of water and s ...
provide clean drinking water in public buildings, parks and public spaces.
History

Ancient fountains
 Ancient civilizations built stone basins to capture and hold precious drinking water. A carved stone basin, dating to around 2000 BC, was discovered in the ruins of the ancient
Ancient civilizations built stone basins to capture and hold precious drinking water. A carved stone basin, dating to around 2000 BC, was discovered in the ruins of the ancient Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian city of Lagash
Lagash (cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian: ''Lagaš''), was an ancient city state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Ash Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash (modern Al-Hiba) w ...
in modern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
. The ancient Assyrians constructed a series of basins in the gorge of the Comel River, carved in solid rock, connected by small channels, descending to a stream. The lowest basin was decorated with carved reliefs of two lions. The ancient Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
had ingenious systems for hoisting water up from the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
for drinking and irrigation, but without a higher source of water it was not possible to make water flow by gravity, There are lion-shaped fountains in the Temple of Dendera
Dendera Temple complex ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Iunet'' or ''Tantere''; the 19th-century English spelling in most sources, including Belzoni, was Tentyra; also spelled Denderah) is located about south-east of Dendera, Egypt. It is one of the best ...
in Qena
Qena ( ar, قنا ' , locally: ; cop, ⲕⲱⲛⲏ ''Konē'') is a city in Upper Egypt, and the capital of the Qena Governorate. Situated on the east bank of the Nile, it was known in antiquity as Kaine (Greek Καινή, meaning "new (city)"; ...
.
The ancient Greeks used aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
and gravity-powered fountains to distribute water. According to ancient historians, fountains existed in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
, and other ancient Greek cities in the 6th century BC as the terminating points of aqueducts which brought water from springs and rivers into the cities. In the 6th century BC, the Athenian ruler Peisistratos
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular ...
built the main fountain of Athens, the ''Enneacrounos'', in the Agora
The agora (; grc, ἀγορά, romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Greek city-states. It is the best representation of a city-state's response to accommodate the social and political order of t ...
, or main square. It had nine large cannons, or spouts, which supplied drinking water to local residents.
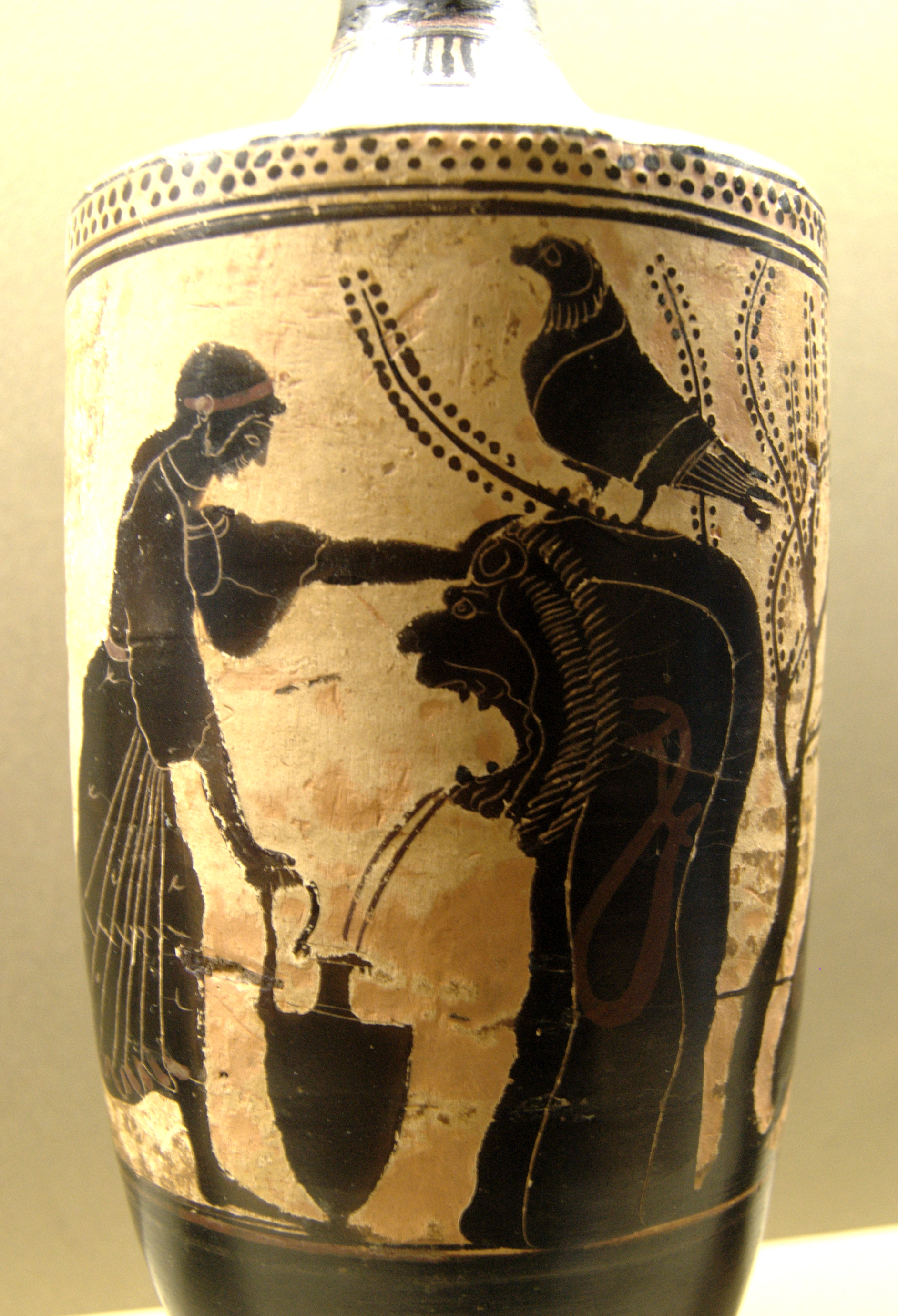
Greek fountains were made of stone or marble, with water flowing through bronze pipes and emerging from the mouth of a sculpted mask that represented the head of a lion or the muzzle of an animal. Most Greek fountains flowed by simple gravity, but they also discovered how to use principle of a siphon
A siphon (from grc, σίφων, síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in a ...
to make water spout, as seen in pictures on Greek vases.Louis Plantier, ''Fontaines de Provence et de la Côte d'Azur'', Édisud, Aix-en-Provence, 2007
Ancient Roman fountains
The Ancient Romans built an extensive system of aqueducts from mountain rivers and lakes to provide water for the fountains and baths of Rome. The Roman engineers used lead pipes instead of bronze to distribute the water throughout the city. The excavations atPompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
, which revealed the city as it was when it was destroyed by Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, uncovered free-standing fountains and basins placed at intervals along city streets, fed by siphoning water upwards from lead pipes under the street. The excavations of Pompeii also showed that the homes of wealthy Romans often had a small fountain in the atrium, or interior courtyard, with water coming from the city water supply and spouting into a small bowl or basin.
Ancient Rome was a city of fountains. According to Sextus Julius Frontinus
Sextus Julius Frontinus (c. 40 – 103 AD) was a prominent Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube ...
, the Roman consul who was named ''curator aquarum
The ''Curator Aquarum'' was a Roman official responsible for managing Rome's water supply and distributing free grain. Curators were appointed by the emperor. The first curator was Agrippa. Another notable ''Curator Aquarum'' was Frontinus, a Ro ...
'' or guardian of the water of Rome in 98 AD, Rome had nine aqueducts which fed 39 monumental fountains and 591 public basins, not counting the water supplied to the Imperial household, baths and owners of private villas. Each of the major fountains was connected to two different aqueducts, in case one was shut down for service.
The Romans were able to make fountains jet water into the air, by using the pressure of water flowing from a distant and higher source of water to create hydraulic head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of liquid pressure above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22.
It is usually measured as a liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, ...
, or force. Illustrations of fountains in gardens spouting water are found on wall paintings in Rome from the 1st century BC, and in the villas of Pompeii. The Villa of Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
in Tivoli featured a large swimming basin with jets of water. Pliny the Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo (61 – c. 113), better known as Pliny the Younger (), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate ...
described the banquet room of a Roman villa where a fountain began to jet water when visitors sat on a marble seat. The water flowed into a basin, where the courses of a banquet were served in floating dishes shaped like boats.Philippe Prevot, pg. 21
Roman engineers built aqueducts and fountains throughout the Roman Empire. Examples can be found today in the ruins of Roman towns in Vaison-la-Romaine
Vaison-la-Romaine (; oc, Vaison) is a town in the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in southeastern France.
Vaison-la-Romaine is famous for its rich Roman ruins and mediaeval town and cathedral. It is also unusual in ...
and Glanum
Glanum (Hellenistic ''Γλανόν'', as well as Glano, Calum, Clano, Clanum, Glanu, Glano) was an ancient and wealthy city which still enjoys a magnificent setting below a gorge on the flanks of the Alpilles mountains. It is located about one kil ...
in France, in Augst
Augst ( Swiss German: ''Augscht'') is a municipality in the district of Liestal in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland. It was known as Augusta Raurica in Roman times.
History
Augst is first mentioned in 615 as ''Augustodunensem prae ...
, Switzerland, and other sites.
Medieval fountains
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
there were public drinking fountain
A drinking fountain, also called a water fountain or water bubbler, is a fountain designed to provide drinking water. It consists of a basin with either continuously running water or a tap. The drinker bends down to the stream of water and s ...
s at least as early as 550 AD. They are called ''dhunge dhara
A dhunge dhara ( ) or hiti ( Newari: ) is a traditional stone drinking fountain found in Nepal. It is an intricately carved stone waterway through which water flows uninterrupted from underground sources. Dhunge dharas are part of a comprehensive d ...
s'' or ''hitis''. They consist of intricately carved stone spouts through which water flows uninterrupted from underground water sources. They are found extensively in Nepal and some of them are still operational. Construction of water conduits like hitis and dug wells are considered as pious acts in Nepal.Water Conduits in the Kathmandu Valley (2 vols.) by Raimund O.A. Becker-Ritterspach, , Published by Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, India, 1995
During the Middle Ages, Roman aqueducts were wrecked or fell into decay, and many fountains throughout Europe stopped working, so fountains existed mainly in art and literature, or in secluded monasteries or palace gardens. Fountains in the Middle Ages were associated with the source of life, purity, wisdom, innocence, and the Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
. In illuminated manuscripts like the ''Tres Riches Heures du Duc de Berry'' (1411–1416), the Garden of Eden was shown with a graceful gothic fountain in the center (see illustration). The Ghent Altarpiece by Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck ( , ; – July 9, 1441) was a painter active in Bruges who was one of the early innovators of what became known as Early Netherlandish painting, and one of the most significant representatives of Early Northern Renaissance art. Ac ...
, finished in 1432, also shows a fountain as a feature of the adoration of the mystic lamb, a scene apparently set in Paradise.
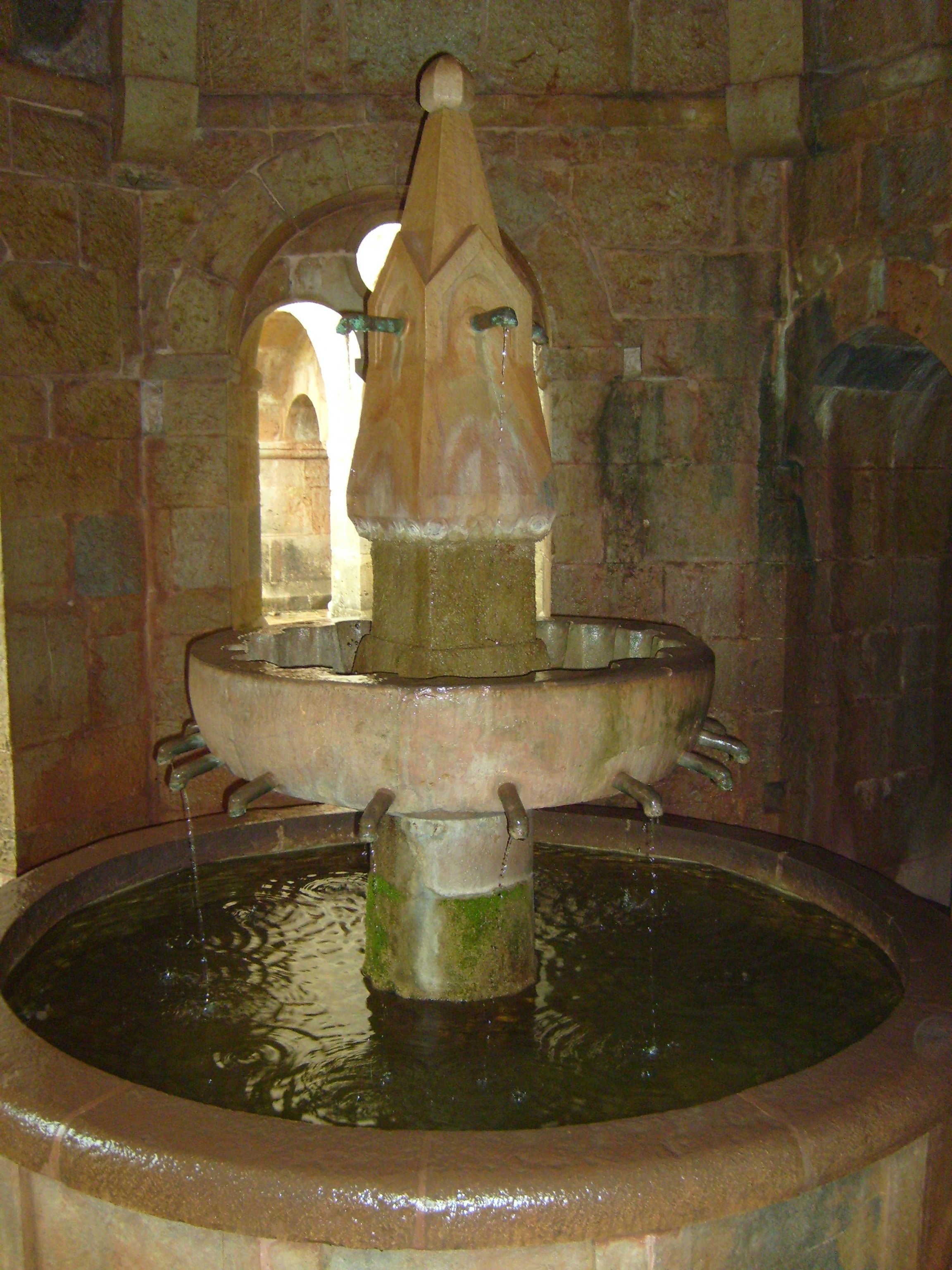
The cloister of a monastery was supposed to be a replica of the Garden of Eden, protected from the outside world. Simple fountains, called lavabos, were placed inside Medieval monasteries such as Le Thoronet Abbey
Thoronet Abbey (french: L'abbaye du Thoronet) is a former Cistercian abbey built in the late twelfth and early thirteenth century, now restored as a museum. It is sited between the towns of Draguignan and Brignoles in the Var Department of Prove ...
in Provence and were used for ritual washing before religious services.
Fountains were also found in the enclosed medieval ''jardins d'amour'', "gardens of courtly love" – ornamental gardens used for courtship and relaxation. The medieval romance The '' Roman de la Rose'' describes a fountain in the center of an enclosed garden, feeding small streams bordered by flowers and fresh herbs.
Some Medieval fountains, like the cathedrals of their time, illustrated biblical stories, local history and the virtues of their time. The Fontana Maggiore
The ''Fontana Maggiore'', a masterpiece of medieval sculpture, placed in the centre of Piazza IV Novembre (formerly Piazza Grande), is the monument symbol of the city of Perugia.
History
The monumental fountain was designed by Frà Bevignate ...
in Perugia, dedicated in 1278, is decorated with stone carvings representing prophets and saints, allegories of the arts, labors of the months, the signs of the zodiac, and scenes from Genesis and Roman history.
Medieval fountains could also provide amusement. The gardens of the Counts of Artois at the Château de Hesdin, built in 1295, contained famous fountains, called ''Les Merveilles de Hesdin'' ("The Wonders of Hesdin") which could be triggered to drench surprised visitors.
Fountains of the Islamic World

 Shortly after the spread of Islam, the Arabs incorporated into their city planning the famous Islamic gardens. Islamic gardens after the 7th century were traditionally enclosed by walls and were designed to represent paradise. The paradise gardens, were laid out in the form of a cross, with four channels representing the rivers of Paradise, dividing the four parts of the world. Water sometimes spouted from a fountain in the center of the cross, representing the spring or fountain, Salsabil, described in the Qur'an as the source of the rivers of Paradise.
In the 9th century, the
Shortly after the spread of Islam, the Arabs incorporated into their city planning the famous Islamic gardens. Islamic gardens after the 7th century were traditionally enclosed by walls and were designed to represent paradise. The paradise gardens, were laid out in the form of a cross, with four channels representing the rivers of Paradise, dividing the four parts of the world. Water sometimes spouted from a fountain in the center of the cross, representing the spring or fountain, Salsabil, described in the Qur'an as the source of the rivers of Paradise.
In the 9th century, the Banū Mūsā
The Banū Mūsā brothers ("Sons of Moses"), namely Abū Jaʿfar, Muḥammad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir (before 803 – February 873); Abū al‐Qāsim, Aḥmad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir (d. 9th century); and Al-Ḥasan ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir (d. 9th ce ...
brothers, a trio of Persian Inventors, were commissioned by the Caliph of Baghdad to summarize the engineering knowledge of the ancient Greek and Roman world. They wrote a book entitled the '' Book of Ingenious Devices'', describing the works of the 1st century Greek Engineer Hero of Alexandria and other engineers, plus many of their own inventions. They described fountains which formed water into different shapes and a wind-powered water pump, but it is not known if any of their fountains were ever actually built.
The Persian rulers of the Middle Ages had elaborate water distribution systems and fountains in their palaces and gardens. Water was carried by a pipe into the palace from a source at a higher elevation. Once inside the palace or garden it came up through a small hole in a marble or stone ornament and poured into a basin or garden channels. The gardens of Pasargades had a system of canals which flowed from basin to basin, both watering the garden and making a pleasant sound. The Persian engineers also used the principle of the syphon (called ''shotor-gelu'' in Persian, literally 'neck of the camel) to create fountains which spouted water or made it resemble a bubbling spring. The garden of Fin, near Kashan, used 171 spouts connected to pipes to create a fountain called the ''Howz-e jush'', or "boiling basin".
The 11th century Persian poet Azraqi described a Persian fountain:
:From a marvelous faucet of gold pours a wave
:whose clarity is more pure than a soul;
:The turquoise and silver form ribbons in the basin
:coming from this faucet of gold ...
Reciprocating motion was first described in 1206 by Iraqi engineer and inventor al-Jazari
Badīʿ az-Zaman Abu l-ʿIzz ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ar-Razāz al-Jazarī (1136–1206, ar, بديع الزمان أَبُ اَلْعِزِ إبْنُ إسْماعِيلِ إبْنُ الرِّزاز الجزري, ) was a polymath: a scholar, ...
when the kings of the Artuqid dynasty in Turkey commissioned him to manufacture a machine to raise water for their palaces. The finest result was a machine called the double-acting reciprocating piston pump, which translated rotary motion to reciprocating motion via the crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
-connecting rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the cranksh ...
mechanism. Ahmad Y HassanThe Crank-Connecting Rod System in a Continuously Rotating Machine
.

Alhambra
The Alhambra (, ; ar, الْحَمْرَاء, Al-Ḥamrāʾ, , ) is a palace and fortress complex located in Granada, Andalusia, Spain. It is one of the most famous monuments of Islamic architecture and one of the best-preserved palaces of the ...
in Granada, had famous fountains. The patio of the Sultan in the gardens of Generalife in Granada (1319) featured spouts of water pouring into a basin, with channels which irrigated orange and myrtle trees. The garden was modified over the centuries – the jets of water which cross the canal today were added in the 19th century.
The fountain in the Court of the Lions of the Alhambra, built from 1362 to 1391, is a large vasque mounted on twelve stone statues of lions. Water spouts upward in the vasque and pours from the mouths of the lions, filling four channels dividing the courtyard into quadrants. The basin dates to the 14th century, but the lions spouting water are believed to be older, dating to the 11th century.
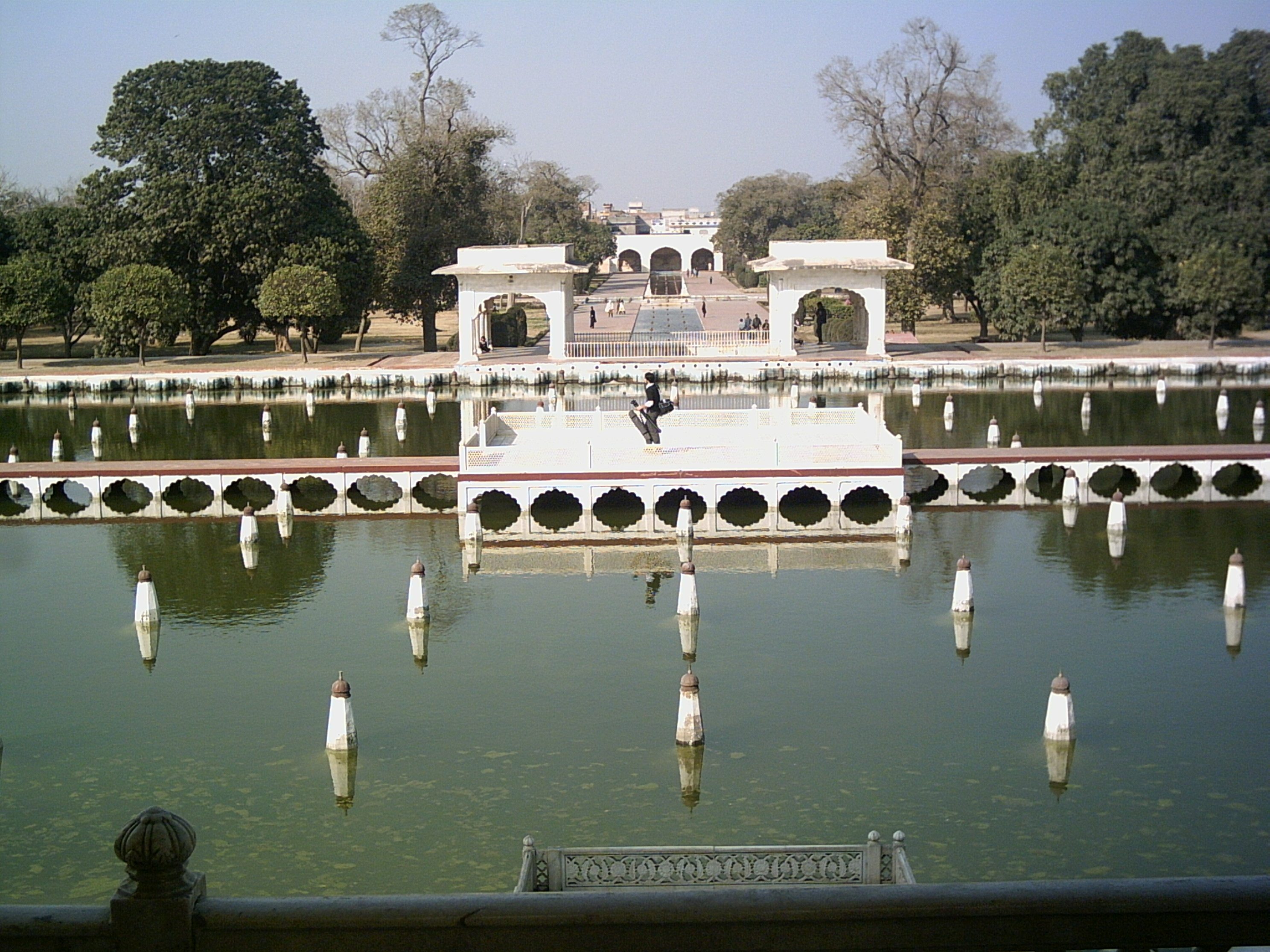
The design of the Islamic garden spread throughout the Islamic world, from Moorish Spain to the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. The Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
built by Emperor Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
in 1641, were said to be ornamented with 410 fountains, which fed into a large basin, canal and marble pools.
In the Ottoman Empire, rulers often built fountains next to mosques so worshippers could do their ritual washing. Examples include the Fountain of Qasim Pasha (1527), Temple Mount, Jerusalem, an ablution
Ablution is the act of washing oneself. It may refer to:
* Ablution as hygiene
* Ablution as ritual purification
** Ablution in Islam:
*** Wudu, daily wash
*** Ghusl, bathing ablution
*** Tayammum, waterless ablution
** Ablution in Christianity
* ...
and drinking fountain built during the Ottoman reign of Suleiman the Magnificent; the Fountain of Ahmed III (1728) at the Topkapı Palace, Istanbul, another Fountain of Ahmed III in Üsküdar (1729) and Tophane Fountain
Tophane Fountain ( tr, Tophane Çeşmesi) is an 18th-century public water fountain built by List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan Mahmud I in the Ottoman architecture, Ottoman rococo architecture and situated in the square of Toph ...
(1732). Palaces themselves often had small decorated fountains, which provided drinking water, cooled the air, and made a pleasant splashing sound. One surviving example is the Fountain of Tears (1764) at the Bakhchisarai Palace, in Crimea; which was made famous by a poem of Alexander Pushkin.
The sebil was a decorated fountain that was often the only source of water for the surrounding neighborhood.
It was often commissioned as an act of Islamic piety by a rich person.
Renaissance fountains (15th–17th centuries)
In the 14th century, Italian humanist scholars began to rediscover and translate forgotten Roman texts on architecture by Vitruvius, on hydraulics by Hero of Alexandria, and descriptions of Roman gardens and fountains byPliny the Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo (61 – c. 113), better known as Pliny the Younger (), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate ...
, Pliny the Elder, and Varro. The treatise on architecture, ''De re aedificatoria'', by Leon Battista Alberti, which described in detail Roman villas, gardens and fountains, became the guidebook for Renaissance builders.
In Rome, Pope Nicholas V (1397–1455), himself a scholar who commissioned hundreds of translations of ancient Greek classics into Latin, decided to embellish the city and make it a worthy capital of the Christian world. In 1453, he began to rebuild the Acqua Vergine, the ruined Roman aqueduct which had brought clean drinking water to the city from eight miles (13 km) away. He also decided to revive the Roman custom of marking the arrival point of an aqueduct with a ''mostra'', a grand commemorative fountain. He commissioned the architect Leon Battista Alberti to build a wall fountain where the Trevi Fountain is now located. The aqueduct he restored, with modifications and extensions, eventually supplied water to the Trevi Fountain and the famous baroque fountains in the Piazza del Popolo and Piazza Navona.
One of the first new fountains to be built in Rome during the Renaissance was the fountain in the piazza in front of the church of Santa Maria in Trastevere (1472), which was placed on the site of an earlier Roman fountain. Its design, based on an earlier Roman model, with a circular vasque on a pedestal pouring water into a basin below, became the model for many other fountains in Rome, and eventually for fountains in other cities, from Paris to London.
In 1503, Pope Julius II decided to recreate a classical pleasure garden in the same place. The new garden, called the Cortile del Belvedere, was designed by Donato Bramante. The garden was decorated with the Pope's famous collection of classical statues, and with fountains. The Venetian Ambassador wrote in 1523, "... On one side of the garden is a most beautiful loggia, at one end of which is a lovely fountain that irrigates the orange trees and the rest of the garden by a little canal in the center of the loggia ... The original garden was split in two by the construction of the Vatican Library in the 16th century, but a new fountain by Carlo Maderno was built in the Cortile del Belvedere, with a jet of water shooting up from a circular stone bowl on an octagonal pedestal in a large basin.
In 1537, in Florence, Cosimo I de' Medici, who had become ruler of the city at the age of only 17, also decided to launch a program of aqueduct and fountain building. The city had previously gotten all its drinking water from wells and reservoirs of rain water, which meant that there was little water or water pressure to run fountains. Cosimo built an aqueduct large enough for the first continually-running fountain in Florence, the Fountain of Neptune in the Piazza della Signoria (1560–1567). This fountain featured an enormous white marble statue of Neptune, resembling Cosimo, by sculptor Bartolomeo Ammannati.
Under the Medicis, fountains were not just sources of water, but advertisements of the power and benevolence of the city's rulers. They became central elements not only of city squares, but of the new Italian Renaissance garden. The great Medici Villa at Castello, built for Cosimo by Benedetto Varchi
Benedetto Varchi (; 1502/15031565) was an Italian humanist, historian, and poet.
Biography
Born in Florence to a family that had originated at Montevarchi, he frequented the neoplatonic academy that Bernardo Rucellai organized in his garden, the ...
, featured two monumental fountains on its central axis; one showing with two bronze figures representing Hercules slaying Antaeus, symbolizing the victory of Cosimo over his enemies; and a second fountain, in the middle of a circular labyrinth of cypresses, laurel, myrtle and roses, had a bronze statue by Giambologna
Giambologna (1529 – 13 August 1608), also known as Jean de Boulogne (French), Jehan Boulongne (Flemish) and Giovanni da Bologna (Italian), was the last significant Italian Renaissance sculptor, with a large workshop producing large and small ...
which showed the goddess Venus wringing her hair. The planet Venus was governed by Capricorn, which was the emblem of Cosimo; the fountain symbolized that he was the absolute master of Florence.
By the middle Renaissance, fountains had become a form of theater, with cascades and jets of water coming from marble statues of animals and mythological figures. The most famous fountains of this kind were found in the Villa d'Este (1550–1572), at Tivoli
Tivoli may refer to:
* Tivoli, Lazio, a town in Lazio, Italy, known for historic sites; the inspiration for other places named Tivoli
Buildings
* Tivoli (Baltimore, Maryland), a mansion built about 1855
* Tivoli Building (Cheyenne, Wyoming), a ...
near Rome, which featured a hillside of basins, fountains and jets of water, as well as a fountain which produced music by pouring water into a chamber, forcing air into a series of flute-like pipes. The gardens also featured ''giochi d'acqua'', water jokes, hidden fountains which suddenly soaked visitors.Helena Attlee, ''Italian Gardens – A Cultural History''
Between 1546 and 1549, the merchants of Paris built the first Renaissance-style fountain in Paris, the Fontaine des Innocents, to commemorate the ceremonial entry of the King into the city. The fountain, which originally stood against the wall of the church of the Holy Innocents, as rebuilt several times and now stands in a square near Les Halles
Les Halles (; 'The Halls') was Paris' central fresh food market. It last operated on January 12, 1973, after which it was "left to the demolition men who will knock down the last three of the eight iron-and-glass pavilions""Les Halles Dead at 200 ...
. It is the oldest fountain in Paris.
Henry constructed an Italian-style garden with a fountain shooting a vertical jet of water for his favorite mistress, Diane de Poitiers, next to the Château de Chenonceau
The Château de Chenonceau () is a French château spanning the river Cher, near the small village of Chenonceaux, Indre-et-Loire, Centre-Val de Loire. It is one of the best-known châteaux of the Loire Valley.
The estate of Chenonceau is firs ...
(1556–1559). At the royal Château de Fontainebleau, he built another fountain with a bronze statue of Diane, goddess of the hunt, modeled after Diane de Poitiers.
Later, after the death of Henry II, his widow, Catherine de Medici, expelled Diane de Poitiers from Chenonceau and built her own fountain and garden there.
King Henry IV of France made an important contribution to French fountains by inviting an Italian hydraulic engineer, Tommaso Francini, who had worked on the fountains of the villa at Pratalino, to make fountains in France. Francini became a French citizen in 1600, built the Medici Fountain, and during the rule of the young King Louis XIII, he was raised to the position of Intendant général des Eaux et Fontaines of the king, a position which was hereditary. His descendants became the royal fountain designers for Louis XIII and for Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
at Versailles.
In 1630, another Medici, Marie de Medici, the widow of Henry IV, built her own monumental fountain in Paris, the Medici Fountain, in the garden of the Palais du Luxembourg. That fountain still exists today, with a long basin of water and statues added in 1866.
Baroque fountains (17th–18th century)
Baroque Fountains of Rome
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
art, which was officially promoted by the Catholic Church as a way to win popular support against the Protestant Reformation; the Council of Trent had declared in the 16th century that the Church should counter austere Protestantism with art that was lavish, animated and emotional. The fountains of Rome, like the paintings of Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
, were examples of the principles of Baroque art. They were crowded with allegorical figures, and filled with emotion and movement. In these fountains, sculpture became the principal element, and the water was used simply to animate and decorate the sculptures. They, like baroque gardens, were "a visual representation of confidence and power."
The first of the Fountains of St. Peter's Square, by Carlo Maderno, (1614) was one of the earliest Baroque fountains in Rome, made to complement the lavish Baroque façade he designed for St. Peter's Basilica behind it. It was fed by water from the Paola aqueduct, restored in 1612, whose source was above sea level, which meant it could shoot water twenty feet up from the fountain. Its form, with a large circular vasque on a pedestal pouring water into a basin and an inverted vasque above it spouting water, was imitated two centuries later in the Fountains of the Place de la Concorde in Paris.
The Triton Fountain in the Piazza Barberini (1642), by Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
, is a masterpiece of Baroque sculpture, representing Triton, half-man and half-fish, blowing his horn to calm the waters, following a text by the Roman poet Ovid in the Metamorphoses. The Triton fountain benefited from its location in a valley, and the fact that it was fed by the Aqua Felice aqueduct, restored in 1587, which arrived in Rome at an elevation of above sea level (fasl), a difference of in elevation between the source and the fountain, which meant that the water from this fountain jetted sixteen feet straight up into the air from the conch shell of the triton.
The Piazza Navona became a grand theater of water, with three fountains, built in a line on the site of the Stadium of Domitian. The fountains at either end are by Giacomo della Porta; the Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
fountain to the north, (1572) shows the God of the Sea spearing an octopus, surrounded by tritons, sea horses and mermaids. At the southern end is Il Moro, possibly also a figure of Neptune riding a fish in a conch
Conch () is a common name of a number of different medium-to-large-sized sea snails. Conch shells typically have a high spire and a noticeable siphonal canal (in other words, the shell comes to a noticeable point at both ends).
In North Am ...
shell. In the center is the Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi, (The Fountain of the Four Rivers) (1648–51), a highly theatrical fountain by Bernini, with statues representing rivers from the four continents; the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
, Danube, Plate River and Ganges. Over the whole structure is a Egyptian obelisk, crowned by a cross with the emblem of the Pamphili family, representing Pope Innocent X, whose family palace was on the piazza. The theme of a fountain with statues symbolizing great rivers was later used in the Place de la Concorde (1836–40) and in the Fountain of Neptune in the Alexanderplatz
() ( en, Alexander Square) is a large public square and transport hub in the central Mitte district of Berlin. The square is named after the Russian Tsar Alexander I, which also denotes the larger neighbourhood stretching from in the nort ...
in Berlin (1891). The fountains of Piazza Navona had one drawback - their water came from the Acqua Vergine, which had only a drop from the source to the fountains, which meant the water could only fall or trickle downwards, not jet very high upwards.
The Trevi Fountain is the largest and most spectacular of Rome's fountains, designed to glorify the three different Popes who created it. It was built beginning in 1730 at the terminus of the reconstructed Acqua Vergine aqueduct, on the site of Renaissance fountain by Leon Battista Alberti. It was the work of architect Nicola Salvi and the successive project of Pope Clement XII
Pope Clement XII ( la, Clemens XII; it, Clemente XII; 7 April 16526 February 1740), born Lorenzo Corsini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 July 1730 to his death in February 1740.
Clement presided over the ...
, Pope Benedict XIV and Pope Clement XIII, whose emblems and inscriptions are carried on the attic story, entablature and central niche. The central figure is Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus (; grc-gre, , Ancient Greek pronunciation: , also Ὠγενός , Ὤγενος , or Ὠγήν ) was a Titan son of Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys, and the father of the river gods a ...
, the personification of all the seas and oceans, in an oyster-shell chariot, surrounded by Tritons and Sea Nymphs.
In fact, the fountain had very little water pressure, because the source of water was, like the source for the Piazza Navona fountains, the Acqua Vergine, with a drop. Salvi compensated for this problem by sinking the fountain down into the ground, and by carefully designing the cascade so that the water churned and tumbled, to add movement and drama.Maria Ann Conneli and Marilyn Symmes, ''Fountains as propaganda'', in ''Fountains, Splash and Spectacle – Water and Design from the Renaissance to the Present.'' Edited by Marilyn Symmes. Thames and Hudson, London Wrote historians Maria Ann Conelli and Marilyn Symmes, "On many levels the Trevi altered the appearance, function and intent of fountains and was a watershed for future designs."
Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
, (1648–51)
File:Fontana della Barcaccia 2.jpg, Fontana della Barcaccia, (1627)
File:It.Fontana.del.Carlo.Maderno.1613.03.jpg, Fountains of St. Peter's Square by Carlo Maderno (1614) and Bernini (1677)
File:Roma Fontana del Tritone.jpg, Triton Fountain by Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
, (1642)
File:RomaBerniniFontanaApi.JPG, Fontana delle Api (Fountains of the Bees) (1644)
Baroque fountains of Versailles
Beginning in 1662, King Louis XIV of France began to build a new kind of garden, the Garden à la française, or French formal garden, at thePalace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
. In this garden, the fountain played a central role. He used fountains to demonstrate the power of man over nature, and to illustrate the grandeur of his rule. In the Gardens of Versailles
The Gardens of Versailles (french: Jardins du château de Versailles ) occupy part of what was once the ''Domaine royal de Versailles'', the royal demesne of the château of Versailles. Situated to the west of the palace, the gardens cover som ...
, instead of falling naturally into a basin, water was shot into the sky, or formed into the shape of a fan or bouquet. Dancing water was combined with music and fireworks to form a grand spectacle. These fountains were the work of the descendants of Tommaso Francini, the Italian hydraulic engineer who had come to France during the time of Henry IV and built the Medici Fountain and the Fountain of Diana at Fontainebleau
Fontainebleau (; ) is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southeast of the centre of Paris. Fontainebleau is a sub-prefecture of the Seine-et-Marne department, and it is the seat of the ''arrondissement ...
.
Two fountains were the centerpieces of the Gardens of Versailles, both taken from the myths about Apollo, the sun god, the emblem of Louis XIV, and both symbolizing his power. The Fontaine Latone (1668–70) designed by André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre (; 12 March 1613 – 15 September 1700), originally rendered as André Le Nostre, was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France. He was the landscape architect who designed the gar ...
and sculpted by Gaspard and Balthazar Marsy, represents the story of how the peasants of Lycia tormented Latona and her children, Diana
Diana most commonly refers to:
* Diana (name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
* Diana (mythology), ancient Roman goddess of the hunt and wild animals; later associated with the Moon
* Diana, Princess of Wales (1961–1997) ...
and Apollo, and were punished by being turned into frogs. This was a reminder of how French peasants had abused Louis's mother, Anne of Austria, during the uprising called the Fronde in the 1650s. When the fountain is turned on, sprays of water pour down on the peasants, who are frenzied as they are transformed into creatures.
The other centerpiece of the Gardens, at the intersection of the main axes of the Gardens of Versailles, is the Bassin d'Apollon (1668–71), designed by Charles Le Brun and sculpted by Jean Baptiste Tuby. This statue shows a theme also depicted in the painted decoration in the Hall of Mirrors of the Palace of Versailles: Apollo in his chariot about to rise from the water, announced by Tritons with seashell trumpets. Historians Mary Anne Conelli and Marilyn Symmes wrote, "Designed for dramatic effect and to flatter the king, the fountain is oriented so that the Sun God rises from the west and travels east toward the chateau, in contradiction to nature."
Besides these two monumental fountains, the Gardens over the years contained dozens of other fountains, including thirty-nine animal fountains in the labyrinth depicting the fables of Jean de La Fontaine
Jean de La Fontaine (, , ; 8 July 162113 April 1695) was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his ''Fables'', which provided a model for subsequent fabulists across Euro ...
.
There were so many fountains at Versailles that it was impossible to have them all running at once; when Louis XIV made his promenades, his fountain-tenders turned on the fountains ahead of him and turned off those behind him. Louis built an enormous pumping station, the Machine de Marly, with fourteen water wheels and 253 pumps to raise the water three hundred feet from the River Seine, and even attempted to divert the River Eure to provide water for his fountains, but the water supply was never enough.
Baroque fountains of Peterhof
In Russia,Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
founded a new capital at St. Petersburg in 1703 and built a small Summer Palace and gardens there beside the Neva River
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it i ...
. The gardens featured a fountain of two sea monsters spouting water, among the earliest fountains in Russia.
In 1709, he began constructing a larger palace, Peterhof Palace, alongside the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
, Peter visited France in 1717 and saw the gardens and fountains of Louis XIV at Versailles, Marly and Fontainebleau
Fontainebleau (; ) is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southeast of the centre of Paris. Fontainebleau is a sub-prefecture of the Seine-et-Marne department, and it is the seat of the ''arrondissement ...
. When he returned he began building a vast Garden à la française with fountains at Peterhof. The central feature of the garden was a water cascade, modeled after the cascade at the Château de Marly
The Château de Marly was a French royal residence located in what is now Marly-le-Roi, the commune on the northern edge of the royal park. This was situated west of the palace and garden complex at Versailles. Marly-le-Roi is the town that develo ...
of Louis XIV, built in 1684. The gardens included trick fountains designed to drench unsuspecting visitors, a popular feature of the Italian Renaissance garden.,
In 1800–1802 the Emperor Paul I of Russia
Paul I (russian: Па́вел I Петро́вич ; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1796 until his assassination. Officially, he was the only son of Peter III of Russia, Peter III and Catherine the Great, although Catherine hinted that he w ...
and his successor, Alexander I of Russia, built a new fountain at the foot of the cascade depicting Samson prying open the mouth of a lion, representing Peter's victory over Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
in the Great Northern War in 1721. The fountains were fed by reservoirs in the upper garden, while the Samson fountain was fed by a specially-constructed aqueduct four kilometers in length.
19th century fountains
Fontaine du Palmier
The Fontaine du Palmier (1806-1808) or Fontaine de la Victoire is a monumental fountain located in the Place du Châtelet, between the Théâtre du Châtelet and the Théâtre de la Ville, in the First Arrondissement of Paris.
It was designed to ...
, Paris (1809)
File:Fontaine des Fleuves.jpg, Fountain in the Place de la Concorde in Paris (1840)
File:Trafalgar Square, London 2 - Jun 2009.jpg, Fountain in Trafalgar Square, (1845)
File:Bethesda Fountain in 2007.jpg, Bethesda Fountain in Central Park, New York City (1873)
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
started construction on the first canals bringing drinking water to Paris, fifteen new fountains, the most famous being the Fontaine du Palmier
The Fontaine du Palmier (1806-1808) or Fontaine de la Victoire is a monumental fountain located in the Place du Châtelet, between the Théâtre du Châtelet and the Théâtre de la Ville, in the First Arrondissement of Paris.
It was designed to ...
in the Place du Châtelet
The Place du Châtelet () is a public square in Paris, on the right bank of the river Seine, on the borderline between the 1st and 4th arrondissements. It lies at the north end of the Pont au Change, a bridge that connects the Île de la Cité, ...
, (1896–1808), celebrating his military victories.
He also restored and put back into service some of the city's oldest fountains, such as the Medici Fountain. Two of Napoleon's fountains, the Chateau d'Eau and the fountain in the Place des Vosges, were the first purely decorative fountains in Paris, without water taps for drinking water.
Louis-Philippe (1830–1848) continued Napoleon's work, and added some of Paris's most famous fountains, notably the Fontaines de la Concorde (1836–1840) and the fountains in the Place des Vosges.
Following a deadly cholera epidemic in 1849, Louis Napoleon decided to completely rebuild the Paris water supply system, separating the water supply for fountains from the water supply for drinking. The most famous fountain built by Louis Napoleon was the Fontaine Saint-Michel, part of his grand reconstruction of Paris boulevards. Louis Napoleon relocated and rebuilt several earlier fountains, such as the Medici Fountain and the Fontaine de Leda
Fontaine is a French word meaning fountain or natural spring or an area of natural springs.
Places France
*Beaulieu-les-Fontaines, in the Oise ''département''
*Bierry-les-Belles-Fontaines, in the Yonne ''département''
*Cailloux-sur-Fontaines, ...
, when their original sites were destroyed by his construction projects.
In the mid-nineteenth century the first fountains were built in the United States, connected to the first aqueducts bringing drinking water from outside the city. The first fountain in Philadelphia, at Centre Square, opened in 1809, and featured a statue by sculptor William Rush. The first fountain in New York City, in City Hall Park, opened in 1842, and the first fountain in Boston was turned on in 1848. The first famous American decorative fountain was the Bethesda Fountain in Central Park in New York City, opened in 1873.
The 19th century also saw the introduction of new materials in fountain construction; cast iron (the Fontaines de la Concorde); glass (the Crystal Fountain in London (1851)) and even aluminium (the Shaftesbury Memorial Fountain in Piccadilly Circus, London, (1897)).Stephen Astley, ''The Fountains in Trafalagar Square'', in ''Fountains- Splash and Spectacle – Water and Design from the Renaissance to the Present'', edited by Marilyn Symmes, 1998.
The invention of steam pumps meant that water could be supplied directly to homes, and pumped upward from fountains. The new fountains in Trafalgar Square (1845) used steam pumps from an artesian well. By the end of the 19th century fountains in big cities were no longer used to supply drinking water, and were simply a form of art and urban decoration.
Another fountain innovation of the 19th century was the illuminated fountain: The Bartholdi Fountain
The Bartholdi Fountain is a monumental public fountain, designed by Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi, who later created the Statue of Liberty. The fountain was originally made for the 1876 Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and is ...
at the Philadelphia Exposition of 1876 was illuminated by gas lamps. In 1884 a fountain in Britain featured electric lights shining upward through the water. The Exposition Universelle (1889)
The Exposition Universelle of 1889 () was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 5 May to 31 October 1889. It was the fourth of eight expositions held in the city between 1855 and 1937. It attracted more than thirty-two million visitors. The ...
which celebrated the 100th anniversary of the French Revolution featured a fountain illuminated by electric lights shining up though the columns of water. The fountains, located in a basin forty meters in diameter, were given color by plates of colored glass inserted over the lamps. The Fountain of Progress gave its show three times each evening, for twenty minutes, with a series of different colors.
20th century fountains
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after the Northern European country's political and financial capital, Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 91,407 (as of 2021). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of ...
, Estonia (1948)
File:Strawinsky fountain (Tinguely fountain) pic1.jpg, Stravinsky Fountain, next to the Pompidou Center, Paris (1983)
File:3872ParigiLouvre.JPG, Fontaine de la Pyramide, Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
of the Louvre, (1988)
File:Cristaux.Jean Yves Lechevallier.jpg, Fontaine Cristaux, Homage to Béla Bartok, Jean-Yves Lechevallier, Paris, (1980)
File:Fountain near Rashtrapati Bhavan.jpg, Fountain at Raisina Hill, Rajpath near Rashtrapati Bhavan in Delhi (1929)
Fountains of International Expositions
The Fountains of International Expositions in London, Paris, New York and other cities between 1851 and 1964 combined architecture, technology and theatre. They introduced the first illuminated fountains, the first fountains made with glass and oth ...
).
Only a handful of fountains were built in Paris between 1940 and 1980. The most important ones built during that period were on the edges of the city, on the west, just outside the city limits, at La Défense
La Défense () is a major business district in France, located west of the city limits of Paris. It is part of the Paris metropolitan area in the Île-de-France region, located in the department of Hauts-de-Seine in the communes of Courbevoie, ...
, and to the east at the Bois de Vincennes.
Between 1981 and 1995, during the terms of President François Mitterrand
François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he ...
and Culture Minister Jack Lang, and of Mitterrand's bitter political rival, Paris Mayor Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac (, , ; 29 November 193226 September 2019) was a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. Chirac was previously Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988, as well as Ma ...
(Mayor from 1977 until 1995), the city experienced a program of monumental fountain building that exceeded that of Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
or Louis Philippe. More than one hundred fountains were built in Paris in the 1980s, mostly in the neighborhoods outside the center of Paris, where there had been few fountains before These included the Fontaine Cristaux, homage to Béla Bartók
Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as H ...
by Jean-Yves Lechevallier (1980); the Stravinsky Fountain next to the Pompidou Center, by sculptors Niki de Saint Phalle and Jean Tinguely (1983); the fountain of the Pyramid of the Louvre by I.M. Pei, (1989), the Buren Fountain by sculptor Daniel Buren
Daniel Buren (born 25 March 1938, in Boulogne-Billancourt) is a French conceptual artist, painter, and sculptor. He has won numerous awards including the Golden Lion for best pavilion at the Venice Biennale (1986), the International Award for ...
, Les Sphérades fountain, both in the Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal ...
, and the fountains of Parc André-Citroën. The Mitterrand-Chirac fountains had no single style or theme. Many of the fountains were designed by famous sculptors or architects, such as Jean Tinguely, I.M. Pei, Claes Oldenburg and Daniel Buren
Daniel Buren (born 25 March 1938, in Boulogne-Billancourt) is a French conceptual artist, painter, and sculptor. He has won numerous awards including the Golden Lion for best pavilion at the Venice Biennale (1986), the International Award for ...
, who had radically different ideas of what a fountain should be. Some were solemn, and others were whimsical. Most made little effort to blend with their surroundings - they were designed to attract attention.
Fountains built in the United States between 1900 and 1950 mostly followed European models and classical styles.
The ''Samuel Francis Dupont Memorial Fountain
The Dupont Circle Fountain, formally known as the Rear Admiral Samuel Francis Dupont Memorial Fountain, is a fountain located in the center of Dupont Circle in Washington, D.C. It honors Rear Admiral Samuel Francis Du Pont, a prominent American ...
'', in Dupont Circle, Washington D.C., was designed and created by Henry Bacon and Daniel Chester French
Daniel Chester French (April 20, 1850 – October 7, 1931) was an American sculptor of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, best known for his 1874 sculpture ''The Minute Man'' in Concord, Massachusetts, and his 1920 monume ...
, the architect and sculptor of the Lincoln Memorial
The Lincoln Memorial is a U.S. national memorial built to honor the 16th president of the United States, Abraham Lincoln. It is on the western end of the National Mall in Washington, D.C., across from the Washington Monument, and is in the ...
, in 1921, in a pure neoclassical style.
The '' Buckingham Fountain'' in Grant Park in Chicago was one of the first American fountains to use powerful modern pumps to shoot water as high as into the air.
The ''Fountain of Prometheus,'' built at the Rockefeller Center in New York City in 1933, was the first American fountain in the Art-Deco style.
After World War II, fountains in the United States became more varied in form. Some, like Ruth Asawa's ''Andrea'' (1968) and the Vaillancourt Fountain (1971), both located in San Francisco, were pure works of sculpture. Other fountains, like the ''Frankin Roosevelt Memorial Waterfall'' (1997), by architect Lawrence Halprin, were designed as landscapes to illustrate themes. This fountain is part of the Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial in Washington D.C., which has four outdoor "rooms" illustrating his presidency. Each "room" contains a cascade or waterfall; the cascade in the third room illustrates the turbulence of the years of the World War II. Halprin wrote at an early stage of the design; "the whole environment of the memorial becomes sculpture: to touch, feel, hear and contact - with all the senses."
The end of the 20th century the development of high-shooting fountains, beginning with the Jet d'eau in Geneva in 1951, and followed by taller and taller fountains in the United States and the Middle East. The highest fountain today in the King Fahd's Fountain
King Fahd's Fountain ( ar, نافورة الملك فهد), also known as the Jeddah Fountain, is in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. It is the tallest fountain of its type in the world.
Overview
The fountain was donated to the city of Jeddah by King Fahd, ...
in Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), also spelled Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; ar, , Jidda, ), is a city in the Hejaz region of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and the country's commercial center. Established in the 6th century BC as a fishing village, Jeddah's pro ...
, Saudi Arabia.
It also saw the increasing popularity of the musical fountain, which combined water, music and light, choreographed by computers. (See Musical fountain below).
Contemporary fountains (2001–present)
 The fountain called Bit.Fall by German artist Julius Popp (2005) uses digital technologies to spell out words with water. The fountain is run by a statistical program which selects words at random from news stories on the Internet. It then recodes these words into pictures. Then 320 nozzles inject the water into electromagnetic valves. The program uses rasterization and bitmap technologies to synchronize the valves so drops of water form an image of the words as they fall. According to Popp, the sheet of water is "a metaphor for the constant flow of information from which we cannot escape."
Crown Fountain is an interactive fountain and
The fountain called Bit.Fall by German artist Julius Popp (2005) uses digital technologies to spell out words with water. The fountain is run by a statistical program which selects words at random from news stories on the Internet. It then recodes these words into pictures. Then 320 nozzles inject the water into electromagnetic valves. The program uses rasterization and bitmap technologies to synchronize the valves so drops of water form an image of the words as they fall. According to Popp, the sheet of water is "a metaphor for the constant flow of information from which we cannot escape."
Crown Fountain is an interactive fountain and video sculpture A video sculpture is a type of video installation that integrates video into an object, environment, site or performance. The nature of video sculpture is that it utilizes the material of video in an innovative way in space and time, different from ...
feature in Chicago's Millennium Park. Designed by Catalan artist Jaume Plensa, it opened in July 2004. The fountain is composed of a black granite reflecting pool placed between a pair of glass brick towers. The towers are tall, and they use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to display digital videos on their inward faces. Construction and design of the ''Crown Fountain'' cost US$17 million. Weather permitting, the water operates from May to October, intermittently cascading down the two towers and spouting through a nozzle on each tower's front face.
Few new fountains have been built in Paris since 2000. The most notable is La Danse de la fontaine emergente
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figure ...
(2008), located on Place Augusta-Holmes, rue Paul Klee, in the 13th arrondissement. It was designed by the French-Chinese sculptor Chen Zhen (1955-2000), shortly before his death in 2000, and finished through the efforts of his spouse and collaborator. It shows a dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
, in stainless steel, glass and plastic, emerging and submerging from the pavement of the square. The fountain is in three parts. A bas-relief of the dragon is fixed on the wall of the structure of the water-supply plant, and the dragon seems to be emerging from the wall and plunging underground. This part of the dragon is opaque. The second and third parts depict the arch of the dragon's back coming out of the pavement. These parts of the dragon are transparent, and water under pressure flows visibly within, and is illuminated at night.
Musical fountains
 Musical fountains create a theatrical spectacle with music, light and water, usually employing a variety of programmable spouts and water jets controlled by a computer.
Musical fountains were first described in the 1st century AD by the Greek scientist and engineer Hero of Alexandria in his book ''Pneumatics''. Hero described and provided drawings of "A bird made to whistle by flowing water," "A Trumpet sounded by flowing water," and "Birds made to sing and be silent alternately by flowing water." In Hero's descriptions, water pushed air through musical instruments to make sounds. It is not known if Hero made working models of any of his designs.
During the Italian Renaissance, the most famous musical fountains were located in the gardens of the Villa d'Este, in
Musical fountains create a theatrical spectacle with music, light and water, usually employing a variety of programmable spouts and water jets controlled by a computer.
Musical fountains were first described in the 1st century AD by the Greek scientist and engineer Hero of Alexandria in his book ''Pneumatics''. Hero described and provided drawings of "A bird made to whistle by flowing water," "A Trumpet sounded by flowing water," and "Birds made to sing and be silent alternately by flowing water." In Hero's descriptions, water pushed air through musical instruments to make sounds. It is not known if Hero made working models of any of his designs.
During the Italian Renaissance, the most famous musical fountains were located in the gardens of the Villa d'Este, in Tivoli
Tivoli may refer to:
* Tivoli, Lazio, a town in Lazio, Italy, known for historic sites; the inspiration for other places named Tivoli
Buildings
* Tivoli (Baltimore, Maryland), a mansion built about 1855
* Tivoli Building (Cheyenne, Wyoming), a ...
. which were created between 1550 and 1572. Following the ideas of Hero of Alexandria, the Fountain of the Owl used a series of bronze pipes like flutes to make the sound of birds. The most famous feature of the garden was the great Organ Fountain. It was described by the French philosopher Michel de Montaigne
Michel Eyquem, Sieur de Montaigne ( ; ; 28 February 1533 – 13 September 1592), also known as the Lord of Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a liter ...
, who visited the garden in 1580: "The music of the Organ Fountain is true music, naturally created ... made by water which falls with great violence into a cave, rounded and vaulted, and agitates the air, which is forced to exit through the pipes of an organ. Other water, passing through a wheel, strikes in a certain order the keyboard of the organ. The organ also imitates the sound of trumpets, the sound of cannon, and the sound of muskets, made by the sudden fall of water ... The Organ Fountain fell into ruins, but it was recently restored and plays music again.
Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
created the idea of the modern musical fountain by staging spectacles in the Gardens of Versailles
The Gardens of Versailles (french: Jardins du château de Versailles ) occupy part of what was once the ''Domaine royal de Versailles'', the royal demesne of the château of Versailles. Situated to the west of the palace, the gardens cover som ...
, using music and fireworks to accompany the flow of the fountains.
The great international expositions held in Philadelphia, London and Paris featured the ancestors of the modern musical fountain. They introduced the first fountains illuminated by gas lights (Philadelphia in 1876); and the first fountains illuminated by electric lights (London in 1884 and Paris in 1889). The Exposition Universelle (1900)
The Exposition Universelle of 1900, better known in English as the 1900 Paris Exposition, was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 14 April to 12 November 1900, to celebrate the achievements of the past century and to accelerate developmen ...
in Paris featured fountains illuminated by colored lights controlled by a keyboard.Virginie Grandval, pg. 229 The Paris Colonial Exposition of 1931 presented the Théâtre d'eau, or water theater, located in a lake, with performance of dancing water. The Exposition Internationale des Arts et Techniques dans la Vie Moderne (1937) had combined arches and columns of water from fountains in the Seine with light, and with music from loudspeakers on eleven rafts anchored in the river, playing the music of the leading composers of the time. (See International Exposition Fountains, above.)
Today some of the best-known musical fountains in the world are at the Bellagio Hotel & Casino in Las Vegas, (2009); the Dubai Fountain
The Dubai Fountain is a choreographed fountain system located on the 12 hectare (30 acre) artificial Burj Khalifa Lake, at the center of the Downtown Dubai development in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It was designed by WET Design, a California-bas ...
in the United Arab Emirates; the World of Color at Disney California Adventure Park (2010) and Aquanura at the Efteling in the Netherlands (2012).
musical fountain
A musical fountain, also known as a fairy fountain, prismatic fountain or dancing fountain, is a type of choreographed fountain that creates aesthetic designs as a form of entertainment. The displays are commonly synchronised to music and also ...
of the Bellagio Hotel & Casino in Las Vegas, with pivoting nozzles to vary the patterns of the water, controlled by computers and accompanied by music (1998)
File:Dubai Fountain 1.JPG, Dubai Fountain
The Dubai Fountain is a choreographed fountain system located on the 12 hectare (30 acre) artificial Burj Khalifa Lake, at the center of the Downtown Dubai development in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It was designed by WET Design, a California-bas ...
in the United Arab Emirates (2009) can shoot water 150 meters in the air, or present computer-choreographed water dancing to music
File:Inventions_Show_Multimedia_Fountain_Roshen.jpg, Multimedia Fountain Roshen
Multimedia Fountain Roshen (Vinnytsia Fountain "Roshen") was built on the river Southern Buh in Vinnytsia City near Festivalny Isle (Kempa Isle). This is the only multimedia fountain in Ukraine and the largest floating fountain in Europe. Fountai ...
is the only one in Ukraine and the largest floating fountain in Europe, built in the river Southern Buh in Vinnytsia City near Festivalny Isle (Kempa Isle)
File:Multimedia Fountain Kangwon Land Resort.jpg, Multimedia Fountain Kangwon Land is considered Asia's largest musical fountain.
Splash fountains

 A splash fountain or bathing fountain is intended for people to come in and cool off on hot summer days. These fountains are also referred to as interactive fountains. These fountains are designed to allow easy access, and feature nonslip surfaces, and have no standing water, to eliminate possible drowning hazards, so that no lifeguards or supervision is required. These splash pads are often located in public pools, public parks, or public playgrounds (known as "spraygrounds"). In some splash fountains, such as Dundas Square in Toronto, Canada, the water is heated by solar energy captured by the special dark-colored granite slabs. The fountain at Dundas Square features 600 ground nozzles arranged in groups of 30 (3 rows of 10 nozzles). Each group of 30 nozzles is located beneath a stainless steel grille. Twenty such grilles are arranged in two rows of 10, in the middle of the main walkway through Dundas Square.
A splash fountain or bathing fountain is intended for people to come in and cool off on hot summer days. These fountains are also referred to as interactive fountains. These fountains are designed to allow easy access, and feature nonslip surfaces, and have no standing water, to eliminate possible drowning hazards, so that no lifeguards or supervision is required. These splash pads are often located in public pools, public parks, or public playgrounds (known as "spraygrounds"). In some splash fountains, such as Dundas Square in Toronto, Canada, the water is heated by solar energy captured by the special dark-colored granite slabs. The fountain at Dundas Square features 600 ground nozzles arranged in groups of 30 (3 rows of 10 nozzles). Each group of 30 nozzles is located beneath a stainless steel grille. Twenty such grilles are arranged in two rows of 10, in the middle of the main walkway through Dundas Square.
Drinking fountain
A water fountain or drinking fountain is designed to provide drinking water and has a basin arrangement with either continuously running water or a tap. The drinker bends down to the stream of water and swallows water directly from the stream. Modern indoor drinking fountains may incorporate filters to remove impurities from the water and chillers to reduce its temperature. In some regional dialects, water fountains are called '' bubblers''. Water fountains are usually found in public places, like schools, rest areas, libraries, and grocery stores. Many jurisdictions require water fountains to be wheelchair accessible (by sticking out horizontally from the wall), and to include an additional unit of a lower height for children and short adults. The design that this replaced often had one spout atop a refrigeration unit. In 1859,The Metropolitan Drinking Fountain and Cattle Trough Association
The Metropolitan Drinking Fountain and Cattle Trough Association was an association set up in London by Samuel Gurney, a member of Parliament and philanthropist, and Edward Thomas Wakefield, a barrister, in 1859 to provide free drinking wat ...
was established to promote the provision of drinking water for people and animals in the United Kingdom and overseas. More recently, in 2010, the FindaFountain campaign was launched in the UK to encourage people to use drinking fountains instead of environmentally damaging bottled water. A map showing the location of UK drinking water fountains is published on the FindaFountain website.
How fountains work

 From Roman times until the end of the 19th century, fountains operated by gravity, requiring a source of water higher than the fountain itself to make the water flow. The greater the difference between the elevation of the source of water and the fountain, the higher the water would go upwards from the fountain.
In Roman cities, water for fountains came from lakes and rivers and springs in the hills, brought into city in aqueducts and then distributed to fountains through a system of lead pipes.
From the Middle Ages onwards, fountains in villages or towns were connected to springs, or to channels which brought water from lakes or rivers. In Provence, a typical village fountain consisted of a pipe or underground duct from a spring at a higher elevation than the fountain. The water from the spring flowed down to the fountain, then up a tube into a bulb-shaped stone vessel, like a large vase with a cover on top. The inside of the vase, called the ''bassin de répartition'', was filled with water up to a level just above the mouths of the canons, or spouts, which slanted downwards. The water poured down through the canons, creating a siphon, so that the fountain ran continually.
In cities and towns, residents filled vessels or jars of water jets from the canons of the fountain or paid a water porter to bring the water to their home. Horses and domestic animals could drink the water in the basin below the fountain. The water not used often flowed into a separate series of basins, a lavoir, used for washing and rinsing clothes. After being used for washing, the same water then ran through a channel to the town's kitchen garden. In Provence, since clothes were washed with ashes, the water that flowed into the garden contained potassium, and was valuable as fertilizer.
The most famous fountains of the Renaissance, at the Villa d'Este in Tivoli, were located on a steep slope near a river; the builders ran a channel from the river to a large fountain at top of the garden, which then fed other fountains and basins on the levels below. The fountains of Rome, built from the Renaissance through the 18th century, took their water from rebuilt Roman aqueducts which brought water from lakes and rivers at a higher elevation than the fountains. Those fountains with a high source of water, such as the Triton Fountain, could shoot water in air. Fountains with a lower source, such as the Trevi Fountain, could only have water pour downwards. The architect of the Trevi Fountain placed it below street level to make the flow of water seem more dramatic.
The fountains of Versailles depended upon water from reservoirs just above the fountains. As King
From Roman times until the end of the 19th century, fountains operated by gravity, requiring a source of water higher than the fountain itself to make the water flow. The greater the difference between the elevation of the source of water and the fountain, the higher the water would go upwards from the fountain.
In Roman cities, water for fountains came from lakes and rivers and springs in the hills, brought into city in aqueducts and then distributed to fountains through a system of lead pipes.
From the Middle Ages onwards, fountains in villages or towns were connected to springs, or to channels which brought water from lakes or rivers. In Provence, a typical village fountain consisted of a pipe or underground duct from a spring at a higher elevation than the fountain. The water from the spring flowed down to the fountain, then up a tube into a bulb-shaped stone vessel, like a large vase with a cover on top. The inside of the vase, called the ''bassin de répartition'', was filled with water up to a level just above the mouths of the canons, or spouts, which slanted downwards. The water poured down through the canons, creating a siphon, so that the fountain ran continually.
In cities and towns, residents filled vessels or jars of water jets from the canons of the fountain or paid a water porter to bring the water to their home. Horses and domestic animals could drink the water in the basin below the fountain. The water not used often flowed into a separate series of basins, a lavoir, used for washing and rinsing clothes. After being used for washing, the same water then ran through a channel to the town's kitchen garden. In Provence, since clothes were washed with ashes, the water that flowed into the garden contained potassium, and was valuable as fertilizer.
The most famous fountains of the Renaissance, at the Villa d'Este in Tivoli, were located on a steep slope near a river; the builders ran a channel from the river to a large fountain at top of the garden, which then fed other fountains and basins on the levels below. The fountains of Rome, built from the Renaissance through the 18th century, took their water from rebuilt Roman aqueducts which brought water from lakes and rivers at a higher elevation than the fountains. Those fountains with a high source of water, such as the Triton Fountain, could shoot water in air. Fountains with a lower source, such as the Trevi Fountain, could only have water pour downwards. The architect of the Trevi Fountain placed it below street level to make the flow of water seem more dramatic.
The fountains of Versailles depended upon water from reservoirs just above the fountains. As King Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
built more fountains, he was forced to construct an enormous complex of pumps, called the Machine de Marly, with fourteen water wheels and 220 pumps, to raise water 162 meters above the Seine River to the reservoirs to keep his fountains flowing. Even with the Machine de Marly, the fountains used so much water that they could not be all turned on at the same time. Fontainiers watched the progress of the King when he toured the gardens and turned on each fountain just before he arrived.
The architects of the fountains at Versailles designed specially-shaped nozzles, or tuyaux, to form the water into different shapes, such as fans, bouquets, and umbrellas.
In Germany, some courts and palace gardens were situated in flat areas, thus fountains depending on pumped pressurized water were developed at a fairly early point in history. The Great Fountain in Herrenhausen Gardens at Hanover was based on ideas of Gottfried Leibniz conceived in 1694 and was inaugurated in 1719 during the visit of George I. After some improvements, it reached a height of some 35 m in 1721 which made it the highest fountain in European courts. The fountains at the Nymphenburg Palace initially were fed by water pumped to water towers, but as from 1803 were operated by the water powered Nymphenburg Pumping Stations which are still working.
Beginning in the 19th century, fountains ceased to be used for drinking water and became purely ornamental. By the beginning of the 20th century, cities began using steam pumps and later electric pumps to send water to the city fountains. Later in the 20th century, urban fountains began to recycle their water through a closed recirculating system. An electric pump, often placed under the water, pushes the water through the pipes. The water must be regularly topped up to offset water lost to evaporation, and allowance must be made to handle overflow after heavy rain.
In modern fountains a water filter, typically a media filter
A media filter is a type of filter that uses a bed of sand, peat, shredded tires, foam, crushed glass, geo-textile fabric, anthracite, crushed granite or other material to filter water for drinking, swimming pools, aquaculture, irrigation, storm ...
, removes particles from the water—this filter requires its own pump to force water through it and plumbing to remove the water from the pool to the filter and then back to the pool. The water may need chlorination or anti-algal treatment, or may use biological methods to filter and clean water.
The pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they u ...
s, filter, electrical switch box and plumbing controls are often housed in a "plant room".
Low-voltage lighting, typically 12 volt direct current, is used to minimise electrical hazards. Lighting is often submerged and must be suitably designed. High wattage lighting (incandescent and halogen) either as submerged lighting
Submerge (and its variants) means to be covered by something (usually a liquid), such as being underwater:
* Submerged arc welding
* Submerged continent
* Submerged forest
* Submerged floating tunnel
* Submerged specific gravity
* Submergent co ...
or accent lighting on waterwall fountains have been implicated in every documented Legionnaires' disease
Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of ''Legionella'' bacteria, quite often '' Legionella pneumophila''. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, muscle pains, and headaches. Naus ...
outbreak associated with fountains. This is detailed in the "Guidelines for Control of Legionella in Ornamental Features".
Floating fountains are also popular for ponds and lakes; they consist of a float pump nozzle and water chamber.
The tallest fountains in the world
 *
* King Fahd's Fountain
King Fahd's Fountain ( ar, نافورة الملك فهد), also known as the Jeddah Fountain, is in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. It is the tallest fountain of its type in the world.
Overview
The fountain was donated to the city of Jeddah by King Fahd, ...
(1985) in Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), also spelled Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; ar, , Jidda, ), is a city in the Hejaz region of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and the country's commercial center. Established in the 6th century BC as a fishing village, Jeddah's pro ...
, Saudi Arabia. The fountain jets water above the Red Sea and is currently the tallest fountain in the world.
* The World Cup Fountain
The World Cup Fountain was a fountain built to commemorate the 2002 FIFA World Cup co-hosted by South Korea and Japan. The World Cup Fountain is located in the Han River in Seoul, South Korea, between the World Cup Stadium and Seonyudo Park. The ...
in the Han-gang River in Seoul, Korea (2002), advertises a height of .
* The Gateway Geyser (1995), next to the Mississippi River in St. Louis, Missouri, shoots water in the air. It is the tallest fountain in the United States.
* Port Fountain (2006) in Karachi, Pakistan, rises to height of making it the fourth tallest fountain.
* Fountain Park, Fountain Hills
Fountain Hills is a town in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States. Known for its impressive fountain, once the tallest in the world, it borders the Fort McDowell Yavapai Nation, Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community, and Scottsdale. The ...
, Arizona (1970). Can reach when all three pumps are operating, but normally runs at .
* The Dubai Fountain
The Dubai Fountain is a choreographed fountain system located on the 12 hectare (30 acre) artificial Burj Khalifa Lake, at the center of the Downtown Dubai development in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It was designed by WET Design, a California-bas ...
, opened in 2009 next to Burj Khalifa
The Burj Khalifa (; ar, برج خليفة, , Khalifa Tower), known as the Burj Dubai prior to its inauguration in 2010, is a skyscraper in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It is known for being the world’s tallest building. With a total height ...
, the world's tallest building. The fountain performs once every half-hour to recorded music, and shoots water to height of . The fountain also has extreme shooters, not used in every show, which can reach .
* The Captain James Cook Memorial Jet in Canberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
(1970),
* The Jet d'eau, in Geneva (1951),
Gallery of notable fountains around the world
Jet d'Eau
The Jet d'Eau (, ''Water-Jet'') is a large fountain in Geneva, Switzerland and is one of the city's most famous landmarks, being featured on the city's official tourism web site and on the official logo for Geneva's hosting of group stage matches ...
fountain in Geneva, Switzerland (1951), the first modern high-shooting fountain
File:Nürnberg Schöner Brunnen Totale.jpg, The Schöner Brunnen
Schöner Brunnen (en:beautiful fountain) is a 14th-century fountain located on Nuremberg's main market next to the town hall and is considered one of the main attractions of the city's Historical Mile. The fountain is approximately 19 meters high a ...
(Beautiful Fountain) in Nuremberg, Germany. (1385–96)
File:Samson and Lion Fountain.jpg, Samson and the Lion Fountain (1800–02), Peterhof, Russia
File:BuckinghamFountain ChicagoIL.jpg, Buckingham Fountain (1927) in Chicago
File:Dubai_Fountain_performing_"Bassbor_Al_Fourgakom".jpg, Dubai Fountain
The Dubai Fountain is a choreographed fountain system located on the 12 hectare (30 acre) artificial Burj Khalifa Lake, at the center of the Downtown Dubai development in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It was designed by WET Design, a California-bas ...
(2008), a computer-programmed musical fountain
A musical fountain, also known as a fairy fountain, prismatic fountain or dancing fountain, is a type of choreographed fountain that creates aesthetic designs as a form of entertainment. The displays are commonly synchronised to music and also ...
, is long and can jet water into the air
File:El Alamein Fountain, Sydney.jpg, The El Alamein Fountain (1959–61) in Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
, designed by Robert Woodward, was the first "dandelion" fountain
File:Tammelantori104, Tampere, Finland.JPG, The Emil Aaltonen Memorial (1969), a 4.5 metres (15 ft) tall fountain at the Tammela Square
Tammelantori is a market square in the Tammela district in the center of Tampere in Pirkanmaa, Finland. It is one of Tampere's most significant marketplaces, which is very popular, especially during the summer. The market is very famous for its c ...
in Tampere, designed by Raimo Utriainen
Raimo Utriainen (24 September 1927, Kuopio — 27 April 1994, Helsinki) was a Finnish visual artist, best known as a modernist sculptor and a moderniser of Finnish sculpture.
Biography
Utriainen initially studied mathematics at the University o ...
File:Parque de la exposicion1.jpg, Fountains in the Park of the Reserve, Lima, Peru
See also
* Wishing well, for the practice of dropping coins into fountainsBibliography
* Helen Attlee, ''Italian Gardens – A Cultural History''. Frances Lincoln Limited, London, 2006. * ''Paris et ses Fontaines, del la Renaissance a nos jours'', edited by Béatrice de Andia, Dominique Massounie, Pauline Prevost-Marcilhacy and Daniel Rabreau, from the Collection Paris et son Patrimoine, Paris, 1995. * Les Aqueducs de la ville de Rome, translation and commentary by Pierre Grimal, Société d'édition Les Belles Lettres, Paris, 1944. * Louis Plantier, ''Fontaines de Provence et de la Côte d'Azur'', Édisud, Aix-en-Provence, 2007 * Frédérick Cope and Tazartes Maurizia, ''Les Fontaines de Rome'', Éditions Citadelles et Mazenod, 2004 * André Jean Tardy, ''Fontaines toulonnaises'', Les Éditions de la Nerthe, 2001. * Hortense Lyon, La Fontaine Stravinsky, Collection Baccalauréat arts plastiques 2004, Centre national de documentation pédagogique * Marilyn Symmes (editor), ''Fountains-Splash and Spectacle- Water and Design from the Renaissance to the Present.'' Thames and Hudson, in cooperation with the Cooper-Hewitt National Design Museum of the Smithsonian Institution. (1998). * Yves Porter et Arthur Thévenart, ''Palais et Jardins de Perse'', Flammarion, Paris (2002). (). * Raimund O.A. Becker-Ritterspach, ''Water Conduits in the Kathmandu Valley'', Munshriram Manoharlal Publishers, Pvt.Ltd, New Delhi 1995,References
External links
King Fahd Fountain tops in the World aTallest fountain
{{Authority control Water Landscape architecture Landscape garden features Architectural elements Outdoor sculptures Public art