Fort Of São Sebastião (Angra Do Heroísmo) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make").
From very early history to modern times,
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make").
From very early history to modern times,

 Many United States Army installations are known as ''forts'', although they are not always fortified. Indeed, during the pioneering era of North America, many outposts on the frontiers, even non-military outposts, were referred to generically as ''forts''. Larger military installations may be called ''fortresses''; smaller ones were once known as ''fortalices''. The word ''fortification'' can also refer to the practice of improving an area's defense with defensive works. City walls are fortifications but are not necessarily called ''fortresses''.
The art of setting out a military camp or constructing a fortification traditionally has been called ''
Many United States Army installations are known as ''forts'', although they are not always fortified. Indeed, during the pioneering era of North America, many outposts on the frontiers, even non-military outposts, were referred to generically as ''forts''. Larger military installations may be called ''fortresses''; smaller ones were once known as ''fortalices''. The word ''fortification'' can also refer to the practice of improving an area's defense with defensive works. City walls are fortifications but are not necessarily called ''fortresses''.
The art of setting out a military camp or constructing a fortification traditionally has been called ''



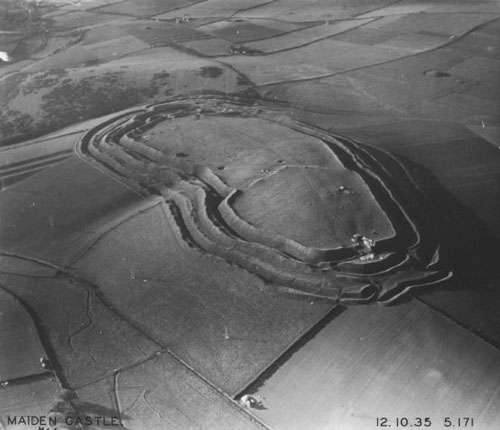
 The Oppidum of Manching (German: Oppidum von Manching) was a large Celtic proto-urban or city-like settlement at modern-day Manching (near Ingolstadt), Bavaria (Germany). The settlement was founded in the 3rd century BC and existed until c. 50–30 BC. It reached its largest extent during the late La Tène period (late 2nd century BC), when it had a size of 380 hectares. At that time, 5,000 to 10,000 people lived within its 7.2 km long walls. The oppidum of
The Oppidum of Manching (German: Oppidum von Manching) was a large Celtic proto-urban or city-like settlement at modern-day Manching (near Ingolstadt), Bavaria (Germany). The settlement was founded in the 3rd century BC and existed until c. 50–30 BC. It reached its largest extent during the late La Tène period (late 2nd century BC), when it had a size of 380 hectares. At that time, 5,000 to 10,000 people lived within its 7.2 km long walls. The oppidum of
 A number of forts dating from the
A number of forts dating from the
 Large tempered earth (i.e. rammed earth) walls were built in
Large tempered earth (i.e. rammed earth) walls were built in
 The Igorots built forts made of stone walls that averaged several meters in width and about two to three times the width in height around 2000 BC.Ancient and Pre-Spanish Era of the Philippines
The Igorots built forts made of stone walls that averaged several meters in width and about two to three times the width in height around 2000 BC.Ancient and Pre-Spanish Era of the Philippines
. Accessed September 04, 2008. The Muslim Filipinos of the south built strong fortresses called ''kota'' or ''moong'' to protect their communities. Usually, many of the occupants of these kotas are entire families rather than just warriors. Lords often had their own kotas to assert their right to rule, it served not only as a military installation but as a palace for the local Lord. It is said that at the height of the Maguindanao Sultanate's power, they blanketed the areas around Western Mindanao with Kotas and other fortifications to block the Spanish advance into the region. These kotas were usually made of stone and bamboo or other light materials and surrounded by trench networks. As a result, some of these kotas were burned easily or destroyed. With further Spanish campaigns in the region, the Sultanate was subdued and majority of Kotas dismantled or destroyed. Kotas were not only used by the Muslims as defense against Spaniards and other foreigners, renegades and rebels also built fortifications in defiance of other chiefs in the area. During the American occupation, rebels built strongholds and the Datus, Rajahs or Sultans often built and reinforced their kotas in a desperate bid to maintain rule over their subjects and their land. Many of these forts were also destroyed by American expeditions, as a result, very very few kotas still stand to this day. Notable Kotas: * Kota Selurong: an outpost of the Bruneian Empire in Luzon, later became the City of Manila. * Kuta Wato/Kota Bato: Literally translates to "stone fort" the first known stone fortification in the country, its ruins exist as the "Kutawato Cave Complex" * Kota Sug/Jolo: The capital and seat of the Sultanate of Sulu. When it was occupied by the Spaniards in the 1870s they converted the kota into the world's smallest walled city.
 During Muhammad's era in Arabia, many tribes made use of fortifications. In the
During Muhammad's era in Arabia, many tribes made use of fortifications. In the

 The founding of urban centres was an important means of territorial expansion and many cities, especially in eastern Europe, were founded precisely for this purpose during the period of Eastern Colonisation. These cities are easy to recognise due to their regular layout and large market spaces. The fortifications of these settlements were continuously improved to reflect the current level of military development.
During the Renaissance era, the Venetian Republic raised great walls around cities, and the finest examples, among others, are in
The founding of urban centres was an important means of territorial expansion and many cities, especially in eastern Europe, were founded precisely for this purpose during the period of Eastern Colonisation. These cities are easy to recognise due to their regular layout and large market spaces. The fortifications of these settlements were continuously improved to reflect the current level of military development.
During the Renaissance era, the Venetian Republic raised great walls around cities, and the finest examples, among others, are in
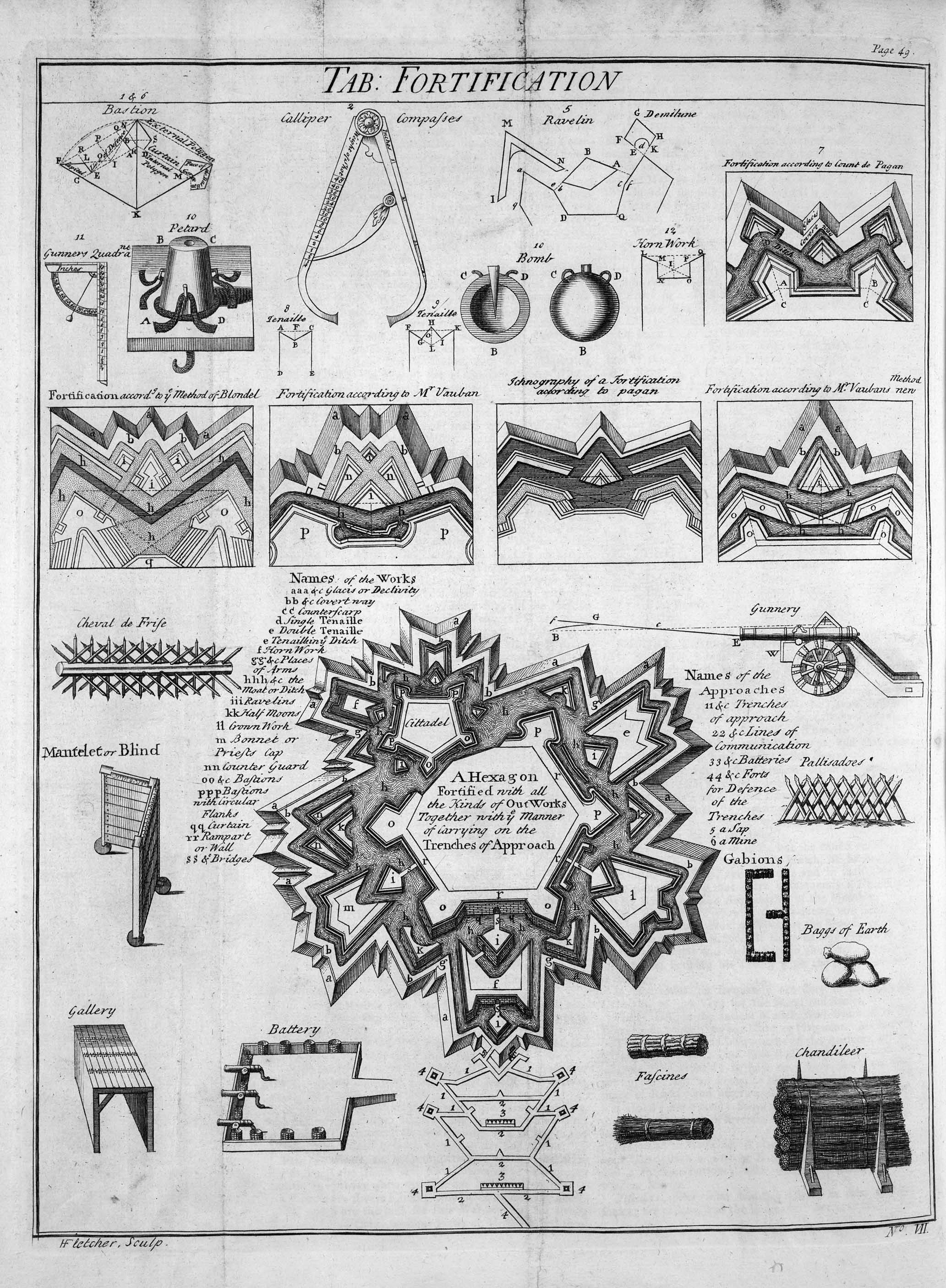 The evolution of this new style of fortification can be seen in transitional forts such as Sarzanello in North West Italy which was built between 1492 and 1502. Sarzanello consists of both crenellated walls with towers typical of the medieval period but also has a
The evolution of this new style of fortification can be seen in transitional forts such as Sarzanello in North West Italy which was built between 1492 and 1502. Sarzanello consists of both crenellated walls with towers typical of the medieval period but also has a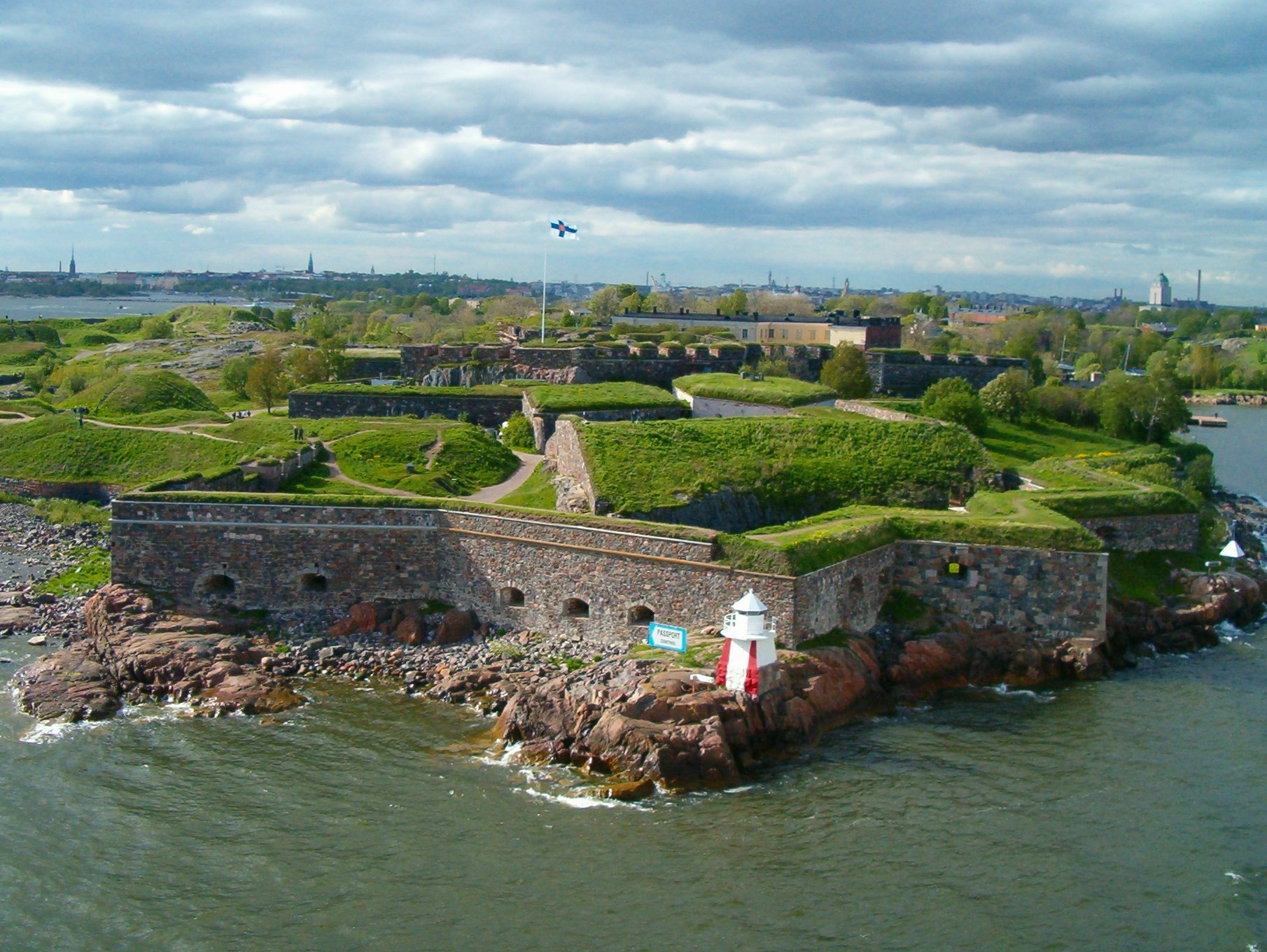  The result was star shaped fortifications with tier upon tier of hornworks and
The result was star shaped fortifications with tier upon tier of hornworks and
 Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the
Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the  Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the
Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the

 Instead field fortification rose to dominate defensive action. Unlike the trench warfare which dominated World War I, these defences were more temporary in nature. This was an advantage because since it was less extensive it formed a less obvious target for enemy force to be directed against.
If sufficient power were massed against one point to penetrate it, the forces based there could be withdrawn and the line could be re-established relatively quickly. Instead of a supposedly impenetrable defensive line, such fortifications emphasized defence in depth, so that as defenders were forced to pull back or were overrun, the lines of defenders behind them could take over the defence.
Because the mobile offensives practised by both sides usually focused on avoiding the strongest points of a defensive line, these defences were usually relatively thin and spread along the length of a line. The defence was usually not equally strong throughout however.
The strength of the defensive line in an area varied according to how rapidly an attacking force could progress in the terrain that was being defended—both the terrain the defensive line was built on and the ground behind it that an attacker might hope to break out into. This was both for reasons of the strategic value of the ground, and its defensive value.
This was possible because while offensive tactics were focused on mobility, so were defensive tactics. The dug in defences consisted primarily of infantry and antitank guns. Defending tanks and tank destroyers would be concentrated in mobile brigades behind the defensive line. If a major offensive was launched against a point in the line, mobile reinforcements would be sent to reinforce that part of the line that was in danger of failing.
Thus the defensive line could be relatively thin because the bulk of the fighting power of the defenders was not concentrated in the line itself but rather in the mobile reserves. A notable exception to this rule was seen in the defensive lines at the Battle of Kursk during World War II, where German forces deliberately attacked into the strongest part of the Soviet defences seeking to crush them utterly.
The terrain that was being defended was of primary importance because open terrain that tanks could move over quickly made possible rapid advances into the defenders' rear areas that were very dangerous to the defenders. Thus such terrain had to be defended at all cost.
In addition, since in theory the defensive line only had to hold out long enough for mobile reserves to reinforce it, terrain that did not permit rapid advance could be held more weakly because the enemy's advance into it would be slower, giving the defenders more time to reinforce that point in the line. For example, the
Instead field fortification rose to dominate defensive action. Unlike the trench warfare which dominated World War I, these defences were more temporary in nature. This was an advantage because since it was less extensive it formed a less obvious target for enemy force to be directed against.
If sufficient power were massed against one point to penetrate it, the forces based there could be withdrawn and the line could be re-established relatively quickly. Instead of a supposedly impenetrable defensive line, such fortifications emphasized defence in depth, so that as defenders were forced to pull back or were overrun, the lines of defenders behind them could take over the defence.
Because the mobile offensives practised by both sides usually focused on avoiding the strongest points of a defensive line, these defences were usually relatively thin and spread along the length of a line. The defence was usually not equally strong throughout however.
The strength of the defensive line in an area varied according to how rapidly an attacking force could progress in the terrain that was being defended—both the terrain the defensive line was built on and the ground behind it that an attacker might hope to break out into. This was both for reasons of the strategic value of the ground, and its defensive value.
This was possible because while offensive tactics were focused on mobility, so were defensive tactics. The dug in defences consisted primarily of infantry and antitank guns. Defending tanks and tank destroyers would be concentrated in mobile brigades behind the defensive line. If a major offensive was launched against a point in the line, mobile reinforcements would be sent to reinforce that part of the line that was in danger of failing.
Thus the defensive line could be relatively thin because the bulk of the fighting power of the defenders was not concentrated in the line itself but rather in the mobile reserves. A notable exception to this rule was seen in the defensive lines at the Battle of Kursk during World War II, where German forces deliberately attacked into the strongest part of the Soviet defences seeking to crush them utterly.
The terrain that was being defended was of primary importance because open terrain that tanks could move over quickly made possible rapid advances into the defenders' rear areas that were very dangerous to the defenders. Thus such terrain had to be defended at all cost.
In addition, since in theory the defensive line only had to hold out long enough for mobile reserves to reinforce it, terrain that did not permit rapid advance could be held more weakly because the enemy's advance into it would be slower, giving the defenders more time to reinforce that point in the line. For example, the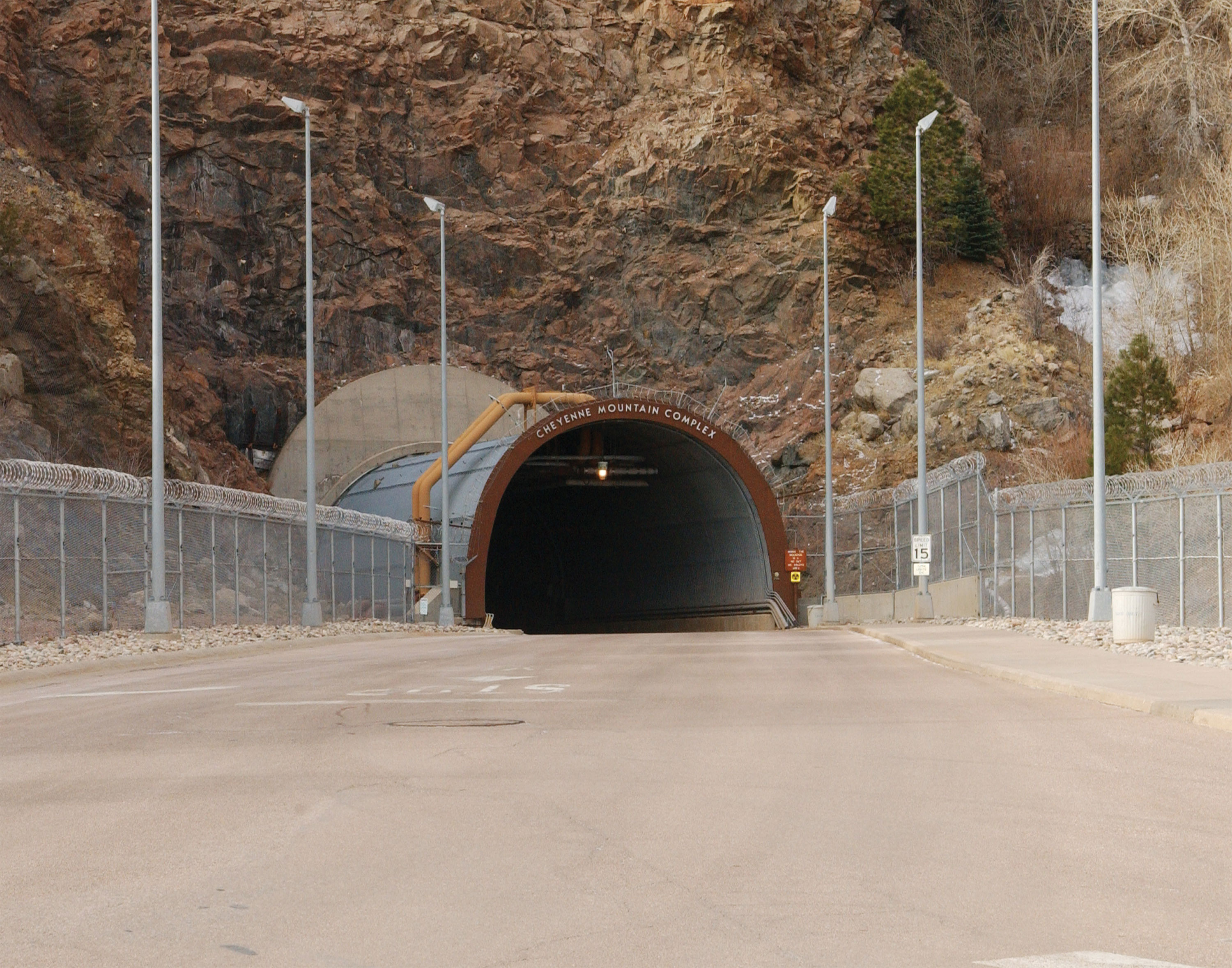  After World War II,
After World War II,
 Forts in modern American usage often refer to space set aside by governments for a permanent military facility; these often do not have any actual fortifications, and can have specializations (military barracks, administration, medical facilities, or intelligence).
However, there are some modern fortifications that are referred to as forts. These are typically small semi permanent fortifications. In urban combat they are built by upgrading existing structures such as houses or public buildings. In field warfare they are often log, sandbag or gabion type construction.
Such forts are typically only used in low level conflict, such as counterinsurgency conflicts or very low level conventional conflicts, such as the
Forts in modern American usage often refer to space set aside by governments for a permanent military facility; these often do not have any actual fortifications, and can have specializations (military barracks, administration, medical facilities, or intelligence).
However, there are some modern fortifications that are referred to as forts. These are typically small semi permanent fortifications. In urban combat they are built by upgrading existing structures such as houses or public buildings. In field warfare they are often log, sandbag or gabion type construction.
Such forts are typically only used in low level conflict, such as counterinsurgency conflicts or very low level conventional conflicts, such as the
copy
* Thornton, John Kelly ''Warfare in Atlantic Africa'', 1500–1800, Routledge: 1999
Fortress Study Group
*
ICOFORT
{{Authority control Military strategy Military installations Forts


 A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make").
From very early history to modern times,
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make").
From very early history to modern times, defensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its ' cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mil ...
, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum
A ''castellum'' in Latin is usually:
* a small Roman fortlet or tower,C. Julius Caesar, Gallic War; 2,30 a diminutive of ('military camp'), often used as a watchtower or signal station like on Hadrian's Wall. It should be distinguished from a ...
or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a border guard rather than a real strongpoint to watch and maintain the border.
The art of setting out a military camp or constructing a fortification traditionally has been called "castrametation" since the time of the Roman legions. Fortification is usually divided into two branches: permanent fortification and field fortification. There is also an intermediate branch known as semi-permanent fortification. Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
s are fortifications which are regarded as being distinct from the generic fort or fortress in that they are a residence of a monarch or noble and command a specific defensive territory.
Roman forts and hill forts were the main antecedents of castles in Europe, which emerged in the 9th century in the Carolingian Empire. The Early Middle Ages saw the creation of some towns built around castles.
Medieval-style fortifications were largely made obsolete by the arrival of cannons in the 14th century. Fortifications in the age of black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
evolved into much lower structures with greater use of ditches and earth ramparts that would absorb and disperse the energy of cannon fire. Walls exposed to direct cannon fire were very vulnerable, so the walls were sunk into ditches fronted by earth slopes to improve protection.
The arrival of explosive shells in the 19th century led to yet another stage in the evolution of fortification. Star fort
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to domin ...
s did not fare well against the effects of high explosive, and the intricate arrangements of bastions, flanking batteries and the carefully constructed lines of fire for the defending cannon could be rapidly disrupted by explosive shells. Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
-and- concrete fortifications were common during the 19th and early 20th centuries. The advances in modern warfare since World War I have made large-scale fortifications obsolete
Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ...
in most situations.
Nomenclature
 Many United States Army installations are known as ''forts'', although they are not always fortified. Indeed, during the pioneering era of North America, many outposts on the frontiers, even non-military outposts, were referred to generically as ''forts''. Larger military installations may be called ''fortresses''; smaller ones were once known as ''fortalices''. The word ''fortification'' can also refer to the practice of improving an area's defense with defensive works. City walls are fortifications but are not necessarily called ''fortresses''.
The art of setting out a military camp or constructing a fortification traditionally has been called ''
Many United States Army installations are known as ''forts'', although they are not always fortified. Indeed, during the pioneering era of North America, many outposts on the frontiers, even non-military outposts, were referred to generically as ''forts''. Larger military installations may be called ''fortresses''; smaller ones were once known as ''fortalices''. The word ''fortification'' can also refer to the practice of improving an area's defense with defensive works. City walls are fortifications but are not necessarily called ''fortresses''.
The art of setting out a military camp or constructing a fortification traditionally has been called ''castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
metation'' since the time of the Roman legions. The art/science of laying siege to a fortification and of destroying it is commonly called '' siegecraft'' or ''siege warfare'' and is formally known as '' poliorcetics''. In some texts this latter term also applies to the art of building a fortification.
Fortification is usually divided into two branches: permanent fortification and field fortification. Permanent fortifications are erected at leisure, with all the resources that a state can supply of constructive and mechanical skill, and are built of enduring materials. Field fortifications—for example breastworks—and often known as ''fieldworks'' or ''earthworks'', are extemporized by troops in the field, perhaps assisted by such local labour and tools as may be procurable and with materials that do not require much preparation, such as earth, brushwood and light timber, or sandbags (see sangar). An example of field fortification was the construction of Fort Necessity by George Washington in 1754.
There is also an intermediate branch known as ''semi-permanent fortification''. This is employed when in the course of a campaign it becomes desirable to protect some locality with the best imitation of permanent defences that can be made in a short time, ample resources and skilled civilian labour being available. An example of this is the construction of Roman forts in England and in other Roman territories where camps were set up with the intention of staying for some time, but not permanently.
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
s are fortifications which are regarded as being distinct from the generic fort or fortress in that it describes a residence of a monarch or noble and commands a specific defensive territory. An example of this is the massive medieval castle of Carcassonne.
History


Neolithic Europe
From very early history to modern times, walls have been a necessity for many cities. In Bulgaria, near the town of Provadia a walled fortified settlement today called Solnitsata starting from 4700 BC had a diameter of about , was home to 350 people living in two-storey houses, and was encircled by a fortified wall. The huge walls around the settlement, which were built very tall and with stone blocks which are high and thick, make it one of the earliest walled settlements in Europe but it is younger than the walled town of Sesklo in Greece from 6800 BC. Uruk in ancientSumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
( Mesopotamia) is one of the world's oldest known walled cities. The Ancient Egyptians also built fortresses on the frontiers of the Nile Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
to protect against invaders from neighbouring territories, as well as circle-shaped mud brick walls around their cities. Many of the fortifications of the ancient world were built with mud brick, often leaving them no more than mounds of dirt for today's archaeologists.
A massive prehistoric stone wall surrounded the ancient temple of Ness of Brodgar 3200 BC in Scotland. Named the "Great Wall of Brodgar" it was thick and 4 metres tall. The wall had some symbolic or ritualistic function. The Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
deployed large labour forces to build new palaces, temples and defensive walls.
Neolithic Indus Valley
Some settlements in theIndus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
were also fortified. By about 3500 BC, hundreds of small farming villages dotted the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
floodplain. Many of these settlements had fortifications and planned streets. The stone and mud brick houses of Kot Diji were clustered behind massive stone flood dykes and defensive walls, for neighbouring communities bickered constantly about the control of prime agricultural land. Mundigak (c. 2500 BC) in present-day south-east Afghanistan has defensive walls and square bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s of sun dried bricks. The entire city of Kerma in Nubia was encompassed by fortified walls surrounded by a ditch. Archaeology has revealed various Bronze Age bastions and foundations constructed of stone together with either baked or unfired brick.

Bronze Age Europe
In Bronze Age Malta, some settlements also began to be fortified. The most notable surviving example is Borġ in-Nadur, where a bastion built in around 1500 BC was found.Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
was one of the most famous cities of the ancient world, especially as a result of the building program of Nebuchadnezzar
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
, who expanded the walls and built the Ishtar Gate. Exceptions were few—notably, ancient Sparta and ancient Rome did not have walls for a long time, choosing to rely on their militaries for defence instead. Initially, these fortifications were simple constructions of wood and earth, which were later replaced by mixed constructions of stones piled on top of each other without mortar. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its ' cyclopean' walls). In classical era Greece, the city of Athens built two parallel stone walls, called the Long Walls, that reached their fortified seaport at Piraeus a few miles away.
In Central Europe, the Celts built large fortified settlements known as oppida, whose walls seem partially influenced by those built in the Mediterranean. The fortifications were continuously being expanded and improved. Around 600 BC, in Heuneburg, Germany, forts were constructed with a limestone foundation supported by a mudbrick
A mudbrick or mud-brick is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of loam, mud, sand and water mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE, though since 4000 BCE, bricks have also bee ...
wall approximately 4 metres tall, probably topped by a roofed walkway, thus reaching a total height of 6 metres. The wall was clad with lime plaster, regularly renewed. Towers protruded outwards from it.
 The Oppidum of Manching (German: Oppidum von Manching) was a large Celtic proto-urban or city-like settlement at modern-day Manching (near Ingolstadt), Bavaria (Germany). The settlement was founded in the 3rd century BC and existed until c. 50–30 BC. It reached its largest extent during the late La Tène period (late 2nd century BC), when it had a size of 380 hectares. At that time, 5,000 to 10,000 people lived within its 7.2 km long walls. The oppidum of
The Oppidum of Manching (German: Oppidum von Manching) was a large Celtic proto-urban or city-like settlement at modern-day Manching (near Ingolstadt), Bavaria (Germany). The settlement was founded in the 3rd century BC and existed until c. 50–30 BC. It reached its largest extent during the late La Tène period (late 2nd century BC), when it had a size of 380 hectares. At that time, 5,000 to 10,000 people lived within its 7.2 km long walls. The oppidum of Bibracte
Bibracte, a Gallic ''oppidum'' or fortified settlement, was the capital of the Aedui and one of the most important hillforts in Gaul. It was situated near modern Autun in Burgundy, France. The material culture of the Aedui corresponded to th ...
is another example of a Gaulish fortified settlement.
Bronze and Iron Age Near East
Ancient Rome
The Mura aureliane are a line of city walls built between 271 AD and 275 AD in Rome, Italy, during the reign of the Roman EmperorsAurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited t ...
and Probus Probus may refer to:
People
* Marcus Valerius Probus (c. 20/30–105 AD), Roman grammarian
* Marcus Pomponius Maecius Probus, consul in 228
* Probus (emperor), Roman Emperor (276–282)
* Probus of Byzantium (–306), Bishop of Byzantium from 293 t ...
. The walls enclosed all the seven hills of Rome plus the Campus Martius and, on the right bank of the Tiber, the Trastevere
Trastevere () is the 13th ''rione'' of Rome: it is identified by the initials R. XIII and it is located within Municipio I. Its name comes from Latin ''trans Tiberim'', literally 'beyond the Tiber'.
Its coat of arms depicts a golden head of a lio ...
district. The river banks within the city limits appear to have been left unfortified, although they were fortified along the Campus Martius. The full circuit ran for surrounding an area of . The walls were constructed in brick-faced concrete, thick and high, with a square tower every 100 Roman feet (). In the 5th century, remodelling doubled the height of the walls to . By 500 AD, the circuit possessed 383 towers, 7,020 crenellations, 18 main gates, 5 postern gates, 116 latrines, and 2,066 large external windows.Claridge, Amanda (1998). ''Rome: An Oxford Archaeological Guide'', First, Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1998, pp. 59, 332–335.
The Romans fortified their cities with massive, mortar-bound stone walls. The most famous of these are the largely extant Aurelian Walls of Rome and the Theodosian Walls of Constantinople, together with partial remains elsewhere. These are mostly city gates, like the Porta Nigra
The Porta Nigra (Latin for ''black gate'') is a large Roman city gate in Trier, Germany. It is today the largest Roman city gate north of the Alps. It was designated as part of the Roman Monuments, Cathedral of St Peter and Church of Our Lady in ...
in Trier or Newport Arch
Newport Arch is a 3rd-century Roman gate in the city of Lincoln, Lincolnshire. It is a Scheduled monument and Grade I listed building and is reputedly the oldest arch in the United Kingdom still used by traffic.
History
The arch was remodelled ...
in Lincoln. Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
was built by the Roman Empire across the width of what is now northern England following a visit by Roman Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
(AD 76–138) in AD 122.
India
 A number of forts dating from the
A number of forts dating from the Later Stone Age
The Later Stone Age (LSA) is a period in African prehistory that follows the Middle Stone Age.
The Later Stone Age is associated with the advent of modern human behavior in Africa, although definitions of this concept and means of studying it ar ...
to the British Raj may be found in India. "Fort" is the word used in India for all old fortifications. Numerous Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
sites exhibit evidences of fortifications. While Dholavira has stone-built fortification walls, Harrapa is fortified using baked bricks; sites such as Kalibangan exhibit mudbrick
A mudbrick or mud-brick is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of loam, mud, sand and water mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE, though since 4000 BCE, bricks have also bee ...
fortifications with bastions and Lothal has a quadrangular fortified layout. Evidence also suggested of fortifications in Mohenjo-daro. Even a small town – for instance, Kotada Bhadli, exhibiting sophisticated fortification-like bastions – shows that nearly all major and minor towns of the Indus Valley Civilization were fortified. Forts also appeared in urban cities of the Gangetic valley during the second urbanisation period between 600 and 200 BC, and as many as 15 fortification sites have been identified by archaeologists throughout the Gangetic valley, such as Kaushambi, Mahasthangarh, Pataliputra, Mathura, Ahichchhatra
Ahichchhatra ( sa, अहिच्छत्र, translit=Ahicchatra) or Ahikshetra ( sa, अहिक्षेत्र, translit=Ahikṣetra), near the modern Ramnagar village in Aonla tehsil, Bareilly district in Uttar Pradesh, India, was the ...
, Rajgir, and Lauria Nandangarh
Lauria Nandangarh, also Lauriya Navandgarh, is a city or town about 14 km from Narkatiaganj (or Shikarpur) and 28 km from Bettiah in West Champaran district of Bihar state in northern India. It is situated near the banks of the Burh ...
. The earliest vedic brick fortification occurs in one of the stupa mounds of Lauria Nandangarh, which is 1.6 km in perimeter and oval in plan and encloses a habitation area. India currently has over 180 forts, with the state of Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
alone having over 70 forts, which are also known as ''durg'', many of them built by Shivaji, founder of the Maratha state. A large majority of forts in India are in North India. The most notable forts are the Red Fort at Delhi, the Red Fort at Agra, the Chittor Fort and Mehrangarh Fort in Rajasthan, the Ranthambhor Fort
Ranthambore Fort lies within the Ranthambore National Park, near the city of Sawai Madhopur in Sawai Madhopur district of Rajasthan, India. the park being the former hunting grounds of the Maharajahs of Jaipur State, Jaipur until the time of P ...
, Amer Fort and Jaisalmer Fort also in Rajasthan and Gwalior Fort in Madhya Pradesh.
China
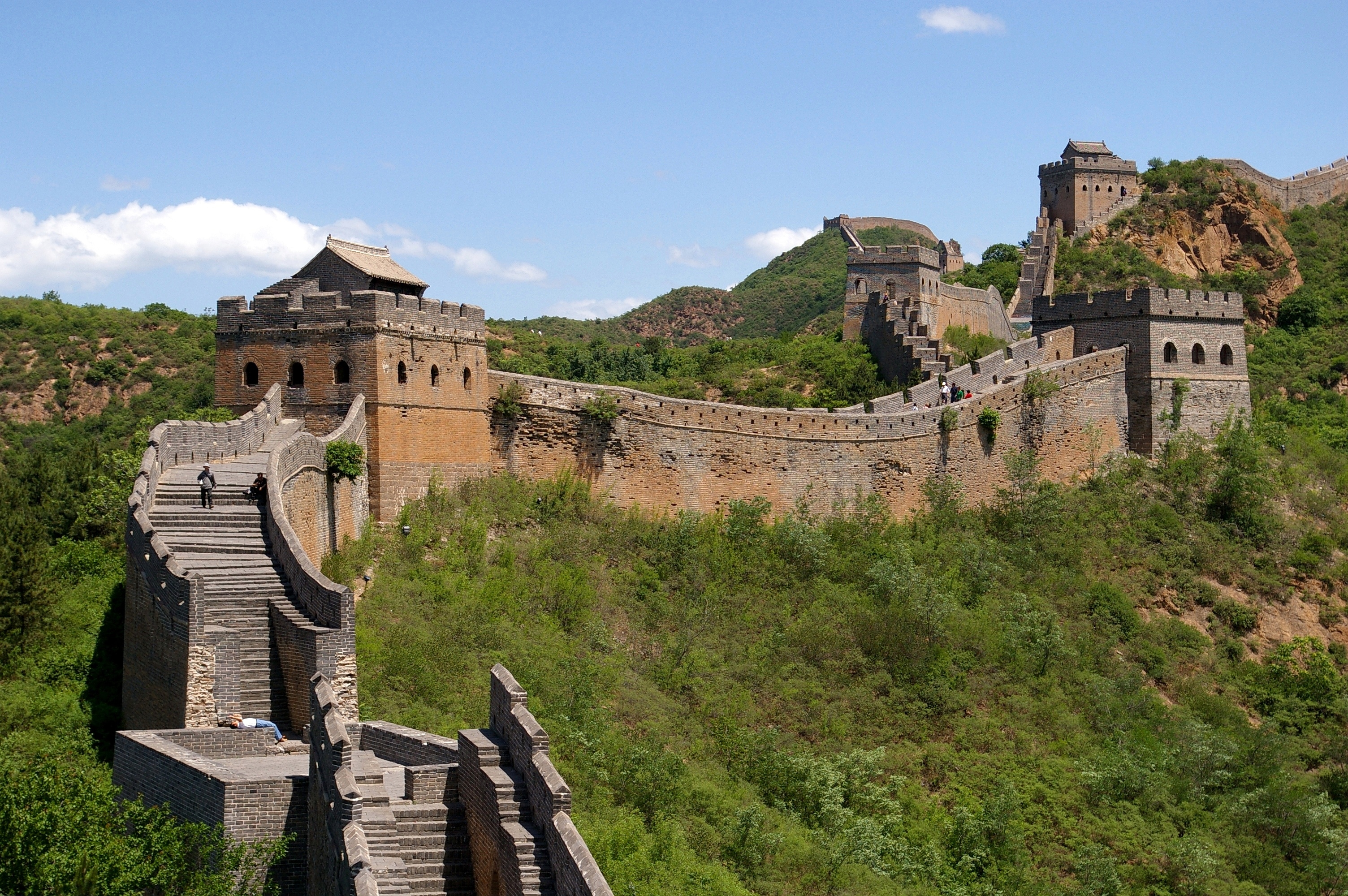
 Large tempered earth (i.e. rammed earth) walls were built in
Large tempered earth (i.e. rammed earth) walls were built in ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
since the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1050 BC); the capital at ancient Ao had enormous walls built in this fashion (see siege for more info). Although stone walls were built in China during the Warring States (481–221 BC), mass conversion to stone architecture did not begin in earnest until the Tang dynasty (618–907 AD). The Great Wall of China had been built since the Qin dynasty (221–207 BC), although its present form was mostly an engineering feat and remodelling of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644 AD).
In addition to the Great Wall, a number of Chinese cities also employed the use of defensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s to defend their cities. Notable Chinese city walls include the city walls of Hangzhou, Nanjing, the Old City of Shanghai, Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trade ...
, Xi'an and the walled villages of Hong Kong. The famous walls of the Forbidden City in Beijing were established in the early 15th century by the Yongle Emperor. The Forbidden City made up the inner portion of the Beijing city fortifications.
Philippines
Spanish colonial fortifications
During the Spanish Era several forts and outposts were built throughout the archipelago. Most notable is Intramuros, the old walled city of Manila located along the southern bank of the Pasig River. The historic city was home to centuries-old churches, schools, convents, government buildings and residences, the best collection of Spanish colonial architecture before much of it was destroyed by the bombs of World War II. Of all the buildings within the 67-acre city, only one building, the San Agustin Church, survived the war. Partial listing of Spanish forts: # Intramuros, Manila # Cuartel de Santo Domingo, Santa Rosa, Laguna # Fuerza de Cuyo, Cuyo, Palawan # Fuerza de Cagayancillo,Cagayancillo
Cagayancillo, officially the Municipality of Cagayancillo ( tgl, Bayan ng Cagayancillo), is a 6th class municipality in the province of Palawan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 6,884 people.
Located between th ...
, Palawan
# Real Fuerza de Nuestra Señora del Pilar de Zaragoza, Zamboanga City
# Fuerza de San Felipe, Cavite City
# Fuerza de San Pedro, Cebu
# Fuerte dela Concepcion y del Triunfo, Ozamiz, Misamis Occidental
# Fuerza de San Antonio Abad, Manila
# Fuerza de Pikit, Pikit, Cotabato
# Fuerza de Santiago, Romblon, Romblon
# Fuerza de Jolo, Jolo, Sulu
# Fuerza de Masbate, Masbate
# Fuerza de Bongabong, Bongabong, Oriental Mindoro
# Cotta de Dapitan, Dapitan, Zamboanga del Norte
# Fuerte de Alfonso XII, Tukuran, Zamboanga del Sur
# Fuerza de Bacolod, Bacolod, Lanao del Norte
Bacolod, officially the Municipality of Bacolod (Maranao: ''Inged a Bacolod''; ceb, Lungsod sa Bacolod; tl, Bayan ng Bacolod), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Lanao del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a pop ...
# Guinsiliban Watchtower, Guinsiliban, Camiguin
# Laguindingan Watchtower, Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental
# Kutang San Diego, Gumaca, Quezon
# Baluarte Luna, Luna, La Union
Local fortifications
The Ivatan people of the northern islands of Batanes built their so-called '' idjang'' on hills and elevated areas to protect themselves during times of war. These fortifications were likened to European castles because of their purpose. Usually, the only entrance to the castles would be via a rope ladder that would only be lowered for the villagers and could be kept away when invaders arrived. The Igorots built forts made of stone walls that averaged several meters in width and about two to three times the width in height around 2000 BC.Ancient and Pre-Spanish Era of the Philippines
The Igorots built forts made of stone walls that averaged several meters in width and about two to three times the width in height around 2000 BC.Ancient and Pre-Spanish Era of the Philippines. Accessed September 04, 2008. The Muslim Filipinos of the south built strong fortresses called ''kota'' or ''moong'' to protect their communities. Usually, many of the occupants of these kotas are entire families rather than just warriors. Lords often had their own kotas to assert their right to rule, it served not only as a military installation but as a palace for the local Lord. It is said that at the height of the Maguindanao Sultanate's power, they blanketed the areas around Western Mindanao with Kotas and other fortifications to block the Spanish advance into the region. These kotas were usually made of stone and bamboo or other light materials and surrounded by trench networks. As a result, some of these kotas were burned easily or destroyed. With further Spanish campaigns in the region, the Sultanate was subdued and majority of Kotas dismantled or destroyed. Kotas were not only used by the Muslims as defense against Spaniards and other foreigners, renegades and rebels also built fortifications in defiance of other chiefs in the area. During the American occupation, rebels built strongholds and the Datus, Rajahs or Sultans often built and reinforced their kotas in a desperate bid to maintain rule over their subjects and their land. Many of these forts were also destroyed by American expeditions, as a result, very very few kotas still stand to this day. Notable Kotas: * Kota Selurong: an outpost of the Bruneian Empire in Luzon, later became the City of Manila. * Kuta Wato/Kota Bato: Literally translates to "stone fort" the first known stone fortification in the country, its ruins exist as the "Kutawato Cave Complex" * Kota Sug/Jolo: The capital and seat of the Sultanate of Sulu. When it was occupied by the Spaniards in the 1870s they converted the kota into the world's smallest walled city.
Pre-Islamic Arabia
During Muhammad's lifetime
 During Muhammad's era in Arabia, many tribes made use of fortifications. In the
During Muhammad's era in Arabia, many tribes made use of fortifications. In the Battle of the Trench
The Battle of the Trench ( ar, غزوة الخندق, Ghazwat al-Khandaq), also known as the Battle of Khandaq ( ar, معركة الخندق, Ma’rakah al-Khandaq) and the Battle of the Confederates ( ar, غزوة الاحزاب, Ghazwat al- ...
, the largely outnumbered defenders of Medina, mainly Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s led by Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God in Islam, God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. So ...
Muhammad, dug a trench, which together with Medina's natural fortifications, rendered the confederate cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
(consisting of horses and camels) useless, locking the two sides in a stalemate. Hoping to make several attacks at once, the confederates persuaded the Medina-allied Banu Qurayza to attack the city from the south. However, Muhammad's diplomacy derailed the negotiations, and broke up the confederacy against him. The well-organized defenders, the sinking of confederate morale, and poor weather conditions caused the siege to end in a fiasco.*
During the Siege of Ta'if in January 630, Note: Shawwal 8AH is January 630AD Muhammad ordered his followers to attack enemies who fled from the Battle of Hunayn and sought refuge in the fortress of Taif.
Islamic world
Africa
The walls of Benin are described as the world's second longest man-made structure, as well as the most extensive earthwork in the world, by the ''Guinness Book of Records, 1974''. The walls may have been constructed between the thirteenth and mid-fifteenth century CE or, during the first millennium CE. Strong citadels were also built other in areas of Africa. Yorubaland for example had several sites surrounded by the full range of earthworks and ramparts seen elsewhere, and sited on ground. This improved defensive potential- such as hills and ridges. Yoruba fortifications were often protected with a double wall of trenches and ramparts, and in the Congo forests concealed ditches and paths, along with the main works, often bristled with rows of sharpened stakes. Inner defenses were laid out to blunt an enemy penetration with a maze of defensive walls allowing for entrapment and crossfire on opposing forces.July, pp. 11–39 A military tactic of the Ashanti was to create powerful logstockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls, made of logs placed side by side vertically, with the tops sharpened as a defensive wall.
Etymology
''Stockade'' is derived from the French word ''estocade''. The French word was derived ...
s at key points. This was employed in later wars against the British to block British advances. Some of these fortifications were over a hundred yard long, with heavy parallel tree trunks. They were impervious to destruction by artillery fire. Behind these stockades numerous Ashanti soldiers were mobilized to check enemy movement. While formidable in construction, many of these strongpoints failed because Ashanti guns, gunpowder and bullets were poor, and provided little sustained killing power in defense. Time and time again British troops overcame or bypassed the stockades by mounting old-fashioned bayonet charges, after laying down some covering fire.
Defensive works were of importance in the tropical African Kingdoms. In the Kingdom of Kongo
The Kingdom of Kongo ( kg, Kongo dya Ntotila or ''Wene wa Kongo;'' pt, Reino do Congo) was a kingdom located in central Africa in present-day northern Angola, the western portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the ...
field fortifications were characterized by trenches and low earthen embankments. Such strongpoints ironically, sometimes held up much better against European cannon than taller, more imposing structures.Thornton, pp. 22–39

Medieval Europe
Roman forts and hill forts were the main antecedents ofcastle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
s in Europe, which emerged in the 9th century in the Carolingian Empire. The Early Middle Ages saw the creation of some towns built around castles. These cities were only rarely protected by simple stone walls and more usually by a combination of both walls and ditches. From the 12th century hundreds of settlements of all sizes were founded all across Europe, which very often obtained the right of fortification soon afterwards.
 The founding of urban centres was an important means of territorial expansion and many cities, especially in eastern Europe, were founded precisely for this purpose during the period of Eastern Colonisation. These cities are easy to recognise due to their regular layout and large market spaces. The fortifications of these settlements were continuously improved to reflect the current level of military development.
During the Renaissance era, the Venetian Republic raised great walls around cities, and the finest examples, among others, are in
The founding of urban centres was an important means of territorial expansion and many cities, especially in eastern Europe, were founded precisely for this purpose during the period of Eastern Colonisation. These cities are easy to recognise due to their regular layout and large market spaces. The fortifications of these settlements were continuously improved to reflect the current level of military development.
During the Renaissance era, the Venetian Republic raised great walls around cities, and the finest examples, among others, are in Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaor ...
(Cyprus), Rocca di Manerba del Garda (Lombardy) and Palmanova (Italy), or Dubrovnik (Croatia), which proved to be futile against attacks but still stand to this day. Unlike Venetians the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
used to built smaller fortifications but in greater numbers, and only rarely fortified entire settlements such as Počitelj, Vratnik and Jajce
Jajce (Јајце) is a town and municipality located in the Central Bosnia Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. According to the 2013 census, the town has a population of 7,172 inhabitants, with ...
in Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
.
Development after introduction of firearms
Medieval-style fortifications were largely made obsolete by the arrival of cannons on the 14th century battlefield. Fortifications in the age ofblack powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
evolved into much lower structures with greater use of ditches and earth ramparts that would absorb and disperse the energy of cannon fire. Walls exposed to direct cannon fire were very vulnerable, so were sunk into ditches fronted by earth slopes.
This placed a heavy emphasis on the geometry of the fortification to allow defensive cannonry interlocking fields of fire to cover all approaches to the lower and thus more vulnerable walls.
 The evolution of this new style of fortification can be seen in transitional forts such as Sarzanello in North West Italy which was built between 1492 and 1502. Sarzanello consists of both crenellated walls with towers typical of the medieval period but also has a
The evolution of this new style of fortification can be seen in transitional forts such as Sarzanello in North West Italy which was built between 1492 and 1502. Sarzanello consists of both crenellated walls with towers typical of the medieval period but also has a ravelin
A ravelin is a triangular fortification or detached outwork, located in front of the innerworks of a fortress (the curtain walls and bastions). Originally called a ''demi-lune'', after the ''lunette'', the ravelin is placed outside a castle ...
like angular gun platform screening one of the curtain walls which is protected from flanking fire from the towers of the main part of the fort. Another example are the fortifications of Rhodes which were ''frozen'' at 1522 so that Rhodes is the only European walled town that still shows the transition between the classical medieval fortification and the modern ones.
Fortifications also extended in depth, with protected batteries for defensive cannonry, to allow them to engage attacking cannon to keep them at a distance and prevent them bearing directly on the vulnerable walls.
 The result was star shaped fortifications with tier upon tier of hornworks and
The result was star shaped fortifications with tier upon tier of hornworks and bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s, of which Fort Bourtange is an excellent example. There are also extensive fortifications from this era in the Nordic states and in Britain, the fortifications of Berwick-upon-Tweed and the harbour archipelago of Suomenlinna
Suomenlinna (; until 1918 Viapori, ), or Sveaborg (), is an inhabited sea fortress the Suomenlinna district is on eight islands of which six have been fortified; it is about 4 km southeast of the city center of Helsinki, the capital of Finla ...
at Helsinki being fine examples.
19th century
The arrival of explosive shells in the 19th century led to yet another stage in the evolution of fortification.Star fort
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to domin ...
s did not fare well against the effects of high explosive and the intricate arrangements of bastions, flanking batteries and the carefully constructed lines of fire for the defending cannon could be rapidly disrupted by explosive shells.
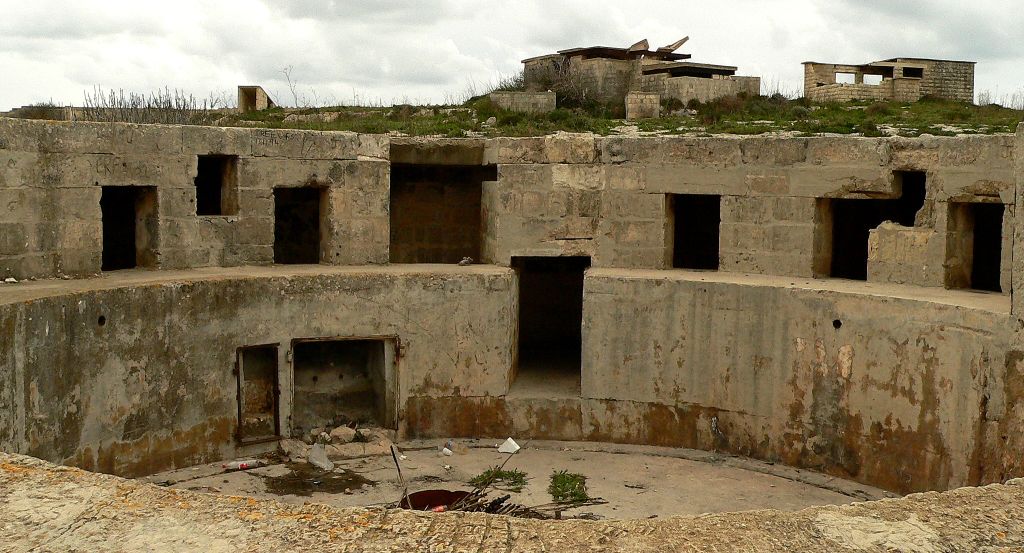
 Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the
Worse, the large open ditches surrounding forts of this type were an integral part of the defensive scheme, as was the covered way at the edge of the counter scarp
A scarp and a counterscarp are the inner and outer sides, respectively, of a ditch or moat used in fortifications. Attackers (if they have not bridged the ditch) must descend the counterscarp and ascend the scarp. In permanent fortifications th ...
. The ditch was extremely vulnerable to bombardment with explosive shells.
In response, military engineers evolved the polygonal style of fortification. The ditch became deep and vertically sided, cut directly into the native rock or soil, laid out as a series of straight lines creating the central fortified area that gives this style of fortification its name.
Wide enough to be an impassable barrier for attacking troops, but narrow enough to be a difficult target for enemy shellfire, the ditch was swept by fire from defensive blockhouses set in the ditch as well as firing positions cut into the outer face of the ditch itself.
The profile of the fort became very low indeed, surrounded outside the ditch covered by caponiers by a gently sloping open area so as to eliminate possible cover for enemy forces, while the fort itself provided a minimal target for enemy fire. The entrypoint became a sunken gatehouse in the inner face of the ditch, reached by a curving ramp that gave access to the gate via a rolling bridge that could be withdrawn into the gatehouse.
 Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the
Much of the fort moved underground. Deep passages and tunnels now connected the blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive stro ...
s and firing points in the ditch to the fort proper, with magazines and machine rooms deep under the surface. The guns, however, were often mounted in open emplacements and protected only by a parapet; both in order to keep a lower profile and also because experience with guns in closed casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
s had seen them put out of action by rubble as their own casemates were collapsed around them.
Gone were citadels surrounding towns: forts were to be moved to the outside of the cities some 12 km to keep the enemy at a distance so their artillery could not bombard the city center. From now on a ring of forts were to be built at a spacing that would allow them to effectively cover the intervals between them.
The new forts abandoned the principle of the bastion, which had also been made obsolete by advances in arms. The outline was a much simplified polygon, surrounded by a ditch. These forts, built in masonry and shaped stone, were designed to shelter their garrison against bombardment. One organizing feature of the new system involved the construction of two defensive curtains: an outer line of forts, backed by an inner ring or line at critical points of terrain or junctions (see, for example, Séré de Rivières system in France).
Traditional fortification however continued to be applied by European armies engaged in warfare in colonies established in Africa against lightly armed attackers from amongst the indigenous population. A relatively small number of defenders in a fort impervious to primitive weaponry could hold out against high odds, the only constraint being the supply of ammunition.
20th and 21st centuries

Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
-and- concrete fortifications were common during the 19th and early 20th centuries. However the advances in modern warfare since World War I have made large-scale fortifications obsolete
Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ...
in most situations. In the 1930s and 1940s, some fortifications were built with designs taking into consideration the new threat of aerial warfare
Aerial warfare is the use of military aircraft and other flying machines in warfare. Aerial warfare includes bombers attacking enemy installations or a concentration of enemy troops or strategic targets; fighter aircraft battling for control o ...
, for example Fort Campbell in Malta. Despite this, only underground bunkers are still able to provide some protection in modern wars. Many historical fortifications were demolished during the modern age, but a considerable number survive as popular tourist destinations and prominent local landmark
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances.
In modern use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures or f ...
s today.
The downfall of permanent fortifications had two causes:
* The ever-escalating power, speed, and reach of artillery and air power meant that almost any target that could be located could be destroyed, if sufficient force were massed against it. As such, the more resources a defender devoted to reinforcing a fortification, the more combat power that fortification justified being devoted to destroying it, if the fortification's destruction was demanded by an attacker's strategy. From World War II, bunker busters were used against fortifications. By 1950, nuclear weapons were capable of destroying entire cities, and produced dangerous radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
. This led to the creation of civilian nuclear air raid shelter
Air raid shelters are structures for the protection of non-combatants as well as combatants against enemy attacks from the air. They are similar to bunkers in many regards, although they are not designed to defend against ground attack (but many ...
s.
* The second weakness of permanent fortification was its very permanency. Because of this it was often easier to go around a fortification and, with the rise of mobile warfare in the beginning of World War II, this became a viable offensive choice. When a defensive line was too extensive to be entirely bypassed, massive offensive might could be massed against one part of the line allowing a breakthrough, after which the rest of the line could be bypassed. Such was the fate of the many defensive lines built before and during World War II, such as the Siegfried Line
The Siegfried Line, known in German as the ''Westwall'', was a German defensive line built during the 1930s (started 1936) opposite the French Maginot Line. It stretched more than ; from Kleve on the border with the Netherlands, along the west ...
, the Stalin Line and the Atlantic Wall
The Atlantic Wall (german: link=no, Atlantikwall) was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticip ...
. This was not the case with the Maginot Line
The Maginot Line (french: Ligne Maginot, ), named after the French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles and weapon installations built by France in the 1930s to deter invasion by Germany and force the ...
; it was designed to force the Germans to invade other countries (Belgium or Switzerland) to go around it, and was successful in that sense.
 Instead field fortification rose to dominate defensive action. Unlike the trench warfare which dominated World War I, these defences were more temporary in nature. This was an advantage because since it was less extensive it formed a less obvious target for enemy force to be directed against.
If sufficient power were massed against one point to penetrate it, the forces based there could be withdrawn and the line could be re-established relatively quickly. Instead of a supposedly impenetrable defensive line, such fortifications emphasized defence in depth, so that as defenders were forced to pull back or were overrun, the lines of defenders behind them could take over the defence.
Because the mobile offensives practised by both sides usually focused on avoiding the strongest points of a defensive line, these defences were usually relatively thin and spread along the length of a line. The defence was usually not equally strong throughout however.
The strength of the defensive line in an area varied according to how rapidly an attacking force could progress in the terrain that was being defended—both the terrain the defensive line was built on and the ground behind it that an attacker might hope to break out into. This was both for reasons of the strategic value of the ground, and its defensive value.
This was possible because while offensive tactics were focused on mobility, so were defensive tactics. The dug in defences consisted primarily of infantry and antitank guns. Defending tanks and tank destroyers would be concentrated in mobile brigades behind the defensive line. If a major offensive was launched against a point in the line, mobile reinforcements would be sent to reinforce that part of the line that was in danger of failing.
Thus the defensive line could be relatively thin because the bulk of the fighting power of the defenders was not concentrated in the line itself but rather in the mobile reserves. A notable exception to this rule was seen in the defensive lines at the Battle of Kursk during World War II, where German forces deliberately attacked into the strongest part of the Soviet defences seeking to crush them utterly.
The terrain that was being defended was of primary importance because open terrain that tanks could move over quickly made possible rapid advances into the defenders' rear areas that were very dangerous to the defenders. Thus such terrain had to be defended at all cost.
In addition, since in theory the defensive line only had to hold out long enough for mobile reserves to reinforce it, terrain that did not permit rapid advance could be held more weakly because the enemy's advance into it would be slower, giving the defenders more time to reinforce that point in the line. For example, the
Instead field fortification rose to dominate defensive action. Unlike the trench warfare which dominated World War I, these defences were more temporary in nature. This was an advantage because since it was less extensive it formed a less obvious target for enemy force to be directed against.
If sufficient power were massed against one point to penetrate it, the forces based there could be withdrawn and the line could be re-established relatively quickly. Instead of a supposedly impenetrable defensive line, such fortifications emphasized defence in depth, so that as defenders were forced to pull back or were overrun, the lines of defenders behind them could take over the defence.
Because the mobile offensives practised by both sides usually focused on avoiding the strongest points of a defensive line, these defences were usually relatively thin and spread along the length of a line. The defence was usually not equally strong throughout however.
The strength of the defensive line in an area varied according to how rapidly an attacking force could progress in the terrain that was being defended—both the terrain the defensive line was built on and the ground behind it that an attacker might hope to break out into. This was both for reasons of the strategic value of the ground, and its defensive value.
This was possible because while offensive tactics were focused on mobility, so were defensive tactics. The dug in defences consisted primarily of infantry and antitank guns. Defending tanks and tank destroyers would be concentrated in mobile brigades behind the defensive line. If a major offensive was launched against a point in the line, mobile reinforcements would be sent to reinforce that part of the line that was in danger of failing.
Thus the defensive line could be relatively thin because the bulk of the fighting power of the defenders was not concentrated in the line itself but rather in the mobile reserves. A notable exception to this rule was seen in the defensive lines at the Battle of Kursk during World War II, where German forces deliberately attacked into the strongest part of the Soviet defences seeking to crush them utterly.
The terrain that was being defended was of primary importance because open terrain that tanks could move over quickly made possible rapid advances into the defenders' rear areas that were very dangerous to the defenders. Thus such terrain had to be defended at all cost.
In addition, since in theory the defensive line only had to hold out long enough for mobile reserves to reinforce it, terrain that did not permit rapid advance could be held more weakly because the enemy's advance into it would be slower, giving the defenders more time to reinforce that point in the line. For example, the Battle of the Hurtgen Forest
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
in Germany during the closing stages of World War II is an excellent example of how difficult terrain could be used to the defenders' advantage.
 After World War II,
After World War II, intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s capable of reaching much of the way around the world were developed, and so speed became an essential characteristic of the strongest militaries and defenses. Missile silos were developed, so missiles could be fired from the middle of a country and hit cities and targets in another country, and airplanes (and air carriers) became major defenses and offensive weapons (leading to an expansion of the use of airports and airstrips as fortifications). Mobile defenses could be had underwater, too, in the form of nuclear submarines capable of firing missiles. Some bunkers in the mid to late 20th century came to be buried deep inside mountains and prominent rocks, such as Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
and the Cheyenne Mountain Complex. On the ground itself, minefield
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automati ...
s have been used as hidden defences in modern warfare, often remaining long after the wars that produced them have ended.
Demilitarized zones along borders are arguably another type of fortification, although a passive kind, providing a buffer between potentially hostile militaries.
Military airfields
Military airfields offer a fixed "target rich" environment for even relatively small enemy forces, using hit-and-run tactics by ground forces, stand-off attacks (mortars and rockets), air attacks, or ballistic missiles. Key targets – aircraft, munitions, fuel, and vital technical personnel – can be protected by fortifications. Aircraft can be protected byrevetment
A revetment in stream restoration, river engineering or coastal engineering is a facing of impact-resistant material (such as stone, concrete, sandbags, or wooden piles) applied to a bank or wall in order to absorb the energy of incoming water
...
s, Hesco barriers, or hardened aircraft shelters which will protect from many types of attack. Larger aircraft types tend to be based outside the operational theatre.
Munition storage follows safety rules which use fortifications (bunkers and bunds) to provide protection against accident and chain reactions (sympathetic detonations). Weapons for rearming aircraft can be stored in small fortified ''expense'' stores closer to the aircraft. At Bien Hoa South Vietnam on the morning of 16 May 1965, as aircraft were being re-fuelled and armed, a chain reaction explosion destroyed 13 aircraft, killed 34 personnel, and injured over 100; this, along with damage and losses of aircraft to enemy attack (by both infiltration
Infiltration may refer to:
Science, medicine, and engineering
*Infiltration (hydrology), downward movement of water into soil
*Infiltration (HVAC), a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning term for air leakage into buildings
*Infiltration (me ...
and stand off attacks), led to the construction of revetments and shelters to protect aircraft throughout South Vietnam.
Aircrew and ground personnel will need protection during enemy attacks and fortifications range from culvert section "duck and cover" shelters to permanent air-raid shelters. Soft locations with high personnel densities such as accommodation and messing facilities can have limited protection by placing prefabricated concrete walls or barriers around them, examples of barriers are Jersey Barriers, T Barriers or Splinter Protection Units (SPUs). Older fortification may prove useful such as the old 'Yugo' pyramid shelters built in the 1980s which were used by US personnel on 8 Jan 2020 when Iran fired 11 ballistic missiles at Ayn al-Asad Airbase in Iraq.
Fuel is volatile and has to comply with rules for storage which provide protection against accident. Fuel in underground bulk fuel installations is well protected though valves and controls are vulnerable to enemy action. Above ground tanks can be susceptible to attack.
Ground support equipment will need to be protected by fortifications to be usable after an enemy attack.
Permanent (concrete) guard fortifications are safer, stronger, last longer and are more cost effective than sandbag fortifications. Prefabricated positions can be made from concrete culvert sections. The British Yarnold Bunker is made from sections of a concrete pipe.
Guard Towers provide increased field of view but a lower level of protection.
Dispersal and camouflage of assets can supplement fortifications against some forms of airfield attack.
Counter-insurgency
Just as in colonial periods, comparatively obsolete fortifications are still used for low-intensity conflicts. Such fortifications range in size from small patrol bases or forward operating bases up to hugeairbase
An air base (sometimes referred to as a military air base, military airfield, military airport, air station, naval air station, air force station, or air force base) is an aerodrome used as a military base by a military force for the operation ...
s such as Camp Bastion
Camp Shorabak (formerly Camp Bastion) is a former British Army airbase, located northwest of the city of Lashkargah in Helmand Province, Afghanistan. The camp was situated in a remote desert area, far from population centres.
The camp was built ...
/ Leatherneck in Afghanistan. Much like in the 18th and 19th century, because the enemy is not a powerful military force with the heavy weaponry required to destroy fortifications, walls of gabion, sandbag or even simple mud can provide protection against small arms and anti-tank weapons – although such fortifications are still vulnerable to mortar and artillery fire.
Forts
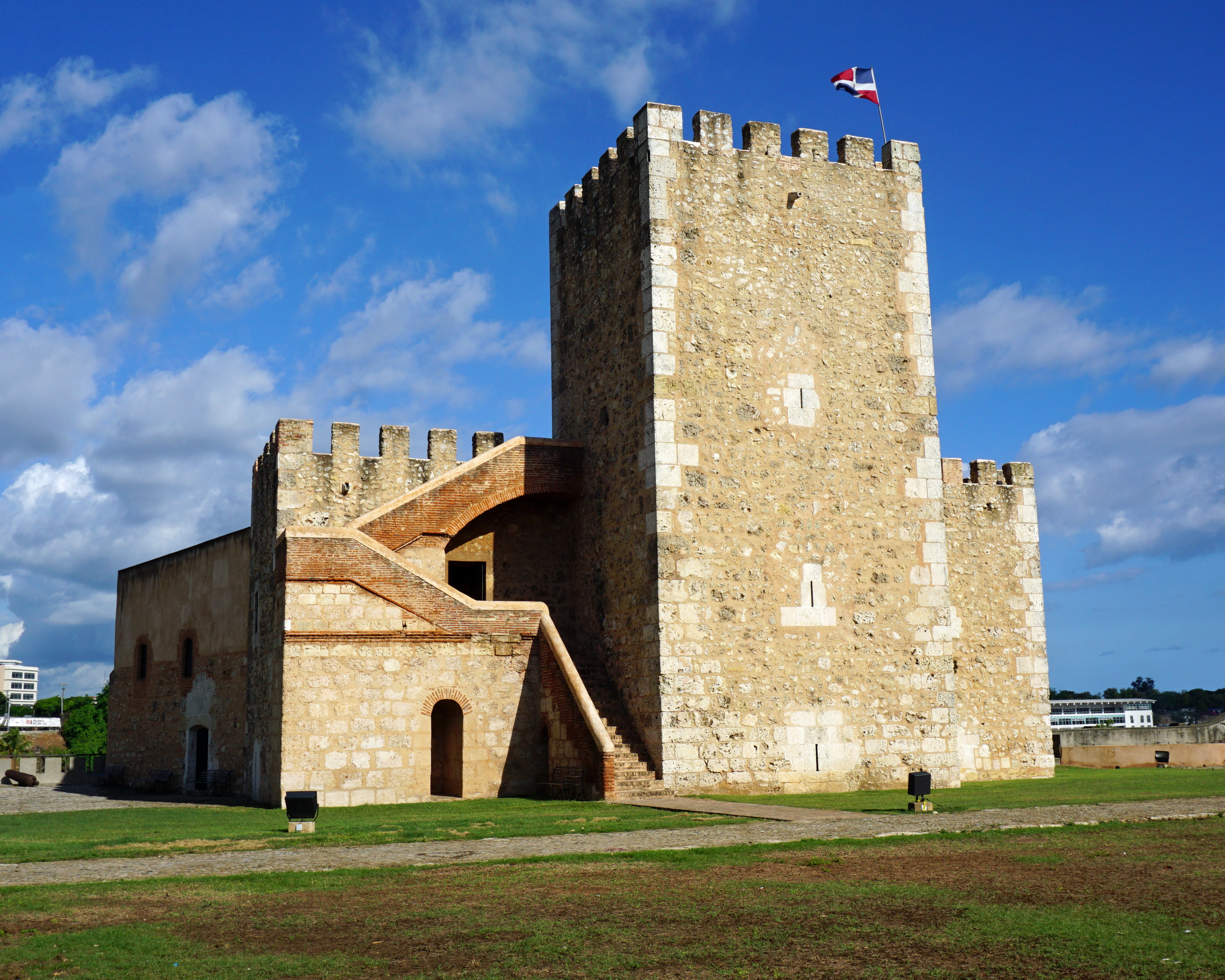
 Forts in modern American usage often refer to space set aside by governments for a permanent military facility; these often do not have any actual fortifications, and can have specializations (military barracks, administration, medical facilities, or intelligence).
However, there are some modern fortifications that are referred to as forts. These are typically small semi permanent fortifications. In urban combat they are built by upgrading existing structures such as houses or public buildings. In field warfare they are often log, sandbag or gabion type construction.
Such forts are typically only used in low level conflict, such as counterinsurgency conflicts or very low level conventional conflicts, such as the
Forts in modern American usage often refer to space set aside by governments for a permanent military facility; these often do not have any actual fortifications, and can have specializations (military barracks, administration, medical facilities, or intelligence).
However, there are some modern fortifications that are referred to as forts. These are typically small semi permanent fortifications. In urban combat they are built by upgrading existing structures such as houses or public buildings. In field warfare they are often log, sandbag or gabion type construction.
Such forts are typically only used in low level conflict, such as counterinsurgency conflicts or very low level conventional conflicts, such as the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation
The Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation or Borneo confrontation (also known by its Indonesian / Malay name, ''Konfrontasi'') was an armed conflict from 1963 to 1966 that stemmed from Indonesia's opposition to the creation of the Federation of ...
, which saw the use of log forts for use by forward platoons and companies. The reason for this is that static above ground forts can not survive modern direct or indirect fire weapons larger than mortars, RPGs and small arms.
Prisons and others
Fortifications designed to keep the inhabitants of a facility in rather than attacker out can also be found, inprisons
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correcti ...
, concentration camps, and other such facilities, with supermaxes having some of the strongest of those. Those are covered in other articles, as most prisons and concentration camps are not primarily military forts (although forts, camps, and garrison towns have been used as prisons and/or concentration camps; such as Theresienstadt, Guantanamo Bay detention camp
The Guantanamo Bay detention camp ( es, Centro de detención de la bahía de Guantánamo) is a United States military prison located within Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, also referred to as Guantánamo, GTMO, and Gitmo (), on the coast of Guant ...
and the Tower of London for example).
See also
* Border barrier *Castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
* Citadel
* Coastal defence and fortification
* Defense line
* Defensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
* Hesco bastion
* Imperial fortress
* Kuruwa, walls of a Japanese castle
* List of fortifications
This is a list of fortifications past and present, a fortification being a major physical defensive structure often composed of a more or less wall-connected series of forts.
Individual fortifications
''listed by name''
*A Famosa, built in the 1 ...
* List of forts
* Military camp
* Slighting
Fort components
* Abatis
* Banquette
* Barbed wire
A close-up view of a barbed wire
Roll of modern agricultural barbed wire
Barbed wire, also known as barb wire, is a type of steel fencing wire constructed with sharp edges or points arranged at intervals along the strands. Its primary use is t ...
, razor wire, wire entanglement, and wire obstacle
* Bartizan
* Bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
* Berm
* Capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
* Caponier
* Casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
* Castle walls
* Czech hedgehog
* Defensive fighting position
* Ditch
* Embrasure
* Glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in bastion fort, early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More genera ...
* Gun turret
* Keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
* Lunette
A lunette (French ''lunette'', "little moon") is a half-moon shaped architectural space, variously filled with sculpture, painted, glazed, filled with recessed masonry, or void.
A lunette may also be segmental, and the arch may be an arc take ...
* Machicolation
A machicolation (french: mâchicoulis) is a floor opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement, through which stones or other material, such as boiling water, hot sand, quicklime or boiling cooking oil, could be dropped on attackers at t ...
* Outwork
An outwork is a minor fortification built or established outside the principal fortification limits, detached or semidetached. Outworks such as ravelins, lunettes (demilunes), flèches and caponiers to shield bastions and fortification curtains ...
* Palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a fence or defensive wall made from iron or wooden stakes, or tree trunks, and used as a defensive structure or enclosure. Palisades can form a stockade.
Etymology
''Palisade' ...
* Parapet
* Pillbox
* Postern
* Ravelin
A ravelin is a triangular fortification or detached outwork, located in front of the innerworks of a fortress (the curtain walls and bastions). Originally called a ''demi-lune'', after the ''lunette'', the ravelin is placed outside a castle ...
* Rampart
* Revetment
A revetment in stream restoration, river engineering or coastal engineering is a facing of impact-resistant material (such as stone, concrete, sandbags, or wooden piles) applied to a bank or wall in order to absorb the energy of incoming water
...
* Sandbag
* Sangar
* Scarp and Counterscarp
* Turret
* '' Zwinger''
Types of forts and fortification
* Bastion fort
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to domin ...
(or star fort)
* Blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive stro ...
* Bunker
* Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
* Chinese city wall
* Compound
* Defensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
* Diaolou
* Fire support base
* Flak tower
* Fortress church or fortified church
* Grad, a Slavic wooden fortified settlement
* Gusuku
often refers to castles or fortresses in the Ryukyu Islands that feature stone walls. However, the origin and essence of ''gusuku'' remain controversial. In the archaeology of Okinawa Prefecture, the ''Gusuku period'' refers to an archaeologica ...
, fortifications in the Ryukyu Islands
* Korean fortress
* Hill fort
* Land battery
* Martello tower
* Medieval fortification
* Missile launch facility
* Pā
The word pā (; often spelled pa in English) can refer to any Māori village or defensive settlement, but often refers to hillforts – fortified settlements with palisades and defensive terraces – and also to fortified villages. Pā sites o ...
, a 19th-century Māori fortification
* Peel tower
Peel towers (also spelt pele) are small fortified keeps or tower houses, built along the English and Scottish borders in the Scottish Marches and North of England, mainly between the mid-14th century and about 1600. They were free-standin ...
* Polygonal fort
* Promontory fort
A promontory fort is a defensive structure located above a steep cliff, often only connected to the mainland by a small neck of land, thus using the topography to reduce the ramparts needed. Although their dating is problematic, most seem to da ...
* Redoubt
* Stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls, made of logs placed side by side vertically, with the tops sharpened as a defensive wall.
Etymology
''Stockade'' is derived from the French word ''estocade''. The French word was derived ...
Fortification and siege warfare
* Medieval warfare
* Military engineering
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics be ...
* Military history
Military history is the study of armed conflict in the history of humanity, and its impact on the societies, cultures and economies thereof, as well as the resulting changes to local and international relationships.
Professional historians norma ...
* Siege
* Siege engine
Notable experts
* Henri Alexis Brialmont
* César Cui
César Antonovich Cui ( rus, Це́зарь Анто́нович Кюи́, , ˈt͡sjezərʲ ɐnˈtonəvʲɪt͡ɕ kʲʊˈi, links=no, Ru-Tsezar-Antonovich-Kyui.ogg; french: Cesarius Benjaminus Cui, links=no, italic=no; 13 March 1918) was a Ru ...
* Bernard de Gomme
* Francesco Laparelli
* Mozi
Mozi (; ; Latinized as Micius ; – ), original name Mo Di (), was a Chinese philosopher who founded the school of Mohism during the Hundred Schools of Thought period (the early portion of the Warring States period, –221 BCE). The ancie ...
* Diades of Pella
* James of Saint George
* Fritz Todt
* Menno van Coehoorn
* Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban
Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Seigneur de Vauban, later Marquis de Vauban (baptised 15 May 163330 March 1707), commonly referred to as ''Vauban'' (), was a French military engineer who worked under Louis XIV. He is generally considered the ...
* Maximilian von Welsch
Notes
References
*Bibliography
* July, Robert ''Pre-Colonial Africa'', Charles Scribner, 1975 * Murray, Nicholas. "The Development of Fortifications," ''The Encyclopedia of War'', Gordon Martel (ed.). WileyBlackwell, 2011. * Murray, Nicholas. ''The Rocky Road to the Great War: The Evolution of Trench Warfare to 1914''. Potomac Books Inc. (an imprint of the University of Nebraska Press), 2013. * Osadolor, Osarhieme Benson, "The Military System of Benin Kingdom 1440–1897", (UD), Hamburg University: 200copy
* Thornton, John Kelly ''Warfare in Atlantic Africa'', 1500–1800, Routledge: 1999
External links
Fortress Study Group
*
ICOFORT
{{Authority control Military strategy Military installations Forts