|
Ancient Assyrians
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC), and post-imperial (609 BC– AD 240) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC, but there is no evidence that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur, in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kings starting with Puzur-Ashur I began ruling the city. Centered in the Assyrian heartland in northern Mesopotamia, Assyrian power fluctuated over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Cuneiform U121B3 MesZL 578
Assyrian may refer to: * Assyrian people, an indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia. * Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire. ** Early Assyrian Period ** Old Assyrian Period ** Middle Assyrian Empire ** Neo-Assyrian Empire ** Post-imperial Assyria * Assyrian language (other) * Assyrian Church (other) * SS ''Assyrian'', several cargo ships * ''The Assyrian'' (novel), a novel by Nicholas Guild * The Assyrian (horse), winner of the 1883 Melbourne Cup See also * Assyria (other) * Syriac (other) * Assyrian homeland, a geographic and cultural region in Northern Mesopotamia traditionally inhabited by Assyrian people * Syriac language, a dialect of Middle Aramaic that is the minority language of Syrian Christians * Upper Mesopotamia * Church of the East (other) Church of the East, also called ''Nestorian Church'', an Eastern Christian denomination formerly spread across Asia, separated since the schism of 1552. Church of the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written and spoken in different varieties for over three thousand years. Aramaic served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires, particularly the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire, and Achaemenid Empire, and also as a language of divine worship and religious study within Judaism, Christianity, and Gnosticism. Several modern varieties of Aramaic are still spoken. The modern eastern branch is spoken by Assyrians, Mandeans, and Mizrahi Jews.{{cite book , last1=Huehnergard , first1=John , author-link1=John Huehnergard , last2=Rubin , first2=Aaron D. , author-link2=Aaron D. Rubin , date=2011 , editor-last=Weninger , editor-first=Stefan , title=The Semitic Languages: An International Handbook , pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( or , meaning "Sin (mythology), Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 705BC until his assassination in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynasty, Sennacherib is one of the most famous Assyrian kings for the role he plays in the Hebrew Bible, which describes his Sennacherib's campaign in the Levant, campaign in the Levant. Other events of his reign include his destruction of the city of Babylon in 689BC and his renovation and expansion of the last great Assyrian capital, Nineveh. Although Sennacherib was one of the most powerful and wide-ranging Assyrian kings, he faced considerable difficulty in controlling Babylonia, which formed the southern portion of his empire. Many of Sennacherib's Babylonian troubles stemmed from the Chaldean tribal chief Marduk-apla-iddina II, who had been List of kings of Babylon, Babylon's king until Sennacherib's father defeated him. Shortly after Sennacherib inherited the throne in 705BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
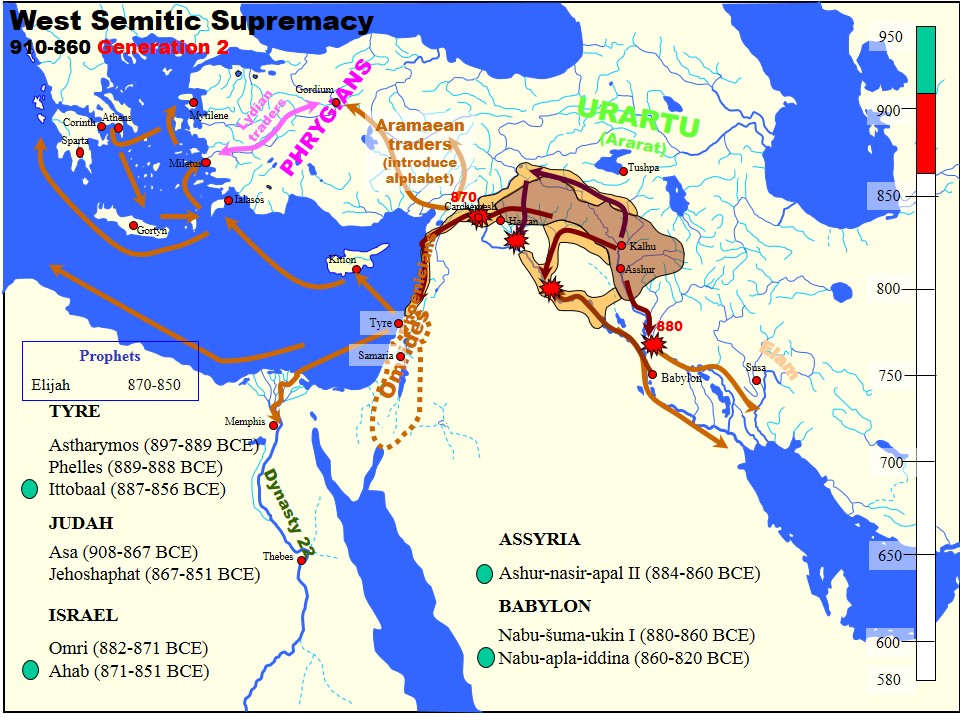
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II (transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning " Ashur is guardian of the heir") was the third king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III and his queen was Mullissu-mukannišat-Ninua. Reign During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. The palaces, temples and other buildings raised by him bear witness to a considerable development of wealth and art. Cruelty Ashurnasirpal II was notorious for his brutality, using enslaved captives to build a new Assyrian capital at Kalhu (Nimrud) in Mesopotamia where he built many impressive monuments. He was also a shrewd administrator, who realized that he could gain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiglath-Pileser I
Tiglath-Pileser I (; from the Hebraic form of , "my trust is in the son of Ešarra") was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian period (1114–1076 BC). According to Georges Roux, Tiglath-Pileser was "one of the two or three great Assyrian monarchs since the days of Shamshi-Adad I". He was known for his "wide-ranging military campaigns, his enthusiasm for building projects, and his interest in cuneiform tablet collections". Under him, Assyria became the leading power of the Ancient Near East, a position the kingdom largely maintained for the next five hundred years. He expanded Assyrian control into Anatolia and Syria, and to the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. From his surviving inscriptions, he seems to have carefully cultivated a fear of himself in his subjects and in his enemies alike. The beginning of Tiglath-Pileser's I reign had heavy involvement in military campaigns, as suggested from translated texts from the Middle Assyrian period. The texts were believed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tukulti-Ninurta I
Tukulti-Ninurta I (meaning: "my trust is in he warrior godNinurta"; reigned 1243–1207 BC) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He is known as the first king to use the title "King of Kings". Reign Tukulti-Ninurta I succeeded Shalmaneser I, his father, as king and won a major victory against the Hittite Empire at the Battle of Nihriya in the first half of his reign, appropriating Hittite territory in Asia Minor Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ... and the Levant. Tukulti-Ninurta I retained Assyrian control of Urartu, and later defeated Kashtiliash IV, the Kassites, Kassite king of Babylonia, and captured the rival city of Babylon to ensure full Assyrian supremacy over Mesopotamia. He set himself up as king of Babylon, and took on the ancient ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashur-uballit I
Ashur-uballit I ''(Aššur-uballiṭ I)'', who reigned between 1363 and 1328 BC, was the first king of the Middle Assyrian Empire. After his father Eriba-Adad I had broken Mitanni influence over Assyria, Ashur-uballit I's defeat of the Mitanni king Shuttarna III marks Assyria's ascendancy over the Hurri-Mitanni Empire, and the beginning of its emergence as a powerful empire. Later on, due to disorder in Babylonia following the death of the Kassite king Burnaburiash II, Ashur-uballit established Kurigalzu II on the Babylonian throne, in the first of what would become a series of Assyrian interventions in Babylonian affairs. Family and personal life Burnaburiash married Muballitat-Sherua of Assyria, the daughter of Ashur-uballit I. Together, they had at least one son, Prince Kara-hardash. They may also have been the parents of Kurigalzu II, or his grandparents. Amarna letters From the Amarna letters, a series of diplomatic letters from various Middle Eastern monarchs t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bel-bani
Bel-bani or Bēl-bāni, inscribed mdEN''-ba-ni'', “the Lord is the creator,” was the king of Assyria Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ... from 1700 to 1691 BC and was the first ruler of what was later to be called the dynasty of the Adasides. His reign marks the inauguration of a new historical phase following the turmoil of the competing claims of the seven usurpers who preceded him. He was the 48th king to appear on the Assyrian King List and reigned for ten years. Biography He was the son of Adasi, the last of the seven monarchs who were “sons of nobody,” i.e. unrelated to previous kings, and who had competed for the throne over a period of six years. He was to be revered by later monarchs, notably Esarhaddon (681–669 BC) but also his second and third s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad (; Amorite: ''Shamshi-Addu''), ruled 1813–1776 BC, was an Amorite warlord and conqueror who had conquered lands across much of Syria, Anatolia, and Upper Mesopotamia.Some of the Mari letters addressed to Shamsi-Adad by his son can be found in the Mari Letters section of His capital was originally at Ekallatum and later moved to Šubat-Enlil. Rise Shamshi-Adad I inherited the throne in Ekallatum from Ila-kabkabu (fl. c. 1836 BC – c. 1833 BC). Ila-kabkabu is mentioned as the father of Shamshi-Adad I in the "Assyrian King List" (AKL); a similar name (not necessarily the same figure) is listed in the preceding section of the AKL among the “kings whose fathers are known”. However, Shamshi-Adad I did not inherit the Assyrian throne from his father but was instead a conqueror. Ila-kabkabu had been an Amorite king not of Assur (Aššur) (in Assyria) but of Ekallatum. According to the '' Mari Eponyms Chronicle'', Ila-kabkabu seized Shuprum (c. 1790 BC), then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erishum I
Erishum I or Erišu(m) I (inscribed m''e-ri-šu'', or mAPIN''-ìš'' in later texts but always with an initial ''i'' in his own seal, inscriptions, and those of his immediate successors, “he has desired,”) 1974–1935 BCE (middle chronology),Some historians quote ca. 1939–1900 BCE (''after'' Amélie Kuhrt, The Ancient Near East, C. 3000-330 BCE, Volume 1, Routledge, 1996, p. 82). son of Ilu-shuma, was the thirty-third ruler of Assyria to appear on the Assyrian King List. He reigned for forty years.Khorsabad kinglist. One of two copies of the Assyrian King ListSDAS Kinglist: m''E-ri-š''">sup>m''E-ri-š''''u'' DUMU mDINGIR''-šum-ma'', 'šá li-ma-ni''? ''-šu-ni'' 10+ 30 MU.MEŠ LUGAL''-ta'' DÙ''-uš''. which include him gives his reign length as only 30 years, but this contrasts with a complete list of his limmu, some 40, which are extant from tabletsKEL A (kt 92/k 193), aCDLI. recovered at Karum Kanesh. He had titled himself both as, " Ashur is king, Erishum is vice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzur-Ashur I
Puzur-Ashur I () was an Assyrian king in the 21st and 20th centuries BC. He is generally regarded as the founder of Assyria as an independent city-state, 2025 BC. He is in the Assyrian King List and is referenced in the inscriptions of later kings (his son and successor Shalim-ahum and the later Ashur-rim-nisheshu and Shalmaneser III.) These later kings mentioned him among the kings who had renewed the city walls of Assur begun by Kikkia. Hildegard Lewy, "Assyria c. 2600-1816 B.C.", ''Cambridge Ancient History. Volume 1, Part 2: Early History of the Middle East'', 729-770, p. 746-747. Puzur-Ashur I may have started a native Assyrian dynasty that endured for eight generations until Erishum II was overthrown by the Amorite Shamshi-Adad I. Hildegard Lewy, writing in the '' Cambridge Ancient History'', rejects this interpretation and sees Puzur-Aššur I as part of a longer dynasty started by one of his predecessors, Sulili. Inscriptions link Puzur-Aššur I to his immedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |