Foreign Trade Of Belgium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The economy of Belgium is a modern, capitalist economy that has capitalised on the country's central geographic location, highly developed transport network, and diversified industrial and commercial base. Belgium was the first country to undergo an Industrial Revolution on the continent of Europe in the early 19th century. It has since developed an excellent transportation infrastructure of ports, canals, railways, and highways, in order to integrate its industry with that of its neighbours.
Industry is concentrated mainly in the populous region of Flanders in the north, around Brussels and in the two biggest Walloon cities,
 About 80% of Belgium's trade is with fellow EU member states. Given this high percentage, it seeks to diversify and expand trade opportunities with non-EU countries. The Belgian authorities are, as a rule, anti-protectionist and try to maintain a hospitable and open trade and investment climate. The European Commission negotiates on trade issues for all member states, which, in turn lessens bilateral trade disputes with Belgium.
The Belgian Government encourages new foreign investment as a means to promote employment. With regional devolution, Flanders, Brussels, and Wallonia are now courting potential foreign investors and offer a host of incentives and benefits. Foreign companies in Belgium account for approximately 11% of the total work force, with the U.S.
Attracted by the EU 1992 single-market program, many foreign firms and lawyers have settled in Brussels since 1989.
About 80% of Belgium's trade is with fellow EU member states. Given this high percentage, it seeks to diversify and expand trade opportunities with non-EU countries. The Belgian authorities are, as a rule, anti-protectionist and try to maintain a hospitable and open trade and investment climate. The European Commission negotiates on trade issues for all member states, which, in turn lessens bilateral trade disputes with Belgium.
The Belgian Government encourages new foreign investment as a means to promote employment. With regional devolution, Flanders, Brussels, and Wallonia are now courting potential foreign investors and offer a host of incentives and benefits. Foreign companies in Belgium account for approximately 11% of the total work force, with the U.S.
Attracted by the EU 1992 single-market program, many foreign firms and lawyers have settled in Brussels since 1989.
 The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation under 5% is in green.
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation under 5% is in green.
OECD's Belgium country Web site
an
OECD Economic Survey of Belgium
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Belgium
Belgian banking digest
{{DEFAULTSORT:Economy of Belgium Belgium Belgium Belgium
Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
and Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
, along the sillon industriel
The ''Sillon industriel'' (, "industrial furrow") is the former industrial backbone of Belgium. It runs across the region of Wallonia, passing from Dour, the region of Borinage, in the west, to Verviers in the east, passing along the way through ...
. Belgium imports raw materials and semi-finished goods that are further processed and re-exported. Except for its coal, which is no longer economical to exploit, Belgium has few natural resources other than fertile soils. Nonetheless, most traditional industrial sectors are represented in the economy, including steel, textiles, refining, chemicals, food processing
Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing includes many forms of processing foods, from grinding grain to make raw flour to home cooking to complex industr ...
, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, electronics, and machinery fabrication. Despite the heavy industrial component, services account for 74.9% of GDP, while agriculture accounts for only 1% of GDP.
With exports equivalent to over two-thirds of GNP, Belgium depends heavily on world trade. Belgium's trade advantages are derived from its central geographic location and a highly skilled, multilingual, and productive work force. One of the founding members of the European Community, Belgium strongly supports deepening the powers of the present-day European Union to integrate European economies further. About three-quarters of its trade is with other EU countries. Together with the Netherlands and Luxembourg, Belgium is also one of Benelux member states. Belgium began circulating the euro currency in January 2002.
As of 2021, Belgium's public debt was about 108% of GDP.
History
In the twentieth century
For 50 years through World War II,French-speaking
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Nor ...
Wallonia was a technically advanced, industrial region, with its industry concentrated along the sillon industriel
The ''Sillon industriel'' (, "industrial furrow") is the former industrial backbone of Belgium. It runs across the region of Wallonia, passing from Dour, the region of Borinage, in the west, to Verviers in the east, passing along the way through ...
, while Dutch-speaking
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' i ...
Flanders was predominantly agricultural with some industry, mainly processing agricultural products and textiles. This disparity began to fade during the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the World War I, First World War to the beginning of the World War II, Second World War. The in ...
. When Belgium emerged from World War II with its industrial infrastructure relatively undamaged thanks to the Galopin doctrine, the stage was set for a period of rapid development, particularly in Flanders. The postwar boom years, enhanced by the establishment of the European Union and NATO headquarters in Brussels, contributed to the rapid expansion of light industry throughout most of Flanders, particularly along a corridor stretching between Brussels and Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, which is the second largest port in Europe after Rotterdam.
Foreign investment contributed significantly to Belgian economic growth in the 1960s. In particular, U.S. firms played a leading role in the expansion of light industrial and petrochemical industries in the 1960s and 1970s.
The older, traditional industries of Wallonia, particularly steel industry, began to lose their competitive edge during this period, but the general growth of world prosperity masked this deterioration until the 1973
Events January
* January 1 - The United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland and Denmark enter the European Economic Community, which later becomes the European Union.
* January 15 – Vietnam War: Citing progress in peace negotiations, U.S. ...
and 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
oil price shocks and resultant shifts in international demand sent the economy into a period of prolonged recession. In the 1980s and 1990s, the economic center of the country continued to shift northwards to Flanders with investments by multinationals ( Automotive industry, Chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials (oil, natural gas, air, water, metals, and minerals) into more than 70,000 different products. The ...
) and a growing local Industrial agriculture (textiles, food).
The early 1980s saw the country facing a difficult period of structural adjustment
Structural adjustment programs (SAPs) consist of loans (structural adjustment loans; SALs) provided by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank (WB) to countries that experience economic crises. Their purpose is to adjust the coun ...
caused by declining demand for its traditional products, deteriorating economic performance, and neglected structural reform. Consequently, the 1980–82 recession shook Belgium to the core—unemployment mounted, social welfare costs increased, personal debt soared, the government deficit
The government budget balance, also alternatively referred to as general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the overall difference between government revenues and spending. A positive balance is called a ''g ...
climbed to 13% of GDP, and the national debt, although mostly held domestically, mushroomed.
Against this grim backdrop, in 1982, Prime Minister Martens' center-right coalition government formulated an economic recovery program to promote export-led growth
Export-oriented industrialization (EOI) sometimes called export substitution industrialization (ESI), export led industrialization (ELI) or export-led growth is a trade and economic policy aiming to speed up the industrialization process of a ...
by enhancing the competitiveness of Belgium's export industries through an 8.5% devaluation. Economic growth rose from 2% in 1984 to a peak of 4% in 1989. In May 1990, the government linked the Belgian franc
The Belgian franc ( nl, Belgische frank, french: Franc belge, german: Belgischer Franken) was the currency of the Kingdom of Belgium from 1832 until 2002 when the Euro was introduced. It was subdivided into 100 subunits, each known as a in Dutch ...
to the Deutsche Mark, primarily through closely tracking German interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, th ...
. Consequently, as German interest rates rose after 1990, Belgian rates have increased and contributed to a decline in the economic growth rate. In 1992–93, the Belgian economy suffered the worst recession since World War II, with the real GDP declining 1.7% in 1993.
On 1 May 1998, Belgium became a first-tier member of the European Monetary Union.
In the twenty-first century
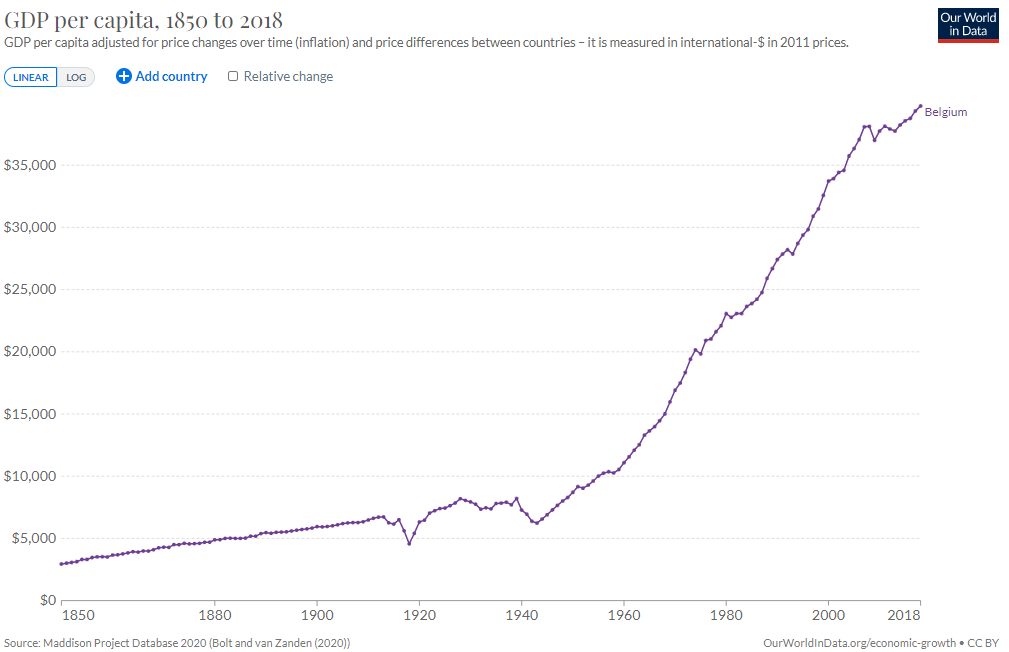
Belgium switched from the Belgian franc to the Euro as its currency after 1 January 2002. Belgian per capita GDP ranks among the world's highest. In 2008, the per capita income (PPP) was $37,500. The federal government has not managed to present balanced budgets in recent years and public debt remains high, at 99% of 2009 GDP. In 2009 Belgium suffered negative growth and increased unemployment, stemming from the worldwide banking crisis. GDP growth in 2009 was negative at −1.5%.Trade unions
Belgium
With 65% of the workers belonging to a union, Belgium is a country with one of the highest percentages of trade union membership. Only the Scandinavian countries have a higher trade union density. The biggest union with around 1.7 million members is the Christian democratConfederation of Christian Trade Unions
The Confederation of Christian Trade Unions ( nl, Algemeen Christelijk Vakverbond, or ACV; french: Confédération des syndicats chrétiens, CSC) is the largest of Belgium's three trade union federations.
History
The federation was founded in ...
(ACV-CSC) which was founded in 1904. The origins of the union can be traced back to the "Anti-Socialist Cotton Workers Union" that was founded in 1886. The second biggest union is the socialist General Federation of Belgian Labour (ABVV-FGTB) which has a membership of more than 1.5 million. The ABVV-FGTB traces its origins to 1857, when the first Belgian union was founded in Ghent by a group of weavers. This and other socialist unions became unified around 1898. The ABVV-FGTB in its current form dates back to 1945. The third major multi-sector union in Belgium is the liberal (classical liberal) union General Confederation of Liberal Trade Unions of Belgium (ACLVB-CGSLB) which is relatively small in comparison to the first two with a little under 290 thousand members. The ACLVB-CGSLB was founded in 1920 in an effort to unite the many small liberal unions. Back then the liberal union was known as the "Nationale Centrale der Liberale Vakbonden van België". In 1930, the ACLVB-CGSLB adopted its current name.
Besides these "big three" there are a number of smaller unions, some more influential than others. These smaller unions tend to specialize in one profession or economic sector. Next to these specialized unions there is also the Neutral and Independent Union that rejects the pillarization of the "big three" trade unions (their affiliation with political parties). There is also a small Flemish nationalist union that exists only in the Flemish-speaking part of Belgium, called the Vlaamse Solidaire Vakbond. The last Belgian union worth mentioning is the very small, but highly active anarchist union called the Vrije Bond.
Trade
Employment
The social security system, which expanded rapidly during the prosperous 1950s and 1960s, includes a medical system, unemployment insurance coverage, child allowances, invalid benefits, and other benefits and pensions. With the onset of a recession in the 1970s, this system became an increasing burden on the economy and accounted for much of the government budget deficits. The national unemployment figures mask considerable differences between Flanders and Wallonia. Unemployment in Wallonia is mainly structural, while in Flanders it is cyclical. Flanders' unemployment levels are generally only about half those of Walloon. The southern region continues a difficult transition out of sunset industries (mainly coal and steel), while sunrise industries (chemicals, high-tech, and services) dominate in Flanders. Belgium's unemployment rate was 6.5% in 2008. A total of 4.99 million people make up Belgium's labor force. The vast majority of these people (80%), work in the service sector. Belgian industry claims 19% of the labor force and agriculture only 1%. As in other industrialized nations, pension and other social entitlement programs have become a major concern as thebaby boom
A baby boom is a period marked by a significant increase of birth rate. This demographic phenomenon is usually ascribed within certain geographical bounds of defined national and cultural populations. People born during these periods are often ca ...
generation approaches retirement.
Budget
Although Belgium is a wealthy country, public expenditures far exceeded income for many years, and taxes were not diligently pursued. The Belgian Government reacted to the 1973 and 1979 oil price hikes by hiring the redundant work force into the public sector and subsidizing industries like coal, steel, textiles, glass, and shipbuilding, which had lost their international competitive edge. As a result, cumulative government debt reached 121% of GDP by the end of the 1980s. However, thanks to Belgium's high personal savings rate, the Belgian Government financed the deficit from mainly domestic savings, minimizing the deleterious effects on the overall economy. The federal government ran a 7.1% budget deficit in 1992 at the time of the EU's Treaty of Maastricht, which established conditions for Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) that led to adoption of the common Euro currency on 1 January 2002. Among other criteria spelled out under the Maastricht treaty, the Belgian Government had to attain a budget deficit of no greater than 3% of GDP by the end of 1997; Belgium achieved this, with a total budget deficit in 2001 (just prior to implementation of the Euro) that amounted to 0.2% of GDP. The government has balanced the budget every year since, until 2009 where it ran a deficit of about $25 billion. Belgium's accumulated public debt remains high at 99% of 2009 GDP. A slight decrease in the accumulated public debt compared to GDP has been seen, however, thanks to a higher economic growth rate compared to the budget growth rate, which pushed the percentage from 99% of GDP in 2009 to 95% of GDP in 2011, a four-point decrease in two years, a feat rare enough to mention in the Western World.Regional differences
The economy of Belgium is varied and cannot be understood without taking the regional differences into account. Indeed, Flemish and Walloon economies differ in many respects (consider for instance Eurostat and OECD statistics), and cities like Brussels, Antwerp,Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
, Bruges, Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
or Ghent also exhibit significant differences. In general, productivity in Flanders is roughly 20% higher (per inhabitant) than in Wallonia. Brussels' GDP per capita is much higher than either region, although this is in many ways artificial, as many of those that work in the Brussels-Capital Region live in Flanders or Wallonia. Their output is counted in Brussels and not where they live, artificially raising the ''per capita'' GDP of Brussels and slightly lowering that of Flanders and Wallonia.
Unemployment has remained consistently more than twice as high in Wallonia than in Flanders, and even more in Brussels, during most of the last 20 years (2012: Flanders: 4.55%; Wallonia: 10.12% and Brussels: 17.47%).
Brussels
Being the de facto European capital, its economy is massively service-oriented. It has a number of regional headquarters of multinational corporations. It is also host to a great number of European institutions, in addition to the Belgian federal government, the government of theFlemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
and the government of the French Community
The French Community (1958–1960; french: Communauté française) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
. Brussels also has many commuters, with 230,000 coming from Flanders, and 130,000 from Wallonia. Much of the success of Brussels is based on the high educational skills of its workforce. As of July 2012, however, the statistical unemployment rate in Brussels was 20.6%.
Flanders
In 2004 the port of Antwerp was the second largest European sea port by cargo volume, and the Antwerp freight railway station accounts for one-third of Belgian freight traffic. Antwerp is the first diamond market in the world, diamond exports account for roughly 1/10 of Belgian exports. The Antwerp-based BASF plant is the largest BASF-base outside Germany, and accounts on its own for about 2% of Belgian exports. Other industrial and service activities include car manufacturing, telecommunications, photographic products. The port of Bruges-Zeebrugge is one of the most important, modern and fastest growing ports in Europe. It is Europe's largest port for RoRo traffic and natural gas. It also is the world's largest port for the import and export of new vehicles. Tourism is also a major component of the economy of Bruges. Due to its pristine medieval city centre, Bruges has become a popular tourist destination. Annually about 2.5 million day tourists visit the city and in 2007 there were about 1.4 million overnight stays. The port of Ghent, in the north of the city, is the third largest port of Belgium. It is accessed by the Ghent–Terneuzen Canal, which ends near the Dutch port ofTerneuzen
Terneuzen () is a city and municipality in the southwestern Netherlands, in the province of Zeeland, in the middle of Zeelandic Flanders. With almost 55,000 inhabitants, it is the most populous municipality of Zeeland.
History
First mentione ...
on the Western Scheldt. The port houses, among others, big companies like ArcelorMittal, Volvo Cars, Volvo Trucks, Volvo Parts, Honda, and Stora Enso. The Ghent University, the second largest university of Belgium by number of students, and a number of research oriented companies are situated in the central and southern part of the city. Tourism is increasingly becoming a major employer in the local area. Begonia
''Begonia'' is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Begoniaceae. The genus contains more than 2,000 different plant species. The Begonias are native to moist subtropical and tropical climates. Some species are commonly grown ind ...
s have been cultivated in the Ghent area since 1860. Belgium is the world's largest producer of begonias, planting 60 million tubers per year. Eighty percent of the crop is exported.
Wallonia
In the past,Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
was one of the most important steel-making centres in Europe. Starting in 1817, John Cockerill extensively developed the iron and steel industry. The industrial complex of Seraing was the largest in the world. Although now a shadow of its former self, steel production and the manufacture of steel goods remain important.
Liège has also been an important centre for gunsmithing since the Middle ages and the arms industry is still strong with the headquarters of FN Herstal
Fabrique Nationale Herstal (), trading as FN Herstal and often referred to as Fabrique Nationale or simply FN, is a leading firearms manufacturer based in Herstal, Belgium. It is currently the largest exporter of military small arms in Europe.
F ...
. The economy of the region is now diversified, the most important centers are mechanical industries (aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many ...
and Spacecraft propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric e ...
), space technology, information technology, biotechnology and also production of water, beer or chocolate. Liège Science Park
Liège Science Park is a business incubator and science park of the University of Liège and is located on the territories of the municipalities of Seraing and Liège in Belgium.
History
In 1953, Marcel Dubuisson, the new president of the Univ ...
south east of the city, near the University of Liège campus, houses spin-offs and high technology businesses. Liège is also a very important logistic center: the city possesses the third largest river port in Europe, directly connected to Antwerp, Rotterdam and Germany via the Meuse river and the Albert Canal. In 2006 Liège Airport was the 8th most important cargo airport in Europe. A new passenger terminal was opened in 2005. It is also the main hub and the headquarters of TNT Airways
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reage ...
.
Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
features an industrial area, iron and steel industry, glassworks, chemicals, and electrical engineering. Charleroi is in the center of a vast coal basin, called ''Pays Noir
The ''Pays Noir'' (French, 'black country') refers to a region of Belgium, centered on Charleroi in the province of Hainaut in Wallonia so named for the geological presence of coal. In the 19th century the region rapidly industrialised first with ...
''. Many slag heaps still surround the city. Charleroi is also known for its publishing industry with Dupuis, one of the main publishers of Franco-Belgian comics, located in Marcinelle.
Data
 The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation under 5% is in green.
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation under 5% is in green.
See also
*Agriculture in Flanders
Agriculture and horticulture in Flanders has traditionally a familial character, but just like agriculture in other regions, is increasingly characterised by an increase in scale, modernisation and expansion. In Flanders, intensive sectors cons ...
* Commemorative coins of Belgium
Euro gold and silver commemorative coins are special euro coins Mint (coin), minted and issued by member states of the Eurozone, mainly in gold and silver, although other precious metals are also used in rare occasions. Belgium was one of the f ...
* Science and technology in Belgium
*List of largest companies in Belgium
This article lists the largest Company, companies in Belgium in terms of their revenue, net profit and total assets, according to the American business magazines ''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'' and ''Forbes''. 2019 ''Fortune'' list
This list disp ...
References
* *External links
OECD's Belgium country Web site
an
OECD Economic Survey of Belgium
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Belgium
Belgian banking digest
{{DEFAULTSORT:Economy of Belgium Belgium Belgium Belgium