
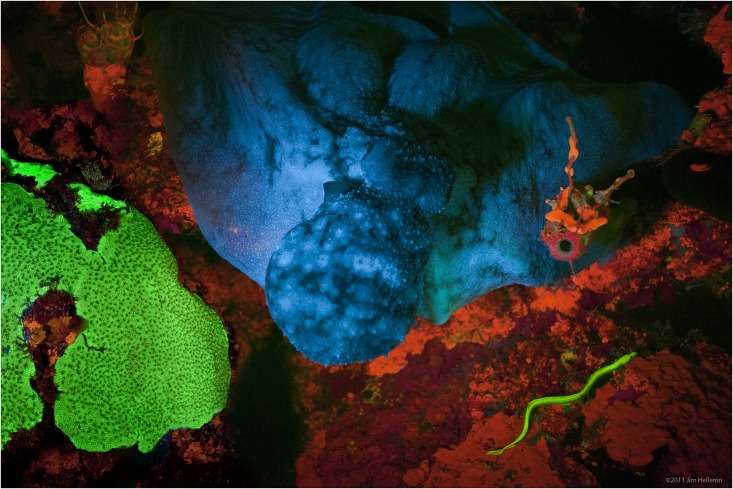

Fluorescence is the emission of
light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
by a substance that has absorbed light or other
electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, inf ...
. It is a form of
luminescence
Luminescence is spontaneous emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; or "cold light".
It is thus a form of cold-body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions or stress on a cryst ...
. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer
wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
, and therefore a lower
photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the
ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
region of the
electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from ...
(invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the
visible region
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visual perception, visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye wil ...
; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct
color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to
UV light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike
phosphorescent
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluor ...
materials, which continue to emit light for some time after.
Fluorescence has many practical applications, including
mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proces ...
,
gemology
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a geoscience and a branch of mineralogy. Some jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identify a ...
,
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, chemical sensors (
fluorescence spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the electron ...
),
fluorescent labelling
In molecular biology and biotechnology, a fluorescent tag, also known as a fluorescent label or fluorescent probe, is a molecule that is attached chemically to aid in the detection of a biomolecule such as a protein, antibody, or amino acid. Gener ...
,
dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
s, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection,
vacuum fluorescent display
A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens.
A VFD operates on the principle of cathodoluminescence, roughly s ...
s, and
cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictur ...
s. Its most common everyday application is in (
gas-discharge)
fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet lig ...
s and
LED lamps
An LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light that produces light using light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps are significantly more energy-efficient than equivalent incandescent lamps
and can be significantly more efficient than mos ...
, in which fluorescent coatings convert UV or blue light into longer-wavelengths resulting in
white light which can even appear indistinguishable from that of the traditional but energy- inefficient
incandescent lamp
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxid ...
.
Fluorescence also occurs frequently in nature in some minerals and in many biological forms across all kingdoms of life. The latter may be referred to as ''biofluorescence'', indicating that the
fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with se ...
is part of or is extracted from a living organism (rather than an inorganic
dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
or
stain
A stain is a discoloration that can be clearly distinguished from the surface, material, or medium it is found upon. They are caused by the chemical or physical interaction of two dissimilar materials. Accidental staining may make materials app ...
). But since fluorescence is due to a specific chemical, which can also be synthesized artificially in most cases, it is sufficient to describe the substance itself as ''fluorescent''.
History
An early observation of fluorescence was described in 1560 by
Bernardino de Sahagún
Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he ...
and in 1565 by
Nicolás Monardes
Nicolás Bautista Monardes (1493 – 10 October 1588) was a Spanish physician and botanist.
Monardes published several books of varying importance. In ''Diálogo llamado pharmacodilosis'' (1536), he examines humanism and suggests studying s ...
in the
infusion
Infusion is the process of extracting chemical compounds or flavors from plant material in a solvent such as water, oil or alcohol, by allowing the material to remain suspended in the solvent over time (a process often called steeping). An inf ...
known as ''
lignum nephriticum
''Lignum nephriticum'' (Latin for "kidney wood") is a traditional diuretic that was derived from the wood of two tree species, the narra (''Pterocarpus indicus'') and the Mexican kidneywood (''Eysenhardtia polystachya''). The wood is capable of t ...
'' (
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "kidney wood"). It was derived from the wood of two tree species, ''
Pterocarpus indicus
''Pterocarpus indicus'' (commonly known as Amboyna wood, Malay padauk, Papua New Guinea rosewood, Philippine mahogany, Andaman redwood, Burmese rosewood, narra and asana in the Philippines, angsana, or Pashu padauk) is a species of ''Pterocarpus ...
'' and ''
Eysenhardtia polystachya
''Eysenhardtia polystachya'', the kidneywood, is a tree from Mexico, growing along forest edges and water courses at elevations of 150–3000 m. Previously it was used as a source of lignum nephriticum.
References
*
polystachya
...
''.
[
][
]
The chemical compound responsible for this fluorescence is matlaline, which is the oxidation product of one of the
flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids ...
s found in this wood.
[
In 1819, E.D. Clarke
and in 1822 ]René Just Haüy
René Just Haüy () FRS MWS FRSE (28 February 1743 – 1 June 1822) was a French priest and mineralogist, commonly styled the Abbé Haüy after he was made an honorary canon of Notre Dame. Due to his innovative work on crystal structure and hi ...
described fluorescence in fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs sca ...
s, Sir David Brewster
Sir David Brewster KH PRSE FRS FSA Scot FSSA MICE (11 December 178110 February 1868) was a British scientist, inventor, author, and academic administrator. In science he is principally remembered for his experimental work in physical optics ...
described the phenomenon for chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
in 1833
and Sir John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical wor ...
did the same for quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cr ...
in 1845.
In his 1852 paper on the "Refrangibility" (wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
change) of light, George Gabriel Stokes
Sir George Gabriel Stokes, 1st Baronet, (; 13 August 1819 – 1 February 1903) was an Irish migration to Great Britain, Irish English physicist and mathematician. Born in County Sligo, Ireland, Stokes spent all of his career at the University ...
described the ability of fluorspar and uranium glass
Uranium glass is glass which has had uranium, usually in oxide diuranate form, added to a glass mix before melting for colouration. The proportion usually varies from trace levels to about 2% uranium by weight, although some 20th-century piec ...
to change invisible light beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum into blue light. He named this phenomenon ''fluorescence''
: "I am almost inclined to coin a word, and call the appearance ''fluorescence'', from fluor-spar .e., fluorite as the analogous term ''opalescence'' is derived from the name of a mineral."[
]
The name was derived from the mineral fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs sca ...
(calcium difluoride), some examples of which contain traces of divalent europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanth ...
, which serves as the fluorescent activator to emit blue light. In a key experiment he used a prism to isolate ultraviolet radiation from sunlight and observed blue light emitted by an ethanol solution of quinine exposed by it.
Physical principles
Mechanism
Fluorescence occurs when an excited molecule, atom, or nanostructure
A nanostructure is a structure of intermediate size between microscopic and molecular structures. Nanostructural detail is microstructure at nanoscale.
In describing nanostructures, it is necessary to differentiate between the number of dimens ...
, relaxes to a lower energy state (usually the ground state
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. ...
) through emission of a photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
without a change in electron spin
In atomic physics, the electron magnetic moment, or more specifically the electron magnetic dipole moment, is the magnetic moment of an electron resulting from its intrinsic properties of spin (physics), spin and electric charge. The value of the ...
. When the initial and final states have different multiplicity (spin), the phenomenon is termed phosphorescence
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluo ...
.
The ground state of most molecules is a singlet state
In quantum mechanics, a singlet state usually refers to a system in which all electrons are paired. The term 'singlet' originally meant a linked set of particles whose net angular momentum is zero, that is, whose overall spin quantum number s=0. A ...
, denoted as S0. A notable exception is molecular oxygen
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (O2), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (O3). Others are:
*A ...
, which has a triplet ground state. Absorption of a photon of energy results in an excited state of the same multiplicity (spin) of the ground state, usually a singlet (Sn with n > 0). In solution, states with n > 1 relax rapidly to the lowest vibrational level of the first excited state (S1) by transferring energy to the solvent molecules through non-radiative processes, including internal conversion followed by vibrational relaxation, in which the energy is dissipated as heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
.frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
according to , where is Planck's constant.
The excited state S1 can relax by other mechanisms that do not involve the emission of light. These processes, called non-radiative processes, compete with fluorescence emission and decrease its efficiency.internal conversion
Internal conversion is a non-radioactive, atomic decay process where an excited nucleus interacts electromagnetically with one of the orbital electrons of an atom. This causes the electron to be emitted (ejected) from the atom. Thus, in internal ...
, intersystem crossing Intersystem crossing (ISC) is an isoenergetic radiationless process involving a transition between the two electronic states with different spin multiplicity.
Excited Singlet and Triplet States
When an electron in a molecule with a singlet ground ...
to the triplet state, and energy transfer to another molecule. An example of energy transfer is Förster resonance energy transfer
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer, resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules ( chromophores). ...
. Relaxation from an excited state can also occur through collisional quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, such as pha ...
, a process where a molecule (the quencher) collides with the fluorescent molecule during its excited state lifetime. Molecular oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
(O2) is an extremely efficient quencher of fluorescence just because of its unusual triplet ground state.
Quantum yield
The fluorescence quantum yield The quantum yield (Φ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system.
Applications
Fluorescence spectroscopy
The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the ratio of the numb ...
gives the efficiency of the fluorescence process. It is defined as the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number of photons absorbed.[
]
:
The maximum possible fluorescence quantum yield is 1.0 (100%); each photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
absorbed results in a photon emitted. Compounds with quantum yields of 0.10 are still considered quite fluorescent. Another way to define the quantum yield of fluorescence is by the rate of excited state decay:
:
where is the rate constant of spontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission is the process in which a quantum mechanical system (such as a molecule, an atom or a subatomic particle) transits from an excited energy state to a lower energy state (e.g., its ground state) and emits a quantized amount of ...
of radiation and
:
is the sum of all rates of excited state decay. Other rates of excited state decay are caused by mechanisms other than photon emission and are, therefore, often called "non-radiative rates", which can include:
* dynamic collisional quenching
* near-field dipole-dipole interaction (or resonance energy transfer
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied Periodic function, periodic force (or a Fourier analysis, Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system ...
)
* internal conversion
* intersystem crossing Intersystem crossing (ISC) is an isoenergetic radiationless process involving a transition between the two electronic states with different spin multiplicity.
Excited Singlet and Triplet States
When an electron in a molecule with a singlet ground ...
Thus, if the rate of any pathway changes, both the excited state lifetime and the fluorescence quantum yield will be affected.
Fluorescence quantum yields are measured by comparison to a standard. The quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cr ...
salt ''quinine sulfate'' in a sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
solution was regarded as the most common fluorescence standard,
however, a recent study revealed that the fluorescence quantum yield of this solution is strongly affected by the temperature, and should no longer be used as the standard solution. The quinine in 0.1 M perchloric acid (Φ=0.60) shows no temperature dependence up to 45°C, therefore it can be considered as a reliable standard solution.
Lifetime
 The fluorescence lifetime refers to the average time the molecule stays in its excited state before emitting a photon. Fluorescence typically follows
The fluorescence lifetime refers to the average time the molecule stays in its excited state before emitting a photon. Fluorescence typically follows first-order kinetics
In chemistry, the rate law or rate equation for a reaction is an equation that links the initial or forward reaction rate with the concentrations or pressures of the reactants and constant parameters (normally rate coefficients and partial reactio ...
:
:
where


 Fluorescence is the emission of
Fluorescence is the emission of  The fluorescence lifetime refers to the average time the molecule stays in its excited state before emitting a photon. Fluorescence typically follows
The fluorescence lifetime refers to the average time the molecule stays in its excited state before emitting a photon. Fluorescence typically follows


 Fluorescence is the emission of
Fluorescence is the emission of