Fluorescent D-amino Acids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fluorescent D-amino acids (FDAAs) are
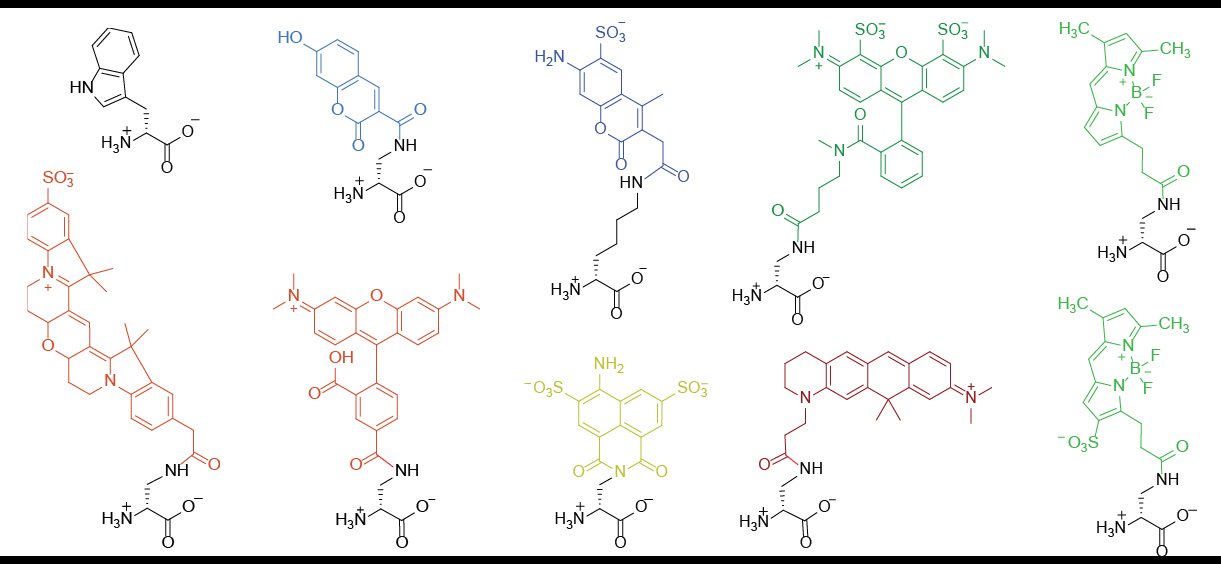 FDAA consists of a D-amino acid and a fluorophore (coupled through the amino acid side chain.) The D-amino acid backbone is required for its incorporation into the bacterial peptidoglycan through the activity of DD-transpeptidases. Once being incorporated, one can use fluorescence-detection techniques to visualize the location of new PG formation as well as the growth rate.
D-alanine is the most well-studied D-amino acids for FDAA development because it is a naturally existing residue in bacterial peptidoglycan structures. On the other hand, various fluorophores have been employed for FDAA applications and each has its features. For example, coumarin-based FDAA (HADA) is small enough to penetrate the bacterial outer-membranes and thus is widely used for Gram-negative bacterial studies; while TAMRA-based FDAA (TADA) features its high brightness and photo/thermo-stability, which is suitable for super-resolution microscopy (strong excitation light is used).
FDAA consists of a D-amino acid and a fluorophore (coupled through the amino acid side chain.) The D-amino acid backbone is required for its incorporation into the bacterial peptidoglycan through the activity of DD-transpeptidases. Once being incorporated, one can use fluorescence-detection techniques to visualize the location of new PG formation as well as the growth rate.
D-alanine is the most well-studied D-amino acids for FDAA development because it is a naturally existing residue in bacterial peptidoglycan structures. On the other hand, various fluorophores have been employed for FDAA applications and each has its features. For example, coumarin-based FDAA (HADA) is small enough to penetrate the bacterial outer-membranes and thus is widely used for Gram-negative bacterial studies; while TAMRA-based FDAA (TADA) features its high brightness and photo/thermo-stability, which is suitable for super-resolution microscopy (strong excitation light is used).
 Peptidoglycan (PG) is a mesh-like structure containing polysaccharides cross-linked by peptide chains.
Peptidoglycan (PG) is a mesh-like structure containing polysaccharides cross-linked by peptide chains.
FDAA website
Amino acids
D-amino acid
D-Amino acids are amino acids where the stereogenic carbon alpha to the amino group has the D-configuration. For most naturally-occurring amino acids, this carbon has the L-configuration. D-Amino acids are occasionally found in nature as residue ...
derivatives whose side-chain terminal is covalently coupled with a fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with se ...
molecule. FDAAs incorporate into the bacterial peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ...
(PG) in live bacteria, resulting in strong peripheral and septal PG labeling without affecting cell growth. They are featured with their ''in-situ'' incorporation mechanisms which enable time-course tracking of new PG formation. To date, FDAAs have been employed for studying the cell wall synthesis in various bacterial species (both Gram-positives and Gram-negatives) through different techniques, such as microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
, mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is use ...
, flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flo ...
.
Structures and general properties
 FDAA consists of a D-amino acid and a fluorophore (coupled through the amino acid side chain.) The D-amino acid backbone is required for its incorporation into the bacterial peptidoglycan through the activity of DD-transpeptidases. Once being incorporated, one can use fluorescence-detection techniques to visualize the location of new PG formation as well as the growth rate.
D-alanine is the most well-studied D-amino acids for FDAA development because it is a naturally existing residue in bacterial peptidoglycan structures. On the other hand, various fluorophores have been employed for FDAA applications and each has its features. For example, coumarin-based FDAA (HADA) is small enough to penetrate the bacterial outer-membranes and thus is widely used for Gram-negative bacterial studies; while TAMRA-based FDAA (TADA) features its high brightness and photo/thermo-stability, which is suitable for super-resolution microscopy (strong excitation light is used).
FDAA consists of a D-amino acid and a fluorophore (coupled through the amino acid side chain.) The D-amino acid backbone is required for its incorporation into the bacterial peptidoglycan through the activity of DD-transpeptidases. Once being incorporated, one can use fluorescence-detection techniques to visualize the location of new PG formation as well as the growth rate.
D-alanine is the most well-studied D-amino acids for FDAA development because it is a naturally existing residue in bacterial peptidoglycan structures. On the other hand, various fluorophores have been employed for FDAA applications and each has its features. For example, coumarin-based FDAA (HADA) is small enough to penetrate the bacterial outer-membranes and thus is widely used for Gram-negative bacterial studies; while TAMRA-based FDAA (TADA) features its high brightness and photo/thermo-stability, which is suitable for super-resolution microscopy (strong excitation light is used).
Proposed FDAA incorporation mechanisms
 Peptidoglycan (PG) is a mesh-like structure containing polysaccharides cross-linked by peptide chains.
Peptidoglycan (PG) is a mesh-like structure containing polysaccharides cross-linked by peptide chains. Penicillin-binding proteins
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are a group of proteins that are characterized by their affinity for and binding of penicillin. They are a normal constituent of many bacteria; the name just reflects the way by which the protein was discove ...
(DD-transpeptidases), in short PBPs, recognize the PG peptides and catalyze the cross-linking reactions. These enzymes are reported to have high specificity toward the chirality center of the amino acid backbone (the D-chiral center) but relatively low specificity toward the side-chain structure. Therefore, when FDAAs are present, they are taken by PBPs for the cross-linking reactions, resulting in their incorporation into the PG peptide chains. At proper concentration, e.g. 1-2 mM, FDAAs labeling does not affect PG synthesis and cell growth because only 1-2% of PG peptide chains are labeled with FDAA.
Applications
Published studies utilizing FDAAs as tools include: * Visualizing bacterial cell wall structures. * Studying bacterial cell wall growth. * Monitoring bacterial cell wall turnover. * Quantifying bacterial cell wall growth activity. * Assaying the anti-cell wall ability of antibiotics. * Screening new anti-cell wall antibiotics. * Tracking transpeptidase activity ''in vitro.''References
{{reflistExternal links
FDAA website
Amino acids