|
Fluorescent D-amino Acids
Fluorescent D-amino acids (FDAAs) are D-amino acid derivatives whose side-chain terminal is covalently coupled with a fluorophore molecule. FDAAs incorporate into the bacterial peptidoglycan (PG) in live bacteria, resulting in strong peripheral and septal PG labeling without affecting cell growth. They are featured with their ''in-situ'' incorporation mechanisms which enable time-course tracking of new PG formation. To date, FDAAs have been employed for studying the cell wall synthesis in various bacterial species (both Gram-positives and Gram-negatives) through different techniques, such as microscopy, mass spectrometry, flow cytometry. Structures and general properties FDAA consists of a D-amino acid and a fluorophore (coupled through the amino acid side chain.) The D-amino acid backbone is required for its incorporation into the bacterial peptidoglycan through the activity of DD-transpeptidases. Once being incorporated, one can use fluorescence-detection techniques to visua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-Amino Acid
D-Amino acids are amino acids where the stereogenic carbon alpha to the amino group has the D-configuration. For most naturally-occurring amino acids, this carbon has the L-configuration. D-Amino acids are occasionally found in nature as residues in proteins. They are formed from ribosomally-derived D-amino acid residues. Amino acids, as components of peptides, peptide hormones, structural and immune proteins, are the most important bioregulators involved in all life processes along with nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids. "Environmental D-amino acids are thought to be derived from organic diagenesis such as racemization and release from bacterial cell walls and even from microbial production." Discovery Their discovery was in the 1950s. "Auclair and Patton (1950) first reported their presence in the blood of insects and mollusks" Furthermore, they also have been identified in various mammalian tissues. The two major types of D-amino acids synthesized in and by mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to a macromolecule, serving as a marker (or dye, or tag, or reporter) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, i.e., fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores. Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most bacteria (domain ''Bacteria''). The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is a oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles. In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flow cytometer instrument. The sample is focused to ideally flow one cell at a time through a laser beam, where the light scattered is characteristic to the cells and their components. Cells are often labeled with fluorescent markers so light is absorbed and then emitted in a band of wavelengths. Tens of thousands of cells can be quickly examined and the data gathered are processed by a computer. Flow cytometry is routinely used in basic research, clinical practice, and clinical trials. Uses for flow cytometry include: * Cell counting * Cell sorting * Determining cell characteristics and function * Detecting microorganisms * Biomarker detection * Protein engineering detection * Diagnosis of health disorders such as blood cancers * Measuring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
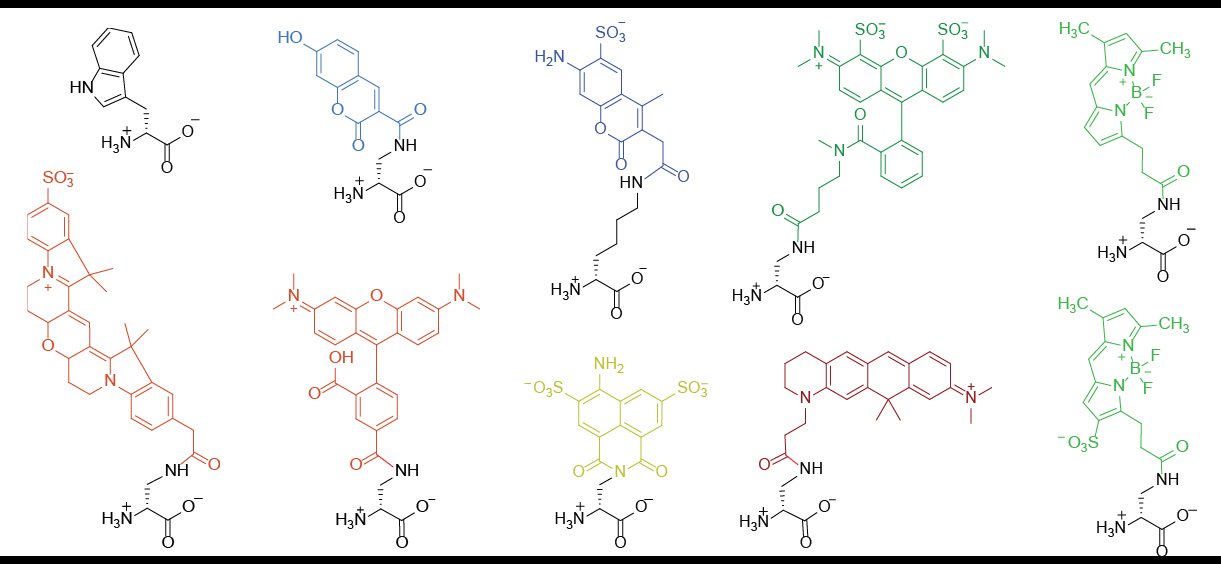
FDAA Structures
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS), initially created under President Jimmy Carter by Presidential Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1978 and implemented by two Executive Orders on April 1, 1979. The agency's primary purpose is to coordinate the response to a disaster that has occurred in the United States and that overwhelms the resources of local and state authorities. The governor of the state in which the disaster occurs must declare a state of emergency and formally request from the President that FEMA and the federal government respond to the disaster. The only exception to the state's gubernatorial declaration requirement occurs when an emergency or disaster takes place on federal property or to a federal asset—for example, the 1995 bombing of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, or the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' in the 2003 return-flight disaster. While on-the- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DD-transpeptidase
DD-transpeptidase (, ''DD-peptidase'', ''DD-transpeptidase'', ''DD-carboxypeptidase'', ''D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase'', ''D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving-peptidase'', ''D-alanine carboxypeptidase'', ''D-alanyl carboxypeptidase'', and ''serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase''.) is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the R-L-aca-D-alanyl moiety of R-L-aca-D-alanyl-D-alanine carbonyl donors to the γ-OH of their active-site serine and from this to a final acceptor. It is involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, namely, the transpeptidation that crosslinks the peptide side chains of peptidoglycan strands. The antibiotic penicillin irreversibly binds to and inhibits the activity of the transpeptidase enzyme by forming a highly stable penicilloyl-enzyme intermediate. Because of the interaction between penicillin and transpeptidase, this enzyme is also known as penicillin-binding protein (PBP). Mechanism DD-transpeptidase is mechanistically similar to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanism Of FDAA Labeling
Mechanism may refer to: *Mechanism (engineering), rigid bodies connected by joints in order to accomplish a desired force and/or motion transmission * Mechanism (biology), explaining how a feature is created *Mechanism (philosophy), a theory that all natural phenomena can be explained by physical causes *Mechanism (sociology), a theory that all social phenomena can be explained by the existence of a deterministic mechanism * "The Mechanism", song by Disclosure * ''The Mechanism'' (TV series), a Netflix TV series See also *Machine * Machine (mechanical) * Linkage (mechanical) * Mechanism design, the art of designing rules of a game to achieve a specific outcome * Mechanism of action, the means by which a drug exerts its biological effects * Defence mechanism, unconscious mechanisms aimed at reducing anxiety *Reaction mechanism, the sequence of reactions by which overall chemical change occurs *Antikythera mechanism The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greece, Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin-binding Proteins
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are a group of proteins that are characterized by their affinity for and binding of penicillin. They are a normal constituent of many bacteria; the name just reflects the way by which the protein was discovered. All β-lactam antibiotics (except for tabtoxinine-β-lactam, which inhibits glutamine synthetase) bind to PBPs, which are essential for bacterial cell wall synthesis. PBPs are members of a subgroup of enzymes called transpeptidases. Specifically, PBPs are DD-transpeptidases. Diversity There are a large number of PBPs, usually several in each organism, and they are found as both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic proteins. For example, Spratt (1977) reports that six different PBPs are routinely detected in all strains of ''E. coli'' ranging in molecular weight from 40,000 to 91,000. The different PBPs occur in different numbers per cell and have varied affinities for penicillin. The PBPs are usually broadly classified into high-molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
