Flexor hallucis brevis muscle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a
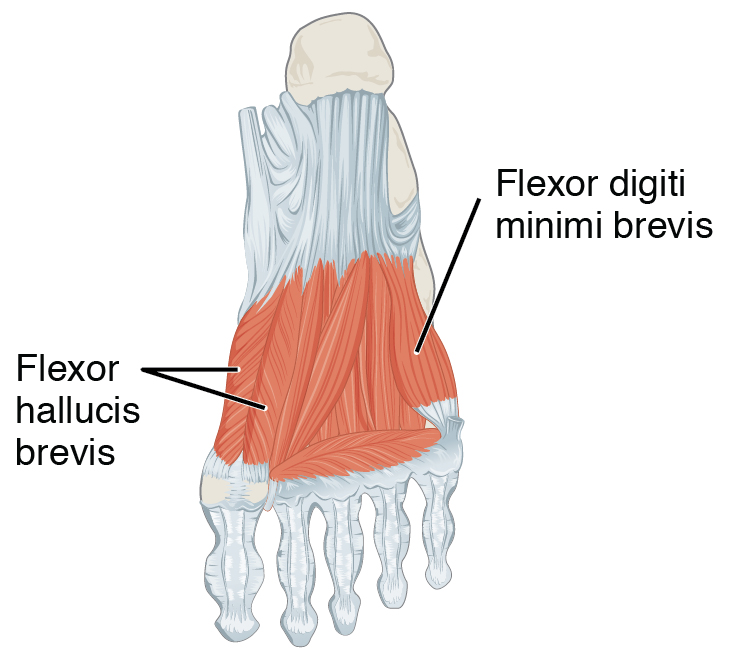 Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the
Image:Gray269.png, Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.
File:Slide1ABA.JPG, Flexor hallucis brevis muscle
File:Slide8ABA.JPG, Flexor hallucis brevis muscle
PTCentral
{{Authority control Foot muscles Muscles of the lower limb
muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are Organ (biology), organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other ...
of the foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg mad ...
that flexes the big toe.
Structure
 Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone
In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.
Structure
The cuboid bone is the most lateral of the bones in the distal row of the tarsus. It is roughly cubical in shape, and presents a prominence in its infe ...
, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedg ...
, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particular ...
of the great toe, a sesamoid
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be prese ...
bone being present in each tendon at its insertion. The medial portion is blended with the abductor hallucis muscle previous to its insertion; the lateral portion (sometimes described as the first plantar interosseus) with the adductor hallucis muscle
The Adductor hallucis (Adductor obliquus hallucis) arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.
Structure Oblique head
The ''obliqu ...
. The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle
The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg that attaches to the plantar surface of the distal phalanx of the great toe. The other deep muscles are the flexor digitorum longu ...
lies in a groove between the two. Its tendon usually contains two sesamoid bones at the point under the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Innervation
The medial and lateral head of the flexor hallucis brevis is innervated by the medial plantar nerve. Both heads are represented by spinal segments S1, S2.Variation
Origin subject to considerable variation; it often receives fibers from thecalcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
...
or long plantar ligament. Attachment to the cuboid bone
In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.
Structure
The cuboid bone is the most lateral of the bones in the distal row of the tarsus. It is roughly cubical in shape, and presents a prominence in its infe ...
sometimes wanting. Slip to first phalanx of the second toe.
Function
Flexor hallucis brevis flexes the first metatarsophalangeal joint, or the big toe. It helps to maintain the medial longitudinal arch. It assists with the toe-off phase of gait providing increased push-off.Clinical significance
Sesamoid bones contained within the tendon of flexor hallucis brevis muscle may become damaged duringexercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic s ...
.
Additional images
References
External links
PTCentral
{{Authority control Foot muscles Muscles of the lower limb