|
Toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plantigrade''; ''unguligrade'' animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes. Structure There are normally five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the proximal, middle, and distal, with the exception of the big toe ( la, hallux). For a minority of people, the little toe also is missing a middle bone. The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. The joints between each phalanx are the interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanx bone of each toe articulates with the metatarsal bone of the foot at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Each toe is surrounded by skin, and present on all five toes is a toenail. The toes are, from medial to lateral: * the first toe, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' plantigrade''; ''unguligrade'' animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes. Structure There are normally five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the proximal, middle, and distal, with the exception of the big toe ( la, hallux). For a minority of people, the little toe also is missing a middle bone. The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. The joints between each phalanx are the interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanx bone of each toe articulates with the metatarsal bone of the foot at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Each toe is surrounded by skin, and present on all five toes is a toenail. The toes are, from medial to lateral: * the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metti (cropped)
A toe ring is a ring made out of metals and non-metals worn on any of the toes. The second toe of either foot is where they are worn most commonly. This is because proportionately it is the longest toe and thus the easiest toe to put a ring on and stay without being connected to anything else. In most western countries they are a relatively new fashion accessory, and typically have no symbolic meaning. They are usually worn with barefoot sandals, anklets, bare feet or flip flops. Like finger rings, toe rings come in many shapes and forms, from intricately designed flowers embedded with jewels to simple bands. Fitted toe rings are rings that are of one size, whereas adjustable toe rings have a gap at the bottom so they can be easily made to fit snugly. Toe rings in India The wearing of toe rings has been practised in India since ancient times. In the Ramayana, there is a mention of Sita, on being abducted by Ravana, throwing her toe ring down so that lord Rama could find her. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unguligrade
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are omnivorous, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanges Of The Foot
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Bone
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. Etymology The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from "Old English fot "foot," from Proto-Germanic *fot (source also of Old Frisian fot, Old Saxon fot, Old Norse fotr, Danish fod, Swedish fot, Dutch voet, Old High German fuoz, German Fuß, Gothic fotus "foot"), from PIE root *ped- "foot". The "plural form feet is an instance of i-mutation." Structure The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones, 33 joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Podiatry Channel, ''Anatomy of the foot and ankle'' The joints of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot On White Background (cropped)
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. Etymology The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from "Old English fot "foot," from Proto-Germanic *fot (source also of Old Frisian fot, Old Saxon fot, Old Norse fotr, Danish fod, Swedish fot, Dutch voet, Old High German fuoz, German Fuß, Gothic fotus "foot"), from PIE root *ped- "foot". The "plural form feet is an instance of i-mutation." Structure The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones, 33 joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Podiatry Channel, ''Anatomy of the foot and ankle'' The joints of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toenail
A nail is a claw-like plate found at the tip of the fingers and toes on most primates. Nails correspond to the claws found in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protective protein called alpha-keratin, which is a polymer. Alpha-keratin is found in the hooves, claws, and horns of vertebrates. Structure The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. Parts of the nail The matrix, sometimes called the ''matrix unguis'', keratogenous membrane, nail matrix, or onychostroma, is the active tissue (or germinal matrix) that generates cells, which harden as they move outward from the nail root to the nail plate. It is the part of the nail bed that is beneath the nail and contains nerves, lymph and blood vessels. The matrix produces cells that become the nail plate. The width and thickness of the nail plate is determined by the size, length, and thickness of the matrix, while the shape of the finger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
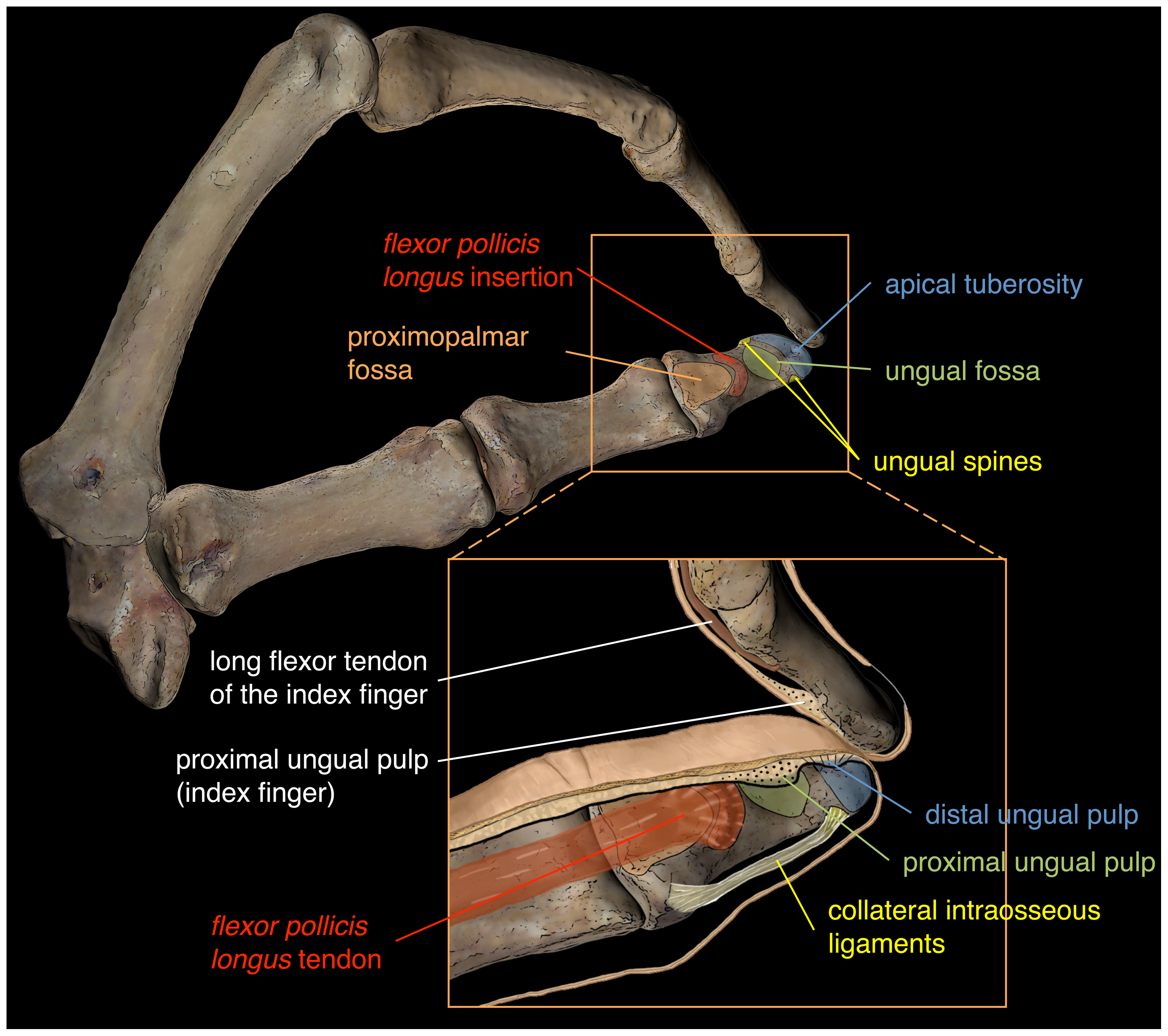
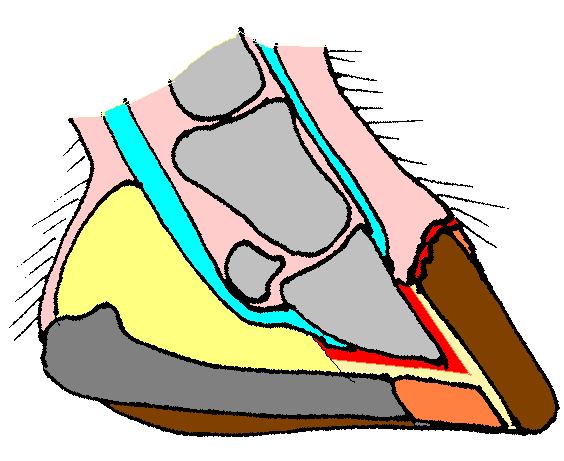
Hoof
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the ruminants with two digits, are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goat, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Hooves are limb structures restricted to placental mammals, which have long pregnancies; however, the marsupial ''Chaeropus'' had hooves. Description The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perform many functions, including supporting the weight of the animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsophalangeal Joints
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints), also informally known as toe knuckles, are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges). The ligaments are the plantar and two collateral. Movements The movements permitted in the metatarsophalangeal joints are flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction. File:The feet of C. H. Unthan, the armless fiddler Wellcome L0034227.jpg, Left: toes adducted (pulled towards the center) and spread (abducted); right, both feet clenched (plantar flexed) File:Footgym rings1.jpg, The upper foot is clenching (plantarflexing) at the MTP joints and at the joints of the toes; the central foot is lifting the toes (dorsiflexing) at the MTP joints; and the foot flat on the ground off to the side is in a neutral positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interphalangeal Joints Of Foot
The interphalangeal joints of the foot are between the phalanx bones of the toes in the foot, feet. Since the Toe#Hallux, great toe only has two phalanx bones (proximal and distal phalanges), it only has one interphalangeal joint, which is often abbreviated as the "IP joint". The rest of the toes each have three phalanx bones (proximal, middle, and distal phalanges), so they have two interphalangeal joints: the proximal interphalangeal joint between the proximal and middle phalanges (abbreviated "PIP joint") and the distal interphalangeal joint between the middle and distal phalanges (abbreviated "DIP joint"). All interphalangeal joints are ginglymoid (hinge) joints, and each has a plantar (underside) and two Collateral ligaments of interphalangeal articulations of foot, collateral ligaments. In the arrangement of these ligaments, Extension (kinesiology), extensor tendons supply the places of Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsal ligaments, which is similar to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Hallucis Muscle
The Adductor hallucis (Adductor obliquus hallucis) arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve. Structure Oblique head The ''oblique head'' is a large, thick, fleshy mass, crossing the foot obliquely and occupying the hollow space under the first, second, third and fourth metatarsal bones. It arises from the bases of the second, third, and fourth metatarsal bones, and from the sheath of the tendon of the Peroneus longus, and is inserted, together with the lateral portion of the Flexor hallucis brevis, into the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe. Transverse head The ''transverse head'' (''Transversus pedis'') is a narrow, flat fasciculus which arises from the plantar metatarsophalangeal ligaments of the third, fourth, and fifth toes (sometimes only from the third and fourth), and from the transverse ligament of the metatarsals. It is insert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)