Flag of New Hampshire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
New Hampshire is a
 Various Algonquian-speaking
Various Algonquian-speaking  Starting in 1952, New Hampshire gained national and international attention for its presidential primary held early in every presidential election year. It immediately became the most important testing ground for candidates for the Republican and Democratic nominations. The media gave New Hampshire and
Starting in 1952, New Hampshire gained national and international attention for its presidential primary held early in every presidential election year. It immediately became the most important testing ground for candidates for the Republican and Democratic nominations. The media gave New Hampshire and

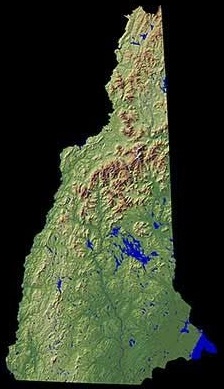

 New Hampshire is part of the six-state New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east; Massachusetts to the south; and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the
New Hampshire is part of the six-state New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east; Massachusetts to the south; and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the  It is the state with the highest percentage of timberland area in the country. New Hampshire is in the
It is the state with the highest percentage of timberland area in the country. New Hampshire is in the
 New Hampshire experiences a
New Hampshire experiences a  Extreme snow is often associated with a
Extreme snow is often associated with a
 Metropolitan areas in the New England region are defined by the
Metropolitan areas in the New England region are defined by the
 As of the
As of the  As of the 2010 census, the population of New Hampshire was 1,316,470. The gender makeup of the state at that time was 49.3% male and 50.7% female. 21.8% of the population were under the age of 18; 64.6% were between the ages of 18 and 64; and 13.5% were 65 years of age or older. Additionally, about 57.3% of the population was born out of state.
As of the 2010 census, the population of New Hampshire was 1,316,470. The gender makeup of the state at that time was 49.3% male and 50.7% female. 21.8% of the population were under the age of 18; 64.6% were between the ages of 18 and 64; and 13.5% were 65 years of age or older. Additionally, about 57.3% of the population was born out of state.
 * Total employment (2016): 594,243
* Number of employer establishments: 37,868
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that New Hampshire's total state product in 2018 was $86billion, ranking 40th in the United States.
* Total employment (2016): 594,243
* Number of employer establishments: 37,868
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that New Hampshire's total state product in 2018 was $86billion, ranking 40th in the United States.
 The governor of New Hampshire, since January 5, 2017, is
The governor of New Hampshire, since January 5, 2017, is
 New Hampshire is internationally known for the New Hampshire primary, the first primary in the quadrennial American presidential election cycle. State law requires that the Secretary of State schedule this election at least one week before any "similar event". While the
New Hampshire is internationally known for the New Hampshire primary, the first primary in the quadrennial American presidential election cycle. State law requires that the Secretary of State schedule this election at least one week before any "similar event". While the
 In the past, New Hampshire has often voted Republican. Between 1856 and 1988, New Hampshire cast its electoral votes for the Democratic presidential ticket six times:
In the past, New Hampshire has often voted Republican. Between 1856 and 1988, New Hampshire cast its electoral votes for the Democratic presidential ticket six times:

 Interstate 93 is the main Interstate highway in New Hampshire and runs north from Salem (on the Massachusetts border) to Littleton (on the Vermont border). I-93 connects the more densely populated southern part of the state to the Lakes Region and the White Mountains further to the north.
*
Interstate 93 is the main Interstate highway in New Hampshire and runs north from Salem (on the Massachusetts border) to Littleton (on the Vermont border). I-93 connects the more densely populated southern part of the state to the Lakes Region and the White Mountains further to the north.
*  Interstate 95 runs north–south briefly along New Hampshire's seacoast to serve the city of
Interstate 95 runs north–south briefly along New Hampshire's seacoast to serve the city of 


 U.S. Route 4 terminates at the
U.S. Route 4 terminates at the 

 New Hampshire has 25 public-use airports, three with some scheduled commercial passenger service. The busiest airport by number of passengers handled is Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester and Londonderry, which serves the
New Hampshire has 25 public-use airports, three with some scheduled commercial passenger service. The busiest airport by number of passengers handled is Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester and Londonderry, which serves the


NH Rocks
' *
NH Roots
' * ''Salmon Press Newspapers'' (family of weekly newspapers covering Lakes Region & North Country) * '' The Liberty Block''
''Land Use in Cornish, N.H.''
a 2006 documentary presentation by James M. Patterson of the ''
New Hampshire Almanac
Visitnh.gov
New Hampshire Office of Travel and Tourism Development
New Hampshire State Guide from the Library of Congress
Energy Facts for New Hampshire
New Hampshire State Facts
USDA Economic Research Service
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of New Hampshire
Internet Movie Database listing of films shot in the state
New Hampshire Historical Society
* * {{coord, 43.5, -71.5, dim:200000_region:US-NH_type:adm1st, name=State of New Hampshire, display=title States of the United States New England states Northeastern United States States and territories established in 1788 States of the East Coast of the United States 1788 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
to the south, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
to the west, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
and the Gulf of Maine
, image =
, alt =
, caption =
, image_bathymetry = GulfofMaine2.jpg
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry = Major features of the Gulf of Maine
, location = Northeast coast of the ...
to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
to the north. Of the 50 U.S. states, New Hampshire is the fifth smallest by area and the tenth least populous, with slightly more than 1.3 million residents. Concord
Concord may refer to:
Meaning "agreement"
* Pact or treaty, frequently between nations (indicating a condition of harmony)
* Harmony, in music
* Agreement (linguistics), a change in the form of a word depending on grammatical features of other ...
is the state capital, while Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
is the largest city. New Hampshire's motto
A motto (derived from the Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of an individual, family, social group, or organisation. Mot ...
, "Live Free or Die
"Live Free or Die" is the official motto of the U.S. state of New Hampshire, adopted by the state in 1945. It is possibly the best-known of all state mottos, partly because it conveys an assertive independence historically found in American pol ...
", reflects its role in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
; its nickname
A nickname is a substitute for the proper name of a familiar person, place or thing. Commonly used to express affection, a form of endearment, and sometimes amusement, it can also be used to express defamation of character. As a concept, it is ...
, "The Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
State", refers to its extensive granite formations and quarries
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their envir ...
. It is well known nationwide for holding the first primary (after the Iowa caucus
The Iowa caucuses are biennial electoral events for members of the Democratic and Republican parties in the U.S. state of Iowa. Unlike primary elections in most other U.S. states, where registered voters go to polling places to cast ballo ...
) in the U.S. presidential election cycle, and for its resulting influence on American electoral politics, leading the adage "As New Hampshire goes, so goes the nation".
New Hampshire was inhabited for thousands of years by Algonquian-speaking peoples such as the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
. Europeans arrived in the early 17th century, with the English establishing some of the earliest non-indigenous settlements. The Province of New Hampshire
The Province of New Hampshire was a colony of England and later a British province in North America. The name was first given in 1629 to the territory between the Merrimack and Piscataqua rivers on the eastern coast of North America, and was n ...
was established in 1629, named after the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
. Following mounting tensions between the British colonies and the crown during the 1760s, New Hampshire saw one of the earliest overt acts of rebellion, with the seizing of Fort William and Mary from the British in 1774. In January 1776, it became the first of the British North American colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
to establish an independent government and state constitution; six months later, it signed the United States Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House ( ...
and contributed troops, ships, and supplies in the war against Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. In June 1788, it was the ninth state to ratify the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the nation ...
, bringing that document into effect.
Through the mid-19th century, New Hampshire was an active center of abolitionism, and fielded close to 32,000 soldiers for the Union during the U.S. Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states t ...
. After the war, the state saw rapid industrialization and population growth, becoming a center of textile manufacturing
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods ...
, shoemaking, and papermaking; the Amoskeag Manufacturing Company
The Amoskeag Manufacturing Company was a textile manufacturer which founded Manchester, New Hampshire, United States. From modest beginnings it grew throughout the 19th century into the largest cotton textile plant in the world.
At its peak, Amos ...
in Manchester was at one time the largest cotton textile plant in the world. The Merrimack and Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
rivers were lined with industrial mills, most of which employed workers from Canada and Europe; French Canadians formed the most significant influx of immigrants, and today roughly a quarter of all New Hampshire residents claim French American
French Americans or Franco-Americans (french: Franco-Américains), are citizens or nationals of the United States who identify themselves with having full or partial French or French-Canadian heritage, ethnicity and/or ancestral ties. They ...
ancestry, second only to Maine.
Reflecting a nationwide trend, New Hampshire's industrial sector declined after the Second World War. Since 1950, its economy has heavily diversified to include financial and professional services, real estate, education, and transportation, with manufacturing still higher than the national average. Beginning in the 1980s, its population surged as major highways connected it to the Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern a ...
and led to more bedroom communities
A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential rather than commercial or industrial. Routine travel from home to work and back is called commuting, which is where the term comes from. A commuter town may be called by many o ...
. In the 21st century, New Hampshire is among the wealthiest states in the U.S., with the seventh-highest median household income and some of the lowest rates of poverty, unemployment, and crime. It is one of only nine states without an income tax, and has no taxes on sales, capital gains, or inheritance; consequently, its overall tax burden is the lowest in the U.S. after Florida. New Hampshire ranks among the top ten states in metrics such as governance, healthcare, socioeconomic opportunity, and fiscal stability.
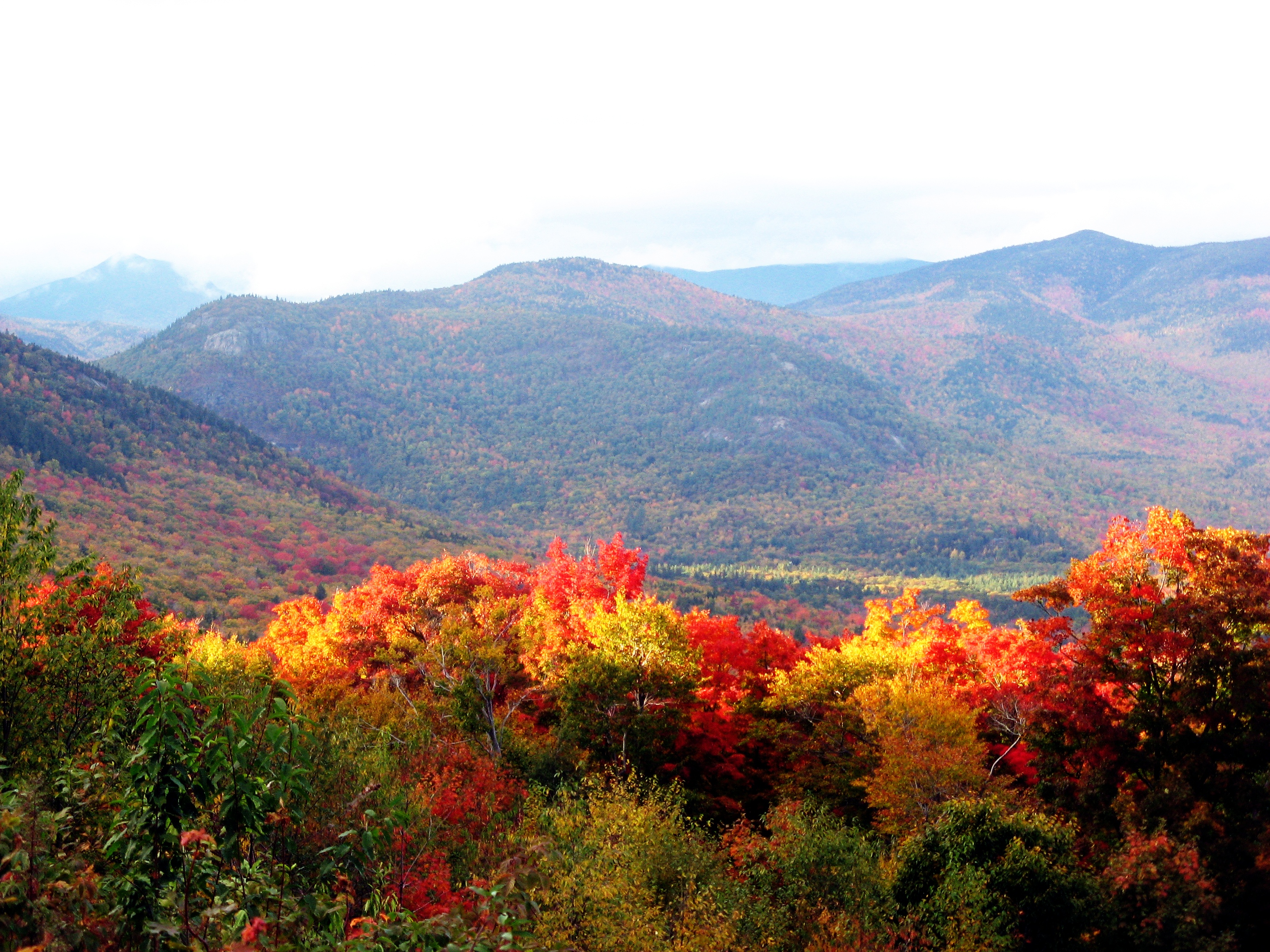
With its mountainous and heavily forested terrain, New Hampshire has a growing tourism sector centered on outdoor recreation. It has some of the highest ski mountains on the East Coast and is a major destination for winter sports; Mount Monadnock is among the most climbed mountains in the U.S. Other activities include observing the fall foliage, summer cottages along many lakes and the seacoast, motorsports at the New Hampshire Motor Speedway
New Hampshire Motor Speedway is a oval speedway located in Loudon, New Hampshire, which has hosted NASCAR racing annually since 1990, as well as the longest-running motorcycle race in North America, the Loudon Classic. Nicknamed "The Magic Mil ...
, and Motorcycle Week, a popular motorcycle rally held in Weirs Beach in Laconia. The White Mountain National Forest
The White Mountain National Forest (WMNF) is a federally managed forest contained within the White Mountains in the northeastern United States. It was established in 1918 as a result of the Weeks Act of 1911; federal acquisition of land had alre ...
links the Vermont and Maine portions of the Appalachian Trail
The Appalachian Trail (also called the A.T.), is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states.Gailey, Chris (2006)"Appalachian ...
, and has the Mount Washington Auto Road
The Mount Washington Auto Road—originally the Mount Washington Carriage Road—is a toll road in southern Coos County, New Hampshire that extends from New Hampshire Route 16 in Green's Grant, just north of Pinkham Notch, westward across Pink ...
, where visitors may drive to the top of Mount Washington
Mount Washington is the highest peak in the Northeastern United States at and the most topographically prominent mountain east of the Mississippi River.
The mountain is notorious for its erratic weather. On the afternoon of April 12, 1934 ...
.
History
 Various Algonquian-speaking
Various Algonquian-speaking Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
tribes, largely divided between the Androscoggin and Pennacook
The Pennacook, also known by the names Penacook and Pennacock, were an Algonquian-speaking Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands who lived in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and southern Maine. They were not a united tribe but a netwo ...
nations, inhabited the area before European settlement. Despite the similar language, they had a very different culture and religion from other Algonquian peoples. English and French explorers visited New Hampshire in 1600–1605, and David Thompson settled at Odiorne's Point in present-day Rye in 1623. The first permanent settlement was at Hilton's Point (present-day Dover). By 1631, the Upper Plantation comprised modern-day Dover, Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
and Stratham; in 1679, it became the " Royal Province". Father Rale's War
Dummer's War (1722–1725) is also known as Father Rale's War, Lovewell's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War, the Wabanaki-New England War, or the Fourth Anglo-Abenaki War. It was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the ...
was fought between the colonists and the Wabanaki Confederacy
The Wabanaki Confederacy (''Wabenaki, Wobanaki'', translated to "People of the Dawn" or "Easterner") is a North American First Nations and Native American confederation of four principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Miꞌkmaq, Maliseet ( ...
throughout New Hampshire.
New Hampshire was one of the thirteen colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th cent ...
that rebelled against British rule during the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
. By the time of the American Revolution, New Hampshire was a divided province. The economic and social life of the Seacoast region revolved around sawmills, shipyards, merchants' warehouses, and established village and town centers. Wealthy merchants built substantial homes, furnished them with the finest luxuries, and invested their capital in trade and land speculation. At the other end of the social scale, there developed a permanent class of day laborers, mariners, indentured servants and even slaves.
]The only battle fought in New Hampshire was the raid on Fort William and Mary
Fort William and Mary was a colonial fortification in Britain's worldwide system of defenses, defended by soldiers of the Province of New Hampshire who reported directly to the royal governor. The fort, originally known as "The Castle," was situ ...
, December 14, 1774, in Portsmouth Harbor
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the riv ...
, which netted the rebellion sizable quantities of gunpowder, small arms, and cannon over the course of two nights. ( General Sullivan, leader of the raid, described it as "remainder of the powder, the small arms, bayonets, and cartouche-boxes, together with the cannon and ordnance stores".) This raid was preceded by a warning to local patriots the previous day, by Paul Revere
Paul Revere (; December 21, 1734 O.S. (January 1, 1735 N.S.)May 10, 1818) was an American silversmith, engraver, early industrialist, Sons of Liberty member, and Patriot and Founding Father. He is best known for his midnight ride to a ...
on December 13, 1774, that the fort was to be reinforced by troops sailing from Boston. According to unverified accounts, the gunpowder was later used at the Battle of Bunker Hill, transported there by Major Demerit, who was one of several New Hampshire patriots who stored the powder in their homes until it was transported elsewhere for use in revolutionary activities. During the raid, the British soldiers fired upon the rebels with cannon and muskets. Although there were apparently no casualties, these were among the first shots in the American Revolutionary period, occurring approximately five months before the Battles of Lexington and Concord. On January 5, 1776, New Hampshire became the first colony to declare independence from Great Britain, almost six months before the Declaration of Independence was signed by the Continental Congress.
The United States Constitution was ratified by New Hampshire on June 21, 1788, when New Hampshire became the ninth state to do so.
New Hampshire was a Jacksonian stronghold; the state sent Franklin Pierce to the White House in the election of 1852. Industrialization took the form of numerous textile mills, which in turn attracted large flows of immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
from Quebec (the "French Canadians") and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
. The northern parts of the state produced lumber, and the mountains provided tourist attractions. After 1960, the textile industry collapsed, but the economy rebounded as a center of high technology and as a service provider.
 Starting in 1952, New Hampshire gained national and international attention for its presidential primary held early in every presidential election year. It immediately became the most important testing ground for candidates for the Republican and Democratic nominations. The media gave New Hampshire and
Starting in 1952, New Hampshire gained national and international attention for its presidential primary held early in every presidential election year. It immediately became the most important testing ground for candidates for the Republican and Democratic nominations. The media gave New Hampshire and Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
about half of all the attention paid to all states in the primary process, magnifying the state's decision powers and spurring repeated efforts by out-of-state politicians to change the rules.
Geography



 New Hampshire is part of the six-state New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east; Massachusetts to the south; and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the
New Hampshire is part of the six-state New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east; Massachusetts to the south; and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the Merrimack Valley
The Merrimack Valley is a bi-state region along the Merrimack River in the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Massachusetts. The Merrimack is one of the larger waterways in New England and has helped to define the livelihood and culture of those ...
, the Monadnock Region
The Monadnock Region is a region in southwestern New Hampshire. It is named after Mount Monadnock, a 3,165 foot isolated mountain, which is the dominant geographic landmark in the region. Although it has no specific borders, the Monadnock Region i ...
, and the Dartmouth-Lake Sunapee area. New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any U.S. coastal state, with a length of , sometimes measured as only .
The White Mountains range in New Hampshire spans the north-central portion of the state. The range includes Mount Washington
Mount Washington is the highest peak in the Northeastern United States at and the most topographically prominent mountain east of the Mississippi River.
The mountain is notorious for its erratic weather. On the afternoon of April 12, 1934 ...
, the tallest in the northeastern U.S.—site of the second-highest wind speed ever recorded— as well as Mount Adams and Mount Jefferson. With hurricane-force winds every third day on average, more than a hundred recorded deaths among visitors, and conspicuous krumholtz (dwarf, matted trees much like a carpet of bonsai trees), the climate on the upper reaches of Mount Washington has inspired the weather observatory on the peak to claim that the area has the "World's Worst Weather". The White Mountains were home to the rock formation called the Old Man of the Mountain
The Old Man of the Mountain, also called the Great Stone Face and the Profile, was a series of five granite cliff ledges on Cannon Mountain in Franconia, New Hampshire, United States, that appeared to be the jagged profile of a human face when ...
, a face-like profile in Franconia Notch
Franconia Notch (elev. ) is a major mountain pass through the White Mountains of New Hampshire. Dominated by Cannon Mountain to the west and Mount Lafayette to the east, it lies principally within Franconia Notch State Park and is traversed by ...
, until the formation disintegrated in May 2003. Even after its loss, the Old Man remains an enduring symbol for the state, seen on state highway signs, automobile license plates, and many government and private entities around New Hampshire.
In the flatter southwest corner of New Hampshire, the landmark Mount Monadnock has given its name to a class of earth-forms—a '' monadnock''—signifying, in geomorphology, any isolated resistant peak rising from a less resistant eroded plain.
Major rivers include the Merrimack River
The Merrimack River (or Merrimac River, an occasional earlier spelling) is a river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into M ...
, which bisects the lower half of the state north–south before passing into Massachusetts and reaching the sea in Newburyport
Newburyport is a coastal city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States, northeast of Boston. The population was 18,289 at the 2020 census. A historic seaport with vibrant tourism industry, Newburyport includes part of Plum Island. The mo ...
. Its tributaries include the Contoocook River
The Contoocook River () is a river in New Hampshire. It flows from Contoocook Lake on the Jaffrey/ Rindge border to Penacook (just north of Concord), where it empties into the Merrimack River. It is one of only a few rivers in New Hampshire that ...
, Pemigewasset River
The Pemigewasset River , known locally as "The Pemi", is a river in the state of New Hampshire, the United States. It is in length and (with its tributaries) drains approximately . The name "Pemigewasset" comes from the Abenaki word ''bemijijoase ...
, and Winnipesaukee River
The Winnipesaukee River is a river that connects Lake Winnipesaukee with the Pemigewasset and Merrimack rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire. The river is in the Lakes Region of central New Hampshire. The river's drainage area is approximately .
...
. The Connecticut River, which starts at New Hampshire's Connecticut Lakes
The Connecticut Lakes are a group of lakes in Coos County, northern New Hampshire, United States, situated along the headwaters of the Connecticut River. They are accessed via the northernmost segment of U.S. Route 3, between the village of Pi ...
and flows south to Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
, defines the western border with Vermont. The state border is not in the center of that river, as is usually the case, but at the low-water mark on the Vermont side; meaning the entire river along the Vermont border (save for areas where the water level has been raised by a dam) lies within New Hampshire. Only one town— Pittsburg—shares a land border with the state of Vermont. The "northwesternmost headwaters" of the Connecticut also define the part of Canada–U.S. border.
The Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the river ...
and its several tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
form the state's only significant ocean port where they flow into the Atlantic at Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
. The Salmon Falls River
The Salmon Falls River is a tributary of the Piscataqua River in the U.S. states of Maine and New Hampshire. It rises at Great East Lake, Newichawannock Canal, and Horn Pond and flows south-southeast for approximately , forming the border betwee ...
and the Piscataqua define the southern portion of the border with Maine. The Piscataqua River boundary was the subject of a border dispute
A territorial dispute or boundary dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities.
Context and definitions
Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of natural resources s ...
between New Hampshire and Maine in 2001, with New Hampshire claiming dominion over several islands (primarily Seavey's Island
Seavey's Island, site of the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, is located in the Piscataqua River in Kittery, Maine, opposite Portsmouth, New Hampshire. It encompasses .
History
What is today called Seavey's Island was originally five separate islands c ...
) that include the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard
The Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, often called the Portsmouth Navy Yard, is a United States Navy shipyard in Kittery on the southern boundary of Maine near the city of Portsmouth, New Hampshire.
Founded in 1800, PNS is U.S. Navy's oldest continuo ...
. The U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
dismissed the case in 2002, leaving ownership of the island with Maine. New Hampshire still claims sovereignty of the base, however.
The largest of New Hampshire's lakes is Lake Winnipesaukee
Lake Winnipesaukee () is the largest lake in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, located in the Lakes Region at the foothills of the White Mountains. It is approximately long (northwest-southeast) and from wide (northeast-southwest), covering & ...
, which covers in the east-central part of New Hampshire. Umbagog Lake
Umbagog Lake is a wilderness lake located in Coös County, New Hampshire, and Oxford County, Maine. It is one of the most pristine lakes in the state of New Hampshire. It lies in the towns of Errol, New Hampshire, and Upton, Maine, as well as the ...
along the Maine border, approximately , is a distant second. Squam Lake
Squam Lake is a lake located in the Lakes Region of central New Hampshire, United States, south of the White Mountains, straddling the borders of Grafton, Carroll, and Belknap counties. The largest town center on the lake is Holderness. Th ...
is the second largest lake entirely in New Hampshire.
New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any state in the United States, approximately long. Hampton Beach is a popular local summer destination. About offshore are the Isles of Shoals
The Isles of Shoals are a group of small islands and tidal ledges situated approximately off the east coast of the United States, straddling the border of the states of Maine and New Hampshire.
They have been occupied for more than 400 years, fi ...
, nine small islands (four of which are in New Hampshire) known as the site of a 19th-century art colony founded by poet Celia Thaxter
Celia Thaxter (née Laighton; June 29, 1835 – August 25, 1894) was an American writer of poetry and stories. For most of her life, she lived with her father on the Isles of Shoals at his Appledore Hotel. How she grew up to become a writer is d ...
, and the alleged location of one of the buried treasures of the pirate Blackbeard
Edward Teach (alternatively spelled Edward Thatch, – 22 November 1718), better known as Blackbeard, was an English pirate who operated around the West Indies and the eastern coast of Britain's North American colonies. Little is known abou ...
.
temperate broadleaf and mixed forests
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
These f ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
. Much of the state, in particular the White Mountains, is covered by the conifers and northern hardwoods of the New England-Acadian forests
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
. The southeast corner of the state and parts of the Connecticut River along the Vermont border are covered by the mixed oaks of the Northeastern coastal forests
The Northeastern coastal forests are a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the northeast and middle Atlantic region of the United States. The ecoregion covers an area of 34,630 sq miles (89,691 km2) encompassing the Piedmont a ...
. The state's numerous forests are popular among autumnal leaf peepers seeking the brilliant foliage of the numerous deciduous tree
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
s.
The northern third of the state is locally referred to as the "north country" or "north of the notches", in reference to the White Mountain passes that channel traffic. It contains less than 5% of the state's population, suffers relatively high poverty, and is steadily losing population as the logging and paper industries decline. However, the tourist industry, in particular visitors who go to northern New Hampshire to ski
A ski is a narrow strip of semi-rigid material worn underfoot to glide over snow. Substantially longer than wide and characteristically employed in pairs, skis are attached to ski boots with ski bindings, with either a free, lockable, or partia ...
, snowboard, hike and mountain bike, has helped offset economic losses from mill closures.
By the 1950s, concern with protecting the environment became a factor, emerging as an active politicized movement by the 1970s. Activists defeated a proposal to build an oil refinery along the coast and one to widen an interstate highway through Franconia Notch
Franconia Notch (elev. ) is a major mountain pass through the White Mountains of New Hampshire. Dominated by Cannon Mountain to the west and Mount Lafayette to the east, it lies principally within Franconia Notch State Park and is traversed by ...
.
Winter season lengths are projected to decline at ski areas across New Hampshire due to the effects of climate change
The effects of climate change impact the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching. They affect the water cycle, oceans, sea and land ice ( glaciers), sea le ...
, which is likely to continue the historic contraction and consolidation of the ski industry and threaten individual ski businesses and communities that rely on ski tourism.
Climate
 New Hampshire experiences a
New Hampshire experiences a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfa'' in some southern areas, ''Dfb'' in most of the state, and ''Dfc'' subarctic in some northern highland areas), with warm, humid summers, and long, cold, and snowy winters. Precipitation is fairly evenly distributed all year. The climate of the southeastern portion is moderated by the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
and averages relatively milder winters (for New Hampshire), while the northern and interior portions experience colder temperatures and lower humidity. Winters are cold and snowy throughout the state, and especially severe in the northern and mountainous areas. Average annual snowfall ranges from to over across the state.
Average daytime highs are in the mid 70s°F to low 80s°F (24–28 °C) throughout the state in July, with overnight lows in the mid 50s°F to low 60s°F (13–15 °C). January temperatures range from an average high of on the coast to overnight lows below in the far north and at high elevations. Average annual precipitation statewide is roughly with some variation occurring in the White Mountains due to differences in elevation and annual snowfall. New Hampshire's highest recorded temperature was in Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
on July 4, 1911, while the lowest recorded temperature was atop Mount Washington
Mount Washington is the highest peak in the Northeastern United States at and the most topographically prominent mountain east of the Mississippi River.
The mountain is notorious for its erratic weather. On the afternoon of April 12, 1934 ...
on January 29, 1934. Mount Washington also saw an unofficial reading on January 22, 1885, which, if made official, would tie the record low for New England (also at Big Black River, Maine, on January 16, 2009, and Bloomfield, Vermont
Bloomfield is a town in Essex County, Vermont, United States. The population was 217 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Berlin, NH–VT Micropolitan Statistical Area.
History
In 1830, an act from the state General Assembly changed t ...
on December 30, 1933).
 Extreme snow is often associated with a
Extreme snow is often associated with a nor'easter
A nor'easter (also northeaster; see below), or an East Coast low is a synoptic-scale extratropical cyclone in the western North Atlantic Ocean. The name derives from the direction of the winds that blow from the northeast. The original use ...
, such as the Blizzard of '78 and the Blizzard of 1993
The 1993 Storm of the Century (also known as the 93 Superstorm, The No Name Storm, or the Great Blizzard of '93/1993) was a cyclonic storm that formed over the Gulf of Mexico on March 12, 1993. The cold weather, heavy snowfall, high winds and st ...
, when several feet accumulated across portions of the state over 24 to 48 hours. Lighter snowfalls of several inches occur frequently throughout winter, often associated with an Alberta Clipper
An Alberta clipper, also known as an Alberta low, Alberta cyclone, Alberta lee cyclone, Canadian clipper, or simply clipper, is a fast-moving low-pressure system that originates in or near the Canadian province of Alberta just east of the Rock ...
.
New Hampshire, on occasion, is affected by hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
and tropical storms—although, by the time they reach the state, they are often extratropical
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
—with most storms striking the southern New England coastline and moving inland or passing by offshore in the Gulf of Maine
, image =
, alt =
, caption =
, image_bathymetry = GulfofMaine2.jpg
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry = Major features of the Gulf of Maine
, location = Northeast coast of the ...
. Most of New Hampshire averages fewer than 20 days of thunderstorms per year and an average of two tornadoes occur annually statewide.
The National Arbor Day Foundation plant hardiness zone map depicts zones 3, 4, 5, and6 occurring throughout the state and indicates the transition from a relatively cooler to warmer climate as one travels southward across New Hampshire. The 1990 USDA
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
plant hardiness zones for New Hampshire range from zone 3b in the north to zone 5b in the south.
Metropolitan areas

U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
as New England City and Town Area A New England city and town area (NECTA) is a geographic and statistical entity defined by the U.S. federal government for use in the six-state New England region of the United States. NECTAs are analogous to metropolitan statistical areas and micr ...
s (NECTAs). The following is a list of NECTAs fully or partially in New Hampshire:
* Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
* Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
–Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
–Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
** Haverhill–Newburyport
Newburyport is a coastal city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States, northeast of Boston. The population was 18,289 at the 2020 census. A historic seaport with vibrant tourism industry, Newburyport includes part of Plum Island. The mo ...
– Amesbury Town NECTA Division
** Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
– Methuen Town– Salem NECTA Division
** Lowell–Billerica
Billerica (, ) is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 42,119 according to the 2020 census. It takes its name from the town of Billericay in Essex, England.
History
In the early 1630s, a Praying India ...
–Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Southend-on-Sea and Colchester. It ...
NECTA Division
** Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
NECTA Division
* Claremont
* Concord
Concord may refer to:
Meaning "agreement"
* Pact or treaty, frequently between nations (indicating a condition of harmony)
* Harmony, in music
* Agreement (linguistics), a change in the form of a word depending on grammatical features of other ...
* Dover–Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
* Franklin
* Keene
* Laconia
* Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
* Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
* Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
Demographics
Population
 As of the
As of the 2020 US census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
, the resident population of New Hampshire was 1,377,529, a 4.6% increase since the 2010 United States Census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servi ...
. The center of population of New Hampshire is in Merrimack County, in the town of Pembroke. The center of population has moved south since 1950, a reflection of the fact that the state's fastest growth has been along its southern border, which is within commuting range of Boston and other Massachusetts cities.
As indicated in the census, in 2020 92.8% of the population were White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
; 1.9% were Black or African American; 0.3% were Native American or Alaskan Native; 3.1% were Asian; 0.1% were Native Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawa ...
or other Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
; and 1.8% were two or more races
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
. 4.4% of the total population were Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
of any race. 18.5% of the population were under 18 years of age; 19.2% were 65 years and over. The female population was 50.1%.
The most densely populated areas generally lie within of the Massachusetts border, and are concentrated in two areas: along the Merrimack River Valley running from Concord
Concord may refer to:
Meaning "agreement"
* Pact or treaty, frequently between nations (indicating a condition of harmony)
* Harmony, in music
* Agreement (linguistics), a change in the form of a word depending on grammatical features of other ...
to Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
, and in the Seacoast Region along an axis stretching from Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
to Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
. Outside of those two regions, only one community, the city of Keene, has a population of over 20,000. The four counties covering these two areas account for 72% of the state population, and one ( Hillsborough) has nearly 30% of the state population, as well as the two most populous communities, Manchester and Nashua. The northern portion of the state is very sparsely populated: the largest county by area, Coos, covers the northern one-fourth of the state and has only around 31,000 people, about a third of whom live in a single community (Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
). The trends over the past several decades have been for the population to shift southward, as many northern communities lack the economic base to maintain their populations, while southern communities have been absorbed by the Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern a ...
metropolis.
 As of the 2010 census, the population of New Hampshire was 1,316,470. The gender makeup of the state at that time was 49.3% male and 50.7% female. 21.8% of the population were under the age of 18; 64.6% were between the ages of 18 and 64; and 13.5% were 65 years of age or older. Additionally, about 57.3% of the population was born out of state.
As of the 2010 census, the population of New Hampshire was 1,316,470. The gender makeup of the state at that time was 49.3% male and 50.7% female. 21.8% of the population were under the age of 18; 64.6% were between the ages of 18 and 64; and 13.5% were 65 years of age or older. Additionally, about 57.3% of the population was born out of state.
Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
of any race were 2.8% of the population in 2010: 0.6% were of Mexican, 0.9% Puerto Rican, 0.1% Cuban
Cuban may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean
* Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent
** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof
* Cuban citizen, a perso ...
, and 1.2% other Hispanic or Latino origin. As of 2019, the Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
population was estimated at 4.0%.
According to the 2012–2017 American Community Survey, the largest ancestry groups in the state were Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
(20.6%), English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(16.5%), French (14.0%), Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
(10.4%), German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(9.1%), French Canadian (8.9%), and American (4.8%).
New Hampshire has the highest percentage (22.9%) of residents with French/French-Canadian/Acadian ancestry of any U.S. state.
According to the Census Bureau's American Community Survey estimates from 2017, 2.1% of the population aged5 and older speak Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
at home, while 1.8% speak French. In Coos County, 9.6% of the population speaks French at home, down from 16% in 2000.
Birth data
''Note: Percentages in the table do not add up to 100, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.'' * Since 2016, data for births ofWhite Hispanic
White Latin Americans, or European Latin Americans, are Latin Americans who are considered white, typically due to European descent. Latin American countries have often tolerated intermarriage between different ethnic groups since the beginning ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Religion
A Pew survey in 2014 showed that the religious affiliations of the people of New Hampshire was as follows:nonreligious
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and ...
36%, Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
30%, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
26%, Jehovah's Witness 2%, LDS
LDS may refer to:
Organizations
* LDS Hospital, Salt Lake City, Utah, US Religion
* Latter Day Saint movement (LDS movement), a collection of independent church groups
**The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the largest group within t ...
(Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into severa ...
) 1%, and Jewish 1%.
A survey suggests people in New Hampshire and Vermont are less likely than other Americans to attend weekly services and only 54% say they are "absolutely certain there is a God" compared to 71% in the rest of the nation. New Hampshire and Vermont are also at the lowest levels among states in religious commitment. In 2012, 23% of New Hampshire residents in a Gallup poll considered themselves "very religious", while 52% considered themselves "non-religious". According to the Association of Religion Data Archives The Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) is a free source of online information related to American and international religion. One of the primary goals of the archive is to democratize access to academic information on religion by making th ...
(ARDA) in 2010, the largest denominations were the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
with 311,028 members; the United Church of Christ
The United Church of Christ (UCC) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination based in the United States, with historical and confessional roots in the Congregational, Calvinist, Lutheran, and Anabaptist traditions, and with approximatel ...
with 26,321 members; and the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelic ...
with 18,029 members.
In 2016, a Gallup Poll found that New Hampshire was the least religious state in the United States. Only 20% of respondents in New Hampshire categorized themselves as "very religious", while the nationwide average was 40%.
According to the 2020 Public Religion Research Institute
The Public Religion Research Institute (PRRI) is an American nonprofit, nonpartisan research and education organization that conducts public opinion polls on a variety of topics, specializing in the quantitative and qualitative study of politic ...
study, 64% of the population was Christian, dominated by Roman Catholicism and evangelical Protestantism. In contrast with varying studies of estimated irreligiosity, the Public Religion Research Institute reported that irreligion declined from 36% at the separate 2014 Pew survey to 25% of the population in 2020.
Economy
 * Total employment (2016): 594,243
* Number of employer establishments: 37,868
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that New Hampshire's total state product in 2018 was $86billion, ranking 40th in the United States.
* Total employment (2016): 594,243
* Number of employer establishments: 37,868
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that New Hampshire's total state product in 2018 was $86billion, ranking 40th in the United States. Median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways o ...
in 2017 was $74,801, the fourth highest in the country (including Washington, DC
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
). Its agricultural outputs are dairy products, nursery stock, cattle, apples and eggs. Its industrial outputs are machinery, electric equipment, rubber and plastic products, and tourism is a major component of the economy.
New Hampshire experienced a major shift in its economic base during the 20th century. Historically, the base was composed of traditional New England textiles, shoemaking, and small machine shops, drawing upon low-wage labor from nearby small farms and parts of Quebec. Today, of the state's total manufacturing dollar value, these sectors contribute only two percent for textiles, two percent for leather goods, and nine percent for machining. They experienced a sharp decline due to obsolete plants and the lure of cheaper wages in the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
.
New Hampshire today has a broad-based and growing economy, with a state GDP growth rate of 2.2% in 2018. The state's largest economic sectors in 2018, based on contribution to GDP, are: 15% real estate and rental and leasing; 13% professional business services; 12% manufacturing; 10% government and government services; and 9% health care and social services.
The state's budget in FY2018 was $5.97billion, including $1.79billion in federal funds. The issue of taxation is controversial in New Hampshire, which has a property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inhe ...
(subject to municipal control) but no broad sales tax or income tax. The state does have narrower taxes on meals, lodging, vehicles, business and investment income, and tolls on state roads.
According to the Energy Information Administration, New Hampshire's energy consumption and per capita energy consumption are among the lowest in the country. The Seabrook Station Nuclear Power Plant
The Seabrook Nuclear Power Plant, more commonly known as Seabrook Station, is a nuclear power plant located in Seabrook, New Hampshire, United States, approximately north of Boston and south of Portsmouth. It has operated since 1990. With its ...
, near Portsmouth, is the largest nuclear reactor in New England and provided 57% of New Hampshire's electricity generation and 27% of its electricity consumption in 2017. In 2016 and 2017, New Hampshire obtained more of its electricity generation from wind power than from coal-fired power plants. Approximately 32% of New Hampshire's electricity consumption came from renewable resources (including nuclear, hydroelectric, wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ho ...
, and other renewable resources
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of ti ...
). New Hampshire was a net exporter of electricity, exporting .
New Hampshire's residential electricity use is low compared with the national average, in part because demand for air conditioning is low during the generally mild summer months and because few households use electricity as their primary energy source for home heating. Nearly half of New Hampshire households use fuel oil for winter heating, which is one of the largest shares in the United States. New Hampshire has potential for renewable energies like wind power, hydroelectricity, and wood fuel
Wood fuel (or fuelwood) is a fuel such as firewood, charcoal, Woodchips, chips, sheets, wood pellets, pellets, and sawdust. The particular form used depends upon factors such as source, quantity, quality and application. In many areas, wood is ...
.
The state has no general sales tax and no personal state income tax
In addition to Federal government of the United States, federal Income tax in the United States, income tax collected by the United States, most individual U.S. states collect a state income tax. Some local governments also impose an income tax, ...
(the state currently does tax, at a five percent rate, income from dividends and interest, but this tax is set to expire in 2027.)
New Hampshire's lack of a broad-based tax system has resulted in the state's local jurisdictions having the 8th-highest property taxes as of a 2019 ranking by the Tax Foundation
The Tax Foundation is an American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 1937 by a group of businessmen in order to "monitor the tax and spending policies of government agencies". The Tax Foundation collects data and publishe ...
. However, the state's overall tax burden is relatively low; in 2010 New Hampshire ranked 8th-lowest among states in combined average state and local tax burden.
The (preliminary) seasonally unemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
in April 2019 was 2.4% based on a 767,500 person civilian workforce with 749,000 people in employment. New Hampshire's workforce is 90% in nonfarm employment, with 18% employed in trade, transportation, and utilities; 17% in education and health care; 12% in government; 11% in professional and business services; and 10% in leisure and hospitality.
Largest employers
In March 2018, 86% of New Hampshire's workforce were employed by the private sector, with 53% of those workers being employed by firms with fewer than 100 employees. About 14% of private-sector employees are employed by firms with more than 1,000 employees. According to community surveys by the Economic & Labor Market Information Bureau of NH Employment Security, the following are the largest private employers in the state: New Hampshire's state government employs approximately 6,100 people. Additionally, theU.S. Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other ...
employs approximately 1,600 people at the National Visa Center in Portsmouth, which processes United States immigrant visa petitions.
Law and government
 The governor of New Hampshire, since January 5, 2017, is
The governor of New Hampshire, since January 5, 2017, is Chris Sununu
Christopher Thomas Sununu ( ; born November 5, 1974) is an American politician and engineer who has served as the 82nd governor of New Hampshire since 2017. A member of the Republican Party, Sununu was a member of the New Hampshire Executive Coun ...
(Republican). New Hampshire's two U.S. senators are Jeanne Shaheen
Cynthia Jeanne Shaheen ( ; née Bowers, born January 28, 1947) is an American retired educator and politician serving as the senior United States senator from New Hampshire since 2009. A member of the Democratic Party, Shaheen served as the 78 ...
and Maggie Hassan
Margaret Coldwell Hassan (; née Wood; born February 27, 1958) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States senator from New Hampshire. A Democrat, Hassan was elected to the Senate in 2016 while serving as the 81st ...
(both Democrats), both of whom are former governors. New Hampshire's two U.S. representatives as of January 2019 are Chris Pappas and Ann McLane Kuster
Ann L. McLane Kuster (born September 5, 1956) is an American lawyer and politician serving as the U.S. representative for since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, she previously worked as a lobbyist.
Early life and education
Kuster was b ...
(both Democrats).
New Hampshire is an alcoholic beverage control state
Alcoholic beverage control states, generally called control states, less often ABC states, are 17 states in the United States that, as of 2016, have state monopoly over the wholesaling or retailing of some or all categories of alcoholic beverage ...
, and through the State Liquor Commission takes in $100million from the sale and distribution of liquor.
New Hampshire is the only state in the U.S. that does not require adults to wear seat belts in their vehicles. It is one of three states that have no mandatory helmet law.
Governing documents
The New Hampshire State Constitution of 1783 is the supreme law of the state, followed by theNew Hampshire Revised Statutes Annotated The New Hampshire Revised Statutes Annotated (RSA) forms the codified law of the state subordinate to the New Hampshire State Constitution.
History
The RSA is a set of law books published by Thomson West. The work of updating the previous codif ...
and the New Hampshire Code of Administrative Rules. These are roughly analogous to the federal United States Constitution, United States Code and Code of Federal Regulations respectively.
Branches of government
New Hampshire has a bifurcated executive branch, consisting of the governor and a five-member executive council which votes on state contracts worth more than $5,000 and "advises and consents" to the governor's nominations to major state positions such as department heads and all judgeships and pardon requests. New Hampshire does not have a lieutenant governor; the Senate president serves as "acting governor" whenever the governor is unable to perform the duties. The legislature is called the General Court. It consists of theHouse of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
and the Senate. There are 400 representatives, making it one of the largest elected bodies in the English-speaking world, and 24 senators. Legislators are paid a nominal salary of $200 per two-year term plus travel costs, the lowest in the U.S. by far. Thus most are effectively volunteers, nearly half of whom are retirees
A pensioner is a person who receives a pension, most commonly because of retirement from the workforce. This is a term typically used in the United Kingdom (along with OAP, initialism of old-age pensioner), Ireland and Australia where someone of p ...
. (For details, see the article on Government of New Hampshire.)
The state's sole appellate court is the New Hampshire Supreme Court
The New Hampshire Supreme Court is the supreme court of the U. S. state of New Hampshire and sole appellate court of the state. The Supreme Court is seated in the state capital, Concord. The Court is composed of a Chief Justice and four Associat ...
. The Superior Court is the court of general jurisdiction and the only court which provides for jury trials in civil
Civil may refer to:
*Civic virtue, or civility
*Civil action, or lawsuit
* Civil affairs
*Civil and political rights
*Civil disobedience
*Civil engineering
*Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism
*Civilian, someone not a membe ...
or criminal cases. The other state courts are the Probate Court
A probate court (sometimes called a surrogate court) is a court that has competence in a jurisdiction to deal with matters of probate and the administration of estates. In some jurisdictions, such courts may be referred to as Orphans' Courts o ...
, District Court, and the Family Division
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Senior Courts of England and Wales. Its name is abbreviated as EWHC (England ...
.
Local government
New Hampshire has 10 counties and 234 cities and towns. New Hampshire is a "Dillon Rule" state, meaning the state retains all powers not specifically granted to municipalities. Even so, the legislature strongly favors local control, particularly concerning land use regulations. New Hampshire municipalities are classified astowns
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
or cities, which differ primarily by the form of government. Most towns generally operate on the town meeting
Town meeting is a form of local government in which most or all of the members of a community are eligible to legislate policy and budgets for local government. It is a town- or city-level meeting in which decisions are made, in contrast with ...
form of government, where the registered voters in the town act as the town legislature, and a board of selectmen acts as the executive of the town. Larger towns and the state's thirteen cities operate either on a council–manager or council–mayor form of government. There is no difference, from the state government's point of view, between towns and cities besides the form of government. All state-level statutes treat all municipalities identically.
New Hampshire has a small number of unincorporated area
An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. Widespread unincorporated communities and areas are a distinguishing feature of the United States and Canada. Most other countries of the world either have ...
s that are titled as grants, locations, purchases, or townships. These locations have limited to no self-government, and services are generally provided for them by neighboring towns or the county or state where needed. As of the 2000 census, there were 25 of these left in New Hampshire, accounting for a total population of 173 people (); several were entirely depopulated. All but two of these unincorporated areas are in Coos County.
Politics
New Hampshire is socially liberal like the rest ofNew England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
, and is the least religious state in the Union as of a 2016 Gallup poll. Yet the Live Free or Die
"Live Free or Die" is the official motto of the U.S. state of New Hampshire, adopted by the state in 1945. It is possibly the best-known of all state mottos, partly because it conveys an assertive independence historically found in American pol ...
state has also long had a great disdain for state taxation and state bureaucracy. As of 2021, New Hampshire has a Republican Governor (Chris Sununu
Christopher Thomas Sununu ( ; born November 5, 1974) is an American politician and engineer who has served as the 82nd governor of New Hampshire since 2017. A member of the Republican Party, Sununu was a member of the New Hampshire Executive Coun ...
), a Republican New Hampshire Senate
The New Hampshire Senate has been meeting since 1784. It is the upper house of the New Hampshire General Court, alongside the lower New Hampshire House of Representatives. It consists of 24 members representing Senate districts based on populatio ...
and a Republican New Hampshire House of Representatives, and is one of nine states (the only one of the American Northeast
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
) to have no general state income tax
In addition to Federal government of the United States, federal Income tax in the United States, income tax collected by the United States, most individual U.S. states collect a state income tax. Some local governments also impose an income tax, ...
imposed on individuals.
The Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
and the Republican Party, in that order, are the two largest parties in the state. A plurality of voters are registered as undeclared, and can choose either ballot in the primary and then regain their undeclared status after voting. The Libertarian Party
Active parties by country
Defunct parties by country
Organizations associated with Libertarian parties
See also
* Liberal parties by country
* List of libertarian organizations
* Lists of political parties
Lists of political part ...
had official party status from 1990 to 1996 and from 2016 to 2018. A movement known as the Free State Project suggests libertarians move to the state to concentrate their power. As of February 1, 2022, there were 869,339 registered voters, of whom 327,365 (37.66%) did not declare a political party affiliation, 276,206 (31.77%) were Democratic, and 265,768 (30.57%) were Republican.
New Hampshire primary
 New Hampshire is internationally known for the New Hampshire primary, the first primary in the quadrennial American presidential election cycle. State law requires that the Secretary of State schedule this election at least one week before any "similar event". While the
New Hampshire is internationally known for the New Hampshire primary, the first primary in the quadrennial American presidential election cycle. State law requires that the Secretary of State schedule this election at least one week before any "similar event". While the Iowa caucus
The Iowa caucuses are biennial electoral events for members of the Democratic and Republican parties in the U.S. state of Iowa. Unlike primary elections in most other U.S. states, where registered voters go to polling places to cast ballo ...
precedes the New Hampshire primary, the New Hampshire election is the nation's first contest that uses the same procedure as the general election, draws more attention than those in other states, and has been decisive in shaping the national contest.
State law permits a town with fewer than 100 residents to open its polls at midnight and close when all registered citizens have cast their ballots. As such, the communities of Dixville Notch in Coos County and Hart's Location in Carroll County, among others, have chosen to implement these provisions. Dixville Notch and Hart's Location are traditionally the first places in both New Hampshire and the U.S. to vote in presidential primaries and elections.
Nominations for all other partisan offices are decided in a separate primary election. In Presidential election cycles, this is the second primary election held in New Hampshire.
Saint Anselm College in Goffstown has become a popular campaign spot for politicians as well as several national presidential debates because of its proximity to Manchester-Boston Regional Airport.
Elections
 In the past, New Hampshire has often voted Republican. Between 1856 and 1988, New Hampshire cast its electoral votes for the Democratic presidential ticket six times:
In the past, New Hampshire has often voted Republican. Between 1856 and 1988, New Hampshire cast its electoral votes for the Democratic presidential ticket six times: Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
(twice), Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
(three times), and Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
(once).
Beginning in 1992, New Hampshire became a swing state
In American politics, the term swing state (also known as battleground state or purple state) refers to any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often referring to pres ...
in national and local elections, and in that time has supported Democrats in all presidential elections except 2000. It was the only state in the country to switch from supporting Republican George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
in the 2000 election to supporting his Democratic challenger in the 2004 election, when John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party, he ...
, a senator from neighboring Massachusetts, won the state.
The Democrats dominated elections in New Hampshire in 2006 and 2008. In 2006, Democrats won both congressional seats (electing Carol Shea-Porter in the first district and Paul Hodes
Paul William Hodes (born March 21, 1951) is an American lawyer, musician, and former U.S. Representative for , serving from 2007 to 2011. He is a member of the Democratic Party, and was New Hampshire's first Jewish representative.
Hodes was an u ...
in the second), re-elected Governor John Lynch, and gained a majority on the Executive Council and in both houses for the first time since 1911. Democrats had not held both the legislature and the governorship since 1874. Neither U.S. Senate seat was up for a vote in 2006. In 2008, Democrats retained their majorities, governorship, and Congressional seats; and former governor Jeanne Shaheen
Cynthia Jeanne Shaheen ( ; née Bowers, born January 28, 1947) is an American retired educator and politician serving as the senior United States senator from New Hampshire since 2009. A member of the Democratic Party, Shaheen served as the 78 ...
defeated incumbent Republican John E. Sununu for the U.S. Senate in a rematch of the 2002 contest.
The 2008 elections resulted in women holding a majority, 13 of the 24 seats, in the New Hampshire Senate, a first for any legislative body in the United States.
In the 2010 midterm elections, Republicans made historic gains in New Hampshire, capturing veto-proof majorities in the state legislature, taking all five seats in the Executive Council, electing a new U.S. senator, Kelly Ayotte
Kelly Ann Ayotte ( ; born June 27, 1968) is an American attorney and politician who served as a United States senator from New Hampshire from 2011 to 2017. A member of the Republican Party, Ayotte served as New Hampshire Attorney General from ...
, winning both U.S. House seats, and reducing the margin of victory of incumbent Governor John Lynch compared to his 2006 and 2008 landslide wins.
In the 2012 state legislative elections, Democrats took back the New Hampshire House of Representatives and narrowed the Republican majority in the New Hampshire Senate
The New Hampshire Senate has been meeting since 1784. It is the upper house of the New Hampshire General Court, alongside the lower New Hampshire House of Representatives. It consists of 24 members representing Senate districts based on populatio ...
to 13–11. In 2012, New Hampshire became the first state in U.S. history to elect an all-female federal delegation: Democratic Congresswomen Carol Shea-Porter of Congressional District 1 and Ann McLane Kuster
Ann L. McLane Kuster (born September 5, 1956) is an American lawyer and politician serving as the U.S. representative for since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, she previously worked as a lobbyist.
Early life and education
Kuster was b ...
of Congressional District 2 accompanied U.S. Senators Jeanne Shaheen
Cynthia Jeanne Shaheen ( ; née Bowers, born January 28, 1947) is an American retired educator and politician serving as the senior United States senator from New Hampshire since 2009. A member of the Democratic Party, Shaheen served as the 78 ...
and Kelly Ayotte
Kelly Ann Ayotte ( ; born June 27, 1968) is an American attorney and politician who served as a United States senator from New Hampshire from 2011 to 2017. A member of the Republican Party, Ayotte served as New Hampshire Attorney General from ...
in 2013. Further, the state elected its second female governor: Democrat Maggie Hassan
Margaret Coldwell Hassan (; née Wood; born February 27, 1958) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States senator from New Hampshire. A Democrat, Hassan was elected to the Senate in 2016 while serving as the 81st ...
.
In the 2014 elections, Republicans retook the New Hampshire House of Representatives with a 239–160 majority and expanded their majority in the New Hampshire Senate
The New Hampshire Senate has been meeting since 1784. It is the upper house of the New Hampshire General Court, alongside the lower New Hampshire House of Representatives. It consists of 24 members representing Senate districts based on populatio ...
to 14 of the Senate's 24 seats. On the national level, incumbent Democratic Senator Jeanne Shaheen
Cynthia Jeanne Shaheen ( ; née Bowers, born January 28, 1947) is an American retired educator and politician serving as the senior United States senator from New Hampshire since 2009. A member of the Democratic Party, Shaheen served as the 78 ...
defeated her Republican challenger, former Massachusetts senator Scott Brown. New Hampshire also elected Frank Guinta (R) for its First Congressional District representative and Ann Kuster (D) for its Second Congressional District representative.
In the 2016 elections, Republicans held the New Hampshire House of Representatives with a majority of 220–175 and held onto their 14 seats in the New Hampshire Senate
The New Hampshire Senate has been meeting since 1784. It is the upper house of the New Hampshire General Court, alongside the lower New Hampshire House of Representatives. It consists of 24 members representing Senate districts based on populatio ...
. In the gubernatorial race, retiring Governor Maggie Hassan
Margaret Coldwell Hassan (; née Wood; born February 27, 1958) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States senator from New Hampshire. A Democrat, Hassan was elected to the Senate in 2016 while serving as the 81st ...
was succeeded by Republican Chris Sununu
Christopher Thomas Sununu ( ; born November 5, 1974) is an American politician and engineer who has served as the 82nd governor of New Hampshire since 2017. A member of the Republican Party, Sununu was a member of the New Hampshire Executive Coun ...
, who defeated Democratic nominee Colin Van Ostern
Colin Van Ostern (born Kevin Colin O’Loughlin; February 14, 1979), is an American businessman and politician who served on the New Hampshire Executive Council from 2013 to 2017, where he represented the state's second district. He is a member o ...
. Sununu became the state's first Republican governor since Craig Benson
Craig R. Benson (born October 8, 1954
...
, who left office in 2005 following defeat by John Lynch. Republicans control the governor's office and both chambers of the state legislature, a governing trifecta in which the Republicans have full governing power. In the presidential race, the state voted for the Democratic nominee, former Secretary of State ...
Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
over the Republican nominee, Donald Trump, by a margin of 2,736 votes, or 0.3%, one of the closest results the state has ever seen in a presidential race, while Libertarian nominee Gary Johnson
Gary Earl Johnson (born January 1, 1953) is an American businessman, author, and politician. He served as the 29th governor of New Mexico from 1995 to 2003 as a member of the Republican Party. He was the Libertarian Party nominee for Presid ...
received 4.12% of the vote. The Democrats also won a competitive race in the Second Congressional District, as well as a competitive senate race. New Hampshire's congressional delegation currently consists of exclusively Democrats. In the 116th United States Congress
The 116th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. It convened in Washington, D.C., on January 3, 2019, and ended on Janu ...
, it is one of only seven states with an entirely Democratic delegation, five of which are in New England (the others are Delaware and Hawaii).
Free State Project
The Free State Project (FSP) is a movement founded in 2001 to recruit at least 20,000 libertarians to move to a single low-population state (New Hampshire, was selected in 2003), to concentrate libertarian activism around a single region. The Free State Project emphasizes decentralized decision-making, encouraging new movers and prior residents of New Hampshire to participate in a way the individual mover deems most appropriate. For example, as of 2017, there were 17 so-called Free Staters elected to the New Hampshire House of Representatives, and in 2021, the New Hampshire Liberty Alliance, which ranks bills and elected representatives based on their adherence to what they see as libertarian principles, scored 150 representatives as "A-" or above rated representatives. Participants also engage with other like-minded activist groups such as Rebuild New Hampshire,Young Americans for Liberty
Young Americans for Liberty (YAL) is a libertarian, classical liberal and conservative student activism organization headquartered in Austin, Texas. Formed in 2008 in the aftermath of the Ron Paul 2008 presidential campaign, YAL establishes ch ...
, and Americans for Prosperity
Americans for Prosperity (AFP), founded in 2004, is a libertarian conservative political advocacy group in the United States funded by Charles Koch and formerly his brother David. As the Koch brothers' primary political advocacy group, it is one ...
. As of April 2022, approximately 6,232 participants have moved to New Hampshire for the Free State Project.
Transportation
Highways
New Hampshire has a well-maintained, well-signed network of Interstate highways, U.S. highways, and state highways. State highway markers still depict theOld Man of the Mountain
The Old Man of the Mountain, also called the Great Stone Face and the Profile, was a series of five granite cliff ledges on Cannon Mountain in Franconia, New Hampshire, United States, that appeared to be the jagged profile of a human face when ...
despite that rock formation's demise in 2003. Several route numbers align with the same route numbers in neighboring states. State highway numbering is arbitrary, with no overall system as with U.S. and Interstate systems. Major routes include:
* Interstate 89
Interstate 89 (I-89) is an Interstate Highway in the New England region of the United States traveling from Bow, New Hampshire, to the Canadian border between Highgate Springs, Vermont, and Saint-Armand, Quebec. As with all odd-numbered p ...
runs northwest from near Concord
Concord may refer to:
Meaning "agreement"
* Pact or treaty, frequently between nations (indicating a condition of harmony)
* Harmony, in music
* Agreement (linguistics), a change in the form of a word depending on grammatical features of other ...
to Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
on the Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
border.
* Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, before entering Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
* U.S. Route 1
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs from Key West, Florida, north to Fort Kent, Maine, at the Canadian border, making ...
runs north–south briefly along New Hampshire's seacoast to the east of and paralleling I-95.
* U.S. Route 2
U.S. Route 2 or U.S. Highway 2 (US 2) is an east–west United States Numbered Highways, U.S. Highway spanning across the northern continental United States. US 2 consists of two segments connected by various roadways in southern ...
runs east–west through Coos County from Maine, intersecting Route 16, skirting the White Mountain National Forest
The White Mountain National Forest (WMNF) is a federally managed forest contained within the White Mountains in the northeastern United States. It was established in 1918 as a result of the Weeks Act of 1911; federal acquisition of land had alre ...
passing through Jefferson and into Vermont.
* U.S. Route 3
U.S. Route 3 (US 3) is a United States highway running from Cambridge, Massachusetts, through New Hampshire, to the Canada–US border near Third Connecticut Lake, where it connects to Quebec Route 257.
Massachusetts Route 3 connects to ...
is the longest numbered route in the state, and the only one to run completely through the state from the Massachusetts border to the Canada–U.S. border. It generally parallels Interstate 93. South of Manchester, it takes a more westerly route through Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
. North of Franconia Notch, U.S.3 takes a more easterly route, before terminating at the Canada–U.S. border.
* Portsmouth Traffic Circle
The Portsmouth Traffic Circle is a four-point rotary in the city of Portsmouth, New Hampshire.
Description
The southern exit of the circle provides access to Interstate 95 north and south, although only northbound I-95 traffic enters here. The e ...
and runs east–west across the southern part of the state connecting Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
, Concord, Boscawen, and Lebanon.
* New Hampshire Route 16
New Hampshire Route 16 (NH 16) is a , north–south state highway in New Hampshire, United States, the main road connecting the Seacoast region to the Lakes Region and the White Mountains. Much of its length is close to the border with Maine. ...
is a major north–south highway in the eastern part of the state that generally parallels the border with Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
, eventually entering Maine as Maine Route 16. The southernmost portion of NH 16 is a four-lane freeway, co-signed with U.S. Route4.
* New Hampshire Route 101
New Hampshire Route 101 (NH 101) is a state-maintained highway in southern New Hampshire extending from Keene to Hampton Beach. It is the major east–west highway in the southern portion of the state.
The western terminus of NH 101 is in Keene ...
is a major east–west highway in the southern part of the state that connects Keene with Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
and the Seacoast region. East of Manchester, NH 101 is a four-lane, limited-access highway that runs to Hampton Beach and I-95.
Air
 New Hampshire has 25 public-use airports, three with some scheduled commercial passenger service. The busiest airport by number of passengers handled is Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester and Londonderry, which serves the
New Hampshire has 25 public-use airports, three with some scheduled commercial passenger service. The busiest airport by number of passengers handled is Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester and Londonderry, which serves the Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern a ...
metropolitan area.
Public transportation
Long-distance intercity passenger rail service is provided byAmtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
's '' Vermonter'' and '' Downeaster'' lines.
Greyhound
The English Greyhound, or simply the Greyhound, is a breed of dog, a sighthound which has been bred for coursing, greyhound racing and hunting. Since the rise in large-scale adoption of retired racing Greyhounds, the breed has seen a resurgenc ...
, Concord Coach, Vermont Translines, and Dartmouth Coach all provide intercity bus connections to and from points in New Hampshire and to long-distance points beyond and in between.
, Boston-centered MBTA Commuter Rail services reach only as far as northern Massachusetts. The New Hampshire Rail Transit Authority is working to extend "Capital Corridor" service from Lowell, Massachusetts
Lowell () is a city in Massachusetts, in the United States. Alongside Cambridge, It is one of two traditional seats of Middlesex County. With an estimated population of 115,554 in 2020, it was the fifth most populous city in Massachusetts as of ...
, to Nashua, Concord, and Manchester, including Manchester-Boston Regional Airport; and "Coastal Corridor" service from Haverhill, Massachusetts, to Plaistow, New Hampshire
Plaistow (, ) is a town in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 7,830 at the 2020 census.
History
Plaistow was officially established as a town in 1749 after the 1739 resolution ...
. Legislation in 2007 created the New Hampshire Rail Transit Authority (NHRTA) with the goal of overseeing the development of commuter rail in the state of New Hampshire. In 2011, Governor John Lynch vetoed HB 218, a bill passed by Republican lawmakers, which would have drastically curtailed the powers and responsibilities of NHRTA. The I-93 Corridor transit study suggested a rail alternative along the Manchester and Lawrence branch line which could provide freight and passenger service. This rail corridor would also have access to Manchester-Boston Regional Airport.
Eleven public transit authorities operate local and regional bus services around the state, and eight private carriers operate express bus services which link with the national intercity bus network. The New Hampshire Department of Transportation
The New Hampshire Department of Transportation (NHDOT) is a government agency of the U.S. state of New Hampshire. The Commissioner of NHDOT is Victoria Sheehan. The main office of the NHDOT is located in the J. O. Morton Building in Concord.
F ...
operates a statewide ride-sharing match service, in addition to independent ride matching and guaranteed ride home programs.
Tourist railroad
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) i ...
s include the Conway Scenic Railroad
The Conway Scenic Railroad is a heritage railroad in North Conway, New Hampshire, United States, owned by Profile Mountain Holdings Corp. The railroad operates over two historic railway routes: a line from North Conway to Conway that was f ...
, Hobo-Winnipesaukee Railroad
The Plymouth & Lincoln Railroad is a class III shortline railroad operating on the Concord- Lincoln rail line in central New Hampshire, United States. The railroad consists of two distinct passenger operations, the Hobo Railroad, which offers pa ...
, and the Mount Washington Cog Railway
The Mount Washington Cog Railway, also known as the Cog, is the world's first mountain-climbing Rack railway, cog railway (rack-and-pinion railway). The railway climbs Mount Washington in New Hampshire, United States. It uses a Rack railway#Mars ...
.
Freight railways
Freight railways in New Hampshire include Claremont & Concord Railroad (CCRR),Pan Am Railways
Pan Am Railways, Inc. (PAR) is a subsidiary of CSX Corporation that operates Class II regional railroads covering northern New England from Mattawamkeag, Maine, to Rotterdam Junction, New York. Pan Am Railways is primarily made up of former Cla ...
via subsidiary Springfield Terminal Railway (ST), the New England Central Railroad
The New England Central Railroad is a regional railroad in the New England region of the United States. It began operations in 1995, as the successor of the Central Vermont Railway (CV). The company was originally a subsidiary of holding comp ...
(NHCR), the St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad
The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad , known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the C ...
(SLR), and New Hampshire Northcoast Corporation (NHN).
Education


High schools
The first public high schools in the state were the Boys' High School and the Girls' High School ofPortsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, established either in 1827 or 1830, depending on the source.
New Hampshire has more than 80 public high schools, many of which serve more than one town. The largest is Pinkerton Academy
Pinkerton Academy is a secondary school in Derry, New Hampshire, United States. It serves roughly 3,269 students, making it by far the largest high school in New Hampshire, more than 1,300 students greater than the Nashua High School South, next ...
in Derry, which is owned by a private non-profit organization and serves as the public high school of several neighboring towns. There are at least 30 private high schools in the state.
New Hampshire is also the home of several prestigious university-preparatory
A college-preparatory school (usually shortened to preparatory school or prep school) is a type of secondary school. The term refers to public, private independent or parochial schools primarily designed to prepare students for higher education ...
schools, such as Phillips Exeter Academy, St. Paul's School, Proctor Academy
Proctor Academy is a coeducational, independent preparatory boarding school for grades 9–12 located on in Andover, New Hampshire. There are about 370 students.
History
Origin
Proctor Academy first began as Andover Academy, established in 1 ...
, Brewster Academy
Brewster Academy is a co-educational independent boarding school located on in Wolfeboro, New Hampshire, United States. It occupies of shoreline along Lake Winnipesaukee. With around 350 students, it serves grades nine through twelve and post-g ...
, and Kimball Union Academy
Kimball Union Academy is a private boarding school located in New Hampshire. Founded in 1813, it is the 22nd oldest boarding school in the United States. The academy's mission is to "create a deep sense of belonging for every member of our commu ...
.
In 2008, the state tied with Massachusetts as having the highest scores on the SAT and ACT standardized tests given to high school students.
Colleges and universities
*Antioch University New England
Antioch University New England is a private graduate school located in Keene, New Hampshire, United States. It is part of the Antioch University system, a private, non-profit, 501(c)(3) institution that includes campuses in Seattle, Washington; ...
* Colby-Sawyer College
* Community College System of New Hampshire
The Community College System of New Hampshire (previously New Hampshire Community Technical Colleges (NHCTC) and prior to that New Hampshire Vocational Technical Colleges (NHVTC)) is an organization of seven public community colleges located thro ...
:
** Great Bay Community College
Great Bay Community College (GBCC) is a public community college in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. It is part of the Community College System of New Hampshire and is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education. The main campus is in ...
** Lakes Region Community College
Lakes Region Community College (LRCC) is a public community college in Laconia, New Hampshire. It is part of the Community College System of New Hampshire.
Academics
The college offers 29 associate degree programs in fields such as Nursing, Fir ...
** Manchester Community College
** Nashua Community College
Nashua Community College (NCC) is a public community college in Nashua, New Hampshire. It is part of the Community College System of New Hampshire. Enrollment was 2,422 students in 2013 and 1,798 students in 2017, most of them part-time.
History ...
** NHTI, Concord's Community College
** River Valley Community College
River Valley Community College (RVCC) is a public community college with campuses in Claremont, Keene, and Lebanon, New Hampshire. It is part of the Community College System of New Hampshire and is accredited by the New England Commission of Hi ...
** White Mountains Community College
White Mountains Community College (WMCC) is a public community college with its main campus in Berlin, New Hampshire, and academic centers in Littleton and North Conway. It is part of the Community College System of New Hampshire.
History
The ...
* Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native ...
** Tuck School of Business
The Tuck School of Business (also known as Tuck, and formally known as the Amos Tuck School of Administration and Finance) is the graduate business school of Dartmouth College, a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire.
Founded ...
** Geisel School of Medicine
The Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth is the graduate medical school of Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire. The fourth oldest medical school in the United States, it was founded in 1797 by New England physician Nathan Smith. It is o ...
** Thayer School of Engineering
Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth (Dartmouth Engineering) offers graduate and undergraduate education in engineering sciences at Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. The school was established in 1867 with funds from C ...
* Franklin Pierce University
Franklin Pierce University is a private university in Rindge, New Hampshire. It was founded as Franklin Pierce College in 1962, combining a liberal arts foundation with coursework for professional preparation.
The school gained university stat ...
* Hellenic American University
* Magdalen College of the Liberal Arts
Magdalen College of the Liberal Arts (formerly Northeast Catholic College, The College of Saint Mary Magdalen, and simply Magdalen College), is a private Catholic liberal arts college in Warner, New Hampshire. It is recognized as a Catholic ...
* MCPHS University
* New England College
New England College (NEC) is a private liberal arts college in Henniker, New Hampshire. As of Fall 2020 New England College's enrollment was 4,327 students (1,776 undergraduate and 2,551 graduate). The college is regionally accredited by the N ...
* New Hampshire Institute of Art
* Rivier University
* Saint Anselm College
* Southern New Hampshire University
Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) is a private university between Manchester and Hooksett, New Hampshire. The university is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education, along with national accreditation for some hospita ...
* Thomas More College of Liberal Arts
The Thomas More College of Liberal Arts is a Private college, private Catholic Church, Roman Catholic liberal arts college in Merrimack, New Hampshire. It emphasizes Classical education movement, classical education in the Catholic intellectual t ...
* University System of New Hampshire:
** University of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire (UNH) is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Durham, New Hampshire. It was founded and incorporated in 1866 as a land grant college in Hanover in connection with Dartmouth College, m ...
*** University of New Hampshire School of Law
The University of New Hampshire Franklin Pierce School of Law is a public law school in Concord, New Hampshire, associated with the University of New Hampshire. It is the only law school in the state and was founded in 1973 by Robert H. Rines ...
*** University of New Hampshire at Manchester
The University of New Hampshire at Manchester (UNH Manchester) is the urban campus of the public University of New Hampshire and is located in Manchester, New Hampshire. It was established in 1985 as the sixth college of the University of New Ham ...
** Granite State College
** Keene State College
Keene State College is a public liberal arts college in Keene, New Hampshire. It is part of the University System of New Hampshire and the Council of Public Liberal Arts Colleges. Founded in 1909 as a teacher's college (originally, Keene Norm ...
** Plymouth State University
Media
Daily newspapers
* '' Berlin Daily Sun'' * ''Concord Monitor
The ''Concord Monitor'' is the daily newspaper for Concord, the state capital of New Hampshire. It also covers surrounding towns in Merrimack County, most of Belknap County, as well as portions of Grafton, Rockingham and Hillsborough counties ...
''
* '' Conway Daily Sun''
* ''The Dartmouth
''The Dartmouth'' is the daily student newspaper at Dartmouth College and America's oldest college newspaper. Originally named the ''Dartmouth Gazette'', the first issue was published on August 27, 1799, under the motto "Here range the world— ...
'' of Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native ...
/Hanover
* ''Eagle Times
The ''Eagle Times'' is a daily newspaper based in Claremont, New Hampshire, US, serving the Connecticut River Valley in New Hampshire and Vermont. It was published from the 1970s. It closed on July 10, 2009, and resumed publishing on October 12, ...
'' of Claremont
* '' Eagle Tribune'' ( Lawrence, Massachusetts area, including parts of southern New Hampshire)
* ''Foster's Daily Democrat
''Foster's Daily Democrat'' is a six-day (Monday–Saturday) morning broadsheet newspaper published in Dover, New Hampshire, United States, covering southeast New Hampshire and southwest Maine.
In addition to its Dover headquarters, ''Foster's'' ...
'' of Dover
* '' Keene Sentinel''
* '' Laconia Citizen''
* ''Laconia Daily Sun
''The Laconia Daily Sun'' is a five-day (Tuesday through Saturday) free morning daily newspaper published in the city of Laconia, New Hampshire, United States, covering Belknap County and the Lakes Region. Each publication day, 18,000 copies of ...
''
* ''New Hampshire Union Leader
The ''New Hampshire Union Leader'' is a daily newspaper from Manchester, the largest city in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. On Sundays, it publishes as the ''New Hampshire Sunday News.''
Founded in 1863, the paper was best known for the cons ...
'' of Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
, formerly known as the ''Manchester Union-Leader''
* ''The Portsmouth Herald
''The Portsmouth Herald'' (and ''Seacoast Weekend'') is a six-day daily newspaper serving greater Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Its coverage area also includes the municipalities of Greenland, New Castle, Newington and Rye, New Hampshire; and Eli ...
''
* ''The Telegraph
''The Telegraph'', ''Daily Telegraph'', ''Sunday Telegraph'' and other variant names are popular names for newspapers. Newspapers with these titles include:
Australia
* ''The Telegraph'' (Adelaide), a newspaper in Adelaide, South Australia, publ ...
'' of Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
* '' The Sun'' (Lowell, Massachusetts
Lowell () is a city in Massachusetts, in the United States. Alongside Cambridge, It is one of two traditional seats of Middlesex County. With an estimated population of 115,554 in 2020, it was the fifth most populous city in Massachusetts as of ...
area, including parts of southern New Hampshire)
* ''Valley News
The ''Valley News'' (and ''Sunday Valley News'') is a seven-day morning daily newspaper based in Lebanon, New Hampshire, covering the Upper Valley region of New Hampshire and Vermont, in the United States.
Although the newspaper's offices are ...
'' of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
Other publications
* '' Area News Group'' * ''Business New Hampshire Magazine'' * ''The Cabinet Press'' ** Milford Cabinet ** Bedford Journal ** Hollis/Brookline Journal ** Merrimack Journal * ''Carriage Towne News'' (covering Kingston and surrounding towns) * ''The Exeter News-Letter Seacoast Media Group is a unit of Local Media Group. Seacoast publishes five weekly newspapers and one daily, ''The Portsmouth Herald'', along the coasts of New Hampshire and York County, Maine, United States.
The group publisher is John Tabor; i ...
''
* ''Free Keene
Keene is a city in, and the seat of Cheshire County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 23,047 at the 2020 census, down from 23,409 at the 2010 census.
Keene is home to Keene State College and Antioch University New England. It ...
''
* ''The Hampton Union Seacoast Media Group is a unit of Local Media Group. Seacoast publishes five weekly newspapers and one daily, ''The Portsmouth Herald'', along the coasts of New Hampshire and York County, Maine, United States.
The group publisher is John Tabor; it ...
''
* ''Hippo Press
HippoPress is the publisher of the free weekly newspaper ''Hippo'', based in Manchester, New Hampshire. ''Hippo'', which is independently owned by Jody Reese, Jeff Rapsis and Dan Szczesny, started in January 2001. In 2004 it launched a second ed ...
'' (covering Manchester, Nashua, and Concord)
* ''Manchester Express The ''Manchester Express'' was a free newspaper serving Manchester, New Hampshire, United States. The paper began publication as ''The Manchester Daily Express'' on May 22, 2006, and was published five days a week until February 27, 2008. The paper ...
''
* ''Manchester Ink Link''
* ''The New Hampshire
''The New Hampshire'' (commonly known as ''TNH'') is the student-run news of the University of New Hampshire (UNH) since 1911. ''TNH'' operates from its headquarters in the Memorial Union Building, covering student life and doings for the colle ...
'' (University of New Hampshire student newspaper)
* ''New Hampshire Business Review
''New Hampshire Business Review'' is a bi-monthly publication, published on newsprint and based in Manchester, covering business-related issues in New Hampshire.
''New Hampshire Business Review'' started in 1978, and was purchased from the Madde ...
''
* '' New Hampshire Free Press''
* '' The New Hampshire Gazette'' (Portsmouth alternative biweekly)
* ''NH Living Magazine''
* NH Rocks
' *
NH Roots
' * ''Salmon Press Newspapers'' (family of weekly newspapers covering Lakes Region & North Country) * '' The Liberty Block''
Radio stations
Television stations
* ABC affiliate WMUR, Channel 9, Manchester *PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
affiliate Channel 11, Durham (New Hampshire Public Television
New Hampshire PBS (NHPBS), known as New Hampshire Public Television (NHPTV) prior to October 1, 2017, is a Public Broadcasting Service ( PBS) member network serving the U.S. state of New Hampshire. It is operated by New Hampshire Public Broadcas ...
); repeater stations in Keene and Littleton
* True Crime Network
True Crime Network (formerly Justice Network) is an American digital multicast television network that is operated by True Crime Network, LLC, a limited liability company, which is owned by Tegna Inc. The network specializes in true crime, in ...
affiliate WWJE, Channel 50, Derry/Manchester
* Ion Television
Ion Television is an American broadcast television network owned by the Katz Broadcasting subsidiary of the E. W. Scripps Company. The network first began broadcasting on August 31, 1998, as Pax TV, focusing primarily on family-oriented en ...
station WPXG, Channel 21, Concord (satellite of WBPX
WBPX-TV (channel 68) is a television station in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, airing programming from the Ion Television network. It is owned by the Ion Media subsidiary of the E. W. Scripps Company, which also owns Woburn-licensed ...
in Boston)
Sports
The following sports teams are based in New Hampshire: TheNew Hampshire Motor Speedway
New Hampshire Motor Speedway is a oval speedway located in Loudon, New Hampshire, which has hosted NASCAR racing annually since 1990, as well as the longest-running motorcycle race in North America, the Loudon Classic. Nicknamed "The Magic Mil ...
in Loudon is an oval track and road course that has been visited by national motorsport championship series such as the NASCAR Cup Series, the NASCAR Xfinity Series
The NASCAR Xfinity Series (NXS) is a stock car racing series organized by NASCAR. It is promoted as NASCAR's second-tier circuit to the organization's top level Cup Series. NXS events are frequently held as a support race on the day prior to a ...
, the NASCAR Camping World Truck Series, NASCAR Whelen Modified Tour
The NASCAR Whelen Modified Tour (NWMT) (previously the NASCAR Winston Modified Tour and NASCAR Featherlite Modified Series from 1985 until 2005) is a modified stock car racing series owned and operated by NASCAR in the Modified Division. The Mod ...
, American Canadian Tour
The American Canadian Tour (ACT) is a late model stock car racing series based in the northeastern United States, and Quebec, Canada. The current American-Canadian Tour Late Model Tour was founded in 1992 as a cost-cutting, regional touring divisi ...
(ACT), the Champ Car
Champ Car World Series (CCWS) was the series sanctioned by Open-Wheel Racing Series Inc., or Champ Car, a sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing that operated from 2004 to 2008. It was the successor to Championship Auto Racing Teams ...
and the IndyCar Series
The IndyCar Series, currently known as the NTT IndyCar Series under sponsorship, is the highest class of regional North American open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars in the United States, which has been conducted under the auspices o ...
. Other motor racing venues include Star Speedway and New England Dragway
New England Dragway is a mile NHRA dragway in Epping, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, United States. The track hosts the New England Nationals event as part of the NHRA Camping World Drag Racing Series. The track also hosts a regional event ...
in Epping Epping may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Epping, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney
** Epping railway station, Sydney
* Electoral district of Epping, the corresponding seat in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly
* Epping Forest, Kearns, a he ...
, Lee USA Speedway
Lee USA Speedway is a short-track oval race track located in Lee, New Hampshire.
History
The facility opened as Lee Raceway in 1964 as a dirt tri-oval, in length. Original owner Bob Bonser later recounted that he initially bought the land the ...
in Lee, Twin State Speedway in Claremont, Monadnock Speedway
Monadnock Speedway is a paved oval race track in Winchester, New Hampshire. Located south of Keene, the track is nestled between New Hampshire Route 10 and the Ashuelot River.
The track hosts various races for regional touring series, includin ...
in Winchester and Canaan Fair Speedway in Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
.
New Hampshire has two universities competing at the NCAA Division I in all collegiate sports: the Dartmouth Big Green
The Dartmouth College Big Green are the varsity and club athletic teams representing Dartmouth College, an American university located in Hanover, New Hampshire. Dartmouth's teams compete at the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) ...
(Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight school ...
) and the New Hampshire Wildcats
The New Hampshire Wildcats, or 'Cats, are the American intercollegiate athletic teams representing the University of New Hampshire (UNH), located in Durham. The wildcat is the school's official mascot, the colors are UNH Blue and white. The Uni ...
(America East Conference
The America East Conference is a collegiate athletic conference affiliated with NCAA Division I founded in 1979, whose members are located in the Northeastern United States.
The conference has nine core members including eight public research ...
), as well as three NCAA Division II teams: Franklin Pierce Ravens, Saint Anselm Hawks, and Southern New Hampshire Penmen (Northeast-10 Conference
The Northeast-10 Conference (NE-10) is a college athletic conference affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) at the Division II level. Member institutions are located in the northeastern United States in the states o ...
). Most other schools compete in NCAA Division III or the NAIA.
Annually since 2002, high-school statewide all-stars compete against Vermont in 10 sports during "Twin State" playoffs.
Culture
In the spring, New Hampshire's many sap houses hold sugaring-off open houses. In summer and early autumn, New Hampshire is home to many county fairs, the largest being theHopkinton State Fair
The Hopkinton State Fair is an annual fair taking place in the village of Contoocook in Hopkinton, New Hampshire, United States. The fair began in 1915 and has continued to grow and become one of the most well known events in New England, and the ...
, in Contoocook. New Hampshire's Lakes Region is home to many summer camps, especially around Lake Winnipesaukee
Lake Winnipesaukee () is the largest lake in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, located in the Lakes Region at the foothills of the White Mountains. It is approximately long (northwest-southeast) and from wide (northeast-southwest), covering & ...
, and is a popular tourist destination. The Peterborough Players have performed every summer in Peterborough
Peterborough () is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, east of England. It is the largest part of the City of Peterborough unitary authority district (which covers a larger area than Peterborough itself). It was part of Northamptonshire until ...
since 1933. The Barnstormers Theatre
The Barnstormers Theatre is located in Tamworth, New Hampshire, and is the oldest ongoing professional summer theatre in the United States. It was founded in 1931 by Francis Cleveland, the son of 22nd president Grover Cleveland. It is one of t ...
in Tamworth, founded in 1931, is one of the longest-running professional summer theaters in the United States.
In September, New Hampshire is host to the New Hampshire Highland Games. New Hampshire has also registered an official tartan
Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Sc ...
with the proper authorities in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
, used to make kilts worn by the Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
Police Department while its officers serve during the games. The fall foliage
Autumn leaf color is a phenomenon that affects the normal green leaves of many deciduous trees and shrubs by which they take on, during a few weeks in the autumn season, various shades of yellow, orange, red, purple, and brown. The phenomenon i ...
peaks in mid-October. In the winter, New Hampshire's ski areas and snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not ...
trails attract visitors from a wide area. After the lakes freeze over they become dotted with ice fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
Shelters
Longe ...
ice houses, known locally as bobhouses.
Funspot, the world's largest video arcade (now termed a museum), is in Laconia.
In fiction
Theater
* The fictional New Hampshire town of Grover's Corners serves as the setting of theThornton Wilder
Thornton Niven Wilder (April 17, 1897 – December 7, 1975) was an American playwright and novelist. He won three Pulitzer Prizes — for the novel '' The Bridge of San Luis Rey'' and for the plays ''Our Town'' and '' The Skin of Our Teeth'' — ...
play ''Our Town
''Our Town'' is a 1938 metatheatrical three-act play by American playwright Thornton Wilder which won the Pulitzer Prize for Drama. The play tells the story of the fictional American small town of Grover's Corners between 1901 and 1913 thro ...
''. Grover's Corners is based, in part, on the real town of Peterborough
Peterborough () is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, east of England. It is the largest part of the City of Peterborough unitary authority district (which covers a larger area than Peterborough itself). It was part of Northamptonshire until ...
. Several local landmarks and nearby towns are mentioned in the text of the play, and Wilder himself spent some time in Peterborough at the MacDowell Colony
MacDowell is an artist's residency program in Peterborough, New Hampshire, United States, founded in 1907 by composer Edward MacDowell and his wife, pianist and philanthropist Marian MacDowell. Prior to July 2020, it was known as the MacDowel ...
, writing at least some of the play while in residence there.
Comics
* Al Capp, creator of the comic strip ''Li'l Abner
''Li'l Abner'' is a satirical American comic strip that appeared in many newspapers in the United States, Canada and Europe. It featured a fictional clan of hillbilly, hillbillies in the impoverished mountain village of Dogpatch, USA. Written a ...
'', used to joke that Dogpatch
Dogpatch was the fictional setting of cartoonist Al Capp's classic comic strip ''Li'l Abner'' (1934–1977).
''Li'l Abner'' comic strip
The inhabitants of Dogpatch were mostly lazy hillbillies, who usually wanted nothing to do with progress. ...
, the setting for the strip, was based on Seabrook, where he would vacation with his wife.
Television
* In the AMC drama '' Breaking Bad'' (" Granite State") series leadWalter White Walter White most often refers to:
* Walter White (''Breaking Bad''), character in the television series ''Breaking Bad''
* Walter Francis White (1893–1955), American leader of the NAACP
Walter White may also refer to:
Fictional characters ...
escapes to a cabin in a fictional county in northern New Hampshire.
* In the sixth season of HBO hit series ''The Sopranos
''The Sopranos'' is an American crime drama television series created by David Chase. The story revolves around Tony Soprano (James Gandolfini), a New Jersey-based Italian-American mobster, portraying his difficulties as he tries to balance ...
'', in an episode named for New Hampshire's famous slogan of "Live Free or Die
"Live Free or Die" is the official motto of the U.S. state of New Hampshire, adopted by the state in 1945. It is possibly the best-known of all state mottos, partly because it conveys an assertive independence historically found in American pol ...
", character Vito Spatafore
This is a list of fictional characters from the HBO series ''The Sopranos'', its video game '' The Sopranos: Road to Respect'' and its prequel film ''The Many Saints of Newark.''
Main characters Cast table
Main character biographies Tony Sopran ...
flees New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
for the small fictional town of Dartford, New Hampshire, because of his inadvertently being outed
Outing is the act of disclosing an LGBT person's sexual orientation or gender identity without that person's consent. It is often done for political reasons, either to instrumentalize homophobia in order to discredit political opponents or to com ...
as a gay man.
Notable people
Prominent individuals from New Hampshire include 14th President of the United States Franklin Pierce,founding father
The following list of national founding figures is a record, by country, of people who were credited with establishing a state. National founders are typically those who played an influential role in setting up the systems of governance, (i.e. ...
Nicholas Gilman, Senator Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison ...
, Revolutionary War hero John Stark
Major-General John Stark (August 28, 1728 – May 8, 1822) was an American military officer who served during the French and Indian War and the Revolutionary War. He became known as the "Hero of Bennington" for his exemplary service at the Batt ...
, editor Horace Greeley, founder of the Christian Science religion Mary Baker Eddy
Mary Baker Eddy (July 16, 1821 – December 3, 1910) was an American religious leader and author who founded The Church of Christ, Scientist, in New England in 1879. She also founded ''The Christian Science Monitor'', a Pulitzer Prize-winning se ...
, poet Robert Frost, astronaut Alan Shepard
Alan Bartlett Shepard Jr. (November 18, 1923 – July 21, 1998) was an American astronaut, naval aviator, test pilot, and businessman. In 1961, he became the second person and the first American to travel into space and, in 1971, he beca ...
, rock musician Ronnie James Dio, author Dan Brown
Daniel Gerhard Brown (born June 22, 1964) is an American author best known for his thriller novels, including the Robert Langdon novels ''Angels & Demons'' (2000), '' The Da Vinci Code'' (2003), ''The Lost Symbol'' (2009), '' Inferno'' (2013), ...
, actor Adam Sandler, inventor Dean Kamen
Dean Lawrence Kamen (born April 5, 1951) is an American engineer, inventor, and businessman. He is known for his invention of the Segway and iBOT, as well as founding the non-profit organization FIRST with Woodie Flowers. Kamen holds over 1, ...
, comedians Sarah Silverman
Sarah Kate Silverman (born December 1, 1970) is an American comedian, actress, and writer.
Silverman was a writer and performer on ''Saturday Night Live'', and she starred in and produced '' The Sarah Silverman Program'', which ran from 2007 to ...
and Seth Meyers, restaurateurs Richard and Maurice McDonald
Richard McDonald (February 1909 – July 14, 1998) and Maurice McDonald (1902 – December 11, 1971), together known as the McDonald Brothers, were American entrepreneurs who founded the fast food company McDonald's. They opened the original Mc ...
, and WWE wrestler Triple H
Paul Michael Levesque (born July 27, 1969), better known by the ring name Triple H, is an American business executive, actor, and retired professional wrestler currently serving as the chief content officer for WWE. He is widely regarded as ...
, aka Paul Michael Levesque.
New Hampshire firsts
* On January 5, 1776, at Exeter, the Provincial Congress of New Hampshire ratified the first independentconstitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
in the Americas, free of British rule.
* On June 12, 1800, Fernald's Island in the Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the river ...
became the first government-sanctioned U.S. Navy shipyard.
* Started in 1822, Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
's Juvenile Library was the first free public library.
* In 1828, the first women's strike in the nation took place at Dover's Cocheco Mills.
* Founded in 1833, the Peterborough
Peterborough () is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, east of England. It is the largest part of the City of Peterborough unitary authority district (which covers a larger area than Peterborough itself). It was part of Northamptonshire until ...
Town Library was the first public library, supported with public funds, in the world.
* On August 3, 1852, Center Harbor was the site of the first intercollegiate athletic event. Harvard defeated Yale
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wor ...
in a rowing race on Lake Winnipesaukee
Lake Winnipesaukee () is the largest lake in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, located in the Lakes Region at the foothills of the White Mountains. It is approximately long (northwest-southeast) and from wide (northeast-southwest), covering & ...
, the first meeting in a rivalry that continues to this day.
* Finished on June 27, 1874, the first trans-Atlantic telecommunications cable between Europe and America stretched from Balinskelligs Bay, Ireland, to Rye, New Hampshire.
* On February 6, 1901, a group of nine conservationists founded the Society for the Protection of New Hampshire Forests The Society for the Protection of New Hampshire Forests (SPNHF) is a private, non-profit, land conservation and sustainable forestry organization based in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. It purchases or is given easements on property, or obtains ou ...
, the first forest-conservation advocacy group in the U.S.
* In 1908, Monsignor Pierre Hevey organized the nation's first credit union
A credit union, a type of financial institution similar to a commercial bank, is a member-owned nonprofit financial cooperative. Credit unions generally provide services to members similar to retail banks, including deposit accounts, provisi ...
, "La Caisse Populaire, Ste-Marie" (The People's Bank) in Manchester, to help mill workers save and borrow money, which is now St. Mary's Bank.
* In 1933, the League of New Hampshire Craftsmen held the first craft
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale pro ...
s fair in the nation.
* In July 1944, the Bretton Woods Agreement
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
, the first fully negotiated system intended to govern monetary relations among independent nation-states, was signed at the Mount Washington Hotel
The Mount Washington Hotel is a hotel in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, near Mount Washington. It was designed by Charles Alling Gifford. In 1944, it hosted the Bretton Woods Conference, which established the International Monetary ...
.
* On May 5, 1961, Alan Shepard
Alan Bartlett Shepard Jr. (November 18, 1923 – July 21, 1998) was an American astronaut, naval aviator, test pilot, and businessman. In 1961, he became the second person and the first American to travel into space and, in 1971, he beca ...
of Derry rode a Mercury spacecraft and became the first American in space.
* In 1963, New Hampshire's legislature approved the nation's first modern state lottery, which began play in 1964.
* In 1966, Ralph Baer of Sanders Associates
Sanders Associates was a defense contractor in Nashua, New Hampshire, United States, from 1951 until it was sold in 1986. It is now part of BAE Systems Electronics & Integrated Solutions, a subsidiary of BAE Systems. It concentrated on developin ...
, Inc., Nashua, recruited engineers to develop the first home video game.
* In January 1974, the first municipal recycling center in the U.S. opened in Nottingham
Nottingham ( , locally ) is a city and unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located north-west of London, south-east of Sheffield and north-east of Birmingham. Nottingham has links to the legend of Robi ...
.
* Christa McAuliffe
Sharon Christa McAuliffe ( Corrigan; September 2, 1948 – January 28, 1986) was an American teacher and astronaut from Concord, New Hampshire, who was killed on the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' on mission STS-51-L where she was serving as a ...
of Concord became the first private citizen selected to venture into space. She perished with her six '' Challenger'' crewmates on January 28, 1986.
* On May 17, 1996, New Hampshire became the first state in the country to install a green LED traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – known also as robots in South Africa are signalling devices positioned at road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order to control flows of traffic.
Traffic light ...
. New Hampshire was selected because it was the first state to install the red and yellow variety statewide.
* On May 31, 2007, New Hampshire became the first state to recognize same-sex unions "without a court order or the threat of one".
See also
*Outline of New Hampshire
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of New Hampshire:
New Hampshire – U.S. state in the New England region of the United States of America, named after the southern English county of H ...
* List of states and territories of the United States
The United States of America is a federal republic consisting of 50 states, a federal district ( Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States), five major territories, and various minor islands. Both the states and the United ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*''Land Use in Cornish, N.H.''
a 2006 documentary presentation by James M. Patterson of the ''
Valley News
The ''Valley News'' (and ''Sunday Valley News'') is a seven-day morning daily newspaper based in Lebanon, New Hampshire, covering the Upper Valley region of New Hampshire and Vermont, in the United States.
Although the newspaper's offices are ...
'', depicts various aspects of the societal and cultural environment of northern New Hampshire.
External links
State government
*New Hampshire Almanac
Visitnh.gov
New Hampshire Office of Travel and Tourism Development
U.S. Government
New Hampshire State Guide from the Library of Congress
Energy Facts for New Hampshire
New Hampshire State Facts
USDA Economic Research Service
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of New Hampshire
Other
Internet Movie Database listing of films shot in the state
New Hampshire Historical Society
* * {{coord, 43.5, -71.5, dim:200000_region:US-NH_type:adm1st, name=State of New Hampshire, display=title States of the United States New England states Northeastern United States States and territories established in 1788 States of the East Coast of the United States 1788 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States