First Battle Of Zürich on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The First Battle of Zurich, from 4 to 7 June 1799, forced French General
 Initially, the rulers of Europe viewed the revolution in France as an event between the French king and his subjects, and not something in which they should interfere. As revolutionary rhetoric grew more strident, they declared the interest of the monarchs of Europe as one with the interests of Louis and his family; this
Initially, the rulers of Europe viewed the revolution in France as an event between the French king and his subjects, and not something in which they should interfere. As revolutionary rhetoric grew more strident, they declared the interest of the monarchs of Europe as one with the interests of Louis and his family; this
 The Austrians had arrayed their own army in a line from the
The Austrians had arrayed their own army in a line from the
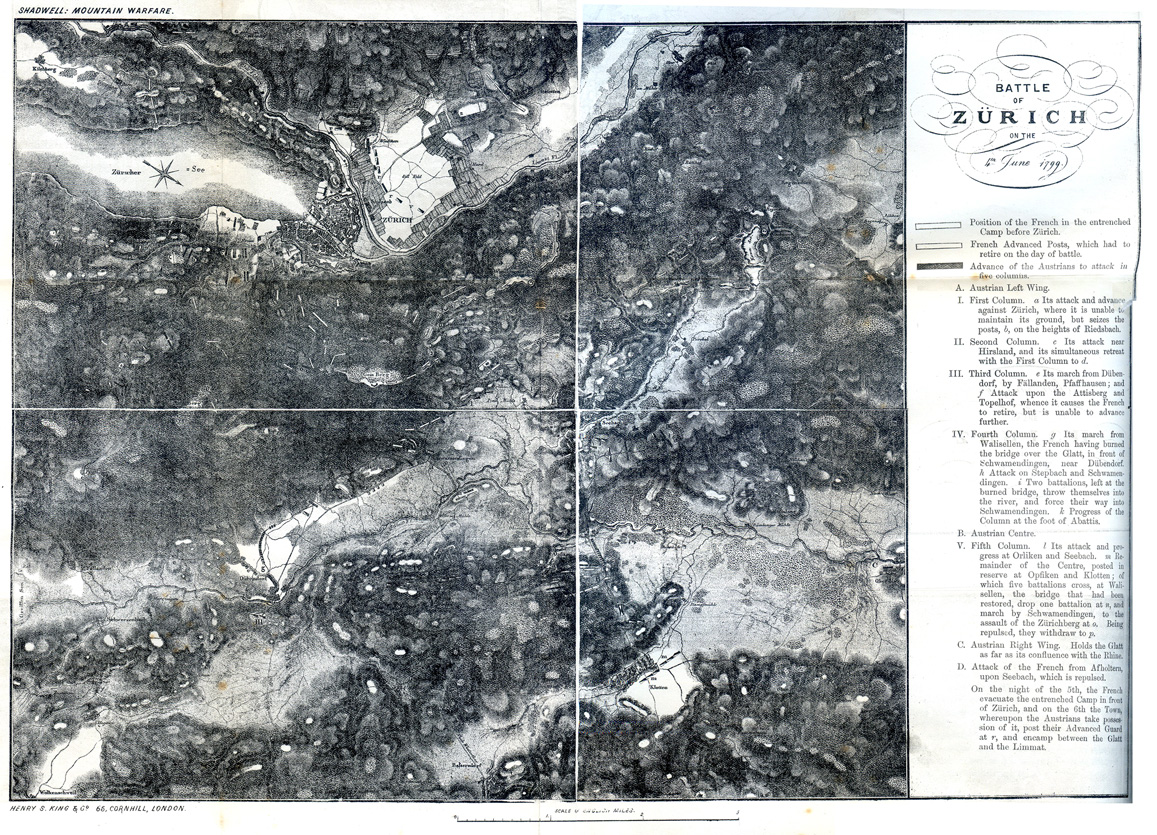 The next day on 4 June, Charles crossed the Glatt and launched a broad attack in five columns:
* On the Austrian left, the First column under Jelačić (five battalions and three squadrons) marched against Zürich along the high road and succeeded in breaking through the
The next day on 4 June, Charles crossed the Glatt and launched a broad attack in five columns:
* On the Austrian left, the First column under Jelačić (five battalions and three squadrons) marched against Zürich along the high road and succeeded in breaking through the
André Masséna
André Masséna, prince d'Essling, duc de Rivoli (; born Andrea Massena; 6 May 1758 – 4 April 1817), was a French military commander of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was one of the original eighteen Marshal of the ...
to yield the city of Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
to the Austrians, under Archduke Charles
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Lawrence of Austria, Duke of Teschen (; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian field marshal, the third son of Emperor Leopold II and his wife, Maria Luisa of Spain. He was also the youn ...
, and to retreat beyond the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, continuing a further 35 km until it reaches the river A ...
, where he managed to fortify his positions, which resulted in a stalemate.
The Helvetic Republic
The Helvetic Republic (; ; ) was a sister republic of France that existed between 1798 and 1803, during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was created following the French invasion and the consequent dissolution of the Old Swiss Confederacy, ma ...
in 1798 became a battlefield of the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
. During the summer, Russian troops, under General Alexander Korsakov, replaced the Austrian troops, and at the Second Battle of Zurich
The Second Battle of Zurich (25–26 September 1799) was a key victory by the Republican French army in Switzerland led by André Masséna over a Russian force commanded by Alexander Korsakov near Zürich. It broke the stalemate that had ...
, the French regained control of the city, along with the rest of Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
.
Background
Political and diplomatic situation
 Initially, the rulers of Europe viewed the revolution in France as an event between the French king and his subjects, and not something in which they should interfere. As revolutionary rhetoric grew more strident, they declared the interest of the monarchs of Europe as one with the interests of Louis and his family; this
Initially, the rulers of Europe viewed the revolution in France as an event between the French king and his subjects, and not something in which they should interfere. As revolutionary rhetoric grew more strident, they declared the interest of the monarchs of Europe as one with the interests of Louis and his family; this Declaration of Pillnitz
The Declaration of Pillnitz was a statement of five sentences issued on 27 August 1791 at Pillnitz Castle near Dresden (Saxony) by Frederick William II of Prussia and the Habsburg Leopold II, Holy Roman Emperor who was Marie Antoinette's brot ...
threatened ambiguous, but quite serious, consequences if anything should happen to the royal family. The French position became increasingly difficult. Compounding problems in international relations, French émigrés continued to agitate for support of a counter-revolution. On 20 April 1792, the French National Convention
The National Convention () was the constituent assembly of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for its first three years during the French Revolution, following the two-year National Constituent Assembly and the ...
declared war on Austria. In this War of the First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition () was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797, initially against the Constitutional Cabinet of Louis XVI, constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French First Republic, Frenc ...
(1792–1798), France ranged itself against most of the European states sharing land or water borders with her, plus Portugal and the Ottoman Empire. Although the Coalition forces achieved several victories at Verdun
Verdun ( , ; ; ; official name before 1970: Verdun-sur-Meuse) is a city in the Meuse (department), Meuse departments of France, department in Grand Est, northeastern France. It is an arrondissement of the department.
In 843, the Treaty of V ...
, Kaiserslautern
Kaiserslautern (; ) is a town in southwest Germany, located in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate at the edge of the Palatinate Forest. The historic centre dates to the 9th century. It is from Paris, from Frankfurt am Main, 666 kilometers (414 m ...
, Neerwinden
Neerwinden () is a village in Belgium, located in the Municipalities of Belgium, municipality of Landen, in the province of Flemish Brabant, Flanders.
The village gives its name to two great historical battles. The first, the Battle of Neerwind ...
, Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
, Amberg
Amberg () is a Town#Germany, town in Bavaria, Germany. It is located in the Upper Palatinate about halfway between Regensburg and Bayreuth.
History
The town was first mentioned in 1034 with the name Ammenberg. It became an important trading c ...
and Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is, after Nuremberg and Fürth, the Franconia#Towns and cities, third-largest city in Franconia located in the north of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Lower Franconia. It sp ...
, the efforts of Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
in northern Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
pushed Austrian forces back and resulted in the negotiation of the Peace of Leoben
The Peace of Leoben was a general armistice and preliminary peace agreement between the Holy Roman Empire and the First French Republic that ended the War of the First Coalition. It was signed at Eggenwaldsches Gartenhaus, near Leoben, on 18 Apri ...
(17 April 1797) and the subsequent Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
(17 October 1797).
The treaty called for meetings between the involved parties to work out the exact territorial and remunerative details. Convened at a small town in the mid-Rhineland, Rastatt
Rastatt () is a town with a Baroque core, District of Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located in the Upper Rhine Plain on the Murg river, above its junction with the Rhine and has a population of around 51,000 (2022). Rastatt was an ...
, the Congress quickly derailed in a mire of intrigue and diplomatic posturing. The French demanded more territory. The Austrians were reluctant to cede the designated territories. Compounding the Congress's problems, tensions grew between France and most of the First Coalition allies. Ferdinand of Naples refused to pay agreed-upon tribute to France, and his subjects followed this refusal with a rebellion. The French invaded Naples and established the Parthenopean Republic
The Parthenopean Republic (, ) or Neapolitan Republic () was a short-lived, semi-autonomous republic located within the Kingdom of Naples and supported by the French First Republic. The republic emerged during the French Revolutionary Wars after ...
. Encouraged by the French Republic, a republican uprising in the Swiss cantons led to the overthrow of the Swiss Confederation and the establishment of the Helvetic Republic
The Helvetic Republic (; ; ) was a sister republic of France that existed between 1798 and 1803, during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was created following the French invasion and the consequent dissolution of the Old Swiss Confederacy, ma ...
. The French Directory
The Directory (also called Directorate; ) was the system of government established by the Constitution of the Year III, French Constitution of 1795. It takes its name from the committee of 5 men vested with executive power. The Directory gov ...
was convinced that the Austrians were planning to start another war. Indeed, the weaker France seemed, the more seriously the Austrians, the Neapolitans, the Russians, and the English discussed this possibility. In mid-spring, the Austrians reached an agreement with Tsar Paul of Russia by which the legendary Alexander Suvorov
Count Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov-Rymniksky, Prince of Italy () was a Russian general and military theorist in the service of the Russian Empire.
Born in Moscow, he studied military history as a young boy and joined the Imperial Russian ...
would come out of retirement to assist Austria in Italy with another 60,000 troops.
Outbreak of war in 1799
The French Directory's military strategy in 1799 called for offensive campaigns on all fronts: central Italy, northern Italy, the Swiss cantons, the upper Rhineland, and Holland. Theoretically, the French had a combined force of 250,000 troops, but this was on paper, not in the field. As winter broke in 1799, GeneralJean-Baptiste Jourdan
Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, 1st Count Jourdan (; 29 April 1762 – 23 November 1833), was a French military commander who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was made a Marshal of the Empire by Emperor Napoleon I i ...
and the Army of the Danube
The Army of the Danube () was a field army of the French Directory in the 1799 southwestern campaign in the Upper Danube valley. It was formed on 2 March 1799 by the simple expedient of renaming the Army of Observation, which had been obs ...
, at a paper strength of 50,000 and an actual strength of 25,000, crossed the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
between Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
and Kehl
Kehl (; ) is a city with around 38,000 inhabitants in the southwestern Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg. It lies in the region of Baden on the Rhine River, at the confluence with the smaller Kinzig (Rhine), Kinzig River, directly oppo ...
on 1 March. This crossing officially violated the Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
. The Army of the Danube advanced through the Black Forest
The Black Forest ( ) is a large forested mountain range in the States of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is th ...
and, by mid-March, established an offensive position at the western and northern edge of the Swiss Plateau by the village of Ostrach
Ostrach is a municipality in the district of Sigmaringen in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Geography
Ostrach lies between the Danube and Lake Constance, about halfway between Sigmaringen and Ravensburg. It lies on the brook of the same name ...
. André Masséna
André Masséna, prince d'Essling, duc de Rivoli (; born Andrea Massena; 6 May 1758 – 4 April 1817), was a French military commander of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was one of the original eighteen Marshal of the ...
had already pushed into Switzerland with his force of 30,000, and successfully passed into the Grison Alps
The Grison Alps are the mountains of the Graubünden canton of Switzerland (Grisons being the English name for the Graubünden region). There are many significant peaks in the Grison Alps, including the Tödi (3,614 m) and the highest peak, Pi ...
, Chur
''
Chur (locally) or ; ; ; ; ; ; or ; , and . is the capital and largest List of towns in Switzerland, town of the Switzerland, Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of the Grisons and lies in the Alpine Rhine, Grisonian Rhine Valley, where ...
, and Finstermünz on the Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway. Before the advent of motorized transportation, they also provided accomm ...
river. Theoretically, his left flank was to link with Jourdan's right flank, commanded by Pierre Marie Barthélemy Ferino
Pierre Marie Barthélemy Ferino, (23 August 1747, Craveggia – 28 June 1816, Paris), was a general and politician of France. Born in the Savoy, he was the son of a low-ranking officer in the Habsburg military. In 1789, during the French Revolu ...
, at the far eastern shore of Lake Constance
Lake Constance (, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein (). These ...
.
 The Austrians had arrayed their own army in a line from the
The Austrians had arrayed their own army in a line from the Tyrol
Tyrol ( ; historically the Tyrole; ; ) is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, f ...
to the Danube. A force of 46,000 under command of Count Heinrich von Bellegarde formed the defence of the Tyrol. Another small Austrian force of 26,000 commanded by Friedrich Freiherr von Hotze
Friedrich Freiherr (Baron) von Hotze (20 April 1739 – 25 September 1799), was a Swiss-born general and Field Marshall- Lieutenant in the Habsburg, Austrian army during the French Revolutionary Wars. He campaigned in the Rhineland during the ...
guarded the Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
. The main Austrian Army—close to 80,000 troops under the command of Archduke Charles
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Lawrence of Austria, Duke of Teschen (; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian field marshal, the third son of Emperor Leopold II and his wife, Maria Luisa of Spain. He was also the youn ...
—had wintered in the Bavarian, Austrian, and Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
territories on the eastern side of the Lech river. At the battles of Ostrach
Ostrach is a municipality in the district of Sigmaringen in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Geography
Ostrach lies between the Danube and Lake Constance, about halfway between Sigmaringen and Ravensburg. It lies on the brook of the same name ...
(21 March) and Stockach
Stockach () is a town in the district of Konstanz, in southern Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
Location
It is situated in the Hegau region, about 5 km northwest of Lake Constance, 13 km north of Radolfzell and 25 km northwest of K ...
(25 March), the main Austrian force pushed the Army of the Danube back into the Black Forest. Charles made plans to cross the upper Rhine at the Swiss town of Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
. Friedrich Freiherr von Hotze brought a portion (approximately 8,000) of his force west, leaving the rest to defend the Vorarlberg. At the same time, Friedrich Joseph, Count of Nauendorf
Friedrich Joseph of Nauendorf, a general in Habsburg service during the French Revolutionary Wars, was noted for his intrepid and daring cavalry raids. Like most Austrian officers of the French Revolutionary Wars, he joined the military as a you ...
, brought the left wing of the main Austrian force across the Rhine by Eglisau. They planned to unite with the main Austrian army, controlling the northern access points of Zürich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
and forcing an engagement with Masséna.
By mid-May, French morale was low. They had suffered terrible losses at Ostrach and Stockach, although these had been made up by reinforcements. Two senior officers of the Army of the Danube, Charles Mathieu Isidore Decaen
Charles Mathieu Isidore Decaen (13 April 1769 – 9 September 1832) was a French Army officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Isle de France from 1803 to 1810. He also served as the governor of French India from 1802 ...
and Jean-Joseph Ange d'Hautpoul
Jean-Joseph Ange d'Hautpoul (; 13 May 1754 – 14 February 1807) was a French cavalry general of the Napoleonic Wars. He came from an old noble family of France whose military tradition extended for several centuries.
Efforts by the French Rev ...
, were facing courts-martial
A court-martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of members of the arme ...
on charges of misconduct, proffered by their senior officer, Jourdan. Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte
Charles XIV John (; 26 January 1763 – 8 March 1844) was King of Sweden and King of Norway, Norway from 1818 until his death in 1844 and the first monarch of the Bernadotte dynasty. In Norway, he is known as Charles III John () and before he be ...
and Laurent de Gouvion Saint-Cyr
Laurent de Gouvion Saint-Cyr, 1st Marquis of Gouvion-Saint-Cyr (; 13 April 1764 – 17 March 1830) was a French military leader of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was a made a Marshal of the Empire in 1812 by Empero ...
were sick, or claimed they were, and had left the army's encampments to recover their health. Masséna's force had been repelled by Hotze's army at Feldkirch, and forced to fall back, and LeCourbe's failure to push through against Bellegarde's Austrian force in the Tyrol, meant Masséna had to pull his southern wing back as well as his center and northern wing, to maintain communication with the retreating armies on his flanks. At this point, also, the Swiss revolted again, this time against the French, and Zürich became the last defensible position Masséna could take.
Dispositions
After pushing theArmy of the Danube
The Army of the Danube () was a field army of the French Directory in the 1799 southwestern campaign in the Upper Danube valley. It was formed on 2 March 1799 by the simple expedient of renaming the Army of Observation, which had been obs ...
out of the northern portion of the Swiss Plateau—the territory north of the Rhine and south of the Danube—following the battles at Ostrach
Ostrach is a municipality in the district of Sigmaringen in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Geography
Ostrach lies between the Danube and Lake Constance, about halfway between Sigmaringen and Ravensburg. It lies on the brook of the same name ...
and Stockach
Stockach () is a town in the district of Konstanz, in southern Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
Location
It is situated in the Hegau region, about 5 km northwest of Lake Constance, 13 km north of Radolfzell and 25 km northwest of K ...
, Archduke Charles' sizable force—about 110,000 strong—crossed the Danube west of Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
, and prepared to join with the Vorarlberg Corps of Friedrich, Baron von Hotze before Zürich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
. During the month of May André Masséna
André Masséna, prince d'Essling, duc de Rivoli (; born Andrea Massena; 6 May 1758 – 4 April 1817), was a French military commander of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was one of the original eighteen Marshal of the ...
, now commander of both the French Army of Helvetia
The Army of Helvetic Republic, Helvetia, or (), was a command of the French Revolutionary Army. It was formed on 8 March 1798 from the remnants of the first unit to be known as the Army of the Rhine (France), Army of the Rhine. It was officially m ...
and the Army of the Danube began pulling back his forces to concentrate towards Zürich. Charles crossed the Rhine at Stein
Stein may refer to:
Places Austria
* Stein, a neighbourhood of Krems an der Donau, Lower Austria
* Stein, Styria, a municipality in the district of Fürstenfeld, Styria
* Stein (Lassing), a village in the district of Liezen, Styria
* Stein a ...
with an advanced corps of 21 battalions and 13 squadrons under Nauendorf on 20 May, while two days later in the evening, Hotze crossed at Meiningen
Meiningen () is a town in the southern part of the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in the region of Franconia and has a population of around 26,000 (2024).
and Balzers
Balzers () is a municipality and village located in southern Liechtenstein. In 2024, the village had a population of 4,806. The main part of the village is situated along the east bank of the Rhine.
History and culture
Historically, the present- ...
with 18 battalions and 13 squadrons. On the 23rd the Archduke led 15 more battalions and 10 squadrons over the Rhine at Büsingen.
Learning of the double-pronged advance, Masséna seized the opportunity to drive a wedge between the two Austrian commands and on 25 May launched attacks against Hotze's Corps to the east and Nauendorf's to the north. Hotze's advance troops under Petrasch were driven from Frauenfeld
Frauenfeld (Alemannic German, Alemannic: ''Frauefäld'') is the capital of the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Canton of Thurgau, Thurgau in Switzerland.
The official language of Frauenfeld is (the Swiss variety of Standard) Swiss Standard Ge ...
by Soult
Marshal General of France, Marshal General Jean-de-Dieu Soult, 1st Duke of Dalmatia (; 29 March 1769 – 26 November 1851) was a French general and statesman. He was a Marshal of the Empire during the Napoleonic Wars, and served three times as P ...
, while against the Archduke Michel Ney
Michel Ney, 1st Prince de la Moskowa, 1st Duke of Elchingen (; 10 January 1769 – 7 December 1815), was a French military commander and Marshal of the Empire who fought in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
The son of ...
erupted from Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
, seized Andelfingen and threw back Nauendorf from Pfyn
Pfyn is a municipality in Frauenfeld District in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
Pfyn gives its name to the ancient Pfyn culture, one of several Neolithic cultures in Switzerland which centered on intensive pig farming and trading, da ...
. Although the French were forced to withdraw on the appearance of Austrian reserves, nevertheless for a loss of 771 men they'd inflicted some 2,000 casualties and 3,000 prisoners on the Austrians.
On the 27th Ney was wounded and his men driven from Winterthur, Masséna thereafter concentrated his forces at Zürich, closely pressed by the Archduke Charles and Hotze.
By the end of the month the French were positioned:
Soult's Division was on the Zürichberg
The Zürichberg is a wooded hill rising to 679 m (2,228 feet), overlooking Lake Zürich and located immediately to the east of the city of Zürich, Switzerland, between the valleys of the Limmat and the Glatt rivers. Its highest point is about 2 ...
overlooking the open country to the north from an entrenched camp constructed by Andréossi. To his left Oudinot's Division lay in support, with Gazan's brigade in the town of Zürich itself. Tharreau's Division continued the line across the Aare
The Aare () or Aar () is the main tributary of the High Rhine (its discharge even exceeds that of the latter at their confluence) and the longest river that both rises and ends entirely within Switzerland.
Its total length from its source to i ...
, with troops under Lorge' guarding the left of the Rhine to Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
. To Soult's right Chabran guarded the south of Lake Zürich
Lake Zurich (, ; ) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zurich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or can be used to describe the lake as a whole, or just that part of the lake downstream of the Hurden peninsula and ...
, with outposts stretched to link with the troops of Lecourbe' at Lucerne
Lucerne ( ) or Luzern ()Other languages: ; ; ; . is a city in central Switzerland, in the Languages of Switzerland, German-speaking portion of the country. Lucerne is the capital of the canton of Lucerne and part of the Lucerne (district), di ...
and the Andermatt valley. In all some 52,000 French and Swiss troops. The entrenchments on the Zürichberg were in a 5-mile long semi-circle from Riesbach to Hongg, but were incomplete.
Charles decided to launch his main attack by the surest (though difficult) route, directly against the Zürichberg with his left and centre, holding his right wing back to protect his line of retreat.
Jelačić's advance against Witikon
On 2 June, Archduke Charles became aware that Hotze's advance guard under Jelačić was advancing up against the main French positions nearWitikon
Witikon is a quarter in the district 7 in Zürich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Z ...
, and sent a message ordering him not to attack until all his other troops were ready; however, from 3:00 am on the 3rd, Jelačić was already engaged against Humbert's brigade by the time these instructions arrived and the action soon grew into a desperate fight. After 4 hours Soult's men were driven from Witikon and the fighting continued all through the day. As things began to look serious for Soult, Masséna, musket in hand, led a counter-attack at the head of his reserve grenadiers. The combined effort eventually pushed back the Austrians and secured the camp after a bloody fight, the French losing 500 killed and wounded, including Masséna's Chief of Staff Chérin mortally wounded.
Attack on the Zürichberg
 The next day on 4 June, Charles crossed the Glatt and launched a broad attack in five columns:
* On the Austrian left, the First column under Jelačić (five battalions and three squadrons) marched against Zürich along the high road and succeeded in breaking through the
The next day on 4 June, Charles crossed the Glatt and launched a broad attack in five columns:
* On the Austrian left, the First column under Jelačić (five battalions and three squadrons) marched against Zürich along the high road and succeeded in breaking through the Rapperswil
Rapperswil (Swiss German: or ;Andres Kristol, ''Rapperswil SG (See)'' in: ''Dictionnaire toponymique des communes suisses – Lexikon der schweizerischen Gemeindenamen – Dizionario toponomastico dei comuni svizzeri (DTS, LSG)'', Centre de dial ...
gate but was driven back by Gazan's brigade of Oudinot's Division, and despite repeated attacks made no further headway.
* To its right, the Second Column under Bey
Bey, also spelled as Baig, Bayg, Beigh, Beig, Bek, Baeg, Begh, or Beg, is a Turkic title for a chieftain, and a royal, aristocratic title traditionally applied to people with special lineages to the leaders or rulers of variously sized areas in ...
(four battalions and three squadrons) seized the village of Hirslanden
Hirslanden is a quarter in the district 7 in Zürich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake ...
and attempted to climb the slopes; however, the French under Brunet counterattacked and forced the Austrians back to join the First Column.
* The Third Column under the Prince of Lorraine found its direct route of march impractical and was diverted via Fällanden
Fällanden is a municipality in the district of Uster in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, and belongs to the Glatt Valley (German: ''Glattal'').
History
Fällanden is first mentioned around 820 as ''Fenichlanda''.
Geography
Fällanden ...
and Pfaffhausen
Pfaffhausen (also known as Pffaffhausen) is a settlement in the municipality of Fällanden in the canton of Zürich, Switzerland. It has an elevation of 597 m, and lies in the valley between the northern flank of the Öschbrig and the southeastern ...
. However, the attack failed before a murderous fire from the entrenchments.
* The Fourth Column under Hotze (seven battalions and 12 squadrons) crossed the Glatt at Dübendorf
Dübendorf is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Uster (district), Uster in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zürich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland.
It is a suburb of Zürich in Switzerland with a population o ...
behind the third column, and advancing through Stettbach, drove the French from Schwamendingen
Schwamendingen is a district in the Switzerland, Swiss city of Zürich. Formerly an independent community, it was incorporated into Zurich in 1934 to build district number 12.
The district comprises the quarters Schwamendingen Mitte, Saatlen a ...
.
* The Fifth Column under the Prince of Reuss (10 battalions and 20 squadrons) carried Seebach and Oerlikon then detached part of its command under Rosenberg on its left at Oerlikon to join in the assault on Zürich.
Oudinot, though missing half of his force in Zürich, nevertheless threw himself on Rosenberg, attempting to drive in the Austrian flank. After a desperate fight, the French were driven back, Oudinot carried from the field wounded by a ball in the chest. Charles' right flank under Nauendorf (15 battalions and 9 squadrons) remained held back to guard Glattfelden
Glattfelden is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Bülach (district), Bülach in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Zurich (canton), Zürich in Switzerland, and belongs to the Glatt Valley (German: ''Glattal'').
...
.
On the Zürichberg
The Zürichberg is a wooded hill rising to 679 m (2,228 feet), overlooking Lake Zürich and located immediately to the east of the city of Zürich, Switzerland, between the valleys of the Limmat and the Glatt rivers. Its highest point is about 2 ...
, Soult's Division was assailed by three columns and pinned down to their trenches. Repeated assaults were beaten off and the fighting bogged down into an intense firefight. At 2:00 pm, Charles assembled five battalions from his reserve including his own Guard of honour
A guard of honour (Commonwealth English), honor guard (American English) or ceremonial guard, is a group of people, typically drawn from the military, appointed to perform ceremonial duties – for example, to receive or guard a head of state ...
and directed Olivier, Count of Wallis
Oliver Remigius, Count von Wallis, Baron von Carrighmain, (1 October 174219 July 1799) the scion of the distinguished Irish Walsh family in Habsburg military service, served in Austria's wars with the Ottoman Empire (1787–1791), and in the Fre ...
to lead these storming up the hill. Leaving one battalion to watch the bridges, Wallis led the other four up a steep and narrow ravine against the French defences. The combat degenerated into close hand-to-hand fighting, with soldiers using the butts of their muskets against the French abatis
An abatis, abattis, or abbattis is a field fortification consisting of an obstacle formed (in the modern era) of the branches of trees laid in a row, with the sharpened tops directed outwards, towards the enemy. The trees are usually interlaced ...
.
At last at 8:00 pm, after a desperate fight, the Austrians were able to break through and pour into the camp behind. Sword in hand, Soult and his staff placed themselves at the head of a few companies of troops, launched a counter-attack against the rear of the Austrian column and drove them back to the bottom of the hill. Masséna urged his artillery to redouble their efforts and brought up his reserve of grenadiers. The Austrian attack crumbled; those in the camp were scattered, those behind driven back.
Over the course of the day, Charles lost 2,000 men, including three generals wounded, and 1,200 prisoners. The French lost more than 1,200 killed and wounded.
Aftermath
After the bloody fighting on the 4th Charles fell back a short distance to recover and devise a second attack for the 6th. Masséna used the time on the 5th to regroup, and that night as the Austrians assembled for their attack, he withdraw to a strong position in front of Zürich, abandoning 28 guns commandeered from Zürich. His forces were now more concentrated, while the lake would oblige his opponent to divide his forces. The second day of battle never came. At noon on the 6th, following aparley
A parley (from – "to speak") is a discussion or conference, especially one designed to end an argument or hostilities between two groups of people. As a verb, the term can be used in both past and present tense; in present tense the term ...
, the French were allowed to leave Zürich, Masséna withdrew to the Uetliberg
__NOTOC__
The Uetliberg (also known as Üetliberg) is a mountain in the Swiss plateau, part of the Albis chain, rising to . The mountain offers a panoramic view of the entire city of Zürich (to the northeast of its summit), Zürichberg and ...
and arrange his line along the banks of the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, continuing a further 35 km until it reaches the river A ...
. In Zürich, Charles found 150 cannons of various calibers. The outcome of the battle also damaged Austro-Russian relations, because Charles failed to follow up on the French defeat.
In terms of personnel, both sides lost a general: Louis Nicolas Hyacinthe Chérin
Louis may refer to:
People
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
Other uses
* Louis (coin), a French coin
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
* ...
and Olivier Wallis.Smith, 158.
See also
* French Revolutionary Wars: Campaigns of 1799Notes
References
* Clausewitz, Carl von (2020). ''Napoleon Absent, Coalition Ascendant: The 1799 Campaign in Italy and Switzerland, Volume 1.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * Clausewitz, Carl von (2021). ''The Coalition Crumbles, Napoleon Returns: The 1799 Campaign in Italy and Switzerland, Volume 2.'' Trans and ed. Nicholas Murray and Christopher Pringle. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. * *Digby Smith, ''Napoleon's Regiments: Battle Histories of the Regiments of the French Army, 1792–1815'', 2000 Greenhill Books, London, United Kingdom. . *. * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Zurich 1799-06 Conflicts in 1799 Battles involving the Helvetic Republic Military history of Zurich 1799 in the Habsburg monarchy 1799 in France Battles of the War of the Second Coalition involving Austria