enterprise content management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Enterprise content management (ECM) extends the concept of
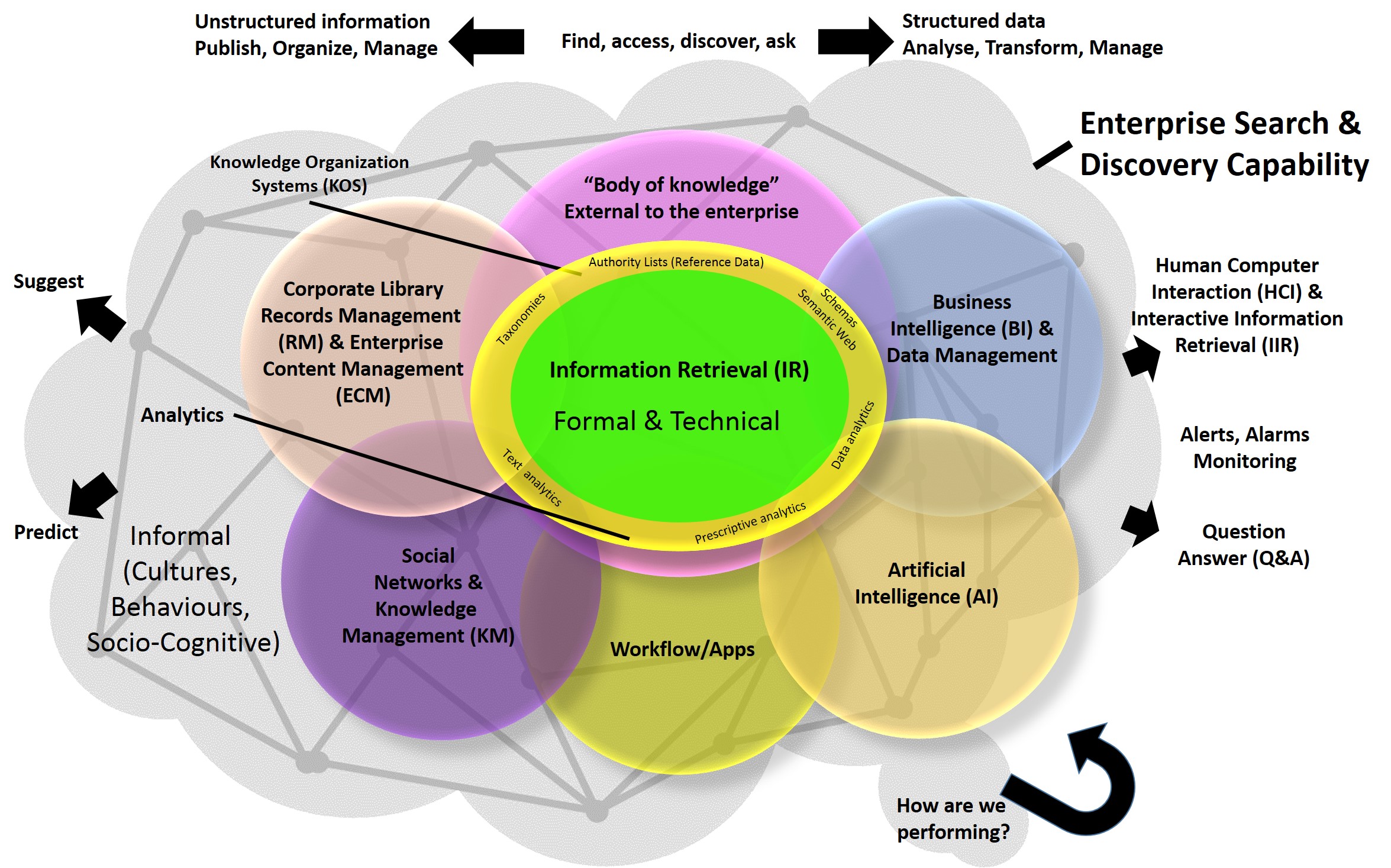
PDF
original source of this Wikipedia article by the German consulting company Project Consult Unternehmensberatung The five ECM components were defined by the Association for Information and Image Management (AIIM) as: *Capture *Manage *Store *Preserve *Deliver
Newgen
and
content management
Content management (CM) is a set of processes and technologies that supports the collection, managing, and publishing of information in any form or medium. When stored and accessed via computers, this information may be more specifically referre ...
by adding a timeline for each content
Content or contents may refer to:
Media
* Content (media), information or experience provided to audience or end-users by publishers or media producers
** Content industry, an umbrella term that encompasses companies owning and providing mas ...
item and, possibly, enforcing processes for its creation, approval and distribution. Systems using ECM generally provide a secure repository for managed items, analog or digital. They also include one (or more) methods for importing content to bring manage new items, and several presentation methods to make items available for use. Although ECM content may be protected by digital rights management (DRM), it is not required. ECM is distinguished from general content management by its cognizance of the processes and procedures of the enterprise for which it is created.
Definitions
* Late 2005: The technology was used to capture, manage, store, preserve, and deliver content and documents related to organizational processes * Early 2006: ECM tools and strategies allowed the management of an organization'sunstructured information
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically text-heavy, but may contain data such as dates, num ...
, wherever that information exists.
* Early 2008: The strategies
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the " ar ...
, methods, and tools were used to capture, manage, store, preserve, and deliver content and documents related to organizational processes. ECM tools and strategies allowed the management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a Government agency, government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includ ...
of an organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
's unstructured information, wherever that information exists
* Early 2010: The strategies, methods, and tools were used to capture, manage, store, preserve, and deliver content and documents related to organizational processes. ECM covered the management of information within the entire scope of an enterprise whether that information is in the form of a paper document, an electronic file, a database print stream, or even an email
* March 2017: The Association for Information and Image Management (AIIM) proposed replacing "enterprise content management" with "intelligent information management". IIM is defined as "the strategies, methods, and tools used to create, capture, automate, deliver, secure, and analyze content and documents related to organizational processes. IIM refers to the management of content AND data, not just content itself."
The latest definition encompasses areas which have traditionally been addressed by records- and document-management systems. It implies the conversion of data to digital and traditional forms, including paper and microfilm.
ECM, as an umbrella term
In linguistics, semantics, general semantics, and ontologies, hyponymy () is a semantic relation between a hyponym denoting a subtype and a hypernym or hyperonym (sometimes called umbrella term or blanket term) denoting a supertype. In other wor ...
, covers document and web content management
A web content management system (WCM or WCMS) is a software content management system (CMS) specifically for web content. It provides website authoring, collaboration, and administration tools that help users with little knowledge of web programm ...
, search, collaboration, records management, digital asset management
Digital asset management (DAM) and the implementation of its use as a computer application is required in the collection of digital assets to ensure that the owner, and possibly their delegates, can perform operations on the data files.
Termi ...
(DAM), workflow management, and capture and scanning. It manages the life cycle of information, from initial publication (or creation) through archival and eventual disposal. It is delivered in four ways:
* On-premises software
On-premises software (abbreviated to on-prem, and incorrectly referred to as on-premise) is installed and runs on computers on the premises of the person or organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility such as a server farm ...
(installed on an organization's network)
* Software as a service
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. SaaS is also known as "on-demand software" and Web-based/Web-hosted software.
SaaS is con ...
(SaaS): Web access to information stored on a software manufacturer's system
* A hybrid of both on-premises and SaaS components
* Infrastructure as a Service
The first major provider of infrastructure as a service (IaaS) was Amazon in 2008. IaaS is a cloud computing service model by means of which computing resources are supplied by a cloud services provider. The IaaS vendor provides the storage, net ...
(IaaS): Online services which abstract the user from infrastructure details like physical computing resources, location, data partitioning, scaling, security, and backup
Benefits to an organization include improved efficiency, better control, and reduced costs. Banks have converted to storing copies of old cheques in ECM systems from the older method of keeping physical cheques in warehouses. Under the old system, a customer request for a copy of a cheque might take weeks; a bank employee had to contact the warehouse where the right box, file and cheque were located. The cheque would be pulled and a copy made and mailed to the bank, which would then mail it to the customer. With an ECM system in place, a bank employee could query the system for the customer's account number and the number of the requested cheque. When an image of the cheque appeared on-screen, the bank could mail a copy immediately to the customer; usually while the customer was still on the phone.

Scope
Enterprise content management, a form ofcontent management
Content management (CM) is a set of processes and technologies that supports the collection, managing, and publishing of information in any form or medium. When stored and accessed via computers, this information may be more specifically referre ...
, combines the capture, search and networking of documents with digital archiving
A document management system (DMS) is usually a computerized system used to store, share, track and manage files or documents. Some systems include history tracking where a log of the various versions created and modified by different users is r ...
, document management and workflow
A workflow consists of an orchestrated and repeatable pattern of activity, enabled by the systematic organization of resources into processes that transform materials, provide services, or process information. It can be depicted as a sequence o ...
. It includes the challenges involved in using and preserving a company's internal (often unstructured) information in all of its forms. Most ECM solutions focus on business-to-employee (B2E) systems.
New ECM components have emerged. As content is checked in and out, each use generates new metadata (automatically, to some extent). Information about how (and when) people use the content can allow the system to acquire new filtering, routing and search pathways, corporate taxonomies
Corporate taxonomy is the hierarchical classification of entities of interest of an enterprise, organization or administration, used to classify documents, digital assets and other information. Taxonomies can cover virtually any type of physical or ...
and semantic network
A semantic network, or frame network is a knowledge base that represents semantic relations between concepts in a network. This is often used as a form of knowledge representation. It is a directed or undirected graph consisting of vertices, ...
s, and retention-rule decisions.
Solutions can provide intranet services to employees (B2E), and can include enterprise portal
An enterprise portal, also known as an enterprise information portal (EIP), is a framework for integrating information, people and processes across organizational boundaries in a manner similar to the more general web portals. Enterprise portals p ...
s for business-to-business (B2B), business-to-government
Business-to-government (B2G),Market Business NewsWhat is B2G or business-to-government? Definition and examples accessed 31 August 2020 also known as business-to-administration (B2A), refers to trade between the business sector as a supplier and a ...
(B2G), government-to-business
Electronic governance or e-governance is the application of information technology for delivering government services, exchange of information, communication transactions, integration of various stand-alone systems between government to cit ...
(G2B), or other business relationships. This category includes most former document-management groupware and workflow solutions that had not, by 2016, fully converted their architecture to ECM but provided a web interface. Digital asset management is a form of ECM involving digitally-stored content. Specialized Healthcare Content Management Systems meet the special regulatory requirements for medical devices
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assura ...
and interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader defi ...
.
History
The technologies which encompassed ECM in 2016 descend from the electronicDocument Management System
A document management system (DMS) is usually a computerized system used to store, share, track and manage files or documents. Some systems include history tracking where a log of the various versions created and modified by different users is r ...
s (DMS) of the late 1980s and early 1990s. The original DMS products were stand-alone, providing functionality in one of four areas: imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
, workflow, document management, and enterprise relationship management Enterprise relationship management or ERM is a business method in relationship management.
See also
* Enterprise feedback management (EFM)
* Business relationship management (BRM)
* Enterprise planning systems
References Primary sources
*
* In ...
(ERM).
A typical early DMS user had a small-scale imaging and workflow system (perhaps one department) to improve a paper-intensive process and work towards a paperless office
A paperless office (or paper-free office) is a work environment in which the use of paper is eliminated or greatly reduced. This is done by converting documents and other papers into digital form, a process known as digitization. Proponents claim t ...
. The first stand-alone DMS technologies intended to save time (or improve information access) by reducing paper handling and storage, reducing document loss and speeding access to information. DMS could provide online access to information formerly available only on paper, microfilm, or microfiche. By improving control over documents and their processes, DMS streamlined business practices. Their audit trail increased document security and measured productivity and efficiency.
DMS product categories were seen as complementary, and organizations wished to use several DMS products. A customer-service department could combine imaging, document management and workflow; an accounting department could access supplier invoices from an ERM system, purchase orders from an imaging system, and contracts from a document-management system. As organizations established an Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
presence, they wanted to manage web content. Organizations which had automated individual departments began to envision a broader deployment.
The movement toward integrated DMS systems reflected a common trend in the software industry: the integration of small systems into more comprehensive ones. Word processing, spreadsheet, and presentation software were standalone products until the early 1990s, when the market shifted toward integration.
Early developers offered multiple stand-alone DMS technologies as a single, packaged "suite", with little (or no) functional integration. Around 2001, the industry began to use the term "enterprise content management" for integrated systems.
In 2006, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washin ...
(with its SharePoint
SharePoint is a web-based collaborative platform that integrates natively with Microsoft Office. Launched in 2001, SharePoint is primarily sold as a document management and storage system, but the product is highly configurable and its usage v ...
product family) and Oracle Corporation (with Oracle Content Management) entered the low-cost ECM market. Open source ECM products are also available.
Government standards, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Kennedy– Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1 ...
(HIPAA), BS 7799
BS 7799 was a standard originally published by BSI Group (BSI) in 1995. It was written by the United Kingdom Government's Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), and consisted of several parts.
The first part, containing the best practices for In ...
and ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard to manage information security. The standard was originally published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2005, ...
, influence the development and use of ECM. In 2016, organizations could deploy a single ECM system to manage information in all departments.
Uses
Businesses adopt ECM to increase efficiency, improve information control, and reduce the overall cost of information management. ECM streamlines access to records with keyword and full-text searching, allowing employees to quickly obtain needed information from their desktops. The management systems can help businesses comply with government and industry regulations such as HIPAA, theSarbanes–Oxley Act
The Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 is a United States federal law that mandates certain practices in financial record keeping and reporting for corporations.
The act, (), also known as the "Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protect ...
, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. Security at the user, function, and record levels protect sensitive data. Some information in a document can be redacted, so the remainder can be shared without compromising identity or key data. Every action in the system is tracked, and can be reported to demonstrate compliance with a wide variety of regulations.
Characteristics
In his ''Computerwoche
''Computerworld'' (abbreviated as CW) is an ongoing decades old professional publication which in 2014 "went digital." Its audience is information technology (IT) and business technology professionals, and is available via a publication website ...
'' article, Ulrich Kampffmeyer characterized ECM as:
*Middleware
Middleware is a type of computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".
Middleware makes it easier for software developers to implement c ...
, eliminating the restrictions of vertical applications and island architecture and transparent to users. ECM offers a third platform, in addition to conventional host and client-server systems. According to Kampffmeyer, enterprise application integration
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications.
Overview
Enterprise application integration is an integration framework comp ...
(EAI) and service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provide ...
(SOA) will play important roles in ECM implementation.
*Independent services, managing information without regard to the source or the required use and available from a variety of applications. For a given use, only one general service is available; this avoids the expense and maintenance of parallel functions. Standards for interfaces connecting different services will play an important role in ECM implementation.
*A uniform repository for information, data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete Value_(semiotics), values that convey information, describing quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of sy ...
and document warehouses combining company information. Information lifecycle management will also play an important role in the implementation of ECM.
ECM is working properly when it is invisible to users. It supports specialized applications as subordinate services. ECM is a multi-layer model which includes technology for handling, delivering, and managing structured data and unstructured information. It manages the information in a web content management system
A web content management system (WCM or WCMS) is a software content management system (CMS) specifically for web content. It provides website authoring, collaboration, and administration tools that help users with little knowledge of web programm ...
and archives as a universal repository.
Components
ECM combines components which can be used as stand-alone systems without being incorporated into an enterprise-wide system.''Trends in Records, Document and Enterprise Content Management''. Whitepaper. S.E.R. conference, Visegrád, September 28th, 200original source of this Wikipedia article by the German consulting company Project Consult Unternehmensberatung The five ECM components were defined by the Association for Information and Image Management (AIIM) as: *Capture *Manage *Store *Preserve *Deliver
Capture
Capture involves converting information from paper documents into an electronic format by scanning, and collects electronic files and information into a consistent structure for management. Capture technologies also encompass the creation of metadata, describing characteristics of a document for easy location through search technology. A medical chart might include the patient ID, name, date of visit and procedure for medical personnel to locate the chart. Earlierdocument automation
Document automation (also known as document assembly or document management) is the design of systems and workflows that assist in the creation of electronic documents. These include logic-based systems that use segments of pre-existing text and/or ...
systems photographed documents for storage on microfilm or microfiche. Image scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' ...
s make digital copies of paper documents. Documents already in digital form can be copied (or linked to) if they are available online. Automatic or semi-automatic capture can use electronic data interchange (EDI) or XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable ...
documents, business and ERP applications, or specialized-application systems as sources.
Recognition technologies
Recognition technologies to extract information from scanned documents and digitalfax
Fax (short for facsimile), sometimes called telecopying or telefax (the latter short for telefacsimile), is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material (both text and images), normally to a telephone number connected to a printer o ...
es include:
*Optical character recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a sc ...
(OCR): Converts images of typeset text into alphanumeric characters
*Handwriting recognition
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwritten input from sources such as paper documents, photographs, touch-screens and other de ...
(HWR): Converts images of handwritten text into alphanumerics
*Intelligent character recognition
In computer science, intelligent character recognition (ICR) is an advanced optical character recognition (OCR) or — rather more specific — handwriting recognition system that allows fonts and different styles of handwriting to be learned by a ...
(ICR): Extends OCR and HWR to use comparison, logical connections, and checks against reference lists and existing data to improve recognition
*Optical mark recognition
Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents.
OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the ...
(OMR): Reads special markings (such as check marks or dots) in predefined fields
*Barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or o ...
recognition: Decodes industry-standard encodings of product and other commercial data
Image cleanup
Image-cleanup features include rotation, straightening, color adjustment, transposition, zoom, aligning, page separation, annotations and noise reduction.Forms processing
Forms processing has two groups of technology, although the information content and character of the documents may be identical. It is the capture of printed forms via scanning; recognition technologies are often used, since well-designed forms enable automatic processing. Automatic processing can capture electronic forms (such as those submitted via webpages) if the layout, structure, logic, and contents are known to the capturing system.Enterprise report management
Enterprise report management (ERM) records reports and other documents on optical disks or other digital storage for ECM systems. The technology was originally used with laserDiscs.Data aggregation
Data aggregation Data aggregation is the compiling of information from databases with intent to prepare combined datasets for data processing.
Description
The United States Geological Survey explains that, “when data are well documented, you know how and where t ...
unifies documents from different applications and sources, forwarding them to storage and processing systems in a uniform structure and format.
Subject indexing
Subject indexing
Subject indexing is the act of describing or classifying a document by index terms, keywords, or other symbols in order to indicate what different documents are ''about'', to summarize their contents or to increase findability. In other words, i ...
improves searches, providing alternative ways of organizing information. Manual indexing assigns index database attributes to content by hand, and is typically used by a "manage" database for administration and access.
Automatic and manual attribute indexing can be facilitated with preset input-design profiles, which can describe document classes that limit the number of possible index values or automatically assign certain criteria. Automatic classification programs can extract index, category, and transfer data autonomously. Based on the information contained in electronic information objects, it can evaluate information based on predefined criteria or in a self-learning process.
Manage
The manage category has five application areas: * Document management (DMS) *Collaborative software
Collaborative software or groupware is application software designed to help people working on a common task to attain their goals. One of the earliest definitions of groupware is "intentional group processes plus software to support them".
As re ...
* Web content management, including web portals
* Records management
* Workflow and business process management
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business p ...
(BPM)
It connects the other components, which can be used in combination or separately. Document management, web content management, collaboration, workflow and business process management address the dynamic part of the information's life cycle. Records management manages finalized documents in accordance with the organization's retention period, which must comply with government mandates and industry practices. Manage components incorporate database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases s ...
s and access-authorization systems.
Document management
Document management system
A document management system (DMS) is usually a computerized system used to store, share, track and manage files or documents. Some systems include history tracking where a log of the various versions created and modified by different users is r ...
s control documents from creation to archiving. They include:
*Check in-check out: Checks stored information for consistency
*Version management: Keeps track of different versions of the same information, with revisions and different formats
*Search and navigation: Finds information and its associated contexts
*Organizing documents in files, folders, and overviews
Document management overlaps with other manage components, office applications (like Microsoft Outlook and Exchange, or Lotus Notes
HCL Notes (formerly IBM Notes and Lotus Notes; see Branding below) and HCL Domino (formerly IBM Domino and Lotus Domino) are the client and server
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provide ...
and Domino), and library services which administer information storage.
Collaboration
Collaboration components in an ECM system help users work together to develop and process content. Many of these components were developed from collaborative-software packages; ECM collaborative systems include elements ofknowledge management
Knowledge management (KM) is the collection of methods relating to creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization. It refers to a multidisciplinary approach to achieve organisational objectives by making ...
.
They use information databases and processing methods which are designed to be used simultaneously by a number of users on the same content item. Collaboration uses skill-based knowledge, resources and background data for joint information processing. Administration components (such as virtual whiteboards for brainstorming, appointment scheduling, and project management systems) and communications applications such as video conferencing may be included. Collaborative ECM may also integrate information from other applications.
Web content management
ECM integratesContent management systems
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content (content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
(CMS), presenting existing information managed in the ECM repository.
File and archive management
Unlike traditional electronic archival systems, file and archive management is the administration of records, important information, and data which companies are required to archive. Independent of storage media, managed information does not need to be stored electronically. File and archive management includes: * Visualization of file plans and other structured indexes for the orderly storage of information * Unambiguous indexing of information, supported by thesauruses or controlled word lists * Management of record-retention and deletion schedules * Protection of information in accordance with its characteristics * International, industry-specific (or company-wide), standardized metadata for the unambiguous identification and description of stored informationWorkflow and business process management
The terms "workflow" and "business process management
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business p ...
" (BPM) are often used interchangeably. Production workflow uses predefined sequences to control processes; in an ''ad-hoc'' workflow, the user determines the process sequence. Users interact in workflow solutions, and workflow engines are a background service controlling information and data flow. Workflow management includes:
* Visualization of process and organization structures
* Capture, administration, visualization, and delivery of information with its associated documents or data
* Incorporation of data-processing tools (such as applications) and documents, such as office products
* Parallel and sequential processing of procedures, including simultaneous saving
* Reminders, deadlines, delegation and other administrative functions
* Monitoring and documentation of process status, routing, and outcomes
* Tools to design and display process
According to the AIIM, BPM is a way of looking at (and controlling) organizational processes.
Store
Store components temporarily store information which is not required, desired, or ready for long-term storage or preservation. Even if the store component uses media suitable for long-term archiving, it is still separate from "preserve." Store components may be divided into three categories: *Repositories: storage locations *Library services: administration components for repositories *Storage technologiesRepositories
ECM repositories may be combined. Types include: * File systems: Used primarily for temporary storage, as input and output caches * Content management systems: Storage and repository systems for content; may be a database or a specialized storage system *Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases s ...
s administer information, and can also store documents, content, or media.
*Data warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integra ...
s: Complex storage systems based on databases, which provide information from a variety of sources. They may be designed with global functions, such as documents or information.
Library services
Library services are ECM administrative components which handle access to information, taking in and storing information from the capture and manage components. They also manage the storage locations in dynamic storage, the store, and the long-term preserve archive. The storage location is determined by information characteristics and classification. The library service works with the manage components' database to provide search and retrieval. It manages online storage (direct access to data and documents),nearline storage
Nearline storage (a portmanteau of " near" and "online storage") is a term used in computer science to describe an intermediate type of data storage that represents a compromise between online storage (supporting frequent, very rapid access to dat ...
(data and documents on a medium which can be accessed quickly, such as data on an optical disc in a storage system's racks but not inserted in a drive that can read it), and offline storage (data and documents on a medium which is not quickly available).
If the document management system does not provide it, the library service must have version management to control the status of information and check-in/check-out for controlled information provision. It generates an audit trail, logs of information usage and editing.
Storage technologies
A variety of technologies can be used to store information, depending on the application and system environment: *Magnetic online media:Hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magne ...
s (typically configured as RAID
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to:
Attack
* Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground
* Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeover in business
* Panty raid, a prankish raid by male college ...
systems) may be locally attached, part of a storage area network
A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from ser ...
, or mounted from another server (network-attached storage
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level (as opposed to block-level storage) computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the tech ...
).
*Magnetic tape: Magnetic tape data storage
Magnetic-tape data storage is a system for storing digital information on magnetic tape using digital recording.
Tape was an important medium for primary data storage in early computers, typically using large open reels of 7-track, later 9- ...
, in the form of tape libraries
In computer storage, a tape library, sometimes called a tape silo, tape robot or tape jukebox, is a storage device that contains one or more tape drives, a number of slots to hold tape cartridges, a barcode reader to identify tape cartridges ...
, use robotics to provide nearline storage
Nearline storage (a portmanteau of " near" and "online storage") is a term used in computer science to describe an intermediate type of data storage that represents a compromise between online storage (supporting frequent, very rapid access to dat ...
. Standalone tape drives may be used for backup.
*Digital optical media: In addition to compact disc
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. In August 1982, the first compact disc was manufactured. It was then released in Oc ...
and DVD
The DVD (common abbreviation for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc) is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 1995 and first released on November 1, 1996, in Japan. The medium can store any kind ...
optical media, storage systems may use magneto-optical drive
A magneto-optical drive is a kind of optical disc drive capable of writing and rewriting data upon a magneto-optical disc. Both 130 mm (5.25 in) and 90 mm (3.5 in) form factors exist. In 1983, just a year after the introduct ...
s; optical jukebox
An optical jukebox is a robotic data storage device that can automatically load and unload optical discs, such as Compact Disc, DVD, Ultra Density Optical or Blu-ray and can provide terabytes (TB) or petabytes (PB) of tertiary storage. The de ...
es can be used for nearline storage. Optical media in jukeboxes may be moved offline.
*Cloud computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage ( cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over mu ...
: Data may be accessed via the Internet.
Preserve
Preserve is the long-term, safe storage and backup of unchanging information. Typically accomplished by ECM records management, it may be designed to help companies comply with government and industry regulations. Content eventually stops changing and becomes static. ECM'sdigital preservation
In library and archival science, digital preservation is a formal endeavor to ensure that digital information of continuing value remains accessible and usable. It involves planning, resource allocation, and application of preservation methods and ...
components also temporarily store information which does not need to be archived. Preserve components have special viewers, conversion and migration tools, and long-term storage media:
*Write once read many
Write once read many (WORM) describes a data storage device in which information, once written, cannot be modified. This write protection affords the assurance that the data cannot be tampered with once it is written to the device, excluding the p ...
(WORM) or optical disc
In computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material, often aluminum, on one of its flat surfaces. ...
s, CD-R
CD-R (Compact disc-recordable) is a digital optical disc storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be written once and read arbitrarily many times.
CD-R discs (CD-Rs) are readable by most CD readers manufactured prior to the i ...
s and DVD-Rs
* Magnetic tapes in secure drives
*Content-addressable storage
Content-addressable storage (CAS), also referred to as content-addressed storage or fixed-content storage, is a way to store information so it can be retrieved based on its content, not its name or location. It has been used for high-speed storage ...
, with software protection against overwriting, erasure, and editing
*Storage networks may be used if they provide edit-proof auditing, with unchangeable storage and protection against manipulation and erasure.
*Microform
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the original document size. ...
s, such as microfilm, microfiche, and aperture card
An aperture card is a type of punched card with a cut-out window into which a chip of microfilm is mounted. Such a card is used for archiving or for making multiple inexpensive copies of a document for ease of distribution. The card is typically ...
s, are typically used to secure electronic information.
*Paper also secures electronic information.
Long-term preservation strategies
To ensure the long term availability of information, severalstrategies
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the " ar ...
are used for electronic archiving. Applications, index data, metadata and objects may be continuously migrated from older systems to newer ones. Emulation of older software allows users to access original data and objects; software can identify the format of preserved objects and display them in a new environment.
Deliver
Enterprise output management
Enterprise output management (EOM) is an information technology practice that deals with the organization, formatting, management and distribution of data that is created by enterprise applications like banking information systems, insurance inf ...
presents information from the manage, store, and preserve components. Its Association for Information and Image Management model for ECM is function-based; the deliver components may enter information into other systems (such as transferring information to portable media or generating output files) or prepare information for storage and preservation.
Deliver components may be divided into three groups: transformation technologies, security technologies, and distribution. Transformation and security are middleware
Middleware is a type of computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".
Middleware makes it easier for software developers to implement c ...
services and should be equally available to all ECM components. For output, primary functions are layout and design (with tools for laying out and formatting output) and electronic publishing (presenting information for distribution).
Transformation technologies
Transformations should be controlled and trackable by background services. They include: * Computer output to laser disc (COLD): When used for delivery COLD prepares output data for distribution and archiving. Applications include lists and formatted output (such as personalized customer letters), journals and logs. *Personalization
Personalization (broadly known as customization) consists of tailoring a service or a product to accommodate specific individuals, sometimes tied to groups or segments of individuals. A wide variety of organizations use personalization to improv ...
: Functions and output customized for a user's needs
* XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable ...
(Extensible Markup Language): Enables the standardized, cross-platform description of interfaces, structures, metadata, and documents
* PDF (Portable Document Format): A cross-platform printing and distribution format which permits content searches, the addition of metadata, and the embedding of electronic signatures. When generated from electronic data, PDFs are resolution-independent and allow crisp reproduction at any scale.
* Open XML Paper Specification
Open XML Paper Specification (also referred to as OpenXPS) is an open specification for a page description language and a fixed-document format. Microsoft developed it as the XML Paper Specification (XPS). In June 2009, Ecma International adopt ...
(OpenXPS): An XML specification, developed by Microsoft, describing the formats and rules for distributing, archiving, rendering, and processing XPS documents.
* Converters and viewers: Generates uniform formats to display (and output) information in different formats.
* Data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressio ...
: Reduces the storage space needed for pictorial information.
* Web syndication
Web syndication is a form of syndication in which content is made available from one website to other sites. Most commonly, websites are made available to provide either summaries or full renditions of a website's recently added content. The term ...
: Presents content in different formats, selections, and forms for multiple use in different forms for different purposes.
Security technologies
Security technologies are available for all ECM components.Electronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as i ...
s are used when documents are sent and in scanning, to document full capture. Public key infrastructure is a basic electronic-signature technology, managing keys and certificates and checking signature authenticity. Other electronic signatures confirm the identity of the sender and the integrity of the sent data.
Digital rights management and watermark
A watermark is an identifying image or pattern in paper that appears as various shades of lightness/darkness when viewed by transmitted light (or when viewed by reflected light, atop a dark background), caused by thickness or density variations ...
ing are used in content syndication and media asset management to manage and secure intellectual property rights and copyrights. Electronic watermarks, embedded in a file, protect use rights for Internet content.
Distribution
ECM is provided to users with a variety of output and distribution media: * Internet **Extranet
An extranet is a controlled private network that allows access to partners, vendors and suppliers or an authorized set of customers – normally to a subset of the information accessible from an organization's intranet. An extranet is similar to ...
s
** Intranets
** Electronic business
Electronic business (or "Online Business" or "e-business") is any kind of business or commercial transaction that includes sharing information across the internet. Commerce constitutes the exchange of products and services between businesses, grou ...
portals
** Employee portals
* Email
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" mean ...
* Fax
* Data transfer in EDI, XML or other formats
* Mobile devices, such as mobile phones and personal digital assistant
A personal digital assistant (PDA), also known as a handheld PC, is a variety mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. PDAs have been mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of highly capable smartphones, in part ...
s
* Data media, such as CDs and DVDs
* Digital television
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative adva ...
and other multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, or video into a single interactive presentation, in contrast to tradit ...
services
* Paper
Methods
On-premises
ECM was developed as a software application which companies implemented on corporate networks; each company manages and maintains the ECM and the network devices storing the data. On-premises ECM systems may be customized for organizational needs. Since paper-document capture requires devices such asimage scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' ...
s or multi-function devices, it is typically performed on-premises; however, it may be outsourced to service bureau
A service bureau is a company that provides business services for a fee. The term has been extensively used to describe technology-based services to financial services companies, particularly banks. Service bureaus are a significant sector within t ...
s for high-volume scanning, indexing and return via web transfer or on CDs, DVDs or other external storage devices.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Software as a service
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. SaaS is also known as "on-demand software" and Web-based/Web-hosted software.
SaaS is con ...
ECM, also known as cloud computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage ( cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over mu ...
, is user-accessible online on demand.
Market development
Before 2003, the ECM market was dominated by medium-sized independent vendors which fell into two categories: those who originated as document-management companies ( Laserfiche, Saros,Documentum
Documentum is an enterprise content management platform, now owned by OpenText, as well as the name of the software company that originally developed the technology. EMC acquired Documentum for $1.7 billion in December, 2003. The Documentum pla ...
, docStarNewgen
and
OpenText
OpenText Corporation (also written ''opentext'') is a Canadian company that develops and sells enterprise information management (EIM) software.
OpenText, headquartered in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, is Canada's fourth-largest software company ...
) and began adding the management of other business content, and those who started as web content management providers ( Interwoven, Vignette
Vignette may refer to:
* Vignette (entertainment), a sketch in a sketch comedy
* Vignette (graphic design), decorative designs in books (originally in the form of leaves and vines) to separate sections or chapters
* Vignette (literature), short, i ...
, and Stellent) tried to branch out into managing business documents and rich media.
In 2002, Documentum added collaboration capabilities with its acquisition of eRoom
eRoom is an on-line project collaboration, or collaborative software product from Opentext Corporation. Originally developed by eRoom Technology Inc., of Cambridge, Massachusetts, product features include e-mail management, calendaring, instan ...
; Interwoven and Vignette countered with their acquisitions of iManage and Intraspect. Documentum purchased Bulldog for its digital asset management (DAM) capabilities; Interwoven and OpenText countered with acquisitions of MediaBin and Artesia. OpenText also acquired the European software companies IXOS and Red Dot. In October 2003, EMC Corporation acquired Documentum. IBM purchased FileNet and Oracle purchased Stellent in 2006; OpenText also purchased Hummingbird Ltd.
Hummingbird Ltd. (previously NASDAQ: HUMC, TSX: HUM) is a subsidiary of OpenText and is a provider of enterprise software solutions including Exceed. Initially founded as a consulting business in 1984, Hummingbird moved into the connectivity ma ...
that year. Hewlett-Packard (HP) acquired the Australian company Tower Software in 2008. In March 2009, Autonomy purchased Interwoven; OpenText acquired Vignette in July of that year and MetaStorm in February 2011. OpenText acquired Global 360 in July 2011, and HP agreed to purchase Autonomy in August 2011.
In April 2007, CMS Watch principal Alan Pelz-Sharpe said: "Some of the biggest names in this business are undergoing substantial transformation that will lead to shifting road maps and product sets over the next few years".
Nuxeo
Nuxeo is a software company making an open source content management system.
Corporate history
Nuxeo was founded in the year 2000 by Stefane Fermigier. Eric Barroca became the CEO and Director of the management Board in December 2008. Sometime ...
and Alfresco
Alfresco may refer to:
* ''Al fresco'', or fresco, a technique of mural painting
* Al fresco dining
* Alfresco Software, an open-source content-management system
* ''Alfresco'' (TV series), a 1980s British television comedy series
* ''Al fresc ...
offered open-source ECM software that year.
Gartner
Gartner, Inc is a technological research and consulting firm based in Stamford, Connecticut that conducts research on technology and shares this research both through private consulting as well as executive programs and conferences. Its client ...
estimated in 2010 that the ECM market was worth approximately $3.5 billion in 2009; this was expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate
Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is a business and investing specific term for the geometric progression ratio that provides a constant rate of return over the time period. CAGR is not an accounting term, but it is often used to describe some ele ...
of 10.1 percent through 2014. The market experienced a number of mergers and acquisitions in 2010. In 2014, Real Story Group (formerly CMS Watch) added cloud-based vendors to its 2014 ECM evaluations.
See also
*Content Management Interoperability Services
Content Management Interoperability Services (CMIS) is an open standard that allows different content management systems to inter-operate over the Internet. Specifically, CMIS defines an abstraction layer for controlling diverse document mana ...
* Enterprise content integration
* Enterprise output management
Enterprise output management (EOM) is an information technology practice that deals with the organization, formatting, management and distribution of data that is created by enterprise applications like banking information systems, insurance inf ...
* Information governance
* Information science
Information science (also known as information studies) is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of informatio ...
* List of content management systems
Content management systems (CMS) are used to organize and facilitate collaborative content creation. Many of them are built on top of separate content management frameworks. The list is limited to notable services.
Open source software
:''T ...
* Repository Open Service Interface Definition
* Content management system
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Enterprise Content Management Content management systems Enterprise application integration Enterprise architecture Records management technology