Exeter Chiefs Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Exeter () is a city in

''Lives of the English Saints: St. German, Bishop of Auxerre'', Ch. X: "Britain in 429, A. D.", p. 92.
James Toovey (London), 1844. although David Nash Ford read it as a reference to Penselwood and thought it more likely to be Lindinis (modern
The 28 Cities of Britain
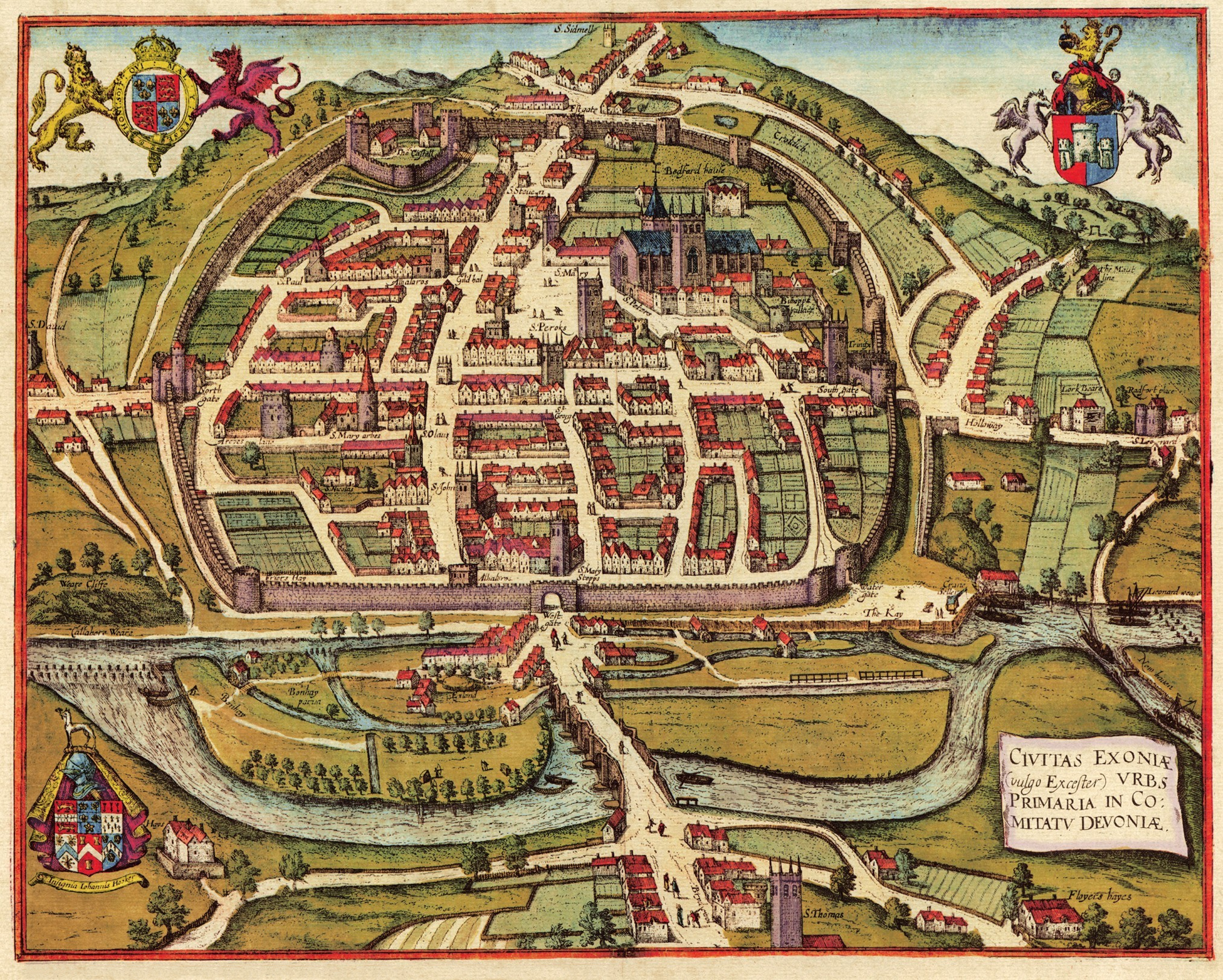
" at Britannia. 2000. Nothing is certainly known of Exeter from the time of the Two years after the Norman conquest of England, Exeter rebelled against King William. Gytha Thorkelsdóttir, the mother of the slain King Harold, was living in the city at the time, and William promptly marched west and initiated a siege. After 18 days, William accepted the city's honourable surrender, swearing an oath not to harm the city or increase its ancient tribute. However, William quickly arranged for the building of Rougemont Castle to strengthen Norman control over the area. Properties owned by Saxon landlords were transferred into Norman hands and, on the death of Bishop Leofric in 1072, the Norman
Two years after the Norman conquest of England, Exeter rebelled against King William. Gytha Thorkelsdóttir, the mother of the slain King Harold, was living in the city at the time, and William promptly marched west and initiated a siege. After 18 days, William accepted the city's honourable surrender, swearing an oath not to harm the city or increase its ancient tribute. However, William quickly arranged for the building of Rougemont Castle to strengthen Norman control over the area. Properties owned by Saxon landlords were transferred into Norman hands and, on the death of Bishop Leofric in 1072, the Norman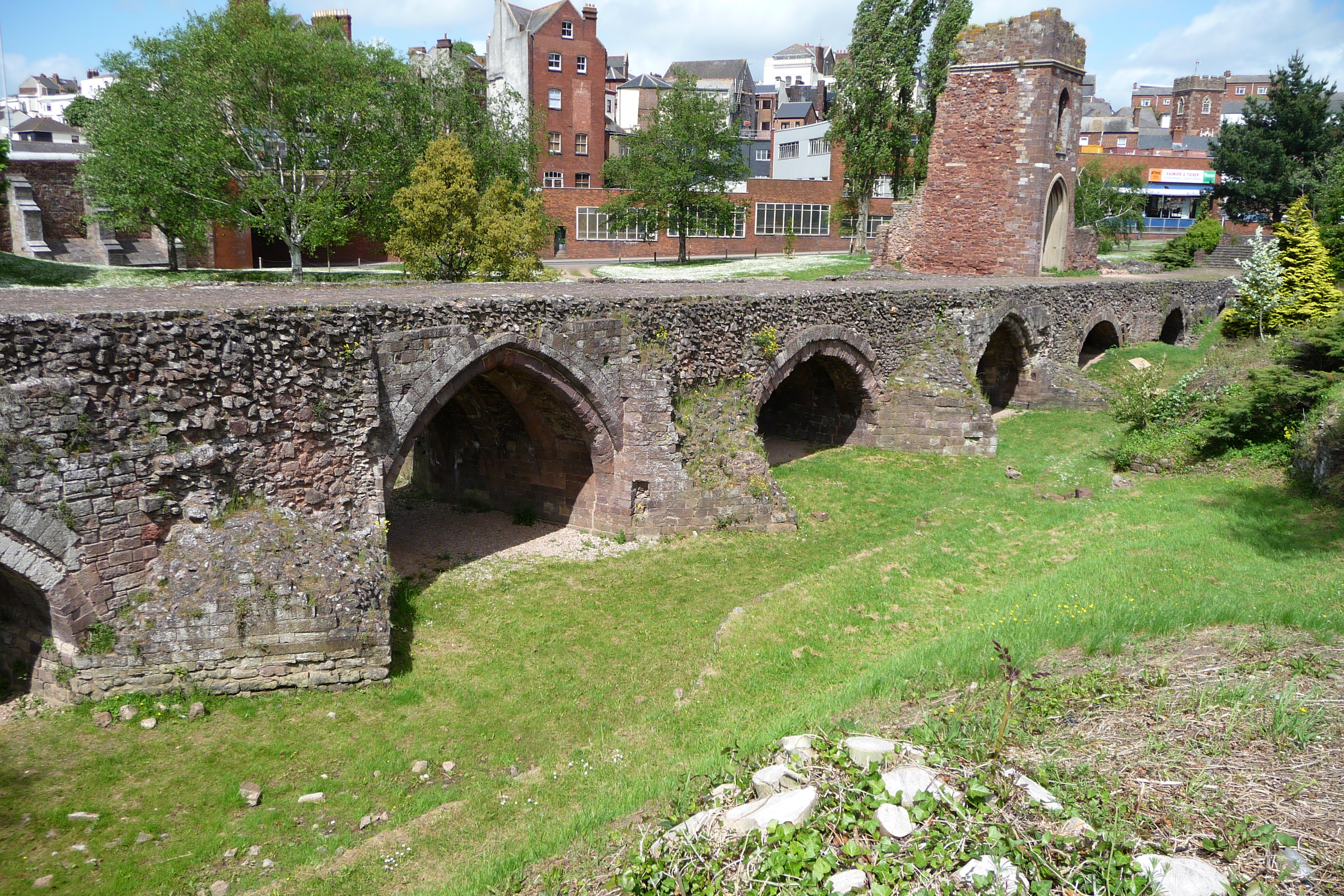  The city held a weekly market for the benefit of its citizens from at least 1213, and by 1281 Exeter was the only town in the south-west to have three market days per week. There are also records of seven annual fairs, the earliest of which dates from 1130, and all of which continued until at least the early 16th century.
Prior to the expulsion of the Jews of England in 1290, Exeter was home to England's most westerly Jewish community.
During the high medieval period, both the cathedral clergy and the citizens enjoyed access to sophisticated aqueduct systems which brought pure drinking water into the city from springs in the neighbouring parish of St Sidwell's. For part of their length, these aqueducts were conveyed through a remarkable network of tunnels, or underground passages, which survive largely intact and which may still be visited today.
Exeter and
The city held a weekly market for the benefit of its citizens from at least 1213, and by 1281 Exeter was the only town in the south-west to have three market days per week. There are also records of seven annual fairs, the earliest of which dates from 1130, and all of which continued until at least the early 16th century.
Prior to the expulsion of the Jews of England in 1290, Exeter was home to England's most westerly Jewish community.
During the high medieval period, both the cathedral clergy and the citizens enjoyed access to sophisticated aqueduct systems which brought pure drinking water into the city from springs in the neighbouring parish of St Sidwell's. For part of their length, these aqueducts were conveyed through a remarkable network of tunnels, or underground passages, which survive largely intact and which may still be visited today.
Exeter and
 ; Tudor and Stuart eras
In 1537, the city was made a
; Tudor and Stuart eras
In 1537, the city was made a 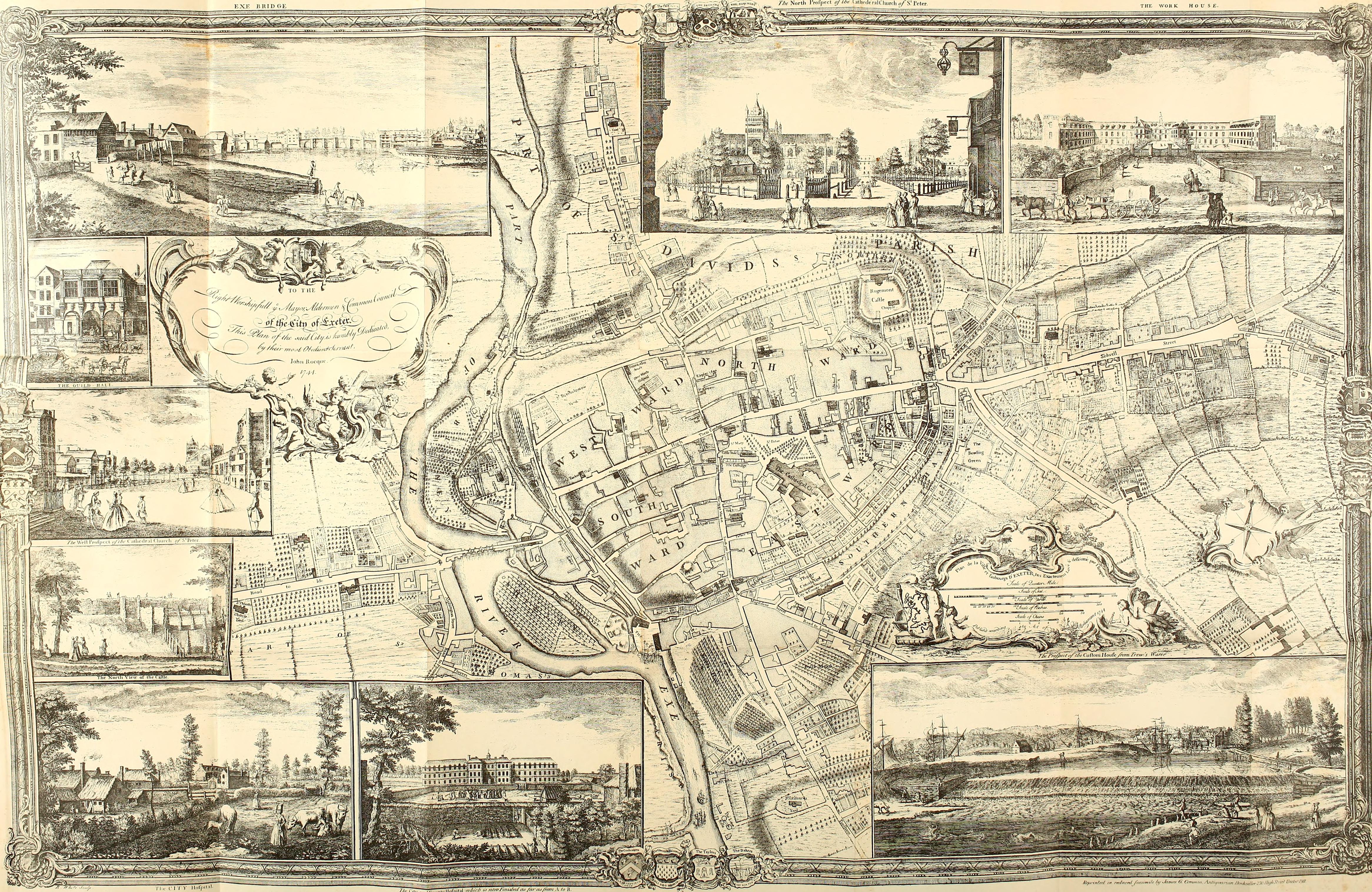 Early in the
Early in the  In 1832, cholera, which had been erupting all across Europe, reached Exeter. The only known documentation of this event was written by Dr Thomas Shapter, one of the medical doctors present during the epidemic.
The first railway to arrive in Exeter was the
In 1832, cholera, which had been erupting all across Europe, reached Exeter. The only known documentation of this event was written by Dr Thomas Shapter, one of the medical doctors present during the epidemic.
The first railway to arrive in Exeter was the  The first electricity in Exeter was provided by the Exeter Electric Light Company, which was formed at the end of the 1880s, but it was municipalised in 1896 and became the City of Exeter Electricity Company.
In 1896 £88,000 was spent constructing sewerage system which reduced the risk of infectious diseases,
The first horse-drawn trams in Exeter were introduced in 1882 with 3 lines radiating from the city's East Gate. One line went to St David's station via New North Road, the Obelisk (where the Clock Tower now stands) and St David's Hill. The second line went out along Heavitree Road to Livery Dole and the third went to Mount Pleasant along Sidwell Street. There was a depot off New North Road.
The first electricity in Exeter was provided by the Exeter Electric Light Company, which was formed at the end of the 1880s, but it was municipalised in 1896 and became the City of Exeter Electricity Company.
In 1896 £88,000 was spent constructing sewerage system which reduced the risk of infectious diseases,
The first horse-drawn trams in Exeter were introduced in 1882 with 3 lines radiating from the city's East Gate. One line went to St David's station via New North Road, the Obelisk (where the Clock Tower now stands) and St David's Hill. The second line went out along Heavitree Road to Livery Dole and the third went to Mount Pleasant along Sidwell Street. There was a depot off New North Road.
 A new bridge across the Exe was opened on 29 March 1905, replacing the former Georgian bridge. Made of
A new bridge across the Exe was opened on 29 March 1905, replacing the former Georgian bridge. Made of  On 27 October 1960, following very heavy rain, the Exe overflowed and flooded large areas of Exeter including Exwick, St Thomas and Alphington. The water rose as high as 2 metres above ground level in places and 150 employees of the local firm Beach Bros were trapped for nine hours. 2,500 properties were flooded. Later the same year on 3 December the river levels rose again, flooding 1,200 properties. These floods led to the construction of new flood defences for Exeter. Work began in 1965, took 12 years to complete and cost £8 million. The defences included three flood relief channels, and were complemented by the construction of two new concrete bridges (built in 1969 and 1972) to replace the old Exe Bridge which had obstructed the flow of the river and made the flooding worse.
A high-profile, random murder of a child occurred in the city in 1997, which today remains one of the UK's highest-profile unsolved murders. 14-year-old Kate Bushell, a pupil at what is now West Exe School, had her throat cut by an unidentified attacker while walking her dog along Exwick Lane, Exwick, on 15 November 1997. Despite the police insisting the killer must be local and repeatedly appealing for locals to come forward with information on ''
On 27 October 1960, following very heavy rain, the Exe overflowed and flooded large areas of Exeter including Exwick, St Thomas and Alphington. The water rose as high as 2 metres above ground level in places and 150 employees of the local firm Beach Bros were trapped for nine hours. 2,500 properties were flooded. Later the same year on 3 December the river levels rose again, flooding 1,200 properties. These floods led to the construction of new flood defences for Exeter. Work began in 1965, took 12 years to complete and cost £8 million. The defences included three flood relief channels, and were complemented by the construction of two new concrete bridges (built in 1969 and 1972) to replace the old Exe Bridge which had obstructed the flow of the river and made the flooding worse.
A high-profile, random murder of a child occurred in the city in 1997, which today remains one of the UK's highest-profile unsolved murders. 14-year-old Kate Bushell, a pupil at what is now West Exe School, had her throat cut by an unidentified attacker while walking her dog along Exwick Lane, Exwick, on 15 November 1997. Despite the police insisting the killer must be local and repeatedly appealing for locals to come forward with information on ''


 The city of Exeter was established on the eastern bank of the
The city of Exeter was established on the eastern bank of the
 From the 2011 Census, the
From the 2011 Census, the
 The
The
 * The
* The
 * The
* The
 The
The
 Exeter is the main rail hub in the South West and is linked to most branch lines in Devon, including to
Exeter is the main rail hub in the South West and is linked to most branch lines in Devon, including to
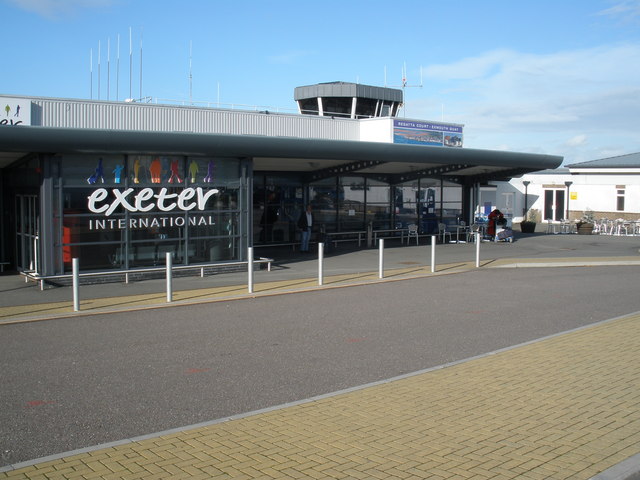 Exeter Airport lies east of the city, and the local airline, previously called Jersey European and British European but later as
Exeter Airport lies east of the city, and the local airline, previously called Jersey European and British European but later as
 The Exeter Canal, also known as the Exeter Ship Canal, was first constructed by John Trew in about 1566, representing one of the oldest artificial waterways in Britain. It was cut to bypass the St James' Weir that had been built across the
The Exeter Canal, also known as the Exeter Ship Canal, was first constructed by John Trew in about 1566, representing one of the oldest artificial waterways in Britain. It was cut to bypass the St James' Weir that had been built across the
 The
The
 Numerous churches, and other religious buildings, are present in Exeter. A majority belong to differing Christian denominations, including a
Numerous churches, and other religious buildings, are present in Exeter. A majority belong to differing Christian denominations, including a


 The ''
The ''
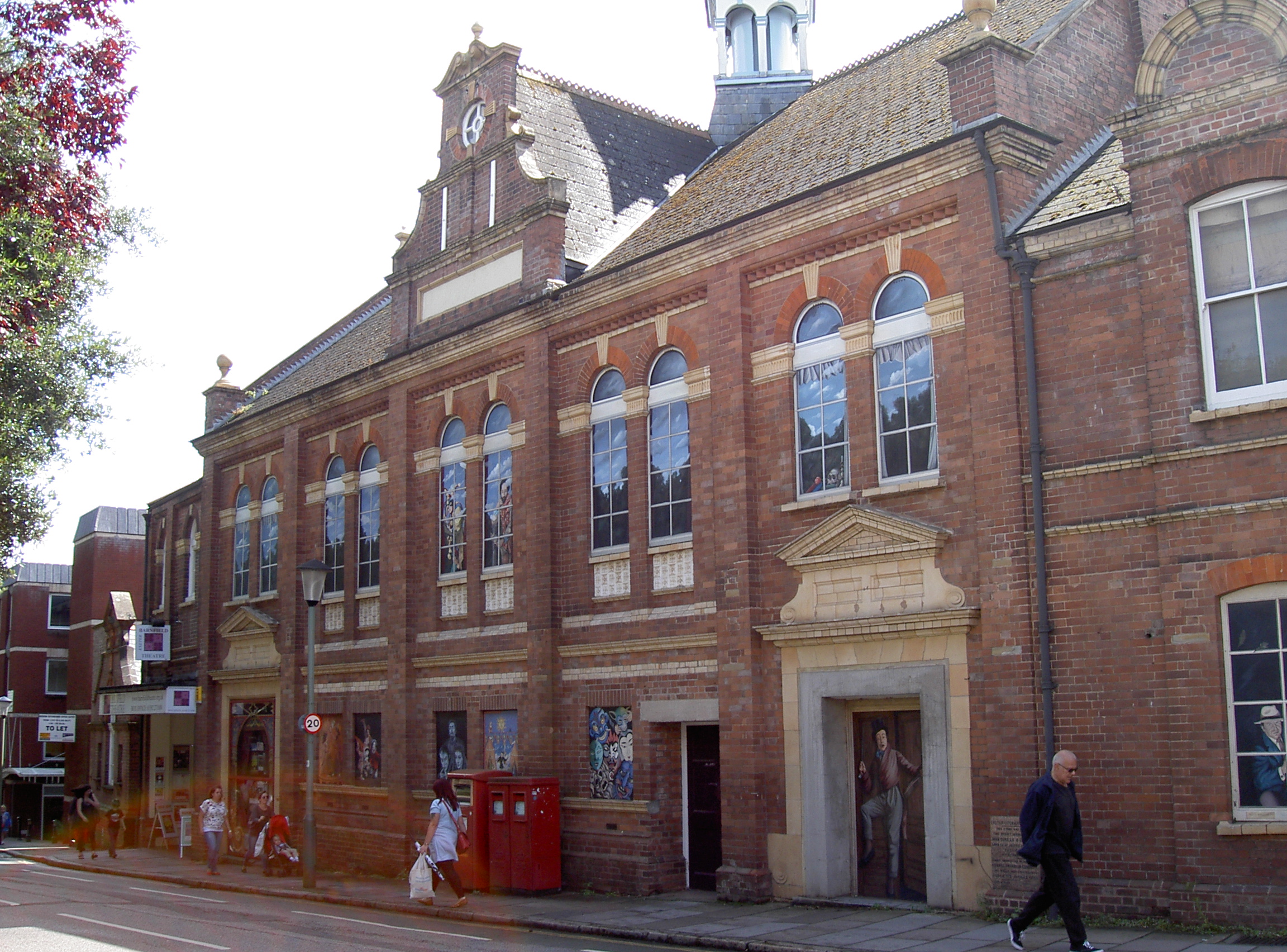 The Barnfield Theatre was originally constructed as Barnfield Hall by Exeter Literary Society towards the end of the 19th century and converted to a theatre in 1972. It is a charity and is used as a venue for amateur and professional theatrical companies.
The Cygnet Theatre in Friars Walk is the home of the Cygnet Training Theatre and is a member of the Conference of Drama Schools. As well as performances given by students in training, this theatre also stages performances from visiting repertory companies.
The Bike Shed Theatre and Cocktail Bar opened in September 2010 before permanently closing in March 2018 because it failed to generate enough profit from the cocktail bar in order to operate the theatre. Operating from basement premises in Fore Street, the theatre offered intimate live music and performances.
Additionally, more innovative and contemporary performances, theatrical productions and dance pieces are programmed by Exeter Phoenix in Exeter City Centre and The Exeter Corn Exchange in Market Street.
The Barnfield Theatre was originally constructed as Barnfield Hall by Exeter Literary Society towards the end of the 19th century and converted to a theatre in 1972. It is a charity and is used as a venue for amateur and professional theatrical companies.
The Cygnet Theatre in Friars Walk is the home of the Cygnet Training Theatre and is a member of the Conference of Drama Schools. As well as performances given by students in training, this theatre also stages performances from visiting repertory companies.
The Bike Shed Theatre and Cocktail Bar opened in September 2010 before permanently closing in March 2018 because it failed to generate enough profit from the cocktail bar in order to operate the theatre. Operating from basement premises in Fore Street, the theatre offered intimate live music and performances.
Additionally, more innovative and contemporary performances, theatrical productions and dance pieces are programmed by Exeter Phoenix in Exeter City Centre and The Exeter Corn Exchange in Market Street.
 Exeter is
Exeter is
Exeter City Council
from White's Devonshire Directory, 1850 * * {{Authority control Roman fortifications in Devon Cities in South West England Towns in Devon County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Devon Staple ports Roman legionary fortresses in England Unparished areas in Devon Boroughs in England
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
, South West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
. It is situated on the River Exe
The River Exe ( ) in England rises at Exe Head, near the village of Simonsbath, on Exmoor in Somerset, from the Bristol Channel coast, but flows more or less directly due south, so that most of its length lies in Devon. It flows for 60 mil ...
, approximately northeast of Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
and southwest of Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
.
In Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta
Legio II Augusta ( Second Legion "Augustus'") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army that was founded during the late Roman republic. Its emblems were the Capricornus, Pegasus, and Mars. It may have taken the name "''Augusta''" from a victory ...
under the personal command of Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Em ...
. Exeter became a religious centre in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
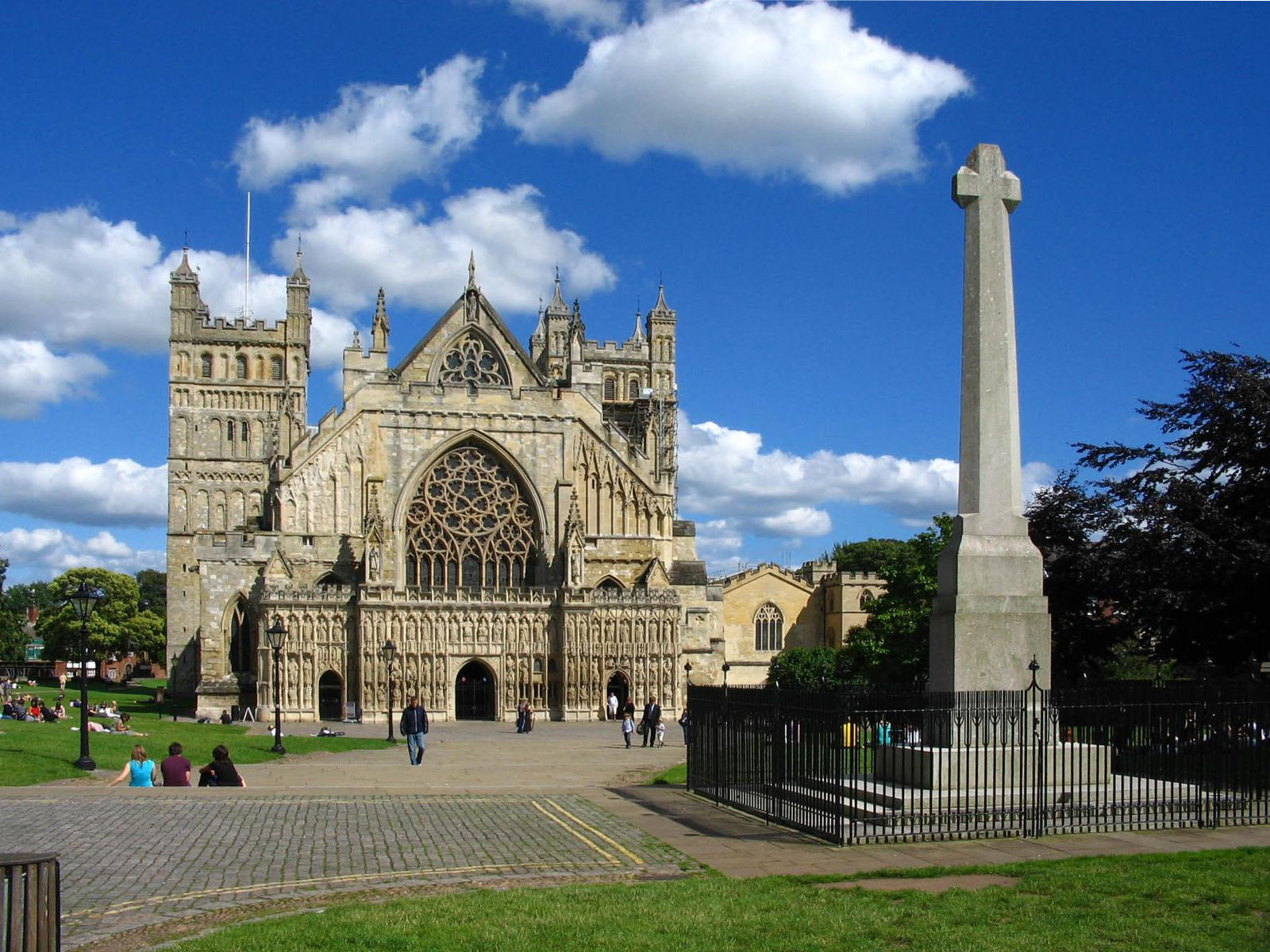
. Exeter Cathedral
Exeter Cathedral, properly known as the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter in Exeter, is an Anglican cathedral, and the seat of the Bishop of Exeter, in the city of Exeter, Devon, in South West England. The present building was complete by about 14 ...
, founded in the mid 11th century, became Anglican in the 16th-century English Reformation. Exeter became an affluent centre for the wool trade
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As an ...
, although by the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
the city was in decline. After the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, much of the city centre was rebuilt and is now a centre for education, business and tourism in Devon and Cornwall. It is home to two of the constituent campuses of the University of Exeter: Streatham and St Luke's.
The administrative area of Exeter has the status of a non-metropolitan district
Non-metropolitan districts, or colloquially "shire districts", are a type of local government district in England. As created, they are sub-divisions of non-metropolitan counties (colloquially ''shire counties'') in a two-tier arrangement. Non ...
under the administration of the County Council. It is the county town of Devon and home to the headquarters of Devon County Council
Devon County Council is the county council administering the English county of Devon. Based in the city of Exeter, the council covers the non-metropolitan county area of Devon. Members of the council (councillors) are elected every four years to ...
. A plan to grant the city unitary authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
status was scrapped by the 2010 coalition government.
Name
The modern name of Exeter is a development of the Old English ''Escanceaster'', from theanglicised
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influen ...
form of the river now known as the Exe and the Old English suffix (as in Dorchester and Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east of t ...
), used to mark important fortresses or fortified towns. (The Welsh name for the city, , similarly means " ''caer'' or fortress on the Exe".) The name "Exe" is a separate development of the Brittonic name—meaning "water" or, more exactly, "full of fish" (cf. Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
''pysg'', "fish")—that also appears in the English Axe and Esk and the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
Usk ( cy, Wysg).
History
Prehistory
Exeter began as settlements on a dry ridge ending in a spur overlooking a navigableriver
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the ...
teeming with fish, with fertile land nearby. Although there have been no major prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
finds, these advantages suggest the site was occupied early.
Coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
have been discovered from the Hellenistic kingdoms
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
, suggesting the existence of a settlement trading with the Mediterranean as early as . Such early towns had been a feature of pre-Roman Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
as described by Julius Caesar in his '' Commentaries'' and it is possible that they existed in Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Gr ...
as well.
The unreliable source Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth ( la, Galfridus Monemutensis, Galfridus Arturus, cy, Gruffudd ap Arthur, Sieffre o Fynwy; 1095 – 1155) was a British cleric from Monmouth, Wales and one of the major figures in the development of British historiograph ...
stated that when Vespasian besieged the city in 49 AD its Celtic name was ''Kaerpenhuelgoit'', meaning 'town on the hill under the high wood'.

Roman times
The Romans established a 'playing-card' shaped (rectangle with round corners and two short and two long sides) fort ( la,castrum
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
) named Isca around AD 55. The fort was the southwest terminus of the Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia ( Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis (Bath), C ...
(Route 15 of the ''Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary ( la, Itinerarium Antonini Augusti, "The Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is a famous '' itinerarium'', a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibl ...
'') and served as the base of the man Second Augustan Legion () at some time led by Vespasian, later Roman Emperor, for the next 20 years before they moved to Caerleon
Caerleon (; cy, Caerllion) is a town and community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Rom ...
in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, which was also known as Isca. To distinguish the two, the Romans also referred to Exeter as , "Watertown of the Dumnonii", and Caerleon as Isca Augusta. A small fort was also maintained at Topsham; a supply depot on the route between the two was excavated at on Topsham Road in 2010.
The presence of the fort built up an unplanned civilian community ( or ) of natives and the soldiers' families, mostly to the northeast of the fort. This settlement served as the tribal capital () of the DumnoniiBidwell, Paul T. ''Roman Exeter: Fortress and Town'', . Exeter City Council (Exeter), 1980. . and was listed as one of their four cities ( grc-gre, poleis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
, script=Latn) by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
in his ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, a ...
'' (it also appeared in the 7th-century ''Ravenna Cosmography
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Tex ...
'', where it appears as an apparently confused
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
entry for ). When the fortress was abandoned around the year 75, its grounds were converted to civilian purposes: its very large bathhouse
Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other cr ...
was demolished to make way for a forum
Forum or The Forum (plural forums or fora) may refer to:
Common uses
*Forum (legal), designated space for public expression in the United States
*Forum (Roman), open public space within a Roman city
**Roman Forum, most famous example
*Internet ...
and a basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
, and a smaller-scale bath was erected to the southeast. This area was excavated in the 1970s, but could not be maintained for public view owing to its proximity to the present-day cathedral. In January 2015, it was announced that Exeter Cathedral had launched a bid to restore the baths and open an underground centre for visitors.
In the late 2nd century, the ditch and rampart defences around the old fortress were replaced by a bank and wall enclosing a much larger area, some 92 acres (37 ha).Bidwell (1980), . Although most of the visible structure is older, the course of the Roman wall was used for Exeter's subsequent city walls. Thus about 70% of the Roman wall remains, and most of its route can be traced on foot. The Devonian Isca seems to have been most prosperous in the first half of the 4th century: more than a thousand Roman coins
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction to the Republic, during the third century BC, well into Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, de ...
have been found around the city and there is evidence for copper and bronze working, a stock-yard, and markets for the livestock, crops, and pottery produced in the surrounding countryside. The dating of the coins so far discovered, however, suggests a rapid decline: virtually none have been discovered dated after the year 380.
Medieval times
Bishop Ussher
James Ussher (or Usher; 4 January 1581 – 21 March 1656) was the Church of Ireland Archbishop of Armagh and Primate of All Ireland between 1625 and 1656. He was a prolific scholar and church leader, who today is most famous for his iden ...
identified the Cair ,Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the '' Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considere ...
(). Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classics, classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19 ...
(). ''Historia Brittonum'', VI. Composed after AD 830. Hosted at Latin Wikisource. listed among the 28 cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
of Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
by the ''History of the Britons
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British (Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Bri ...
'', as Isca,Newman, John Henry & al''Lives of the English Saints: St. German, Bishop of Auxerre'', Ch. X: "Britain in 429, A. D.", p. 92.
James Toovey (London), 1844. although David Nash Ford read it as a reference to Penselwood and thought it more likely to be Lindinis (modern
Ilchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parishes in England, civil parish, situated on the River Yeo (South Somerset), River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the England, English county of Somerset. Originally a Roman Britain, Roman town, and ...
).Ford, David Nash.The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. Nothing is certainly known of Exeter from the time of the
Roman withdrawal from Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew t ...
around the year 410 until the seventh century.Hoskins 2004, p. 15 By that time, the city was held by the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the No ...
, who had arrived in Exeter after defeating the British Dumnonia
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for a Brythonic kingdom that existed in Sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries CE in the more westerly parts of present-day South West England. It was centred in the area of modern Devon, ...
ns at Peonnum in Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lor ...
in 658. It seems likely that the Saxons maintained a quarter of the city for the Britons under their own laws around present-day Bartholomew Street, which was known as "Britayne" Street until 1637 in memory of its former occupants.
Exeter was known to the Saxons as Escanceaster. In 876, it was attacked and briefly captured by Danish Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
. Alfred the Great drove them out the next summer. Over the next few years, he elevated Exeter to one of the four ''burh
A burh () or burg was an Old English fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new const ...
s'' in Devon, rebuilding its walls on the Roman lines.Sellman (1985), . These permitted the city to fend off another attack and siege by the Danes in 893. King Athelstan
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
again strengthened the walls around 928, and at the same time drove out the remaining Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs m ...
from the city.Hoskins (2004), . (It is uncertain, though, whether they had lived in the city continuously since the Roman period or returned from the countryside when Alfred strengthened its defences.) According to William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as "a ...
, they were sent beyond the River Tamar
The Tamar (; kw, Dowr Tamar) is a river in south west England, that forms most of the border between Devon (to the east) and Cornwall (to the west). A part of the Tamar Valley is a World Heritage Site due to its historic mining activities.
T ...
, which was fixed as the boundary of Devon. (This may, however, have served as a territorial boundary within the former kingdom of Dumnonia
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for a Brythonic kingdom that existed in Sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries CE in the more westerly parts of present-day South West England. It was centred in the area of modern Devon, ...
as well.) Other references suggest that the British simply moved to what is now the area, not far outside Exeter's walls. The quarter vacated by the Britons was apparently adapted as "the earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form '' jarl'', and meant " chieftain", partic ...
's burh" and was still named Irlesberi in the 12th century. In 1001, the Danes again failed to get into the city, but they were able to plunder it in 1003 because they were let in, for unknown reasons, by the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
reeve
Reeve may refer to:
Titles
*Reeve (Canada), an elected chief executive of some counties, townships, and equivalents
*Reeve (England), an official elected annually by the serfs to supervise lands for a lord
*High-reeve, a title taken by some Englis ...
of Emma of Normandy
Emma of Normandy (referred to as Ælfgifu in royal documents; c. 984 – 6 March 1052) was a Norman-born noblewoman who became the English, Danish, and Norwegian queen through her marriages to the Anglo-Saxon king Æthelred the Unready and th ...
, who had been given the city as part of her dowry on her marriage to Æthelred the Unready
Æthelred II ( ang, Æþelræd, ;Different spellings of this king’s name most commonly found in modern texts are "Ethelred" and "Æthelred" (or "Aethelred"), the latter being closer to the original Old English form . Compare the modern dial ...
the previous year.
 Two years after the Norman conquest of England, Exeter rebelled against King William. Gytha Thorkelsdóttir, the mother of the slain King Harold, was living in the city at the time, and William promptly marched west and initiated a siege. After 18 days, William accepted the city's honourable surrender, swearing an oath not to harm the city or increase its ancient tribute. However, William quickly arranged for the building of Rougemont Castle to strengthen Norman control over the area. Properties owned by Saxon landlords were transferred into Norman hands and, on the death of Bishop Leofric in 1072, the Norman
Two years after the Norman conquest of England, Exeter rebelled against King William. Gytha Thorkelsdóttir, the mother of the slain King Harold, was living in the city at the time, and William promptly marched west and initiated a siege. After 18 days, William accepted the city's honourable surrender, swearing an oath not to harm the city or increase its ancient tribute. However, William quickly arranged for the building of Rougemont Castle to strengthen Norman control over the area. Properties owned by Saxon landlords were transferred into Norman hands and, on the death of Bishop Leofric in 1072, the Norman Osbern FitzOsbern
__NOTOC__
Osbern FitzOsbern (–1103) was a Norman churchman. He was a relative of King Edward the Confessor as well as being a royal chaplain.Barlow ''Edward the Confessor'' p. 164 During Edward's reign he received the church at Bosham, near C ...
was appointed his successor.
In 1136, early in the Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legi ...
, Rougemont Castle was held against King Stephen by Baldwin de Redvers. Redvers submitted only after a three-month siege, not when the three wells in the castle ran dry, but only after the exhaustion of the large supplies of wine that the garrison was using for drinking, baking, cooking, and putting out fires set by the besiegers. During the siege, King Stephen built an earthen fortification at the site now known (erroneously) as Danes Castle.
 The city held a weekly market for the benefit of its citizens from at least 1213, and by 1281 Exeter was the only town in the south-west to have three market days per week. There are also records of seven annual fairs, the earliest of which dates from 1130, and all of which continued until at least the early 16th century.
Prior to the expulsion of the Jews of England in 1290, Exeter was home to England's most westerly Jewish community.
During the high medieval period, both the cathedral clergy and the citizens enjoyed access to sophisticated aqueduct systems which brought pure drinking water into the city from springs in the neighbouring parish of St Sidwell's. For part of their length, these aqueducts were conveyed through a remarkable network of tunnels, or underground passages, which survive largely intact and which may still be visited today.
Exeter and
The city held a weekly market for the benefit of its citizens from at least 1213, and by 1281 Exeter was the only town in the south-west to have three market days per week. There are also records of seven annual fairs, the earliest of which dates from 1130, and all of which continued until at least the early 16th century.
Prior to the expulsion of the Jews of England in 1290, Exeter was home to England's most westerly Jewish community.
During the high medieval period, both the cathedral clergy and the citizens enjoyed access to sophisticated aqueduct systems which brought pure drinking water into the city from springs in the neighbouring parish of St Sidwell's. For part of their length, these aqueducts were conveyed through a remarkable network of tunnels, or underground passages, which survive largely intact and which may still be visited today.
Exeter and Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
hosted the first recorded Common Council in the Medieval England. The first detailed and continuous evidence of its existence and activity was founded after 1345. Formed by twelve "better and more discreet men" (in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
: ''duodecim meliores''), reelected each year, it was originally designed to control the abuse of the Major and of his four stewards
Steward may refer to:
Positions or roles
* Steward (office), a representative of a monarch
* Steward (Methodism), a leader in a congregation and/or district
* Steward, a person responsible for supplies of food to a college, club, or other inst ...
, which respectively presided over the borough court and the provost court. The members of the Common Council come from the same elite of wealthy citizens, as did the major and the stewards and this concern introduced a second conflict of interests in the government organism of the city.
Modern times
 ; Tudor and Stuart eras
In 1537, the city was made a
; Tudor and Stuart eras
In 1537, the city was made a county corporate
A county corporate or corporate county was a type of subnational division used for local government in England, Wales, and Ireland.
Counties corporate were created during the Middle Ages, and were effectively small self-governing county-empowere ...
. In 1549, the city successfully withstood a month-long siege by the so-called Prayer Book rebels: Devon and Cornish folk who had been infuriated by the radical religious policies of King Edward VI. The insurgents occupied the suburbs of Exeter, burnt down two of the city gates and attempted to undermine the city walls, but were eventually forced to abandon the siege after they had been worsted in a series of bloody battles with the king's army. A number of rebels were executed in the immediate aftermath of the siege. The Livery Dole
Livery Dole in Exeter, Devon, is an ancient triangular site between what is today Heavitree Road and Magdalen Road, in the eastern suburbs of Exeter. It was most notoriously used as a place for executions, and has contained an almshouse and ch ...
almshouse
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) was charitable housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the medieval era. They were often targeted at the poor of a locality, at those from certain ...
s and chapel at Heavitree
Heavitree is a historic village and parish situated formerly outside the walls of the City of Exeter in Devon, England, and is today an eastern district of that city. It was formerly the first significant village outside the city on the road to ...
were founded in March 1591 and finished in 1594.
When John Hooker John Hooker may refer to:
*John Hooker (English constitutionalist) (c. 1527–1601), English writer, solicitor, antiquary, civic administrator and advocate of republican government
*John Lee Hooker (1912–2001), American blues singer-songwriter an ...
was appointed to the city payroll in 1561, he created the Court of Orphans as a municipal government for families broken by the premature death of their major economic source. He also was made the Common Council as the legal owner of any estate left to the orphan children of Exeter, until they have reached the age of 21 to be partially paid back. The orphan tax was used to fund the construction of the Exeter canal.
The city's motto, ''Semper fidelis
''Semper fidelis'' () is a Latin phrase that means "always faithful" or "always loyal" (Fidelis or Fidelity). It is the motto of the United States Marine Corps, usually shortened to Semper Fi. It is also in use as a motto for towns, families, ...
'', is traditionally held to have been suggested by Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
, in acknowledgement of the city's contribution of ships to help defeat the Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an a ...
in 1588; however its first documented use is in 1660. Schools in Exeter teach that the motto was bestowed by Charles II in 1660 at the Restoration due to Exeter's role in the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians ("Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of Kingdom of England, England's governanc ...
.
When in 1638 Reverend John Wheelwright was exiled from the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
and subsequently established a community on the banks of the Squamscott River, he named the region Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal c ...
after its Devonian counterpart. During the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolu ...
it became the capital of New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the nor ...
.
Exeter was secured for Parliament at the beginning of the English Civil War, and its defences very much strengthened, but in September 1643 it was captured by the Cornish Royalist Army led by Prince Maurice. Thereafter, the city remained firmly under the king's control until near the end of the war, being one of the final Royalist cities to fall into Parliamentarian hands. The surrender of Exeter was negotiated in April 1646 at Poltimore House
Poltimore House is an 18th-century country house in Poltimore, Devon, England. The Manor of Poltimore was from the 13th to the 20th century the seat of the Bampfylde family, which acquired the title Baron Poltimore in 1831. The house retain ...
by Thomas Fairfax
Thomas Fairfax, 3rd Lord Fairfax of Cameron (17 January 161212 November 1671), also known as Sir Thomas Fairfax, was an English politician, general and Parliamentary commander-in-chief during the English Civil War. An adept and talented comman ...
. During this period, Exeter was an economically powerful city, with a strong trade of wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
...
. This was partly due to the surrounding area which was "more fertile and better inhabited than that passed over the preceding day" according to Count Lorenzo Magalotti
Lorenzo Magalotti (24 October 1637 – 2 March 1712) was an Italian philosopher, author, diplomat and poet.
Magalotti was born in Rome into an aristocratic family, the son of Ottavio Magalotti, Prefect of the Pontifical Mail: his uncle Lorenz ...
who visited the city when he was 26 years old. Magalotti writes of over thirty thousand people being employed in the county of Devon as part of the wool and cloth industries, merchandise that was sold to "the West Indies, Spain, France and Italy". Celia Fiennes also visited Exeter during this period, in the early 18th century. She remarked on the "vast trade" and "incredible quantity" in Exeter, recording that "it turns the most money in a week of anything in England", between £10,000 and £15,000.
; Georgian and Victorian eras
 Early in the
Early in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, Exeter's industry developed on the basis of locally available agricultural products and, since the city's location on a fast-flowing river gave it ready access to water power
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a ...
, an early industrial site developed on drained marshland to the west of the city, at Exe Island
Exe Island was the early industrial area of Exeter, England, and was an area of marshland between the city walls and the River Exe, reclaimed by the construction of a series of leat
A leat (; also lete or leet, or millstream) is the name, c ...
. However, when steam power
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be tr ...
replaced water in the 19th century, Exeter was too far from sources of coal (or iron) to develop further. As a result, the city declined in relative importance and was spared the rapid 19th-century development that changed many historic European cities. Extensive canal redevelopments during this period further expanded Exeter's economy, with "vessels of 15 to 16 tons burthen ringingup goods and merchandise from Topsham to the City Quay
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more berths ( mooring locati ...
". In 1778 a new bridge across the Exe was opened to replace the old medieval bridge. Built at a cost of £30,000, it had three arches and was built of stone.
 In 1832, cholera, which had been erupting all across Europe, reached Exeter. The only known documentation of this event was written by Dr Thomas Shapter, one of the medical doctors present during the epidemic.
The first railway to arrive in Exeter was the
In 1832, cholera, which had been erupting all across Europe, reached Exeter. The only known documentation of this event was written by Dr Thomas Shapter, one of the medical doctors present during the epidemic.
The first railway to arrive in Exeter was the Bristol and Exeter Railway
The Bristol & Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with t ...
that opened a station at St Davids
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , "David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint David, W ...
on the western edge in 1844. The South Devon Railway Company
The South Devon Railway Company built and operated the railway from Exeter to Plymouth and Torquay in Devon, England. It was a broad gauge railway built by Isambard Kingdom Brunel.
The line had to traverse difficult hilly terrain, and the compa ...
extended the line westwards to Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
, opening their own smaller station at St Thomas, above Cowick Street. A more central railway station, that at Queen Street, was opened by the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exete ...
in 1860 when it opened its alternative route to London. Butchers Lloyd Maunder
Lloyd Maunder are an Exeter, Devon based group of West Country retail butchers, a major producer of locally reared beef, pork and chicken products.
History
FJP Maunder established a meat processing facility at Witheridge, Devon in 1879. He ope ...
moved to their present base in 1915, to gain better access to the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 mill ...
for transportation of meat products to London.
 The first electricity in Exeter was provided by the Exeter Electric Light Company, which was formed at the end of the 1880s, but it was municipalised in 1896 and became the City of Exeter Electricity Company.
In 1896 £88,000 was spent constructing sewerage system which reduced the risk of infectious diseases,
The first horse-drawn trams in Exeter were introduced in 1882 with 3 lines radiating from the city's East Gate. One line went to St David's station via New North Road, the Obelisk (where the Clock Tower now stands) and St David's Hill. The second line went out along Heavitree Road to Livery Dole and the third went to Mount Pleasant along Sidwell Street. There was a depot off New North Road.
The first electricity in Exeter was provided by the Exeter Electric Light Company, which was formed at the end of the 1880s, but it was municipalised in 1896 and became the City of Exeter Electricity Company.
In 1896 £88,000 was spent constructing sewerage system which reduced the risk of infectious diseases,
The first horse-drawn trams in Exeter were introduced in 1882 with 3 lines radiating from the city's East Gate. One line went to St David's station via New North Road, the Obelisk (where the Clock Tower now stands) and St David's Hill. The second line went out along Heavitree Road to Livery Dole and the third went to Mount Pleasant along Sidwell Street. There was a depot off New North Road.
20th century
 A new bridge across the Exe was opened on 29 March 1905, replacing the former Georgian bridge. Made of
A new bridge across the Exe was opened on 29 March 1905, replacing the former Georgian bridge. Made of cast-iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
and steel with a three hinged arch design, it cost £25,000 and was designed by Sir John Wolfe Barry
Sir John Wolfe Barry (7 December 1836 – 22 January 1918), the youngest son of famous architect Sir Charles Barry, was an English civil engineer of the late 19th and early 20th century. His most famous project is Tower Bridge over the River ...
. Also in 1905, electric trams replaced the horse trams with a new route which passed along the High Street, down Fore Street and over the new Exe Bridge. Once across the Exe the line divided, with one route along Alphington Road and another along Cowick Street. The line to St David's Station travelled along Queen Street instead of along New North Road and the line to Heavitree was extended. On 17 March 1917, a tram went out of control going down Fore Street, hit a horse-drawn wagon, then overturned on Exe Bridge; one female passenger was killed. By the 1920s there were problems with congestion caused by the trams, a need for expensive track renewal work and the slow speed of the trams in Exeter's narrow streets. After much discussion, the council decided to replace the tram service with double-decker buses and the last tram ran on 19 August 1931. The only remaining Exeter tram in service is car 19, now at the Seaton Tramway
The Seaton Tramway is a narrow gauge electric tramway in the East Devon district of South West England. The route runs alongside the Axe Estuary and the River Coly, running between the coastal resort of Seaton, the village of Colyford, ...
.
Exeter was bombed by the German Luftwaffe during the Second World War when a total of 18 raids between 1940 and 1942 flattened much of the city centre. Between April 1941 and April 1943, Exeter was defended from enemy bombers by the No. 307 Polish Night Fighter Squadron
No. 307 (Polish) Squadron, also known as No. 307 (City of Lwów) Squadron ( pl, 307 Dywizjon Myśliwski Nocny "Lwowskich Puchaczy" ) was one of several Polish squadrons in the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the Second World War. It was formed as p ...
, nicknamed the 'Lwów Eagle Owls', who were based at Exeter Airport. The city of Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
shared the same motto as the city of Exeter – 'Semper Fidelis' (Always faithful).
In April and May 1942, as part of the Baedeker Blitz
The Baedeker Blitz or Baedeker raids were a series of aerial attacks in April and May 1942 by the German ''Luftwaffe'' on English cities during the Second World War. The name derives from Baedeker, a series of German tourist guide books, inclu ...
and specifically in response to the RAF bombing of Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
and Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
, 40 acres (16 ha) of the city were leveled by incendiary bombing. Many historic buildings in the center—particularly adjacent to High Street and Sidwell Street—were destroyed, and others, including the cathedral, were damaged. On the night of 4 May, the Polish 307 Squadron dispatched four available aircraft against forty German Junkers Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a Nazi Germany, German World War II ''Luftwaffe'' twin-engined multirole combat aircraft. Junkers, Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works (JFM) designed the plane in the mid-1930s as a so-called ''Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") th ...
bombers, preventing four German aircraft from releasing their load of bombs on Exeter. 156 people were killed, but the squadron suffered no casualties in the process.
To commemorate the friendship that had formed between the 307 Squadron and Exeter, the squadron presented the city with a Polish flag on 15 November 1942 (the first British city to have had that honour) outside Exeter Cathedral
Exeter Cathedral, properly known as the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter in Exeter, is an Anglican cathedral, and the seat of the Bishop of Exeter, in the city of Exeter, Devon, in South West England. The present building was complete by about 14 ...
. Since 2012, a Polish flag is raised over the city's Guildhall on 15 November; the day is now known as '307 Squadron Day' in Exeter. On 15 November 2017, a plaque in memory of the squadron was unveiled in the St James Chapel of Exeter Cathedral by the Polish Ambassador Arkady Rzegocki.
Large areas of the city centre were rebuilt in the 1950s, with little attempt to preserve or restore historic buildings. The street plan was altered in an attempt to improve traffic circulation, and former landmarks like St Lawrence, the College of the Vicars Choral, and Bedford circus disappeared. The modern architecture stands in sharp contrast to the red sandstone of buildings that survived the Blitz.
 On 27 October 1960, following very heavy rain, the Exe overflowed and flooded large areas of Exeter including Exwick, St Thomas and Alphington. The water rose as high as 2 metres above ground level in places and 150 employees of the local firm Beach Bros were trapped for nine hours. 2,500 properties were flooded. Later the same year on 3 December the river levels rose again, flooding 1,200 properties. These floods led to the construction of new flood defences for Exeter. Work began in 1965, took 12 years to complete and cost £8 million. The defences included three flood relief channels, and were complemented by the construction of two new concrete bridges (built in 1969 and 1972) to replace the old Exe Bridge which had obstructed the flow of the river and made the flooding worse.
A high-profile, random murder of a child occurred in the city in 1997, which today remains one of the UK's highest-profile unsolved murders. 14-year-old Kate Bushell, a pupil at what is now West Exe School, had her throat cut by an unidentified attacker while walking her dog along Exwick Lane, Exwick, on 15 November 1997. Despite the police insisting the killer must be local and repeatedly appealing for locals to come forward with information on ''
On 27 October 1960, following very heavy rain, the Exe overflowed and flooded large areas of Exeter including Exwick, St Thomas and Alphington. The water rose as high as 2 metres above ground level in places and 150 employees of the local firm Beach Bros were trapped for nine hours. 2,500 properties were flooded. Later the same year on 3 December the river levels rose again, flooding 1,200 properties. These floods led to the construction of new flood defences for Exeter. Work began in 1965, took 12 years to complete and cost £8 million. The defences included three flood relief channels, and were complemented by the construction of two new concrete bridges (built in 1969 and 1972) to replace the old Exe Bridge which had obstructed the flow of the river and made the flooding worse.
A high-profile, random murder of a child occurred in the city in 1997, which today remains one of the UK's highest-profile unsolved murders. 14-year-old Kate Bushell, a pupil at what is now West Exe School, had her throat cut by an unidentified attacker while walking her dog along Exwick Lane, Exwick, on 15 November 1997. Despite the police insisting the killer must be local and repeatedly appealing for locals to come forward with information on ''Crimewatch
''Crimewatch'' (formerly ''Crimewatch UK'') is a British television programme produced by the BBC, that reconstructs major unsolved crimes in order to gain information from the public which may assist in solving the case. The programme was o ...
'', the attacker has never been identified. Police believe Bushell's murder is possibly linked to the murder of dogwalker Lyn Bryant in Cornwall only one year later in 1998. Police have DNA evidence in the Bryant case and there remains a £10,000 reward for information in both cases.
21st century
The Princesshay shopping centre adjoining the Cathedral Close and the High Street was redeveloped between 2005 and 2007, despite some local opposition. It incorporates 123 varied residential units. To enable people with limited mobility to enjoy the city, Exeter Community Transport Association provides manual and powered wheelchairs and scooters ('Shopmobility') for use by anyone suffering from short- or long-term mobility impairment to access the city centre shopping facilities, events and meetings with friends. In May 2008 there was an attempted terrorist attack on the Giraffe cafe in Princesshay, but the bomber was the only one injured. A £30 million improvement scheme for the flood defences was approved in March 2015. The plans involve the removal of check weirs and a deeper, "meandering stream" in the centre of the drainage channels to improve flow. The plans followed a study by theEnvironment Agency
The Environment Agency (EA) is a non-departmental public body, established in 1996 and sponsored by the United Kingdom government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, with responsibilities relating to the protection and en ...
that revealed weaknesses in the current defences. A community currency
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, t ...
for the city, the Exeter Pound, was introduced in 2015 and dissolved in 2018.
A serious fire broke out in buildings in central Exeter on 28 October 2016. The Royal Clarence Hotel, 18 Cathedral Yard and The Well House Tavern were severely damaged in the fire. In July 2017 the restoration plans were officially unveiled, with the rebuild expected to be completed in 18 months and a scheduled reopening of the hotel in 2019. 18 Cathedral Yard was repaired by November 2018, but there was a second round of bids for the work to complete repairs to The Well House, and to rebuild the Royal Clarence Hotel as a 74-bedroom hotel. However, in late 2021 it was announced that the hotel scheme was "significantly unviable", and the Royal Clarence site would be converted into twenty-three luxury apartments with the ground floor acting as a leisure and hospitality space. The plans were officially granted permission on 11 October 2022. The work, involving the demolition and reconstruction of the remaining fabric, will last just under eighteen months and is due to begin in the summer of 2023.
On 27 February 2021 a Second World War bomb was uncovered at a construction site and more than 2,600 people were evacuated. Bomb Disposal
Bomb disposal is an explosives engineering profession using the process by which hazardous explosive devices are rendered safe. ''Bomb disposal'' is an all-encompassing term to describe the separate, but interrelated functions in the militar ...
squads used approximately 400 tons of sand to secure it. It was safely detonated at 18:12. By 1 March hundreds of people had spent a third night away from home, however, because the detonation of the bomb had damaged nearby buildings. On 2 March Exeter City Council lifted the safety cordon to allow residents to return to their properties but said that many would be "uninhabitable at this stage". The University of Exeter said that about 300 of the 1,400 evacuated students had not yet returned.
Homelessness
Exeter has the 6th highest number of rough sleepers on a single night of all local authorities in England (as of the autumn of 2020), marking a 19% increase from 2019. In 2014, Exeter had "...the unenviable status of having the highest per capita rate of rough sleeping outside of London". During the COVID-19 pandemic, 102 people in Exeter rough sleeping, or at risk of rough sleeping were accommodated as part of the government's 'Everybody In' directive. In Exeter City Council's recent 'Rough Sleeping Delivery Plan', a total of £3,351,347 was allocated for the purpose of reducing rough sleeping for the 2020–2021 period. The government's Next Steps Accommodation Programme also provided Exeter City Council with £440,000 to help reduce the number of rough sleepers on Exeter's streets. The council has also focussed its efforts on reducing rough sleeping in the long term, with a "£3 million Capital programme bid orthe creation of 31 units of new long term move-on accommodation with dedicated support to be delivered before 31 March 2021".Governance


Parliamentary
Exeter is in two parliamentary constituencies, the majority of the city is in the Exeter constituency but two wards (St Loyes and Topsham) are inEast Devon
East Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council has been based in Honiton since February 2019, and the largest town is Exmouth (with a population of 34,432 at the time of the 2011 census).
The district was formed ...
. Since World War II until recently, Exeter itself was relatively marginal, with its Member of Parliament usually drawn from the governing party. Nowadays the Exeter seat is increasingly becoming a Labour stronghold. The Exeter MP is Ben Bradshaw
Benjamin Peter James Bradshaw (born 30 August 1960) is a British politician who served as Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport from 2009 to 2010. A member of the Labour Party, he has been Member of Parliament (MP) for Exeter since 1 ...
, with the Youth MP being Georgia Howell, and Simon Jupp represents East Devon. Prior to Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAE ...
in 2020, Exeter was part of the South West England European constituency, which elected 6 MEP MEP may refer to:
Organisations and politics
* Mahajana Eksath Peramuna, a political party in Sri Lanka
* Mahajana Eksath Peramuna (1956), a former political alliance in Sri Lanka
* Maison européenne de la photographie, a photography centre ...
s.
Local Government
Exeter'scity council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
is a district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
authority, and shares responsibility for local government with the Devon County Council
Devon County Council is the county council administering the English county of Devon. Based in the city of Exeter, the council covers the non-metropolitan county area of Devon. Members of the council (councillors) are elected every four years to ...
. In May 2012 Labour became the majority party on the council. Exeter City Council
Exeter City Council is the council and local government of the city of Exeter, Devon.
History
Proposed unitary authority status
The government proposed that the city should become an independent unitary authority within Devon, much like neig ...
's bid for the city to become a Unitary Authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
was initially approved by ministers in February 2010. A judicial review was called by Devon County Council and the Court held that the Minister had acted unlawfully in granting Unitary status to Exeter at the same time, however, following the 2010 general election the new coalition government announced in May 2010 that the reorganisation would be blocked.
From Saxon times, it was in the hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to des ...
of Wonford
Wonford is a former village, manor and ecclesiastical parish in Devon, England, now a part of the City of Exeter. The 13th century St Loye's Chapel situated within the parish now gives its name to the surrounding location. Wonford is situated n ...
. Exeter has had a mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as ...
since at least 1207 and until 2002, the city was the oldest 'Right Worshipful' Mayoralty in England. As part of the Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II
The Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II was the international celebration held in 2002 marking the 50th anniversary of the accession of Queen Elizabeth II on 6 February 1952. It was intended by the Queen to be both a commemoration of her 50 years a ...
Exeter was chosen to receive the title of Lord Mayor. Councillor Granville Baldwin became the first Lord Mayor of Exeter on 1 May 2002 when Letters Patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, t ...
were awarded to the city during a visit by the Queen.
The Lord Mayor is elected each year from amongst the 39 Exeter city councillor
A councillor is an elected representative for a local government council in some countries.
Canada
Due to the control that the provinces have over their municipal governments, terms that councillors serve vary from province to province. Unl ...
s and is non-political for the term of office.
Public services
Policing in Exeter is provided by the Devon and Cornwall Constabulary who have their headquarters at Middlemoor in the east of the city. Thefire service
A fire department (American English) or fire brigade ( Commonwealth English), also known as a fire authority, fire district, fire and rescue, or fire service in some areas, is an organization that provides fire prevention and fire suppression ...
is provided by the Devon and Somerset Fire and Rescue Service, which is headquartered at Clyst St George near Exeter. It has two fire stations located at Danes Castle and Middlemoor.
The Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust
The Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust ran Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Honeylands Children's Centre (for specialist assessment and support for children with special needs and their families), the Exeter Mobility Centre (providin ...
has a large hospital located to the south-east of the city centre. Ambulance services in Exeter are provided by South Western Ambulance Service NHS Trust. The West Trust Divisional HQ and 999 control is in Exeter which provides cover for Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
, Cornwall, Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lor ...
and the Isles of Scilly.
Geography
 The city of Exeter was established on the eastern bank of the
The city of Exeter was established on the eastern bank of the River Exe
The River Exe ( ) in England rises at Exe Head, near the village of Simonsbath, on Exmoor in Somerset, from the Bristol Channel coast, but flows more or less directly due south, so that most of its length lies in Devon. It flows for 60 mil ...
on a ridge of land backed by a steep hill. It is at this point that the Exe, having just been joined by the River Creedy, opens onto a wide flood plain and estuary which results in quite common flooding. Historically this was the lowest bridging point
The lowest bridging point (or lowest crossing point) is the location on a river which is crossed by a bridge at its closest point to the sea.
Historically - that is, before the development of engineering technology that allowed the construction of ...
of the River Exe which was tidal and navigable up to the city until the construction of weirs later in its history. This combined with the easily defensible higher ground of the ridge made the current location of the city a natural choice for settlement and trade. In George Oliver's ''The History of the City of Exeter'', it is noted that the most likely reasons for the original settling of what would become modern Exeter was the "fertility of the surrounding countryside" and the area's "beautiful and commanding elevation ndits rapid and navigable river".
Its woodland would also have been ideal for natural resources and hunting.
Exeter sits predominantly on sandstone and conglomerate geology, although the structure of the surrounding areas is varied.
The topography of the ridge which forms the backbone of the city includes a volcanic plug
A volcanic plug, also called a volcanic neck or lava neck, is a volcanic object created when magma hardens within a vent on an active volcano. When present, a plug can cause an extreme build-up of high gas pressure if rising volatile-charged m ...
, on which the Rougemont Castle is situated. The cathedral is located on the edge of this ridge and is therefore visible for a considerable distance.
Exeter is west-southwest of Salisbury
Salisbury ( ) is a cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers Avon, Nadder and Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath.
Salisbury is in the southeast of Wil ...
, west-southwest of London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, north of Torquay
Torquay ( ) is a seaside town in Devon, England, part of the unitary authority area of Torbay. It lies south of the county town of Exeter and east-north-east of Plymouth, on the north of Tor Bay, adjoining the neighbouring town of Paignt ...
, northeast of Plymouth and east-northeast of Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro c ...
.
Climate
Exeter has mild wet winters, punctuated by colder spells that are usually short-lived. Summer is characterised by warm and changeable weather with hot and cooler rainy spells. Temperatures do not vary much throughout the year compared to other locations at this latitude; however, the topography of Exeter can enhance the diurnal range by a couple degrees Celsius, as spots along the sheltered valley of the River Exe such as Quayside, St Thomas and Exwick see colder nights and warmer days, the only exception to this is with foggy and frosty weather in the winter during anticyclonic activity when fog can linger all day and keep daytime temperatures suppressed. Similarly, the same weather patterns can elevate the maximum daily temperatures, The hottest month is July with an average high of , and the coldest month is January with an average high of . October is the wettest month with of rain. The weather station for these reading is at Exeter Airport; adding one degree Celsius to the readings from the maximum daily temperature and deducting a degree from the overnight minima broadly covers the location disparity. It is precisely because of shelter fromDartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous ...
that Exeter is more frost-prone than areas to the southwest, such as Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
. It is also drier and warmer in the summer for the same reason. The highest recorded temperature in Exeter stands at recorded in June 1976, while the lowest recorded temperature is recorded in December 2010.
Demographics
Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for ...
published that Exeter's district area population was 117,773; 6,697 more people than that of the last census from 2001, which indicated that Exeter had a population of 111,076. At the time of the 2011 UK census, the ethnic composition of Exeter's population was 93.1% White
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the ...
, with the largest minority ethnic group being Chinese at 1.7%. The White British, White Irish and other ethnic group all declined in numbers since the 2001 census (−1%, -6% and −10% respectively). Meanwhile, the Chinese and ''Other Asian'' had the largest increases (429% and 434% respectively). This excludes the two new ethnic groups added to the 2011 census of Gypsy or Irish Traveller and Arab. Below are the 10 largest immigrant groups in Exeter .
In 2011, the City of Exeter had a population of 117,773, while its inner urban subdivision had a population of 113,507. The Exeter USD (urban subdivision) does not include the town of Topsham, which while it is administratively part of the city, it is often considered a separate individual settlement as well as the fact its excluded from the city's constituency.
In 2011, 11.9% of the population of the Exeter USD were non-white British, compared with 11.7% for the actual city and surrounding borough of Exeter.
In 2009, Exeter City was 89.1% White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population w ...
, compared with 88.3% in 2011.
The Exeter Urban Area had a population of 124,079 in 2014, compared with 124,328 for the city and borough of Exeter. While the Exeter Metropolitan Area had a population of 467,257 in the same year and includes Exeter along with Teignbridge
Teignbridge is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based in Newton Abbot.
Other towns in the district include Ashburton, Buckfastleigh, Dawlish and Teignmouth. It is named for the old Teignbridge hundred. ...
, Mid Devon
Mid Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based in Tiverton.
The district was formed under the Local Government Act 1972, on 1 April 1974 by the merger of the borough of Tiverton and Crediton urban distri ...
and East Devon
East Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council has been based in Honiton since February 2019, and the largest town is Exmouth (with a population of 34,432 at the time of the 2011 census).
The district was formed ...
. Out of all the Devon districts, Exeter receives the largest number of commuters from East Devon, followed by Teignbridge. Most of the city's ethnic minority population live in the central, northwestern and eastern suburbs of the city. Outlying areas such as Pinhoe
Pinhoe is a former village, manor and ecclesiastical parish, now a suburb on the north eastern outskirts of the City of Exeter in the English county of Devon. The 2001 census recorded a population of 6,108 people resident within Pinhoe Ward, o ...
, Cowick and the expensive suburb of Topsham are all 95% White British as of 2011.
Ethnicity
The ethnicity of the City of Exeter from 1991 to 2021 is below:Religion
Economy
 The
The Met Office
The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and is led by CEO Penelope ...
, the main weather forecasting organisation for the United Kingdom and one of the most significant in the world, relocated from Bracknell
Bracknell () is a large town and civil parish in Berkshire, England, the westernmost area within the Greater London Urban Area and the administrative centre of the Borough of Bracknell Forest. It lies to the east of Reading, south of Maidenhe ...
in Berkshire to Exeter in early 2004. It is one of the largest employers in the area (together with the University of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light"
, established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter)
, type = Public
, ...
, Devon County Council
Devon County Council is the county council administering the English county of Devon. Based in the city of Exeter, the council covers the non-metropolitan county area of Devon. Members of the council (councillors) are elected every four years to ...
and the Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
The Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust ran Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Honeylands Children's Centre (for specialist assessment and support for children with special needs and their families), the Exeter Mobility Centre (providing ...
).
Around 35,000 people commute into Exeter on a daily basis, from nearby surrounding towns. Exeter provides services, employment and shopping for local residents within the city limits and also from nearby towns in Teignbridge
Teignbridge is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based in Newton Abbot.
Other towns in the district include Ashburton, Buckfastleigh, Dawlish and Teignmouth. It is named for the old Teignbridge hundred. ...
, Mid Devon
Mid Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based in Tiverton.
The district was formed under the Local Government Act 1972, on 1 April 1974 by the merger of the borough of Tiverton and Crediton urban distri ...
and East Devon
East Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council has been based in Honiton since February 2019, and the largest town is Exmouth (with a population of 34,432 at the time of the 2011 census).
The district was formed ...
, together sometimes known as the Exeter & Heart of Devon area (EHOD). Exeter therefore provides for the EHOD area population of 457,400.
Exeter has been identified among the top ten most profitable locations for a business to be based.
The city centre provides substantial shopping facilities. The High Street is mainly devoted to branches of national chains: a NEF
Nef or NEF may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* National Energy Foundation, a British charity
* National Enrichment Facility, an American uranium enrichment plant
* New Economics Foundation, a British think-tank
* Near East Foundation, ...
survey in 2005 rated Exeter as the worst example of a clone town in the UK, with only a single independent store in the city's High Street, and less diversity (in terms of different categories of shop) than any other town surveyed. In 2010, a similar survey reported the city was still the worst clone town. As of 2019, the last independent store on the high street is closed. Three significant shopping areas that connect to the High Street provide a somewhat more varied menu. Princesshay, a post-war
In Western usage, the phrase post-war era (or postwar era) usually refers to the time since the end of World War II. More broadly, a post-war period (or postwar period) is the interval immediately following the end of a war. A post-war period ...
retail area connecting to the south side of the High Street was home to a number of independent stores prior to redevelopment in 2007, but is now also largely occupied by national chains. It is still intended that a number of the new units will be let to local independent stores. The House of Fraser
House of Fraser (also operating as Frasers) is a British department store group with 44 locations across the United Kingdom, which is now part of Frasers Group. It was established in Glasgow, Scotland in 1849 as Arthur and Fraser. By 1891, it w ...
building on the high street has been bought by a local wealth performance management firm, Prydis, who have released their plans to redevelop the building as a three-storey hotel with a rooftop bar and retail shops.
On the other side of the High Street, the partly-undercover Guildhall Shopping Centre houses a mixture of national and more regional shops, and connects to the wholly enclosed Harlequins Centre where smaller businesses predominate. Smaller streets off the High Street such as Gandy Street also offer a range of independent shops.
On 26 June 2004, Exeter was granted Fairtrade City
The Fair Trade Towns campaign is the result of a grass-roots citizens movement that started in the UK in 2001 (see below). It allows citizens to get together in order to self-proclaim their town (or other local geographical area) as a region that ...
status.
Although Exeter contains a number of tourist attractions, the city is not dominated by tourism, with only 7% of employment dependent on tourism compared with 13% for Devon as a whole (2005 figures).
There are also plans to build on land in the Teignbridge and East Devon areas, which border Exeter's boundaries, as part of the "Exeter Growth Point" strategy. This includes the new town
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
of Cranbrook, located about east of the city in East Devon, where construction began in 2011 and which is now home to several thousand residents.
Landmarks
Among the notable buildings in Exeter are:Religious buildings
 * The
* The cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
, founded in 1050 when the bishop's seat was moved from the nearby town of Crediton
Crediton is a town and civil parish in the Mid Devon district of Devon in England. It stands on the A377 Exeter to Barnstaple road at the junction with the A3072 road to Tiverton, about north west of Exeter and around from the M5 motorwa ...
(birthplace of Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations o ...
) because Exeter's Roman walls offered better protection against "pirates", presumably Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and s ...
s. A statue of Richard Hooker
Richard Hooker (25 March 1554 – 2 November 1600) was an English priest in the Church of England and an influential theologian.The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church by F. L. Cross (Editor), E. A. Livingstone (Editor) Oxford University ...
, the 16th century Anglican theologian, who was born in Exeter, has a prominent place in the Cathedral Close.
* St Nicholas Priory
The Benedictine Priory of St Nicholas or just St Nicholas Priory was a Benedictine monastery founded in Exeter, England, in 1087. At the Dissolution of the Monasteries the church and chapter house range were pulled down but the domestic buildin ...
in Mint Lane, the remains of a monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whic ...
, later used as a private house and now a museum owned by the city council. The priory was founded in medieval times and was home to Benedictine monks for over 400 years, until it was closed and partly demolished by Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagr ...
. The remaining buildings were then sold off in 1602 and became the home of the locally wealthy Hurst family. The property has been fully renovated by Exeter City Council, and the small garden area features Tudor plants and herbs
* A number of medieval churches including St Mary Steps which has an elaborate clock.
* The Exeter Synagogue is the third oldest synagogue in Britain, completed in 1763.
* St Thomas' Church, originally built in the 13th century just outside the city walls. Destroyed by fire and rebuilt in the 17th century; grade I listed.
Secular buildings and features
 * The
* The ruins
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate ...
of Rougemont Castle; later parts of the castle were still in use as a County Court until early 2006 when a new Crown Court
The Crown Court is the court of first instance of England and Wales responsible for hearing all indictable offences, some either way offences and appeals lied to it by the magistrates' courts. It is one of three Senior Courts of England and Wale ...
s building opened. A plaque near the surviving medieval gatehouse recalls the fate of Alice Molland, tried for witchcraft
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have u ...
at Exeter in 1685, and reputedly the last person in England to have been executed for that crime; others convicted of witchcraft had been hanged in Exeter in 1581, 1610, and 1682.
* The Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
, which has medieval foundations and has been claimed to be the oldest municipal building in England still in use.
* Mol's Coffee House, a historic building in the Cathedral Close.
* Tuckers' Hall, a 15th-century guild hall for the incorporation of Weavers, Fullers and Shearmen, that is still in use today.
* The Custom House
A custom house or customs house was traditionally a building housing the offices for a jurisdictional government whose officials oversaw the functions associated with importing and exporting goods into and out of a country, such as collecting ...
in the Quay area, which is the oldest brick building surviving in the city.
* "The House That Moved", a 14th-century Tudor building, earned its name in 1961 when it was moved from its original location on the corner of Edmund Street in order for a new road to be built in its place. Weighing more than twenty-one tonnes, it was strapped together and slowly moved a few inches at a time to its present-day position.
* Parliament Street in the city centre is one of the narrowest streets in the world.
* The Butts Ferry, an ancient cable ferry
A cable ferry (including the terms chain ferry, swing ferry, floating bridge, or punt) is a ferry that is guided (and in many cases propelled) across a river or large body of water by cables connected to both shores. Early cable ferries often ...
across the River Exe.
* Wyvern Barracks
Wyvern Barracks is a military installation on Topsham Road in Exeter.
History
The site was established as an artillery barracks for the Board of Ordnance under the name of Topsham Barracks around 1800. In 1873 a system of recruiting areas based ...
, a former artillery barracks, dates back to about 1800.
* Higher Barracks, a former cavalry barracks, dates back to 1794.
* The Devon County War Memorial in the Cathedral Close, designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens
Sir Edwin Landseer Lutyens ( ; 29 March 1869 – 1 January 1944) was an English architect known for imaginatively adapting traditional architectural styles to the requirements of his era. He designed many English country houses, war memoria ...
and unveiled in 1922 by Edward, Prince of Wales.
Many of Exeter's old buildings are made from the local dark red sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, which gives its name to the castle and the park that now surrounds it (Rougemont means 'red hill'). The pavements on Queen Street are composed of the rock diorite
Diorite ( ) is an intrusive igneous rock formed by the slow cooling underground of magma (molten rock) that has a moderate content of silica and a relatively low content of alkali metals. It is intermediate in composition between low-sil ...
and exhibit feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feld ...
crystals, while those around Princesshay are composed of granodiorite
Granodiorite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar.
The term banatite is sometimes used informally for various rocks ranging from gr ...
.
Northernhay Gardens
Located just outside the castle, Northernhay Gardens is the oldest public open space in England, being originally laid out in 1612 as a pleasure walk for Exeter residents.Transport
Car
 The
The M5 motorway
The M5 is a motorway in England linking the Midlands with the South West England, South West. It runs from junction 8 of the M6 motorway, M6 at West Bromwich near Birmingham to Exeter in Devon. Heading south-west, the M5 runs east of West Brom ...
to Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
and Exeter starts at Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, and connects at Bristol with the M4 to London and South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
. The older A30 road
The A30 is a major road in England, running WSW from London to Land's End.
The road has been a principal axis in Britain from the 17th century to early 19th century, as a major coaching route. It used to provide the fastest route from Londo ...
provides a more direct route to London via the A303
The A303 is a trunk road in southern England, running between Basingstoke in Hampshire and Honiton in Devon via Stonehenge. Connecting the M3 and the A30, it is part of one of the main routes from London to Devon and Cornwall. It is a prim ...
and M3. The M5 is the modern lowest bridging point of the River Exe
The River Exe ( ) in England rises at Exe Head, near the village of Simonsbath, on Exmoor in Somerset, from the Bristol Channel coast, but flows more or less directly due south, so that most of its length lies in Devon. It flows for 60 mil ...
. Going westwards, the A38 connects Exeter to Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
and south east Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlan ...
, whilst the A30 continues via Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based in the town (east and west). ...
to Cornwall and ends at Penzance
Penzance ( ; kw, Pennsans) is a town, civil parish and port in the Penwith district of Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is the most westerly major town in Cornwall and is about west-southwest of Plymouth and west-southwest of London. Situ ...
. The cities of Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
, Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
, Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, Salisbury
Salisbury ( ) is a cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers Avon, Nadder and Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath.
Salisbury is in the southeast of Wil ...
and Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro c ...
can all be reached within two hours.
Travel by car in the city is often difficult with regular jams centred on the Exe Bridges area. Historically, the bridges were a significant bottleneck for holiday traffic heading to southwest England, leading to the construction of the first bypass in the mid-1930s over Countess Wear Bridge, followed by the M5 in 1977. To further address the problem of congestion in the city centre, Devon County Council
Devon County Council is the county council administering the English county of Devon. Based in the city of Exeter, the council covers the non-metropolitan county area of Devon. Members of the council (councillors) are elected every four years to ...
has park and ride services, and in 2006 considered the introduction of congestion charges.
Bus
Exeter's main operator of local buses isStagecoach South West
Stagecoach South West is a bus operator providing services in Devon and East Cornwall along with coach services to Bristol. It is a subsidiary of Stagecoach.
History Devon General
The Devon General Omnibus and Touring Company commenced operat ...
, which operates most of the services in the city. Dartline, is a minor operator in the city. Former operator Cooks Coaches were taken over by Stagecoach
A stagecoach is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are draw ...
forming Stagecoach South West. Western Greyhound was also a main operator connecting Exeter to Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlan ...
until its services were taken over by First Devon & Cornwall, and Stagecoach South West
Stagecoach South West is a bus operator providing services in Devon and East Cornwall along with coach services to Bristol. It is a subsidiary of Stagecoach.
History Devon General
The Devon General Omnibus and Touring Company commenced operat ...
in March 2015. There is a bus station
A bus station or a bus interchange is a structure where city or intercity buses stop to pick up and drop off passengers. While the term bus depot can also be used to refer to a bus station, it generally refers to a bus garage. A bus station is ...
.
Railway
 Exeter is the main rail hub in the South West and is linked to most branch lines in Devon, including to
Exeter is the main rail hub in the South West and is linked to most branch lines in Devon, including to Paignton
Paignton ( ) is a seaside town on the coast of Tor Bay in Devon, England. Together with Torquay and Brixham it forms the borough of Torbay which was created in 1998. The Torbay area is a holiday destination known as the English Riviera. Paign ...
, Exmouth
Exmouth is a port town, civil parish and seaside resort, sited on the east bank of the mouth of the River Exe and southeast of Exeter.
In 2011 it had a population of 34,432, making Exmouth the 5th most populous settlement in Devon.
Histo ...
, Barnstaple
Barnstaple ( or ) is a river-port town in North Devon, England, at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool and won great wealth. Later it imported Irish wool, but ...
and Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based in the town (east and west). ...
. This makes it possible to reach most stations in Devon directly from Exeter St Davids.
Exeter is served by three main railway stations. Exeter St Davids is served by all services and is a major interchange station
An interchange station or a transfer station is a train station for more than one railway route in a public transport system that allows passengers to change from one route to another, often without having to leave a station or pay an additional ...
within the South West Peninsula's rail network, whilst Exeter Central is more convenient for the city centre but served only by local services and the main line route to London Waterloo. In the south-west of the city, Exeter St Thomas
Exeter St Thomas railway station is a suburban railway station in Exeter, England, serving the suburb of St Thomas and the riverside area. The station is elevated on a low viaduct with entrances on Cowick Street. It is down the line from a ...
serves the western side of the city. There are also six suburban stations, Topsham, St James Park, Polsloe Bridge, Pinhoe
Pinhoe is a former village, manor and ecclesiastical parish, now a suburb on the north eastern outskirts of the City of Exeter in the English county of Devon. The 2001 census recorded a population of 6,108 people resident within Pinhoe Ward, o ...
, Digby & Sowton and Newcourt, served only by local services.
There are two main line railway routes from Exeter to London, the faster route via Taunton and Reading to London Paddington and the slower West of England Main Line
The West of England line (also known as the West of England Main Line) is a British railway line from , Hampshire, to in Devon, England. Passenger services run between London Waterloo station and Exeter; the line intersects with the Wessex M ...
via Salisbury
Salisbury ( ) is a cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers Avon, Nadder and Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath.
Salisbury is in the southeast of Wil ...
and Basingstoke
Basingstoke ( ) is the largest town in the county of Hampshire. It is situated in south-central England and lies across a valley at the source of the River Loddon, at the far western edge of The North Downs. It is located north-east of Southa ...
to London Waterloo. Another main line, the Cross Country Route
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a sal ...
, links Exeter with Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
, Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby gain ...
, Leeds
Leeds () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the thi ...
, Newcastle, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
and Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), ...
. Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 mill ...
and CrossCountry services continue westwards along the Exeter to Plymouth Line, variously serving Torquay
Torquay ( ) is a seaside town in Devon, England, part of the unitary authority area of Torbay. It lies south of the county town of Exeter and east-north-east of Plymouth, on the north of Tor Bay, adjoining the neighbouring town of Paignt ...
, Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
and Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlan ...
. Local branch lines run to Paignton
Paignton ( ) is a seaside town on the coast of Tor Bay in Devon, England. Together with Torquay and Brixham it forms the borough of Torbay which was created in 1998. The Torbay area is a holiday destination known as the English Riviera. Paign ...
(see Riviera Line), Exmouth
Exmouth is a port town, civil parish and seaside resort, sited on the east bank of the mouth of the River Exe and southeast of Exeter.
In 2011 it had a population of 34,432, making Exmouth the 5th most populous settlement in Devon.
Histo ...
(see Avocet Line) and Barnstaple
Barnstaple ( or ) is a river-port town in North Devon, England, at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool and won great wealth. Later it imported Irish wool, but ...
(see Tarka Line
The Tarka Line, also known as the North Devon Line, is a local railway line in Devon, England, linking the city of Exeter with the town of Barnstaple via a number of local villages, operated by Great Western Railway (GWR). The line opened in 18 ...
). There is also a summer weekend service to Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based in the town (east and west). ...
for access to Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous ...
.
The Exeter to Plymouth line of the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) used to provide an alternative route via Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based in the town (east and west). ...
connecting north Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlan ...
and Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
to Exeter and the rest of the UK railway system until its closure in 1968. There are proposals to reopen the line from Okehampton via Tavistock to Bere Alston, for a through service to Plymouth. On the night of 4 February 2014, amid high winds and extremely rough seas, part of the South Devon Railway sea wall
The South Devon Railway sea wall is situated on the south coast of Devon in England. A footpath runs alongside the railway between Dawlish Warren and Dawlish, then another footpath forms a continuation to the sea front promenade at Teignmouth. ...
at Dawlish was breached, washing away around of the wall and the ballast under the railway immediately behind and closing the Exeter to Plymouth Line. Network Rail
Network Rail Limited is the owner (via its subsidiary Network Rail Infrastructure Limited, which was known as Railtrack plc before 2002) and infrastructure manager of most of the railway network in Great Britain. Network Rail is an "arm's leng ...
began repair work and the line reopened on 4 April 2014. In the wake of widespread disruption caused by damage to the mainline track at Dawlish
Dawlish is an English seaside resort town and civil parish in Teignbridge on the south coast of Devon, from the county town of Exeter and from the larger resort of Torquay. Its 2011 population of 11,312 was estimated at 13,355 in 2019. It is t ...
by coastal storms in February 2014, Network Rail
Network Rail Limited is the owner (via its subsidiary Network Rail Infrastructure Limited, which was known as Railtrack plc before 2002) and infrastructure manager of most of the railway network in Great Britain. Network Rail is an "arm's leng ...
is considering reopening the Bere Alston to Okehampton and Exeter section of the former LSWR line as an alternative to the coastal route.
Air
 Exeter Airport lies east of the city, and the local airline, previously called Jersey European and British European but later as
Exeter Airport lies east of the city, and the local airline, previously called Jersey European and British European but later as Flybe
Flybe (pronounced ), styled as flybe, is a British airline based at Birmingham Airport, England.
History
The airline traces its history back to Jersey European Airways, which was set up in 1979 following the merger of Intra Airways and Expr ...
, was a significant local employer until its collapse in 2020. It is also a base for TUI Airways
TUI Airways Limited (formerly Thomsonfly and Thomson Airways) is a British charter airline, offering scheduled and charter flights from the United Kingdom and Ireland to destinations in Europe, Africa, Asia and North America.
The airline is t ...
with flights to Faro, Mallorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Bale ...
, Lanzarote
Lanzarote (, , ) is a Spanish island, the easternmost of the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean. It is located approximately off the north coast of Africa and from the Iberian Peninsula. Covering , Lanzarote is the fourth-largest of the i ...
and elsewhere. The airport offers a range of scheduled flights to British and Irish regional airports and charter flights. Connections to international hubs began with Paris-Charles de Gaulle in 2005 and later a daily service to Amsterdam Schiphol Airport
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol , known informally as Schiphol Airport ( nl, Luchthaven Schiphol, ), is the main international airport of the Netherlands. It is located southwest of Amsterdam, in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer in the provin ...
which ended with the collapse of Flybe in 2020. Ryanair
Ryanair is an Irish ultra low-cost carrier founded in 1984. It is headquartered in Swords, Dublin, Ireland and has its primary operational bases at Dublin and London Stansted airports. It forms the largest part of the Ryanair Holdings family ...
started flights in 2019 to Luqa, Naples and Málaga. Shortly adding Alicante but stopping the Naples and Luqa flights.
Canal
 The Exeter Canal, also known as the Exeter Ship Canal, was first constructed by John Trew in about 1566, representing one of the oldest artificial waterways in Britain. It was cut to bypass the St James' Weir that had been built across the
The Exeter Canal, also known as the Exeter Ship Canal, was first constructed by John Trew in about 1566, representing one of the oldest artificial waterways in Britain. It was cut to bypass the St James' Weir that had been built across the River Exe
The River Exe ( ) in England rises at Exe Head, near the village of Simonsbath, on Exmoor in Somerset, from the Bristol Channel coast, but flows more or less directly due south, so that most of its length lies in Devon. It flows for 60 mil ...
at Duckes Marsh to provide a leat to a mill constructed just below the confluence of the Northbrook, in what became the village of Countess Weir. The weir had the effect of preventing water-borne trade in the City of Exeter and forced boats to load and unload at Topsham from where the Earls of Devon were able to exact large tolls to transport goods to and from Exeter.
Originally deep and wide, the canal ran from the confluence of the Matford Brook, just above Bridge Road in Countess Weir to Haven Banks, close to the centre of Exeter. In order to maintain a consistent navigable water level, another weir was constructed by Trew, just below the point the canal joins the river. The canal was later extended south to Topsham Lock , deepened and widened, and later still it was extended to Turf Lock near Powderham . The canal was successful until the middle of the 19th century since when its use gradually declined – the last commercial use was in 1972. However it is now widely used for leisure purposes, and the city basin is part of a £24 million redevelopment scheme.
Education
 The
The University of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light"
, established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter)
, type = Public
, ...
, which has two campuses in the city, includes the Business School
A business school is a university-level institution that confers degrees in business administration or management. A business school may also be referred to as school of management, management school, school of business administration, o ...
, the Bill Douglas Cinema Museum, the Henry Wellcome
Sir Henry Solomon Wellcome (August 21, 1853 – July 25, 1936) was an American pharmaceutical entrepreneur. He founded the pharmaceutical company Burroughs Wellcome & Company with his colleague Silas Burroughs in 1880, which is one of the f ...
building for Biocatalysis, and, as of September 2018, the Exeter Centre for Circular Economy.
Exeter College is a further education college. It previously operated as the sole sixth form
In the education systems of England, Northern Ireland, Wales, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago and some other Commonwealth countries, sixth form represents the final two years of secondary education, ages 16 to 18. Pupils typically prepare for A-l ...
for the entire maintained school sector in the city. However, in 2014 Exeter Mathematics School
Exeter Mathematics School is a maths school located in Exeter in the English county of Devon.
It opened in September 2014 under the free schools initiative and is sponsored by Exeter College and the University of Exeter. It is intended to be ...
was established, a free school
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything
* Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism
* Emancipate, to procure ...
sixth form with a specialism in Mathematics.
For about 30 years the city of Exeter operated a maintained school system in which the divisions between phases came at different ages from most of the United Kingdom, with first, middle and high rather than infant, junior and secondary schools, so that children transferred between schools at the age of about 8 and 12 rather than 7 and 11. From 2005, however, it has adopted the more usual pattern, because of the pressures of the UK National Curriculum A national curriculum is a common programme of study in schools that is designed to ensure nationwide uniformity of content and standards in education. It is usually legislated by the national government, possibly in consultation with state or other ...
. The changeover back to the more typical structure led to a citywide, PFI funded, rebuilding programme for the high schools and led to the changing of names for some schools. Following the reorganisation there are 25 primary schools, four referral schools, three special school
Special education (known as special-needs education, aided education, exceptional education, alternative provision, exceptional student education, special ed., SDC, or SPED) is the practice of educating students in a way that accommodates th ...
s and five secondary schools within Exeter. The secondary schools are Isca Academy (formerly Priory High School), St James School (formerly St James High School), St Luke's Church of England School
St Luke's Church of England School is a co-educational secondary school located in Exeter in the English county of Devon. It is a Church of England school under the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Exeter.
It was originally known as St Luke's Chu ...
(formerly Vincent Thompson High School), St Peter's Church of England Aided School (a consolidation of the former Bishop Blackall High School for Girls and Heles High School for Boys) and West Exe School (formerly St Thomas High School).
The city has a number of independent schools, including Exeter School
Exeter School is an independent co-educational day school for pupils between the ages of 7 and 18 in Exeter, Devon, England. In 2019, there were around 200 pupils in the Junior School and 700 in the Senior School.
History
The School traces i ...
, Exeter Cathedral School, The Maynard School and St Wilfrid's School.
There are specialist schools for pupils with sensory needs, including Exeter Royal Academy for Deaf Education, and the West of England School for the Partially Sighted.
The Atkinson Unit is a secure specialist residential and educational complex for children in care or remanded
Remand may refer to:
* Remand (court procedure), when an appellate court sends a case back to the trial court or lower appellate court
* Pre-trial detention, detention of a suspect prior to a trial, conviction, or sentencing
See also
*'' Remando ...
by the courts.
Religion
 Numerous churches, and other religious buildings, are present in Exeter. A majority belong to differing Christian denominations, including a
Numerous churches, and other religious buildings, are present in Exeter. A majority belong to differing Christian denominations, including a Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
cathedral. The medieval city of Exeter had nearly 70 churches, chapels, monasteries and almshouses.
Exeter Cathedral
Exeter Cathedral, properly known as the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter in Exeter, is an Anglican cathedral, and the seat of the Bishop of Exeter, in the city of Exeter, Devon, in South West England. The present building was complete by about 14 ...
is the seat of the Bishop of Exeter
The Bishop of Exeter is the ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Exeter in the Province of Canterbury. Since 30 April 2014 the ordinary has been Robert Atwell.
. The erection of the present building was completed in approximately 1400, and possesses the longest uninterrupted vaulted ceiling in England, as well as other noticeable characteristics. A collective of Anglican churches form the Exeter Deanery.
There are two Catholic Churches: the Sacred Heart
The Most Sacred Heart of Jesus ( la, Cor Jesu Sacratissimum) is one of the most widely practised and well-known Catholic devotions, wherein the heart of Jesus is viewed as a symbol of "God's boundless and passionate love for mankind". This de ...
and the Blessed Sacrament, with congregations reflecting the nature of older and more recent immigration.
Exeter Synagogue, located within a near proximity to Mary Arches Street, was completely erected in 1763.
Exeter's mosque and Islamic centre are located on York Road. The first mosque was opened in 1977. The purpose-built mosque opened in 2011.
At the 2001 census, 69.12% of Exeter's population stated their religion as Christian, which is mildly lower than the regional average of 73.99% and the national average of 71.74%. Despite this, all other religions had exceeded the regional average at just under 1%. Although, they were much lower than the national average with the exemption of Buddhism. 20.45% of Exeter's population stated they had no religion, which was higher than the regional average of 16.75% and the national average of 14.59%.
Anglican churches

John Betjeman
Sir John Betjeman (; 28 August 190619 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster. He was Poet Laureate from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of The Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architectu ...
(writing in 1958) selects St David's
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , "David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint David, W ...
(" Caroe's best church"), St Martin's ("characteristic little city church, 15th century"), St Mary Steps ("medieval city church; font"), St Michael's ("Victorian, on a fine site"), and St Thomas's ("fittings"). His coverage of St Mary Arches is more detailed: "worth seeing ... as the completest Norman church in Devon: beautifully light and airy after its restoration from the bombing in 1942. 18th-century altar arrangements. Memorials to Exeter worthies, 16th to 18th centuries."
The aforementioned collective of Anglican churches include St David's Church, located near to St David's Station. The church was envisaged by W. D. Caroe, with the windows being manufactured by Kempe & Tower, and was later constructed between 1897 and 1900. A tower stands on the northeast side, with the overall design being described as "highly picturesque" by Nikolaus Pevsner.
St Edmund-on-the-Bridge was built on the Exe Bridge ca. 1230–40. Two arches of the bridge remain under the undercroft though the church was rebuilt in the Perpendicular style in 1835, using the old materials.
St Martin's is in the Cathedral Close; the plan is odd, and there are numerous items of church furniture, though these are not of high aesthetic value. St Mary Arches is a Norman church with aisles. St Mary Steps was originally by the West Gate of the city; the font is Norman, and there is a remarkable early clock. St Michael, Heavitree was built in 1844–46 and extended later in the century. St Pancras is of the 13th century and has a nave and chancel only; the font is Norman. The plan of St Petroc's church is highly unusual: a second chancel has been added facing north while the original chancel has another use and faces east. There are two aisles on the south, one of 1413 and another of the 16th century.
St Sidwell's church is by W. Burgess, 1812, in the Perpendicular style. St Stephen's church is partly of the 13th century but most of the structure is as rebuilt in 1826. St Michael and All Angels Church
St Michael and All Angels Church may refer to:
Africa
* St Michael and All Angels Church, Blantyre Malawi
* St. Michael and All Angels' Anglican Church, Weltevreden Park, Johannesburg, South Africa
America
* Cathedral Church of Saint Michael and ...
on Mount Dinham has a spire which exceeds the height of the towers of Exeter Cathedral.
Sport
Rugby union
The city's professionalrugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a Contact sport#Terminology, close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the Comparison of rugby league and rugby union, two codes of ru ...
team is the Exeter Chiefs
Exeter Chiefs (officially Exeter Rugby Club) is an English professional rugby union club based in Exeter, Devon. They play in Premiership Rugby, England's top division of rugby.
The club was founded in 1871 and since 2006 has played its home m ...
. Founded in 1871, as Exeter Rugby Club, the team have played their home games at Sandy Park
Sandy Park is a rugby union stadium and conference and banqueting centre in Exeter, England. It is the home ground of Exeter Chiefs, who from the 2010–11 season have been playing in the Gallagher Premiership, the top flight of the English rugb ...
stadium, located adjacent to junction 30 of the M5, since 2006 after relocating from their previous stadium at the County Ground which had been used continually from 1905. They have been continuous members of the highest division of English rugby, the Premiership, since 2010. They have been English champions twice, in 2017
File:2017 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The War Against ISIS at the Battle of Mosul (2016-2017); aftermath of the Manchester Arena bombing; The Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017 ("Great American Eclipse"); North Korea tests a ser ...
, and 2020. Anglo-Welsh Cup winners twice, in 2014 and 2018. In 2020, the club became European Champions for the first time in their history, defeating Parisian based club Racing 92 in the final at Bristol's Ashton Gate Stadium 31–27.
The city also has two other clubs: Wessex Rugby Club, which is located in Exwick, and Exeter Saracens Rugby Club, which is located in Whipton.
Football
Exeter City is Exeter's only Professional Association football club. Currently members of League One, they have played their home games at St James Park since their formation in 1904. The club were founder members of theFootball League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in the world. It was the top-level football league in Engla ...
's Third Division
In sport, the Third Division, also called Division 3, Division Three, or Division III, is often the third-highest division of a league, and will often have promotion and relegation with divisions above and below.
Association football
*Belgian Thir ...
(south) in 1920, but have never progressed higher than the third tier of the English football league system, and in 2003 were relegated to the Conference
A conference is a meeting of two or more experts to discuss and exchange opinions or new information about a particular topic.
Conferences can be used as a form of group decision-making, although discussion, not always decisions, are the main ...
.
Other sports
Exeter Cricket Club administer three teams that play in the Devon Cricket League. The first of which plays in the Premier Division at first XI level and the next plays at second XI level. The club play their home games at County Ground where they have remained for over 180 years. ExeterRowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically at ...
Club competes both locally and nationally, and has a recorded history originating in the early 19th century. The City of Exeter Rowing Regatta is run annually in July, and is the eldest and largest regatta in the South West, with racing first recorded on the river in the 1860s.
Exeter's speedway team, Exeter Falcons
The Exeter Falcons were a speedway team based in the city of Exeter. The Falcons operated from 1947 to 2005 at the County Ground Stadium in Exeter.
History
In 1947, the Falcons competed in a league for the first time when they finished fou ...
, was established in 1929 and were located at the County Ground until its permanent closure in 2005. The team was revived in 2015, but are currently based in Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
. Speedway was also staged briefly at tracks in Alphington and Peamore after the Second World War.
Culture

Literature
 The ''
The ''Exeter Book
The Exeter Book, also known as the Codex Exoniensis or Exeter Cathedral Library MS 3501, is a large codex of Old English poetry, believed to have been produced in the late tenth century AD. It is one of the four major manuscripts of Old Engli ...
'', an anthology of Anglo Saxon poetry, is conserved in the vaults of Exeter Cathedral. The Exeter Book originates from the 10th century and is one of four manuscripts that between them encompass all surviving poetry composed in Old English. Predominantly, the Book incorporates shorter poems, several religious pieces, and a series of riddle
A riddle is a statement, question or phrase having a double or veiled meaning, put forth as a puzzle to be solved. Riddles are of two types: ''enigmas'', which are problems generally expressed in metaphorical or allegorical language that requi ...
s, a handful of which are famously lewd. A selection of the aforementioned riddles are inscribed on a highly polished steel obelisk situated in High Street, placed there on 30 March 2005.
Another famous piece of literature is the '' Exon Domesday'', a composite land and tax register of 1086. The piece contains a variety of administrative materials concerning the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset and Wiltshire. This piece is also conserved in Exeter Cathedral.
In 2019, the city became a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
City of Literature
UNESCO's City of Literature programme is part of the wider Creative Cities Network.
The ''Network'' was launched in 2004, and now has member cities in seven creative fields. The other creative fields are: Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Ga ...
.
Theatre
Exeter has several theatres. TheNorthcott Theatre
The Northcott Theatre is a theatre situated on the Streatham Campus of the University of Exeter, Exeter, Devon, England. It opened in 1967 and was run until 2010 by the Northcott Theatre Foundation, when the company ceased operating after a p ...
is situated in the Streatham campus of the University of Exeter and is one of relatively few provincial English theatres to maintain its own repertory company. This theatre is the successor to the former Theatre Royal, Exeter which was permanently closed in 1962.
 The Barnfield Theatre was originally constructed as Barnfield Hall by Exeter Literary Society towards the end of the 19th century and converted to a theatre in 1972. It is a charity and is used as a venue for amateur and professional theatrical companies.
The Cygnet Theatre in Friars Walk is the home of the Cygnet Training Theatre and is a member of the Conference of Drama Schools. As well as performances given by students in training, this theatre also stages performances from visiting repertory companies.
The Bike Shed Theatre and Cocktail Bar opened in September 2010 before permanently closing in March 2018 because it failed to generate enough profit from the cocktail bar in order to operate the theatre. Operating from basement premises in Fore Street, the theatre offered intimate live music and performances.
Additionally, more innovative and contemporary performances, theatrical productions and dance pieces are programmed by Exeter Phoenix in Exeter City Centre and The Exeter Corn Exchange in Market Street.
The Barnfield Theatre was originally constructed as Barnfield Hall by Exeter Literary Society towards the end of the 19th century and converted to a theatre in 1972. It is a charity and is used as a venue for amateur and professional theatrical companies.
The Cygnet Theatre in Friars Walk is the home of the Cygnet Training Theatre and is a member of the Conference of Drama Schools. As well as performances given by students in training, this theatre also stages performances from visiting repertory companies.
The Bike Shed Theatre and Cocktail Bar opened in September 2010 before permanently closing in March 2018 because it failed to generate enough profit from the cocktail bar in order to operate the theatre. Operating from basement premises in Fore Street, the theatre offered intimate live music and performances.
Additionally, more innovative and contemporary performances, theatrical productions and dance pieces are programmed by Exeter Phoenix in Exeter City Centre and The Exeter Corn Exchange in Market Street.
Music
The largest orchestra based in Exeter is the EMG Symphony Orchestra.Chris Martin
Christopher Anthony John Martin (born 2 March 1977) is an English singer-songwriter and musician. He is best known as the lead vocalist, pianist, rhythm guitarist and co-founder of the rock band Coldplay. Born in Exeter, Devon, he went to Uni ...
, lead singer of internationally famous band Coldplay
Coldplay are a British Rock music, rock band formed in London in 1997. They consist of vocalist and pianist Chris Martin, guitarist Jonny Buckland, bassist Guy Berryman, drummer Will Champion and creative director Phil Harvey (manager), Phil H ...
, grew up in a Grade II-listed Georgian house set in eight acres of grounds in the nearby village of Whitestone.
Museums and galleries
* TheRoyal Albert Memorial Museum
Royal Albert Memorial Museum & Art Gallery (RAMM) is a museum and art gallery in Exeter, Devon, the largest in the city. It holds significant and diverse collections in areas such as zoology, anthropology, fine art, local and overseas archaeol ...
in Queen Street is Exeter's predominant museum. The museum maintains its own collections of regional, national and international importance. Recently, the museum underwent an extensive refurbishment. It reopened on 14 December 2011, and was subsequently awarded the National Art Fund Prize – UK Museum of the Year 2012. The Museum also runs St Nicholas Priory in Mint Lane, near Fore Street.
* Additionally, the University of Exeter has an extensive fine art collection and an assortment of exhibition spaces across its Streatham campus. Showing a vibrant programme of exhibitions, performances, films and visual arts. The sculpture collection contains works by artists including Barbara Hepworth, Peter Thursby, Geoffrey Clark and Elaine M. Goodwin. It can be located using the Sculpture Trail.
* Exeter Phoenix is one of South West England's leading contemporary arts venues. The venue occupies the former university site in Gandy Street and programmes international, national and outstanding regional artists.
* Until its closure in 2017, Spacex (art gallery), was a contemporary arts organisation, that programmed exhibitions of contemporary art and promoted artist-led projects, events and research.
Newspapers
* ''Express and Echo
The ''Express & Echo'' is a paid-for newspaper for Exeter and the surrounding area.
History
The ''Express & Echo'' was established in 1904 as the result of a merger between the ''Western Echo'' and the ''Devon Evening Express'', which was found ...
'', published weekly on Thursdays.
* '' Exeter Flying Post'', published weekly. Originally discontinued in 1917, but was revived in 1976 as an alternative community magazine. The last issue was in 2012.
* ''The Western Morning News
The ''Western Morning News'' is a daily regional newspaper founded in 1860, and covering the West Country including Devon, Cornwall, the Isles of Scilly and parts of Somerset and Dorset in the South West of England.
Organisation
The ''Western ...
'', a Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
printed daily regional paper.
* ''Exeposé
''Exeposé'' is the official student-run newspaper of the University of Exeter. With an estimated print circulation of around 3,500. ''Exeposé'' is free and published fortnightly during term time.
'', the university's student newspaper, printed fortnightly.
Radio
BBC Radio Devon
BBC Radio Devon is the BBC's local radio station serving the county of Devon.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios in the Mannamead area of Plymouth.
According to RAJAR, the station has a weekly audience of ...
broadcasts to Exeter locally on FM (95.8) and AM (990 AM/MW), although the majority of programming originates in Plymouth. In the evenings, BBC Radio Devon joins the South West Regional service. Heart West formerly Gemini FM and Devonair, broadcasts on 97.0 FM, with East Devon
East Devon is a local government district in Devon, England. Its council has been based in Honiton since February 2019, and the largest town is Exmouth (with a population of 34,432 at the time of the 2011 census).
The district was formed ...
and Torbay
Torbay is a borough and unitary authority in Devon, south west England. It is governed by Torbay Council and consists of of land, including the resort towns of Torquay, Paignton and Brixham, located on east-facing Tor Bay, part of Lyme ...
utilising their own frequencies. Both Heart West and BBC Radio Devon broadcast from the St Thomas transmitter. AM radio is broadcast from Pearce's Hill located at J31 of the M5.
Other radio stations include Radio Exe
Radio Exe (formerly Exeter FM) is an Independent Local Radio station based in Exeter, Devon, England.
As of March 2023, the station broadcasts to a weekly audience of 39,000, according to RAJAR.
Presenters
Presenters include Matt Rogers, N ...
, an easy listening station broadcasting on 107.3 FM, Phonic.FM which provides a "no adverts no playlist" alternative on 106.8 FM or online at www.phonic.fm, VI, a station broadcasting from the West of England School and College on 1386 AM/MW.
Additionally, Exeter University has a well established student station, Xpression FM, which broadcasts on 87.7 FM using two low-powered transmitters, although it can be heard over much of the north of the city.
The local commercial radio
Commercial broadcasting (also called private broadcasting) is the broadcasting of television programs and radio programming by privately owned corporate media, as opposed to state sponsorship. It was the United States′ first model of radio (a ...
station is Radio Exe
Radio Exe (formerly Exeter FM) is an Independent Local Radio station based in Exeter, Devon, England.
As of March 2023, the station broadcasts to a weekly audience of 39,000, according to RAJAR.
Presenters
Presenters include Matt Rogers, N ...
. The local community radio
Community radio is a radio service offering a third model of radio broadcasting in addition to commercial and public broadcasting. Community stations serve geographic communities and communities of interest. They broadcast content that is popul ...
station is Phonic FM.
Television
Both BBC Spotlight and ITV West Country provide Exeter with regional news outputs. BBC Spotlight is broadcast from Plymouth and ITV Westcountry is broadcast from Bristol, although both services do have newsrooms in Exeter. The St Thomas andStockland Hill transmitting station
The Stockland Hill transmitting station is a transmitting facility of FM Radio and UHF television located near Honiton, Devon, England. This transmitter mainly serves the East of Devon and West Dorset.
It was constructed in 1961 by the IBA to ...
both provide the city's coverage with both transmitters having completed the digital switchover
The digital television transition, also called the digital switchover (DSO), the analogue switch/sign-off (ASO), the digital migration, or the analogue shutdown, is the process in which older analogue television broadcasting technology is con ...
.
Twin towns
 Exeter is
Exeter is twinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with Rennes
Rennes (; br, Roazhon ; Gallo: ''Resnn''; ) is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the Ille and the Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine departm ...
in France, Bad Homburg
Bad Homburg vor der Höhe () is the district town of the Hochtaunuskreis, Hesse, on the southern slope of the Taunus mountains. Bad Homburg is part of the Frankfurt Rhein-Main urban area. The town's official name is ''Bad Homburg v.d.Höhe'', w ...
in Germany, Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl ( rus, Ярослáвль, p=jɪrɐˈsɫavlʲ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluence ...
in Russia, and Terracina
Terracina is an Italian city and ''comune'' of the province of Latina, located on the coast southeast of Rome on the Via Appia ( by rail). The site has been continuously occupied since antiquity.
History Ancient times
Terracina appears in anci ...
in Italy.
Freedom of the City
The following people and military units have received theFreedom of the City
The Freedom of the City (or Borough in some parts of the UK) is an honour bestowed by a municipality upon a valued member of the community, or upon a visiting celebrity or dignitary. Arising from the medieval practice of granting respected ...
of Exeter.
Individuals
* Admiral Rt Hon Lord Nelson : 15 January 1801. * Gareth Steenson: 7 October 2021. * Richard Jacobs: 1 December 2021. * Philip Bostock: 18 July 2022.Military units
* TheRoyal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
: April 1977
* 243 (The Wessex) Field Hospital (V): July 2002
* The Rifles
The Rifles is an infantry regiment of the British Army. Formed in 2007, it consists of four Regular battalions and three Reserve battalions, plus a number of companies in other Army Reserve battalions. Each battalion of The Rifles was formerly ...
(formerly The Devonshire and Dorset Regiment
The Devonshire and Dorset Regiment (11th, 39th and 54th), usually just known as the Devon and Dorsets, was an infantry regiment of the British Army formed in 1958 by the amalgamation of two county regiments, the Devonshire Regiment and the Do ...
): June 2007
* The Coldstream Guards
The Coldstream Guards is the oldest continuously serving regular regiment in the British Army. As part of the Household Division, one of its principal roles is the protection of the monarchy; due to this, it often participates in state ceremoni ...
: July 2011
* RAF Brize Norton
Royal Air Force Brize Norton or RAF Brize Norton in Oxfordshire, about west north-west of London, is the largest station of the Royal Air Force. It is close to the village of Brize Norton, and the towns of Carterton and Witney.
The statio ...
: 21 October 2013.
* , RN: March 2014
Notable people
:''See List of people from Exeter and :People from Exeter''See also
*Exeter (HM Prison)
HM Prison Exeter is a category B local and resettlement men's prison, located in Exeter in the county of Devon, England. It holds men sentenced by the courts of Devon, Cornwall, Dorset and Somerset. There are also prisoners from further afi ...
* Henry Phillpotts
Henry Phillpotts (6 May 177818 September 1869), often called "Henry of Exeter", was the Anglican Bishop of Exeter from 1830 to 1869. One of England's longest serving bishops since the 14th century, Phillpotts was a striking figure of the 19t ...
References
Sources and further reading
* * * * * * * * *External links
Exeter City Council
from White's Devonshire Directory, 1850 * * {{Authority control Roman fortifications in Devon Cities in South West England Towns in Devon County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Devon Staple ports Roman legionary fortresses in England Unparished areas in Devon Boroughs in England