Evolutionary Clock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Evolution is the change in the
 Evolution in organisms occurs through changes in heritable characteristics—the inherited characteristics of an organism. In humans, for example,
Evolution in organisms occurs through changes in heritable characteristics—the inherited characteristics of an organism. In humans, for example,
 Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of a cell's genome and are the ultimate source of genetic variation in all organisms. When mutations occur, they may alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning, or have no effect.
About half of the mutations in the coding regions of protein-coding genes are deleterious — the other half are neutral. A small percentage of the total mutations in this region confer a fitness benefit. Some of the mutations in other parts of the genome are deleterious but the vast majority are neutral. A few are beneficial.
Mutations can involve large sections of a chromosome becoming duplicated (usually by
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of a cell's genome and are the ultimate source of genetic variation in all organisms. When mutations occur, they may alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning, or have no effect.
About half of the mutations in the coding regions of protein-coding genes are deleterious — the other half are neutral. A small percentage of the total mutations in this region confer a fitness benefit. Some of the mutations in other parts of the genome are deleterious but the vast majority are neutral. A few are beneficial.
Mutations can involve large sections of a chromosome becoming duplicated (usually by
 The two-fold cost of sex was first described by
The two-fold cost of sex was first described by
 From a neo-Darwinian perspective, evolution occurs when there are changes in the frequencies of alleles within a population of interbreeding organisms, for example, the allele for black colour in a population of moths becoming more common. Mechanisms that can lead to changes in allele frequencies include natural selection, genetic drift, and mutation bias.
From a neo-Darwinian perspective, evolution occurs when there are changes in the frequencies of alleles within a population of interbreeding organisms, for example, the allele for black colour in a population of moths becoming more common. Mechanisms that can lead to changes in allele frequencies include natural selection, genetic drift, and mutation bias.
 Natural selection within a population for a trait that can vary across a range of values, such as height, can be categorised into three different types. The first is
Natural selection within a population for a trait that can vary across a range of values, such as height, can be categorised into three different types. The first is
 Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of
Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of
 A special case of natural selection is sexual selection, which is selection for any trait that increases mating success by increasing the attractiveness of an organism to potential mates. Traits that evolved through sexual selection are particularly prominent among males of several animal species. Although sexually favoured, traits such as cumbersome antlers, mating calls, large body size and bright colours often attract predation, which compromises the survival of individual males. This survival disadvantage is balanced by higher reproductive success in males that show these hard-to-fake, sexually selected traits.
A special case of natural selection is sexual selection, which is selection for any trait that increases mating success by increasing the attractiveness of an organism to potential mates. Traits that evolved through sexual selection are particularly prominent among males of several animal species. Although sexually favoured, traits such as cumbersome antlers, mating calls, large body size and bright colours often attract predation, which compromises the survival of individual males. This survival disadvantage is balanced by higher reproductive success in males that show these hard-to-fake, sexually selected traits.
 Adaptation is the process that makes organisms better suited to their habitat. Also, the term adaptation may refer to a trait that is important for an organism's survival. For example, the adaptation of horses' teeth to the grinding of grass. By using the term ''adaptation'' for the evolutionary process and ''adaptive trait'' for the product (the bodily part or function), the two senses of the word may be distinguished. Adaptations are produced by natural selection. The following definitions are due to Theodosius Dobzhansky:
# ''Adaptation'' is the evolutionary process whereby an organism becomes better able to live in its habitat or habitats.
# ''Adaptedness'' is the state of being adapted: the degree to which an organism is able to live and reproduce in a given set of habitats.
# An ''adaptive trait'' is an aspect of the developmental pattern of the organism which enables or enhances the probability of that organism surviving and reproducing.
Adaptation may cause either the gain of a new feature, or the loss of an ancestral feature. An example that shows both types of change is bacterial adaptation to antibiotic selection, with genetic changes causing antibiotic resistance by both modifying the target of the drug, or increasing the activity of transporters that pump the drug out of the cell. Other striking examples are the bacteria ''
Adaptation is the process that makes organisms better suited to their habitat. Also, the term adaptation may refer to a trait that is important for an organism's survival. For example, the adaptation of horses' teeth to the grinding of grass. By using the term ''adaptation'' for the evolutionary process and ''adaptive trait'' for the product (the bodily part or function), the two senses of the word may be distinguished. Adaptations are produced by natural selection. The following definitions are due to Theodosius Dobzhansky:
# ''Adaptation'' is the evolutionary process whereby an organism becomes better able to live in its habitat or habitats.
# ''Adaptedness'' is the state of being adapted: the degree to which an organism is able to live and reproduce in a given set of habitats.
# An ''adaptive trait'' is an aspect of the developmental pattern of the organism which enables or enhances the probability of that organism surviving and reproducing.
Adaptation may cause either the gain of a new feature, or the loss of an ancestral feature. An example that shows both types of change is bacterial adaptation to antibiotic selection, with genetic changes causing antibiotic resistance by both modifying the target of the drug, or increasing the activity of transporters that pump the drug out of the cell. Other striking examples are the bacteria '' Adaptation occurs through the gradual modification of existing structures. Consequently, structures with similar internal organisation may have different functions in related organisms. This is the result of a single ancestral structure being adapted to function in different ways. The bones within bat wings, for example, are very similar to those in mice feet and
Adaptation occurs through the gradual modification of existing structures. Consequently, structures with similar internal organisation may have different functions in related organisms. This is the result of a single ancestral structure being adapted to function in different ways. The bones within bat wings, for example, are very similar to those in mice feet and
 Interactions between organisms can produce both conflict and cooperation. When the interaction is between pairs of species, such as a
Interactions between organisms can produce both conflict and cooperation. When the interaction is between pairs of species, such as a
 Speciation is the process where a species diverges into two or more descendant species.
There are multiple ways to define the concept of "species". The choice of definition is dependent on the particularities of the species concerned. For example, some species concepts apply more readily toward sexually reproducing organisms while others lend themselves better toward asexual organisms. Despite the diversity of various species concepts, these various concepts can be placed into one of three broad philosophical approaches: interbreeding, ecological and phylogenetic. The Biological Species Concept (BSC) is a classic example of the interbreeding approach. Defined by evolutionary biologist
Speciation is the process where a species diverges into two or more descendant species.
There are multiple ways to define the concept of "species". The choice of definition is dependent on the particularities of the species concerned. For example, some species concepts apply more readily toward sexually reproducing organisms while others lend themselves better toward asexual organisms. Despite the diversity of various species concepts, these various concepts can be placed into one of three broad philosophical approaches: interbreeding, ecological and phylogenetic. The Biological Species Concept (BSC) is a classic example of the interbreeding approach. Defined by evolutionary biologist
 Extinction is the disappearance of an entire species. Extinction is not an unusual event, as species regularly appear through speciation and disappear through extinction. Nearly all animal and plant species that have lived on Earth are now extinct, and extinction appears to be the ultimate fate of all species. These extinctions have happened continuously throughout the history of life, although the rate of extinction spikes in occasional mass
Extinction is the disappearance of an entire species. Extinction is not an unusual event, as species regularly appear through speciation and disappear through extinction. Nearly all animal and plant species that have lived on Earth are now extinct, and extinction appears to be the ultimate fate of all species. These extinctions have happened continuously throughout the history of life, although the rate of extinction spikes in occasional mass
 Due to horizontal gene transfer, this "tree of life" may be more complicated than a simple branching tree, since some genes have spread independently between distantly related species. To solve this problem and others, some authors prefer to use the " Coral of life" as a metaphor or a mathematical model to illustrate the evolution of life. This view dates back to an idea briefly mentioned by Darwin but later abandoned.
Past species have also left records of their evolutionary history. Fossils, along with the comparative anatomy of present-day organisms, constitute the morphological, or anatomical, record. By comparing the anatomies of both modern and extinct species, palaeontologists can infer the lineages of those species. However, this approach is most successful for organisms that had hard body parts, such as shells, bones or teeth. Further, as prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea share a limited set of common morphologies, their fossils do not provide information on their ancestry.
More recently, evidence for common descent has come from the study of biochemical similarities between organisms. For example, all living cells use the same basic set of nucleotides and
Due to horizontal gene transfer, this "tree of life" may be more complicated than a simple branching tree, since some genes have spread independently between distantly related species. To solve this problem and others, some authors prefer to use the " Coral of life" as a metaphor or a mathematical model to illustrate the evolution of life. This view dates back to an idea briefly mentioned by Darwin but later abandoned.
Past species have also left records of their evolutionary history. Fossils, along with the comparative anatomy of present-day organisms, constitute the morphological, or anatomical, record. By comparing the anatomies of both modern and extinct species, palaeontologists can infer the lineages of those species. However, this approach is most successful for organisms that had hard body parts, such as shells, bones or teeth. Further, as prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea share a limited set of common morphologies, their fossils do not provide information on their ancestry.
More recently, evidence for common descent has come from the study of biochemical similarities between organisms. For example, all living cells use the same basic set of nucleotides and




 In 1880, Marsh caught the attention of the scientific world with the publication of ''Odontornithes: a Monograph on Extinct Birds of North America,'' which included his discoveries of birds with teeth. These skeletons helped bridge the gap between dinosaurs and birds, and provided invaluable support for Darwin's theory of evolution. Darwin wrote to Marsh saying, "Your work on these old birds & on the many fossil animals of N. America has afforded the best support to the theory of evolution, which has appeared within the last 20 years" (since Darwin's publication of ''Origin of Species).
In 1880, Marsh caught the attention of the scientific world with the publication of ''Odontornithes: a Monograph on Extinct Birds of North America,'' which included his discoveries of birds with teeth. These skeletons helped bridge the gap between dinosaurs and birds, and provided invaluable support for Darwin's theory of evolution. Darwin wrote to Marsh saying, "Your work on these old birds & on the many fossil animals of N. America has afforded the best support to the theory of evolution, which has appeared within the last 20 years" (since Darwin's publication of ''Origin of Species).
The Complete Work of Charles Darwin Online
. Retrieved 2019-10-09. * The book is available fro
The Complete Work of Charles Darwin Online
. Retrieved 2014-11-21. * * * * * * * * * * "Proceedings of a symposium held at the American Museum of Natural History in New York, 2002." * * * * * * * * * * * . Retrieved 2014-11-29. * * * * * * * "Papers from the Symposium on the Limits of Reductionism in Biology, held at the Novartis Foundation, London, May 13–15, 1997." * * * * * * "Based on a conference held in Bellagio, Italy, June 25–30, 1989" * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
History of Evolution in the United States
.
heritable
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of Phenotypic trait, traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cell (biology), cells or orga ...
characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
and genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as random genetic drift, allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the Allele frequency, frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene va ...
act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
at every level of biological organisation
Biological organization is the organization of complex biological structures and systems that define life using a reductionistic approach. The traditional hierarchy, as detailed below, extends from atoms to biospheres. The higher levels of t ...
.
The scientific theory
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the universe, natural world that can be or that has been reproducibility, repeatedly tested and has corroborating evidence in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocol (s ...
of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
and Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 pap ...
, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'')The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by M ...
''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) traits vary among individuals with respect to their morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
, physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
, and behaviour; (3) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness); and (4) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of Animal husbandry, breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. T ...
of fitness). In successive generations, members of a population are therefore more likely to be replaced by the offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring ...
of parents with favourable characteristics for that environment.
In the early 20th century, competing ideas of evolution were refuted and evolution was combined with Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularize ...
and population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, s ...
to give rise to modern evolutionary theory. In this synthesis the basis for heredity is in DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
molecules that pass information from generation to generation. The processes that change DNA in a population include natural selection, genetic drift, mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
, and gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
.
All life on Earth—including humanity
Humanity most commonly refers to:
* Human, also humankind
* Humanity (virtue)
Humanity may also refer to:
Literature
* ''Humanity: A Moral History of the Twentieth Century'', a 1999 book by Jonathan Glover
* ''Humanity'', a 1990 science fiction n ...
—shares a last universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the hypothesized common ancestral cell from which the three domains of life, the Bacteria, the Archaea, and the Eukarya originated. The cell had a lipid bilayer; it possessed the genetic code a ...
(LUCA), which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. The fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
record includes a progression from early biogenic
A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. While the term originally was specific to metabolite compounds that had toxic effects on other organisms, it has developed to encompass any constituents, secretions, and metabolites of p ...
graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
to microbial mat
A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet or biofilm of microbial colonies, composed of mainly bacteria and/or archaea. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few surviv ...
fossils to fossilised multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped by repeated formations of new species (speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
), changes within species (anagenesis
Anagenesis is the gradual evolution of a species that continues to exist as an interbreeding population. This contrasts with cladogenesis, which occurs when branching or splitting occurs, leading to two or more lineages and resulting in separate ...
), and loss of species (extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
) throughout the evolutionary history of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and extinct organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for '' gigaannum'') and ...
on Earth. Morphological and biochemical
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, ...
traits tend to be more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
, which historically was used to reconstruct phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
s, although direct comparison of genetic sequences is a more common method today.
Evolutionary biologists
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary bi ...
have continued to study various aspects of evolution by forming and testing hypotheses
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific method, scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educ ...
as well as constructing theories based on evidence
Evidence for a proposition is what supports the proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the proposition is truth, true. The exact definition and role of evidence vary across different fields. In epistemology, evidence is what J ...
from the field or laboratory and on data generated by the methods of mathematical and theoretical biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development ...
. Their discoveries have influenced not just the development of biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
but also other fields including agriculture, medicine, and computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
.
Heredity
 Evolution in organisms occurs through changes in heritable characteristics—the inherited characteristics of an organism. In humans, for example,
Evolution in organisms occurs through changes in heritable characteristics—the inherited characteristics of an organism. In humans, for example, eye colour
Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic trait determined by two factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.
In humans, the pigmentation of ...
is an inherited characteristic and an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of their parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
(genetic material) is called its ''genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
''.
The complete set of observable traits that make up the structure and behaviour of an organism is called its ''phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
''. Some of these traits come from the interaction of its genotype with the environment while others are neutral. Some observable characteristics are not inherited. For example, suntanned skin comes from the interaction between a person's genotype and sunlight; thus, suntans are not passed on to people's children. The phenotype is the ability of the skin to tan when exposed to sunlight. However, some people tan more easily than others, due to differences in genotypic variation; a striking example are people with the inherited trait of albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.
Varied use and interpretation of ...
, who do not tan at all and are very sensitive to sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin tha ...
.
Heritable characteristics are passed from one generation to the next via DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, a molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
that encodes genetic information. DNA is a long biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, ...
composed of four types of bases. The sequence of bases along a particular DNA molecule specifies the genetic information, in a manner similar to a sequence of letters spelling out a sentence. Before a cell divides, the DNA is copied, so that each of the resulting two cells will inherit the DNA sequence. Portions of a DNA molecule that specify a single functional unit are called genes; different genes have different sequences of bases. Within cells, each long strand of DNA is called a chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
. The specific location of a DNA sequence within a chromosome is known as a locus. If the DNA sequence at a locus varies between individuals, the different forms of this sequence are called alleles. DNA sequences can change through mutations, producing new alleles. If a mutation occurs within a gene, the new allele may affect the trait that the gene controls, altering the phenotype of the organism. However, while this simple correspondence between an allele and a trait works in some cases, most traits are influenced by multiple genes in a quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis
...
or epistatic
Epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics in which the effect of a gene mutation is dependent on the presence or absence of mutations in one or more other genes, respectively termed modifier genes. In other words, the effect of the mutation is depe ...
manner.
Sources of variation
Evolution can occur if there is genetic variation within a population. Variation comes from mutations in the genome, reshuffling of genes throughsexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
and migration between populations (gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
). Despite the constant introduction of new variation through mutation and gene flow, most of the genome of a species is very similar among all individuals of that species. However, discoveries in the field of evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. ...
have demonstrated that even relatively small differences in genotype can lead to dramatic differences in phenotype both within and between species.
An individual organism's phenotype results from both its genotype and the influence of the environment it has lived in. The modern evolutionary synthesis defines evolution as the change over time in this genetic variation. The frequency of one particular allele will become more or less prevalent relative to other forms of that gene. Variation disappears when a new allele reaches the point of fixation—when it either disappears from the population or replaces the ancestral allele entirely.
Mutation
genetic recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryot ...
), which can introduce extra copies of a gene into a genome. Extra copies of genes are a major source of the raw material needed for new genes to evolve. This is important because most new genes evolve within gene families
A gene family is a set of several similar genes, formed by duplication of a single original gene, and generally with similar biochemical functions. One such family are the genes for human hemoglobin subunits; the ten genes are in two clusters on ...
from pre-existing genes that share common ancestors. For example, the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to light, visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and Balance (ability), keeping balance.
The eye can be considered as a living ...
uses four genes to make structures that sense light: three for colour vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different frequencies independently of light intensity.
Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a co ...
and one for night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night v ...
; all four are descended from a single ancestral gene.
New genes can be generated from an ancestral gene when a duplicate copy mutates and acquires a new function. This process is easier once a gene has been duplicated because it increases the redundancy of the system; one gene in the pair can acquire a new function while the other copy continues to perform its original function. Other types of mutations can even generate entirely new genes from previously noncoding DNA, a phenomenon termed ''de novo'' gene birth.
The generation of new genes can also involve small parts of several genes being duplicated, with these fragments then recombining to form new combinations with new functions (exon shuffling
Exon shuffling is a molecular mechanism for the formation of new genes. It is a process through which two or more exons from different genes can be brought together ectopically, or the same exon can be duplicated, to create a new exon-intron st ...
). When new genes are assembled from shuffling pre-existing parts, domains act as modules with simple independent functions, which can be mixed together to produce new combinations with new and complex functions. For example, polyketide synthase
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi- domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share ...
s are large enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s that make antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s; they contain up to 100 independent domains that each catalyse one step in the overall process, like a step in an assembly line.
One example of mutation is wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
piglets. They are camouflage coloured and show a characteristic pattern of dark and light longitudinal stripes. However, mutations in the ''melanocortin 1 receptor
The melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), also known as melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MSHR), melanin-activating peptide receptor, or melanotropin receptor, is a G protein–coupled receptor that binds to a class of pituitary peptide hormon ...
'' (''MC1R'') disrupt the pattern. The majority of pig breeds carry MC1R mutations disrupting wild-type colour and different mutations causing dominant black colouring.
Sex and recombination
Inasexual
Asexual or Asexuals may refer to:
*Asexual reproduction
**Asexual reproduction in starfish
*Asexuality, the lack of sexual attraction to anyone or lack of interest in or desire for sexual activity.
**Gray asexuality, the spectrum between asexualit ...
organisms, genes are inherited together, or ''linked'', as they cannot mix with genes of other organisms during reproduction. In contrast, the offspring of sexual organisms contain random mixtures of their parents' chromosomes that are produced through independent assortment. In a related process called homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organi ...
, sexual organisms exchange DNA between two matching chromosomes. Recombination and reassortment do not alter allele frequencies, but instead change which alleles are associated with each other, producing offspring with new combinations of alleles. Sex usually increases genetic variation and may increase the rate of evolution.
John Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith (6 January 1920 – 19 April 2004) was a British mathematical and theoretical biology, theoretical and mathematical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he ...
. The first cost is that in sexually dimorphic species only one of the two sexes can bear young. This cost does not apply to hermaphroditic species, like most plants and many invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s. The second cost is that any individual who reproduces sexually can only pass on 50% of its genes to any individual offspring, with even less passed on as each new generation passes. Yet sexual reproduction is the more common means of reproduction among eukaryotes and multicellular organisms. The Red Queen hypothesis
The Red Queen's hypothesis is a hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposed in 1973, that species must constantly adapt, evolve, and proliferate in order to survive while pitted against ever-evolving opposing species. The hypothesis was intende ...
has been used to explain the significance of sexual reproduction as a means to enable continual evolution and adaptation in response to coevolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well a ...
with other species in an ever-changing environment. Another hypothesis is that sexual reproduction is primarily an adaptation for promoting accurate recombinational repair of damage in germline DNA, and that increased diversity is a byproduct of this process that may sometimes be adaptively beneficial.
Gene flow
Gene flow is the exchange of genes between populations and between species. It can therefore be a source of variation that is new to a population or to a species. Gene flow can be caused by the movement of individuals between separate populations of organisms, as might be caused by the movement of mice between inland and coastal populations, or the movement ofpollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
between heavy-metal-tolerant and heavy-metal-sensitive populations of grasses.
Gene transfer between species includes the formation of hybrid
Hybrid may refer to:
Science
* Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding
** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species
** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two diff ...
organisms and horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
. Horizontal gene transfer is the transfer of genetic material from one organism to another organism that is not its offspring; this is most common among bacteria. In medicine, this contributes to the spread of antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis ...
, as when one bacteria acquires resistance genes it can rapidly transfer them to other species. Horizontal transfer of genes from bacteria to eukaryotes such as the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'' and the adzuki bean weevil ''Callosobruchus chinensis
''Callosobruchus chinensis'', also known as the adzuki bean weevil, pulse beetle, Chinese bruchid or cowpea bruchid, is a common species of beetle found in the bean weevil subfamily. Although it is commonly known as the "adzuki bean weevil" it i ...
'' has occurred. An example of larger-scale transfers are the eukaryotic bdelloid rotifers
Bdelloidea (from Greek βδέλλα, ''bdella'' 'leech') is a class of rotifers found in freshwater habitats all over the world. There are over 450 described species of bdelloid rotifers (or 'bdelloids'), distinguished from each other mainly o ...
, which have received a range of genes from bacteria, fungi and plants. Viruses can also carry DNA between organisms, allowing transfer of genes even across biological domains.
Large-scale gene transfer has also occurred between the ancestors of eukaryotic cell
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Out ...
s and bacteria, during the acquisition of chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s and mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
. It is possible that eukaryotes themselves originated from horizontal gene transfers between bacteria and archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
.
Epigenetics
Some heritable changes cannot be explained by changes to the sequence ofnucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s in the DNA. These phenomena are classed as epigenetic inheritance systems. DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter (genetics), promoter, DNA methylati ...
marking chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
, self-sustaining metabolic loops, gene silencing by RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by ...
and the three-dimensional conformation of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s (such as prion
A prion () is a Proteinopathy, misfolded protein that induces misfolding in normal variants of the same protein, leading to cellular death. Prions are responsible for prion diseases, known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSEs), w ...
s) are areas where epigenetic inheritance systems have been discovered at the organismic level. Developmental biologists suggest that complex interactions in genetic networks and communication among cells can lead to heritable variations that may underlay some of the mechanics in developmental plasticity
Developmental plasticity refers to changes in neural connections during growth, influenced by environmental interactions and learning. Similar to brain plasticity, it specifically involves how neurons and synapses adapt during development. Most of ...
and canalisation. Heritability may also occur at even larger scales. For example, ecological inheritance through the process of niche construction
Niche construction is the ecological process by which an organism alters its own (or another species') local environment. These alterations can be a physical change to the organism’s environment, or it can encompass the active movement of an or ...
is defined by the regular and repeated activities of organisms in their environment. This generates a legacy of effects that modify and feed back into the selection regime of subsequent generations. Other examples of heritability in evolution that are not under the direct control of genes include the inheritance of cultural traits and symbiogenesis
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibl ...
.
Evolutionary forces
Natural selection
Evolution by natural selection is the process by which traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in successive generations of a population. It embodies three principles: * Variation exists within populations of organisms with respect to morphology, physiology and behaviour (phenotypic variation). * Different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness). * These traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). More offspring are produced than can possibly survive, and these conditions produce competition between organisms for survival and reproduction. Consequently, organisms with traits that give them an advantage over their competitors are more likely to pass on their traits to the next generation than those with traits that do not confer an advantage. Thisteleonomy
Teleonomy is the quality of apparent purposefulness and of goal-directedness of structures and functions in living organisms brought about by natural processes like natural selection. The term derives from two Greek words, τέλος, from τελε ...
is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Consequences of selection include nonrandom mating and genetic hitchhiking
Genetic hitchhiking, also called genetic draft or the hitchhiking effect, is when an allele changes frequency not because it itself is under natural selection, but because it is near another gene that is undergoing a selective sweep and that is ...
.
The central concept of natural selection is the evolutionary fitness of an organism. Fitness is measured by an organism's ability to survive and reproduce, which determines the size of its genetic contribution to the next generation. However, fitness is not the same as the total number of offspring: instead fitness is indicated by the proportion of subsequent generations that carry an organism's genes. For example, if an organism could survive well and reproduce rapidly, but its offspring were all too small and weak to survive, this organism would make little genetic contribution to future generations and would thus have low fitness.
If an allele increases fitness more than the other alleles of that gene, then with each generation this allele has a higher probability of becoming common within the population. These traits are said to be selected for. Examples of traits that can increase fitness are enhanced survival and increased fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the capability to produc ...
. Conversely, the lower fitness caused by having a less beneficial or deleterious allele results in this allele likely becoming rarer—they are selected against.
Importantly, the fitness of an allele is not a fixed characteristic; if the environment changes, previously neutral or harmful traits may become beneficial and previously beneficial traits become harmful. However, even if the direction of selection does reverse in this way, traits that were lost in the past may not re-evolve in an identical form. However, a re-activation of dormant genes, as long as they have not been eliminated from the genome and were only suppressed perhaps for hundreds of generations, can lead to the re-occurrence of traits thought to be lost like hindlegs in dolphins, teeth in chickens, wings in wingless stick insects, tails and additional nipples in humans etc. "Throwbacks" such as these are known as atavism
In biology, an atavism is a modification of a biological traits structure or behavior whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change in previous generations. Atavisms can occur in several ways, ...
s.
directional selection
In population genetics, directional selection is a type of natural selection in which one extreme phenotype is favored over both the other extreme and moderate phenotypes. This genetic selection causes the allele frequency to shift toward the ...
, which is a shift in the average value of a trait over time—for example, organisms slowly getting taller. Secondly, disruptive selection
In evolutionary biology, disruptive selection, also called diversifying selection, describes changes in population genetics in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values. In this case, the variance of the trait in ...
is selection for extreme trait values and often results in two different values becoming most common, with selection against the average value. This would be when either short or tall organisms had an advantage, but not those of medium height. Finally, in stabilising selection
Stabilizing selection (not to be confused with negative or purifying selection) is a type of natural selection in which the population mean stabilizes on a particular non-extreme trait value. This is thought to be the most common mechanism of ...
there is selection against extreme trait values on both ends, which causes a decrease in variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion ...
around the average value and less diversity. This would, for example, cause organisms to eventually have a similar height.
Natural selection most generally makes nature the measure against which individuals and individual traits, are more or less likely to survive. "Nature" in this sense refers to an ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
, that is, a system in which organisms interact with every other element, physical as well as biological
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of ...
, in their local environment. Eugene Odum
Eugene Pleasants Odum (September 17, 1913 – August 10, 2002) was an American biologist at the University of Georgia known for his pioneering work on ecosystem ecology. He and his brother Howard T. Odum wrote the popular ecology textbook, ''Fun ...
, a founder of ecology, defined an ecosystem as: "Any unit that includes all of the organisms...in a given area interacting with the physical environment so that a flow of energy leads to clearly defined trophic structure, biotic diversity, and material cycles (i.e., exchange of materials between living and nonliving parts) within the system...." Each population within an ecosystem occupies a distinct niche, or position, with distinct relationships to other parts of the system. These relationships involve the life history of the organism, its position in the food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
and its geographic range. This broad understanding of nature enables scientists to delineate specific forces which, together, comprise natural selection.
Natural selection can act at different levels of organisation, such as genes, cells, individual organisms, groups of organisms and species. Selection can act at multiple levels simultaneously. An example of selection occurring below the level of the individual organism are genes called transposons
A transposable element (TE), also transposon, or jumping gene, is a type of mobile genetic element, a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome.
The discovery of mobile genetic elements earned Barbara McClinto ...
, which can replicate and spread throughout a genome. Selection at a level above the individual, such as group selection
Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection acts at the level of the group, instead of at the level of the individual or gene.
Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the beha ...
, may allow the evolution of cooperation.
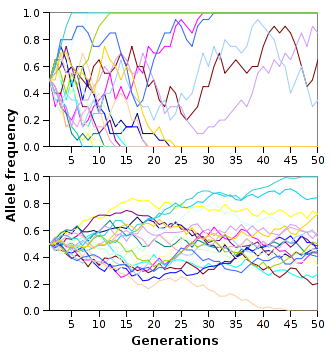
Genetic drift
 Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of
Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies
Allele frequency, or gene frequency, is the relative frequency of an allele (variant of a gene) at a particular locus in a population, expressed as a fraction or percentage. Specifically, it is the fraction of all chromosomes in the population tha ...
within a population from one generation to the next. When selective forces are absent or relatively weak, allele frequencies are equally likely to ''drift'' upward or downward in each successive generation because the alleles are subject to sampling error
In statistics, sampling errors are incurred when the statistical characteristics of a population are estimated from a subset, or sample, of that population. Since the sample does not include all members of the population, statistics of the sample ...
. This drift halts when an allele eventually becomes fixed, either by disappearing from the population or by replacing the other alleles entirely. Genetic drift may therefore eliminate some alleles from a population due to chance alone. Even in the absence of selective forces, genetic drift can cause two separate populations that begin with the same genetic structure to drift apart into two divergent populations with different sets of alleles.
According to the neutral theory of molecular evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution holds that most evolutionary changes occur at the molecular level, and most of the variation within and between species are due to random genetic drift of mutant alleles that are selectively neutral. The ...
most evolutionary changes are the result of the fixation of neutral mutation
Neutral mutations are changes in DNA sequence that are neither beneficial nor detrimental to the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce. In population genetics, mutations in which natural selection does not affect the spread of the mutatio ...
s by genetic drift. In this model, most genetic changes in a population are thus the result of constant mutation pressure and genetic drift. This form of the neutral theory has been debated since it does not seem to fit some genetic variation seen in nature. A better-supported version of this model is the nearly neutral theory
The nearly neutral theory of molecular evolution is a modification of the neutral theory of molecular evolution that accounts for the fact that not all mutations are either so deleterious such that they can be ignored, or else neutral. Slightly del ...
, according to which a mutation that would be effectively neutral in a small population is not necessarily neutral in a large population. Other theories propose that genetic drift is dwarfed by other stochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
forces in evolution, such as genetic hitchhiking, also known as genetic draft. Another concept is constructive neutral evolution
Constructive neutral evolution (CNE) is a theory that seeks to explain how complex systems can evolve through neutral transitions and spread through a population by chance fixation (genetic drift). Constructive neutral evolution is a competitor fo ...
(CNE), which explains that complex systems can emerge and spread into a population through neutral transitions due to the principles of excess capacity, presuppression, and ratcheting, and it has been applied in areas ranging from the origins of the spliceosome
A spliceosome is a large ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear RNAs ( snRNA) and numerous proteins. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules bind to sp ...
to the complex interdependence of microbial communities.
The time it takes a neutral allele to become fixed by genetic drift depends on population size; fixation is more rapid in smaller populations. The number of individuals in a population is not critical, but instead a measure known as the effective population size. The effective population is usually smaller than the total population since it takes into account factors such as the level of inbreeding and the stage of the lifecycle in which the population is the smallest. The effective population size may not be the same for every gene in the same population.
It is usually difficult to measure the relative importance of selection and neutral processes, including drift. The comparative importance of adaptive and non-adaptive forces in driving evolutionary change is an area of current research.
Mutation bias
Mutation bias is usually conceived as a difference in expected rates for two different kinds of mutation, e.g., transition-transversion bias, GC-AT bias, deletion-insertion bias. This is related to the idea ofdevelopmental bias In evolutionary biology, developmental bias refers to the production against or towards certain Ontogeny, ontogenetic trajectories which ultimately influence the direction and outcome of evolutionary change by affecting the rates, magnitudes, direct ...
. J. B. S. Haldane
John Burdon Sanderson Haldane (; 5 November 18921 December 1964), nicknamed "Jack" or "JBS", was a British-born scientist who later moved to India and acquired Indian citizenship. He worked in the fields of physiology, genetics, evolutionary ...
and Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who a ...
argued that, because mutation is a weak pressure easily overcome by selection, tendencies of mutation would be ineffectual except under conditions of neutral evolution or extraordinarily high mutation rates. This opposing-pressures argument was long used to dismiss the possibility of internal tendencies in evolution, until the molecular era prompted renewed interest in neutral evolution.
Noboru Sueoka and Ernst Freese proposed that systematic biases in mutation might be responsible for systematic differences in genomic GC composition between species. The identification of a GC-biased ''E. coli'' mutator strain in 1967, along with the proposal of the neutral theory Neutral theory may refer to one of these two related theories:
* Neutral theory of molecular evolution
* Unified neutral theory of biodiversity
The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography (here "Unified Theory" or "UNTB") is a t ...
, established the plausibility of mutational explanations for molecular patterns, which are now common in the molecular evolution literature.
For instance, mutation biases are frequently invoked in models of codon usage. Such models also include effects of selection, following the mutation-selection-drift model, which allows both for mutation biases and differential selection based on effects on translation. Hypotheses of mutation bias have played an important role in the development of thinking about the evolution of genome composition, including isochores. Different insertion vs. deletion biases in different taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
can lead to the evolution of different genome sizes. The hypothesis of Lynch regarding genome size relies on mutational biases toward increase or decrease in genome size.
However, mutational hypotheses for the evolution of composition suffered a reduction in scope when it was discovered that (1) GC-biased gene conversion makes an important contribution to composition in diploid organisms such as mammals and (2) bacterial genomes frequently have AT-biased mutation.
Contemporary thinking about the role of mutation biases reflects a different theory from that of Haldane and Fisher. More recent work showed that the original "pressures" theory assumes that evolution is based on standing variation: when evolution depends on events of mutation that introduce new alleles, mutational and developmental biases in the introduction of variation (arrival biases) can impose biases on evolution without requiring neutral evolution or high mutation rates.
Several studies report that the mutations implicated in adaptation reflect common mutation biases though others dispute this interpretation.
Genetic hitchhiking
Recombination allows alleles on the same strand of DNA to become separated. However, the rate of recombination is low (approximately two events per chromosome per generation). As a result, genes close together on a chromosome may not always be shuffled away from each other and genes that are close together tend to be inherited together, a phenomenon known as linkage. This tendency is measured by finding how often two alleles occur together on a single chromosome compared to expectations, which is called theirlinkage disequilibrium Linkage disequilibrium, often abbreviated to LD, is a term in population genetics referring to the association of genes, usually linked genes, in a population. It has become an important tool in medical genetics and other fields
In defining LD, it ...
. A set of alleles that is usually inherited in a group is called a haplotype
A haplotype (haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material (DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA orga ...
. This can be important when one allele in a particular haplotype is strongly beneficial: natural selection can drive a selective sweep
In genetics, a selective sweep is the process through which a new beneficial mutation that increases its frequency and becomes fixed (i.e., reaches a frequency of 1) in the population leads to the reduction or elimination of genetic variation amon ...
that will also cause the other alleles in the haplotype to become more common in the population; this effect is called genetic hitchhiking or genetic draft. Genetic draft caused by the fact that some neutral genes are genetically linked to others that are under selection can be partially captured by an appropriate effective population size.
Sexual selection
 A special case of natural selection is sexual selection, which is selection for any trait that increases mating success by increasing the attractiveness of an organism to potential mates. Traits that evolved through sexual selection are particularly prominent among males of several animal species. Although sexually favoured, traits such as cumbersome antlers, mating calls, large body size and bright colours often attract predation, which compromises the survival of individual males. This survival disadvantage is balanced by higher reproductive success in males that show these hard-to-fake, sexually selected traits.
A special case of natural selection is sexual selection, which is selection for any trait that increases mating success by increasing the attractiveness of an organism to potential mates. Traits that evolved through sexual selection are particularly prominent among males of several animal species. Although sexually favoured, traits such as cumbersome antlers, mating calls, large body size and bright colours often attract predation, which compromises the survival of individual males. This survival disadvantage is balanced by higher reproductive success in males that show these hard-to-fake, sexually selected traits.
Natural outcomes
Evolution influences every aspect of the form and behaviour of organisms. Most prominent are the specific behavioural and physical adaptations that are the outcome of natural selection. These adaptations increase fitness by aiding activities such as finding food, avoidingpredators
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
or attracting mates. Organisms can also respond to selection by cooperating with each other, usually by aiding their relatives or engaging in mutually beneficial symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can fo ...
. In the longer term, evolution produces new species through splitting ancestral populations of organisms into new groups that cannot or will not interbreed. These outcomes of evolution are distinguished based on time scale as macroevolution
Macroevolution comprises the evolutionary processes and patterns which occur at and above the species level. In contrast, microevolution is evolution occurring within the population(s) of a single species. In other words, microevolution is the ...
versus microevolution. Macroevolution refers to evolution that occurs at or above the level of species, in particular speciation and extinction, whereas microevolution refers to smaller evolutionary changes within a species or population, in particular shifts in allele frequency and adaptation. Macroevolution is the outcome of long periods of microevolution. Thus, the distinction between micro- and macroevolution is not a fundamental one—the difference is simply the time involved. However, in macroevolution, the traits of the entire species may be important. For instance, a large amount of variation among individuals allows a species to rapidly adapt to new habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
s, lessening the chance of it going extinct, while a wide geographic range increases the chance of speciation, by making it more likely that part of the population will become isolated. In this sense, microevolution and macroevolution might involve selection at different levels—with microevolution acting on genes and organisms, versus macroevolutionary processes such as species selection
A unit of selection is a biological entity within the hierarchy of biological organization (for example, an entity such as: a self-replicating molecule, a gene, a cell, an organism, a group, or a species) that is subject to natural selection. T ...
acting on entire species and affecting their rates of speciation and extinction.
A common misconception is that evolution has goals, long-term plans, or an innate tendency for "progress", as expressed in beliefs such as orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is an Superseded theories in science, obsolete biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolution, evolve ...
and evolutionism; realistically, however, evolution has no long-term goal and does not necessarily produce greater complexity. Although complex species have evolved, they occur as a side effect of the overall number of organisms increasing, and simple forms of life still remain more common in the biosphere. For example, the overwhelming majority of species are microscopic prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s, which form about half the world's biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
despite their small size and constitute the vast majority of Earth's biodiversity. Simple organisms have therefore been the dominant form of life on Earth throughout its history and continue to be the main form of life up to the present day, with complex life only appearing more diverse because it is more noticeable. Indeed, the evolution of microorganisms is particularly important to evolutionary research since their rapid reproduction allows the study of experimental evolution
Experimental evolution is the use of laboratory experiments or controlled field manipulations to explore evolutionary dynamics. Evolution may be observed in the laboratory as populations adapt to new environmental conditions by natural selection. ...
and the observation of evolution and adaptation in real time.
Adaptation
Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' evolving the ability to use citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a Transparency and translucency, colorless Weak acid, weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in Citrus, citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, ...
as a nutrient in a long-term laboratory experiment, ''Flavobacterium
''Flavobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative, nonmotile and motile, rod-shaped bacteria that consists of 130 recognized species. Flavobacteria are found in soil and fresh water in a variety of environments. Several species are known to cause ...
'' evolving a novel enzyme that allows these bacteria to grow on the by-products of nylon manufacturing, and the soil bacterium '' Sphingobium'' evolving an entirely new metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
that degrades the synthetic pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
pentachlorophenol
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) is an organochlorine compound used as a pesticide and a disinfectant. First produced in the 1930s, it is marketed under many trade names. It can be found as pure PCP, or as the sodium salt of PCP, the latter of which disso ...
. An interesting but still controversial idea is that some adaptations might increase the ability of organisms to generate genetic diversity and adapt by natural selection (increasing organisms' evolvability).
 Adaptation occurs through the gradual modification of existing structures. Consequently, structures with similar internal organisation may have different functions in related organisms. This is the result of a single ancestral structure being adapted to function in different ways. The bones within bat wings, for example, are very similar to those in mice feet and
Adaptation occurs through the gradual modification of existing structures. Consequently, structures with similar internal organisation may have different functions in related organisms. This is the result of a single ancestral structure being adapted to function in different ways. The bones within bat wings, for example, are very similar to those in mice feet and primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
hands, due to the descent of all these structures from a common mammalian ancestor. However, since all living organisms are related to some extent, even organs that appear to have little or no structural similarity, such as arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
, squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ...
and vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
eyes, or the limbs and wings of arthropods and vertebrates, can depend on a common set of homologous genes that control their assembly and function; this is called deep homology
In evolutionary developmental biology, the concept of deep homology is used to describe cases where growth and differentiation processes are governed by genetic mechanisms that are homologous and deeply conserved across a wide range of specie ...
.
During evolution, some structures may lose their original function and become vestigial structures. Such structures may have little or no function in a current species, yet have a clear function in ancestral species, or other closely related species. Examples include pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Pseudogenes can be formed from both protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. In the case of protein-coding genes, most pseudogenes arise as superfluous copies of fun ...
s, the non-functional remains of eyes in blind cave-dwelling fish, wings in flightless birds, the presence of hip bones in whales and snakes, and sexual traits in organisms that reproduce via asexual reproduction. Examples of vestigial structures in humans include wisdom teeth
The third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is the most posterior of the three molars in each quadrant of the human dentition. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens a ...
, the coccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
, the vermiform appendix
The appendix (: appendices or appendixes; also vermiform appendix; cecal (or caecal, cæcal) appendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo.
The cecum ...
, and other behavioural vestiges such as goose bumps
Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose pimples are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is Tickling, tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousa ...
and primitive reflexes
Primitive reflexes are reflex actions originating in the central nervous system that are exhibited by normal infants, but not neurologically intact adults, in response to particular stimuli. These reflexes are suppressed by the development of th ...
.
However, many traits that appear to be simple adaptations are in fact exaptation
Exaptation or co-option is a shift in the function of a trait during evolution. For example, a trait can evolve because it served one particular function, but subsequently it may come to serve another. Exaptations are common in both anatomy and be ...
s: structures originally adapted for one function, but which coincidentally became somewhat useful for some other function in the process. One example is the African lizard ''Holaspis guentheri'', which developed an extremely flat head for hiding in crevices, as can be seen by looking at its near relatives. However, in this species, the head has become so flattened that it assists in gliding from tree to tree—an exaptation. Within cells, molecular machine
Molecular machines are a class of molecules typically described as an assembly of a discrete number of molecular components intended to produce mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli, mimicking macromolecular devices such as switch ...
s such as the bacterial flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
and protein sorting machinery evolved by the recruitment of several pre-existing proteins that previously had different functions. Another example is the recruitment of enzymes from glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
and xenobiotic metabolism
Xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos (Greek), xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal bi ...
to serve as structural proteins called crystallin
In anatomy, a crystallin is a water-soluble structural protein found in the lens and the cornea of the eye accounting for the transparency of the structure. It has also been identified in other places such as the heart, and in aggressive breast ...
s within the lenses of organisms' eyes.
An area of current investigation in evolutionary developmental biology is the developmental basis of adaptations and exaptations. This research addresses the origin and evolution of embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
and how modifications of development and developmental processes produce novel features. These studies have shown that evolution can alter development to produce new structures, such as embryonic bone structures that develop into the jaw in other animals instead forming part of the middle ear in mammals. It is also possible for structures that have been lost in evolution to reappear due to changes in developmental genes, such as a mutation in chickens causing embryos to grow teeth similar to those of crocodiles. It is now becoming clear that most alterations in the form of organisms are due to changes in a small set of conserved genes.
Coevolution
 Interactions between organisms can produce both conflict and cooperation. When the interaction is between pairs of species, such as a
Interactions between organisms can produce both conflict and cooperation. When the interaction is between pairs of species, such as a pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
and a host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
* Host Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica
People
* ...
, or a predator and its prey, these species can develop matched sets of adaptations. Here, the evolution of one species causes adaptations in a second species. These changes in the second species then, in turn, cause new adaptations in the first species. This cycle of selection and response is called coevolution. An example is the production of tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an Order (biology), order that includes Tetraodontidae, pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Alt ...
in the rough-skinned newt
The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt (''Taricha granulosa'') is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin.
Appearance
A stocky newt with rounded snout, it ranges from light brown to olive or brownish-black on t ...
and the evolution of tetrodotoxin resistance in its predator, the common garter snake. In this predator-prey pair, an evolutionary arms race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling the ...
has produced high levels of toxin in the newt and correspondingly high levels of toxin resistance in the snake.
Cooperation
Not all co-evolved interactions between species involve conflict. Many cases of mutually beneficial interactions have evolved. For instance, an extreme cooperation exists between plants and themycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza (; , mycorrhiza, or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, the plant root system and its surroundings. Mycorrhizae play ...
l fungi that grow on their roots and aid the plant in absorbing nutrients from the soil. This is a reciprocal
Reciprocal may refer to:
In mathematics
* Multiplicative inverse, in mathematics, the number 1/''x'', which multiplied by ''x'' gives the product 1, also known as a ''reciprocal''
* Reciprocal polynomial, a polynomial obtained from another pol ...
relationship as the plants provide the fungi with sugars from photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
. Here, the fungi actually grow inside plant cells, allowing them to exchange nutrients with their hosts, while sending signals
A signal is both the process and the result of Signal transmission, transmission of data over some transmission media, media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processin ...
that suppress the plant immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
.
Coalitions between organisms of the same species have also evolved. An extreme case is the eusociality
Eusociality ( Greek 'good' and social) is the highest level of organization of sociality. It is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations wit ...
found in social insects, such as bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamil ...
s, termite
Termites are a group of detritivore, detritophagous Eusociality, eusocial cockroaches which consume a variety of Detritus, decaying plant material, generally in the form of wood, Plant litter, leaf litter, and Humus, soil humus. They are dist ...
s and ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
s, where sterile insects feed and guard the small number of organisms in a colony
A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule, which rules the territory and its indigenous peoples separated from the foreign rulers, the colonizer, and their ''metropole'' (or "mother country"). This separated rule was often orga ...
that are able to reproduce. On an even smaller scale, the somatic cells that make up the body of an animal limit their reproduction so they can maintain a stable organism, which then supports a small number of the animal's germ cells to produce offspring. Here, somatic cells respond to specific signals that instruct them whether to grow, remain as they are, or die. If cells ignore these signals and multiply inappropriately, their uncontrolled growth causes cancer.
Such cooperation within species may have evolved through the process of kin selection
Kin selection is a process whereby natural selection favours a trait due to its positive effects on the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even when at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction. Kin selection can lead ...
, which is where one organism acts to help raise a relative's offspring. This activity is selected for because if the ''helping'' individual contains alleles which promote the helping activity, it is likely that its kin will ''also'' contain these alleles and thus those alleles will be passed on. Other processes that may promote cooperation include group selection, where cooperation provides benefits to a group of organisms.
Speciation
Ernst Mayr
Ernst Walter Mayr ( ; ; 5 July 1904 – 3 February 2005) was a German-American evolutionary biologist. He was also a renowned Taxonomy (biology), taxonomist, tropical explorer, ornithologist, Philosophy of biology, philosopher of biology, and ...
in 1942, the BSC states that "species are groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations, which are reproductively isolated from other such groups." Despite its wide and long-term use, the BSC like other species concepts is not without controversy, for example, because genetic recombination among prokaryotes is not an intrinsic aspect of reproduction; this is called the species problem
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. Some researchers have attempted a unifying monistic definition of species, while others adopt a pluralistic approach and suggest that there may be different ways to logically interpret the definition of a species.
Barriers to reproduction between two diverging sexual populations are required for the populations to become new species. Gene flow may slow this process by spreading the new genetic variants also to the other populations. Depending on how far two species have diverged since their most recent common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
, it may still be possible for them to produce offspring, as with horses and donkeys mating to produce mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
s. Such hybrids are generally infertile
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's sta ...
. In this case, closely related species may regularly interbreed, but hybrids will be selected against and the species will remain distinct. However, viable hybrids are occasionally formed and these new species can either have properties intermediate between their parent species, or possess a totally new phenotype. The importance of hybridisation in producing new species of animals is unclear, although cases have been seen in many types of animals, with the grey tree frog
The gray treefrog (''Dryophytes versicolor'') is a species of small arboreal holarctic tree frog native to much of the eastern United States and southeastern Canada.
It is sometimes referred to as the eastern gray treefrog, northern gray treef ...
being a particularly well-studied example.
Speciation has been observed multiple times under both controlled laboratory conditions and in nature. In sexually reproducing organisms, speciation results from reproductive isolation followed by genealogical divergence. There are four primary geographic modes of speciation. The most common in animals is allopatric speciation
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from ...
, which occurs in populations initially isolated geographically, such as by habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological proces ...
or migration. Selection under these conditions can produce very rapid changes in the appearance and behaviour of organisms. As selection and drift act independently on populations isolated from the rest of their species, separation may eventually produce organisms that cannot interbreed.
The second mode of speciation is peripatric speciation
Peripatric speciation is a mode of speciation in which a new species is formed from an isolated peripheral population. Since peripatric speciation resembles allopatric speciation, in that populations are isolated and prevented from Gene flow, ex ...
, which occurs when small populations of organisms become isolated in a new environment. This differs from allopatric speciation in that the isolated populations are numerically much smaller than the parental population. Here, the founder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, us ...
causes rapid speciation after an increase in inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genet ...
increases selection on homozygotes, leading to rapid genetic change.
The third mode is parapatric speciation. This is similar to peripatric speciation in that a small population enters a new habitat, but differs in that there is no physical separation between these two populations. Instead, speciation results from the evolution of mechanisms that reduce gene flow between the two populations. Generally this occurs when there has been a drastic change in the environment within the parental species' habitat. One example is the grass ''Anthoxanthum
''Anthoxanthum'' (Latinised Greek for "yellow blossom"), commonly known as hornworts, vernal grasses, or vernalgrasses, is a genus of plants in the grass family. The generic name means 'Yellow flower' in Botanical Latin, referring to the colo ...
odoratum'', which can undergo parapatric speciation in response to localised metal pollution from mines. Here, plants evolve that have resistance to high levels of metals in the soil. Selection against interbreeding with the metal-sensitive parental population produced a gradual change in the flowering time of the metal-resistant plants, which eventually produced complete reproductive isolation. Selection against hybrids between the two populations may cause reinforcement
In Behaviorism, behavioral psychology, reinforcement refers to consequences that increase the likelihood of an organism's future behavior, typically in the presence of a particular ''Antecedent (behavioral psychology), antecedent stimulus''. Fo ...
, which is the evolution of traits that promote mating within a species, as well as character displacement
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to Theoph ...
, which is when two species become more distinct in appearance.
Finally, in sympatric speciation
Sympatric speciation is the evolution of a new species from a surviving Common descent, ancestral species while both continue to inhabit the same geographic region. In evolutionary biology and biogeography, ''sympatric'' and ''sympatry'' are ter ...
species diverge without geographic isolation or changes in habitat. This form is rare since even a small amount of gene flow may remove genetic differences between parts of a population. Generally, sympatric speciation in animals requires the evolution of both genetic differences and nonrandom mating, to allow reproductive isolation to evolve.
One type of sympatric speciation involves crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. A domestic animal of unknown ancestry, where the breed status of only one parent or grandparent is known, may also be called a crossbreed though ...
ing of two related species to produce a new hybrid species. This is not common in animals as animal hybrids are usually sterile. This is because during meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
the homologous chromosome
Homologous chromosomes or homologs are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis. Homologs have the same genes in the same locus (genetics), loci, where they provide points along e ...
s from each parent are from different species and cannot successfully pair. However, it is more common in plants because plants often double their number of chromosomes, to form polyploids
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one fro ...
. This allows the chromosomes from each parental species to form matching pairs during meiosis, since each parent's chromosomes are represented by a pair already. An example of such a speciation event is when the plant species ''Arabidopsis thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small plant from the mustard family (Brassicaceae), native to Eurasia and Africa. Commonly found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land, it is generally ...
'' and ''Arabidopsis arenosa
''Arabidopsis arenosa'', the sand rock-cress, is a species of flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae. It is found mostly in Central Europe in both a diploid and an autotetraploid form. This sets it apart from the other, mostly diploid, ''Ara ...
'' crossbred to give the new species ''Arabidopsis suecica''. This happened about 20,000 years ago, and the speciation process has been repeated in the laboratory, which allows the study of the genetic mechanisms involved in this process. Indeed, chromosome doubling within a species may be a common cause of reproductive isolation, as half the doubled chromosomes will be unmatched when breeding with undoubled organisms.
Speciation events are important in the theory of punctuated equilibrium
In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a Scientific theory, theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolution, evol ...
, which accounts for the pattern in the fossil record of short "bursts" of evolution interspersed with relatively long periods of stasis, where species remain relatively unchanged. In this theory, speciation and rapid evolution
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
are linked, with natural selection and genetic drift acting most strongly on organisms undergoing speciation in novel habitats or small populations. As a result, the periods of stasis in the fossil record correspond to the parental population and the organisms undergoing speciation and rapid evolution are found in small populations or geographically restricted habitats and therefore rarely being preserved as fossils.
Extinction
 Extinction is the disappearance of an entire species. Extinction is not an unusual event, as species regularly appear through speciation and disappear through extinction. Nearly all animal and plant species that have lived on Earth are now extinct, and extinction appears to be the ultimate fate of all species. These extinctions have happened continuously throughout the history of life, although the rate of extinction spikes in occasional mass
Extinction is the disappearance of an entire species. Extinction is not an unusual event, as species regularly appear through speciation and disappear through extinction. Nearly all animal and plant species that have lived on Earth are now extinct, and extinction appears to be the ultimate fate of all species. These extinctions have happened continuously throughout the history of life, although the rate of extinction spikes in occasional mass extinction event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occ ...
s. The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event cau ...
, during which the non-avian dinosaurs became extinct, is the most well-known, but the earlier Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic extinction event (also known as the P–T extinction event, the Late Permian extinction event, the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian extinction event, and colloquially as the Great Dying,) was an extinction ...
was even more severe, with approximately 96% of all marine species driven to extinction. The Holocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families ...
event is an ongoing mass extinction associated with humanity's expansion across the globe over the past few thousand years. Present-day extinction rates are 100–1000 times greater than the background rate and up to 30% of current species may be extinct by the mid 21st century. Human activities are now the primary cause of the ongoing extinction event; global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
may further accelerate it in the future. Despite the estimated extinction of more than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, about 1 trillion species are estimated to be on Earth currently with only one-thousandth of 1% described.
The role of extinction in evolution is not very well understood and may depend on which type of extinction is considered. The causes of the continuous "low-level" extinction events, which form the majority of extinctions, may be the result of competition between species for limited resources (the competitive exclusion principle
In ecology, the competitive exclusion principle, sometimes referred to as Gause's law, is a proposition that two species which compete for the same limited resource cannot coexist at constant population values. When one species has even the slig ...
). If one species can out-compete another, this could produce species selection, with the fitter species surviving and the other species being driven to extinction. The intermittent mass extinctions are also important, but instead of acting as a selective force, they drastically reduce diversity in a nonspecific manner and promote bursts of rapid evolution and speciation in survivors.
Applications
Concepts and models used in evolutionary biology, such as natural selection, have many applications. Artificial selection is the intentional selection of traits in a population of organisms. This has been used for thousands of years in thedomestication
Domestication is a multi-generational Mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a st ...
of plants and animals. More recently, such selection has become a vital part of genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of Genetic engineering techniques, technologies used to change the genet ...
, with selectable marker
A selectable marker is a gene introduced into cell (biology), cells, especially bacteria or cells in cell culture, culture, which confers one or more traits suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory micr ...
s such as antibiotic resistance genes being used to manipulate DNA. Proteins with valuable properties have evolved by repeated rounds of mutation and selection (for example modified enzymes and new antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
) in a process called directed evolution
Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis (cre ...
.
Understanding the changes that have occurred during an organism's evolution can reveal the genes needed to construct parts of the body, genes which may be involved in human genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s. For example, the Mexican tetra
The Mexican tetra (''Astyanax mexicanus''), also known as the blind cave fish, blind cave characin or the blind cave tetra, is a freshwater fish in the Characidae family (tetras and relatives) of the order Characiformes. The type species of its ...
is an albino
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.
Varied use and interpretation of ...
cavefish that lost its eyesight during evolution. Breeding together different populations of this blind fish produced some offspring with functional eyes, since different mutations had occurred in the isolated populations that had evolved in different caves. This helped identify genes required for vision and pigmentation.
Evolutionary theory has many applications in medicine. Many human diseases are not static phenomena, but capable of evolution. Viruses, bacteria, fungi and cancers evolve to be resistant to host immune defences, as well as to pharmaceutical drug
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
s. These same problems occur in agriculture with pesticide and herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
resistance. It is possible that we are facing the end of the effective life of most of available antibiotics and predicting the evolution and evolvability of our pathogens and devising strategies to slow or circumvent it is requiring deeper knowledge of the complex forces driving evolution at the molecular level.
In computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, simulations of evolution using evolutionary algorithm
Evolutionary algorithms (EA) reproduce essential elements of the biological evolution in a computer algorithm in order to solve "difficult" problems, at least Approximation, approximately, for which no exact or satisfactory solution methods are k ...
s and artificial life
Artificial life (ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine systems related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline ...
started in the 1960s and were extended with simulation of artificial selection. Artificial evolution became a widely recognised optimisation method as a result of the work of Ingo Rechenberg
Ingo Rechenberg (20 November 1934 – 25 September 2021) was a German researcher and professor in the field of bionics. Rechenberg was a pioneer of the fields of evolutionary computation and artificial evolution. In the 1960s and 1970s he invent ...
in the 1960s. He used evolution strategies
Evolution strategy (ES) from computer science is a subclass of evolutionary algorithms, which serves as an optimization (mathematics), optimization technique. It uses the major genetic operators mutation (evolutionary algorithm), mutation, recomb ...
to solve complex engineering problems. Genetic algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ...
s in particular became popular through the writing of John Henry Holland
John Henry Holland (February 2, 1929 – August 9, 2015) was an American scientist and professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of Michigan. He was a pioneer in what became known as genetic algorithms.
Biograph ...
. Practical applications also include automatic evolution of computer programmes. Evolutionary algorithms are now used to solve multi-dimensional problems more efficiently than software produced by human designers and also to optimise the design of systems.
Evolutionary history of life
Origin of life
The Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates from at least 3.5 billion years ago, during theEoarchean
The Eoarchean ( ; also spelled Eoarchaean) is the first Era (geology), era of the Archean, Archean Eon of the geologic record. It spans 431 million years, from the end of the Hadean Eon 4031 annum, Mya to the start of the Paleoarchean Era 3600 M ...
Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is the first and oldest of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, starting with the planet's formation about 4.6 billion years ago (estimated 4567.30 ± 0.16 million years ago set by the age of the oldest solid material ...
Eon. Microbial mat fossils have been found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasediment
In geology, metasedimentary rock is a type of metamorphic rock. Such a rock was first formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occu ...
ary rocks discovered in Western Greenland as well as "remains of biotic life" found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. Commenting on the Australian findings, Stephen Blair Hedges
file:Stephen Hedges.jpg, Blair Hedges
Stephen Blair Hedges (known as S. Blair Hedges) is Laura H. Carnell Professor of Science and director of the Center for Biodiversity at Temple University where he researches the Tree of life (biology), tree o ...
wrote: "If life arose relatively quickly on Earth, then it could be common in the universe." In July 2016, scientists reported identifying a set of 355 gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s from the last universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the hypothesized common ancestral cell from which the three domains of life, the Bacteria, the Archaea, and the Eukarya originated. The cell had a lipid bilayer; it possessed the genetic code a ...
(LUCA) of all organisms living on Earth.
More than 99% of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.9 million are estimated to have been named and 1.6 million documented in a central database to date, leaving at least 80% not yet described.
Highly energetic chemistry is thought to have produced a self-replicating molecule around 4 billion years ago, and half a billion years later the last common ancestor of all life existed. The current scientific consensus is that the complex biochemistry that makes up life came from simpler chemical reactions. The beginning of life may have included self-replicating molecules such as RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
and the assembly of simple cells.
Common descent
All organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor or ancestralgene pool
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species.
Description
A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survi ...
. Current species are a stage in the process of evolution, with their diversity the product of a long series of speciation and extinction events. The common descent of organisms was first deduced from four simple facts about organisms: First, they have geographic distributions that cannot be explained by local adaptation. Second, the diversity of life is not a set of completely unique organisms, but organisms that share morphological similarities. Third, vestigial traits with no clear purpose resemble functional ancestral traits. Fourth, organisms can be classified using these similarities into a hierarchy of nested groups, similar to a family tree.
 Due to horizontal gene transfer, this "tree of life" may be more complicated than a simple branching tree, since some genes have spread independently between distantly related species. To solve this problem and others, some authors prefer to use the " Coral of life" as a metaphor or a mathematical model to illustrate the evolution of life. This view dates back to an idea briefly mentioned by Darwin but later abandoned.
Past species have also left records of their evolutionary history. Fossils, along with the comparative anatomy of present-day organisms, constitute the morphological, or anatomical, record. By comparing the anatomies of both modern and extinct species, palaeontologists can infer the lineages of those species. However, this approach is most successful for organisms that had hard body parts, such as shells, bones or teeth. Further, as prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea share a limited set of common morphologies, their fossils do not provide information on their ancestry.
More recently, evidence for common descent has come from the study of biochemical similarities between organisms. For example, all living cells use the same basic set of nucleotides and
Due to horizontal gene transfer, this "tree of life" may be more complicated than a simple branching tree, since some genes have spread independently between distantly related species. To solve this problem and others, some authors prefer to use the " Coral of life" as a metaphor or a mathematical model to illustrate the evolution of life. This view dates back to an idea briefly mentioned by Darwin but later abandoned.
Past species have also left records of their evolutionary history. Fossils, along with the comparative anatomy of present-day organisms, constitute the morphological, or anatomical, record. By comparing the anatomies of both modern and extinct species, palaeontologists can infer the lineages of those species. However, this approach is most successful for organisms that had hard body parts, such as shells, bones or teeth. Further, as prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea share a limited set of common morphologies, their fossils do not provide information on their ancestry.
More recently, evidence for common descent has come from the study of biochemical similarities between organisms. For example, all living cells use the same basic set of nucleotides and amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s. The development of molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is a branch of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the st ...
has revealed the record of evolution left in organisms' genomes: dating when species diverged through the molecular clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleot ...
produced by mutations. For example, these DNA sequence comparisons have revealed that humans and chimpanzees share 98% of their genomes and analysing the few areas where they differ helps shed light on when the common ancestor of these species existed.
Evolution of life
Prokaryotes inhabited the Earth from approximately 3–4 billion years ago. No obvious changes in morphology or cellular organisation occurred in these organisms over the next few billion years. The eukaryotic cells emerged between 1.6 and 2.7 billion years ago. The next major change in cell structure came when bacteria were engulfed by eukaryotic cells, in a cooperative association calledendosymbiosis
An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), whi ...
. The engulfed bacteria and the host cell then underwent coevolution, with the bacteria evolving into either mitochondria or hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some Anaerobic organism, anaerobic Ciliate, ciliates, Flagellate, flagellates, Fungus, fungi, and three species of Loricifera, loriciferans. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles t ...
s. Another engulfment of cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
l-like organisms led to the formation of chloroplasts in algae and plants.
The history of life was that of the unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
eukaryotes, prokaryotes and archaea until around 1.7 billion years ago, when multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s began to appear, with differentiated cells performing specialised functions. The evolution of multicellularity occurred in multiple independent events, in organisms as diverse as sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and a ...
s, brown algae
Brown algae (: alga) are a large group of multicellular algae comprising the class (biology), class Phaeophyceae. They include many seaweeds located in colder waters of the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate ...
, cyanobacteria, slime moulds
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to a polyphyletic assemblage of unrelated eukaryotic organisms in the Stramenopiles, Rhizaria, Discoba, Amoebozoa and Holomycota clades. Most are near-microscopic; those in the Myxogastria fo ...
and myxobacteria
The myxobacteria ("slime bacteria") are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except ...
. In January 2016, scientists reported that, about 800 million years ago, a minor genetic change in a single molecule called GK-PID may have allowed organisms to go from a single cell organism to one of many cells.
Approximately 538.8 million years ago, a remarkable amount of biological diversity appeared over a span of around 10 million years in what is called the Cambrian explosion. Here, the majority of types
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
of modern animals appeared in the fossil record, as well as unique lineages that subsequently became extinct. Various triggers for the Cambrian explosion have been proposed, including the accumulation of oxygen in the atmosphere from photosynthesis.
About 500 million years ago, plants and fungi colonised the land and were soon followed by arthropods and other animals. Insects were particularly successful and even today make up the majority of animal species. Amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s first appeared around 364 million years ago, followed by early amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tet ...
s and birds around 155 million years ago (both from "reptile"-like lineages), mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s around 129 million years ago, Homininae
Homininae (the hominines) is a subfamily of the family Hominidae (hominids). (The Homininae——encompass humans, and are also called "African hominids" or "African apes".) This subfamily includes two tribes, Hominini and Gorillini, both having ...
around 10 million years ago and modern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligen ...
around 250,000 years ago. However, despite the evolution of these large animals, smaller organisms similar to the types that evolved early in this process continue to be highly successful and dominate the Earth, with the majority of both biomass and species being prokaryotes.
History of evolutionary thought




Classical antiquity
The proposal that one type of organism could descend from another type goes back to some of the firstpre-Socratic
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of the ...
Greek philosophers, such as Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
and Empedocles
Empedocles (; ; , 444–443 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is known best for originating the Cosmogony, cosmogonic theory of the four cla ...
. Such proposals survived into Roman times. The poet and philosopher Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus ( ; ; – October 15, 55 BC) was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is the philosophical poem '' De rerum natura'', a didactic work about the tenets and philosophy of Epicureanism, which usually is t ...
followed Empedocles in his masterwork ''De rerum natura
(; ''On the Nature of Things'') is a first-century BC Didacticism, didactic poem by the Roman Republic, Roman poet and philosopher Lucretius () with the goal of explaining Epicureanism, Epicurean philosophy to a Roman audience. The poem, writte ...
'' ().
Middle Ages
In contrast to these materialistic views,Aristotelianism
Aristotelianism ( ) is a philosophical tradition inspired by the work of Aristotle, usually characterized by Prior Analytics, deductive logic and an Posterior Analytics, analytic inductive method in the study of natural philosophy and metaphysics ...
had considered all natural things as actualisations of fixed natural possibilities, known as forms. This became part of a medieval teleological
Teleology (from , and )Partridge, Eric. 1977''Origins: A Short Etymological Dictionary of Modern English'' London: Routledge, p. 4187. or finalityDubray, Charles. 2020 912Teleology. In ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'' 14. New York: Robert Applet ...
understanding of nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
in which all things have an intended role to play in a divine
Divinity (from Latin ) refers to the quality, presence, or nature of that which is divine—a term that, before the rise of monotheism, evoked a broad and dynamic field of sacred power. In the ancient world, divinity was not limited to a singl ...
cosmic order. Variations of this idea became the standard understanding of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and were integrated into Christian learning, but Aristotle did not demand that real types of organisms always correspond one-for-one with exact metaphysical forms and specifically gave examples of how new types of living things could come to be.
A number of Arab Muslim scholars wrote about evolution, most notably Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732–808 Hijri year, AH) was an Arabs, Arab Islamic scholar, historian, philosopher and sociologist. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest social scientists of the Middle Ages, and cons ...
, who wrote the book ''Muqaddimah
The ''Muqaddimah'' ( "Introduction"), also known as the ''Muqaddimah of Ibn Khaldun'' () or ''Ibn Khaldun's Introduction (writing), Prolegomena'' (), is a book written by the historian Ibn Khaldun in 1377 which presents a view of Universal histo ...
'' in 1377, in which he asserted that humans developed from "the world of the monkeys", in a process by which "species become more numerous".Kiros, Teodros. ''Explorations in African Political Thought''. 2001, page 55
Pre-Darwinian
The "New Science" of the 17th century rejected the Aristotelian approach. It sought to explain natural phenomena in terms ofphysical law
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) ...
s that were the same for all visible things and that did not require the existence of any fixed natural categories or divine cosmic order. However, this new approach was slow to take root in the biological sciences: the last bastion of the concept of fixed natural types. John Ray
John Ray Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (November 29, 1627 – January 17, 1705) was a Christian England, English Natural history, naturalist widely regarded as one of the earliest of the English parson-naturalists. Until 1670, he wrote his ...
applied one of the previously more general terms for fixed natural types, "species", to plant and animal types, but he strictly identified each type of living thing as a species and proposed that each species could be defined by the features that perpetuated themselves generation after generation. The biological classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon), and these groups are give ...
introduced by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
in 1735 explicitly recognised the hierarchical nature of species relationships, but still viewed species as fixed according to a divine plan.
Other naturalists
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
of this time speculated on the evolutionary change of species over time according to natural laws. In 1751, Pierre Louis Maupertuis
Pierre Louis Moreau de Maupertuis (; ; 1698 – 27 July 1759) was a French mathematician, philosopher and man of letters. He became the director of the Académie des Sciences and the first president of the Prussian Academy of Science, at the ...
wrote of natural modifications occurring during reproduction and accumulating over many generations to produce new species. Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (; 7 September 1707 – 16 April 1788) was a French Natural history, naturalist, mathematician, and cosmology, cosmologist. He held the position of ''intendant'' (director) at the ''Jardin du Roi'', now ca ...
, suggested that species could degenerate into different organisms, and Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosophy, natural philosopher, physiology, physiologist, Society for Effecting the ...
proposed that all warm-blooded animals could have descended from a single microorganism (or "filament"). The first full-fledged evolutionary scheme was Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biologi ...
's "transmutation" theory of 1809, which envisaged spontaneous generation
Spontaneous generation is a superseded scientific theory that held that living creatures could arise from non-living matter and that such processes were commonplace and regular. It was hypothesized that certain forms, such as fleas, could ...
continually producing simple forms of life that developed greater complexity in parallel lineages with an inherent progressive tendency, and postulated that on a local level, these lineages adapted to the environment by inheriting changes caused by their use or disuse in parents. (The latter process was later called Lamarckism
Lamarckism, also known as Lamarckian inheritance or neo-Lamarckism, is the notion that an organism can pass on to its offspring physical characteristics that the parent organism acquired through use or disuse during its lifetime. It is also calle ...
.) These ideas were condemned by established naturalists as speculation lacking empirical support. In particular, Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuv ...
insisted that species were unrelated and fixed, their similarities reflecting divine design for functional needs. In the meantime, Ray's ideas of benevolent design had been developed by William Paley
William Paley (July 174325 May 1805) was an English Anglican clergyman, Christian apologetics, Christian apologist, philosopher, and Utilitarianism, utilitarian. He is best known for his natural theology exposition of the teleological argument ...
into the ''Natural Theology or Evidences of the Existence and Attributes of the Deity
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part ...
'' (1802), which proposed complex adaptations as evidence of divine design and which was admired by Charles Darwin.
* Letter 2532, 22 November 1859.
Darwinian revolution
The crucial break from the concept of constant typological classes or types in biology came with the theory of evolution through natural selection, which was formulated byCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
and Alfred Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 pap ...
in terms of variable populations. Darwin used the expression ''descent with modification'' rather than ''evolution''. Partly influenced by ''An Essay on the Principle of Population
The book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'' was first published anonymously in 1798, but the author was soon identified as Thomas Robert Malthus. The book warned of future difficulties, on an interpretation of the population increasing ...
'' (1798) by Thomas Robert Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English economist, cleric, and scholar influential in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
, Darwin noted that population growth would lead to a "struggle for existence" in which favourable variations prevailed as others perished. In each generation, many offspring fail to survive to an age of reproduction because of limited resources. This could explain the diversity of plants and animals from a common ancestry through the working of natural laws in the same way for all types of organism. Darwin developed his theory of "natural selection" from 1838 onwards and was writing up his "big book" on the subject when Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 pap ...
sent him a version of virtually the same theory in 1858. Their separate papers were presented together at an 1858 meeting of the Linnean Society of London
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript a ...
. At the end of 1859, Darwin's publication of his "abstract" as ''On the Origin of Species'' explained natural selection in detail and in a way that led to an increasingly wide acceptance of Darwin's concepts of evolution at the expense of alternative theories. Thomas Henry Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist who specialized in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The stor ...
applied Darwin's ideas to humans, using palaeontology
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geo ...
and comparative anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species).
The science began in the classical era, continuing in t ...
to provide strong evidence that humans and ape
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a superfamily of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and Europe in prehistory, and counting humans are found global ...
s shared a common ancestry. Some were disturbed by this since it implied that humans did not have a special place in the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
.
Othniel C. Marsh, America's first palaeontologist, was the first to provide solid fossil evidence to support Darwin's theory of evolution by unearthing the ancestors of the modern horse. In 1877, Marsh delivered a very influential speech before the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, providing a demonstrative argument for evolution. For the first time, Marsh traced the evolution of vertebrates from fish all the way through humans. Sparing no detail, he listed a wealth of fossil examples of past life forms. The significance of this speech was immediately recognised by the scientific community, and it was printed in its entirety in several scientific journals.
 In 1880, Marsh caught the attention of the scientific world with the publication of ''Odontornithes: a Monograph on Extinct Birds of North America,'' which included his discoveries of birds with teeth. These skeletons helped bridge the gap between dinosaurs and birds, and provided invaluable support for Darwin's theory of evolution. Darwin wrote to Marsh saying, "Your work on these old birds & on the many fossil animals of N. America has afforded the best support to the theory of evolution, which has appeared within the last 20 years" (since Darwin's publication of ''Origin of Species).
In 1880, Marsh caught the attention of the scientific world with the publication of ''Odontornithes: a Monograph on Extinct Birds of North America,'' which included his discoveries of birds with teeth. These skeletons helped bridge the gap between dinosaurs and birds, and provided invaluable support for Darwin's theory of evolution. Darwin wrote to Marsh saying, "Your work on these old birds & on the many fossil animals of N. America has afforded the best support to the theory of evolution, which has appeared within the last 20 years" (since Darwin's publication of ''Origin of Species).
Pangenesis and heredity
The mechanisms of reproductive heritability and the origin of new traits remained a mystery. Towards this end, Darwin developed his provisional theory ofpangenesis
Pangenesis was Charles Darwin's hypothetical mechanism for heredity, in which he proposed that each part of the body continually emitted its own type of small organic particles called gemmules that aggregated in the gonads, contributing heritabl ...
. In 1865, Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel Order of Saint Augustine, OSA (; ; ; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinians, Augustinian friar and abbot of St Thomas's Abbey, Brno, St. Thom ...
reported that traits were inherited in a predictable manner through the independent assortment
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularized ...
and segregation of elements (later known as genes). Mendel's laws of inheritance eventually supplanted most of Darwin's pangenesis theory. August Weismann
August Friedrich Leopold Weismann (; 17 January 18345 November 1914) was a German evolutionary biology, evolutionary biologist. Fellow German Ernst Mayr ranked him as the second most notable evolutionary theorist of the 19th century, after Charl ...
made the important distinction between germ cell
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they unde ...
s that give rise to gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s (such as sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
and egg cell
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female Reproduction, reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female game ...
s) and the somatic cell
In cellular biology, a somatic cell (), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Somatic cells compose the body of an organism ...
s of the body, demonstrating that heredity passes through the germ line only. Hugo de Vries
Hugo Marie de Vries (; 16 February 1848 – 21 May 1935) was a Dutch botanist and one of the first geneticists. He is known chiefly for suggesting the concept of genes, rediscovering the laws of heredity in the 1890s while apparently unaware of ...
connected Darwin's pangenesis theory to Weismann's germ/soma cell distinction and proposed that Darwin's pangenes were concentrated in the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
and when expressed they could move into the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
to change the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
's structure. De Vries was also one of the researchers who made Mendel's work well known, believing that Mendelian traits corresponded to the transfer of heritable variations along the germline. To explain how new variants originate, de Vries developed a mutation theory that led to a temporary rift between those who accepted Darwinian evolution and biometricians who allied with de Vries. In the 1930s, pioneers in the field of population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, s ...
, such as Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who a ...
, Sewall Wright
Sewall Green Wright ForMemRS
HonFRSE (December 21, 1889March 3, 1988) was an American geneticist known for his influential work on evolutionary theory and also for his work on path analysis. He was a founder of population genetics alongside ...
and J. B. S. Haldane
John Burdon Sanderson Haldane (; 5 November 18921 December 1964), nicknamed "Jack" or "JBS", was a British-born scientist who later moved to India and acquired Indian citizenship. He worked in the fields of physiology, genetics, evolutionary ...
set the foundations of evolution onto a robust statistical philosophy. The false contradiction between Darwin's theory, genetic mutations, and Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularize ...
was thus reconciled.
The 'modern synthesis'
In the 1920s and 1930s, themodern synthesis
Modern synthesis or modern evolutionary synthesis refers to several perspectives on evolutionary biology, namely:
* Modern synthesis (20th century), the term coined by Julian Huxley in 1942 to denote the synthesis between Mendelian genetics and s ...
connected natural selection and population genetics, based on Mendelian inheritance, into a unified theory that included random genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow. This new version of evolutionary theory focused on changes in allele frequencies in population. It explained patterns observed across species in populations, through fossil transitions in palaeontology.
Further syntheses
Since then, further syntheses have extended evolution's explanatory power in the light of numerous discoveries, to cover biological phenomena across the whole of the biological hierarchy from genes to populations. The publication of the structure ofDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
by James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biology, molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' proposing the Nucleic acid ...
and Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid doub ...
with contribution of Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 192016 April 1958) was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer. Her work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal ...
in 1953 demonstrated a physical mechanism for inheritance. Molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
improved understanding of the relationship between genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
and phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
. Advances were also made in phylogenetic systematics
Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phy ...
, mapping the transition of traits into a comparative and testable framework through the publication and use of evolutionary trees. In 1973, evolutionary biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky
Theodosius Grigorievich Dobzhansky (; ; January 25, 1900 – December 18, 1975) was a Russian-born American geneticist and evolutionary biologist. He was a central figure in the field of evolutionary biology for his work in shaping the modern ...
penned that "nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution
"Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution" is a 1973 essay by the evolutionary biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky, criticising anti-evolution creationism and espousing theistic evolution. The essay was first published in ''Am ...
", because it has brought to light the relations of what first seemed disjointed facts in natural history into a coherent explanatory
An explanation is a set of Statement (logic), statements usually constructed to description, describe a set of facts that clarifies the causality, causes, wiktionary:context, context, and Logical consequence, consequences of those facts. It may ...
body of knowledge that describes and predicts many observable facts about life on this planet.
One extension, known as evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. ...
and informally called "evo-devo", emphasises how changes between generations (evolution) act on patterns of change within individual organisms (development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
). Since the beginning of the 21st century, some biologists have argued for an extended evolutionary synthesis
The Extended Evolutionary Synthesis (EES) consists of a set of theoretical concepts argued to be more comprehensive than the earlier modern synthesis of evolutionary biology that took place between 1918 and 1942. The extended evolutionary synthe ...
, which would account for the effects of non-genetic inheritance modes, such as epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
, parental effects, ecological inheritance and cultural inheritance, and evolvability
Evolvability is defined as the capacity of a system for adaptive evolution. Evolvability is the ability of a population of organisms to not merely generate genetic diversity, but to generate '' adaptive'' genetic diversity, and thereby evolve thr ...
.
Social and cultural responses
In the 19th century, particularly after the publication of ''On the Origin of Species'' in 1859, the idea that life had evolved was an active source of academic debate centred on the philosophical, social and religious implications of evolution. Today, the modern evolutionary synthesis is accepted by a vast majority of scientists. However, evolution remains a contentious concept for sometheists
Theism is broadly defined as the belief in the existence of at least one deity. In common parlance, or when contrasted with ''deism'', the term often describes the philosophical conception of God that is found in classical theism—or the conc ...
.
While various religions and denominations have reconciled their beliefs with evolution through concepts such as theistic evolution
Theistic evolution (also known as theistic evolutionism or God-guided evolution), alternatively called evolutionary creationism, is a view that God acts and creates through laws of nature. Here, God is taken as the primary cause while natural cau ...
, there are creationists
Creationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation, and is often pseudoscientific. Gunn 2004, p. 9, "The ''Concise Oxford Dictionary ...
who believe that evolution is contradicted by the creation myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Cre ...
s found in their religions and who raise various objections to evolution
Objections to evolution have been raised since evolutionary ideas came to prominence in the 19th century. When Charles Darwin published his 1859 book ''On the Origin of Species'', his theory of evolution (the idea that species arose through desc ...
. As had been demonstrated by responses to the publication of ''Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation
''Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation'' is an 1844 work of speculative natural history and philosophy by Robert Chambers. Published anonymously in England, it brought together various ideas of stellar evolution with the progressive tra ...
'' in 1844, the most controversial aspect of evolutionary biology is the implication of human evolution
''Homo sapiens'' is a distinct species of the hominid family of primates, which also includes all the great apes. Over their evolutionary history, humans gradually developed traits such as Human skeletal changes due to bipedalism, bipedalism, de ...
that humans share common ancestry with apes and that the mental and moral faculties of humanity have the same types of natural causes as other inherited traits in animals. In some countries, notably the United States, these tensions between science and religion have fuelled the current creation–evolution controversy, a religious conflict focusing on politics and public education
A state school, public school, or government school is a primary school, primary or secondary school that educates all students without charge. They are funded in whole or in part by taxation and operated by the government of the state. State-f ...
. While other scientific fields such as cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
and Earth science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
also conflict with literal interpretations of many religious text
Religious texts, including scripture, are texts which various religions consider to be of central importance to their religious tradition. They often feature a compilation or discussion of beliefs, ritual practices, moral commandments and ...
s, evolutionary biology experiences significantly more opposition from religious literalists.
The teaching of evolution in American secondary school biology classes was uncommon in most of the first half of the 20th century. The Scopes Trial decision of 1925 caused the subject to become very rare in American secondary biology textbooks for a generation, but it was gradually re-introduced later and became legally protected with the 1968 '' Epperson v. Arkansas'' decision. Since then, the competing religious belief of creationism was legally disallowed in secondary school curricula in various decisions in the 1970s and 1980s, but it returned in pseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable cl ...
form as intelligent design
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins".#Numbers 2006, Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for it ...
(ID), to be excluded once again in the 2005 '' Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District'' case. The debate over Darwin's ideas did not generate significant controversy in China.
See also
* *Chronospecies
A chronospecies is a species derived from a sequential development pattern that involves continual and uniform changes from an extinct ancestral form on an evolutionary scale. The sequence of alterations eventually produces a population that is p ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * The notebook is available froThe Complete Work of Charles Darwin Online
. Retrieved 2019-10-09. * The book is available fro
The Complete Work of Charles Darwin Online
. Retrieved 2014-11-21. * * * * * * * * * * "Proceedings of a symposium held at the American Museum of Natural History in New York, 2002." * * * * * * * * * * * . Retrieved 2014-11-29. * * * * * * * "Papers from the Symposium on the Limits of Reductionism in Biology, held at the Novartis Foundation, London, May 13–15, 1997." * * * * * * "Based on a conference held in Bellagio, Italy, June 25–30, 1989" * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
;Introductory reading * * * * * ** American version. * * * ;Advanced reading * * * * * * * *External links
;General information * * * * * Adobe Flash required. *History of Evolution in the United States
.
Salon
Salon may refer to:
Common meanings
* Beauty salon
A beauty salon or beauty parlor is an establishment that provides Cosmetics, cosmetic treatments for people. Other variations of this type of business include hair salons, spas, day spas, ...
. Retrieved 2021-08-24.
*
;Experiments
*
*
;Online lectures
*
*
{{Authority control
Biology theories
*