|
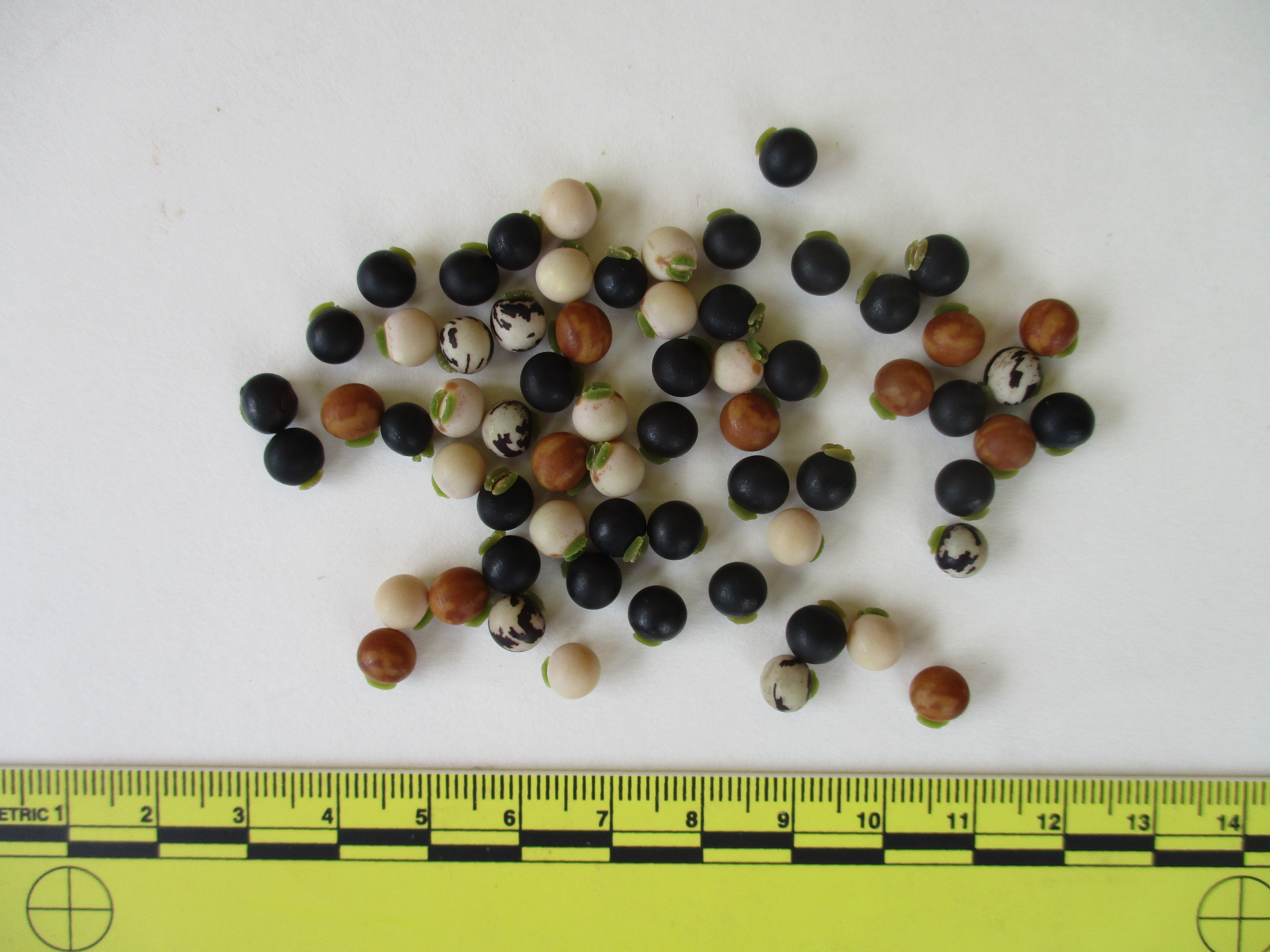
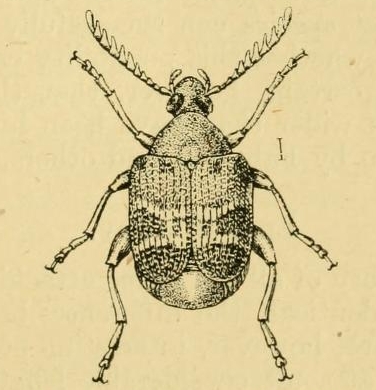
Callosobruchus Chinensis
''Callosobruchus chinensis'' is a common species of beetle found in the bean weevil subfamily, and is known to be a pest to many stored legumes. Although it is commonly known as the adzuki bean weevil it is in fact not a true weevil, belonging instead to the leaf beetle family, Chrysomelidae. Other common names include the pulse beetle, Chinese bruchid and cowpea bruchid. This species has a very similar lifestyle and habitat to ''Callosobruchus maculatus'' and their identities are often mistaken for each other. This beetle is a common pest targeting many different species of stored legumes and it is distributed across the tropical and subtropical regions of the world. ''C. chinensis'' is one of the most damaging crop pests to the stored legume industry due to their generalized legume diets and wide distribution. The first recorded sighting and description of ''C. chinensis'' was in China which is where the beetle gets its species name. Habitat and distribution ''C. chinensis'' di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeon Pea
The pigeon pea (''Cajanus cajan'') is a perennial legume from the family Fabaceae native to the Old World. The pigeon pea is widely cultivated in tropical and semitropical regions around the world, being commonly consumed in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean. Etymology and other names Scientific epithet The scientific name for the genus ''Cajanus'' and the species ''cajan'' derive from the Malay word ''katjang'' meaning legume in reference to the bean of the plant. Common English names In English they are commonly referred to as pigeon pea which originates from the historical utilization of the pulse as pigeon fodder in Barbados. The term Congo pea and Angola pea developed due to the presence of its cultivation in Africa and the association of its utilization with those of African descent. The names no-eye pea and red gram both refer to the characteristics of the seed, with no-eye pea in reference to the lack of a hilum on most varieties, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congener (biology)
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organisms or constituents of living organisms of being special or doing something special. Each animal or plant species is special. It differs in some way from all other species...biological specificity is the major problem about understanding life." Biological specificity within ''Homo sapiens'' ''Homo sapiens'' has many characteristics that show the biological specificity in the form of behavior and morphological traits. Morphologically, humans have an enlarged cranial capacity and more gracile features in comparison to other hominins. The reduction of dentition is a feature that allows for the advantage of adaptability in diet and survival. As a species, humans are culture dependent and much of human survival relies on the culture and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
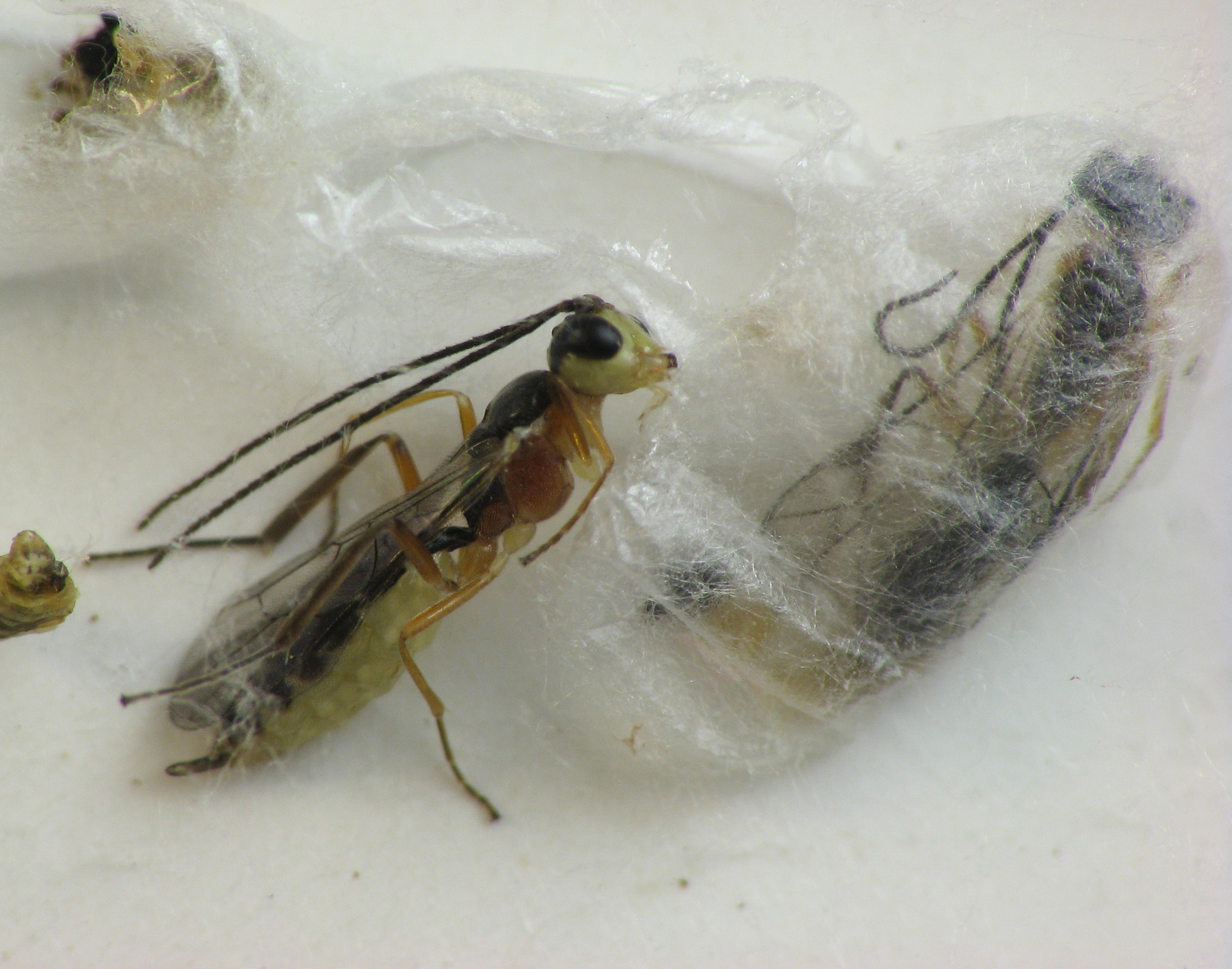
Parasitoid Wasps
Parasitoid wasps are a large group of hymenopteran superfamilies, with all but the wood wasps (Orussoidea) being in the wasp-waisted Apocrita. As parasitoids, they lay their eggs on or in the bodies of other arthropods, sooner or later causing the death of these hosts. Different species specialise in hosts from different insect orders, most often Lepidoptera, though some select beetles, flies, or bugs; the spider wasps (Pompilidae) exclusively attack spiders. Parasitoid wasp species differ in which host life-stage they attack: eggs, larvae, pupae, or adults. They mainly follow one of two major strategies within parasitism: either they are endoparasitic, developing inside the host, and koinobiont, allowing the host to continue to feed, develop, and moult; or they are ectoparasitic, developing outside the host, and idiobiont, paralysing the host immediately. Some endoparasitic wasps of the superfamily Ichneumonoidea have a mutualistic relationship with polydnaviruses, the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanatosis
Apparent death, colloquially known as playing dead, feigning death, or playing possum, is a behavior in which animals take on the appearance of being dead. It is an immobile state most often triggered by a predatory attack and can be found in a wide range of animals from insects and crustaceans to mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Apparent death is also referred to as thanatosis, animal hypnosis, immobilization catatonia, or tonic immobility, the latter of which is preferred in the scientific literature on the subject. Apparent death is separate from the freezing behavior seen in some animals. Apparent death is a form of animal deception considered to be an anti-predator strategy, but it can also be used as a form of aggressive mimicry. When induced by humans, the state is sometimes colloquially known as animal hypnosis. The earliest written record of "animal hypnosis" dates back to the year 1646 in a report by Athanasius Kircher, in which he subdued chickens. Desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intromittent Organ
An intromittent organ is any external organ of a male organism that is specialized to deliver sperm during copulation. Intromittent organs are found most often in terrestrial species, as most non-mammalian aquatic species fertilize their eggs externally, although there are exceptions. For many species in the animal kingdom, the male intromittent organ is a hallmark characteristic of internal fertilization. Species with intromittent organs Invertebrates Molluscs Male cephalopods have a specialized arm, the hectocotylus, which is inserted into the female's mantle cavity to deliver a spermatophore during copulation. In some species, the hectocotylus breaks off inside the female's mantle cavity; in others, it can be used repeatedly to copulate with different females. Arachnids In spiders the intromittent organs are the male pedipalps, even though these are not primarily sexual organs, but serve as indirect mating organs; in the male the pedipalps have hollow, clubbed tips, oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerites
A sclerite (Greek , ', meaning "hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates. Sclerites in combination Sclerites may occur practically isolated in an organism, such as the sting of a cone shell. Also, they can be more or less scattered, such as tufts of defensive sharp, mineralised bristles as in many marine Polychaetes. Or, they can occur as structured, but unconnected or loosely connected arrays, such as the mineral "teeth" in the radula of many Mollusca, the valves of Chitons, the beak of Cephalopod, or the articulated exoskeletons of Arthropoda. When sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the natural capability to produce offspring, measured by the number of gametes (eggs), seed set, or asexual propagules. Superfecundity refers to an organism's ability to store another organism's sperm (after copulation) and fertilize its own eggs from that store after a period of time, essentially making it appear as though fertilization occurred without sperm (i.e. parthenogenesis). Human demography Human demography considers only human fecundity, at its culturally differing rates, while population biology studies all organisms. The term ''fecundity'' in population biology is often used to describe the rate of offspring production after one time step (often annual). In this sense, fecundity may include both birth rates and survival of young to that time step. Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, individuals, economic and social groups, etc. The rivalry can be over attainment of any exclusive goal, including Recognition (sociology), recognition: Competition occurs in nature, between living organisms which co-exist in the same natural environment, environment. Animals compete over water supplies, food, mates, and other resource (biology), biological resources. Humans usually Survival of the fittest, compete for food and mates, though when these needs are met deep rivalries often arise over the pursuit of wealth, power, prestige, and celebrity, fame when in a static, repetitive, or unchanging environment. Competition is a major tenet of market economy, market economies and business, often associated with business competition as companies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pupation
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their life cycle, the stages thereof being egg, larva, pupa, and imago. The processes of entering and completing the pupal stage are controlled by the insect's hormones, especially juvenile hormone, prothoracicotropic hormone, and ecdysone. The act of becoming a pupa is called pupation, and the act of emerging from the pupal case is called eclosion or emergence. The pupae of different groups of insects have different names such as ''chrysalis'' for the pupae of butterflies and ''tumbler'' for those of the mosquito family. Pupae may further be enclosed in other structures such as cocoons, nests, or shells. Position in life cycle The pupal stage follows the larval stage and precedes adulthood (''imago'') in insects with complete metamorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pupae
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their life cycle, the stages thereof being egg, larva, pupa, and imago. The processes of entering and completing the pupal stage are controlled by the insect's hormones, especially juvenile hormone, prothoracicotropic hormone, and ecdysone. The act of becoming a pupa is called pupation, and the act of emerging from the pupal case is called eclosion or emergence. The pupae of different groups of insects have different names such as ''chrysalis'' for the pupae of butterflies and ''tumbler'' for those of the mosquito family. Pupae may further be enclosed in other structures such as cocoons, nests, or shells. Position in life cycle The pupal stage follows the larval stage and precedes adulthood (''imago'') in insects with complete metamorphosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larvae
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(7686081848).jpg)





_mating_with_emerging_butterfly_from_pupa_in_Hyderabad%2C_AP_W_IMG_9437.jpg)
