Estonian Crusade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military
File:Baltic Tribes c 1200.svg,
File:Ancient Estonian counties.png, Counties of Ancient Estonia
File:Danmarks flag 1219 Lorentzen.jpg, Dannebrog falling from the sky during the Battle of Lindanise, 1219.

 The last Estonian county to hold out against the invaders was the island country of Saaremaa (Ösel), whose war fleets had continued to raid Denmark and Sweden during the years of fighting against the German crusaders.
In 1206, a Danish army led by the king
The last Estonian county to hold out against the invaders was the island country of Saaremaa (Ösel), whose war fleets had continued to raid Denmark and Sweden during the years of fighting against the German crusaders.
In 1206, a Danish army led by the king
 Following the defeat of the Estonians, the crusade moved against
Following the defeat of the Estonians, the crusade moved against
 According to the ''
According to the ''

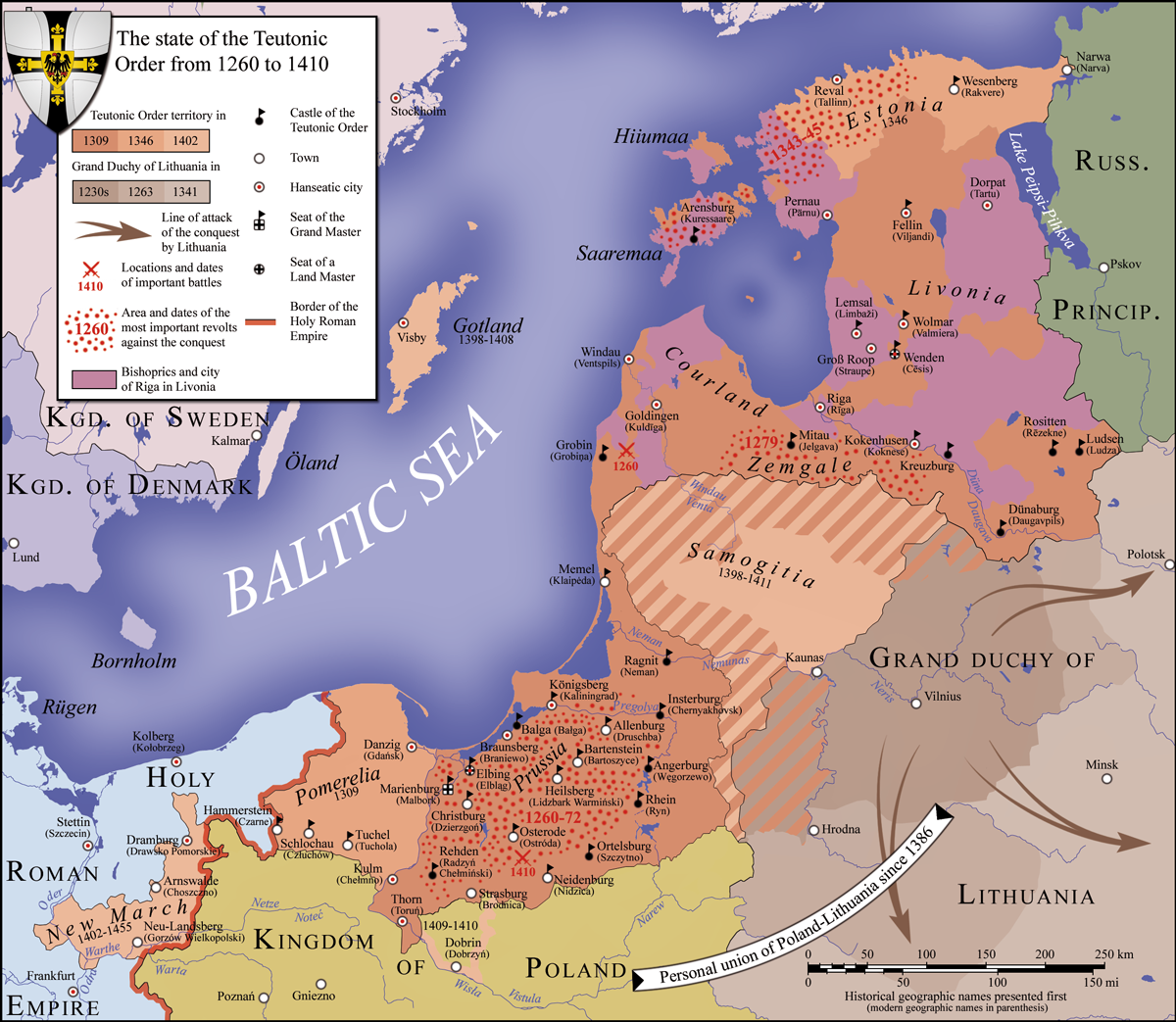 In 1227 the
In 1227 the
Saaremaa 1100–1227
13th century in Denmark 13th-century conflicts 13th-century crusades Conflicts involving the Livonian Order History of Livonia Medieval Sweden Military history of Estonia Military history of Latvia Northern Crusades Wars involving Denmark Wars involving Estonia Wars involving Latvia Wars involving Livonia Wars involving Sweden
Christianisation
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
campaigns in medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
– in what is now Latvia and Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
– during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christian colonization and Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Christian military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the pagan Baltic, Finnic and West Slavic peoples around th ...
in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was conducted mostly by the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
and the Kingdom of Denmark. It ended with the creation of Terra Mariana
Terra Mariana (Medieval Latin for "Land of Mary") was the official name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia ( nds, Oolt-Livland, liv, Jemā-Līvõmō, et, Vana-Liivimaa, lv, Livonija). It was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade ...
and the Danish duchy of Estonia. The lands on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
were one of the last parts of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
to be Christianised.
On 2 February 1207, in the territories conquered, an ecclesiastical state called ''Terra Mariana'' was established as a principality of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and proclaimed by Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
in 1215 as a subject of the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
. After the success of the crusade, the Teutonic- and Danish- occupied territory was divided into six feudal principalities by William of Modena
William of Modena ( – 31 March 1251), also known as ''William of Sabina'', ''Guglielmo de Chartreaux'', ''Guglielmo de Savoy'', ''Guillelmus'', was an Italian clergyman and papal diplomat.
.
Wars against Livs and Latgalians (1198–1209)
By the timeGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
traders began to arrive in the second half of the 12th century to trade along the ancient trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a medieval trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Eastern Roman Empire. The route allowed merchants along its length to establish a direct prosperous trade with the Empir ...
, some natives had already been baptized.
Saint Meinhard of Segeberg arrived in Ikšķile
Ikšķile (; german: Uexküll; liv, Ikškilā; et, Üksküla; also known as ''Üxküll'') is a town in Latvia, in Ogre Municipality. It was the first capital of the Roman Catholic Bishopric of Livonia, known by the German name of Üxküll ...
in 1184 with the mission of converting the pagan Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs ( Livonian: ''līvlizt''; Estonian: ''liivlased''; Latvian: ''līvi'', ''lībieši''), are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to northern and northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian, a Uralic language c ...
, and was consecrated as Bishop of Üxküll in 1186. In those days the riverside town was the center of the missionary activities in the Livonian area.
The indigenous Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs ( Livonian: ''līvlizt''; Estonian: ''liivlased''; Latvian: ''līvi'', ''lībieši''), are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to northern and northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian, a Uralic language c ...
(''Līvi''), who had been paying tribute to the East Slavic Principality of Polotsk
The Principality of Polotsk ( be, По́лацкае кня́ства, ''Polackaje kniastva''; la, Polocensis Ducatus), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality of the Early East Slavs. The origin and ...
, and were often under attack by their southern neighbours the Semigallians
Semigallians ( Latvian ''Zemgaļi''; lt, Žiemgaliai, also ''Zemgalians, Semigalls, Semigalians'') were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance ...
, at first considered the Low Germans (Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
) to be useful allies. The first prominent Livonian to be converted was their leader Caupo of Turaida
Caupo of Turaida, or Kaupo (died 21 September 1217) was a leader of the Finnic-speaking Livonian people in the beginning of the 13th century, in what is now part of Latvia and Estonia. He is sometimes called a 'King of Livonia', the Chronicle ...
, who was baptized around 1189.
Pope Celestine III had called for a crusade against pagans in Northern Europe in 1193. When peaceful means of conversion failed to produce results, the impatient Meinhard plotted to convert Livonians forcibly but was thwarted. He died in 1196, having failed in his mission. His appointed replacement, bishop Berthold of Hanover
Berthold of Hanover (died 24 July 1198) was a German Cistercian and Bishop of Livonia, who met his death in a crusade against the pagan Livonians.
Life
He was Abbot of the Cistercian monastery of Lockum in Hanover. At the death of Saint Meinh ...
, a Cistercian abbot of Loccum
Loccum Abbey (Kloster Loccum) is a Lutheran monastery in the town of Rehburg-Loccum, Lower Saxony, near Steinhude Lake.
History
Originating as a foundation of Count Wilbrand of Hallermund, Loccum Abbey was settled from Volkenroda Abbey under the ...
arrived with a large contingent of crusaders in 1198. Shortly afterwards, while riding ahead of his troops in battle, Berthold was surrounded and killed, and his forces were defeated by Livonians.
To avenge Berthold's defeat, Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
issued a bull declaring a crusade against the Livonians. Albert von Buxthoeven, consecrated as a bishop in 1199,
arrived the following year with a large force, and established Riga as the seat of his Bishopric of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga ( la, Archiepiscopatus Rigensis, nds, Erzbisdom Riga) was an archbishopric in Medieval Livonia, a subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 as the bishopric of Livonia at Ikšķile, then after moving to R ...
in 1201. In 1202 he formed the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword ( la, Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, german: Schwertbrüderorden) was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theoderi ...
to aid in the conversion of the pagans to Christianity and, more importantly, to protect German trade and secure German control over commerce.
As the German grip tightened, the Livonians and their christened chief rebelled against the crusaders. Caupo's forces were defeated at Turaida in 1206, and the Livonians were declared to be converted. Caupo subsequently remained an ally of the crusaders until his death in the Battle of St. Matthew's Day
The Battle of Matthew's Day ( et, Madisepäeva lahing) was fought near Viljandi (probably in Vanamõisa) on 21 September 1217Battle of St. Matthew's Day (September 21) @ during the Livonian Crusade. The adversaries were the Sword Brethren ...
in 1217.
By 1208 the important Daugava trading posts of Salaspils
Salaspils (; german: Kircholm; sv, Kirkholm) is a town in Latvia, the administrative centre of Salaspils Municipality. The town is situated on the northern bank of the Daugava river, 18 kilometers to the south-east of the city of Riga.
His ...
(Holme), Koknese
Koknese () is a town in Aizkraukle Municipality in the Vidzeme region of Latvia, on the right bank of the Daugava River. It has a population of nearly 3,000.
According to the provisions of the 2021 Latvian administrative reform, Koknese gained ...
(Kokenhusen) and Sēlpils Castle (Selburg) had been taken over as a result of Albert's energetic campaigning. In the same year, the rulers of the Latgalian counties Tālava
Tālava was a Latgalian country in the northern Vidzeme and northern Latgale region of today's Latvia. It was bordered by the Latgalian Principality of Jersika to the south, the Livonian counties of Metsepole and Idumeja to the west, the Estonian ...
, Satekle, and Autine established military alliances with the Order, and construction began on both Cēsis Castle
Cēsis Castle () is one of the most iconic and best preserved medieval castles in Latvia. The foundations of the castle were laid 800 years ago by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword. The most prosperous period Cēsis Castle experienced was durin ...
and a stone Koknese Castle
Koknese Castle ( lv, Kokneses pils, german: Burg Kokenhusen) is a complex in Koknese, Latvia, dating from the 13th century. The castle was situated on a high bluff overlooking the Daugava river valley. In 1965 a hydroelectric dam was built downri ...
, where the Daugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic ...
and Pērse
Pērse is a right tributary to the river Daugava in Latvia, flowing through Ērgļi, Pļaviņas and Koknese municipalities. The river crosses roads A6, P79, P80 and Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city ...
rivers meet, replacing the wooden castle of Latgalians.
In 1209 Albert, leading the forces of the Order, captured the capital of the Latgalian Principality of Jersika
The principality of Jersika ( la, Gerzika, terra Lettia, german: Gerzika, Zargrad, russian: Ерсика, Герцике; also known as ''Лотыголa'') was an early medieval Latgalian principality in eastern modern-day Latvia and one of th ...
, and took the wife of the ruler Visvaldis
Visvaldis (Latin language, Latin: Vissewalde rex de Gerzika, Russian language, Russian: Всеволод, Belarusian language, Belarusian: Усевалад) was a Latgalians, Latgalian nobleman, Duke of the Principality of Jersika in the 12th-13th ...
captive. Visvaldis was forced to submit his kingdom to Albert as a grant to the Archbishopric of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga ( la, Archiepiscopatus Rigensis, nds, Erzbisdom Riga) was an archbishopric in Medieval Livonia, a subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 as the bishopric of Livonia at Ikšķile, then after moving to Rig ...
, and received back a portion of it as a fief. Tālava, weakened in wars with Estonians and Russians, became a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of the Archbishopric of Riga in 1214, and in 1224 was finally divided between the Archbishopric and the Order.
Baltic Tribes
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the number ...
, c. 1200.
File:Talava.tif, Lands of Tālava
File:Lotigola.jpg, Lands of Lotigola
Wars against Estonians (1208–27)
Conquest of the Estonian hinterland
By 1208 the Crusaders were strong enough to begin operations against theEstonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic ethnic group native to Estonia who speak the Estonian language.
The Estonian language is spoken as the first language by the vast majority of Estonians; it is closely related to oth ...
, who were at that time divided into eight major and seven smaller Counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
, led by elders, with limited co-operation between them. With the help of the newly converted local tribes of Livs and Latgalians
Latgalians (, nds, Letti, Lethi, modern ; variant translations also include Latgallians, Lettigalls or Lettigallians) were an ancient Baltic tribe.
They likely spoke the Latvian language, which probably became the ''lingua franca'' in present-d ...
, the crusaders initiated raids into Sakala and Ugaunia
Ugandi (Latin: ''Ungannia'' or ''Ugaunia''; lv, Ugaunija; Low German: ''Uggn'') was an independent county between the east coast of Lake Võrtsjärv and west coast of Lake Pskov, bordered by Vaiga, Mõhu, Nurmekund, Sakala, Tālava, and Th ...
in Southern Estonia. The Estonian tribes fiercely resisted the attacks from Riga and occasionally sacked territories controlled by the crusaders.
In 1208–27, war parties of the different sides rampaged through Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
, Latgalia, and other Estonian counties, with the Livs, Latgalians and Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
of the Republic of Novgorod
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of mod ...
serving variously as allies of both crusaders and Estonians. Hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
s, which were the key centers of Estonian counties, were besieged, captured, and re-captured a number of times. A truce between the war-weary sides was established for three years (1213–1215). It proved generally more favourable to the Germans, who consolidated their political position, while the Estonians were unable to develop their system of loose alliances into a centralised state. They were led by Lembitu of Lehola, the elder of Sackalia
Sakala County (Estonian: ''Sakala'', Latin: ''Saccalia'') was an ancient Estonian county that was first mentioned in print by Henry of Latvia in the early 13th century.
Geography
Sakala County is in northwestern Livonia, covering approximately ...
, who by 1211 had come to the attention of German chroniclers as the central figure of the Estonian resistance. The Livonian leader Caupo was killed in the Battle of St. Matthew's Day
The Battle of Matthew's Day ( et, Madisepäeva lahing) was fought near Viljandi (probably in Vanamõisa) on 21 September 1217Battle of St. Matthew's Day (September 21) @ during the Livonian Crusade. The adversaries were the Sword Brethren ...
near Viljandi (Fellin) on September 21, 1217, but Lembitu was also killed, and the battle was a crushing defeat for the Estonians.
The Christian kingdoms of Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
and Sweden were also eager for expansion on the eastern shores of the Baltic. In 1218 Albert asked King Valdemar II of Denmark
Valdemar (28 June 1170 – 28 March 1241), later remembered as Valdemar the Victorious (), was the King of Denmark (being Valdemar II) from 1202 until his death in 1241.
Background
He was the second son of King Valdemar I of Denmark and Sophi ...
for assistance, but Valdemar instead arranged a deal with the Order. The king was victorious in the Battle of Lindanise in Revelia
Revala (also ''Rävälä'', la, Revalia, by Henry of Livonia ''Revele'', by Danish Census Book ''Revælæ'') was an Ancient Estonian county. It was located in northern Estonia, by the Gulf of Finland and corresponded roughly to the present terri ...
in 1219, to which the origin of the Flag of Denmark is attributed. He subsequently founded the fortress Castrum Danorum
Toompea castle ( et, Toompea loss) is a medieval castle on Toompea hill in the central part of Tallinn, the capital of Estonia. In modern times, it houses the Parliament of Estonia.
History
The Toompea castle's predecessor, an ancient Estonia ...
, which was unsuccessfully besieged by the Estonians in 1220 and 1223. King John I of Sweden
John I ( sv, Johan Sverkersson; c. 1201 – 10 March 1222) was the king of Sweden from 1216 until his death.
Background
John was the son of King Sverker II of Sweden of the House of Sverker and Queen Ingegerd of the Bjälbo dynasty. When he was ...
tried to establish a Swedish presence in the province of Wiek, but his troops were defeated by the Oeselians
Oeselians ( la, Oesel, , sv, Ösel, da, Øsel, fi, Saarenmaa) is a term historically applied before the Northern Crusades up to the 13th century to people who were living on the island of Saaremaa or Oesel as it was known back then, an island ...
in the Battle of Lihula
The Battle of Lihula or Battle of Leal was fought between invading Swedes and Estonians for the control of a castle in Lihula, Estonia in 1220. The exact date remains uncertain, though some historians suggest that the battle took place on Augu ...
in 1220. Revelia, Harrien
Harju County ( et, Harju maakond or ''Harjumaa''), is one of the fifteen counties of Estonia. It is situated in Northern Estonia, on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland, and borders Lääne-Viru County to the east, Järva County to the sout ...
, and Vironia
Virumaa ( la, Vironia; Low German: ''Wierland''; Old Norse: ''Virland'') is a former independent county in Ancient Estonia. Now it is divided into Ida-Viru County or Eastern Vironia and Lääne-Viru County or Western Vironia. Vironians built ...
, the whole of northern Estonia, fell to Danish control.
During the uprising of 1223, all Christian strongholds in Estonia save Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju '' ...
fell into Estonian hands, with their defenders killed. By 1224 all of the larger fortresses were reconquered by the crusaders, except for Tharbata, which was defended by a determined Estonian garrison and 200 Russian mercenaries. The leader of the Russian troops was Vyachko
Vyachko of Koknese, also ''Vetseke of Kokenhusen'' ( la, Rex Vesceka de Kukenois, lv, Vetseke, russian: Вячко) was the ruler of the Principality of Koknese in present-day Latvia, a vassal of Polotsk, who unsuccessfully tried to establish hi ...
, to whom the Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of mod ...
had promised the fortress and its surrounding lands "if he could conquer them for himself". Tharbata was finally captured by the crusaders in August 1224 and all its defenders were killed.
Early in 1224 Emperor Frederick II had announced at Catania that Livonia, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, Sambia
Sambia (russian: Самбийский полуостров, lit=Sambian Peninsula, translit=Sambiysky poluostrov) or Samland (russian: Земландский полуостров, lit=Zemlandic Peninsula, translit=Zemlandsky poluostrov) or Kalini ...
and a number of neighboring provinces would henceforth be considered '' reichsfrei'', that is, subordinate directly to the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
only, as opposed to being under the jurisdiction of local rulers. At the end of the year Pope Honorius III
Pope Honorius III (c. 1150 – 18 March 1227), born Cencio Savelli, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 18 July 1216 to his death. A canon at the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore, he came to hold a number of impor ...
announced the appointment of Bishop William of Modena
William of Modena ( – 31 March 1251), also known as ''William of Sabina'', ''Guglielmo de Chartreaux'', ''Guglielmo de Savoy'', ''Guillelmus'', was an Italian clergyman and papal diplomat.
as papal legate for Livonia, Prussia, and other countries.
In 1224 the Livonian Brothers of the Sword established their headquarters at Fellin (Viljandi) in Sackalia, where the walls of the Master's castle are still standing. Other strongholds included Wenden (Cēsis), Segewold (Sigulda), and Ascheraden (Aizkraukle).
The Chronicle of Henry of Livonia
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry'' ( la, Heinrici Cronicon Lyvoniae) offers a Latin narrative of events in Livonia (roughly corresponding to today's inland Estonia and the northern part of Latvia) and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. It was ...
, one of the greatest medieval narratives, was written probably as a report for William of Modena, giving him the history of the Church in Livonia up to his time. It relates how in 1226, in the stronghold Tarwanpe
Rakvere is a town in northern Estonia and the administrative centre of the Lääne-Viru ''maakond'' (county), 20 km south of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea. Rakvere is the 8th most populous urban area in Estonia. Rakvere has a total ...
, William of Modena successfully mediated a peace between the Germans, the Danes and the Vironians
The Vironians ({{Lang-et, Virulased) were one of the Finnic tribes that later formed the Estonian nation.
History
They lived in Vironia (''Virumaa'' in Estonian, ''Wierland'' in German and ''Virland'' in Scandinavian, now Ida-Viru County and L ...
.
War against Saaremaa (1206–61)

 The last Estonian county to hold out against the invaders was the island country of Saaremaa (Ösel), whose war fleets had continued to raid Denmark and Sweden during the years of fighting against the German crusaders.
In 1206, a Danish army led by the king
The last Estonian county to hold out against the invaders was the island country of Saaremaa (Ösel), whose war fleets had continued to raid Denmark and Sweden during the years of fighting against the German crusaders.
In 1206, a Danish army led by the king Valdemar II
Valdemar (28 June 1170 – 28 March 1241), later remembered as Valdemar the Victorious (), was the King of Denmark (being Valdemar II) from 1202 until his death in 1241.
Background
He was the second son of King Valdemar I of Denmark and Soph ...
and Andreas, the Bishop of Lund, landed on Saaremaa and attempted to establish a stronghold, without success. In 1216 the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword ( la, Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, german: Schwertbrüderorden) was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theoderi ...
and the bishop Theodorich joined forces and invaded Saaremaa over the frozen sea. The Oeselians retaliated by raiding German-held territories in Latvia the following spring. In 1220 a Swedish army led by the king John I of Sweden
John I ( sv, Johan Sverkersson; c. 1201 – 10 March 1222) was the king of Sweden from 1216 until his death.
Background
John was the son of King Sverker II of Sweden of the House of Sverker and Queen Ingegerd of the Bjälbo dynasty. When he was ...
and the bishop Karl of Linköping captured Lihula
Lihula is a town in Lääneranna Parish, Pärnu County, Estonia.
Lihula castle
The castle of Lihula (german: Leal) was first mentioned in 1211, but it appears the site was used as a fortress since the Iron Age. In 1220, a Swedish army starte ...
in Rotalia in Western Estonia. The Oeselians attacked the Swedish stronghold later the same year and killed the entire garrison, including the Bishop of Linköping.
In 1222, the Danish king Valdemar II
Valdemar (28 June 1170 – 28 March 1241), later remembered as Valdemar the Victorious (), was the King of Denmark (being Valdemar II) from 1202 until his death in 1241.
Background
He was the second son of King Valdemar I of Denmark and Soph ...
attempted the second conquest of Saaremaa, this time establishing a stone fortress housing a strong garrison. The stronghold was besieged and surrendered within five days, the Danish garrison returning to Revel while leaving Bishop Albert of Riga
Albert of Riga or Albert of Livonia or Albrecht (german: Albert von Buxthoeven, lv, Alberts fon Buksthēvdens; c.1165 – 17 January 1229) was the third Bishop of Riga in Livonia. In 1201 he allegedly founded Riga, the modern capital of Latv ...
's brother Theodoric and others behind as hostages for peace. The castle was leveled by the Oeselians.
In 1227, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword, the town of Riga, and the Bishop of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga ( la, Archiepiscopatus Rigensis, nds, Erzbisdom Riga) was an archbishopric in Medieval Livonia, a subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 as the bishopric of Livonia at Ikšķile, then after moving to Rig ...
organized a combined attack against Saaremaa. After the destruction of Muhu Stronghold and the surrender of Valjala Stronghold
The Valjala Stronghold ( la, Castrum Waldia, et, Valjala Maalinn) was a major ringfort on the island of Saaremaa in Estonia. Established in the 12th century, at the time it was the most important Oeselian stronghold. Its surrender in 1227 fina ...
, the Oeselians formally accepted Christianity.
After the defeat of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword in the Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule ( lt, Saulės mūšis / Šiaulių mūšis; german: Schlacht von Schaulen; lv, Saules kauja) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Betwe ...
in 1236 fighting again broke out on Saaremaa. In 1241 the Oeselians once again accepted Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
by signing treaties with the Livonian Order's Master Andreas de Velven and the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
. This was followed by a treaty signed in 1255 by the Master of the Order, Anno Sangerhausenn, and, on behalf of the Oeselians, elders whose names were phonetically transcribed by Latin scribes as Ylle, Culle, Enu, Muntelene, Tappete, Yalde, Melete, and Cake. The treaty granted the Oeselians several distinctive rights regarding the ownership and inheritance of land, the social order, and the practice of religion.
Warfare erupted in 1261 as the Oeselians once more renounced Christianity and killed all the Germans on the island. A peace treaty was signed after the united forces of the Livonian Order, the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, and Danish Estonia
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
, including mainland Estonians and Latvians, defeated the Oeselians by capturing their stronghold at Kaarma. Soon thereafter, the Livonian Order established a stone fort at Pöide
Pöide (german: Peude) is a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County, on the eastern part of Saaremaa Island, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the n ...
.
On July 24, 1343, the Oeselians arose yet again, killing all the Germans on the island, drowning all the clerics, and besieging the Livonian Order's castle at Pöide. After the garrison surrendered the Oeselians massacred the defenders and destroyed the castle. In February 1344 Burchard von Dreileben Burchard (and all variant spellings) may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People
* Burchard (name), Burchard and all related spellings as a given name and surname
* Burckhardt, or (de) Bourcard, a family of the Basel patriciate
* Burchard-Bélaváry family, an a ...
led a campaign over the frozen sea to Saaremaa. The Oeselians' stronghold was conquered and their leader Vesse was hanged. In the early spring of 1345, the next campaign of the Livonian Order ended with a treaty mentioned in the Chronicle of Hermann von Wartberge and the Novgorod First Chronicle
The Novgorod First Chronicle (russian: Новгородская первая летопись) or The Chronicle of Novgorod, 1016–1471 is the most ancient extant Old Russian chronicle of the Novgorodian Rus'. It reflects a tradition different ...
.
Saaremaa remained the vassal of the master of the Livonian Order and the Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek until 1559.
Wars against Curonians (1242–67)
 Following the defeat of the Estonians, the crusade moved against
Following the defeat of the Estonians, the crusade moved against Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs ( lv, kurši; lt, kuršiai; german: Kuren; non, Kúrir; orv, кърсь) were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in what are now the western p ...
and Semigallians
Semigallians ( Latvian ''Zemgaļi''; lt, Žiemgaliai, also ''Zemgalians, Semigalls, Semigalians'') were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance ...
, Baltic tribes living to the south and west of the Daugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic ...
river and closely allied with Samogitians
Samogitians ( Samogitian: ''žemaitē'', lt, žemaičiai, lv, žemaiši) are an ethnographic group of Lithuanians of the Samogitia region, an ethnographic region of Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian language, which in Lithuania is mostly co ...
.
In July 1210 Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs ( lv, kurši; lt, kuršiai; german: Kuren; non, Kúrir; orv, кърсь) were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in what are now the western p ...
attacked Riga. After a day of fighting, the Curonians were unable to break through the city walls. They crossed to the other bank of the Daugava to burn their dead and mourn for three days. In 1228 Curonians together with Semigallians
Semigallians ( Latvian ''Zemgaļi''; lt, Žiemgaliai, also ''Zemgalians, Semigalls, Semigalians'') were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance ...
again attacked Riga. Although they were again unsuccessful in storming the city, they destroyed a monastery in Daugavgriva and killed all the monks.
After the defeat of Estonians and Osilians in 1227, the Curonians were confronted by Lithuanian enemies in the east and south, and harassed by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword ( la, Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, german: Schwertbrüderorden) was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theoderi ...
from the north; in the west, on the sea-shore, their arch-enemies, the Danes and Swedes, were lurking, waiting for an opportunity. In this hopeless situation, further aggravated by famine, the Curonians preferred to try to make peace with the Christian conquerors, inviting the monks into their country thereby escaping attacks by the Scandinavian nations. Edgar V. Saks. ''Aestii''. 1960. p. 244. In 1230 the Curonians in the northern part of Courland, under their ruler (''rex'') , signed a peace treaty with the Germans, and the lands they inhabited thus became known as ''Vredecuronia'' or ''Peace Courland''. The southern Curonians, however, continued to resist the invaders.
In 1260, the Curonians were involved in the Battle of Durbe, one of the biggest battles in Livonia in the 13th century. They were forced to fight on the crusader side. When the battle started, the Curonians abandoned the knights. Peter von Dusburg Peter of Dusburg (german: Peter von Dusburg; la, Petrus de Dusburg; died after 1326), also known as Peter of Duisburg, was a Priest-Brother and chronicler of the Teutonic Knights. He is known for writing the ''Chronicon terrae Prussiae'', which des ...
alleged that the Curonians even attacked the Knights from the rear. The Estonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic ethnic group native to Estonia who speak the Estonian language.
The Estonian language is spoken as the first language by the vast majority of Estonians; it is closely related to oth ...
and other local people soon followed the Curonians and abandoned the Knights and that allowed the Samogitians
Samogitians ( Samogitian: ''žemaitē'', lt, žemaičiai, lv, žemaiši) are an ethnographic group of Lithuanians of the Samogitia region, an ethnographic region of Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian language, which in Lithuania is mostly co ...
to gain victory over the Livonian Order. It was a heavy defeat for the Order and uprisings against the crusaders soon afterwards broke out in the Curonian and Prussian
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
lands.
Curonian resistance was finally subdued in 1266 when the whole of Courland was partitioned between the Livonian Order and the Archbishop of Riga. The Curonian nobles, among them 40 clans of the descendants of the Curonian Kings, who lived in the town of Kuldīga
Kuldīga () (german: Goldingen) is a town in the Courland region of Latvia, in the western part of the country. It is the center of Kuldīga Municipality with a population of approximately 13,500.
Kuldīga was first mentioned in 1242. It join ...
, preserved personal freedom and some of their privileges.
Wars against Semigallians (1219–90)
Livonian Chronicle of Henry
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry'' ( la, Heinrici Cronicon Lyvoniae) offers a Latin narrative of events in Livonia (roughly corresponding to today's inland Estonia and the northern part of Latvia) and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. It was ...
'', Semigallians formed an alliance with bishop Albert of Riga
Albert of Riga or Albert of Livonia or Albrecht (german: Albert von Buxthoeven, lv, Alberts fon Buksthēvdens; c.1165 – 17 January 1229) was the third Bishop of Riga in Livonia. In 1201 he allegedly founded Riga, the modern capital of Latv ...
against rebellious Livonians
The Livonians, or Livs ( Livonian: ''līvlizt''; Estonian: ''liivlased''; Latvian: ''līvi'', ''lībieši''), are a Balto-Finnic people indigenous to northern and northwestern Latvia. Livonians historically spoke Livonian, a Uralic language c ...
before 1203, and received military support to hold back Lithuanian attacks in 1205. In 1207, the Semigallian duke Viestards
Viestards (also ''Viesthard, Vesthardus, Viesturs''; died 1230) was one of the greatest Semigallian dukes in the 13th century, referred to as King Vester ( goh, konic Vesters).
Life
His capital was Tērvete hillfort. During the first decades of ...
( la, dux Semigallorum) helped the christened Livonian chief Caupo conquer back his Turaida Castle
Turaida Castle ( lv, Turaidas pils, german: Treiden, Treyden, russian: Турайдский замок; meaning ''Thor's garden'' in Livonian) is a recently reconstructed medieval castle in Turaida, in the Vidzeme region of Latvia, on the opposite ...
from pagan rebels.
In 1219, the Semigallian–German alliance was cancelled after a crusader invasion in Semigallia. Duke Viestards promptly formed an alliance with Lithuanians and Curonians. In 1228, Semigallians and Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs ( lv, kurši; lt, kuršiai; german: Kuren; non, Kúrir; orv, кърсь) were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in what are now the western p ...
attacked the Daugavgrīva monastery, the main crusader stronghold at the Daugava river delta. The crusaders took revenge and invaded Semigallia. The Semigallians in turn pillaged land around the Aizkraukle
Aizkraukle (german: Ascheraden) is a town in Vidzeme region in Latvia, the administrative centre of Aizkraukle Municipality on the right bank of the Daugava River. The population in 2020 was 7,018.
History
In the second half of the 14th century ...
hillfort.
In 1236, Semigallians attacked crusaders retreating to Riga after the Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule ( lt, Saulės mūšis / Šiaulių mūšis; german: Schlacht von Schaulen; lv, Saules kauja) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Betwe ...
, killing many of them.
After regular attacks, the Livonian Order partly subdued the Semigallians in 1254.
In 1270, the Lithuanian Grand Duke Traidenis
Traidenis ( pl, Trojden, be, Трайдзень) (died 1282) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1270 (or 1269) until 1282. He is the second most prominent, after Mindaugas, Grand Duke of Lithuania in the 13th century. His reign ended a seven-y ...
, together with Semigallians, attacked Livonia and Saaremaa
Saaremaa is the largest island in Estonia, measuring . The main island of Saare County, it is located in the Baltic Sea, south of Hiiumaa island and west of Muhu island, and belongs to the West Estonian Archipelago. The capital of the isla ...
. During the Battle of Karuse on the frozen Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia ( lv, Rīgas līcis, et, Liivi laht) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia.
The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main c ...
, the Livonian Order was defeated, and its master Otto von Lutterberg was killed.
In 1287, around 1400 Semigallians attacked a crusader stronghold in Ikšķile
Ikšķile (; german: Uexküll; liv, Ikškilā; et, Üksküla; also known as ''Üxküll'') is a town in Latvia, in Ogre Municipality. It was the first capital of the Roman Catholic Bishopric of Livonia, known by the German name of Üxküll ...
and plundered nearby lands. As they returned to Semigallia they were caught by the Order's forces, and the great Battle of Garoza began near the Garoza river. The crusader forces were besieged and badly defeated. More than 40 knights were killed, including the master of the Livonian Order Willekin von Endorp, and an unknown number of crusader allies. It was the last Semigallian victory over the growing forces of the Livonian Order.
In 1279, after the Battle of Aizkraukle
The Battle of Aizkraukle or Ascheraden was fought on 5 March 1279 between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led by Traidenis, and the Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order near Aizkraukle (german: Ascheraden) in present-day Latvia. The order suffere ...
, Grand Duke Traidenis of Lithuania supported a Semigallian revolt against the Livonian Order led by Duke Nameisis.
In the 1280s, the Livonian Order started a massive campaign against the Semigallians, which included burning their fields and thus causing famine. Semigallians continued their resistance until 1290, when they burned their last castle in and moved southwards. The ''Rhymed Chronicle
The ''Livonian Rhymed Chronicle'' (german: Livländische Reimchronik) is a chronicle written in Middle High German by an anonymous author. It covers the period 1180 – 1343 and contains a wealth of detail about Livonia — modern South Estonia a ...
'' claims that 100,000 migrated to Lithuania and once there continued to fight against the Germans.
The unconquered southern parts of Curonian and Semigallian territories ( Sidabrė, Raktė, Ceklis, Mėguva etc.) were united under the rule of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
.
Aftermath
 In 1227 the
In 1227 the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword ( la, Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, german: Schwertbrüderorden) was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theoderi ...
conquered all Danish territories in Northern Estonia. After the Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule ( lt, Saulės mūšis / Šiaulių mūšis; german: Schlacht von Schaulen; lv, Saules kauja) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Betwe ...
the surviving members of the Brothers of the Sword merged into the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
of Prussia in 1237 and became known as Livonian Order. On 7 June 1238, by the Treaty of Stensby, the Teutonic knights returned the Duchy of Estonia to Valdemar II, until in 1346, after St. George's Night Uprising, the lands were sold back to the order and became part of the Ordensstaat.
After the conquest, all of the remaining local population were ostensibly Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
. In 1535, the first extant native language book was printed, a Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
catechism. The conquerors upheld military control through their network of castles throughout Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
and Latvia.
The land was divided into six feudal principalities by Papal Legate William of Modena
William of Modena ( – 31 March 1251), also known as ''William of Sabina'', ''Guglielmo de Chartreaux'', ''Guglielmo de Savoy'', ''Guillelmus'', was an Italian clergyman and papal diplomat.
: Archbishopric of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga ( la, Archiepiscopatus Rigensis, nds, Erzbisdom Riga) was an archbishopric in Medieval Livonia, a subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 as the bishopric of Livonia at Ikšķile, then after moving to Rig ...
, Bishopric of Courland
The Bishopric of Courland ( la, Episcopatus Curoniensis, Low German: ''Bisdom Curland'') was the second smallest (4500 km2) ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade. During the Livo ...
, Bishopric of Dorpat
The Bishopric of Dorpat ( et, Tartu piiskopkond; nds, Bisdom Dorpat; la, Ecclesia Tarbatensis) was a medieval prince-bishopric, i.e. both a diocese of the Roman Catholic Church and a temporal principality ruled by the bishop of the diocese. I ...
, Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, the lands ruled by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword ( la, Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, german: Schwertbrüderorden) was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theoderi ...
and Dominum directum ''Dominium directum et utile'' is a legal Latin term used to refer to the two separate estates in land that a fief was split into under feudal land tenure. This system is more commonly known as ''duplex dominium'' or double domain. This can be contr ...
of King of Denmark, the Duchy of Estonia.
Battles
* Battle of Riga (1203) * Battle of Koknese (1205) * Battle of Salaspils (1206) * Battle of Turaida (1206) * Battle of Saaremaa, 1206 * Battle of Koknese (1208) * Battle of Otepää (1208) * Battle of Jersika, 1209 * Battle of Otepää (1210) *Battle of Cēsis (1210)
The Battle of Cēsis was fought between native Estonian forces and the Germanic knights (known as the Livonian Brothers of the Sword) and their allies during the Livonian Crusade.
In 1210 the Estonian counties launched several raids on the stro ...
* Battle of Ümera, 1210
* Battle of Turaida (1211)
* Battle of Viljandi, 1211
* Battle of Lehola, 1215
* Battle of Riga (1215)
* Battle of Soontagana, 1215
* Battle of Otepää, 1217
* Battle of Soontagana, 1217
*Battle of St. Matthew's Day
The Battle of Matthew's Day ( et, Madisepäeva lahing) was fought near Viljandi (probably in Vanamõisa) on 21 September 1217Battle of St. Matthew's Day (September 21) @ during the Livonian Crusade. The adversaries were the Sword Brethren ...
, 1217
* Battle of Lindanise, 1219
* Siege of Mežotne, 1219
*Battle of Lihula
The Battle of Lihula or Battle of Leal was fought between invading Swedes and Estonians for the control of a castle in Lihula, Estonia in 1220. The exact date remains uncertain, though some historians suggest that the battle took place on Augu ...
, 1220
*Siege of Tallinn
Victory over the Swedish army in the Battle of Lihula inspired the Oeselians to further fighting. In 1221 they tried to conquer the Danish stronghold in Tallinn with the help of Revalians, Harrians, and Vironians. They besieged the stronghold ...
, 1221
* Battle of Soela, 1223
* Battle of the Ümera River Bridge, 1223
* Battle of Viljandi (1223)
* Siege of Tallinn (1223)
* Siege of Tartu, 1224
*Battle of Muhu
The Battle of Muhu was a military engagement fought between a force of Baltic and Germanic crusaders and pagan Oeselians. The battle, fought in Muhu, Estonia, resulted in the crusaders storming and capturing a fortress held by the Oeselians.
Hi ...
, 1227
* Siege of Aizkraukle (1229)
*Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule ( lt, Saulės mūšis / Šiaulių mūšis; german: Schlacht von Schaulen; lv, Saules kauja) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Betwe ...
, 1236
*Battle on the Ice
The Battle on the Ice (german: Schlacht auf dem Eise; russian: Ледовое побоище, ''Ledovoye poboishche''; et, Jäälahing), alternatively known as the Battle of Lake Peipus (german: Schlacht auf dem Peipussee), took place on 5 Apr ...
, 1242
* Battle of Durbe, 1260
* Siege of Tērvete (1259)
* Battle of Tērvete (1270)
*Battle of Aizkraukle
The Battle of Aizkraukle or Ascheraden was fought on 5 March 1279 between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led by Traidenis, and the Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order near Aizkraukle (german: Ascheraden) in present-day Latvia. The order suffere ...
* Siege of Dobele (1279)
* Siege of Kernavė (1279)
* Battle of Tērvete (1280)
* Siege of Dobele (1281)
* Battle of Riga (1281)
* Battle of Tērvete (1281)
* Battle of Garoza 1287
* Battle of Dobele (1290)
See also
*Chronicle of Henry of Livonia
The ''Livonian Chronicle of Henry'' ( la, Heinrici Cronicon Lyvoniae) offers a Latin narrative of events in Livonia (roughly corresponding to today's inland Estonia and the northern part of Latvia) and surrounding areas from 1180 to 1227. It was ...
*Wendish Crusade
The Wendish Crusade (german: Wendenkreuzzug) was a military campaign in 1147, one of the Northern Crusades and a part of the Second Crusade, led primarily by the Kingdom of Germany within the Holy Roman Empire and directed against the Polabian Sl ...
* Baltic paganism
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Saaremaa 1100–1227
13th century in Denmark 13th-century conflicts 13th-century crusades Conflicts involving the Livonian Order History of Livonia Medieval Sweden Military history of Estonia Military history of Latvia Northern Crusades Wars involving Denmark Wars involving Estonia Wars involving Latvia Wars involving Livonia Wars involving Sweden