Ergine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ergine, also known as d-lysergic acid amide (LSA) and d-lysergamide, is an
 The biosynthetic pathway to ergine starts like most other ergoline alkaloid- with the formation of the ergoline scaffold. This synthesis starts with the
The biosynthetic pathway to ergine starts like most other ergoline alkaloid- with the formation of the ergoline scaffold. This synthesis starts with the  From here, the biosynthesis diverges and the products formed are plant and fungus-specific. The biosynthesis of ergine in C''laviceps purpurea'' will be exemplified, in which
From here, the biosynthesis diverges and the products formed are plant and fungus-specific. The biosynthesis of ergine in C''laviceps purpurea'' will be exemplified, in which 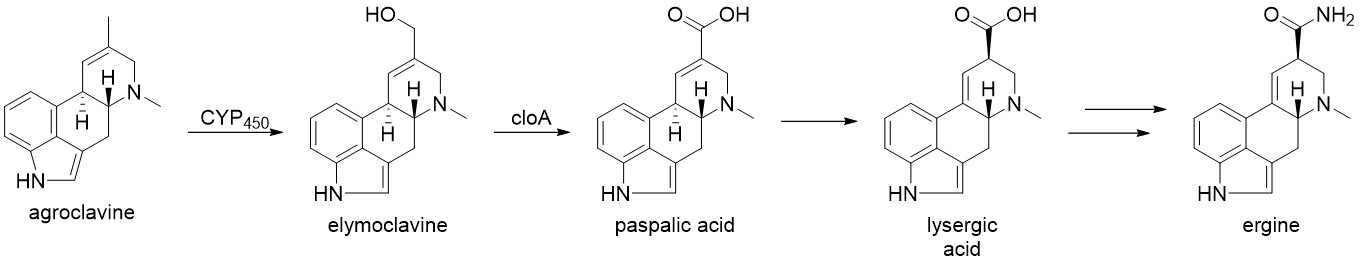
Hofmann, A. ''Teonanácatl and Ololiuqui, two ancient magic drugs of Mexico'' Bulletin on Narcotics 1971 1 3
TiHKAL (A & A Shulgin) #26
LSA Vault
–
ergoline
Ergoline is a chemical compound whose structural skeleton is contained in a variety of alkaloids, referred to as ergoline derivatives or ergoline alkaloids. Ergoline alkaloids, one being ergine, were initially characterized in ergot. Some of thes ...
alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
that occurs in various species of vines of the Convolvulaceae
Convolvulaceae (), commonly called the bindweeds or morning glories, is a family of about 60 genera and more than 1,650 species. These species are primarily herbaceous vines, but also include trees, shrubs and herbs. The tubers of several spe ...
and some species of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
. The psychedelic properties in the seeds of ololiuhqui, Hawaiian baby woodrose
''Argyreia nervosa'' is a perennial climbing vine native to the Indian subcontinent and introduced to numerous areas worldwide, including Hawaii, Africa, and the Caribbean. Though it can be invasive, it is often prized for its aesthetic and med ...
and morning glories
Morning glory (also written as morning-glory) is the common name for over 1,000 species of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, whose current taxonomy and systematics are in flux. Morning glory species belong to many genera, some of ...
have been linked to ergine and/or isoergine, its epimer
In stereochemistry, an epimer is one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers have opposite configuration at only one stereogenic center out of at least two. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each. Epimerization i ...
, as it is an alkaloid present in the seeds.
Occurrence in nature
Ergine has been found in high concentrations of 20 μg/g dry weight in the sleepygrass infected with an ''Acremonium
''Acremonium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae. It used to be known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Description
''Acremonium'' species are usually slow-growing and are initially compact and moist. Their hyphae are fine and hyaline, and pro ...
'' endophytic
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; h ...
fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
together with other ergot alkaloids.
Ergine is a component of the alkaloids contained in the ergot fungus, which grows on the heads of infected rye grasses.
It is also found in the seeds of several varieties of morning glories
Morning glory (also written as morning-glory) is the common name for over 1,000 species of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, whose current taxonomy and systematics are in flux. Morning glory species belong to many genera, some of ...
in concentrations of approximately 10 μg per seed, as well as Hawaiian baby woodrose
''Argyreia nervosa'' is a perennial climbing vine native to the Indian subcontinent and introduced to numerous areas worldwide, including Hawaii, Africa, and the Caribbean. Though it can be invasive, it is often prized for its aesthetic and med ...
seeds, at a concentration of around 0.13% of dry weight.
History
''Ololiuhqui'' was used by South American healers in shamanic healing ceremonies. Similarly, ingestion ofmorning glory
Morning glory (also written as morning-glory) is the common name for over 1,000 species of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, whose current taxonomy and systematics are in flux. Morning glory species belong to many genera, some of ...
seeds by Mazatec
The Mazatec are an indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit the Sierra Mazateca in the state of Oaxaca and some communities in the adjacent states of Puebla and Veracruz.
Language family
The Mazatecan languages are part of the Popolocan family wh ...
tribes to "commune with their gods" was reported by Richard Schultes
Richard Evans Schultes (''SHULL-tees'';Jonathan Kandell ''The New York Times'', April 13, 2001, Accessed April 26, 2020. January 12, 1915 – April 10, 2001) was an American biologist. He may be considered the father of modern ethnobotany. He i ...
in 1941 and is still practiced today.
Additional reports of the use of ergine were made by Don Thomes MacDougall. He reported that the seeds of ''Ipomoea violacea
''Ipomoea violacea'' is a perennial species of ''Ipomoea'' that occurs throughout the world with the exception of the European continent. It is most commonly called beach moonflower or sea moonflower as the flowers open at night.
Description
The ...
'' were used as sacrament
A sacrament is a Christianity, Christian Rite (Christianity), rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments ...
s by certain Zapotecs, sometimes in conjunction with the seeds of ''Rivea corymbosa
''Ipomoea corymbosa'' is a species of morning glory, native throughout Latin America from Mexico as far south as Peru and widely naturalised elsewhere. Its common names include Christmasvine, Christmaspops, and snakeplant.
Description and names
...
'', another species which has a similar chemical composition, with lysergol
Lysergol is an alkaloid of the ergoline family that occurs as a minor constituent in some species of fungi (most within ''Claviceps''), and in the morning glory family of plants (Convolvulaceae), including the Psychedelics, dissociatives and deli ...
instead of ergometrine
Ergometrine, also known as ergonovine and sold under the brand names Ergotrate, Ergostat, and Syntometrine among others, is a medication used to cause contractions of the uterus to treat heavy vaginal bleeding after childbirth. It can be used ei ...
.
Ergine was assayed for human activity by Albert Hofmann
Albert Hofmann (11 January 1906 – 29 April 2008) was a Swiss chemist known for being the first to synthesize, ingest, and learn of the psychedelic effects of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Hofmann's team also isolated, named and synthesi ...
in self-trials in 1947, well before it was known to be a natural compound. Intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have ...
administration of a 500 microgram dose led to a tired, dreamy state, with an inability to maintain clear thoughts. After a short period of sleep the effects were gone, and normal baseline was recovered within five hours.
In 1956, the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
conducted research on the psychedelic properties of the ergine in the seeds of ''Rivea corymbosa'', as Subproject 22 of MKULTRA
Project MKUltra (or MK-Ultra) was an illegal human experimentation program designed and undertaken by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), intended to develop procedures and identify drugs that could be used in interrogations to weak ...
.
In 1959, Hofmann was the first to isolate chemically pure ergine from the seeds of Turbina corymbosa
''Ipomoea corymbosa'' is a species of morning glory, native throughout Latin America from Mexico as far south as Peru and widely naturalised elsewhere. Its common names include Christmasvine, Christmaspops, and snakeplant.
Description and names ...
, determining that it, and other alkaloids, were acting as the main active components in the seeds. Twenty years prior to its isolation, ergine was first chemically defined by English chemists S. Smith and G. M. Timmis as the cleavage product of ergot alkaloids. Additionally, Guarin and Youngkin reportedly isolated the crude alkaloid in 1964 from morning glory seeds.
Ingestion
Like other psychedelics, ergine is not considered to be addictive. Additionally, there are no knowndeath
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
s directly associated with pharmacological
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
effects of ergine consumption. All associated deaths are due to indirect causes, such as self-harm, impaired judgement, and adverse drug interaction
Drug interactions occur when a drug's mechanism of action is disturbed by the concomitant administration of substances such as foods, beverages, or other drugs. The cause is often the inhibition of the specific receptors available to the drug, ...
s. One known case involved a suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
that was reported in 1964 after ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms ingest ...
of morning glory
Morning glory (also written as morning-glory) is the common name for over 1,000 species of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, whose current taxonomy and systematics are in flux. Morning glory species belong to many genera, some of ...
seeds
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm pl ...
. Another instance is a death due to falling off of a building
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and fun ...
after ingestion of Hawaiian baby woodrose
''Argyreia nervosa'' is a perennial climbing vine native to the Indian subcontinent and introduced to numerous areas worldwide, including Hawaii, Africa, and the Caribbean. Though it can be invasive, it is often prized for its aesthetic and med ...
seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s and alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
.
Physiological effects
While its physiological effects vary from person to person, the following symptoms have been attributed to the consumption of ergine or ergine containing seeds: *Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, ...
* Visual and auditory hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the qualities of a real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. Hallucination is a combinatio ...
s
* Euphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
* Loss of motor control
* Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
* Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessel ...
* Delusion
A delusion is a false fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some o ...
* Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
* Paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concer ...
* Irregular heartbeat
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
Kremer, C., Paulke, A., Wunder, C., & Toennes, S. W. (2012). Variable adverse effects in subjects after ingestion of equal doses of Argyreia nervosa seeds. Forensic science international, 214(1-3), e6-e8.
* Sexual arousalSubramoniam, A., Madhavachandran, V., Ravi, K., & Anuja, V. S. (2007). Aphrodisiac property of the elephant creeper Argyreia nervosa. J Endocrinol Reprod, 11(2), 82-85.
* Tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (su ...
Marneros A, Gutmann P, Uhlmann F. Self-amputation of penis and tongue after use of Angel's Trumpet. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006 Oct;256(7):458-9. doi: 10.1007/s00406-006-0666-2. Epub 2006 Jun 16. PMID 16783491.
* Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs.
Normally, as ...
* Hypertonia
Hypertonia is a term sometimes used synonymously with spasticity and rigidity in the literature surrounding damage to the central nervous system, namely upper motor neuron lesions. Impaired ability of damaged motor neurons to regulate descending ...
* Respiratory disturbances
* Cramps
A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, painful skeletal muscle contraction or overshortening associated with electrical activity; while generally temporary and non-damaging, they can cause significant pain and a paralysis-like immobility of the aff ...
One study found that 2 of 4 human subjects experienced cardiovascular dysregulation and the study had to be halted, concluding that the drug is more dangerous than commonly believed. The same study also observed that reactions were highly differing in type and intensity between different subjects. Another study in mice found that the drug had aphrodisiac properties, inducing increased sexual behavior.
A study gave mice 3000 mg/kg with no lethal effects.
Psychedelic component
Ergine is thought to be aserotonergic psychedelic
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science of ...
and its psychedelic effects are thought to be due to it being a partial agonist
In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered ligands which display both agonistic and antagonistic e ...
of the 5-HT2A receptor. Though, the reason as to why this may be hallucinogenic remains elusive.
The idea that ergine is the main psychedelic component in ergine containing seeds (morning glory, Hawaiian baby woodrose) is well debated, as the effects of isolated synthetic ergine are reported to be only mildly psychedelic. Thus, the overall psychedelic experience after consumption of such seeds has been proposed to be due to a mixture of ergoline alkaloids.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Ergine interacts withserotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
, dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
, and adrenergic receptor
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta ...
s similarly to but with lower affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Par ...
than lysergic acid diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, vi ...
(LSD). The psychedelic effects of ergine can be attributed to activation of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors.
Chemistry
Biosynthesis
 The biosynthetic pathway to ergine starts like most other ergoline alkaloid- with the formation of the ergoline scaffold. This synthesis starts with the
The biosynthetic pathway to ergine starts like most other ergoline alkaloid- with the formation of the ergoline scaffold. This synthesis starts with the prenylation
Prenylation (also known as isoprenylation or lipidation) is the addition of hydrophobic molecules to a protein or a biomolecule. It is usually assumed that prenyl groups (3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) facilitate attachment to cell membranes, similar to ...
of L-tryptophan in an SN1 fashion with dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) as the prenyl donor and catalyzed by prenyltransferase 4-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase (DMATS), to form 4-L-dimethylallyltryptophan (4-L-DMAT). The DMAPP is derived from mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate ...
. A three strep mechanism is proposed to form 4-L-DMAT: the formation of an allylic carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountere ...
, a nucleophilic attack of the indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C8 H7 N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environmen ...
nucleus to the cation, followed by deprotonation to restore aromaticity and to generate 4-L-DMAT. 4-Dimethylallyltyptophan ''N''-methyltransferase (EasF) catalyzes the ''N''-methylation of 4-L-DMAT at the amino of the tryptophan backbone, using S-Adenosyl methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throug ...
(SAM) as the methyl source, to form 4-dimethylallyl-L-abrine (4-DMA-L-abrine). The conversion of 4-DMA-L-abrine to chanoclavine-I is thought to occur through a decarboxylation and two oxidation steps, catalyzed by the FAD dependent oxidoreductase, EasE, and the catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting t ...
, EasC. The chanoclavine intermediate is then oxidized to chanoclavine-l-aldehyde, catalyzed by the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR), EasD.
 From here, the biosynthesis diverges and the products formed are plant and fungus-specific. The biosynthesis of ergine in C''laviceps purpurea'' will be exemplified, in which
From here, the biosynthesis diverges and the products formed are plant and fungus-specific. The biosynthesis of ergine in C''laviceps purpurea'' will be exemplified, in which agroclavine
Agroclavine belongs to the group of ergot alkaloids, such as ergotamine
Ergotamine, sold under the brand names Cafergot (with caffeine) and Ergomar among others, is an ergopeptine and part of the ergot family of alkaloids; it is structurally a ...
is produced following the formation of chanoclavine-l-aldehyde, catalyzed by EasA through a keto-enol tautomerization
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydr ...
to facilitate rotation about the C-C bond, followed by tautomerization back to the aldehyde and condensation with the proximal secondary amine to form an iminium species, which is subsequently reduced to the tertiary amine and yielding argoclavine. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compo ...
s (CYP450) are then thought to catalyze the formation of elymoclavine
Elymoclavine is an ergot alkaloid (ergoline alkaloid). It can be produced from ''C. fusiformis'' from ''Pennisetum typhoideum''. It is a precursor in the biosynthesis of lysergic acid, D-(+)-lysergic acid. Ergot alkaloids are natural products deri ...
from argoclavine via a 2 electron oxidation. This is further converted to paspalic acid via a 4 electron oxidation, catalyzed by ''cloA'', a CYP450 monooxygenase. Paspalic acid then undergoes isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomeriz ...
of the C-C double bond in conjugation with the acid to form D-lysergic acid
Lysergic acid, also known as -lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of ''Turbina corymbosa'' (ololiuhqui), ''Argyreia nervosa'' (Ha ...
. While the specifics of the formation of ergine from D-lysergic acid
Lysergic acid, also known as -lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of ''Turbina corymbosa'' (ololiuhqui), ''Argyreia nervosa'' (Ha ...
are not known, it is proposed to occur through a nonribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS) with two enzymes primarily involve: D-lysergyl peptide synthase (LPS) 1 and 2.

Legal status
The legality of consuming, cultivating, and possessing ergine varies depending on the country. There are no laws against possession of ergine-containing seeds in the USA. However, possession of the pure compound without a prescription or DEA license would be prosecuted, as ergine, under the name "lysergic acid amide", is listed under Schedule III of theControlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) is the statute establishing federal government of the United States, federal drug policy of the United States, U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use, and distribution of ...
. Similarly, ergine is considered a Class A substance in the United Kingdom, categorized as a precursor to LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, vi ...
.
In most Australian states, the consumption of ergine containing materials is prohibited under state legislation.
In Canada, ergine is not illegal to possess as it is not listed under Canada's Controlled Drugs and Substances Act
The ''Controlled Drugs and Substances Act'' (french: Loi réglementant certaines drogues et autres substances) (the ''Act'') is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals ...
, though it is likely illegal to sell for human consumption.
In New Zealand, ergine is a controlled drug, however the plants and seeds of the morning glory species are legal to possess, cultivate, buy, and distribute.
See also
*Argyreia nervosa
''Argyreia nervosa'' is a perennial climbing vine native to the Indian subcontinent and introduced to numerous areas worldwide, including Hawaii, Africa, and the Caribbean. Though it can be invasive, it is often prized for its aesthetic and me ...
* List of entheogenic/hallucinogenic species
* List of psychoactive plants
This is a list of plant species that, when consumed by humans, are known or suspected to produce psychoactive effects: changes in nervous system function that alter perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior. Many of these plants ...
* Tlitliltzin
''Ipomoea tricolor'', the Mexican morning glory or just morning glory, is a species of flowering plant in the family Convolvulaceae, native to the New World tropics, and widely cultivated and naturalised elsewhere. It is an herbaceous annual or ...
(''Ipomoea violacea'')
Notes
* * * *References
External links
Hofmann, A. ''Teonanácatl and Ololiuqui, two ancient magic drugs of Mexico'' Bulletin on Narcotics 1971 1 3
TiHKAL (A & A Shulgin) #26
LSA Vault
–
Erowid
Erowid, also called Erowid Center, is a non-profit educational organization that provides information about psychoactive plants and chemicals.
Erowid documents legal and illegal substances, including their intended and adverse effects. Informat ...
{{Drug use
Alkaloids found in fungi
Lysergamides
Plant toxins
Quinoline alkaloids
Serotonin receptor agonists
Tryptamine alkaloids
Vasoconstrictors