|
Lysergic Acid
Lysergic acid, also known as -lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of ''Turbina corymbosa'' (ololiuhqui), ''Argyreia nervosa'' (Hawaiian baby woodrose), and ''Ipomoea tricolor'' (morning glories, tlitliltzin). Amides of lysergic acid, lysergamides, are widely used as pharmaceuticals and as psychedelic drugs (LSD). Lysergic acid is listed as a Table I precursor under the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. Lysergic acid received its name as it was a product of the lysis of various ergot alkaloids. Total synthesis Lysergic acid is generally produced by hydrolysis of natural lysergamides, but can also be synthesized in the laboratory by a complex total synthesis, for example by Robert Burns Woodward's team in 1956. An enantioselective total synthesis based on a palladium-catalyzed domino cyclization reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergoline
Ergoline is a chemical compound whose structural skeleton is contained in a variety of alkaloids, referred to as ergoline derivatives or ergoline alkaloids. Ergoline alkaloids, one being ergine, were initially characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives. Others, such as lysergic acid diethylamide, better known as LSD, a semi-synthetic derivative, and ergine, a natural derivative found in ''Argyreia nervosa'', ''Ipomoea tricolor'' and related species, are known psychedelic substances. Natural occurrence Ergoline alkaloids are found in lower fungi and some species of flowering plants: the Mexican specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful. Often, the aim is to discover a new route of synthesis for a target molecule for which there already exist known routes. Sometimes, however, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereocenter
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups creates a new stereoisomer. Stereocenters are also referred to as stereogenic centers. A stereocenter is geometrically defined as a point (location) in a molecule; a stereocenter is usually but not always a specific atom, often carbon. Stereocenters can exist on chiral or achiral molecules; stereocenters can contain single bonds or double bonds. The number of hypothetical stereoisomers can be predicted by using 2''n'', with ''n'' being the number of tetrahedral stereocenters; however, exceptions such as meso compounds can reduce the prediction to below the expected 2''n''. Chirality centers are a type of stereocenter with four different substituent groups; chirality centers are a specific subset of stereocenters because they can only hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral () if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (). The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (''cheir'') 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers; they are often distinguished as either "right-handed" or "left-handed" by their absolute configuration or some other criterion. The two enantiomers have the same chemical properties, except when reacting with other chiral compounds. They also have the same physical properties, except that they often have opposite optical activities. A homogeneous mixture of the two enantiomers in equal parts is said to be racemic, and it usually differs chemically and physically from the pure enantiomers. Chiral molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomerization. When the isomerization occurs intramolecularly it may be called a rearrangement reaction. When the activation energy for the isomerization reaction is sufficiently small, both isomers will exist in a temperature-dependent equilibrium with each other. Many values of the standard free energy difference, \Delta G^\circ, have been calculated, with good agreement between observed and calculated data. Examples and applications Alkanes Skeletal isomerization occurs in the cracking process, used in the petrochemical industry. As well as reducing the average chain length, straight-chain hydrocarbons are converted to branched isomers in the process, as illustrated the following reaction of ''n''-butane to ''i''-butane. :\overset -> ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
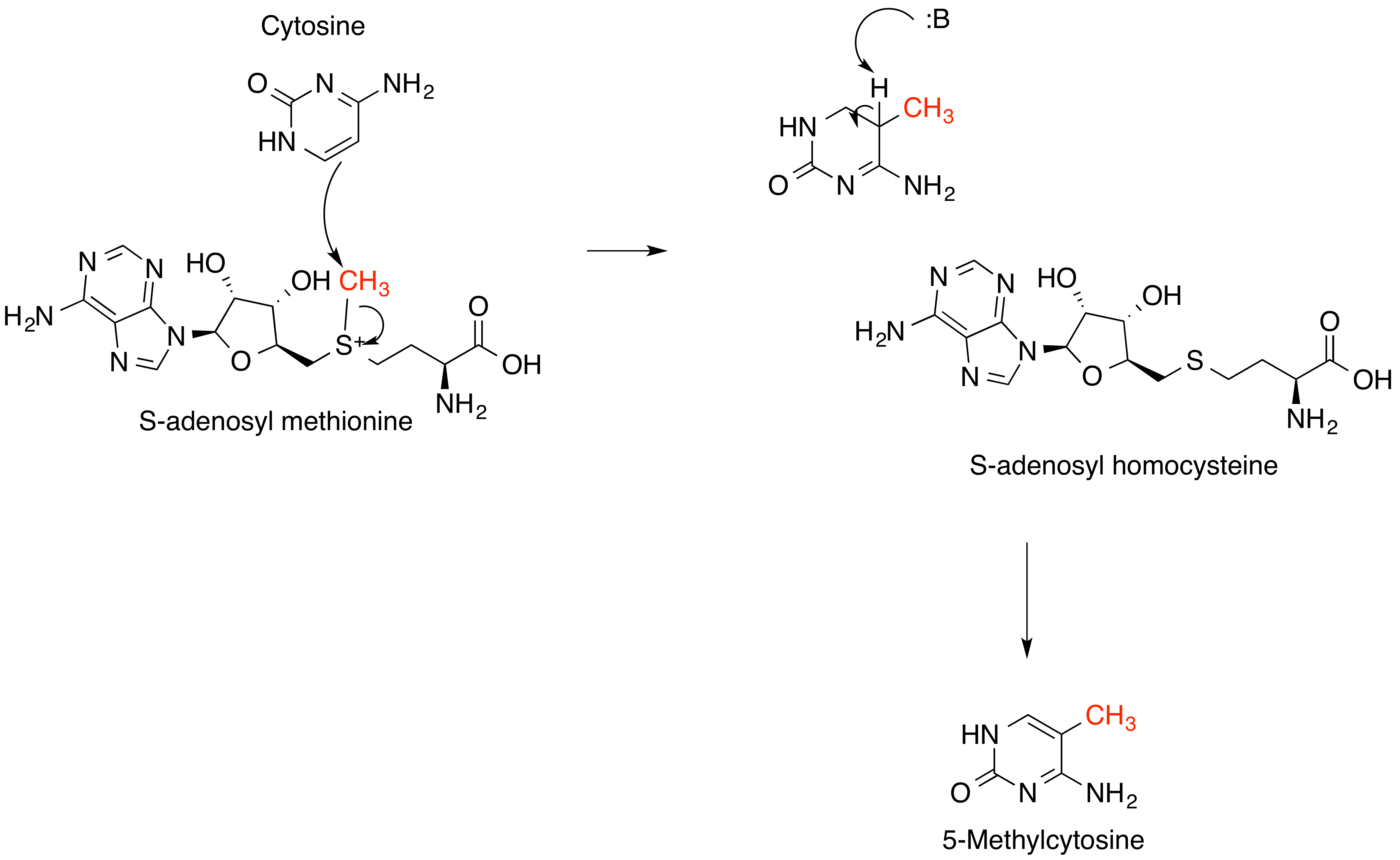
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevalonic Acid
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate'' and is of major pharmaceutical importance. Drugs like statins (which lower levels of cholesterol) stop the production of mevalonate by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Chemistry Mevalonic acid is very soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It exists in equilibrium with its lactone form, called mevalonolactone, that is formed by internal condensation of its terminal alcohol and carboxylic acid functional groups. Biology Mevalonic acid is a precursor in the biosynthetic pathway known as the mevalonate pathway that produces terpenes and steroids. Mevalonic acid is the primary precursor of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), that is in turn the basis for all terpenoids. Mevalonic acid is chiral and the (3''R'')-enantiomer In chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. Isoprene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers are the main component of natural rubber. C. G. Williams named the compound in 1860 after obtaining it from thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) of natural rubber; he correctly deduced the empirical formula C5H8. Natural occurrences Isoprene is produced and emitted by many species of trees (major producers are oaks, poplars, eucalyptus, and some legumes). Yearly production of isoprene emissions by vegetation is around 600 million metric tons, half from tropical broadleaf trees and the remainder primarily from shrubs. This is about equivalent to methane emissions and accounts for around one-third of all hydrocarbons released into the atmosphere. In deciduous forests, isoprene makes up approximately 80% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylallyl Diphosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP. In the mevalonate pathway DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway. At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpene Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes ar ...s and terpenoids, such as in plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. It is essential in humans, meaning that the body cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained from the diet. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3. It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Function Amino acids, including tryptophan, are used as building blocks in protein biosynthesis, and proteins are required to sustain lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylation
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion ( carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new cova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclization Reaction
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present ( heterocyclic compounds). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of small size (e.g., < 17 total atoms) numbers in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |