Environmental effects of wind power on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The environmental impact of electricity generation from wind power is minor when compared to that of fossil fuel power. Wind turbines have some of the lowest global warming potential per unit of electricity generated: far less greenhouse gas is emitted than for the average unit of electricity, so wind power helps limit climate change. Wind power consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months.
Onshore (on-land) wind farms can have a significant visual impact and impact on the landscape. Due to a very low surface power density and spacing requirements, wind farms typically need to be spread over more land than other power stations.What are the pros and cons of onshore wind energy?
The environmental impact of electricity generation from wind power is minor when compared to that of fossil fuel power. Wind turbines have some of the lowest global warming potential per unit of electricity generated: far less greenhouse gas is emitted than for the average unit of electricity, so wind power helps limit climate change. Wind power consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months.
Onshore (on-land) wind farms can have a significant visual impact and impact on the landscape. Due to a very low surface power density and spacing requirements, wind farms typically need to be spread over more land than other power stations.What are the pros and cons of onshore wind energy?
Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment. January 2018. Their network of turbines, access roads, transmission lines, and substations can result in "energy sprawl";Nathan F. Jones, Liba Pejchar, Joseph M. Kiesecker. " The Energy Footprint: How Oil, Natural Gas, and Wind Energy Affect Land for Biodiversity and the Flow of Ecosystem Services". ''
Water Consumption of Energy Resource Extraction, Processing, and Conversion
'' Harvard Kennedy School'', October 2010. Accessed: 1 February 2011. for continuous operation and has near negligible emissions directly related to its electricity production. Wind turbines when isolated from the electric grid, produce negligible amounts of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide,
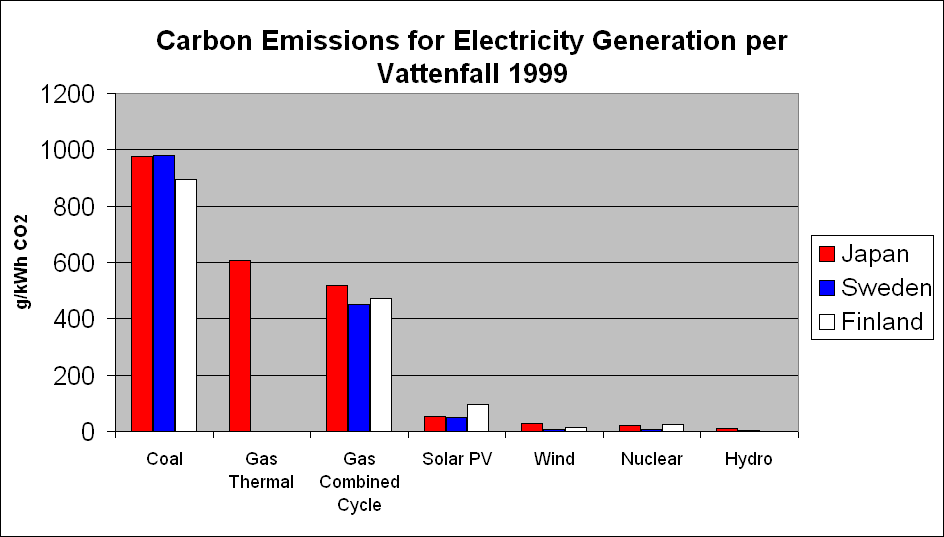 A typical study of a wind farm's Life cycle assessment, when not connected to the electric grid, usually results in similar findings as the following 2006 analysis of 3 installations in the US Midwest, where the carbon dioxide () emissions of wind power ranged from per GWh (14–33 g/
A typical study of a wind farm's Life cycle assessment, when not connected to the electric grid, usually results in similar findings as the following 2006 analysis of 3 installations in the US Midwest, where the carbon dioxide () emissions of wind power ranged from per GWh (14–33 g/
Developing greener, cheaper magnets
'' Ames Laboratory''. Accessed: 10 March 2011. Research is underway on turbine and generator designs which reduce the need for neodymium, or eliminate the use of rare-earth metals altogether. Additionally, the large wind turbine manufacturer
/ref>
 As much as 80% of the wind turbine structure can be
As much as 80% of the wind turbine structure can be
The wind energy fact sheet
Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water, p. 13 A study by the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory of US wind farms built between 2000 and 2009 found that, on average, only 1.1 percent of the total wind farm area suffered surface disturbance, and only 0.43 percent was permanently disturbed by wind power installations. On average, there were of total wind farm area per MW of capacity, but only of permanently disturbed area per MW of wind power capacity. In the UK many prime wind farm sites – locations with the best average wind speeds – are in upland areas that are frequently covered by blanket bog. This type of habitat exists in areas of relatively high rainfall where large areas of land remain permanently sodden. Construction work may create a risk of disruption to peatland hydrology which could cause localised areas of peat within the area of a wind farm to dry out, disintegrate, and so release their stored carbon. At the same time, the warming climate which renewable energy schemes seek to mitigate could itself pose an existential threat to peatlands throughout the UK. A Scottish
/ref> This usually takes the clearing of 5,000 m2 per wind turbine.Windkraftanlagen in Brandenburgs Wäldern
Statement of the Government of Brandenburg, Germany. During construction of wind farms in Scotland in 2007–2008 over 3.4 million trees were removed on 6202 acres of forest, out of which 31.5% has been replanted. Turbines are not generally installed in urban areas. Buildings interfere with the wind, turbines must be sited a safe distance ("setback") from residences in case of failure, and the value of land is high. There are a few notable exceptions to this. The WindShare ExPlace wind turbine was erected in December 2002, on the grounds of Exhibition Place, in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was the first wind turbine installed in a major North American urban city centre. Steel Winds also has a 20 MW urban project south of Buffalo, New York. Both of these projects are in urban locations, but benefit from being on uninhabited lakeshore property. In Greece, wind turbine sites have been installed "on mountain peaks, in forests, near archaeological sites, on islands, in protected habitats" and in highly populated tourist areas, causing disruption to hospitality business and protests of residents.
National Wind Coordinating Collaborative
identified fewer than 14 and typically less than four bird deaths per installed megawatt per year, but a wider variation in the number of bat deaths. Like other investigations, it concluded that some species (e.g. migrating bats and songbirds) are known to be harmed more than others and that factors such as turbine siting can be important. However, many details, as well as the overall impact from the growing number of turbines, remain unclear. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory maintains
database
of the scientific literature on the subject.
 The impact of wind energy on birds, which can fly into turbines, or have their habitats degraded by wind development, is complex. Displacement is thought to be more of a threat to species than collisions. Habitat loss is highly variable between species.Fitch, Davey
The impact of wind energy on birds, which can fly into turbines, or have their habitats degraded by wind development, is complex. Displacement is thought to be more of a threat to species than collisions. Habitat loss is highly variable between species.Fitch, Davey
Upland birds face displacement threat from poorly sited wind turbines
(press release), Royal Society for the Protection of Birds website, September 26, 2009. Retrieved August 2, 2013. This press release in turn cites: * Hundreds of thousands of birds, including raptors and migrants, are killed each year because of wind turbines and their power lines, but this is less than the number killed (or not born) because of fossil fuel (coal and gas) power stations. Wind farms are estimated to be responsible for losing less than 0.4 birds per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity generated, compared to over 5 birds per GWh for fossil fueled power stations. As well as threatening extinction, one of the effects of climate change is to already cause a decline in bird population, and this is the main cause of bird loss from fossil power. On some important migration routes turbines are banned, or birds may alter their flight paths to avoid them. Biological surveys beforehand and correctly siting turbines is very important, especially for raptors as they are slow to breed. Methods to help birds avoid turbines include painting of one of the turbine blades black, and making ultrasonic noise. Some approaching birds can be spotted, for example by avian radar, in time for turbines to be slowed to a speed which is safe for them. Wind farms may need more power lines, and lines may be made less damaging to compensate. Making permits for the number of birds (such as eagles) killed tradeable has been suggested, in order to save the most birds at the least cost.
600,000 bats killed at wind energy facilities in 2012, study says
'' Los Angeles Times'', November 8, 2013.
, Science Daily. A number of studies have used climate models to study the effect of extremely large wind farms. One study reports simulations that show detectable changes in global climate for very high wind farm usage, on the order of 10% of the world's land area. Wind power has a negligible effect on global mean surface temperature, and it would deliver "enormous global benefits by reducing emissions of and air pollutants". Another peer-reviewed study suggested that using wind turbines to meet 10 percent of global energy demand in 2100 could actually have a warming effect, causing temperatures to rise by in the regions on land where the wind farms are installed, including a smaller increase in areas beyond those regions. This is due to the effect of wind turbines on both horizontal and vertical atmospheric circulation. Whilst turbines installed in water would have a cooling effect, the net impact on global surface temperatures would be an increase of . Author Ron Prinn cautioned against interpreting the study "as an argument against wind power, urging that it be used to guide future research". "We're not pessimistic about wind," he said. "We haven't absolutely proven this effect, and we'd rather see that people undertake further research".
MIT, 2010. Another study by David Keith and Lee Miller on climactic impacts of wind power which predicted warming when considering the area of the United States has been criticized by
 Aesthetic considerations of wind power stations have often a significant role in their evaluation process.Thomas Kirchhoff (2014)
Aesthetic considerations of wind power stations have often a significant role in their evaluation process.Thomas Kirchhoff (2014)
Energiewende und Landschaftsästhetik. Versachlichung ästhetischer Bewertungen von Energieanlagen durch Bezugnahme auf drei intersubjektive Landschaftsideale
in: Naturschutz und Landschaftsplanung 46 (1), 10–16. To some, the perceived
Diana Schödl, Windkraft und Tourismus – planerische Erfassung der Konfliktbereiche, in Marius Mayer, Hubert Job, 5 December 2013, Arbeitsgruppe "Tourismus und Regionalentwicklung" der Landesarbeitsgemeinschaft Bayern der ARL, p 125. ff Wind power stations are less likely to be perceived negatively in urbanized and industrial regions.Günter Ratzbor (2011)
Windenergieanlagen und Landschaftsbild. Zur Auswirkung von Windrädern auf das Landschaftsbild. Thesenpapier des Deutschen Naturschutzrings DNR
, pp. 17–19 Aesthetic issues are subjective and some people find wind farms pleasant or see them as symbols of energy independence and local prosperity.Gourlay, Simon
Wind farms are not only beautiful, they're absolutely necessary
'' The Guardian'', 12 August 2008. While studies in Scotland predict wind farms will damage tourism, in other countries some wind farms have themselves become tourist attractions, – The Copper Interpretation Centre of
Cutting the carbon-energy cord: Is the answer blowin' in the wind?
EDN Network website, December 15, 2006.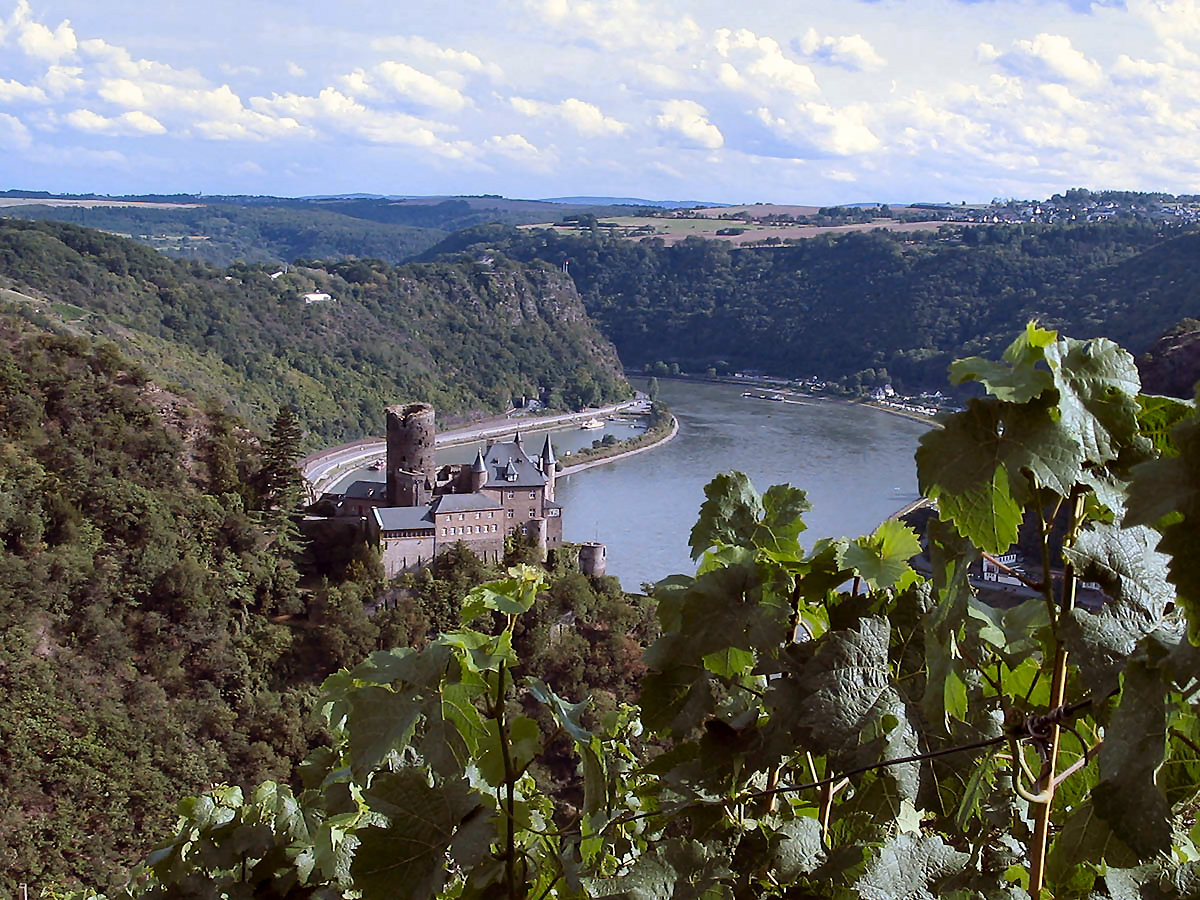 Wind power stations can impact on important sight relations which are a key part of culturally important landscapes, such as in the Rhine Gorge or Moselle valley. Conflicts between the heritage status of certain areas and wind power projects have arisen in various countries. In 2011 UNESCO raised concerns regarding a proposed wind farm 17 kilometres away from the French island abbey of Mont-Saint-Michel. In Germany, the impact of wind farms on valuable
Wind power stations can impact on important sight relations which are a key part of culturally important landscapes, such as in the Rhine Gorge or Moselle valley. Conflicts between the heritage status of certain areas and wind power projects have arisen in various countries. In 2011 UNESCO raised concerns regarding a proposed wind farm 17 kilometres away from the French island abbey of Mont-Saint-Michel. In Germany, the impact of wind farms on valuable
Landschaftsästhetische Auswirkungen von Windkraftanlagen
p.2, 8 For example, sensitive parts of the Moselle valley and the background of the
Ästhetik und Windräder
Neues Gutachten zu "Windenergienutzung und bedeutenden Kulturlandschaften" in Rheinland-Pfalz, Kultur heute, 30 July 2013 Wind turbines require aircraft warning lights, which may create light pollution. Complaints about these lights have caused the US FAA to consider allowing fewer lights per turbine in certain areas. Residents near turbines may complain of "shadow flicker" caused by rotating turbine blades, when the sun passes behind the turbine. This can be avoided by locating the wind farm to avoid unacceptable shadow flicker, or by turning the turbine off for the time of the day when the sun is at the angle that causes flicker. If a turbine is poorly sited and adjacent to many homes, the duration of shadow flicker on a neighbourhood can last hours. New South Wales Government (1 November 2010)
The wind energy fact sheet
, Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water of New South Wales, p. 12.
/ref> Loud or persistent noise increases stress which could then lead to diseases. Wind turbines do not affect human health with their noise when properly placed.W. David Colby, Robert Dobie, Geoff Leventhall, David M. Lipscomb, Robert J. McCunney, Michael T. Seilo, Bo Søndergaard
"Wind Turbine Sound and Health Effects: An Expert Panel Review"
Canadian Wind Energy Association, December 2009. However, when improperly sited, data from the monitoring of two groups of growing geese revealed substantially lower body weights and higher concentrations of a stress hormone in the blood of the first group of geese who were situated 50 meters away compared to a second group which was at a distance of 500 meters from the turbine. A 2014 study by Health Canada involving 1238 households (representing 79 percent of the households in the geographic area studied) and 4000 hours of testing in Ontario and on Prince Edward Island includes the following supportive statements of wind turbine low frequency noise annoyance in its summary: "Wind turbines emit low frequency noise, which can enter the home with little or no reduction in energy, potentially resulting in.. annoyance." Regarding the comparison of low frequency wind turbine noise annoyance to transportation noise annoyance, the Health Canada study summary states: "Studies have consistently shown.. that, in comparison to the scientific literature on noise annoyance to transportation noise sources such as rail or road traffic, community annoyance with (low frequency) wind turbine noise begins at a lower sound level and increases more rapidly with increasing wind turbine noise." The summary also includes the following three findings of its own study: "Statistically significant exposure-response relationships were found between increasing wind turbine noise levels and the prevalence of reporting high annoyance. These associations were found with annoyance due to noise, vibrations, blinking lights, shadow and visual impacts from wind turbines. In all cases, annoyance increased with increasing exposure to wind turbine noise levels." "Community annoyance was observed to drop at distances between 1–2 kilometers (0.6 to 1.2 miles) in Ontario." (It dropped off at 550 meters (1/3 mile) on Prince Edward Island.) "Annoyance was significantly lower among the 110 participants who received personal benefit, which could include rent, payments or other indirect benefits of having wind turbines in the area e.g., community improvements." The above Health Canada summary states that "no statistically significant association was observed between measured blood pressure, resting heart rate, (hair cortisol concentrations) and wind turbine noise exposure." Wind turbine syndrome, a
 The environmental impact of electricity generation from wind power is minor when compared to that of fossil fuel power. Wind turbines have some of the lowest global warming potential per unit of electricity generated: far less greenhouse gas is emitted than for the average unit of electricity, so wind power helps limit climate change. Wind power consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months.
Onshore (on-land) wind farms can have a significant visual impact and impact on the landscape. Due to a very low surface power density and spacing requirements, wind farms typically need to be spread over more land than other power stations.What are the pros and cons of onshore wind energy?
The environmental impact of electricity generation from wind power is minor when compared to that of fossil fuel power. Wind turbines have some of the lowest global warming potential per unit of electricity generated: far less greenhouse gas is emitted than for the average unit of electricity, so wind power helps limit climate change. Wind power consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months.
Onshore (on-land) wind farms can have a significant visual impact and impact on the landscape. Due to a very low surface power density and spacing requirements, wind farms typically need to be spread over more land than other power stations.What are the pros and cons of onshore wind energy?Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment. January 2018. Their network of turbines, access roads, transmission lines, and substations can result in "energy sprawl";Nathan F. Jones, Liba Pejchar, Joseph M. Kiesecker. " The Energy Footprint: How Oil, Natural Gas, and Wind Energy Affect Land for Biodiversity and the Flow of Ecosystem Services". ''
BioScience
''BioScience'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Institute of Biological Sciences. It was established in 1964 and was preceded by the ''AIBS Bulletin'' (1951–19 ...
'', Volume 65, Issue 3, March 2015. pp. 290–301 although land between the turbines and roads can still be used for agriculture.
Conflicts arise especially in scenic and culturally-important landscapes. Siting restrictions (such as setbacks) may be implemented to limit the impact.Loren D. Knopper, Christopher A. Ollson, Lindsay C. McCallum, Melissa L. Whitfield Aslund, Robert G. Berger, Kathleen Souweine, and Mary McDaniel, Wind Turbines and Human Health, rontiers of Public Health June 19, 2014; 2: 63. The land between the turbines and access roads can still be used for farming and grazing. They also need to be built away from urban areas, which can lead to "industrialization of the countryside".Szarka, Joseph. ''Wind Power in Europe: Politics, Business and Society''. Springer, 2007. p.176 Some wind farms are opposed for potentially spoiling protected scenic areas, archaeological landscapes and heritage sites. A report by the Mountaineering Council of Scotland concluded that wind farms harmed tourism in areas known for natural landscapes and panoramic views.
Habitat loss and fragmentation are the greatest potential impacts on wildlife of onshore wind farms, but they are small and can be mitigated if proper monitoring and mitigation strategies are implemented. The worldwide ecological impact is minimal. Thousands of birds and bats, including rare species, have been killed by wind turbine blades, as there are around other manmade structures, though wind turbines are responsible for far fewer bird deaths than fossil-fueled power stations. This can be mitigated with proper wildlife monitoring.
Many wind turbine blades are made of fiberglass and some only had a lifetime of 10 to 20 years. Previously, there was no market for recycling these old blades, and they were commonly disposed of in landfills. Because blades are hollow, they take up a large volume compared to their mass. Since 2019, some landfill operators have begun requiring blades to be crushed before being landfilled. Blades manufactured in the 2020s are more likely to be designed to be completely recyclable.
Wind turbines also generate noise. At a distance of this may be around 45 dB, which is slightly louder than a refrigerator. At distance they become inaudible. There are anecdotal reports of negative health effects on people who live very close to wind turbines. Peer-reviewed research has generally not supported these claims. Pile-driving to construct non-floating wind farms is noisy underwater, but in operation offshore wind is much quieter than ships.
Basic operational considerations
Pollution and effects on the grid
Pollution costs
Compared with otherlow-carbon power
Low-carbon power is electricity produced with substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions than conventional fossil fuel power generation. The energy transition to low-carbon power is one of the most important actions required to limit climate ...
sources, wind turbines have one of the lowest global warming potentials per unit of electrical energy generated by any power source. According to the IPCC, in assessments of the life-cycle global warming potential of energy sources, wind turbines have a median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic fe ...
value of between 15 and 11 ( g eq/kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
) depending on whether offshore or onshore turbines are being assessed.
Wind power doesn't consume waterMielke, ErikWater Consumption of Energy Resource Extraction, Processing, and Conversion
'' Harvard Kennedy School'', October 2010. Accessed: 1 February 2011. for continuous operation and has near negligible emissions directly related to its electricity production. Wind turbines when isolated from the electric grid, produce negligible amounts of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide,
sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
, nitrogen dioxide, mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
and radioactive waste when in operation, unlike fossil fuel sources and nuclear energy station fuel production, respectively.
With the construction phase largely to blame, wind turbines emit slightly more particulate matter
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The ter ...
(PM), a form of air pollution, at an "exception" rate higher per unit of energy generated(kWh) than a fossil gas electricity station(" NGCC"), and also emit more heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
and PM than nuclear stations, per unit of energy generated. Wind power externality
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either co ...
costs are negligible compared to the cost of electricity generation.
Findings when connected to the grid
kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
) of energy produced, with most of the emission intensity coming from producing steel, concrete, and plastic/fiberglass composites for the turbine structure and foundation. By combining similar data from numerous individual studies in a meta-analysis, the median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic fe ...
global warming potential for wind power was found to be 11–12 g CO2/kWh and unlikely to change significantly.
However these relatively low pollution values begin to increase as greater and greater wind energy is added to the grid, or wind power ' electric grid penetration' levels are reached. Due to the effects of attempting to balance out the energy demands on the grid, from Intermittent power sources e.g. wind power (sources which have low capacity factors due to the weather), this either requires the construction of large energy storage projects, which have their own emission intensity which must be added to wind power's system-wide pollution effects, or it requires more frequent reliance on fossil fuels than the spinning reserve requirements necessary to back up more dependable sources. The latter combination is presently the more common.
This higher dependence on back-up/ Load following power plants to ensure a steady power grid output has the knock-on-effect of more frequent inefficient (in e g/kWh) throttling up and down of these other power sources in the grid to facilitate the intermittent power source's variable output. When one includes the total effect of intermittent sources on other power sources in the grid system, that is, including these inefficient start up emissions of backup power sources to cater for wind energy, into wind energy's total system-wide life cycle, this results in a higher real-world wind energy emission intensity. Higher than the direct g/kWh value that is determined from looking at the power source in isolation and thus ignores all down-stream detrimental/inefficiency effects it has on the grid.
This higher dependence on back-up/ Load following power plants to ensure a steady power grid output forces fossil power plants to operate in less efficient states.
In comparison to other low carbon power sources Wind turbines, when assessed in isolation, have a median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic fe ...
life cycle emission value of between 11 and 12 ( g eq/kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
). While an increase in emissions due to the practical issues of load balancing is an issue, Pehnt et al. still conclude that these 20 and 80 g CO2-eq/kWh added penalties still result in wind being roughly ten times less polluting than fossil gas and coal which emit ~400 and 900 g CO2-eq/kWh respectively. As these losses occur due to the cycling of fossil power plants, they may at some point become smaller when more than 20–30% of wind energy is added to the power grid, as fossil power plants are replaced, however this has yet to occur in practice.
Rare-earth use
The production of permanent magnets used in some wind turbines makes use of neodymium. Pollution concerns associated with the extraction of this rare-earth element, which is primarily exported by China, have prompted government action in recent years, and international research attempts to refine the extraction process.Ingebretsen, MarkDeveloping greener, cheaper magnets
'' Ames Laboratory''. Accessed: 10 March 2011. Research is underway on turbine and generator designs which reduce the need for neodymium, or eliminate the use of rare-earth metals altogether. Additionally, the large wind turbine manufacturer
Enercon GmbH
Enercon GmbH is a wind turbine manufacturer based in Aurich, Lower Saxony, Germany. It has been the market leader in Germany since the mid-1990s. Enercon has production facilities in Germany (Aurich, Emden and Magdeburg), Brazil, India, Canada, ...
chose very early not to use permanent magnets for its direct drive turbines, to avoid responsibility for the adverse environmental impact of rare-earth mining.Enercon explanation on p.4 on avoidance of Neodymium use/ref>
Material inputs
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing carb ...
study projects the demand for mined resources such as lithium, graphite, cobalt, copper, nickel and rare earths will rise 4x by 2040 and notes insufficient supply of these materials to match demand imposed by expected large-scale deployments of decentralized technologies solar and wind power, and required grid upgrades. For example, an on-shore wind farm requires 9x more materials than a similar fossil gas plant. According to a 2018 study significant increase of wind power would require 1000% increase in supply of these metals by 2060, requiring significant increase in mining operations.
Waste, recycling, repurposing
Modern wind turbine blades are made from plastic/ fiberglass composite designs that provide a service lifetime of less than about 20 years. , there was no economical technology and market for recycling these old blades, and the most common disposal procedure is to truck them tolandfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
s. Other options for disposing of the blades includes incinerating the material or grinding it up into powder, but both of these methods are not only expensive, but also inefficient and involves additional energy usage. Blade incineration emits a significant amount of green house gases, though it can be used as a source of heat and power, which somewhat offsets these emissions. Because of their hollow design for less weight, blades can take up an enormous volume compared to their mass, making road transport difficult, expensive, and dangerous due to wide turning berths, extra safety vehicles, and longer flatbed trucks.
Since many blades are still trashed, landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
operators have started requiring blades to be cut to pieces and sometimes crushed before they can be landfilled, which consumes further energy. Along with ongoing development work to extend the generating efficiency and service life of newer turbines, blade recycling solutions continue to be pursued that are economical, energy efficient, and market scalable.
There may be as much as 45% additional waste resulting from processes that occur during the lifecycle of the turbine blades, and it is estimated that total annual blade waste of all countries may reach 2.9 million tons by 2050. In comparison, global solar photovoltaic cell
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and c ...
waste is expected to reach about 78 million tons by 2050.
Recycling and repurposing
 As much as 80% of the wind turbine structure can be
As much as 80% of the wind turbine structure can be recycled
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the p ...
, though this does not include the foundation of the structure, which is typically made from reinforced concrete
Reinforced concrete (RC), also called reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and ferroconcrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having hig ...
, or the blades. Alternatively, these components of the turbine structure that are not easily recycled into new turbines can still be repurposed and used in other ways.
The large volume of the turbine blades, while difficult to handle, is advantageous in repurposing the blades as playground
A playground, playpark, or play area is a place designed to provide an environment for children that facilitates play, typically outdoors. While a playground is usually designed for children, some are designed for other age groups, or people ...
structures, bike
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
...
shelters and footbridges. Other recycling methods include creating pellets for waterproof boards and injectable plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their Plasticity (physics), plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be Injection moulding, moulded, Extrusion, e ...
, as well as pyrolysis for producing paints, glues
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
, and both cement and concrete.
Carbon fiber blades can now be recycled
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the p ...
, the fiber first being separated from the epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also coll ...
resin binder, then chopped into small particles. After the separation
Separation may refer to:
Films
* ''Separation'' (1967 film), a British feature film written by and starring Jane Arden and directed by Jack Bond
* ''La Séparation'', 1994 French film
* ''A Separation'', 2011 Iranian film
* ''Separation'' (20 ...
, the resin is used as a fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
source for the next materials to be processed. After pyrolysis, the resulting material can be further separated and the glass fibers extracted to be used in insulation or fiber reinforcement.
The blades may also be repurposed into building materials and structural components. Research indicates that turbine blades could successfully be repurposed as electrical transmission poles as their strength and structural stability was found to be comparable to the materials that are typically used. Sections of the blades have been adapted to create roofs for small house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
s and these structures meet the requirements of building codes and may prove to be a viable way to reuse blade materials without extensive processes needed to make the material usable. Components of the turbine could be reused by implementing segmentation, where the object is divided into different elements. Research on segmentation suggests that the resulting materials are better than conventional construction materials when measuring specific flexural stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a b ...
and flexural strength.
Overall, there are several different avenues through which wind turbine components can be recycled, reused, or repurposed, all with their advantages and disadvantages, and there continues to be research conducted to determine even more ways that the materials can economically utilized. While various methods for recycling or repurposing the turbine blades have been proven effective, they have not been implemented on a large enough scale to adequately address the rapidly rising amounts of turbine blade waste being produced.
Alternative building materials
In addition to carbon fiber blades sometimes being installed due to lower weight and higher strength and durability compared to fiberglass-epoxy composites, as of 2020 there is now a wind turbine with a modular wooden structural support trunk in Gothenburg, Sweden, which is stronger, lighter, easier to recycle and transport, and more carbon-neutral than steel. These wooden towers would not need to be recycled as often as steel due to their fire-resistance and higher tolerance of metal-oxidizing chemicals. Other alternative building materials include recyclable polymers ( thermoplastic, recyclable thermosets, polyurethane), bamboo,natural fiber
Natural fibers or natural fibres (see spelling differences) are fibers that are produced by geological processes, or from the bodies of plants or animals.
They can be used as a component of composite materials, where the orientation of fibers ...
composites, biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
resins, and bio-based carbon fibers
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are fibers about in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high stren ...
.
Research on wind turbine materials also focuses on how to make the turbine blades more resistant to damage as this would extend their lifespan and reduce the replacement turnover (frequency of replacements). In addition to adapting the materials used in the blades to increase their resistance to damage, there are also potential methods of altering the turbine's activity during certain weather events in order to decrease any damage caused by wind or rain.
Ecology
Land use
Wind power has low life-cycle surface power density of 1.84 W/m2 which is three orders of magnitude (103 times, which is equivalent to 1,000x) less thannuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
or fossil fuel power and 3x less than PV.
Wind farms are often built on land that has already been impacted by land clearing. The vegetation clearing and ground disturbance required for wind farms are minimal compared with coal mines and coal-fired power stations. If wind farms are decommissioned, the landscape can be returned to its previous condition.New South Wales Government (1 November 2010)The wind energy fact sheet
Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water, p. 13 A study by the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory of US wind farms built between 2000 and 2009 found that, on average, only 1.1 percent of the total wind farm area suffered surface disturbance, and only 0.43 percent was permanently disturbed by wind power installations. On average, there were of total wind farm area per MW of capacity, but only of permanently disturbed area per MW of wind power capacity. In the UK many prime wind farm sites – locations with the best average wind speeds – are in upland areas that are frequently covered by blanket bog. This type of habitat exists in areas of relatively high rainfall where large areas of land remain permanently sodden. Construction work may create a risk of disruption to peatland hydrology which could cause localised areas of peat within the area of a wind farm to dry out, disintegrate, and so release their stored carbon. At the same time, the warming climate which renewable energy schemes seek to mitigate could itself pose an existential threat to peatlands throughout the UK. A Scottish
MEP MEP may refer to:
Organisations and politics
* Mahajana Eksath Peramuna, a political party in Sri Lanka
* Mahajana Eksath Peramuna (1956), a former political alliance in Sri Lanka
* Maison européenne de la photographie, a photography centre ...
campaigned for a moratorium on wind developments on peatlands saying that "Damaging the peat causes the release of more carbon dioxide than wind farms save". A 2014 report for the Northern Ireland Environment Agency noted that siting wind turbines on peatland could release considerable carbon dioxide from the peat, and also damage the peatland contributions to flood control and water quality: "The potential knock-on effects of using the peatland resource for wind turbines are considerable and it is arguable that the impacts on this facet of biodiversity will have the most noticeable and greatest financial implications for Northern Ireland." Wind farm construction near wetlands has been linked to several bog landslides in Ireland that have polluted rivers, such as at Derrybrien
Derrybrien () is a tiny village in County Galway, Ireland. It lies along the R353 road in the Slieve Aughty Mountains. The village church is dedicated to Saint Patrick and is part of the Roman Catholic Parish of Ballinakill and Derrybrien.
...
(2003) and Meenbog (2020). Such incidents could be prevented with stricter planning procedures and siting guidelines.
Wind-energy advocates contend that less than 1% of the land is used for foundations and access roads, the other 99% can still be used for farming. A wind turbine needs about 200–400 m2 for the foundation. With the increasing size of the wind turbine the relative size of the foundation decreases.Erich Hau. ''Windkraftanlagen: Grundlagen, Technik, Einsatz, Wirtschaftlichkeit'', Berlin: Heidelberg 2008, pp. 621–23. (German). (For the english Edition see Erich Hau, ''Wind Turbines: Fundamentals, Technologies, Application, Economics'', Springer 2005) Critics point out that on some locations in forests the clearing of trees around tower bases may be necessary for installation sites on mountain ridges, such as in the northeastern U.S.Forest clearance for Meyersdale, Pa., wind power facility/ref> This usually takes the clearing of 5,000 m2 per wind turbine.Windkraftanlagen in Brandenburgs Wäldern
Statement of the Government of Brandenburg, Germany. During construction of wind farms in Scotland in 2007–2008 over 3.4 million trees were removed on 6202 acres of forest, out of which 31.5% has been replanted. Turbines are not generally installed in urban areas. Buildings interfere with the wind, turbines must be sited a safe distance ("setback") from residences in case of failure, and the value of land is high. There are a few notable exceptions to this. The WindShare ExPlace wind turbine was erected in December 2002, on the grounds of Exhibition Place, in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was the first wind turbine installed in a major North American urban city centre. Steel Winds also has a 20 MW urban project south of Buffalo, New York. Both of these projects are in urban locations, but benefit from being on uninhabited lakeshore property. In Greece, wind turbine sites have been installed "on mountain peaks, in forests, near archaeological sites, on islands, in protected habitats" and in highly populated tourist areas, causing disruption to hospitality business and protests of residents.
Livestock
The land can still be used for farming and cattle grazing. Livestock is unaffected by the presence of wind farms. International experience shows that livestock will "graze right up to the base of wind turbines and often use them as rubbing posts or for shade". In 2014, a first of its kind veterinary study attempted to determine the effects of rearing livestock near a wind turbine, the study compared the health effects of a wind turbine on the development of two groups of growing geese, preliminary results found that geese raised within 50 meters of a wind turbine gained less weight and had a higher concentration of the stress hormonecortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland ...
in their blood than geese at a distance of 500 meters.
Semi-domestic reindeer avoid the construction activity, but seem unaffected when the turbines are operating.
Impact on wildlife
Environmental assessments are routinely carried out for wind farm proposals, and potential impacts on the local environment (e.g. plants, animals, soils) are evaluated. Turbine locations and operations are often modified as part of the approval process to avoid or minimise impacts on threatened species and their habitats. Any unavoidable impacts can be offset with conservation improvements of similar ecosystems which are unaffected by the proposal. A research agenda from a coalition of researchers from universities, industry, and government, supported by the Atkinson Center for a Sustainable Future, suggests modeling the spatiotemporal patterns of migratory and residential wildlife with respect to geographic features and weather, to provide a basis for science-based decisions about where to site new wind projects. More specifically, it suggests: * Use existing data on migratory and other movements of wildlife to develop predictive models of risk. * Use new and emerging technologies, including radar, acoustics, and thermal imaging, to fill gaps in knowledge of wildlife movements. * Identify specific species or sets of species most at risk in areas of high potential wind resources. Wind turbines, like many other human activities and buildings, also increase the death rate of avian creatures such as birds and bats. A summary of the existing field studies compiled in 2010 from thNational Wind Coordinating Collaborative
identified fewer than 14 and typically less than four bird deaths per installed megawatt per year, but a wider variation in the number of bat deaths. Like other investigations, it concluded that some species (e.g. migrating bats and songbirds) are known to be harmed more than others and that factors such as turbine siting can be important. However, many details, as well as the overall impact from the growing number of turbines, remain unclear. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory maintains
database
of the scientific literature on the subject.
Birds
 The impact of wind energy on birds, which can fly into turbines, or have their habitats degraded by wind development, is complex. Displacement is thought to be more of a threat to species than collisions. Habitat loss is highly variable between species.Fitch, Davey
The impact of wind energy on birds, which can fly into turbines, or have their habitats degraded by wind development, is complex. Displacement is thought to be more of a threat to species than collisions. Habitat loss is highly variable between species.Fitch, DaveyUpland birds face displacement threat from poorly sited wind turbines
(press release), Royal Society for the Protection of Birds website, September 26, 2009. Retrieved August 2, 2013. This press release in turn cites: * Hundreds of thousands of birds, including raptors and migrants, are killed each year because of wind turbines and their power lines, but this is less than the number killed (or not born) because of fossil fuel (coal and gas) power stations. Wind farms are estimated to be responsible for losing less than 0.4 birds per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity generated, compared to over 5 birds per GWh for fossil fueled power stations. As well as threatening extinction, one of the effects of climate change is to already cause a decline in bird population, and this is the main cause of bird loss from fossil power. On some important migration routes turbines are banned, or birds may alter their flight paths to avoid them. Biological surveys beforehand and correctly siting turbines is very important, especially for raptors as they are slow to breed. Methods to help birds avoid turbines include painting of one of the turbine blades black, and making ultrasonic noise. Some approaching birds can be spotted, for example by avian radar, in time for turbines to be slowed to a speed which is safe for them. Wind farms may need more power lines, and lines may be made less damaging to compensate. Making permits for the number of birds (such as eagles) killed tradeable has been suggested, in order to save the most birds at the least cost.
Bats
Bats may be injured by direct impact with turbine blades, towers, or transmission lines. Recent research shows that bats may also be killed when suddenly passing through a low air pressure region surrounding the turbine blade tips. * includes audio podcast of interview with author. The numbers of bats killed by existing onshore and near-shore facilities have troubled bat enthusiasts. In April 2009 the Bats and Wind Energy Cooperative released initial study results showing a 73% drop in bat fatalities when wind farm operations are stopped during low wind conditions, when bats are most active. Bats avoid radar transmitters, and placing microwave transmitters on wind turbine towers may reduce the number of bat collisions. * It is hypothesized that a portion of bat fatalities are attributed to the wind displacement caused by the wind turbine blades as they move through the air causing insects in the area to become disoriented making it a dense area of prey – an attractive hunting ground for bats. To combat this phenomenon ultrasonic deterrents have been tested on select wind turbines and has been shown to reduce bat fatalities from collision and barotrauma. Testing of the ultrasonic deterrents has shown significantly reduced bat activity around wind turbines; according to study done in Zzyzyx, California, bat activity was reduced by 89.6–97.5% when ultrasonic acoustic deterrents were used. A 2013 study produced an estimate that wind turbines killed more than 600,000 bats in the U.S. the previous year, with the greatest mortality occurring in the Appalachian Mountains. Some earlier studies had produced estimates of between 33,000 and 888,000 bat deaths per year.Morin, Monte600,000 bats killed at wind energy facilities in 2012, study says
'' Los Angeles Times'', November 8, 2013.
Mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
, specifically in migratory birds and bats, seems to be increased in locations where wind patterns seem to facilitate both migration paths and energy production.
Marine life
Wind farms designed to be more efficient from lack of airflow-impeding obstacles, offshore wind farms, have altered marine ecosystems by providing refuge from humans in the form of fishing-restricted areas due to safety concerns of moving blades. Interestingly, the regions of refuge are not directly at the location of the wind turbines but rather slightly closer to shore. As an example, new colonies of Blue Mussels in the North Sea fed byphytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
are a food source for other predators, namely fish and crabs, and further up the food chain, pinnipeds, colloquially known as seals. Blue Mussels also reduce turbidity in the ocean water, making for greater underwater visibility, and leave behind their shells as shelter, further altering possible inhabitants of their coastal domain.
Weather and climate change
Wind farms may affect weather in their immediate vicinity. Turbulence from spinning wind turbine rotors increases vertical mixing of heat and water vapor that affects the meteorological conditions downwind, including rainfall. Overall, wind farms lead to a slight warming at night and a slight cooling during the day time. This effect can be reduced by using more efficient rotors or placing wind farms in regions with high natural turbulence. Warming at night could "benefit agriculture by decreasing frost damage and extending the growing season. Many farmers already do this with air circulators".Wind farms impacting weather, Science Daily. A number of studies have used climate models to study the effect of extremely large wind farms. One study reports simulations that show detectable changes in global climate for very high wind farm usage, on the order of 10% of the world's land area. Wind power has a negligible effect on global mean surface temperature, and it would deliver "enormous global benefits by reducing emissions of and air pollutants". Another peer-reviewed study suggested that using wind turbines to meet 10 percent of global energy demand in 2100 could actually have a warming effect, causing temperatures to rise by in the regions on land where the wind farms are installed, including a smaller increase in areas beyond those regions. This is due to the effect of wind turbines on both horizontal and vertical atmospheric circulation. Whilst turbines installed in water would have a cooling effect, the net impact on global surface temperatures would be an increase of . Author Ron Prinn cautioned against interpreting the study "as an argument against wind power, urging that it be used to guide future research". "We're not pessimistic about wind," he said. "We haven't absolutely proven this effect, and we'd rather see that people undertake further research".
MIT, 2010. Another study by David Keith and Lee Miller on climactic impacts of wind power which predicted warming when considering the area of the United States has been criticized by
Mark Z. Jacobson
Mark Zachary Jacobson (born 1965) is a professor of civil and environmental engineering at Stanford University and director of its Atmosphere/Energy Program. He is also a co-founder of the non-profit, Solutions Project.
Jacobson's career has focus ...
on the grounds of its limited geographical scope, with the argument that a large-scale wind energy extraction would significantly lower global temperatures.
Impacts on people
Aesthetics
 Aesthetic considerations of wind power stations have often a significant role in their evaluation process.Thomas Kirchhoff (2014)
Aesthetic considerations of wind power stations have often a significant role in their evaluation process.Thomas Kirchhoff (2014)Energiewende und Landschaftsästhetik. Versachlichung ästhetischer Bewertungen von Energieanlagen durch Bezugnahme auf drei intersubjektive Landschaftsideale
in: Naturschutz und Landschaftsplanung 46 (1), 10–16. To some, the perceived
aesthetic
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed th ...
aspects of wind power stations may conflict with the protection of historical sites.Tourismus und Regionalentwicklung in BayernDiana Schödl, Windkraft und Tourismus – planerische Erfassung der Konfliktbereiche, in Marius Mayer, Hubert Job, 5 December 2013, Arbeitsgruppe "Tourismus und Regionalentwicklung" der Landesarbeitsgemeinschaft Bayern der ARL, p 125. ff Wind power stations are less likely to be perceived negatively in urbanized and industrial regions.Günter Ratzbor (2011)
Windenergieanlagen und Landschaftsbild. Zur Auswirkung von Windrädern auf das Landschaftsbild. Thesenpapier des Deutschen Naturschutzrings DNR
, pp. 17–19 Aesthetic issues are subjective and some people find wind farms pleasant or see them as symbols of energy independence and local prosperity.Gourlay, Simon
Wind farms are not only beautiful, they're absolutely necessary
'' The Guardian'', 12 August 2008. While studies in Scotland predict wind farms will damage tourism, in other countries some wind farms have themselves become tourist attractions, – The Copper Interpretation Centre of
Murdochville
Murdochville is a town in Quebec, Canada, one of only a few inland communities on the Gaspé Peninsula. Its population (as of 2016) is 651.
Murdochville is located along Quebec Route 198 in the geographic township of Holland, south of L'Anse-P ...
, Canada features tours of a wind turbine on Miller Mountain. with several having visitor centers
A visitor center or centre (see American and British English spelling differences), visitor information center, tourist information center, is a physical location that provides tourist information to visitors.
Types of visitor center
A visit ...
at ground level or even observation decks atop turbine towers.
In the 1980s, wind energy was being discussed as part of a soft energy path.Windenergie in Deutschland: Konstellationen, Dynamiken und Regulierungspotenziale Im Innovationsprozess, Bö Ohlhorst, Springer-Verlag, 2009, p.90 ff Renewable energy commercialization led to an increasing industrial image of wind power, which is being criticized by various stakeholders in the planning process, including nature protection associations.Windenergie in Deutschland: Konstellationen, Dynamiken und Regulierungspotenziale Im Innovationsprozess, Bö Ohlhorst, Springer-Verlag, 2009, p.163, "Kritik an zunehmend industrieller Charakter der Windenergienutzung" Newer wind farms have larger, more widely spaced turbines, and have a less cluttered appearance than older installations. Wind farms are often built on land that has already been impacted by land clearing and they coexist easily with other land uses.
Coastal areas and areas of higher altitude such as ridgelines are considered prime for wind farms, due to constant wind speeds. However, both locations tend to be areas of high visual impact and can be a contributing factor in local communities' resistance to some projects. Both the proximity to densely populated areas and the necessary wind speeds make coastal locations ideal for wind farms.Dipert, BrianCutting the carbon-energy cord: Is the answer blowin' in the wind?
EDN Network website, December 15, 2006.
 Wind power stations can impact on important sight relations which are a key part of culturally important landscapes, such as in the Rhine Gorge or Moselle valley. Conflicts between the heritage status of certain areas and wind power projects have arisen in various countries. In 2011 UNESCO raised concerns regarding a proposed wind farm 17 kilometres away from the French island abbey of Mont-Saint-Michel. In Germany, the impact of wind farms on valuable
Wind power stations can impact on important sight relations which are a key part of culturally important landscapes, such as in the Rhine Gorge or Moselle valley. Conflicts between the heritage status of certain areas and wind power projects have arisen in various countries. In 2011 UNESCO raised concerns regarding a proposed wind farm 17 kilometres away from the French island abbey of Mont-Saint-Michel. In Germany, the impact of wind farms on valuable cultural landscape
Cultural landscape is a term used in the fields of geography, ecology, and heritage studies, to describe a symbiosis of human activity and environment. As defined by the World Heritage Committee, it is the "cultural properties hatrepresent the co ...
s has implications on zoning and land-use planning
Land use planning is the process of regulating the use of land by a central authority. Usually, this is done to promote more desirable social and environmental outcomes as well as a more efficient use of resources. More specifically, the goals ...
.Sören Schöbel (2012): Windenergie und Landschaftsästhetik: Zur landschaftsgerechten Anordnung von Windfarmen, Jovis-Verlag, BerlinNohl, Werner (2009)Landschaftsästhetische Auswirkungen von Windkraftanlagen
p.2, 8 For example, sensitive parts of the Moselle valley and the background of the
Hambach Castle
Hambach Castle (german: Hambacher Schloss) is a castle near the urban district Hambach of Neustadt an der Weinstraße in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is considered a symbol of the German democracy movement because of the Hambacher Fest whic ...
, according to the plans of the state government, will be kept free of wind turbines.Fittkau, LudgerÄsthetik und Windräder
Neues Gutachten zu "Windenergienutzung und bedeutenden Kulturlandschaften" in Rheinland-Pfalz, Kultur heute, 30 July 2013 Wind turbines require aircraft warning lights, which may create light pollution. Complaints about these lights have caused the US FAA to consider allowing fewer lights per turbine in certain areas. Residents near turbines may complain of "shadow flicker" caused by rotating turbine blades, when the sun passes behind the turbine. This can be avoided by locating the wind farm to avoid unacceptable shadow flicker, or by turning the turbine off for the time of the day when the sun is at the angle that causes flicker. If a turbine is poorly sited and adjacent to many homes, the duration of shadow flicker on a neighbourhood can last hours. New South Wales Government (1 November 2010)
The wind energy fact sheet
, Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water of New South Wales, p. 12.
Noise
Wind turbines also generate noise, and at a residential distance of this may be around 45 dB; however, at a distance of , most wind turbines become inaudible.Wind Energy Comes of Age By Paul Gipe/ref> Loud or persistent noise increases stress which could then lead to diseases. Wind turbines do not affect human health with their noise when properly placed.W. David Colby, Robert Dobie, Geoff Leventhall, David M. Lipscomb, Robert J. McCunney, Michael T. Seilo, Bo Søndergaard
"Wind Turbine Sound and Health Effects: An Expert Panel Review"
Canadian Wind Energy Association, December 2009. However, when improperly sited, data from the monitoring of two groups of growing geese revealed substantially lower body weights and higher concentrations of a stress hormone in the blood of the first group of geese who were situated 50 meters away compared to a second group which was at a distance of 500 meters from the turbine. A 2014 study by Health Canada involving 1238 households (representing 79 percent of the households in the geographic area studied) and 4000 hours of testing in Ontario and on Prince Edward Island includes the following supportive statements of wind turbine low frequency noise annoyance in its summary: "Wind turbines emit low frequency noise, which can enter the home with little or no reduction in energy, potentially resulting in.. annoyance." Regarding the comparison of low frequency wind turbine noise annoyance to transportation noise annoyance, the Health Canada study summary states: "Studies have consistently shown.. that, in comparison to the scientific literature on noise annoyance to transportation noise sources such as rail or road traffic, community annoyance with (low frequency) wind turbine noise begins at a lower sound level and increases more rapidly with increasing wind turbine noise." The summary also includes the following three findings of its own study: "Statistically significant exposure-response relationships were found between increasing wind turbine noise levels and the prevalence of reporting high annoyance. These associations were found with annoyance due to noise, vibrations, blinking lights, shadow and visual impacts from wind turbines. In all cases, annoyance increased with increasing exposure to wind turbine noise levels." "Community annoyance was observed to drop at distances between 1–2 kilometers (0.6 to 1.2 miles) in Ontario." (It dropped off at 550 meters (1/3 mile) on Prince Edward Island.) "Annoyance was significantly lower among the 110 participants who received personal benefit, which could include rent, payments or other indirect benefits of having wind turbines in the area e.g., community improvements." The above Health Canada summary states that "no statistically significant association was observed between measured blood pressure, resting heart rate, (hair cortisol concentrations) and wind turbine noise exposure." Wind turbine syndrome, a
psychosomatic
A somatic symptom disorder, formerly known as a somatoform disorder,(2013) Committee on Environmental Impacts of Wind Energy Projects, National Research Council (2007)
''Environmental Impacts of Wind-Energy Projects'', pp. 158–59
BusinessGreen.com website.UK Offshore Energy: Strategic Environmental Assessment
UK Department of Energy and Climate Change, January 2009. There does not seem to have been much consideration however of the likely impact of displacement of fishing activities from traditional fishing grounds. A study published in 2014 suggests that some seals prefer to hunt near turbines, likely due to the laid stones functioning as artificial reefs which attract invertebrates and fish.Warwicker, Michelle.
Seals 'feed' at offshore wind farms, study shows
'' BBC'', 21 July 2014. Accessed: 22 July 2014
Video of seal path
/ref> Offshore wind is similar to terrestrial wind technologies, as a large windmill-like turbine located in a fresh or saltwater environment. Wind causes the blades to rotate, which is then turned into electricity and connected to the grid with cables. The advantages of offshore wind are that winds are stronger and more consistent, allowing turbines of much larger size to be erected by vessels. The disadvantages are the difficulties of placing a structure in a dynamic ocean environment. The turbines are often scaled-up versions of existing land technologies. However, the foundations are unique to offshore wind and are listed below:
National Wind Coordinating Collaborative website
facilitated by the American Wind and Wildlife Institute, includes its updated summaries of wind-wildlife interactions from 2010. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Environmental Effects Of Wind Power Bird mortality Wind power Wind power
''Environmental Impacts of Wind-Energy Projects'', pp. 158–59
Offshore
Many offshore wind farms have contributed to electricity needs in Europe and Asia for years, and as of 2014 the first offshore wind farms are under development in U.S. waters. While the offshore wind industry has grown dramatically over the last several decades, especially in Europe, there is still some uncertainty associated with how the construction and operation of these wind farms affect marine animals and the marine environment. Traditional offshore wind turbines are attached to the seabed in shallower waters within the near-shore marine environment. As offshore wind technologies become more advanced, floating structures have begun to be used in deeper waters where more wind resources exist. Common environmental concerns associated with offshore wind developments include: * The risk to seabirds being struck by wind turbine blades or being displaced from critical habitats; * Underwater noise associated with the installation process of monopile turbines; * The physical presence of offshore wind farms altering the behavior of marine mammals, fish, and seabirds by reasons of either attraction or avoidance; * Potential disruption of the near-field and far-field marine environments from large offshore wind projects. Germany restricts underwater noise during pile driving to less than 160 dB. Due to the landscape protection status of large areas of theWadden Sea
The Wadden Sea ( nl, Waddenzee ; german: Wattenmeer; nds, Wattensee or ; da, Vadehavet; fy, Waadsee, longname=yes; frr, di Heef) is an intertidal zone in the southeastern part of the North Sea. It lies between the coast of northwestern conti ...
, a major World Heritage Site with various national parks (e.g. Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park) German offshore installations are mostly restricted on areas outside the territorial waters. Offshore capacity in Germany is therefore way behind the British or Danish near coast installments, which face much lower restrictions.
In 2009, a comprehensive government environmental study of coastal waters in the United Kingdom concluded that there is scope for between 5,000 and 7,000 offshore wind turbine
Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. There are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of c ...
s to be installed without an adverse impact on the marine environment. The studywhich forms part of the Department of Energy and Climate Change's Offshore Energy Strategic Environmental Assessmentis based on more than a year's research. It included analysis of seabed geology, as well as surveys of sea birds and marine mammals.Study finds offshore wind farms can co-exist with marine environmentBusinessGreen.com website.UK Offshore Energy: Strategic Environmental Assessment
UK Department of Energy and Climate Change, January 2009. There does not seem to have been much consideration however of the likely impact of displacement of fishing activities from traditional fishing grounds. A study published in 2014 suggests that some seals prefer to hunt near turbines, likely due to the laid stones functioning as artificial reefs which attract invertebrates and fish.Warwicker, Michelle.
Seals 'feed' at offshore wind farms, study shows
'' BBC'', 21 July 2014. Accessed: 22 July 2014
Video of seal path
/ref> Offshore wind is similar to terrestrial wind technologies, as a large windmill-like turbine located in a fresh or saltwater environment. Wind causes the blades to rotate, which is then turned into electricity and connected to the grid with cables. The advantages of offshore wind are that winds are stronger and more consistent, allowing turbines of much larger size to be erected by vessels. The disadvantages are the difficulties of placing a structure in a dynamic ocean environment. The turbines are often scaled-up versions of existing land technologies. However, the foundations are unique to offshore wind and are listed below:
Monopile foundation
Monopile foundations are used in shallow depth applications (0–30 m) and consist of a pile being driven to varying depths into the seabed (10–40 m) depending on the soil conditions. The pile-driving construction process is an environmental concern as the noise produced is incredibly loud and propagates far in the water, even after mitigation strategies such as bubble shields, slow start, and acoustic cladding. The footprint is relatively small, but may still cause scouring or artificial reefs. Transmission lines also produce an electromagnetic field that may be harmful to some marine organisms.Tripod fixed bottom
Tripod fixed bottom foundations are used in transitional depth applications (20–80 m) and consist of three legs connecting to a central shaft that supports the turbine base. Each leg has a pile driven into the seabed, though less depth is necessary because of the wide foundation. The environmental effects are a combination of those for monopile and gravity foundations.Gravity foundation
Gravity foundations are used in shallow depth applications (0–30 m) and consist of a large and heavy base constructed of steel or concrete to rest on the seabed. The footprint is relatively large and may cause scouring, artificial reefs, or physical destruction of habitat upon introduction. Transmission lines also produce an electromagnetic field that may be harmful to some marine organisms.Gravity tripod
Gravity tripod foundations are used in transitional depth applications (10–40 m) and consist of two heavy concrete structures connected by three legs, one structure sitting on the seabed while the other is above the water. As of 2013, no offshore windfarms are currently using this foundation. The environmental concerns are identical to those of gravity foundations, though the scouring effect may be less significant depending on the design.Floating structure
Floating structure foundations are used in deep depth applications (40–900 m) and consist of a balanced floating structure moored to the seabed with fixed cables. The floating structure may be stabilized using buoyancy, the mooring lines, or a ballast. The mooring lines may cause minor scouring or a potential for collision. Transmission lines also produce an electromagnetic field that may be harmful to some marine organisms.See also
* Environmental movement *Environmental effects of coal
The health and environmental impact of the coal industry includes issues such as land use, waste management, water and air pollution, caused by the coal mining, processing and the use of its products. In addition to atmospheric pollution, c ...
* Environmental effects of nuclear power
* Environmental issues with energy
* Low-carbon economy
* Renewable energy debate
Policy makers often debate the constraints and opportunities of renewable energy.
Renewable electricity production, from sources such as wind power and solar power, is sometimes criticized for being variable or intermittent. The International En ...
References
External links
* NWCC.National Wind Coordinating Collaborative website
facilitated by the American Wind and Wildlife Institute, includes its updated summaries of wind-wildlife interactions from 2010. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Environmental Effects Of Wind Power Bird mortality Wind power Wind power