Enhanced Vegetation Index on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
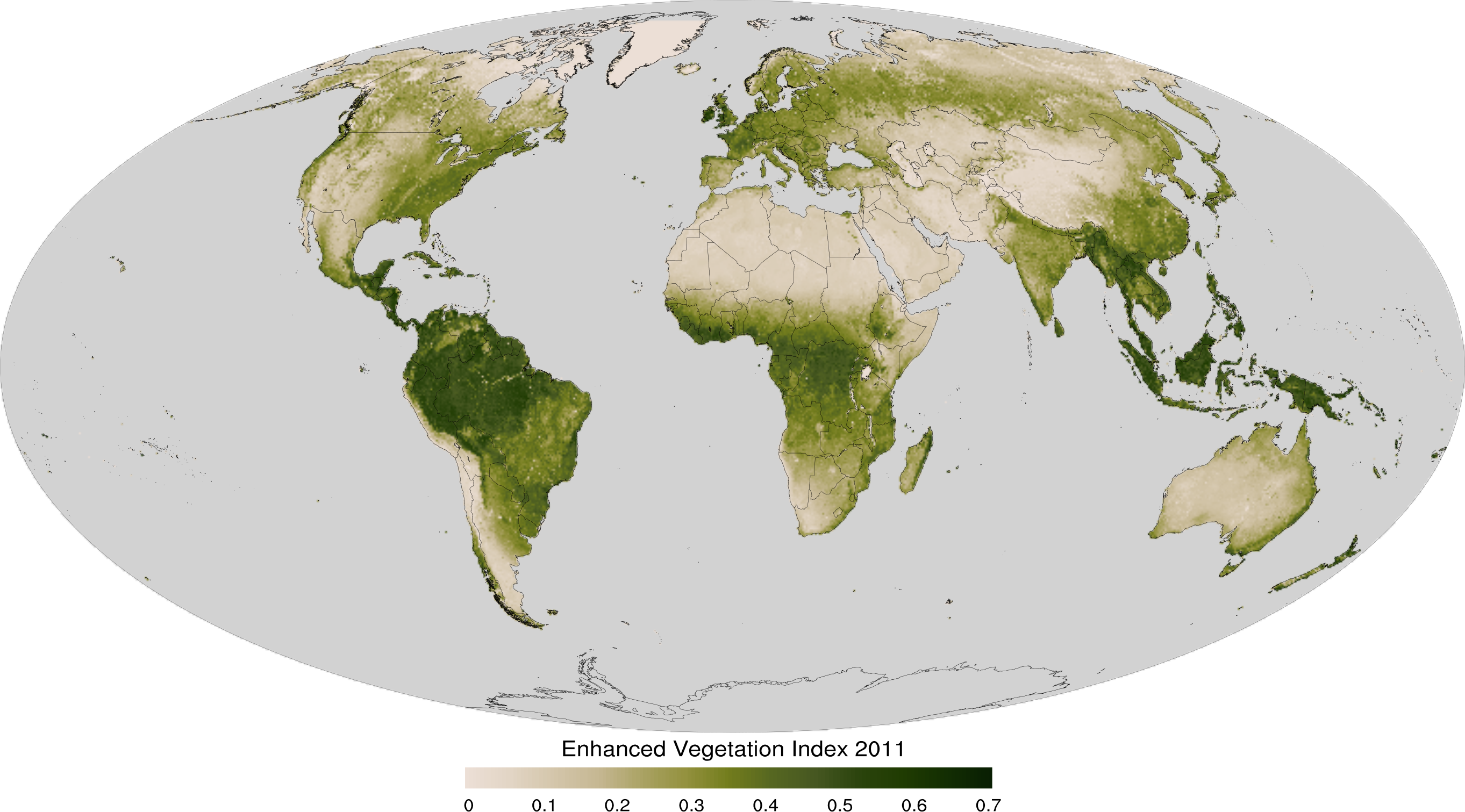 The enhanced vegetation index (EVI) is an 'optimized' vegetation index designed to enhance the vegetation signal with improved sensitivity in high biomass regions and improved vegetation monitoring through a de-coupling of the
The enhanced vegetation index (EVI) is an 'optimized' vegetation index designed to enhance the vegetation signal with improved sensitivity in high biomass regions and improved vegetation monitoring through a de-coupling of the
Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices
Remote Sensing of Environment 83(2002) 195-213 . Starting 2000, and after the launch of the two
standard product
by NASA and became extremely popular with users due to its ability to eliminate background and atmosphere noises, as well as its non saturation, a typical
Spectral compatibility of vegetation indices across sensors: band decomposition analysis with Hyperion data
J. Appl. Remote Sens, 4(1), 043520, {{doi:10.1117/1.3400635.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20061219160331/http://edcdaac.usgs.gov/main.asp The USGS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center
the MODIS Vegetation Product suite
MODIS NATIONAL AERONAUTICS AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION
Satellite meteorology
 The enhanced vegetation index (EVI) is an 'optimized' vegetation index designed to enhance the vegetation signal with improved sensitivity in high biomass regions and improved vegetation monitoring through a de-coupling of the
The enhanced vegetation index (EVI) is an 'optimized' vegetation index designed to enhance the vegetation signal with improved sensitivity in high biomass regions and improved vegetation monitoring through a de-coupling of the canopy
Canopy may refer to:
Plants
* Canopy (biology), aboveground portion of plant community or crop (including forests)
* Canopy (grape), aboveground portion of grapes
Religion and ceremonies
* Baldachin or canopy of state, typically placed over an a ...
background signal and a reduction in atmosphere influences. EVI is computed following this equation:
where:
* NIR/red/blue are atmospherically-corrected and partially atmosphere corrected ( Rayleigh and ozone absorption) surface reflectances
* L is the canopy background adjustment that addresses non-linear, differential NIR and red radiant transfer through a canopy, and
* C1, C2 are the coefficients of the aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog o ...
resistance term, which uses the blue band to correct for aerosol influences in the red band.
The coefficients adopted in the MODIS-EVI algorithm are: L=1, C1 = 6, C2 = 7.5, and G (gain factor) = 2.5.
Whereas the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, often from a space platform, assessing whether or not the target being observed contains live green veget ...
(NDVI) is chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
sensitive, the EVI is more responsive to canopy structural variations, including leaf area index (LAI), canopy type, plant physiognomy, and canopy architecture. The two vegetation indices complement each other in global vegetation studies and improve upon the detection of vegetation changes and extraction of canopy biophysical parameters.
Another difference between Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, often from a space platform, assessing whether or not the target being observed contains live green veget ...
(NDVI) and EVI is that in the presence of snow, NDVI decreases, while EVI increases (Huete, 2002).A. Huete, K. Didan, T. Miura, E. P. Rodriguez, X. Gao, L. G. FerreiraOverview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices
Remote Sensing of Environment 83(2002) 195-213 . Starting 2000, and after the launch of the two
MODIS
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a satellite-based sensor used for earth and climate measurements. There are two MODIS sensors in Earth orbit: one on board the Terra (EOS AM) satellite, launched by NASA in 1999 ...
sensors on Terra (satellite)
Terra (EOS AM-1) is a multi-national, NASA scientific research satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit around the Earth that takes simultaneous measurements of Earth's atmosphere, land, and water to understand how Earth is changing and to identify ...
and Aqua (satellite)
Aqua (EOS PM-1) is a NASA scientific research satellite in orbit around the Earth, studying the precipitation, evaporation, and cycling of water. It is the second major component of the Earth Observing System (EOS) preceded by Terra (launched 199 ...
by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
, EVI was adopted as astandard product
by NASA and became extremely popular with users due to its ability to eliminate background and atmosphere noises, as well as its non saturation, a typical
NDVI
The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, often from a space platform, assessing whether or not the target being observed contains live green veget ...
problem. EVI is currently distributed for free by the USGS LP DAAC.
Two-band EVI
Two reasons drive the search for a two-band EVI: # Extending the EVI back in time, using the AVHRR record. The AVHRR sensors lacks a blue band, hence using a three-band EVI version is not possible. This could potentially lead to a 30-year EVI record that complements the NDVI record. # The blue band has always been problematic, and its Signal to Noise ratio (S/N) quite poor. This is mainly due to the nature of the reflected energy in this part of the spectrum over land, which is extremely low. As such, a two-band EVI is useful. We'll call the two-band EVI "EVI2", and the three-band EVI simply "EVI". A number of EVI2 approaches are available; the one of Jiang et al. 2008 is: * Define EVI2 as a two-band index in the form of * Find coefficients G, L, and C (organic) to minimize the difference between EVI2 and EVI. They play a similar role to the analogous factors in EVI, but are not actually grounded in physics but found by mathematics. ** This leads to multiple (infinite) solutions but a few (vaguely physics-based) conditions could be imposed on the solution to generate the best coefficients. * With MODIS data, we have . Jiang's EVI2 has the best similarity with the 3-band EVI, particularly when atmospheric effects are insignificant and data quality is good. EVI2 can be used for sensors without a blue band, such as the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR), and may reveal different vegetation dynamics in comparison with the current AVHRR NDVI dataset. There exist some other EVI2s, one being that of Miura 2008 for ASTER . The ASTER sensors have a different spectral range compared to the MODIS ones.Application of EVI
An example of the utility of EVI was reported by Huete ''et al.'' (2006). Previously, the Amazon rainforest was viewed as having a monotonous growing season, where there is no particular seasonality to plant growth. Using the MODIS EVI product, Huete ''et al.'' showed that the Amazon forest exhibits a distinct increase in growth during the dry season. This phenomenon has implications for our understanding of thecarbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as ...
and sinks in the region, though it is unclear whether this is a long-standing pattern or an emergent shift associated with climate change.
References
* Kim, Y., Huete, A. R., Miura, T., Jiang, Z. (2010)Spectral compatibility of vegetation indices across sensors: band decomposition analysis with Hyperion data
J. Appl. Remote Sens, 4(1), 043520, {{doi:10.1117/1.3400635.
External links
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20061219160331/http://edcdaac.usgs.gov/main.asp The USGS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center
the MODIS Vegetation Product suite
MODIS NATIONAL AERONAUTICS AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION
Satellite meteorology