Engineering College on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Engineering education is the activity of
Surabaya University (UBAYA)
''


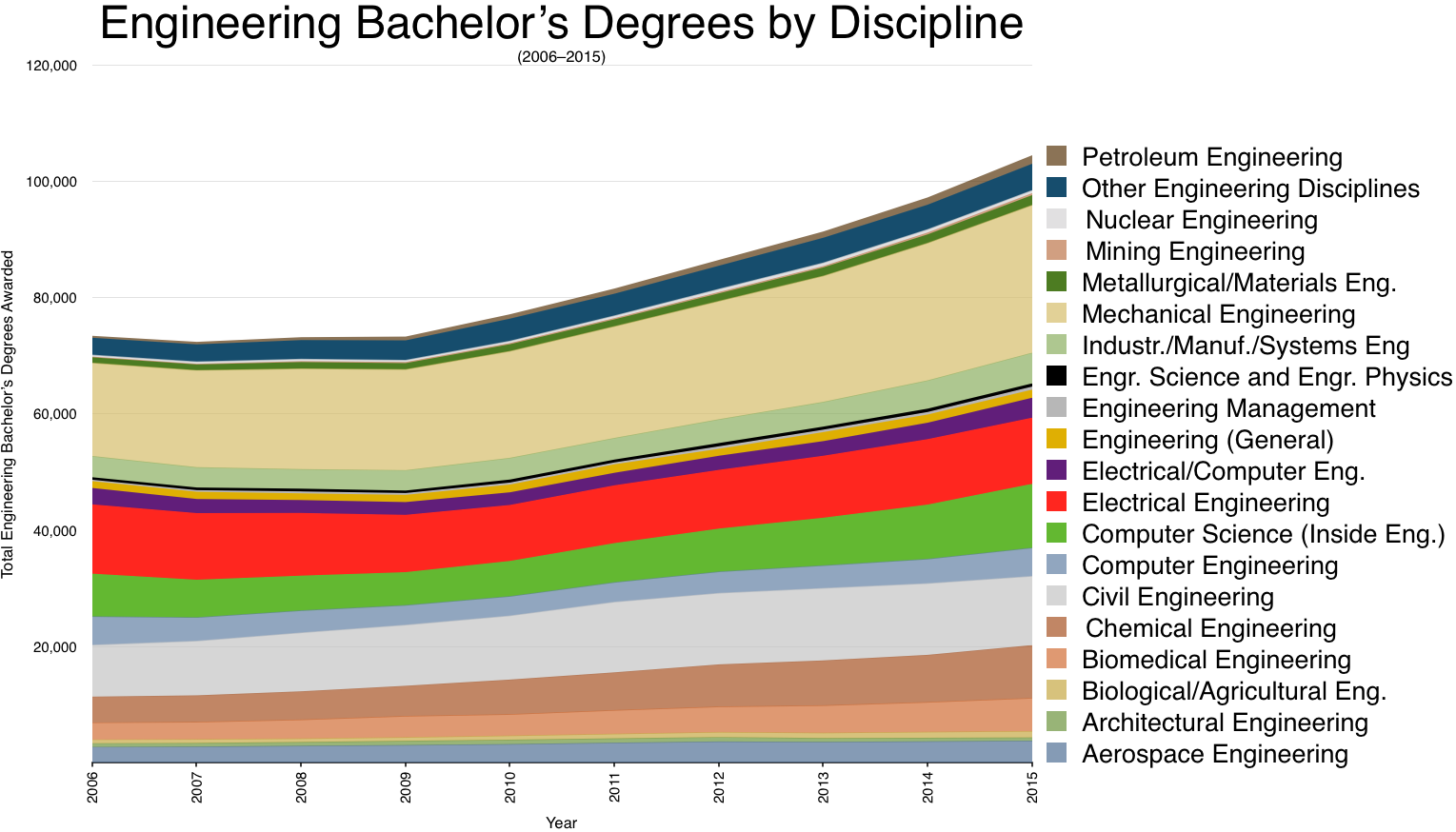 The first professional degree in engineering is a bachelor's degree with few exceptions. Interest in engineering has grown since 1999; the number of bachelor's degrees issued has increased by 20%.Reyes-Guerra, D. R. (2011). Engineering. In J. M. Castagno, P. Barrows, L. Brearley, & K. Fairchild (Eds.), Grolier online. Most bachelor's degree engineering programs are four years long and require about two years of core courses followed by two years of specialized discipline specific courses. This is where a typical engineering student would learn mathematics (single- and multi-variable
The first professional degree in engineering is a bachelor's degree with few exceptions. Interest in engineering has grown since 1999; the number of bachelor's degrees issued has increased by 20%.Reyes-Guerra, D. R. (2011). Engineering. In J. M. Castagno, P. Barrows, L. Brearley, & K. Fairchild (Eds.), Grolier online. Most bachelor's degree engineering programs are four years long and require about two years of core courses followed by two years of specialized discipline specific courses. This is where a typical engineering student would learn mathematics (single- and multi-variable
teaching
Teaching is the practice implemented by a ''teacher'' aimed at transmitting skills (knowledge, know-how, and interpersonal skills) to a learner, a student, or any other audience in the context of an educational institution. Teaching is closely ...
knowledge and principles to the professional practice of engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
. It includes an initial education (bachelor's
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six ...
and/or master's degree
A master's degree (from Latin ) is an academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice.
), and any advanced education and specializations that follow. Engineering education is typically accompanied by additional postgraduate examinations and supervised training as the requirements for a professional engineering license. The length of education, and training to qualify as a basic professional engineer, is typically 5 years, with 15–20 years for an engineer who takes responsibility for major projects.
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) is an umbrella term used to group together the distinct but related technical disciplines of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. The term is typically used in the context o ...
(STEM) education in primary and secondary schools often serves as the foundation for engineering education at the university level. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, engineering education is a part of the STEM initiative in public schools. Service-learning in engineering education Many engineering educators see service-learning as the solution to several prevalent problems in engineering education today. In the past, engineering curriculum has fluctuated between emphasizing engineering science to focusing more on practical ...
is gaining popularity within the variety of disciplinary focuses within engineering education including chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials in ...
, civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
, mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, ...
, industrial engineering
Industrial engineering is an engineering profession that is concerned with the optimization of complex processes, systems, or organizations by developing, improving and implementing integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information an ...
, computer engineering
Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer enginee ...
, electrical engineering, architectural engineering
Architectural engineers apply and theoretical knowledge to the engineering design of buildings and building systems. The goal is to engineer high performance buildings that are sustainable, economically viable and ensure the safety health.
Archi ...
, and other engineering education.
Africa
Kenya
Engineering training inKenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
is typically provided by the universities. Registration of engineers is governed by the Engineers Registration Act. A candidate stands to qualify as a registered engineer, R.Eng., if they are a holder of a minimum four years post-secondary Engineering Education and a minimum of three years of postgraduate work experience.
All registrations are undertaken by the Engineers Registration Board which is a statutory body established through an Act of the Kenyan Parliament in 1969. A minor revision was done in 1992 to accommodate Technician Engineer grade. The board has been given the responsibility of regulating the activities and conduct of Practicing Engineers in the Republic of Kenya in accordance with the functions and powers conferred upon it by the Act. Under CAP 530 of the Laws of Kenya, it is illegal for an engineer to practice or call themself an engineer if not registered with the board. Registration with the board is thus a license to practice engineering in Kenya.
South Africa
Engineering training in South Africa is typically provided by the universities, universities of technology and colleges for Technical and Vocational Education and Training (previously Further Education and Training). The qualifications provided by these institutions must have an Engineering Council of South Africa (ECSA) accreditation for the qualification for graduates and diplomats of these institutions to be registered as Candidate Certificated Engineers, Candidate Engineers, Candidate Engineering Technologists and Candidate Engineering Technicians. There are many benefits to these attributes. The academic training performed by the universities is typically in the form of a four-year BSc(Eng), BIng or BEng degree. For the degree to be accredited, the course material must conform to the ECSA Graduate Attibutes (GA). Professional Engineers (Pr Eng) are persons that are accredited by ECSA as engineering professionals. Legally, a Professional Engineer's sign off is required for any major project to be implemented, in order to ensure the safety and standards of the project. Professional Engineering Technologists (Pr Tech Eng) and Professional Engineering Technicians (Pr Techni Eng) are other members of the engineering team. Professional Certificated Engineers (Pr Cert Eng) are people who hold one of seven Government Certificates of Competency and who have been registered by ECSA as engineering professionals. The categories of professionals are differentiated by the degree of complexity of work carried out, where Professional Engineers are expected to solve complex engineering problems, Professional Engineering Technologists and Professional Certificated Engineers, broadly defined engineering problems and Professional Engineering Technicians, well-defined engineering problems.Tanzania
Engineering training in Tanzania is typically provided by various universities and technical institutions in the country. Graduate engineers are registered by the Engineers Registration Board (ERB) after undergoing three years of practical training. A candidate stands to qualify as a professional engineer, P.Eng., if they are a holder of a minimum four years post-secondary Engineering Education and a minimum of three years of postgraduate work experience. Engineers Registration Board is a statutory body established through an Act of the Tanzanian Parliament in 1968. Minor revision was done in 1997 to address the issue of engineering professional excellence in the country. The board has been given the responsibility of regulating the activities and conduct of Practicing Engineers in the United Republic of Tanzania in accordance with the functions and powers conferred upon it by the Act. According to Tanzania Laws, it is illegal for an engineer to practice or call themself an engineer if not registered with the board. Registration with the board is thus a license to practice engineering in United Republic of Tanzania.Asia
Bangladesh
List of engineering schools in Bangladesh
* Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET) *Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology
Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, Gazipur ( bn, ঢাকা প্রকৌশল ও প্রযুক্তি বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়, গাজীপুর ) or DUET is a public university in Gazipur, Banglad ...
(DUET)
* Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology (RUET)
* Chittagong University of Engineering & Technology (CUET)
* Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET)
* Islamic University of Technology (IUT)
* Sylhet Engineering College
Sylhet Engineering College (SEC; bn, সিলেট প্রকৌশল মহাবিদ্যালয়) is a public undergraduate (B.Sc. Engineering) College, established in 2007. It is affiliated with the "Shahjalal University of Sci ...
(SEC)
* Mymensingh Engineering College (MEC)
Hong Kong
In Hong Kong, engineering degree programmes (4-year bachelor's degree) are offered by public universities funded by the University Grant Committee (UGC). There are 94 UGC-funded programmes in engineering and technology offered byCity University of Hong Kong
City University of Hong Kong (CityU) is a world-class public research university located in Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong. It was founded in 1984 as City Polytechnic of Hong Kong and became a fully accredited university in 1994. Currently, CityU is ...
, the Chinese University of Hong Kong
The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) is a public research university in Ma Liu Shui, Hong Kong, formally established in 1963 by a charter granted by the Legislative Council of Hong Kong. It is the territory's second-oldest university a ...
, the Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) is a public university, public research university located in Hung Hom, Hong Kong near Hung Hom station. The University is one of the eight University Grants Committee (Hong Kong), government-funded ...
, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) is a public research university in Clear Water Bay Peninsula, New Territories, Hong Kong. Founded in 1991 by the British Hong Kong Government, it was the territory's third institution ...
, and the University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong (HKU) (Chinese: 香港大學) is a public university, public research university in Hong Kong. Founded in 1887 as the Hong Kong College of Medicine for Chinese, it is the oldest Higher education in Hong Kong, tertia ...
. For example, the Faculty of Engineering of the University of Hong Kong (HKU) has five departments providing undergraduate, postgraduate and research degrees in civil engineering, Computer Science, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering, as well as Mechanical Engineering. All programmes of Bachelor of Engineering under the Joint University Programmes Admissions System (JUPAS) code 6963 being offered are accredited by the Hong Kong Institution of Engineers (HKIE). With that standing, the professional qualification of HKU engineering graduates is mutually recognized by most countries, such as the United States, Australia, Canada, Japan, Korea, New Zealand, Singapore and South Africa. Applicants with other local / international /national qualifications such as GCE A-level, International Baccalaureate (IB) or SAT can apply through the Non-JUPAS Route.
The Hong Kong Institution of Engineers (the HKIE) accredits individual engineering degree programmes. The process of professional accreditation also considers the appropriate Faculty in terms of its overall philosophy, objectives and resources. The professional accreditation of engineering degree programmes in the universities is normally initiated by a university issuing an invitation to the HKIE's Accreditation Board to carry out appropriate accreditation exercises.
To become a professional engineer, senior secondary (Form 4 to Form 6) school students start by choosing science and technology related subjects, while at least passing English and Mathematics in the Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education
The Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education Examination (HKDSE) is an examination organised by the Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority (HKEAA). The HKDSE examination is Hong Kong's university entrance examination, administere ...
examinations. Secondary school graduates have to enroll in an HKIE accredited engineering programme, join the universities’ engineering students society and join the HKIE as a student member. After completing a bachelor's degree in engineering, graduates undergo two to three years of engineering graduate training and gaining another two to three years relevant working experience. Upon passing the Professional Assessment, the candidate will be conferred member by the HKIE, finally becoming a Professional Engineer. The engineering profession in Hong Kong has 21 engineering disciplines, namely Aircraft, Biomedical, Building, Building Services, Chemical, Civil Control, Automation & Instrumentation, Electrical, Electronics, Energy, Environmental, Fire, Gas, Geotechnical, Information, Logistics & Transportation, Manufacturing & Industrial, Marine & Naval Architecture, Materials, Mechanical, as well as Structural engineering.
In 2019, the Asian Society of Engineering Education (AsiaSEE) is founded in Hong Kong by Dr. Cecilia K.Y. Chan and over twenty founding members around Asia. AsiaSEE is the first Asian regional network of higher educational institutions leaders with commitment to improve engineering education. The vision of AsiaSEE is to be the trusted body in Asia to facilitate communications and cooperation in engineering education between members, institutions, industries, stakeholders and like-minded societies in the world. The mission of AsiaSEE is to contribute to the advancement and enhancement in engineering education via research and practice for the future generation.}
Central Asia
Uzbekistan
List of engineering schools in Uzbekistan
* Turin Polytechnic University in Tashkent * Tashkent State Technical University *Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Melioration
The Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers (TIIAME), formerly Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Melioration (TIIME) ( (TIQXMMI)) is a university in Central Asia, which works for the development of the water ...
*Tashkent Automobile and Road Construction Institut
India
More than 5,000 universities and colleges offer engineering courses in India.Indonesia
List of engineering schools in Indonesia
* Sepuluh Nopember Institute of Technology *Bandung Institute of Technology
The Bandung Institute of Technology ( id, Institut Teknologi Bandung, abbreviated as ITB) is a national research university located in Bandung, Indonesia. Since its establishment in 1920, ITB has been consistently recognized as Indonesia's premi ...
* Faculty of Engineering of Sebelas Maret University
*Faculty of Engineering of Ahmad Dahlan University
* Faculty of Engineering of Andalas University
* Faculty of Engineering of Sultan Ageng Tirtayasa University
Sultan Ageng Tirtayasa University (abbreviated as Untirta) is the only state university in the province of Banten, Indonesia. The main campus is in Serang Regency, the faculty of engineering is at Cilegon, and Faculty of Education most of it is ...
* Faculty of Engineering of University of Indonesia
The University of Indonesia ( id, Universitas Indonesia, abbreviated as UI) is a public university in Depok, West Java and Salemba, Jakarta, Indonesia. It is one of the oldest tertiary-level educational institutions in Indonesia (known as the ...
* Faculty of Engineering of Gadjah Mada University
Gadjah Mada University ( jv, ꦈꦤꦶꦥ꦳ꦼꦂꦱꦶꦠꦱ꧀ꦓꦗꦃꦩꦢ; id, Universitas Gadjah Mada, abbreviated as UGM) is a public research university located in Sleman, Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Officially founded on ...
* Faculty of Engineering of University of Lampung
* Faculty of Engineering of Diponegoro University
Diponegoro University ( jv, ꦈꦤꦶꦥ꦳ꦼꦂꦱꦶꦠꦱ꧀ꦢꦶꦥꦤꦼꦒꦫ; id, Universitas Diponegoro, abbreviated as Undip) is a public university in Semarang, Central Java, Indonesia. Founded in 1957 as a private university by th ...
* Faculty of Engineering of Universitas Negeri Padang
* Faculty of Engineering of Universitas Negeri Malang
* Faculty of Engineering of Hasanuddin University
* Faculty of Engineering of 'Surabaya University (UBAYA)
''
Malaysia
Activities on engineering education in Malaysia are spearheaded by the Society of Engineering Education Malaysia (SEEM). SEEM was established in 2008 and launched on 23 February 2009. The idea of establishing the Society of Engineering Education was initiated on April, 2005 with the creating of a Pro-team Committee for SEEM. The objectives of this society are to contribute to the development of education in the fields of engineering education and science and technology, including teaching and learning, counseling, research, service and public relations. *Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
, image_name = UTM-LOGO.png
, image_size =
, caption = Seal
, latin_name =
, motto = Kerana Tuhan Untuk Manusia
, mottoeng = In the Name of God for Mankind
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public research university
, affiliatio ...
* Centre For Engineering Education, CEE
* Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (abbreviated as UTAR; ) is a non-profit private research university in Malaysia. It is ranked top 100 in the Times Higher Education Asia University Rankings 2018 and top 1200 in the Times Higher Education Wo ...
* Tunku Abdul Rahman University College
* Southern University College
Southern University College (abbreviated as Southern UC), is a non-profit, private university college in Malaysia. It is the first non-profit higher education institute and private university college in Skudai, Johor.
Currently, Southern UC h ...
* Universiti Malaysia Pahang
Pakistan
In Pakistan, engineering education is accredited by thePakistan Engineering Council
The Pakistan Engineering Council (Urdu: ; acronym: PEC) is a professional body for accreditation of engineering education and regulation of engineering profession in Pakistan. It was established on 10 January 1976 by the Parliament under the ...
, a statutory body, constituted under the PEC Act No. V of 1976 of the constitution of Pakistan and amended vide Ordinance No.XXIII of 2006, to regulate the engineering profession in the country. It aims to achieve rapid and sustainable growth in all national, economic and social fields. The council is responsible for maintaining realistic and internationally relevant standards of professional competence and ethics for engineers in the country. PEC interacts with the Government, both at the Federal and Provincial level by participating in Commissions, Committees and Advisory Bodies. PEC is a fully representative body of the engineering community in the country. PEC has a full signatory status with Washington Accord.
Philippines
TheProfessional Regulation Commission
The Professional Regulation Commission, ( fil, Komisyon sa Regulasyon ng mga Propesyon) otherwise known as the PRC, is a three-man commission attached to Department of Labor and Employment (DOLE). Its mandate is to regulate and supervise the p ...
is the regulating body for engineers in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
Sri Lanka
Taiwan
Engineering is one of the most popular majors among universities in Taiwan. The engineering degrees are over a quarter of the bachelor's degrees in Taiwan.Europe
Austria
InAustria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, similar to Germany, an engineering degree can be obtained from either universities or Fachhochschulen (universities of applied sciences). As in most of Europe, the education usually consists of a 3-year bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six ...
and a 2-year master's degree
A master's degree (from Latin ) is an academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice.
.
A lower engineering degree is offered by Höheren Technische Lehranstalten, (HTL, Higher Technical Institute), a form of secondary college which reaches from grade 9 to 13. There are disciplines like civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
, electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system ...
, etc.
In the 5th year of HTL, as in other secondary schools in Austria, there is a final exam, called Matura
or its translated terms (''Mature'', ''Matur'', , , , , , ) is a Latin name for the secondary school exit exam or "maturity diploma" in various European countries, including Albania, Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cz ...
. Graduates obtain an ''Ingenieur'' engineering degree after three years of work in the studied field.
Bulgaria
The beginning of higher engineering education inBulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
is established by the Law for Establishing a Higher Technical School in Sofia in 1941. Only two years later however because of the bombs flying over Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. ...
, the school was evacuated in Lovech
Lovech ( bg, Ловеч, Lovech, ) is a city in north-central Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the Lovech Province and of the subordinate Lovech Municipality. The city is located about northeast from the capital city of Sofia. Near L ...
, and the regular classes were discontinued. The learning process started again in 1945 when the university became a State Polytechnic.
In Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
, engineers are trained in the three basic degrees – bachelor, master and doctor. Since the Bologna declaration
The Bologna declaration (in full, Joint Declaration of the European Ministers of Education convened in Bologna on 19 June 1999) is the main guiding document of the Bologna process. It was adopted by ministers of education of 29 European countries ...
, students receive a bachelor's degree (4 years of studies), optionally followed by a master's degree
A master's degree (from Latin ) is an academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice.
(1 years of studies). The science and engineering courses include lecture and laboratory education. The main subjects to be studied are mathematics, physics, chemistry, electrical engineering, etc. The degree received after completing with a state exam or defense of a thesis. Absolvents are awarded with the ''Ing''. title always put in front of one's name.
Some of engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
specialties are completely traditional, such as machine building, computer and software engineering, automation, electrical engineering, electronics. Newer specialties are engineering design
The engineering design process is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative - parts of the process often need to be repeated many times before another can be enter ...
, mechatronics, aviation engineering, industrial engineering.
The following technical universities prepare mainly engineers in Bulgaria:
* Technical University Sofia
* Technical University Varna
* Technical University Gabrovo
* University of Forestry
* University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy
* University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy Sofia
* Agricultural University Plovdiv
* University of Mining and Geology “St. Ivan Rilski”
The Bulgarian engineers are united in the Federation of Scientific and Technical Unions, established in 1949. It comprises 33 territorial and 19 national unions.
Denmark
In Denmark, the engineering degree is delivered by either universities or engineering colleges (e.g. Engineering College of Aarhus). Students receive first a baccalaureate degree (3 years of studies) followed by a master's degree (1–2 years of studies) according to the principles of the Bologna declaration, though traditionally. The engineering doctorate degree is the ''PhD PHD or PhD may refer to:
* Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), an academic qualification
Entertainment
* '' PhD: Phantasy Degree'', a Korean comic series
* ''Piled Higher and Deeper
''Piled Higher and Deeper'' (also known as ''PhD Comics''), is a newsp ...
'' (3 years of studies).
The quality of Danish engineering expertise has long been much vaunted. Danish engineers, especially from engineering colleges, have also been praised at being very practical (i.e. skilled at physical work related to their discipline), ascribed to the high quality of the apprenticeship courses many Danish engineers go through as part of their education.
Finland
Finland's system is derived from Germany's system. Two kinds of universities are recognized, the universities and theuniversities of applied sciences
A ''Fachhochschule'' (; plural ''Fachhochschulen''), abbreviated FH, is a university of applied sciences (UAS), in other words a German tertiary education institution that provides professional education in many applied sciences and applied ar ...
.
Universities award typically 'Bachelor of Science in Technology' and 'Master of Science in Technology' degrees. Bachelor's degree is a three-year degree as master's degree is equivalent for two-year full-time studies. In Finnish the master's degree is called diplomi-insinööri, similarly as in Germany (''Diplom-Ingenieur''). The degrees are awarded by engineering schools or faculties in universities (in Aalto University
Aalto University ( fi, Aalto-yliopisto; sv, Aalto-universitetet) is a public research university located in Espoo, Finland. It was established in 2010 as a merger of three major Finnish universities: the Helsinki University of Technology, the H ...
, Oulu
Oulu ( , ; sv, Uleåborg ) is a city, municipality and a seaside resort of about 210,000 inhabitants in the region of North Ostrobothnia, Finland. It is the most populous city in northern Finland and the fifth most populous in the country after ...
, Turku
Turku ( ; ; sv, Åbo, ) is a city and former capital on the southwest coast of Finland at the mouth of the Aura River, in the region of Finland Proper (''Varsinais-Suomi'') and the former Turku and Pori Province (''Turun ja Porin lääni''; ...
, Vaasa
Vaasa (; sv, Vasa, , Sweden ), in the years 1855–1917 as Nikolainkaupunki ( sv, Nikolajstad; literally meaning "city of Nicholas),
and Åbo Akademi University
Åbo Akademi University ( sv, Åbo Akademi , ) is the only exclusively Swedish language multi-faculty university in Finland (or anywhere outside Sweden). It is located mainly in Turku (Åbo is the Swedish name of the city) but has also activit ...
) or by separate universities of technology ( Tampere UT and Lappeenranta UT). The degree is a scientific, theoretical taught master's degree. Master's thesis is important part of master's degree studies. Master's degree qualifies for further study into Licentiate or doctorate. Because of the Bologna process, the degree ''tekniikan kandidaatti'' ("Bachelor of Technology"), corresponding to three years of study into the master's degree, has been introduced.
The universities of applied sciences are regional universities that award 3.5-, to 4-year engineer degrees insinööri (amk). An engineer's degree is normally 240 ECTS. There are 20 universities of applied sciences in Finland with a vide range of disciplines. The aim of the degree is professional competency with an emphasis on practical problem solving in engineering. Normally the teaching language is Finnish but there are also universities with Swedish as language of instruction, and most universities of applied sciences offer some degrees in English, too. These universities also award a Master of Engineering degree, designed for engineers already involved in the working life with at least two years of professional experience.
France
In France, the engineering degree is mainly delivered by " Grandes Écoles d'Ingénieurs" (graduate schools of engineering) upon completion of 3 years of Master's studies. Many Écoles recruit undergraduate students from CPGE (two- or three-year high level program after theBaccalauréat
The ''baccalauréat'' (; ), often known in France colloquially as the ''bac'', is a French national academic qualification that students can obtain at the completion of their secondary education (at the end of the ''lycée'') by meeting certain ...
), even though some of them include an integrated undergraduate cycle. Other students accessing these Grandes Ecoles may come from other horizons, such as DUT or BTS (technical two-year university degrees) or standard two-year university degrees. In all cases, recruitment is highly selective. Hence graduate engineers in France have studied a minimum of five years after the baccalaureate. Since 2013, the French engineering degree is recognized by the AACRAO as a Master of Science in Engineering.
To be able to deliver the engineering degree, an École Master 's curriculum has to be validated by the Commission des titres d'ingénieur
Commission des Titres d'Ingénieur (CTI) is the main committee responsible for evaluation and accreditation of higher education institutions for the training of professional engineers in France. It regulates the issuance of the ''Diplôme d'ingén ...
( Commission of the Engineering Title). It is important for the external observer to note that the system in France is extremely demanding in its entrance requirements (numerus clausus
''Numerus clausus'' ("closed number" in Latin) is one of many methods used to limit the number of students who may study at a university. In many cases, the goal of the ''numerus clausus'' is simply to limit the number of students to the maximum ...
, using student rank in exams as the only criterion), despite being almost free of tuition fees, and much stricter in regards to the academic level of applying students than many other systems. The system focuses solely on selecting students by their engineering fundamental disciplines (mathematics, physics) abilities rather than their financial ability to finance large tuition fees, thus enabling a wider population access to higher education. In fact, being a graduate engineer in France is considered as being near/at the top of the social/professional ladder. The engineering profession grew from the military and the nobility in the 18th century. Before the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
, engineers were trained in schools for technical officers, like "École d'Arts et Métiers" (Arts et Métiers ParisTech
Arts et Métiers ParisTech is a French engineering and research institute of higher education. It is a '' grande école'', recognized for leading in the fields of mechanics and industrialization. Founded in 1780, it is among the oldest French in ...
) established in 1780. Then, other schools were created, for instance the École Polytechnique
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern Franc ...
and the Conservatoire national des arts et métiers
A music school is an educational institution specialized in the study, training, and research of music. Such an institution can also be known as a school of music, music academy, music faculty, college of music, music department (of a larger in ...
which was established in 1794. Polytechnique is one of the ''grandes écoles'' that have traditionally prepared technocrats to lead French government and industry, and has been one of the most privileged routes into the elite divisions of the civil service known as the "grands corps de l'État".
Inside a French company the title of ''Ingénieur'' refers to a rank in qualification and is not restricted. Therefore, there are sometimes ''Ingénieurs des Ventes'' (Sales Engineers), ''Ingénieur Marketing'', ''Ingénieur Bancaire'' (Banking Engineer), ''Ingénieur Recherche & Développement'' (R&D Engineer), etc.
Germany
InGermany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, the term ''Ingenieur'' (engineer) is legally protected and may only be used by graduates of a university degree program in engineering. Such degrees are offered by universities (''Universitäten''), including ''Technische Universitäten'' (universities of technology) and ''Technische Hochschule
A ''Technische Hochschule'' (, plural: ''Technische Hochschulen'', abbreviated ''TH'') is a type of university focusing on engineering sciences in Germany. Previously, it also existed in Austria, Switzerland, the Netherlands (), and Finland (, ) ...
n'', or ''Fachhochschulen'' (universities of applied sciences).
Since the Bologna reforms, students receive a bachelor's degree (3–4 years of studies), optionally followed by a master's degree (1–2 years of studies). Prior to the country adopting the Bologna system, the first and only pre-doctorate degree received after completing engineering education at university was the German ''Diplom
A ''Diplom'' (, from grc, δίπλωμα ''diploma'') is an academic degree in the German-speaking countries Germany, Austria, and Switzerland and a similarly named degree in some other European countries including Albania, Bulgaria, Belaru ...
ingenieur'' (Dipl.-Ing.). The engineering doctorate
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism '' ...
is the ''Doktoringenieur
The Doktoringenieur (acronym Dr.-Ing., also ''Doktor der Ingenieurwissenschaften'') is the German engineering doctorate degree, comparable to the Doctor of Engineering, Engineering Doctorate, Doctor of Science (Engineering), Doctor of Science (T ...
'' (Dr.-Ing.).
The quality of German engineering expertise has long been much vaunted, especially in the field of mechanical engineering. This is supported by the degree to which the various theories governing aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
and structural mechanics
Structural mechanics or Mechanics of structures is the computation of deformations, deflections, and internal forces or stresses (''stress equivalents'') within structures, either for design or for performance evaluation of existing structures. ...
are named after German scientists and engineers such as Ludwig Prandtl
Ludwig Prandtl (4 February 1875 – 15 August 1953) was a German fluid dynamicist, physicist and aerospace scientist. He was a pioneer in the development of rigorous systematic mathematical analyses which he used for underlying the science of ...
. German engineers have also been praised at being very practical (i.e. skilled at physical work related to their discipline), ascribed to the high quality of the apprenticeship courses many German engineers go through as part of their education.
Italy
InItaly
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, the engineering degree and "engineer" title is delivered by polytechnic universities upon completion of 3 years of studies (laurea). Additional master's degree (2 years) and doctorate programs (3 years) provide the title of "dottore di ricerca in ingegneria". Students that started studies in polytechnic universities before 2005 (when Italy adopted the Bologna declaration) need to complete a 5-year program to get the engineer title. In this case the master's degree is obtained after 1 year of studies.
Only people with an engineer title can be employed as "engineers". Still, some with competence and experience in an engineering field that do not have such a title, can still be employed to perform engineering tasks as "specialist", "assistant", "technologist" or "technician". But, only engineers can take legal responsibility and provide guarantee upon the work done by a team in their area of expertise. Sometimes a company working in this area, which temporarily does not have any employees with an engineer title must pay for an external service of an engineering audit to provide legal guarantee for their products or services.
The Netherlands
In theNetherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
there are two ways to study engineering, i.e. at the Dutch 'technical hogeschool
A university of applied sciences (UAS), nowadays much less commonly called a polytechnic university or vocational university, is an institution of higher education and sometimes research that provides vocational education and grants academic de ...
', which is a professional school
Professional development is learning to earn or maintain professional credentials such as academic degrees to formal coursework, attending conferences, and informal learning opportunities situated in practice. It has been described as intensiv ...
(equivalent to a university of applied sciences
A university of applied sciences (UAS), nowadays much less commonly called a polytechnic university or vocational university, is an institution of higher education and sometimes research that provides vocational education and grants academic d ...
internationally) and awards a practically orientated degree with the pre-nominal ''ing.'' after four years study. Or at the university, which offers a more academically oriented degree with the pre-nominal ''ir.'' after five years study. Both are abbreviations of the title Ingenieur
An engineer's degree is an advanced academic degree in engineering which is conferred in Europe, some countries of Latin America, North Africa and a few institutions in the United States. The degree may require a thesis but always requires a non- ...
.
In 2002 when the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
switched to the Bachelor-Master system. This is a consequence of the Bologna process. In this accord 29 European countries agreed to harmonize their higher education system and create a European higher education area
The European Higher Education Area (EHEA) was launched in March 2010, during the Budapest-Vienna Ministerial Conference, on the occasion of the 10th anniversary of the Bologna Process.
As the main objective of the Bologna Process since its ince ...
. In this system the professional schools award bachelor's degrees like ''BEng'' or ''BASc'' after four years study. And the universities with engineering programs award the bachelor's degree ''BSc'' after the third year. A university bachelor is usually continuing his education for one or two more years to earn his master's degree ''MSc''. Adjacent to these degrees, the old titles of the pre-populated system are still in use. A ''vocational'' bachelor may be admitted to a university master's degree program although often they are required to take additional courses.
Poland
InPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
after 3,5–4 years of technical studies, one gets inżynier degree (inż.), which corresponds to ''B.Sc.'' or ''B.Eng.'' After that, one can continue studies, and after 2 years of post-graduate programme (supplementary studies) can obtain additional ''M.Sc.'' (or ''M.Eng.'') degree, called magister, mgr, and that time one has two degrees: magister inżynier, mgr inż. (literally: ''master engineer''). The ''mgr'' degree formerly (until full adaptation of Bologna process by university) could be obtained in integrated 5 years B.Sc.-M.Sc. programme studies. Graduates having ''magister inżynier'' degree, can start 4 years doctorate studies (Ph.D.), which require opening of doctoral proceedings (''przewód doktorski''), carrying out own research, passing some exams (''e.g.'' foreign language, philosophy, economy, leading subjects), writing and defense of doctoral thesis. Some Ph.D. students have also classes with undergraduate students (B.Sc., M.Sc.). Graduate of doctorate studies of technical university holds ''scientific degree'' of doktor nauk technicznych, dr inż., (literally: ''"doctor of technical sciences"'') or other ''e.g.'' ''Doktor Nauk Chemicznych'' (lit. ''"doctor of chemical sciences"'').
Portugal
In Portugal, there are two paths to study engineering: thepolytechnic
Polytechnic is most commonly used to refer to schools, colleges, or universities that qualify as an institute of technology or vocational university also sometimes called universities of applied sciences.
Polytechnic may also refer to:
Educat ...
and the university paths. In theory, but many times not so much in practice, the polytechnic path is more practical oriented, the university path being more research oriented.
In this system, the polytechnic institutes award a ''licenciatura'' (bachelor) in engineering degree after three years of study, that can be complemented by a ''mestrado'' (master) in engineering after two plus years of study.
Regarding the universities, they offer both engineering programs similar to those of the polytechnics (three years ''licenciatura'' plus two years ''mestrado'') as ''mestrado integrados'' (integrated master's) in engineering programs. The ''mestrado integrado'' programs take five years of study to complete, awarding a ''licenciatura'' degree in engineering sciences after the first three years and a ''mestrado'' degree in engineering after the whole five years. Further, the universities also offer ''doutoramento'' (Ph.D.) programs in engineering.
Being an holder of an academic degree in engineering is not enough to practice the profession of engineer and to have the legal right of the use of the title ''engenheiro'' (engineer) in Portugal. For that, it is necessary to be admitted and be a member of the Ordem dos Engenheiros (Portuguese institution of engineers). At the Ordem dos Engenheiros, an engineer is classified as an E1, E2 or E3 grade engineer, accordingly with the higher engineer degree he or she holds. Holders of the ancient pre-Bologna declaration five years ''licenciatura'' degrees in engineering are classified as E2 engineers.
Romania
InRomania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, the engineering degree and "engineer" title is delivered by technology and polytechnics universities upon completion of 4 years of studies. Additional master's degree (2 years) and doctorate programs (4–5 years) provide the title of "doctor inginer". Students that started studies in polytechnic universities before 2005 (when Romania adopted the Bologna declaration) needed to complete a 5-year program to get the engineer title. In this case the master's degree is obtained after 1 year of studies.
Only people with an engineer title can be employed as engineers. Still, some with competence and experience in an engineering field that do not have such a title, can still be employed to perform engineering tasks as "specialist", "assistant", "technologist" or "technician". But, only engineers can take legal responsibility and provide guarantee upon the work done by a team in their area of expertise. Sometimes a company working in this area, which temporarily does not have any employees with an engineer title must pay for an external service of an engineering audit to provide legal guarantee for their products or services.
Russia
Moscow School of Mathematics and Navigation was a first Russian educational institution founded byPeter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
in 1701. It provided Russians with technical education for the first time and much of its curriculum was devoted to producing sailors, engineers, cartographers and bombardiers to support Russian expanding navy and army.
Then in 1810, the Saint Petersburg Military engineering-technical university
The Saint Petersburg Military Engineering-Technical University (Nikolaevsky) (russian: Санкт-Петербургский Военный инженерно-технический университет, VITU), previously known as the Saint Pet ...
becomes the first engineering higher learning institution in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
, after addition of officers classes and application of five-year term of teaching. So initially more rigorisms of standards and teaching terms became the traditional historical feature of the Russian engineering education in the 19th century.
Slovakia
InSlovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
, an engineer (''inžinier'') is considered to be a person holding master's degree in technical sciences or economics. Several technical and economic universities offer 4-5-year master study in the fields of chemistry, agriculture, material technology, computer science, electrical and mechanical engineering, nuclear physics and technology or economics. A bachelor's degree in similar field is prerequisite. Absolvents are awarded with the ''Ing.'' title always put in front of one's name; eventual follow-up doctoral study is offered both by universities and some institutes of the Slovak Academy of Sciences
The Slovak Academy of Sciences ( sk, Slovenská akadémia vied, or SAV) is the main scientific and research institution in Slovakia fostering basic and strategic basic research. It was founded in 1942, closed after World War II, and then reestab ...
.
Spain
InSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, the engineering degree is delivered by universities in Engineering Schools, called "Escuelas de Ingeniería". Like with any other degree in Spain, students need to pass a series of examinations based on Bachillerato's subjects (Selectividad), select their bachelor's degree, and their marks determine whether they are access the degree they want or not.
Students receive first a grado degree (4 years of studies) followed by a master's degree (1–2 years of studies) according to the principles of the Bologna declaration, though traditionally, the degree received after completing an engineering education is the Spanish title of "Ingeniero". Using the title "Ingeniero" is legally regulated and limited to the according academic graduates.
Sweden
An institution offering engineering education is called "teknisk högskola" (institute of technology). These schools primarily offers five-year programmes resulting in the ''civilingenjör'' degree (not to be confused with the narrower English term "civil engineer"), internationally corresponding to aMaster of Science in Engineering
A Master of Science in Engineering (abbreviated MSE, M.Sc.Eng. or MScEng) is a type of Master of Science awarded by universities in many countries. It is an academic degree to be differentiated from a Master of Engineering. A Master of Science in ...
degree. These programmes typically offers a strong backing in the natural sciences, and the degree also opens up for doctoral (PHD) studies towards the degree "teknologie doktor". Civilingenjör programmes are offered in a broad range of fields: Engineering physics
Engineering physics, or engineering science, refers to the study of the combined disciplines of physics, mathematics, chemistry, biology, and engineering, particularly computer, nuclear, electrical, electronic, aerospace, materials or mechanical en ...
, Chemistry, Civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
, surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ...
, Industrial engineering and management, etc. There also are shorter three-year programmes called ''högskoleingenjör'' (Bachelor of Science in Engineering
A Bachelor of Engineering (BEng) or a Bachelor of Science in Engineering (BSE) is an academic undergraduate degree awarded to a student after three to five years of studying engineering at an accredited college or university.
In the UK, a Bache ...
) that are typically more applied.
Turkey
InTurkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, engineering degrees range from a bachelor's degree in engineering (for a four-year period), to a master's degree (adding two years), and to a doctoral degree (usually four to five years).
The title is limited by law to people with an engineering degree, and the use of the title by others (even persons with much more work experience) is illegal.
The Union of Chambers of Turkish Engineers and Architects (UCTEA) was established in 1954 and separates engineers and architects to professional branches, with the condition of being within the framework of laws and regulations and in accordance with the present conditions, requirements and possibilities and to also establishes new Chambers for the group of engineers and architects, whose professional or working areas are similar or the same.
UCTEA is maintaining its activities with its 23 Chambers, 194 branches of its Chambers and 39 Provincial Coordination Councils. Approximately, graduates of 70 related academic disciplines in engineering, architecture and city planning are members of the Chambers of UCTEA.
United Kingdom
In the UK, like in the United States andCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
, most professional engineers are trained in universities, but some can start in a technical apprenticeship
Apprenticeship is a system for training a new generation of practitioners of a trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study (classroom work and reading). Apprenticeships can also enable practitioners to gain a ...
and either enroll in a university engineering degree later, or enroll in one of the Engineering Council UK programmes (level 6 – bachelor's and 7 – master's) administered by the City and Guilds of London Institute
The City and Guilds of London Institute is an educational organisation in the United Kingdom. Founded on 11 November 1878 by the City of London and 16 livery companies – to develop a national system of technical education, the institute has ...
. A recent trend has seen the rise of both bachelor's and master's degree higher engineering apprenticeships. All accredited engineering courses and apprenticeships are assessed and approved by the various professional engineering institutions reflecting the subject by engineering discipline covered; IMechE
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) is an independent professional association and learned society headquartered in London, United Kingdom, that represents mechanical engineers and the engineering profession. With over 120,000 mem ...
, IET, BCS, ICE
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
, IStructE etc. Many of these institutions date back to the 19th century, and have previously administered their own engineering examination programmes. They have become globally renowned as premier learned societies.
The degree then counts in part to qualifying as a Chartered Engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thro ...
after a period (usually 4–8 years beyond the first degree) of structured professional practice, professional practice peer review and, if required, further exams to then become a corporate member of the relevant professional body. The term 'Chartered Engineer' is regulated by Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in othe ...
and its use is restricted only to those registered; the awarding of this status is devolved to the professional institutions by the Engineering Council.
In the UK (except Scotland), most engineering courses take three years for an undergraduate bachelors (BEng
A Bachelor of Engineering (BEng) or a Bachelor of Science in Engineering (BSE) is an academic undergraduate degree awarded to a student after three to five years of studying engineering at an accredited college or university.
In the UK, a ...
) and four years for an undergraduate master's. Students who read a four-year engineering course are awarded a Masters of Engineering (as opposed to Masters of Science in Engineering) Some universities allow a student to opt out after one year before completion of the programme and receive a Higher National Diploma
Higher National Diploma (HND), part of the Higher Nationals suite of qualifications, is an academic higher education qualification in the United Kingdom and various other countries. They were first introduced in England and Wales in 1920 alongs ...
if a student has successfully completed the second year, or a Higher National Certificate A Higher National Certificate (HNC), part of the Higher Nationals suite of qualifications, is a higher education/ further education qualification in the United Kingdom.
Overview
In England, Wales and Northern Ireland, the HNC is a BTEC qualificati ...
if only successfully completed year one. Many courses also include an option of a year in industry, which is usually a year before completion. Students who opt for this are awarded a 'sandwich degree
A sandwich degree, or sandwich course, is an academic degree or higher education course (also known as tertiary education) involving practical work experience in addition to academic study. The work experience is often referred as an industrial pl ...
'.
BEng graduates may be registered as an "Incorporated Engineer
An engineering technologist is a professional trained in certain aspects of development and implementation of a respective area of technology. Engineering technology education is even more applied and less theoretical than engineering education ...
" by the Engineering Council after a period of structured professional practice, professional practice peer review and, if required, further exams to then become a member of the relevant professional body. Again, the term 'Incorporated Engineer' is regulated by Royal Assent and its use is restricted only to those registered; the awarding of this status is devolved to the professional institutions by the Engineering Council.
Unlike the US and Canada, engineers do not require a licence to practice the profession in the UK. In the UK, the term "engineer" can be applied to non-degree vocations such as technologists, technicians
A technician is a worker in a field of technology who is proficient in the relevant skill and technique, with a relatively practical understanding of the theoretical principles.
Specialisation
The term technician covers many different speciali ...
, draftsmen
A drafter (also draughtsman / draughtswoman in British and Commonwealth English, draftsman / draftswoman or drafting technician in American and Canadian English) is an engineering technician who makes detailed technical drawings or plans ...
, machinists
A machinist is a tradesperson or trained professional who not only operates machine tools, but also has the knowledge of tooling and materials required to create set ups on machine tools such as milling machines, grinders, lathes, and drilling ...
, mechanic
A mechanic is an artisan, skilled tradesperson, or technician who uses tools to build, maintain, or repair machinery, especially cars.
Duties
Most mechanics specialize in a particular field, such as auto body mechanics, air conditioning and ...
s, plumbers
A plumber is a tradesperson who specializes in installing and maintaining systems used for potable (drinking) water, and for sewage and drainage in plumbing systems.
, electricians, repair people, semi-skilled and even unskilled occupations.
In recent developments by government and industry, to address the growing skills deficit in many fields of UK engineering, there has been a strong emphasis placed on dealing with engineering in school and providing students with positive role models from a young age.
North America
Canada
Engineering degree education in Canada is highly regulated by the Canadian Council of Professional Engineers (Engineers Canada) and its Canadian Engineering Accreditation Board (CEAB). InCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
, there are 43 institutions offering 278 engineering accredited programs delivering a bachelor's degree after a term of 4 years. Many schools also offer graduate level degrees in the applied sciences. ''Accreditation'' means that students who successfully complete the accredited program will have received sufficient engineering knowledge in order to meet the knowledge requirements of licensure as a Professional Engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thro ...
. Alternately, Canadian graduates of unaccredited 3-year diploma, BSc, B.Tech., or B.Eng. programs can qualify for professional license by association examinations. Some of the schools include: Concordia University
Concordia University (French: ''Université Concordia'') is a public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1974 following the merger of Loyola College and Sir George Williams University, Concordia is one of the th ...
, École de technologie supérieure
École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS) is a public engineering faculty in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Founded in 1974, the École de technologie supérieure is a constituent of Université du Québec system. Specialized in applied teaching in ...
, École Polytechnique de Montréal
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
, University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institu ...
, University of Manitoba
The University of Manitoba (U of M, UManitoba, or UM) is a Canadian public research university in the province of Manitoba.University of Saskatchewan
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which ...
, University of Victoria
The University of Victoria (UVic or Victoria) is a public research university located in the municipalities of Oak Bay and Saanich, British Columbia, Canada. The university traces its roots to Victoria College, the first post-secondary insti ...
, University of Calgary
The University of Calgary (U of C or UCalgary) is a public research university located in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. The University of Calgary started in 1944 as the Calgary branch of the University of Alberta, founded in 1908, prior to being inst ...
, University of Alberta
The University of Alberta, also known as U of A or UAlberta, is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford,"A Gentleman of Strathcona – Alexander Cameron Ruth ...
, University of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a public university, public research university with campuses near Vancouver and in Kelowna, British Columbia. Established in 1908, it is British Columbia's oldest university. The university ranks a ...
, McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 by royal charter granted by King George IV,Frost, Stanley Brice. ''McGill Universit ...
, Dalhousie University
Dalhousie University (commonly known as Dal) is a large public research university in Nova Scotia, Canada, with three campuses in Halifax, a fourth in Bible Hill, and a second medical school campus in Saint John, New Brunswick. Dalhousie offer ...
, Toronto Metropolitan University
Toronto Metropolitan University (TMU or Toronto Met) is a public research university located in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The university's core campus is situated within the Garden District, although it also operates facilities elsewhere in To ...
, York University
York University (french: Université York), also known as YorkU or simply YU, is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is Canada's fourth-largest university, and it has approximately 55,700 students, 7,000 faculty and staf ...
, University of Regina
The University of Regina is a public research university located in Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada. Founded in 1911 as a private denominational high school of the Methodist Church of Canada, it began an association with the University of Saskatche ...
, Carleton University
Carleton University is an English-language public research university in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Founded in 1942 as Carleton College, the institution originally operated as a private, non-denominational evening college to serve returning Worl ...
, McMaster University
McMaster University (McMaster or Mac) is a public research university in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. The main McMaster campus is on of land near the residential neighbourhoods of Ainslie Wood and Westdale, adjacent to the Royal Botanical ...
, University of Ottawa
The University of Ottawa (french: Université d'Ottawa), often referred to as uOttawa or U of O, is a bilingual public research university in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is located on directly to the northeast of Downtown Ottaw ...
, Queen's University, University of New Brunswick
The University of New Brunswick (UNB) is a public university with two primary campuses in Fredericton and Saint John, New Brunswick, Saint John, New Brunswick. It is the oldest English-language university in Canada, and among the oldest public un ...
, UOIT, University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also operates ...
, University of Guelph
, mottoeng = "to learn the reasons of realities"
, established = May 8, 1964 ()As constituents: OAC: (1874) Macdonald Institute: (1903) OVC: (1922)
, type = Public university
, chancellor ...
, University of Windsor
, mottoeng = Goodness, Discipline and Knowledge
, established =
, academic_affiliations = CARL, COU, Universities Canada
, former_names = Assumption College (1857-1956)Assumption University of Windsor (1956-1963)
, type = Public univers ...
, Memorial University of Newfoundland, and Royal Military College of Canada
'')
, established = 1876
, type = Military academy
, chancellor = Anita Anand ('' la, ex officio, label=none'' as Defence Minister)
, principal = Harry Kowal
, head_label ...
just to name a few. Every university offering engineering degrees in Canada needs to be accredited by the CEAB (Canadian Engineering Accreditation Board), thus ensuring high standards are enforced at all universities. Engineering degrees in Canada are distinct from degrees in engineering technology
An engineering technologist is a professional trained in certain aspects of development and implementation of a respective area of technology. Engineering technology education is even more applied and less theoretical than engineering educatio ...
which are more applied degrees or diplomas. An engineering education in Canada can culminate by qualifying as a professional engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thro ...
(P.Eng.) licensee.
Mexico
In the case of Mexico, education in the engineering field could be taken from public and private universities. Both types of colleges and universities can confer degrees of B.Eng., B.Sc., M.Eng., M.Sc. and Ph.D. through the presentation and dissertation of a thesis or other kind of requirements such as technical reports and knowledge exams among others. The first University in Mexico to offers degrees in some engineering fields was theRoyal and Pontifical University of Mexico
The Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico (in es, Real y Pontificia Universidad de México) was founded on 21 September 1551 by Royal Decree signed by Charles I of Spain, in Valladolid, Spain. It is generally considered the first university o ...
, established under the Spanish rule; the degrees offered included Mines Engineering and Physical Mathematical state-of-the-art knowledge from Europe.
Then came the 19th century and lack of political stability. The universities founded under Spanish rule were closed and reopened and the Engineering teaching tradition was lost; the University of Mexico, University of Guadalajara and University of Mérida suffered this. Then the liberal rule created the Arts and Handcraft schools were opened without the same success as the universities. In the 20th century and with the success of the Mexican Revolution some of the old colleges were reopened and the old Arts and Handcraft schools were joined to the new universities. In 1936 the National Polytechnic Institute of Mexico
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
was created as an educational alternative for workers' sons and their families. A short time later the Regional Institutes of Technology were founded as a branch of the Polytechnic Institute in a few states of the republic, though most of them do not have any university in their own territory.
Right now the Regional Institutes of Technology have been merged into one single entity labeled as Mexican National Technological Institute. The National Polytechnic Institute is the ensign university of the Mexican federal government on engineering education.
United States


 The first professional degree in engineering is a bachelor's degree with few exceptions. Interest in engineering has grown since 1999; the number of bachelor's degrees issued has increased by 20%.Reyes-Guerra, D. R. (2011). Engineering. In J. M. Castagno, P. Barrows, L. Brearley, & K. Fairchild (Eds.), Grolier online. Most bachelor's degree engineering programs are four years long and require about two years of core courses followed by two years of specialized discipline specific courses. This is where a typical engineering student would learn mathematics (single- and multi-variable
The first professional degree in engineering is a bachelor's degree with few exceptions. Interest in engineering has grown since 1999; the number of bachelor's degrees issued has increased by 20%.Reyes-Guerra, D. R. (2011). Engineering. In J. M. Castagno, P. Barrows, L. Brearley, & K. Fairchild (Eds.), Grolier online. Most bachelor's degree engineering programs are four years long and require about two years of core courses followed by two years of specialized discipline specific courses. This is where a typical engineering student would learn mathematics (single- and multi-variable calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
and elementary differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, a ...
s), general chemistry, English composition
The term composition (from Latin ''com-'' "with" and ''ponere'' "to place") as it refers to writing, can describe writers' decisions about, processes for designing, and sometimes the final product of, a document. In original use, it tended to desc ...
, general and modern physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which rel ...
, computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (includin ...
(typically programming), and introductory engineering in several areas that are required for a satisfactory engineering background and to be successful in their program of choice. Several courses in social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soc ...
s or humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at th ...
are often also required, but are commonly elective course
In higher education a course is a unit of teaching that typically lasts one academic term, is led by one or more instructors (teachers or professors), and has a fixed roster of students. A course usually covers an individual subject. Courses gener ...
s from a broad choice. Required common engineering courses typically include engineering drawing
An engineering drawing is a type of technical drawing that is used to convey information about an object. A common use is to specify the geometry necessary for the construction of a component and is called a detail drawing. Usually, a number o ...
/computer-aided-design, materials engineering, statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque (also called moment) acting on physical systems that do not experience an acceleration (''a''=0), but rather, are in static equilibrium with t ...
and dynamics, strength of materials
The field of strength of materials, also called mechanics of materials, typically refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The methods employed to predict the re ...
, basic circuits, thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws o ...
, fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them.
It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and ...
, and perhaps some systems or industrial engineering. The science and engineering courses include lecture and laboratory education, either in the same course(s) or in separate courses. However, some professors and educators believe that engineering programs should change to focus more on professional engineering practice, and engineering courses should be taught more by professional engineering practitioners and not by engineering researchers.
Many engineering degree programs admit students directly to a specialization as a first-year, but those which don't often require students to decide on a specialization by the end of the first or second year of study. Specializations often include architectural engineering
Architectural engineers apply and theoretical knowledge to the engineering design of buildings and building systems. The goal is to engineer high performance buildings that are sustainable, economically viable and ensure the safety health.
Archi ...
, civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
(including structural engineering
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and muscles' that create the form and shape of man-made structures. Structural engineers also must understand and ca ...
), mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, ...
, electrical engineering (often including computer engineering
Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer enginee ...
), chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials in ...
, nuclear engineering
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of breaking down atomic nuclei (fission) or of combining atomic nuclei ( fusion), or with the application of other sub-atomic processes based on the principles of nu ...
, biological engineering
Biological engineering or
bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically-viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number o ...
, industrial engineering
Industrial engineering is an engineering profession that is concerned with the optimization of complex processes, systems, or organizations by developing, improving and implementing integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information an ...
, aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s ...
, materials engineering (including metallurgical engineering
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
), agricultural engineering
Agricultural engineering, also known as agricultural and biosystems engineering, is the field of study and application of engineering science and designs principles for agriculture purposes, combining the various disciplines of mechanical, civil ...
, and many other specializations. After choosing a specialization, an engineering student will begin to take classes that will build on the fundamentals and gain their specialized knowledge and skills. Toward the end of their undergraduate education, engineering students often undertake an open-ended design
A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' ...
or other special project specific to their field.
It is common for University students who are studying engineering to partake in different forms of career development during their undergraduate studies. These often take the form of paid internships, cooperative education programs (also referred to as "co-ops"), research experiences, or service learning. These types of experiences may be facilitated by the students' universities, or sought out by the students independently.
Internships
Engineering internships are typically pursued by undergraduate students during the summer recess between the Spring and Fall semesters of the standard semester-based academic cycle (although some US universities abide by a 'quarter' or 'trimester' cycle). These internships usually have a duration of 8–12 weeks and may be part-time or full-time as well as paid or unpaid depending on the company; sometimes, students receive academic credit as an alternative or in addition to a wage. Shorter duration full-time internships over winter and other breaks are often available too, especially for those who have completed summer internships with the same firm. Internships are offered as temporary positions by engineering companies, and are often competitive in certain fields. They provide a way for companies to recruit and get familiar with individual students as potential full-time employment after graduation. Engineering internships also have numerous benefits for participating students. They provide hands-on learning outside of the classroom as well as an opportunity for the student to discover if her current choice of engineering discipline is appropriate based on her level of enjoyment of her internship role. Additionally, research and internship experiences have been shown to have a positive effect on engineering task self-efficacy (ETSE), a measure of a students' perception of her ability to perform engineering functions and related tasks. It is also considered advantageous to have internship or co-op experience before completion of undergraduate studies, as students who have practical engineering experience are considered to be more attractive to engineering employers.Cooperative Education Programs
Cooperative Education Programs (often referred to as 'co-ops') are similar to internships insofar as they are employment opportunities offered to undergraduate students by engineering employers; however, they are intended to take place concurrently with the students' academic studies. Co-ops are sometimes part-time roles that are ongoing throughout the academic semester, with the student expected to invest between 10 and 30 hours a week depending on the severity of their course load. Some American universities, such asNortheastern University
Northeastern University (NU) is a private research university with its main campus in Boston. Established in 1898, the university offers undergraduate and graduate programs on its main campus as well as satellite campuses in Charlotte, North C ...
and Drexel University
Drexel University is a private research university with its main campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Drexel's undergraduate school was founded in 1891 by Anthony J. Drexel, a financier and philanthropist. Founded as Drexel Institute of Ar ...
, incorporate co-ops into their students' plan of study in the form of alternating semesters of full-time work and full-time classes; these programs typically take an additional year to complete compared to most 4-year undergraduate engineering programs in the US, even though Northeastern currently has a 4-year undergraduate program that integrates full-time co-ops with full-time studies. Co-ops are considered to be a valuable form of professional development, and may be undertaken by students who are looking to bolster their resumes with hopes of securing better salary offers when looking to secure their first job.
Licensing
After formal education, the engineer will often enter aninternship
An internship is a period of work experience offered by an organization for a limited period of time. Once confined to medical graduates, internship is used practice for a wide range of placements in businesses, non-profit organizations and gover ...
or engineer in training status for approximately four years. To achieve Engineering Intern (E.I.) or Engineer-in-Training (EIT) status, an individual must be the recipient of an engineering degree from an institution accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission (EAC) of the ABET
The ABET (incorporated as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc.) is a non-governmental organization that accredits post-secondary education programs in applied and natural sciences, computing, engineering and engineerin ...
, formerly the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc., as well as pass the Fundamentals of Engineering Exam (often abbreviated to the 'FE Exam'). The FE Exam is offered by the National Council for Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (NCEES
The National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (NCEES) is an American non-profit organization dedicated to advancing professional licensure for engineers and surveyors. The Council’s members are the engineering and surveying lice ...
) for the following disciplines: Mechanical Engineering, Civil Engineering, Industrial & Systems Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Environmental Engineering, or Other Disciplines (also referred to as "General Engineering"). The FE Exam is held at remote testing locations four times throughout the year and can be taken by college graduates as well as current college students. After successfully passing the Fundamentals of Engineering Exam and receiving an ABET-accredited engineering degree, an aspiring engineer may apply for engineer-in-training status with their state's licensing board. If granted, they may use the suffix E.I.T. to denote their status as an engineer-in-training.
After that time, the engineer in training can decide whether or not to take a state licensing test to make them a Professional Engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thro ...
. The licensing process varies state-by-state, but generally they require the engineer-in-training to possess four years of verifiable work experience in their engineering field, as well as successfully pass the NCEES Principles and Practice of Engineering (PE) Exam for their engineering discipline. After successful completion of that test, the Professional engineer can place the suffix P.E. after their name signifying that they are now a Professional Engineer and they can affix their P.E. seal to drawings and reports, for example. They can also serve as expert witnesses in their areas of expertise.
Achieving the status of ' Professional Engineer is one of the highest levels of achievement one can attain in the engineering industry. Engineers with this status are generally highly sought-after by employers, especially in the field of Civil Engineering.
There are also graduate degree
Postgraduate or graduate education refers to academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate (bachelor's) degree.
The organization and struc ...
options for an engineer. Many engineers decide to complete a master's degree in some field of engineering or business administration or get education in law, medicine, or other field.
Two types of doctorate are available also, the traditional Ph.D. or the Doctor of Engineering
The Doctor of Engineering, or Engineering Doctorate, (abbreviated DEng, EngD, or Dr-Ing) is a degree awarded on the basis of advanced study and a practical project in the engineering and applied science for solving problems in the industry. In the ...
. The Ph.D. focuses on research and academic excellence, whereas the doctor of engineering focuses on practical engineering. The education requirements are the same for both degrees; however, the dissertation required is different. The Ph.D. also requires the standard research problem, where the doctor of engineering focuses on a practical dissertation.
In present undergraduate engineering education, the emphasis on linear systems develops a way of thinking that dismisses nonlinear dynamics as spurious oscillations. The linear systems approach oversimplifies the dynamics of nonlinear systems. Hence, the undergraduate students and teachers should recognize the educational value of chaotic
Chaotic was originally a Danish trading card game. It expanded to an online game in America which then became a television program based on the game. The program was able to be seen on 4Kids TV (Fox affiliates, nationwide), Jetix, The CW4Kids ...
dynamics. Practicing engineers will also have more insight of nonlinear circuits and systems by having an exposure to chaotic phenomena.
After graduation, continuing education
Continuing education (similar to further education in the United Kingdom and Ireland) is an all-encompassing term within a broad list of post-secondary learning activities and programs. The term is used mainly in the United States and Canada.
...
courses may be needed to keep a government-issued professional engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thro ...
(PE) license valid, to keep skills fresh, to expand skills, or to keep up with new technology.
Caribbean
Trinidad and Tobago
Engineering degree education in Trinidad and Tobago is not regulated by the Board of Professional Engineers of Trinidad and Tobago (BOETT) or the location Engineering Association (APETT). Professional Engineers registed with BOETT are given the credentials "r.Eng.".South America
Argentina
Engineering education programs at universities in Argentina span a variety of disciplines and typically require 5–6 years of studies to complete. Most degree programs begin with foundational courses in mathematics, statistics, and the physical sciences during the first and second years, then move on to courses specific to the students' plan of study. After receiving a degree, an engineering student will go on to complete an external evaluation in order to become accredited as an engineer.Javier Alvarez Del Castillo (2000) Evaluation and accreditation of engineering programmes in Latin America, European Journal of Engineering Education, 25:3,281-290, DOI: 10.1080/030437900438702 There are many universities and technical schools across Argentina that offer degree programs in engineering education. The National Technological University (''Universidad Tecnológica Nacional'', UTN) is recognized as one of the best engineering institutions in the country, with degrees in the following disciplines offered across its 33 campuses: * Aeronautical Engineering * Civil Engineering * Electrical Engineering * Electronics Engineering * Electro-mechanical Engineering * Automotive Engineering * Information Systems Engineering * Railway Engineering * Mechanical Engineering * Metallurgical Engineering * Naval Engineering * Fisheries Engineering * Chemical Engineering * Textile Engineering Outlined in the Argentinian Law 'Ley de Educacion Superior No. 24521' is the requirement for all universities to include a compulsory external evaluation for accreditation of certain professions, such as Law, Medicine, and Engineering, which are also strictly governed by other laws. Accreditation of engineers in Argentina is under the authority of the CONEAU (Comision Nacional de Evaluación y Acreditación Universitaria 1997), which performs the functions of coordinating and executing external evaluations and accrediting graduate and post-graduate university studies in the field of engineering.Brazil
In Brazil, education in engineering is offered by both public and private institutions. A degree in engineering requires five to six years of studies, comprising the core courses, specific subjects, an internship and a ''Course Completion Paper''. Due to the nature of college admissions in Brazil, most students have to declare their major before entering college. This said, the first two years of a degree in engineering consist mostly of the core courses (calculus, physics, programming, etc.) along with a few specific subjects as well as some courses in humanities. After this period, some institutions offer specializations within the different fields of engineering (i.e. a student majoring in electrical engineering can choose to specialize in electronics or telecommunications) although most institutions balance their workload in order to give the students a consistent knowledge of every specialization. Towards the end of their undergraduate education, students are required to develop the Course Completion Paper under the guidance of an adviser to be presented to and graded by a number of professors. In some institutions, students are also required to pursue an internship (the amount of time depends on the institution). In order to pursue a career in engineering, graduates must first register with and abide by the rules of the Regional Counsel of Engineering and Agronomy of their state, a regional representative of the Federal Counsel of Engineering and Agronomy, a certification board for engineers, agronomists, geologists and other professionals of the applied sciences.See also
* List of engineering schools *Education and training of electrical and electronics engineers
Both electrical and electronics engineers typically possess an academic degree with a major in electrical/ electronics engineering. The length of study for such a degree is usually three or four years and the completed degree may be designated a ...
*'' Education for Chemical Engineers''
* Engineering education research
*Engineer's degree
An engineer's degree is an advanced academic degree in engineering which is conferred in Europe, some countries of Latin America, North Africa and a few institutions in the United States. The degree may require a thesis but always requires a non- ...
*Global Engineering Education
Global Engineering Education is a field of study that focuses on the impact of globalization on the engineering industry.
History
Over the past decade or so educators and researchers have made an effort to transform engineering education in li ...
*Institute of technology
An institute of technology (also referred to as: technological university, technical university, university of technology, technological educational institute, technical college, polytechnic university or just polytechnic) is an institution of t ...
*Problem-based learning
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered pedagogy in which students learn about a subject through the experience of solving an open-ended problem found in trigger material. The PBL process does not focus on problem solving with a defin ...
*Project-based learning
Project-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered pedagogy that involves a dynamic classroom approach in which it is believed that students acquire a deeper knowledge through active exploration of real-world challenges and problems. Students l ...
Notes
References
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Engineering Education