electronic book on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An ebook (short for electronic book), also known as an e-book or eBook, is a
An ebook (short for electronic book), also known as an e-book or eBook, is a
. Mediabistro.com (June 15, 2012). Retrieved August 28, 2013. The main reasons for people buying e-books are possibly lower prices, increased comfort (as they can buy from home or on the go with mobile devices) and a larger selection of titles. With e-books, "electronic
book
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this phys ...
publication made available in digital form, consisting of text, images, or both, readable on the flat-panel display of computers or other electronic devices. Although sometimes defined as "an electronic version of a printed book", some e-books exist without a printed equivalent. E-books can be read on dedicated e-reader
An e-reader, also called an e-book reader or e-book device, is a mobile electronic device that is designed primarily for the purpose of reading digital e-books and periodicals.
Any device that can display text on a screen may act as an e-re ...
devices, but also on any computer device that features a controllable viewing screen, including desktop computer
A desktop computer (often abbreviated desktop) is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply ...
s, laptops, tablets and smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
s.
In the 2000s, there was a trend of print and e-book sales moving to the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists ...
, where readers buy traditional paper books and e-books on website
A website (also written as a web site) is a collection of web pages and related content that is identified by a common domain name and published on at least one web server. Examples of notable websites are Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Wikip ...
s using e-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the activity of electronically buying or selling of products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain mana ...
systems. With print books, readers are increasingly browsing through image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensio ...
s of the covers of books on publisher or bookstore websites and selecting and ordering titles online; the paper books are then delivered to the reader by mail or another delivery service. With e-books, users can browse through titles online, and then when they select and order titles, the e-book can be sent to them online or the user can download the e-book. By the early 2010s, e-books had begun to overtake hardcover by overall publication figures in the U.S.eBook Revenues Top Hardcover – GalleyCat. Mediabistro.com (June 15, 2012). Retrieved August 28, 2013. The main reasons for people buying e-books are possibly lower prices, increased comfort (as they can buy from home or on the go with mobile devices) and a larger selection of titles. With e-books, "electronic
bookmarks
A bookmark is used to keep one's place in a printed work. It can also refer to:
* Bookmark (digital), a pointer in a web browser and other software
* ''Bookmarks'' (album) by Five for Fighting
* ''Bookmarks'' (magazine), an American literary ma ...
make referencing easier, and e-book readers may allow the user to annotate pages." "Although fiction and non-fiction books come in e-book formats, technical material is especially suited for e-book delivery because it can be digitally searched" for keywords. In addition, for programming books, code examples can be copied. The amount of e-book reading is increasing in the U.S.; by 2014, 28% of adults had read an e-book, compared to 23% in 2013; and by 2014, 50% of American adults had an e-reader
An e-reader, also called an e-book reader or e-book device, is a mobile electronic device that is designed primarily for the purpose of reading digital e-books and periodicals.
Any device that can display text on a screen may act as an e-re ...
or a tablet, compared to 30% owning such devices in 2013.
Besides published books and magazines that have a digital equivalent, there are also digital textbooks, that are intended to serve as the text for a class and help in technology-based education.
Terminology
E-books are also referred to as "ebooks", "eBooks", "Ebooks", "e-Books", "e-journals", "e-editions", or "digital books". A device that is designed specifically for reading e-books is called an "e-reader", "ebook device", or "eReader".History
''The Readies'' (1930)
Some trace the concept of an e-reader, a device that would enable the user to view books on a screen, to a 1930 manifesto by Bob Brown, written after watching his first " talkie" (movie with sound). He titled it ''The Readies'', playing off the idea of the "talkie". In his book, Brown says movies have outmaneuvered the book by creating the "talkies" and, as a result, reading should find a new medium: Brown's notion, however, was much more focused on reformingorthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and mo ...
and vocabulary, than on medium ("It is time to pull out the stopper" and begin "a bloody revolution of the word."): introducing huge numbers of portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of words Brown believed that the e-reader (and his notions for changing text itself) would bring a completely new life to reading. Schuessler correlates it with a DJ spinning bits of old songs to create a beat or an entirely new song, as opposed to just a remix of a familiar song.
 In 1992,
In 1992,
 As e-book formats emerged and proliferated, some garnered support from major software companies, such as
As e-book formats emerged and proliferated, some garnered support from major software companies, such as
including
 An
An
 Some of the major book retailers and multiple third-party developers offer free (and in some third-party cases, premium paid) e-reader software applications (apps) for the Mac and PC computers as well as for Android, Blackberry, iPad, iPhone, Windows Phone and Palm OS devices to allow the reading of e-books and other documents independently of dedicated e-book devices. Examples are apps for the Amazon Kindle, Barnes & Noble Nook, iBooks, Kobo eReader and Sony Reader.
Some of the major book retailers and multiple third-party developers offer free (and in some third-party cases, premium paid) e-reader software applications (apps) for the Mac and PC computers as well as for Android, Blackberry, iPad, iPhone, Windows Phone and Palm OS devices to allow the reading of e-books and other documents independently of dedicated e-book devices. Examples are apps for the Amazon Kindle, Barnes & Noble Nook, iBooks, Kobo eReader and Sony Reader.
 * F. Crugnola and I. Rigamonti design and create the first e-reader, called Incipit, as a thesis project at the Polytechnic University of Milan.
*
* F. Crugnola and I. Rigamonti design and create the first e-reader, called Incipit, as a thesis project at the Polytechnic University of Milan.
*
Inventor
The inventor of the first e-book is not widely agreed upon. Some notable candidates include the following:Roberto Busa (1946–1970)
The first e-book may be the '' Index Thomisticus'', a heavily annotated electronic index to the works ofThomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
, prepared by Roberto Busa, S.J. beginning in 1946 and completed in the 1970s. Although originally stored on a single computer, a distributable CD-ROM version appeared in 1989. However, this work is sometimes omitted; perhaps because the digitized text was a means for studying written texts and developing linguistic concordances, rather than as a published edition in its own right.
In 2005, the Index was published online.
Ángela Ruiz Robles (1949)
In 1949, Ángela Ruiz Robles, a teacher from Ferrol, Spain, patented the ''Enciclopedia Mecánica'', or the Mechanical Encyclopedia, a mechanical device which operated on compressed air where text and graphics were contained on spools that users would load onto rotating spindles. Her idea was to create a device which would decrease the number of books that her pupils carried to school. The final device was planned to include audio recordings, a magnifying glass, a calculator and an electric light for night reading. Her device was never put into production but a prototype is kept in the National Museum of Science and Technology inA Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and ...
.
Douglas Engelbart and Andries van Dam (1960s)
Alternatively, some historians consider electronic books to have started in the early 1960s, with the NLS project headed by Douglas Engelbart at Stanford Research Institute (SRI), and the Hypertext Editing System and FRESS projects headed by Andries van Dam at Brown University... FRESS documents ran on IBM mainframes and were structure-oriented rather than line-oriented; they were formatted dynamically for different users, display hardware, window sizes, and so on, as well as having automated tables of contents, indexes, and so on. All these systems also provided extensive hyperlinking, graphics, and other capabilities. Van Dam is generally thought to have coined the term "electronic book", and it was established enough to use in an article title by 1985. FRESS was used for reading extensive primary texts online, as well as for annotation and online discussions in several courses, including English Poetry and Biochemistry. Brown's faculty made extensive use of FRESS; for example the philosopher Roderick Chisholm used it to produce several of his books. Thus in the Preface to ''Person and Object'' (1979) he writes "The book would not have been completed without the epoch-making File Retrieval and Editing System..." Brown University's work in electronic book systems continued for many years, includingUS Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
funded projects for electronic repair-manuals;"An experimental system for creating and presenting interactive graphical documents." ACM Transactions on Graphics 1(1), Jan. 1982 a large-scale distributed hypermedia system known as InterMedia;
a spinoff company Electronic Book Technologies that built DynaText, the first SGML
The Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML; ISO 8879:1986) is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates":
* Declarative: Markup should d ...
-based e-reader system; and the Scholarly Technology Group's extensive work on the Open eBook
Open eBook (OEB), or formally, the Open eBook Publication Structure (OEBPS), is a legacy e-book format which has been superseded by the EPUB format. It was "based primarily on technology developed by SoftBook Press". and on XML. OEB was released wi ...
standard.
Michael S. Hart (1971)
Despite the extensive earlier history, several publications reportMichael S. Hart
Michael Stern Hart (March 8, 1947 – September 6, 2011) was an American author, best known as the inventor of the e-book and the founder of Project Gutenberg (PG), the first project to make e-books freely available via the Internet. H ...
as the inventor of the e-book.
In 1971, the operators of the Xerox Sigma V mainframe at the University of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Unive ...
gave Hart extensive computer-time. Seeking a worthy use of this resource, he created his first electronic document by typing the United States Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House ...
into a computer in plain text. Hart planned to create documents using plain text to make them as easy as possible to download and view on devices. After Hart first adapted the U.S. Declaration of Independence into an electronic document in 1971, ''Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
'' was launched to create electronic copies of more texts, especially books.
Early hardware implementations
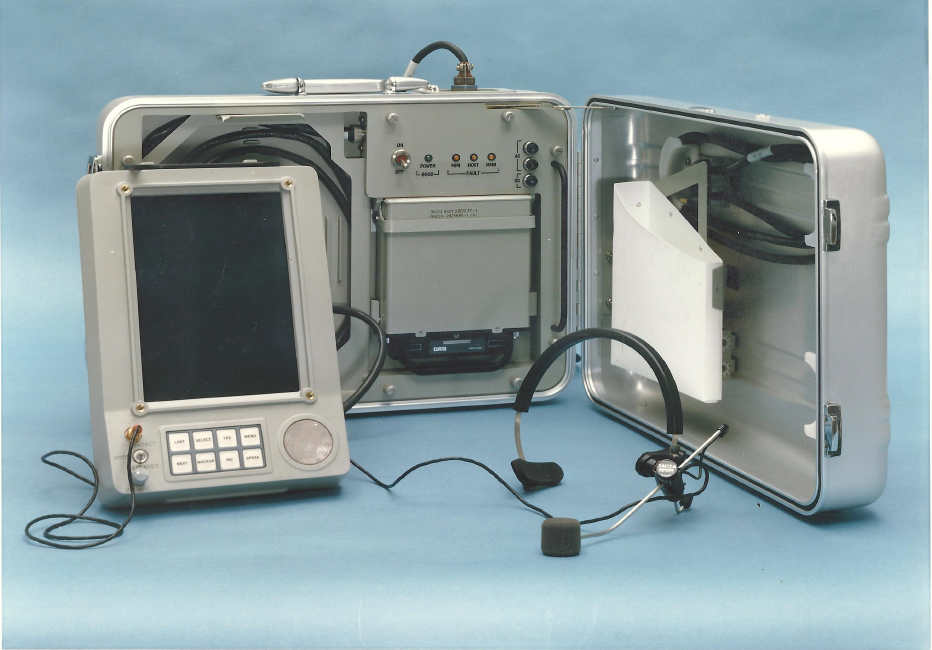
Dedicated hardware devices for ebook reading began to appear in the 70s and 80s, in addition to the mainframe and laptop solutions, and collections of data per se. One early e-book implementation was the desktop prototype for a proposed notebook computer, the '' Dynabook,'' in the 1970s at PARC: a general-purpose portable personal computer capable of displaying books for reading. In 1980, the U.S. Department of Defense began concept development for a portable electronic delivery device for technical maintenance information called project PEAM, the Portable Electronic Aid for Maintenance. Detailed specifications were completed in FY 1981/82, and prototype development began withTexas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globa ...
that same year. Four prototypes were produced and delivered for testing in 1986, and tests were completed in 1987. The final summary report was produced in 1989 by the U.S. Army Research Institute for the Behavioral and Social Sciences, authored by Robert Wisher and J. Peter Kincaid. A patent application for the PEAM device, titled "Apparatus for delivering procedural type instructions", was submitted by Texas Instruments on December 4, 1985, listing John K. Harkins and Stephen H. Morriss as inventors.
 In 1992,
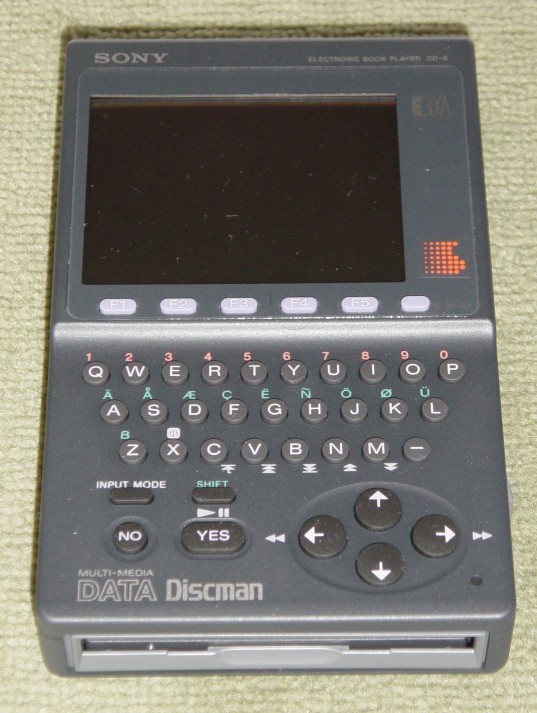
In 1992, Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
launched the Data Discman, an electronic book reader that could read e-books that were stored on CDs. One of the electronic publications that could be played on the Data Discman was called ''The Library of the Future''. Early e-books were generally written for specialty areas and a limited audience, meant to be read only by small and devoted interest groups. The scope of the subject matter of these e-books included technical manuals for hardware, manufacturing techniques, and other subjects. In the 1990s, the general availability of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists ...
made transferring electronic files much easier, including e-books.
In 1993, Paul Baim released a freeware HyperCard stack, called EBook, that allowed easy import of any text file to create a pageable version similar to an electronic paperback book. A notable feature was automatic tracking of the last page read so that on returning to the 'book' you were taken back to where you had previously left off reading. The title of this stack may have helped popularize the term 'ebook'.
E-book formats
 As e-book formats emerged and proliferated, some garnered support from major software companies, such as
As e-book formats emerged and proliferated, some garnered support from major software companies, such as Adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for '' mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of ...
with its PDF format that was introduced in 1993. Unlike most other formats, PDF documents are generally tied to a particular dimension and layout, rather than adjusting dynamically to the current page, window, or another size. Different e-reader devices followed different formats, most of them accepting books in only one or a few formats, thereby fragmenting the e-book market even more. Due to the exclusiveness and limited readerships of e-books, the fractured market of independent publishers and specialty authors lacked consensus regarding a standard for packaging and selling e-books.
Meanwhile, scholars formed the Text Encoding Initiative, which developed consensus guidelines for encoding books and other materials of scholarly interest for a variety of analytic uses as well as reading, and countless literary and other works have been developed using the TEI approach. In the late 1990s, a consortium formed to develop the Open eBook
Open eBook (OEB), or formally, the Open eBook Publication Structure (OEBPS), is a legacy e-book format which has been superseded by the EPUB format. It was "based primarily on technology developed by SoftBook Press". and on XML. OEB was released wi ...
format as a way for authors and publishers to provide a single source-document which many book-reading software and hardware platforms could handle. Several scholars from the TEI were closely involved in the early development of Open eBooincluding
Allen Renear Allen, Allen's or Allens may refer to:
Buildings
* Allen Arena, an indoor arena at Lipscomb University in Nashville, Tennessee
* Allen Center, a skyscraper complex in downtown Houston, Texas
* Allen Fieldhouse, an indoor sports arena on the Univer ...
, Elli Mylonas
In Norse mythology (a subset of Germanic mythology), Elli (Old Norse: , "old age"Orchard (1997:38).) is a personification of old age who, in the ''Prose Edda'' book ''Gylfaginning'', defeats Thor in a wrestling match.Graeme Davis (2013). ''Thor: ...
, and Steven DeRose, all from Brown. Focused on portability, Open eBook as defined required subsets of XHTML
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
While HTML, prior ...
and CSS; a set of multimedia formats (others could be used, but there must also be a fallback in one of the required formats), and an XML schema for a "manifest", to list the components of a given e-book, identify a table of contents, cover art, and so on. This format led to the open format EPUB. Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
has converted many public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, ...
works to this open format.
In 2010, e-books continued to gain in their own specialist and underground markets. Many e-book publishers began distributing books that were in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, ...
. At the same time, authors with books that were not accepted by publishers offered their works online so they could be seen by others. Unofficial (and occasionally unauthorized) catalogs of books became available on the web, and sites devoted to e-books began disseminating information about e-books to the public. Nearly two-thirds of the U.S. Consumer e-book publishing market are controlled by the "Big Five". The "Big Five" publishers are: Hachette Hachette may refer to:
* Hachette (surname)
* Hachette (publisher), a French publisher, the imprint of Lagardère Publishing
** Hachette Book Group, the American subsidiary
** Hachette Distribution Services, the distribution arm
See also
* Hachett ...
, HarperCollins
HarperCollins Publishers LLC is one of the Big Five English-language publishing companies, alongside Penguin Random House, Simon & Schuster, Hachette, and Macmillan. The company is headquartered in New York City and is a subsidiary of News C ...
, Macmillan, Penguin Random House
Penguin Random House LLC is an Anglo-American multinational conglomerate publishing company formed on July 1, 2013, from the merger of Penguin Group and Random House.
On April 2, 2020, Bertelsmann announced the completion of its purchase o ...
and Simon & Schuster
Simon & Schuster () is an American publishing company and a subsidiary of Paramount Global. It was founded in New York City on January 2, 1924 by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. As of 2016, Simon & Schuster was the third largest pub ...
.
Libraries
U.S. libraries began to offer free e-books to the public in 1998 through their websites and associated services, although the e-books were primarily scholarly, technical or professional in nature, and could not be downloaded. In 2003, libraries began offering free downloadable popular fiction and non-fiction e-books to the public, launching an e-book lending model that worked much more successfully for public libraries. The number of library e-book distributors and lending models continued to increase over the next few years. From 2005 to 2008, libraries experienced a 60% growth in e-book collections. In 2010, a Public Library Funding and Technology Access Study by theAmerican Library Association
The American Library Association (ALA) is a nonprofit organization based in the United States that promotes libraries and library education internationally. It is the oldest and largest library association in the world, with 49,727 members ...
found that 66% of public libraries in the U.S. were offering e-books, and a large movement in the library industry began to seriously examine the issues relating to e-book lending, acknowledging a " tipping point" when e-book technology would become widely established. Content from public libraries can be downloaded to e-readers using application software
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a ...
like Overdrive and Hoopla.
The U.S. National Library of Medicine
The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), operated by the United States federal government, is the world's largest medical library.
Located in Bethesda, Maryland, the NLM is an institute within the National Institutes of Health. Its ...
has for many years provided PubMed
PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintain ...
, a comprehensive bibliography of medical literature. In early 2000, NLM set up the PubMed Central repository, which stores full-text e-book versions of many medical journal articles and books, through cooperation with scholars and publishers in the field. Pubmed Central also now provides archiving and access to over 4.1 million articles, maintained in a standard XML format known as the Journal Article Tag Suite (or "JATS").
Despite the widespread adoption of e-books, some publishers and authors have not endorsed the concept of electronic publishing, citing issues with user demand, copyright infringement
Copyright infringement (at times referred to as piracy) is the use of works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, ...
and challenges with proprietary devices and systems. In a survey of interlibrary loan
Interlibrary loan (abbreviated ILL, and sometimes called interloan, interlending, document delivery, document supply, or interlibrary services, abbreviated ILS) is a service where patrons of one library can borrow materials and receive photocopies ...
(ILL) librarians, it was found that 92% of libraries held e-books in their collections and that 27% of those libraries had negotiated ILL rights for some of their e-books. This survey found significant barriers to conducting interlibrary loan for e-books. Patron-driven acquisition (PDA) has been available for several years in public libraries, allowing vendors to streamline the acquisition process by offering to match a library's selection profile to the vendor's e-book titles. The library's catalog is then populated with records for all of the e-books that match the profile. The decision to purchase the title is left to the patrons, although the library can set purchasing conditions such as a maximum price and purchasing caps so that the dedicated funds are spent according to the library's budget. The 2012 meeting of the Association of American University Presses included a panel on the PDA of books produced by university presses, based on a preliminary report by Joseph Esposito, a digital publishing consultant who has studied the implications of PDA with a grant from the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation.
Challenges
Although the demand for e-book services in libraries has grown in the first two decades of the 21st century, difficulties keep libraries from providing some e-books to clients. Publishers will sell e-books to libraries, but in most cases they will only give libraries a limited license to the title, meaning that the library does not ''own'' the electronic text but is allowed to circulate it for either a certain period of time, or a certain number of check outs, or both. When a library purchases an e-book license, the cost is at least three times what it would be for a personal consumer. E-book licenses are more expensive than paper-format editions because publishers are concerned that an e-book that is sold could theoretically be read and/or checked out by a huge number of users, potentially damaging sales. However, some studies have found the opposite effect to be true (for example, Hilton and Wikey 2010).Archival storage
TheInternet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music ...
and Open Library
Open Library is an online project intended to create "one web page for every book ever published". Created by Aaron Swartz, Brewster Kahle, Alexis Rossi, Anand Chitipothu, and Rebecca Malamud, Open Library is a project of the Internet Archive, ...
offer more than six million fully accessible public domain e-books. Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
has over 52,000 freely available public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, ...
e-books.
Dedicated hardware readers and mobile software
e-reader
An e-reader, also called an e-book reader or e-book device, is a mobile electronic device that is designed primarily for the purpose of reading digital e-books and periodicals.
Any device that can display text on a screen may act as an e-re ...
, also called an e-book reader or e-book device, is a mobile electronic device that is designed primarily for the purpose of reading e-books and digital periodicals. An e-reader is similar in form, but more limited in purpose than a tablet. In comparison to tablets, many e-readers are better than tablets for reading because they are more portable, have better readability in sunlight and have longer battery life. In July 2010, online bookseller Amazon.com reported sales of e-books for its proprietary Kindle
Kindle may refer to:
Companies and products
* Amazon Kindle, an e-reader line by Amazon.com
** Kindle Direct Publishing, an e-book publishing platform by Amazon
** Kindle Store, an online e-book e-commerce store by Amazon
* Kindle Banking Systems, ...
outnumbered sales of hardcover books for the first time ever during the second quarter of 2010, saying it sold 140 e-books for every 100 hardcover books, including hardcovers for which there was no digital edition. By January 2011, e-book sales at Amazon had surpassed its paperback sales. In the overall US market, paperback book sales are still much larger than either hardcover or e-book; the American Publishing Association estimated e-books represented 8.5% of sales as of mid-2010, up from 3% a year before. At the end of the first quarter of 2012, e-book sales in the United States surpassed hardcover book sales for the first time.
Until late 2013, use of an e-reader was not allowed on airplanes during takeoff and landing by the FAA. In November 2013, the FAA allowed use of e-readers on airplanes at all times if it is in Airplane Mode, which means all radios turned off, and Europe followed this guidance the next month. In 2014, ''The New York Times'' predicted that by 2018 e-books will make up over 50% of total consumer publishing revenue in the United States and Great Britain.
Applications
Timeline
Before the 1980s
;c. 1949 * Ángela Ruiz Robles patents the idea of the electronic book, called the Mechanical Encyclopedia, in Galicia, Spain. * Roberto Busa begins planning the ''Index Thomisticus''. ;c. 1963 * Douglas Engelbart starts the NLS (and later Augment) projects. ;c. 1965 * Andries van Dam starts the HES (and later FRESS) projects, with assistance from Ted Nelson, to develop and use electronic textbooks forhumanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at th ...
and in pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
.
;1971
* Michael S. Hart
Michael Stern Hart (March 8, 1947 – September 6, 2011) was an American author, best known as the inventor of the e-book and the founder of Project Gutenberg (PG), the first project to make e-books freely available via the Internet. H ...
types the US Declaration of Independence into a computer to create the first e-book available on the Internet and launches Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
in order to create electronic copies of more books.
;c. 1979
* Roberto Busa finishes the ''Index Thomisticus'', a complete lemmatisation of the 56 printed volumes of Saint Thomas Aquinas and of a few related authors.
1980s and 1990s
;1986 *Judy Malloy
Judy Malloy (born Judith Ann Powers January 9, 1942) is a poet whose works embrace the intersection of hypernarrative, magic realism, and information art. Beginning with ''Uncle Roger'' in 1986, Malloy has composed works in both new media lite ...
writes and programmes the first online hypertext fiction, ''Uncle Roger'', with links that take the narrative in different directions depending on the reader's choice.
;1989
* Franklin Computer releases an electronic edition of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts o ...
that can only be read with a stand-alone device.
;1990
* Eastgate Systems
Eastgate Systems is a publisher and software company headquartered in Watertown, Massachusetts, which publishes hypertext.
Eastgate is a pioneer in hypertext publishing and electronic literature and one of the best known publishers of hypertext f ...
publishes the first hypertext fiction released on floppy disk, ''afternoon, a story
''afternoon, a story'', spelled with a lowercase 'a', is a work of electronic literature written in 1987 by American author Michael Joyce. It was published by Eastgate Systems in 1990 and is known as one of the first works of hypertext fiction.
...
'', by Michael Joyce.
* Electronic Book Technologies releases DynaText, the first SGML-based system for delivering large-scale books such as aircraft technical manuals. It was later tested on a US aircraft carrier as replacement for paper manuals.
* Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
launches the Data Discman e-book player.
;1991
* Voyager Company develops Expanded Books, which are books on CD-ROM in a digital format.
;1992 * F. Crugnola and I. Rigamonti design and create the first e-reader, called Incipit, as a thesis project at the Polytechnic University of Milan.
*
* F. Crugnola and I. Rigamonti design and create the first e-reader, called Incipit, as a thesis project at the Polytechnic University of Milan.
*Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
starts using its DocViewer format "to distribute documentation to developers in an electronic form", which effectively meant Inside Macintosh books.
;1993
* Peter James publishes his novel ''Host'' on two floppy disks, which at the time was called the "world's first electronic novel"; a copy of it is stored at the Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in ...
.
* Hugo Award and Nebula Award nominee works are included on a CD-ROM by Brad Templeton.
* Launch of Bibliobytes, a website for obtaining e-books, both for free and for sale on the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists ...
.
* Paul Baim releases the EBook 1.0 HyperCard stack that allows the user to easily convert any text file into a HyperCard based pageable book.
;1994
* C & M Online is founded in Raleigh, North Carolina
Raleigh (; ) is the capital city of the state of North Carolina and the seat of Wake County in the United States. It is the second-most populous city in North Carolina, after Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the South ...
and begins publishing e-books through its imprint, Boson Books
Boson Books is an independent publisher based in Raleigh, North Carolina. It was founded in 1994 by Nancy McAllister, President and Director of Acquisitions, and David McAllister, Vice President and Director of Technical Operations. The company pu ...
; authors include Fred Chappell, Kelly Cherry
Kelly Cherry (December 21, 1940 – March 18, 2022) was a novelist, poet, essayist, professor, and literary criticLeon Katz,
 * The International Digital Publishing Forum releases EPUB to replace Open eBook.
* In November, Amazon.com releases the
* The International Digital Publishing Forum releases EPUB to replace Open eBook.
* In November, Amazon.com releases the
 * Five major US e-book publishers, as part of their settlement of a price-fixing suit, are ordered to refund about $3 for every electronic copy of a New York Times best-seller that they sold from April 2010 to May 2012. This could equal $160 million in settlement charges.
* Barnes & Noble releases the Nook Glowlight, which has a 6-inch touchscreen using E Ink Pearl and Regal, with built-in front LED lights.
* July – US District Court Judge
* Five major US e-book publishers, as part of their settlement of a price-fixing suit, are ordered to refund about $3 for every electronic copy of a New York Times best-seller that they sold from April 2010 to May 2012. This could equal $160 million in settlement charges.
* Barnes & Noble releases the Nook Glowlight, which has a 6-inch touchscreen using E Ink Pearl and Regal, with built-in front LED lights.
* July – US District Court Judge
. Slate. February 13, 2015. One obstacle to wide adoption of the e-book is that a large portion of people value the printed book as an object itself, including aspects such as the texture, smell, weight and appearance on the shelf. Print books are also considered valuable cultural items, and symbols of liberal education and the
The Electronic Book: Looking Beyond the Physical Codex
''SciNet'' *
Ebooks: Neither E, Nor Books
''O'Reilly Emerging Technologies Conference'' * Lynch, Clifford (May 28, 2001)
The Battle to Define the Future of the Book in the Digital World
''First Monday – Peer reviewed journal''. * * . * Dene Grigar & Stuart Moulthrop (2013–2016
"Pathfinders: Documenting the Experience of Early Digital Literature"
''
Richard Popkin
Richard Henry Popkin (December 27, 1923 – April 14, 2005) was an American academic philosopher who specialized in the history of enlightenment philosophy and early modern anti-dogmatism. His 1960 work ''The History of Scepticism from Erasmus to ...
, and Robert Rodman.
* More than two dozen volumes of Inside Macintosh are published together on a single CD-ROM in Apple DocViewer format. Apple subsequently switches to using Adobe Acrobat.
* The popular format for publishing e-books changes from plain text to HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...
.
;1995
* Online poet Alexis Kirke discusses the need for wireless internet electronic paper
Electronic paper, also sometimes electronic ink, e-ink or electrophoretic display, are display devices that mimic the appearance of ordinary ink on paper. Unlike conventional flat panel displays that emit light, an electronic paper display ...
readers in his article "The Emuse".
;1996
* Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
reaches 1,000 titles.
* Joseph Jacobson works at MIT to create electronic ink, a high-contrast, low-cost, read/write/erase medium to display e-books.
;1997
* E Ink Corporation is co-founded by MIT undergraduates J.D. Albert, Barrett Comiskey, MIT professor Joseph Jacobson, as well as Jeremy Rubin and Russ Wilcox to create an electronic printing technology. This technology is later used on the displays of the Sony Reader, Barnes & Noble Nook, and Amazon Kindle.
;1998
* NuvoMedia releases the first handheld e-reader, the Rocket eBook.
* SoftBook launches its SoftBook reader. This e-reader, with expandable storage, could store up to 100,000 pages of content, including text, graphics and pictures.
* The Cybook is sold and manufactured at first by Cytale (1998–2003) and later by Bookeen.
;1999
* The NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sc ...
releases the Open eBook
Open eBook (OEB), or formally, the Open eBook Publication Structure (OEBPS), is a legacy e-book format which has been superseded by the EPUB format. It was "based primarily on technology developed by SoftBook Press". and on XML. OEB was released wi ...
format based on XML to the public domain; most future e-book formats derive from Open eBook.
* Publisher Simon & Schuster
Simon & Schuster () is an American publishing company and a subsidiary of Paramount Global. It was founded in New York City on January 2, 1924 by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. As of 2016, Simon & Schuster was the third largest pub ...
creates a new imprint called iBooks and becomes the first trade publisher to simultaneously publish some of its titles in e-book and print format.
* Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print book ...
makes a selection of its books available as e-books through netLibrary.
* Publisher Baen Books
Baen Books () is an American publishing house for science fiction and fantasy. In science fiction, it emphasizes space opera, hard science fiction, and military science fiction. The company was established in 1983 by science fiction publisher ...
opens up the Baen Free Library
The Baen Free Library is a digital library of the science fiction and fantasy publishing house Baen Books where 61 e-books as of June 2016 (112 e-books as of December 2008) can be downloaded free in a number of formats, without copy protection. ...
to make available Baen titles as free e-books.
* Kim Blagg, via her company Books OnScreen, begins selling multimedia-enhanced e-books on CDs through retailers including Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
, Barnes & Noble and Borders Books.
2000s
;2000 * Joseph Jacobson, Barrett O. Comiskey and Jonathan D. Albert are granted US patents related to displaying electronic books, these patents are later used in the displays for most e-readers. *Stephen King
Stephen Edwin King (born September 21, 1947) is an American author of horror, supernatural fiction, suspense, crime, science-fiction, and fantasy novels. Described as the "King of Horror", a play on his surname and a reference to his high ...
releases his novella '' Riding the Bullet'' exclusively online and it became the first mass-market e-book, selling 500,000 copies in 48 hours.
* Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at th ...
releases the Microsoft Reader with ClearType for increased readability on PCs and handheld devices.
* Microsoft and Amazon work together to sell e-books that can be purchased on Amazon, and using Microsoft software downloaded to PCs and handhelds.
* A digitized version of the Gutenberg Bible is made available online at the British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the Briti ...
.
;2001
* Adobe releases Adobe Acrobat Reader 5.0 allowing users to underline, take notes and bookmark.
;2002
* Palm, Inc and OverDrive, Inc make Palm Reader e-books available worldwide, offering over 5,000 e-books in several languages; these could be read on Palm PDAs or using a computer application.
* Random House
Random House is an American book publisher and the largest general-interest paperback publisher in the world. The company has several independently managed subsidiaries around the world. It is part of Penguin Random House, which is owned by Ger ...
and HarperCollins
HarperCollins Publishers LLC is one of the Big Five English-language publishing companies, alongside Penguin Random House, Simon & Schuster, Hachette, and Macmillan. The company is headquartered in New York City and is a subsidiary of News C ...
start to sell digital versions of their titles in English.
;2004
* Sony Librie, the first e-reader using an E Ink
E Ink (electronic ink) is a brand of electronic paper (e-paper) display technology commercialized by the E Ink Corporation, which was co-founded in 1997 by MIT undergraduates JD Albert and Barrett Comiskey, MIT Media Lab professor Joseph Jacobson ...
display is released; it has a six-inch screen.
* Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
announces plans to digitize the holdings of several major libraries, as part of what would later be called the Google Books Library Project
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
.
;2005
* Amazon buys Mobipocket, the creator of the mobi e-book file format and e-reader software.
* Google is sued for copyright infringement
Copyright infringement (at times referred to as piracy) is the use of works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, ...
by the Authors Guild for scanning books still in copyright.
;2006
* Sony Reader PRS-500, with an E Ink screen and two weeks of battery life, is released.
* LibreDigital launches BookBrowse as an online reader for publisher content.
;2007 * The International Digital Publishing Forum releases EPUB to replace Open eBook.
* In November, Amazon.com releases the
* The International Digital Publishing Forum releases EPUB to replace Open eBook.
* In November, Amazon.com releases the Kindle
Kindle may refer to:
Companies and products
* Amazon Kindle, an e-reader line by Amazon.com
** Kindle Direct Publishing, an e-book publishing platform by Amazon
** Kindle Store, an online e-book e-commerce store by Amazon
* Kindle Banking Systems, ...
e-reader with 6-inch E Ink screen in the US and it sells outs in 5.5 hours. Simultaneously, the Kindle Store opens, with initially more than 88,000 e-books available.
* Bookeen launches Cybook Gen3 in Europe; it can display e-books and play audiobooks.
;2008
* Adobe and Sony agree to share their technologies ( Adobe Reader and DRM) with each other.
* Sony sells the Sony Reader PRS-505 in UK and France.
;2009
* Bookeen releases the Cybook Opus in the US and Europe.
* Sony releases the Reader Pocket Edition and Reader Touch Edition.
* Amazon releases the Kindle 2 that includes a text-to-speech feature.
* Amazon releases the Kindle DX that has a 9.7-inch screen in the U.S.
* Barnes & Noble releases the Nook e-reader in the US.
* Amazon releases the Kindle for PC application
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a c ...
in late 2009, making the Kindle Store library available for the first time outside Kindle hardware.
2010s
;2010 * January – Amazon releases the Kindle DX International Edition worldwide. * April –Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
releases the iPad
The iPad is a brand of iOS and iPadOS-based tablet computers that are developed by Apple Inc. The iPad was conceived before the related iPhone but the iPhone was developed and released first. Speculation about the development, operati ...
bundled with an e-book app called iBooks.
* May – Kobo Inc. releases its Kobo eReader to be sold at Indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', ...
/ Chapters in Canada and Borders in the United States.
* July – Amazon reports that its e-book sales outnumbered sales of hardcover books for the first time during the second quarter of 2010.
* August – PocketBook
PocketBook is a multinational company which produces e-book readers based on E Ink technology (an electronic paper technology) under the ''PocketBook'' brand. The company was founded in 2007 in Kyiv, Ukraine, and its headquarters were shifted t ...
expands its line with an Android e-reader.
* August – Amazon releases the third generation Kindle, available in Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio w ...
and 3G & Wi-Fi versions.
* October – Bookeen reveals the Cybook Orizon at CES.
* October – Kobo Inc. releases an updated Kobo eReader, which includes Wi-Fi capability.
* November – ''The Sentimentalists
The Sentimentalists, also known as the "Clark Sisters" (and also as the "Original" Clark Sisters; so-called to distinguish them from the current gospel music group of the same name), were an American close harmony singing group, consisting of si ...
'' wins the prestigious national Giller Prize in Canada; due to the small scale of the novel's publisher, the book is not widely available in printed form, so the e-book edition becomes the top-selling title on Kobo devices for 2010.
* November – Barnes & Noble releases the Nook Color, a color LCD tablet.
* December – Google launches Google eBooks offering over 3 million titles, becoming the world's largest e-book store to date.
;2011
* May – Amazon.com announces that its e-book sales in the US now exceed all of its printed book sales.
* June – Barnes & Noble releases the Nook Simple Touch
The Nook Simple Touch (also called the Nook Touch) is the second generation Nook e-reader developed by Barnes & Noble. It features an 600x800 E Ink screen with a touchscreen that uses a network of infrared beams slightly above the screen surfac ...
e-reader and Nook Tablet
The Nook Tablet (sometimes styled NOOK Tablet) is a tablet e-reader/media player that was produced and marketed by Barnes & Noble. It followed the Nook Color and was intended to compete with both e-book readers and tablet computers.
Barnes & Nob ...
.
* August – Bookeen launches its own e-books store, BookeenStore.com, and starts to sell digital versions of titles in French.
* September – Nature Publishing releases the pilot version of '' Principles of Biology'', a customizable, modular textbook, with no corresponding paper edition.
* June/November – As the e-reader market grows in Spain, companies like Telefónica, Fnac, and Casa del Libro launch their e-readers with the Spanish brand "bq readers".
* November – Amazon launches the Kindle Fire and Kindle Touch
Amazon Kindle is a series of e-readers designed and marketed by Amazon. Amazon Kindle devices enable users to browse, buy, download, and read e-books, newspapers, magazines and other digital media via wireless networking to the Kindle Store. T ...
, both devices designed for e-reading.
;2012
* E-book sales in the US market collect over three billion in revenue.
* January – Apple releases iBooks Author, software for creating iPad
The iPad is a brand of iOS and iPadOS-based tablet computers that are developed by Apple Inc. The iPad was conceived before the related iPhone but the iPhone was developed and released first. Speculation about the development, operati ...
e-books to be directly published in its iBooks bookstore or to be shared as PDF files.
* January – Apple opens a textbook
A textbook is a book containing a comprehensive compilation of content in a branch of study with the intention of explaining it. Textbooks are produced to meet the needs of educators, usually at educational institutions. Schoolbooks are textboo ...
section in its iBooks bookstore.
* February – Nature Publishing announces the worldwide release of ''Principles of Biology'', following the success of the pilot version some months earlier.
* February – Library.nu (previously called ebooksclub.org and gigapedia.com, a popular linking website for downloading e-books) is accused of copyright infringement
Copyright infringement (at times referred to as piracy) is the use of works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, ...
and closed down by court order.
* March – The publishing companies Random House
Random House is an American book publisher and the largest general-interest paperback publisher in the world. The company has several independently managed subsidiaries around the world. It is part of Penguin Random House, which is owned by Ger ...
, Holtzbrinck, and arvato bring to market an e-book library called Skoobe.
* March – US Department of Justice prepares anti-trust lawsuit against Apple, Simon & Schuster
Simon & Schuster () is an American publishing company and a subsidiary of Paramount Global. It was founded in New York City on January 2, 1924 by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. As of 2016, Simon & Schuster was the third largest pub ...
, Hachette Book Group, Penguin Group
Penguin Group is a British trade book publisher and part of Penguin Random House, which is owned by the German media conglomerate Bertelsmann. The new company was created by a merger that was finalised on 1 July 2013, with Bertelsmann initial ...
, Macmillan, and HarperCollins
HarperCollins Publishers LLC is one of the Big Five English-language publishing companies, alongside Penguin Random House, Simon & Schuster, Hachette, and Macmillan. The company is headquartered in New York City and is a subsidiary of News C ...
, alleging collusion to increase the price of books sold on Amazon.
* March – PocketBook releases the PocketBook Touch, an E Ink Pearl e-reader, winning awards from German magazines ''Tablet PC'' and '' Computer Bild''.
* June – Kbuuk releases the cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
-based e-book self-publishing SaaS platform on the Pubsoft digital publishing engine.
* September – Amazon releases the Kindle Paperwhite, its first e-reader with built-in front LED lights.
;2013
* April – Kobo releases the Kobo Aura HD with a 6.8-inch screen, which is larger than the current models produced by its US competitors.
* May – Mofibo launches the first Scandinavian unlimited access e-book subscription service.
* June – Association of American Publishers
The Association of American Publishers (AAP) is the national trade association of the American book publishing industry. AAP lobbies for book, journal, and education publishers in the United States. AAP members include most of the major commercia ...
announces that e-books now account for about 20% of book sales. Barnes & Noble estimates it has a 27% share of the US e-book market.
* June – Barnes & Noble announces its intention to discontinue manufacturing Nook tablets, but to continue producing black-and-white e-readers such as the Nook Simple Touch.
* June – Apple executive Keith Moerer testifies in the e-book price fixing trial that the iBookstore held approximately 20% of the e-book market share in the United States within the months after launch – a figure that ''Publishers Weekly
''Publishers Weekly'' (''PW'') is an American weekly trade news magazine targeted at publishers, librarians, booksellers, and literary agents. Published continuously since 1872, it has carried the tagline, "The International News Magazine of ...
'' reports is roughly double many of the previous estimates made by third parties. Moerer further testified that iBookstore acquired about an additional 20% by adding Random House in 2011.
 * Five major US e-book publishers, as part of their settlement of a price-fixing suit, are ordered to refund about $3 for every electronic copy of a New York Times best-seller that they sold from April 2010 to May 2012. This could equal $160 million in settlement charges.
* Barnes & Noble releases the Nook Glowlight, which has a 6-inch touchscreen using E Ink Pearl and Regal, with built-in front LED lights.
* July – US District Court Judge
* Five major US e-book publishers, as part of their settlement of a price-fixing suit, are ordered to refund about $3 for every electronic copy of a New York Times best-seller that they sold from April 2010 to May 2012. This could equal $160 million in settlement charges.
* Barnes & Noble releases the Nook Glowlight, which has a 6-inch touchscreen using E Ink Pearl and Regal, with built-in front LED lights.
* July – US District Court Judge Denise Cote
Denise Louise Cote (born October 13, 1946) is a Senior United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York.
Early life and education
Cote was born in St. Cloud, Minnesota. She received a Bache ...
finds Apple guilty of conspiring to raise the retail price of e-books and schedules a trial in 2014 to determine damages.
* August – Kobo releases the Kobo Aura, a baseline touchscreen six-inch e-reader.
* September – Oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not a ...
launches its unlimited access e-book subscription service.
* November – US District Judge Chin sides with Google in '' Authors Guild v. Google'', citing fair use. The authors said they would appeal.
* December – Scribd
Scribd Inc. is an American e-book and audiobook subscription service that includes one million titles. Scribd hosts 60 million documents on its open publishing platform.
The company was founded in 2007 by Trip Adler, Jared Friedman, and Tik ...
launches the first public unlimited access subscription service for e-books.
;2014
* April – Kobo releases the Aura H₂0
The Kobo eReader is an e-reader produced by Toronto-based Kobo Inc. The company's name is an anagram of "book". The original version was released in May 2010 and was marketed as a minimalist alternative to the more expensive e-book readers availa ...
, the world's first waterproof commercially produced e-reader.
* June – US District Court Judge Cote grants class action certification to plaintiffs in a lawsuit over Apple's alleged e-book price conspiracy; the plaintiffs are seeking $840 million in damages. Apple appeals the decision.
* June – Apple settles the e-book antitrust case that alleged Apple conspired to e-book price fixing out of court with the States; however if Judge Cote's ruling is overturned in appeal the settlement would be reversed.
* July – Amazon launches Kindle Unlimited, an unlimited-access e-book and audiobook subscription service.
;2015
* June – The 2nd US Circuit Court of Appeals with a 2:1 vote concurs with Judge Cote that Apple conspired to e-book price fixing and violated federal antitrust law. Apple appealed the decision.
* June – Amazon releases the Kindle Paperwhite (3rd generation) that is the first e-reader to feature Bookerly
Bookerly is a serif typeface designed by Dalton Maag as an exclusive font for reading on Amazon's Kindle devices and apps. Combined with a new typesetting engine, Amazon.com asserts that the font helps the user "read faster with less eyestrain." ...
, a font exclusively designed for e-readers.
* September – Oyster announces its unlimited access e-book subscription service would be shut down in early 2016 and that it would be acquired by Google.
* September – Malaysian e-book company, e-Sentral, introduces for the first time geo-location distribution technology for e-books via bluetooth beacon. It was first demonstrated in a large scale at Kuala Lumpur International Airport.
* October – Amazon releases the Kindle Voyage
Amazon Kindle is a series of e-readers designed and marketed by Amazon. Amazon Kindle devices enable users to browse, buy, download, and read e-books, newspapers, magazines and other digital media via wireless networking to the Kindle Stor ...
that has a 6-inch, 300 ppi E Ink Carta HD display, which was the highest resolution and contrast available in e-readers as of 2014. It also features adaptive LED lights and page turn sensors on the sides of the device.
* October – Barnes & Noble releases the Glowlight Plus, its first waterproof e-reader.
* October – The US appeals court sides with Google instead of the Authors' Guild, declaring that Google did not violate copyright law in its book scanning project.
* December – Playster launches an unlimited-access subscription service including e-books and audiobooks.
* By the end of 2015, Google Books scanned more than 25 million books.
* By 2015, over 70 million e-readers had been shipped worldwide.
;2016
* March – The Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point ...
declines to hear Apple's appeal against the court's decision of July 2013 that the company conspired to e-book price fixing, hence the previous court decision stands, obliging Apple to pay $450 million.
* April – The Supreme Court declines to hear the Authors Guild's appeal of its book scanning case, so the lower court's decision stands; the result means that Google can scan library books and display snippets in search results without violating US copyright law.
* April – Amazon releases the Kindle Oasis
Amazon Kindle is a series of e-readers designed and marketed by Amazon. Amazon Kindle devices enable users to browse, buy, download, and read e-books, newspapers, magazines and other digital media via wireless networking to the Kindle Stor ...
, its first e-reader in five years to have physical page turn buttons and, as a premium product, it includes a leather case with a battery inside; without including the case, it is the lightest e-reader on the market to date.
* August – Kobo releases the Aura One, the first commercial e-reader with a 7.8-inch E Ink Carta HD display.
* By the end of the year, smartphones and tablets have both individually overtaken e-readers as methods for reading an e-book, and paperback book sales are now higher than e-book sales.
;2017
* February – The Association of American Publishers
The Association of American Publishers (AAP) is the national trade association of the American book publishing industry. AAP lobbies for book, journal, and education publishers in the United States. AAP members include most of the major commercia ...
releases data showing that the US adult e-book market declined 16.9% in the first nine months of 2016 over the same period in 2015, and Nielsen Book determines that the e-book market had an overall total decline of 16% in 2016 over 2015, including all age groups. This decline is partly due to widespread e-book price increases by major publishers, which has increased the average e-book price from $6 to almost $10.
* February – The US version of Kindle Unlimited comprises more than 1.5 million titles, including over 290,000 foreign language titles.
* March – ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide ...
'' reports that sales of physical books are outperforming digital titles in the UK, since it can be cheaper to buy the physical version of a book when compared to the digital version due to Amazon's deal with publishers that allows agency pricing.
* April – The ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the ...
'' reports that, in 2016, sales of hardcover books were higher than e-books for the first time in five years.
* October – Amazon releases the Oasis 2, the first Kindle to be IPX8 rated meaning that it is water resistant up to 2 meters for up to 60 minutes; it is also the first Kindle to enable white text on a black background, a feature that may be helpful for nighttime reading.
;2018
*January – U.S. public libraries report record-breaking borrowing of OverDrive e-books over the course of the year, with more than 274 million e-books loaned to card holders, a 22% increase over the 2017 figure.
* October – The EU allowed its member countries to charge the same VAT for ebooks as for paper books.
;2019
* May – Barnes & Noble releases the GlowLight Plus e-reader, the largest Nook e-reader to date with a 7.8-inch E Ink screen.
Formats
Writers and publishers have many formats to choose from when publishing e-books. Each format has advantages and disadvantages. The most popular e-readers and their natively supported formats are shown below:Digital rights management
Most e-book publishers do not warn their customers about the possible implications of thedigital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures (TPM) such as access control technologies can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted work ...
tied to their products. Generally, they claim that digital rights management is meant to prevent illegal copying of the e-book. However, in many cases, it is also possible that digital rights management will result in the complete denial of access by the purchaser to the e-book. The e-books sold by most major publishers and electronic retailers, which are Amazon.com, Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
, Barnes & Noble, Kobo Inc. and Apple Inc., are DRM-protected and tied to the publisher's e-reader
An e-reader, also called an e-book reader or e-book device, is a mobile electronic device that is designed primarily for the purpose of reading digital e-books and periodicals.
Any device that can display text on a screen may act as an e-re ...
software or hardware. The first major publisher to omit DRM was Tor Books, one of the largest publishers of science fiction and fantasy, in 2012. Smaller e-book publishers such as O'Reilly Media, Carina Press and Baen Books
Baen Books () is an American publishing house for science fiction and fantasy. In science fiction, it emphasizes space opera, hard science fiction, and military science fiction. The company was established in 1983 by science fiction publisher ...
had already forgone DRM previously.
Production
Some e-books are produced simultaneously with the production of a printed format, as described in electronic publishing, though in many instances they may not be put on sale until later. Often, e-books are produced from pre-existing hard-copy books, generally by document scanning, sometimes with the use ofrobotic book scanner
Book scanning or book digitization (also: magazine scanning or magazine digitization) is the process of converting physical books and magazines into digital media such as images, electronic text, or electronic books (e-books) by using an image ...
s, having the technology to quickly scan books without damaging the original print edition. Scanning a book produces a set of image files, which may additionally be converted into text format by an OCR program. Occasionally, as in some projects, an e-book may be produced by re-entering the text from a keyboard. Sometimes only the electronic version of a book is produced by the publisher. It is possible to release an e-book chapter by chapter as each chapter is written. This is useful in fields such as information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system ...
where topics can change quickly in the months that it takes to write a typical book. It is also possible to convert an electronic book to a printed book by print on demand
Print on demand (POD) is a printing technology and business process in which book copies (or other documents, packaging or materials) are not printed until the company receives an order, allowing prints of single or small quantities. While oth ...
. However, these are exceptions as tradition dictates that a book be launched in the print format and later if the author wishes an electronic version is produced. ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' keeps a list of best-selling e-books, for both fiction and non-fiction.
Reading data
All of the e-readers and reading apps are capable of tracking e-book reading data, and the data could contain which e-books users open, how long the users spend reading each e-book and how much of each e-book is finished. In December 2014, Kobo released e-book reading data collected from over 21 million of its users worldwide. Some of the results were that only 44.4% of UK readers finished the bestselling e-book ''The Goldfinch'' and the 2014 top selling e-book in the UK, "One Cold Night", was finished by 69% of readers; this is evidence that while popular e-books are being completely read, some e-books are only sampled.Comparison to printed books
Advantages
In the space that a comparably sized physical book takes up, an e-reader can contain thousands of e-books, limited only by its memory capacity. Depending on the device, an e-book may be readable in low light or even total darkness. Many e-readers have a built-in light source, can enlarge or change fonts, use text-to-speech software to read the text aloud for visually impaired, elderly or dyslexic people or just for convenience. Additionally, e-readers allow readers to look up words or find more information about the topic immediately using an online dictionary. Amazon reports that 85% of its e-book readers look up a word while reading. Printed books use three times more raw materials and 78 times more water to produce when compared to e-books. A 2017 study found that even when accounting for the emissions created in manufacturing the e-reader device, substituting more than 4.7 print books a year resulted in lessgreenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
than print. While an e-reader costs more than most individual books, e-books may have a lower cost than paper books. E-books may be made available for less than the price of traditional books using on-demand book printers. Moreover, numerous e-books are available online free of charge on sites such as Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
. For example, all books printed before 1923 are in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, ...
in the United States, which enables websites to host ebook versions of such titles for free.
Depending on possible digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures (TPM) such as access control technologies can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted work ...
, e-books (unlike physical books) can be backed up and recovered in the case of loss or damage to the device on which they are stored, a new copy can be downloaded without incurring an additional cost from the distributor. Readers can synchronize their reading location, highlights and bookmarks across several devices.
Disadvantages
There may be a lack ofprivacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
for the user's e-book reading activities; for example, Amazon knows the user's identity, what the user is reading, whether the user has finished the book, what page the user is on, how long the user has spent on each page, and which passages the user may have highlighted.The Fifty Shades of Grey Paradox. Slate. February 13, 2015. One obstacle to wide adoption of the e-book is that a large portion of people value the printed book as an object itself, including aspects such as the texture, smell, weight and appearance on the shelf. Print books are also considered valuable cultural items, and symbols of liberal education and the
humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at th ...
. Kobo found that 60% of e-books that are purchased from their e-book store are never opened and found that the more expensive the book is, the more likely the reader would at least open the e-book.
Joe Queenan has written about the pros and cons of e-books:
Apart from all the emotional and habitual aspects, there are also some readability and usability issues that need to be addressed by publishers and software developers. Many e-book readers who complain about eyestrain, lack of overview and distractions could be helped if they could use a more suitable device or a more user-friendly reading application, but when they buy or borrow a DRM-protected e-book, they often have to read the book on the default device or application, even if it has insufficient functionality.
While a paper book is vulnerable to various threats, including water damage, mold and theft, e-books files may be corrupted, deleted or otherwise lost as well as pirated. Where the ownership of a paper book is fairly straightforward (albeit subject to restrictions on renting or copying pages, depending on the book), the purchaser of an e-book's digital file has conditional access with the possible loss of access to the e-book due to digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures (TPM) such as access control technologies can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted work ...
provisions, copyright issues, the provider's business failing or possibly if the user's credit card expired.
Market share
United States
According to the Association of American Publishers 2018 annual report, ebooks accounted for 12.4% of the total trade revenue. Publishers of books in all formats made $22.6 billion in print form and $2.04 billion in e-books, according to the Association of American Publishers’ annual report 2019.Canada
Spain
In 2013, Carrenho estimates that e-books would have a 15% market share in Spain in 2015.UK
According to Nielsen Book Research, e-book share went up from 20% to 33% between 2012 and 2014, but down to 29% in the first quarter of 2015. Amazon-published and self-published titles accounted for 17 million of those books (worth £58m) in 2014, representing 5% of the overall book market and 15% of the digital market. The volume and value sales, although similar to 2013, had seen a 70% increase since 2012.Germany
The Wischenbart Report 2015 estimates the e-book market share to be 4.3%.Brazil
The Brazilian e-book market is only emerging. Brazilians are technology savvy, and that attitude is shared by the government. In 2013, around 2.5% of all trade titles sold were in digital format. This was a 400% growth over 2012 when only 0.5% of trade titles were digital. In 2014, the growth was slower, and Brazil had 3.5% of its trade titles being sold as e-books.China
The Wischenbart Report 2015 estimates the e-book market share to be around 1%.Public domain books
Public domain books are those whose copyrights have expired, meaning they can be copied, edited, and sold freely without restrictions. Many of these books can be downloaded for free from websites like theInternet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music ...
, in formats that many e-readers support, such as PDF, TXT, and EPUB. Books in other formats may be converted to an e-reader-compatible format using e-book writing software, for example Calibre.
See also
* Accessible publishing * Book scanning *Blook
A blook is a printed book that contains or is based on content from a blog.
The first printed blook was User Interface Design for Programmers, by Joel Spolsky, published by Apress on June 26, 2001, based on his blog Joel on Software. An early bl ...
* Cell phone novel
* Digital library
A digital library, also called an online library, an internet library, a digital repository, or a digital collection is an online database of digital objects that can include text, still images, audio, video, digital documents, or other digital ...
* Braille e-book
* Electronic publishing
* List of digital library projects
This is a list of digital library projects.
See also
* Bibliographic database
* List of academic databases and search engines
* List of online databases
* List of online encyclopedias
* List of open-access journals
This is a list of open-a ...
* Networked book
A networked book is an open book designed to be written, edited, and read in a networked environment. It is also a platform for social exchange, and is potentially linked to other books and other discussions. Wikipedia can be considered a network ...
* Online book
* TeX and LaTeX
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosper ...
* Web fiction
* Braille translator
* Perkins Brailler
* Comparison of e-readers
References
External links
* James, Bradley (November 20, 2002)The Electronic Book: Looking Beyond the Physical Codex
''SciNet'' *
Cory Doctorow
Cory Efram Doctorow (; born July 17, 1971) is a Canadian-British blogger, journalist, and science fiction author who served as co-editor of the blog '' Boing Boing''. He is an activist in favour of liberalising copyright laws and a proponent o ...
(February 12, 2004)Ebooks: Neither E, Nor Books
''O'Reilly Emerging Technologies Conference'' * Lynch, Clifford (May 28, 2001)
The Battle to Define the Future of the Book in the Digital World
''First Monday – Peer reviewed journal''. * * . * Dene Grigar & Stuart Moulthrop (2013–2016
"Pathfinders: Documenting the Experience of Early Digital Literature"
''
Washington State University Vancouver
Washington State University Vancouver also known as WSU Vancouver is a campus of Washington State University. WSU Vancouver is located on a campus outside of Vancouver, Washington, approximately eight miles (13 km) north of the Columbia ...
'', July 1, 2013.
*
{{Authority control
Book formats
Electronic publishing
Electronic paper technology
Web fiction
New media
Fiction forms