Economy of Bulgaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The economy of Bulgaria functions on the principles of the
 The country suffered a difficult start to 2009, after gas supplies were cut in the Russia-Ukraine gas dispute. Industrial output suffered, as well as public services, exposing Bulgaria's overdependence on Russian raw materials.
The
The country suffered a difficult start to 2009, after gas supplies were cut in the Russia-Ukraine gas dispute. Industrial output suffered, as well as public services, exposing Bulgaria's overdependence on Russian raw materials.
The

 Household income or consumption by percentage share:
* ''lowest 10%:'' 2.9%
* ''highest 10%:'' 25.4% (25.4)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
36.6% (2013)
Industrial production growth rate:
11.3% (Third Quarter)
Electricity:
* ''production:'' 45.7
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
* ''lowest 10%:'' 2.9%
* ''highest 10%:'' 25.4% (25.4)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
36.6% (2013)
Industrial production growth rate:
11.3% (Third Quarter)
Electricity:
* ''production:'' 45.7
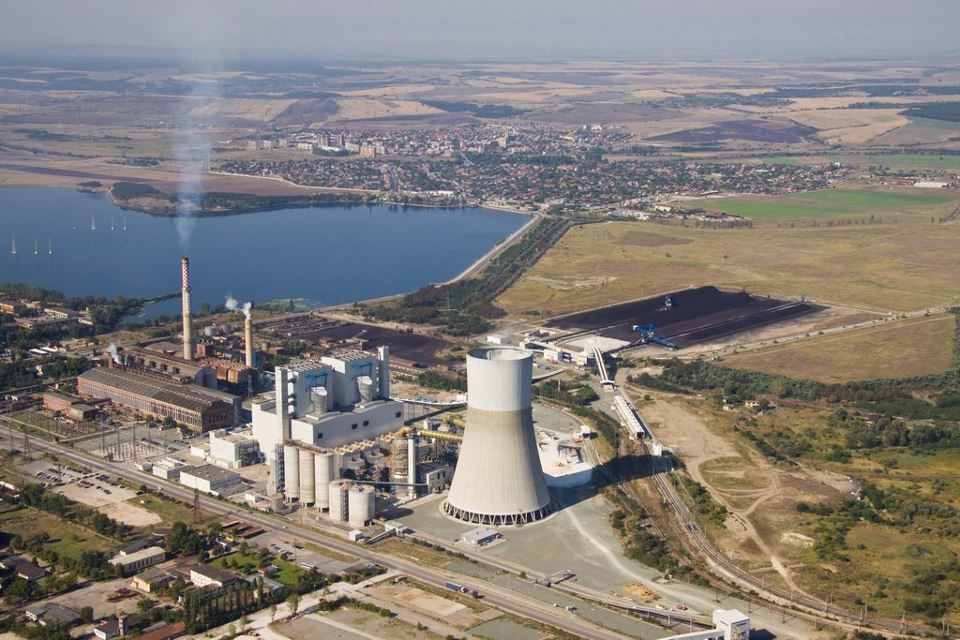 Bulgaria relies on imported oil and natural gas (most of which comes from
Bulgaria relies on imported oil and natural gas (most of which comes from
Electricity production as of 2006
(in comparison,
 In 2004 an estimated one-third of Bulgaria's land mass was covered by forests, of which about 40 percent was conifers. Between 1980 and 2000, the forested area increased by 4.6 percent. In 2002 a total of 4,800 tons of timber was harvested, 44 percent of which was fuel wood and 20 percent, pulpwood. Although nominal state timber standards are very strict, in 2004 an estimated 45 percent of Bulgaria's timber harvest was logged illegally because of corruption in the forest service. Some 7.5 percent of forests are protected from all uses, and 65 percent are designated for ecological and commercial use. In 2005 about 70 percent of the total forest resource was rated economically viable.
Since Bulgaria stopped high-seas fishing in 1995, the country has imported increasing amounts of fish. The fish farming industry (particularly sturgeon) has expanded in the early 2000s, and some environmental improvements in the Black Sea and the Danube River, the principal sources of fish, may increase the take in future years. However, the catch from those sources has decreased sharply in recent decades, yielding only a few species of fish for domestic markets in 2004. Between 1999 and 2001, Bulgaria's total fish harvest, wild and cultivated, dropped from 18,600 tons to 8,100 tons, but in 2003 the harvest had recovered to 16,500 tons.Bulgaria country profile, p. 10.
Production of the most important crops (according to the
In 2004 an estimated one-third of Bulgaria's land mass was covered by forests, of which about 40 percent was conifers. Between 1980 and 2000, the forested area increased by 4.6 percent. In 2002 a total of 4,800 tons of timber was harvested, 44 percent of which was fuel wood and 20 percent, pulpwood. Although nominal state timber standards are very strict, in 2004 an estimated 45 percent of Bulgaria's timber harvest was logged illegally because of corruption in the forest service. Some 7.5 percent of forests are protected from all uses, and 65 percent are designated for ecological and commercial use. In 2005 about 70 percent of the total forest resource was rated economically viable.
Since Bulgaria stopped high-seas fishing in 1995, the country has imported increasing amounts of fish. The fish farming industry (particularly sturgeon) has expanded in the early 2000s, and some environmental improvements in the Black Sea and the Danube River, the principal sources of fish, may increase the take in future years. However, the catch from those sources has decreased sharply in recent decades, yielding only a few species of fish for domestic markets in 2004. Between 1999 and 2001, Bulgaria's total fish harvest, wild and cultivated, dropped from 18,600 tons to 8,100 tons, but in 2003 the harvest had recovered to 16,500 tons.Bulgaria country profile, p. 10.
Production of the most important crops (according to the
 Bulgaria's national road network has a total length of , of which are paved.Library of Congress Country Study, Transportation and Telecommunications, p. 14 The
Bulgaria's national road network has a total length of , of which are paved.Library of Congress Country Study, Transportation and Telecommunications, p. 14 The
free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any o ...
, having a large private sector and a smaller public one. Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
is an industrialised upper-middle-income country according to the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
, and is a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EU), the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
(WTO), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
(OSCE) and the Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation
The Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation (BSEC) is a regional international organization focusing on multilateral political and economic initiatives aimed at fostering cooperation, peace, stability and prosperity in the Black Sea ...
(BSEC). The Bulgarian economy has experienced significant growth (538%), starting from $13.15 billion (nominal, 2000) and reaching estimated gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
(GDP) of $86 billion (nominal, 2022 est.) or $203 billion (PPP, 2022 est.), GDP per capita of $31,148 (PPP, 2022 est.), average gross monthly salary of 1,787 leva
Leva may refer to:
* Bulgarian lev, Bulgarian currency
* ''Leva'' (grasshopper), a genus of insects
* Levice
Levice (; hu, Léva, Hungarian pronunciation: ; german: Lewenz, literally lionesses) is a town in western Slovakia. The town lies o ...
(913 euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
) (September 2022), and average net monthly salary of $1,863 (adjusted for living costs in PPP) (2022). The national currency is the lev
Lev may refer to:
Common uses
*Bulgarian lev, the currency of Bulgaria
*an abbreviation for Leviticus, the third book of the Hebrew Bible and the Torah
People and fictional characters
*Lev (given name)
*Lev (surname)
Places
*Lev, Azerbaijan, a ...
(plural leva), pegged to the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
at a rate of 1.95583 leva for 1 euro. The lev is the strongest and most stable currency in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
.
The strongest sectors in the economy are energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
, mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
, metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
, machine building, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
. Primary industrial exports are clothing, iron and steel, machinery and refined fuels.
Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
is the capital and economic heart of Bulgaria and home to most major Bulgarian and international companies operating in the country, as well as the Bulgarian National Bank
The Bulgarian National Bank ( bg, Българска народна банка, Bohlgarska narodna banka, ), or BNB, is the central bank of the Republic of Bulgaria. Headquartered in Sofia, the bank was established in 1879. It is the 13th oldest ...
and the Bulgarian Stock Exchange
The Bulgarian Stock Exchange ( bg, Българска фондова борса, ''Balgarska fondova borsa'', abbreviated BSE) is a stock exchange operating in Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. It was founded as First Bulgarian Stock Exchange on 1 ...
. Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
is the second-largest city and has one of the largest economies in Bulgaria. Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
is the third largest city in Bulgaria and the largest city and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast
The Bulgarian Black Sea Coast (), also known as the Bulgarian Riviera, covers the entire eastern bound of Bulgaria stretching from the Romanian Black Sea resorts in the north to European Turkey in the south, along 378 km of coast ...
. Situated strategically in the Gulf of Varna
The Gulf of Varna ( bg, Варненски залив, ''Varnenski zaliv'') is a gulf on the Bulgarian Black Sea coast. The length of the gulf is . Its maximum width is , and its depth ranges from . The Port of Varna
Port of Varna ( bg, Прис ...
, economically, Varna is among the best-performing and fastest-growing Bulgarian cities.
The Bulgarian economy has developed significantly in the last 26 years, despite all difficulties after the disband of Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (, ; English abbreviation COMECON, CMEA, CEMA, or CAME) was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc along wi ...
in 1991. In the early 1990s, the country's slow pace of privatization, contradictory government tax and investment policies, and bureaucratic red tape kept the foreign direct investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business in one country by an entity based in another country. It is thus distinguished from a foreign portfolio investment by a notion of direct co ...
(FDI) among the lowest in the region. Total FDI from 1991 through 1996 was $831 million.
In December 1996, Bulgaria joined the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
. In the years since 1997, Bulgaria begun to attract substantial foreign investment. In 2004 alone, over 2.72 billion euro ($3.47 billion) were invested by foreign companies. In 2005, economists observed a slowdown to about 1.8 billion euro ($2.3 billion) in the FDI, which is attributed mainly to the end of the privatization of the major state owned companies.
After joining the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
in 2007, Bulgaria registered a peak in foreign investment of about 6 bln euro.
Low productivity and competitiveness on the European and world markets alike due to inadequate R&D funding, however, still remain a significant obstacle for foreign investment.
Nevertheless, according to the latest Annual report of the Economic Research Institute at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences
The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (abbreviated BAS; bg, Българска академия на науките, ''Balgarska akademiya na naukite'', abbreviated ''БАН'') is the National Academy of Bulgaria, established in 1869.
The Academy ...
, the average salary in Bulgaria is a quarter (1/4) of the average salary in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, and should be two times higher when the labour productivity is calculated in the formula.
During the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
, Bulgaria saw its economy decline by 5.5% in 2009, but quickly restored positive growth levels to 0.2% in 2010, in contrast to other Balkan
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
countries. However, the growth continued to be weak in the following years, and GDP only reached pre-crisis levels in 2014.
History
During the 17th and 18th century Bulgaria had a largely undeveloped industry with agriculture, crafts, and partly trade being the only developed industry sectors. Bulgaria was one of the more dynamic industrial areas of the Ottoman Empire. Bulgaria experienced an economic boom in export-oriented textiles in the period 1815–65, even while the Ottoman Empire's economy was in decline. Bulgaria had comparatively weak economic growth from the 1870s to World War I. The Bulgarian export sector collapsed after Bulgarian independence in 1878. By 1903, industrial output in Bulgaria was far lower than in 1870. During the 1930s, the Bulgarian economy was described as an economy militarily bound to Germany. In the early 1940s, as Germany began to lose the Second World War, the Bulgarian economy suffered a decline. In the interwar period, there was considerable economic modernization in Bulgaria's agricultural sector, setting the conditions for rapid growth after World War II.Cold War period
During the Socialism era, Bulgarian economy continued to be industrialized, although free market trade substantially decreased, as private market initiatives became state-regulated. Still, the Bulgarian economy made significant overall progress in modernizingroad infrastructure
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
, airline transportation, as well as developing the tourism sector by building tourist resorts along the Black sea coast and the mountain regions.
From the end of World War II until the widespread change of regime in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
in November 1989, the Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP; bg, Българска Комунистическа Партия (БКП), Balgarska komunisticheska partiya (BKP)) was the founding and ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria from 1946 until 198 ...
(BCP) exerted complete economic, social and political control in Bulgaria. The party's ascent to power in 1944 had marked the beginning of economic change towards planned economy
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, part ...
. During that time, Bulgaria followed the Soviet model of economic development more closely than any other member of the Eastern Bloc, while becoming one of the first members of Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (, ; English abbreviation COMECON, CMEA, CEMA, or CAME) was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc along wi ...
. The new regime shifted the economy type from a predominantly agrarian one towards an industrial economy
In economics, industrial organization is a field that builds on the theory of the firm by examining the structure of (and, therefore, the boundaries between) firms and markets. Industrial organization adds real-world complications to the perf ...
, while encouraging the relocation of the labour force from the countryside to the cities, thus providing workers for the newly built large-scale industrial complexes. At the same time, the focus of Bulgarian international trade shifted from Central Europe to Eastern Europe and the USSR.
These new policies resulted in impressive initial rates of economic development. Bulgarian economy closely resembled that of the Soviet Union. Soviet-style centralised planning formed by consecutive five-year plan periods had more immediate benefits there compared to the other Eastern European states where it was first applied in the early 1950s. Throughout the postwar period, economic progress was also substantially assisted by a level of internal political stability unseen in other Eastern European countries during the same period. That represented a change on the Bulgarian political scene as political turbulence was common before BCP's ascent to power.
Nonetheless, beginning in the early 1960s, low capital and labour productivity, as well as expensive material inputs, plagued the Bulgarian economy. With disappointing rates of growth came a high degree of economic experimentation. This experimentation took place within the socialist economic framework, although never approaching a market-based economy.
In the late 1980s, continuing poor economic performance intensified economic hardship. By that time, the misdirection and irrationality of BCP economic policies had become quite clear. Bulgaria's economy contracted dramatically after 1987, shortly before Comecon, with which the Bulgarian economy had integrated closely, dissolved in 1991. On 10 November 1989, at the November plenum of BCP, Todor Zhivkov
Todor Hristov Zhivkov ( bg, Тодор Христов Живков ; 7 September 1911 – 5 August 1998) was a Bulgarian communist statesman who served as the ''de facto'' leader of the People's Republic of Bulgaria (PRB) from 1954 until 1989 ...
was dismissed from his long-held party leader and head of state positions. The communist regime gave way to democratic elections and government. Unlike the communist parties in most other Eastern European states, the BCP (changing its name to Bulgarian Socialist Party) retained power by winning the first free national elections in June 1990. That was made possible by changes in party leadership, programme, reduction of its power base and other moves which permitted economic re-orientation toward a market system. This difficult transition combined with political vagueness and unpreparedness of the Bulgarian people for social and economic changes led to dramatically worsening economic conditions during the early 1990s.
1990–2000
Economic performance declined dramatically at the beginning of the 1990s after the disbandment of theComecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (, ; English abbreviation COMECON, CMEA, CEMA, or CAME) was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc along wi ...
system and the loss of the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Comecon market, to which the country had been entirely tied. Also, as a result of political unrest with the first attempts to re-establish a democratic political system and free market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
the standard of living
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
fell by about 40%, and only started to stabilize significantly after 1998 after the fall of Jean Videnov
Zhan Vasilev Videnov ( bg, Жан Василев Виденов ; born 22 March 1959), sometimes spelled in English as Jean Videnov, was Prime Minister of Bulgaria from 25 January 1995 until 13 February 1997, a term remembered for the most severe ...
's socialist government. It regained pre-1989 levels by June 2004.
First signs of recovery showed in 1994 when GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
grew by 1.4%. This progress continued with a 2.5% rise in 1995. Inflation, which surged to 122% in 1994, fell to normal rates of 32.9% in 1995. During 1996, however, the economy collapsed during Jean Videnov's government. That was due to the Bulgarian Socialist Party's inability to introduce vital economic reforms and failure to set legislative standards for banking and financial institutions, thus forcing an unstable banking system. All this led to an inflation rate of 311%, and the collapse of the lev
Lev may refer to:
Common uses
*Bulgarian lev, the currency of Bulgaria
*an abbreviation for Leviticus, the third book of the Hebrew Bible and the Torah
People and fictional characters
*Lev (given name)
*Lev (surname)
Places
*Lev, Azerbaijan, a ...
. In the spring 1997, the pro-reform United Democratic Forces
The United Democratic Forces ( bg, Обединени Демократични Сили, ОДС/ODS) were a center-right electoral alliance in Bulgaria, led by the Union of Democratic Forces.
Members of the coalition
1997
* Union of Democrati ...
coalition came to power with its ambitious economic reform package. The reforms included introduction of a currency board regime, which was agreed to with the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
and the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
, and allowed the economy to stabilize. The 2000s saw a steady pace of growth and budget surpluses, but shaky inflation.
Successful foreign direct investment and successive governments have demonstrated a commitment to economic reforms and responsible fiscal planning that have contributed greatly to the Bulgarian economy, with a historical growth rate average of 6% a year. Corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
in the public administration and a weak judiciary have continued to be long-term problems, with presence of organized crime remaining very high.
Although politicians were giving warranties that the late-2000s recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At t ...
would not hit Bulgaria, the economy suffered a 5.5% GDP decline in that period. Unemployment rose for at least five-quarters bringing Bulgaria's worst recession since the early 1990s. Still, economic circumstances were not too severe when compared to the rest of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. Future prospects are tied to the country's increasingly important integration with the European Union member states.
Reforms of the 1990s and early 2000s
Members of the government promised to move forward on cash and massprivatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
upon taking office in January 1995 but were slow to act. United Nations sanctions against Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
(1990–2003), two of the country's most significant trading partners, took a heavy toll on the Bulgarian economy. The first signs of recovery emerged in 1994 when the GDP grew and inflation fell. The first round of mass privatisation finally began in January 1996, and auctions began toward the end of that year. The second and third rounds were conducted in Spring 1997 under a new government. In July 1998, the UDF-led government and the IMF reached an agreement on a 3-year loan worth about $800 million, which replaced the 14-month stand-by agreement that expired in June 1998. The loan was used to develop financial markets, improve social safety net
The social safety net (SSN) consists of non-contributory assistance existing to improve lives of vulnerable families and individuals experiencing poverty and destitution. Examples of SSNs are previously-contributory social pensions, in-kind and fo ...
programmes, strengthen the tax system, reform agricultural and energy sectors, and further liberalise trade. The European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body o ...
, in its 2002 country report, recognised Bulgaria as a functioning market economy, acknowledging the progress made by Prime Minister Ivan Kostov
Ivan Yordanov Kostov ( bg, Иван Йорданов Костов ) (born 23 December 1949, in Sofia) was the 47th Prime Minister of Bulgaria in office from May 1997 to July 2001 and leader of the Union of Democratic Forces (UDF) between Dec ...
's government toward market-oriented reforms.
Rebound from the February 1997 crisis
In April 1997, the Union of Democratic Forces (SDS) won pre-term parliamentaryelections
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operate ...
and introduced an IMF currency board system which succeeded in stabilizing the economy. The triple digit inflation of 1996 and 1997 has given way to an official economic growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of ...
, but forecasters predicted accelerated growth over the next several years. The government's structural reform program includes:
# privatization and, where appropriate, liquidation of state-owned enterprises (SOEs);
# liberalization of agricultural policies, including creating conditions for the development of a land market;
# reform of the country's social insurance programs; and
# reforms to strengthen contract enforcement and fight crime and corruption.
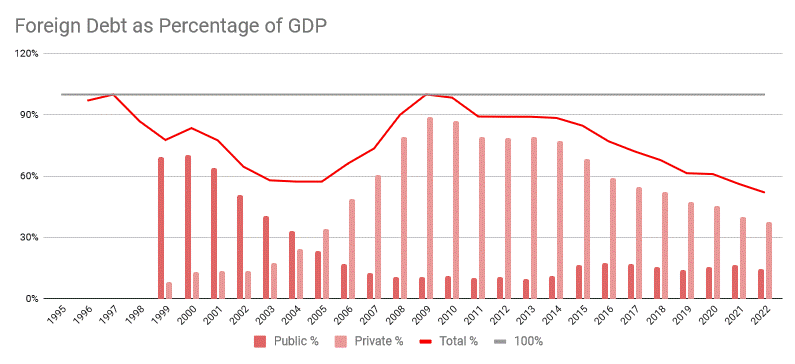
Despite reforms, weak control over privatization led many successful state enterprises to bankruptcy. The SDS government also failed to stop the growing negative account balance, which has since then continued to increase, reaching a negative of $12.65 billion in 2008. The government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
elected in 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which Casualties of the September 11 attacks, killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a Participants in ...
pledged to maintain the fundamental economic policy objectives adopted by its predecessor in 1997, specifically: retaining the Currency Board, implementing sound financial policies, accelerating privatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
, and pursuing structural reforms. Both governments failed to implement sound social policies.
The economy really took off between 2003 and 2008 and growth figures quickly shot up, fluctuating between figures as high as 6.6% (2004) and 5.0% (2003). Even in the last pre-crisis year, 2008, the Bulgarian economy was growing rapidly at 6.0%, despite significantly slowing down in the last quarter.
Part of the European Union
On 1 January 2007 Bulgaria entered theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
. This led to some immediate international trade liberalization, but there was no shock to the economy. The government ran annual surpluses of above 3%. This fact, together with annual GDP growth of above 5%, has brought the government indebtedness to 22.8% of GDP in 2006 from 67.3% five years earlier. This is to be contrasted with enormous current account deficits. Low interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, th ...
s guaranteed availability of funds for investment and consumption. For example, a boom in the real estate market
Real estate business is the profession of buying, selling, or renting real estate (land, buildings, or housing)."Real estate": Oxford English Dictionary online: Retrieved September 18, 2011
Sales and marketing
It is common practice for an intermed ...
started around 2003. At the same time annual inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
in the economy was variable and during the last five years (2003–2007) has seen a low of 2.3% and high of 7.3%. Most importantly, this poses a threat to the country's accession to the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies ...
. The Bulgarian government
The Council of Ministers ( bg, Министерски съвет, ''Ministerski savet'') is the main authority of the executive power in the Republic of Bulgaria. It consists of the Prime Minister of Bulgaria and all the specialized ministers ...
originally planned to adopt the Euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
no sooner than 2015. Although Bulgaria will have to adopt the euro as a condition to membership, plans have since been postponed for better economic times. From a political point of view, there is a trade-off between Bulgaria's economic growth and the stability required for early accession to the monetary union
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any further integration (such as an economic and monetary union, ...
. Bulgaria's per-capita PPP GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
is still only about a half of the EU27 average, while the country's nominal GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
per capita is about 20% of the EU27 average. However, Bulgaria ranks 38th (2015) in the Ease of Doing Business rank list, higher than most other Eastern European states, and 40th (2012) in the Economic Freedom of the World
''Economic Freedom of the World'' is an annual survey published by the Canadian think tank Fraser Institute.
; ; The survey attempts to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations. It has been used in peer-reviewed studies som ...
index, outperforming Belgium, Spain, Poland, Hungary, Portugal. Bulgaria also has the lowest personal and corporate income tax rates in the EU, as well as the second lowest public debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
of all European Union member states at 16.2% of GDP in 2010.
Financial crisis of 2007–2008

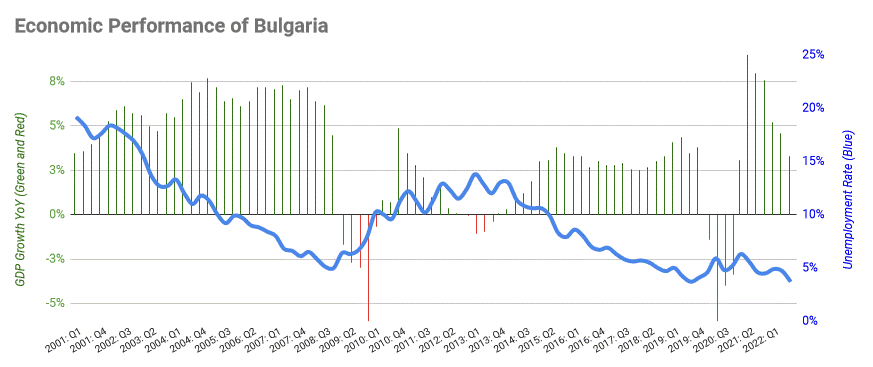
 The country suffered a difficult start to 2009, after gas supplies were cut in the Russia-Ukraine gas dispute. Industrial output suffered, as well as public services, exposing Bulgaria's overdependence on Russian raw materials.
The
The country suffered a difficult start to 2009, after gas supplies were cut in the Russia-Ukraine gas dispute. Industrial output suffered, as well as public services, exposing Bulgaria's overdependence on Russian raw materials.
The financial crisis of 2007–2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fi ...
applied downward pressure on growth and employment by the last quarter of 2008. The real estate market, although not plummeting, ground to a halt and growth was significantly lower in the short-to-medium run.
During 2009, the grim forecasts for the effects of the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
on the Bulgarian economy largely materialized. Although suffering less than the worst-hit countries, Bulgaria recorded its worst economic results since the 1997 meltdown. GDP shrank by around 5% and unemployment jumped. Consumer spending and foreign investment dropped dramatically and depressed growth in 2010 to 0.3%. Unemployment remains consistently high at around 10%.
New government and fiscal discipline
The government of Boyko Borisov elected in 2009 undertook steps to restore economic growth, while attempting to maintain a strict financial policy. The fiscal discipline set by Finance Minister Djankov proved successful and together with reduced budget spending it placed Bulgarian economy on the stage of steadily though slowly growing in the midst of world crisis. On 1 December 2009,Standard & Poor's
S&P Global Ratings (previously Standard & Poor's and informally known as S&P) is an American credit rating agency (CRA) and a division of S&P Global that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks, bonds, and commodities. S&P is con ...
upgraded Bulgaria's investment outlook from "negative" to "stable," which made Bulgaria the only country in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
to receive positive upgrade that year. In January 2010 Moody's followed with an upgrade of its rating perspective from "stable" to "positive."
Bulgaria was expected to join the Eurozone in 2013 but after the rise of some instability in the zone Bulgaria is withholding its positions towards the Euro, combining positive and realistic attitudes. The Bulgarian lev is anyway bound to the euro. Bulgaria regards becoming a member of the Eurozone at present as too risky. The 2012 Transatlantic Trends poll found that 72 percent of Bulgarians did not approve of the economic policy pursued by the government of the (then) ruling center-right GERB party and Prime Minister Boyko Borisov.
Economic statistics
Data
Data
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2017. Inflation under 2% is in green. Actual Current and Past Data
 Household income or consumption by percentage share:
* ''lowest 10%:'' 2.9%
* ''highest 10%:'' 25.4% (25.4)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
36.6% (2013)
Industrial production growth rate:
11.3% (Third Quarter)
Electricity:
* ''production:'' 45.7
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
* ''lowest 10%:'' 2.9%
* ''highest 10%:'' 25.4% (25.4)
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
36.6% (2013)
Industrial production growth rate:
11.3% (Third Quarter)
Electricity:
* ''production:'' 45.7 TWh TWH or twh could refer to:
* Tai Dón language, a language of Vietnam, Laos, and China
* Tai Wo Hau station, Hong Kong; MTR station code
* Tennessee Walking Horse, a breed of horse
* Toronto Western Hospital, a hospital in Toronto, Canada
* Tun ...
(2006)
* ''consumption:'' 37.4 TWh (2006)
* ''exports:'' 7.8 TWh (2006)
* ''imports:'' 0 TWh (2006)
Electricity - production by source:
* ''fossil fuel:'' 47.8%
* ''hydro:'' 8.1%
* ''nuclear:'' 44.1%
* ''other:'' 0% (2001)
Oil:
* ''production:'' 3,000 bbl/day (2005 est.)
* ''consumption:'' 131,400 bbl/day (2005 est.)
* ''exports:'' 51,000 (2005 est.)
* ''imports:'' 138,800 (2004 est.)
* ''proved reserves:'' 15 million bbl (1 January 2006)
Natural gas:
* ''production:'' 407,000 cu m (2005 est.)
* ''consumption:'' 5.179 billion cu m (2005 est.)
* ''exports:'' 0 cu m (2005 est.)
* ''imports:'' 5.8 billion cu m (2005)
* ''proved reserves:'' 5.703 billion cu m (1 January 2006 est.)
Agriculture - products:
vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, ...
s, fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
s, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
, wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
, sunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a large annual forb of the genus ''Helianthus'' grown as a crop for its edible oily seeds. Apart from cooking oil production, it is also used as livestock forage (as a meal or a silage plant), as ...
s, sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together wi ...
s
Current account balance:
$ -5.01 billion (2006 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange & gold:
$11.78 billion (2006 est.)
Exchange rates:
Sectors
Industry and construction
Much of Bulgaria's communist-era industry was heavy industry, although biochemicals and computers were significant products beginning in the 1980s. Because Bulgarian industry was configured to Soviet markets, the end of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact caused a severe crisis in the 1990s. After showing its first growth since the communist era in 2000, Bulgaria's industrial sector has grown slowly but steadily in the early 2000s. The performance of individual manufacturing industries has been uneven, however. Food processing and tobacco processing suffered from the loss of Soviet markets and have not maintained standards high enough to compete in Western Europe. Textile processing generally has declined since the mid-1990s, although clothing exports have grown steadily since 2000. Oil refining survived the shocks of the 1990s because of a continuing export market and the purchase of the Burgas refinery by the Russian oil giant LUKoil. The chemical industry has remained in good overall condition but is subject to fluctuating natural gas prices. Growth in ferrous metallurgy, which is dominated by the Kremikovtsi Metals Combine, has been delayed by a complex privatization process and by obsolete capital equipment. Non-ferrous metallurgy has prospered because the Pirdop copper smelting plant was bought by Union Minière of Belgium and because export markets have been favourable. The end of the Warsaw Pact alliance and the loss of Third World markets were grave blows to the defence industry. In the early 2000s, the industry's plan for survival has included upgrading products to satisfy Western markets and doing cooperative manufacturing with Russian companies. The electronics industry, which also was configured in the 1980s to serve Soviet markets, has not been able to compete with Western computer manufacturers. The industry now relies on contract agreements with European firms and attracting foreign investment. The automotive industry has ceased the manufacture of cars, trucks, and buses. Manufacture of forklifts, a speciality in the communist era, also has stopped. In the early 2000s, shipbuilding has prospered at the major Varna and Ruse yards because of foreign ownership (Ruse) and privatization (Varna). Only in recent years electronics and electric equipment production has regained higher levels. The largest centres includeSofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
, Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
and the surrounding area, Botevgrad
Botevgrad ( bg, Ботевград ) is a town in western Bulgaria. It is located in Sofia Province and is close to Pravets. Botevgrad lies 47 km from Sofia.
History and name
The village was called Samundzhievo (Самунджиево) until ...
, Stara Zagora
Stara Zagora ( bg, Стара Загора, ) is the sixth-largest city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of the homonymous Stara Zagora Province.
Name
The name comes from the Slavic root ''star'' ("old") and the name of the medieva ...
, Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
, Pravets
Pravets or Pravetz ( bg, Правец, also transliterated as Pravec, ) is a town in Pravets Municipality in central western Bulgaria, located approximately from the capital Sofia. Pravets is home town of Pravetz computers.
Pravets has a populat ...
and many other cities. Household appliance
A home appliance, also referred to as a domestic appliance, an electric appliance or a household appliance, is a machine which assists in household functions such as cooking, cleaning and food preservation.
Appliances are divided into three ...
s, computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s, CDs, telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
s, medical
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
and scientific equipment are being produced. In 2008 the electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
industry shipped more than $260 million in exports, primarily of components, computers and consumer electronics.
Many factories producing transportation equipment still do not operate at full capacity. Plants produce trains (Burgas
Burgas ( bg, Бургас, ), sometimes transliterated as ''Bourgas'', is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the fourth-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, and Varna, with a popu ...
, Dryanovo
Dryanovo ( bg, Дряново, ) is a Bulgarian town situated at the northern foot of the Balkan Mountains in Gabrovo Province; amphitheatrically along the two banks of Dryanovo River, a tributary to the Yantra River. The town is a centre of the ...
), trams (Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
), trolleys (Dupnitsa
Dupnitsa, or Dupnica ( bg, Дупница (previously ), ), is a town in Western Bulgaria. It is at the foot of the highest mountains in the Balkan Peninsula – the Rila Mountains, and about south of the capital Sofia. Dupnitsa is the second la ...
), buses (Botevgrad
Botevgrad ( bg, Ботевград ) is a town in western Bulgaria. It is located in Sofia Province and is close to Pravets. Botevgrad lies 47 km from Sofia.
History and name
The village was called Samundzhievo (Самунджиево) until ...
), trucks (Shumen
Shumen ( bg, Шумен, also romanized as ''Shoumen'' or ''Šumen'', ) is the tenth largest city in Bulgaria and the administrative and economic capital of Shumen Province.
Etymology
The city was first mentioned as ''Šimeonis'' in 1153 by t ...
), motor trucks (Plovdiv, Lom, Sofia, Lovech). Lovech has an automotive assembly plant. Rousse
Ruse (also transliterated as Rousse, Russe; bg, Русе ) is the fifth largest city in Bulgaria. Ruse is in the northeastern part of the country, on the right bank of the Danube, opposite the Romanian city of Giurgiu, approximately south of ...
serves as the main centre for agricultural machinery. Bulgarian arms production mainly operates in central Bulgaria (Kazanlak
Kazanlak ( bg, Казанлък , Thracian and Greek Σευθόπολις (''Seuthopolis''), tr, Kazanlık) is a Bulgarian town in Stara Zagora Province, located in the middle of the plain of the same name, at the foot of the Balkan mountai ...
, Sopot
Sopot is a seaside resort city in Pomerelia on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland, with a population of approximately 40,000. It is located in Pomeranian Voivodeship, and has the status of the county, being the smallest ci ...
, Karlovo
Karlovo ( bg, Карлово ) is a historically important town in central Bulgaria located in a fertile valley along the river Stryama at the southern foot of the Balkan Mountains. It is administratively part of Plovdiv Province and has a p ...
).
Construction output fell dramatically in the 1990s as industrial and housing construction declined, but a recovery began in the early 2000s. The sector, now dominated by private firms, has resumed the foreign building programs that led to prosperity in the communist era. The Glavbolgarstroy firm has major building projects in Kazakhstan, Russia, and Ukraine as well as domestic contracts.Bulgaria country profile, p. 11.
One of the biggest Romanian investments in Bulgaria is in the construction/retail industry, namely the Budmax brand of construction supply stores (owned by Arabesque
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foli ...
).
Energy
 Bulgaria relies on imported oil and natural gas (most of which comes from
Bulgaria relies on imported oil and natural gas (most of which comes from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
), together with domestic generation of electricity from coal-powered and hydro plants, and the Kozloduy nuclear plant. Bulgaria imports 97% of its natural gas from Russia. The economy remains energy-intensive because conservation practices have developed slowly. The country is a major regional electricity producer. Bulgaria produced 38.07 billion kWh of electricity in 2006
Photius.comElectricity production as of 2006
(in comparison,
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, which has a population nearly three times larger than Bulgaria, produced 51.7 billion kW·h in the same year). The domestic power-generating industry, which was privatized in 2004 by sales to interests from Europe, Japan, Russia, and the United States, suffers from obsolete equipment and a weak oversight agency. To solve the latter problem, in 2008 the government set up a state-owned energy holding-company (Bulgarian Energy Holding EAD Bulgarian Energy Holding EAD (BEH EAD) is a state owned energy holding company in Bulgaria. It was incorporated on 18 September 2008 after renaming Bulgargaz Holding EAD.
In November 2009, the Bulgarian Government decided to list the company at t ...
), composed of gas company Bulgargaz
Bulgargaz is the largest Bulgarian natural gas distribution company. It is a subsidiary of Bulgarian Energy Holding EAD,
a holding company established on 18 September 2008. As of November 2009 the company is listed on the Bulgarian Stock Excha ...
, Bulgartransgaz
Bulgartransgaz EAD is a natural gas transmission and storage system operator of Bulgaria. It is a subsidiary of Bulgarian Energy Holding EAD.
Bulgartransgaz was created on 15 January 2007 in Sofia. In November 2009, the Bulgarian Government de ...
, power company NEK EAD
Natsionalna Elektricheska Kompania EAD (NEK) ( bg, Национална електрическа компания ЕАД ; en, National Electricity Company) is a single-owned joint-stock electric company headquartered in Sofia, Bulgaria. Bulgarian ...
, Electricity System Operator EAD, Kozloduy nuclear power station, Maritza-Iztok II thermal power station, the Mini Maritza Iztok (Maritza Iztok mines), and Bulgartel EAD. The state holds a 100% stake in the holding company. Most of Bulgaria's conventional power stations will require large-scale modernization in the near future. Bulgaria has some 64 small hydroelectric plants, which together produce 19 percent of the country's power output.
The Kozloduy nuclear plant, which in 2005 supplied more than 40 percent of Bulgaria's electric power, will play a diminishing role because two of its remaining four reactors (two were closed in 2002) must be closed by 2007 to comply with European Union (EU) standards. Kozloduy, which exported 14 percent of its output in 2006, was expected to cease all exportation in 2007. Construction of the long-delayed Belene nuclear plant resumed in 2006 although the project was canceled in 2012. Despite that there were attempts to restart the project. Belene, planned in the 1980s but then rejected, was revived by the safety controversy at Kozloduy.
Oil exploration is ongoing offshore in the Black Sea (the Shabla block) and on the Romanian border, but Bulgaria's chief oil income is likely to come as a transfer point on east–west and north–south transit lines. Burgas is Bulgaria's main oil port on the Black Sea. Bulgaria's largest oil refinery, Neftochim, was purchased by Russian oil giant LUKoil in 1999 and underwent modernization in 2005. Bulgaria's only significant coal resource is low-quality lignite, mainly from the state-owned Maritsa-Iztok and Bobov Dol complexes and used in local thermoelectric power stations.
Thermal power station
A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a stea ...
s (TPPs) provide a significant amount of energy, with most of the capacity concentrated in the Maritsa Iztok Complex
The Maritsa Iztok Complex is the largest energy complex in South Eastern Europe. It is located in Stara Zagora Province, south-central Bulgaria. It consists of three lignite-fired thermal power stations. The complex is located in a large lig ...
. The largest TPPs include:
* "Maritsa Iztok 2" - 1,450 MW
* "Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
" - 1,260 MW
* "Maritsa Iztok 3" - 870 MW
* "Bobov Dol
Bobov Dol ( bg, Бобов дол ; also Bobovdol) is a town in Bobov Dol Municipality, Kyustendil Province, southwestern Bulgaria. Bobov Dol lies near the geographic centre of the Balkan Peninsula and is known for its coal mines and thermal powe ...
" - 630 MW
* " Ruse Iztok" - 600 MW
* "Maritsa Iztok 1/ TETS Galabovo" - 650 MW
A$1.4 bln. project for the construction of an additional block for the Maritza Iztok 1 Thermal Power Station was completed on 3 June 2011.
Bulgaria ranks as a minor oil producer (97th in the world) with a total production of 3,520 bbl/day.
Prospectors discovered Bulgaria's first oil field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence ...
near Tyulenovo in 1951. Proved reserves
Proven reserves (also called measured reserves, 1P, and reserves) is a measure of fossil fuel energy reserves, such as oil reserves, natural gas reserves, and coal reserves. It is defined as the " antity of energy sources estimated with reasona ...
amount to .
Natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
production halted in the late 1990s. Proved reserves of natural gas amount to 5.663 bln. cu m. The LUKOIL Neftochim oil refinery is Bulgaria's largest refining facility with annual revenues amounting to more than 4 billion leva (2 billion euro).
have seen a steady increase in electricity production from renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. Wind energy has large-scale prospects, with up to 3,400 MW of installed capacity potential. Bulgaria operates more than 70 wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s with a total capacity of 112.6 MW, and plans to increase their number nearly threefold to reach a total capacity of 300 MW in 2010.
From 2010 to 2017, the import of waste for energy production increased for almost five times. Since 2014, the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body o ...
financed the installation of a plant for cogeneration
Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.
Cogeneration is a more efficient use of fuel or heat, because otherwise- wasted heat from elect ...
of heat and electricity from refuse-derived fuel
Refuse-derived fuel (RDF) is a fuel produced from various types of waste such as municipal solid waste (MSW), industrial waste or commercial waste.
The World Business Council for Sustainable Development provides a definition:
''"Selected wast ...
to be located in Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
. In 2017, the Bulgaria's Ministry of Environment and Waters reported to the Basel convention
The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal, usually known as the Basel Convention, is an international treaty that was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations ...
that Bulgaria had imported "69,683 tonnes of waste for incineration in a form of RDF, SRF, pretreated mixed waste and mixed contaminated plastics."
As of March 2021, the total amount of tons of waste annually imported is substantially unknown.
Services and tourism
Although the contribution of services to gross domestic product (GDP) has more than doubled in the post-communist era, a substantial share of that growth has been in government services, and the qualitative level of services varies greatly. The Bulgarian banking system, which was weak in the first post-communist years, was fully reformed in the late 1990s, including stronger oversight from the National Bank of Bulgaria and gradual privatisation. In 2003 the banking system was fully privatised, and substantial consolidation began making the system more efficient in 2004. Several smaller banks grew substantially between 2004 and 2006. These processes increased public confidence in the banks. Although the system still requires consolidation, loan activity to individuals and businesses increased in the early 2000s. The insurance industry has grown rapidly since a market reform in 1997, with the help of foreign firms. An example is the Bulgarian Insurance Group (BIG), a pension-fund and insurance management company owned by the Dutch-Israeli TBI Holding Company and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD). The introduction of health and pension insurance plans has expanded the private insurance industry. A series of reform laws in the early 2000s enabled the Bulgarian Stock Exchange to begin regular operation. As of 2005, stock market activity was limited by lack of transparency, although the growth rate increased beginning in 2004. After a decline in the 1990s, in the 21st century the tourism industry has grown rapidly. In 2016 some 10 million foreigners visited Bulgaria, up from 4 million in 2004 and 2.3 million in 2000. This trend is based on a number of attractive destinations, low costs, and restoration of facilities. Most of the industry had been privatised by 2004. Infrastructure items such as recreation facilities and booking services require improvement. Development of Bulgaria's retail sales sector was slow until the early 2000s, when a large number of Western-style outlets began to appear, and Sofia developed as a retail center. By 2006, several major European retail chains had opened stores, and others planned to enter the Bulgarian market.Bulgaria country profile, p. 12. Bulgaria has attracted considerable investment from foreigners buying property either for their own use or for investment. In 2006, more than 29% of property deals were signed by foreigners, more than half of whom were British citizens. Various companies, such as Bulgarian Dreams, actively marketed Bulgarian properties to buyers overseas. In 2007 Bulgaria was visited by 5,200,000 tourists, ranking 39th in the world. Tourists from Greece, Romania and Germany account for 40% of visitors. Significant numbers ofBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
(+300,000), Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
(+200,000), Serbian (+150,000), Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
(+130,000) and Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
(+100,000) tourists also visit Bulgaria. Most of them are attracted by the varying and beautiful landscapes, well-preserved historical and cultural heritage, and the tranquility of rural and mountain areas.
In Easter of 2018 it was reported that around 90% of tourists in Varna, one of Bulgaria's largest tourism locations, came from Romania.
Main destinations include the capital Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
, coastal resorts Sunny Beach, Albena
Albena ( bg, Албена) is a major Black Sea resort in northeastern Bulgaria, Balchik Municipality, situated from Balchik and from Varna. Albena is served by Varna Airport. Since 2005 is considered as a settlement by the National Statistical ...
, Sozopol
Sozopol ( bg, Созопол , el, Σωζόπολη, translit=Sozopoli) is an ancient seaside town located 35 km south of Burgas on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Today it is one of the major seaside resorts in the country, known for th ...
, Sveti Vlas
Sveti Vlas (also known as St. Vlas; bg, Свети Влас; ), is a town and resort on the Black Sea coast in Nesebar municipality, Burgas Province, Bulgaria. In July, 2007 its population was 3,869.
History
The town is located at the foot of th ...
; winter resorts Bansko
Bansko ( bg, Банско ) is a town in southwestern Bulgaria, located at the foot of the Pirin, Pirin Mountains at an elevation of 1200m AMSL, above sea level. It is a ski resort.
Legends
There are several legends about who founded Bansko. Ac ...
, Pamporovo
Pamporovo ( bg, Пампорово, ''pronunciation'': /pam'porovo/) is a popular ski resort in Smolyan Province, southern Bulgaria. It is set amongst Norway spruce forests and is primarily visited during the winter for skiing and snowboarding. It ...
, Chepelare
Chepelare ( bg, Чепеларе ) is the principal town in Chepelare Municipality, part of Smolyan Province in Southern Bulgaria. It is situated in the central part of the Rhodopes, on the banks of Chepelare River. Chepelare is a popular wint ...
and Borovetz
Borovets ( bg, Боровец ), known as Chamkoria ( ) until the middle of the 20th century, is a popular Bulgarian mountain resort situated in Sofia Province, on the northern slopes of Rila, at an altitude of 1350 m. Borovets is located app ...
. Arbanasi and Bozhentsi
Bozhentsi ( bg, Боженци ; also variously transliterated as ''Bozhenci, Bojenci, Bojenzi, Boženci, Bojentsi, Bojentzi, Bozhentzi'', etc.), officially but not commonly Bozhentsite (Боженците), is a village and architectural reserve ...
are rural tourist destinations with well-preserved ethnographic traditions. Other popular attractions are the 10th century Rila Monastery
The Monastery of Saint John of Rila, also known as Rila Monastery "Sveti Ivan Rilski" ( bg, Рилски манастир „Свети Иван Рилски“), is the largest and most famous Eastern Orthodox monastery in Bulgaria. It is situate ...
and the 19th century Euxinograd
Euxinograd ( bg, Евксиноград , also transliterated as ''Evksinograd'') is a late 19th-century Bulgarian former royal summer palace and park on the Black Sea coast, north of downtown Varna. The palace is currently a governmental and ...
château
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions.
Nowaday ...
.
Agriculture, forestry, and fishing
In the communist era, Bulgaria's agriculture was heavily centralized, integrated with agriculture-related industries, and state-run. In the postcommunist era, the process of restoring agricultural land to private owners has been in a form that ensures productivity has been slow. Bank investment and insecurity in the land market contributed to slow development in the 1990s. By 2004 some 98 percent of the workforce and output of Bulgaria's agricultural sector was private, including a number of large private cooperative enterprises. A significant amount of food also is produced for direct consumption by non-farmers on small plots, which are an important support for parts of the population. In 2000 and 2003, droughts limited agricultural production, and floods had the same effect in 2005. Bulgaria's main field crops are wheat, corn, and barley. The main industrial crops are sugar beets, sunflowers, and tobacco. Tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers are the most important vegetable exports. Production of apples and grapes, Bulgaria's largest fruit products, has decreased since the communist era, but the export of wine has increased significantly. The most important types of livestock are cattle, sheep, poultry, pigs, and buffaloes, and the main dairy products are yogurt, cow and sheep cheese.Bulgaria country profile, p. 9. Bulgaria is the world's 13th largestsheep milk
Sheep's milk (or ewes' milk) is the milk of domestic sheep. It is commonly used to make cultured dairy products such as cheese. Some of the most popular sheep cheeses include feta (Greece), ricotta (Italy), and Roquefort (France).
Sheep breeds
S ...
producer and is the 15th largest producer of tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
and 13th largest producer of raspberries
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with ...
in Europe. Specialized equipment amounts to some 25,000 tractor
A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a trailer or machinery such as that used in agriculture, mining or construction. Most common ...
s and 5,500 combine harvester
The modern combine harvester, or simply combine, is a versatile machine designed to efficiently harvest a variety of grain crops. The name derives from its combining four separate harvesting operations—reaping, threshing, gathering, and winnow ...
s, with a fleet of light aircraft.
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
) in 2006 (in '000 tons) amounted to: wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
3301.9; sunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a large annual forb of the genus ''Helianthus'' grown as a crop for its edible oily seeds. Apart from cooking oil production, it is also used as livestock forage (as a meal or a silage plant), as ...
1196.6; maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
1587.8; grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
s 266.2; tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
42.0; tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
es 213.0; barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
546.3; potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es 386.1; peppers
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
156.7; cucumber
Cucumber (''Cucumis sativus'') is a widely-cultivated Vine#Horticultural climbing plants, creeping vine plant in the Cucurbitaceae family that bears usually cylindrical Fruit, fruits, which are used as culinary vegetables.
s 61.5; cherries 18.2; watermelon
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 varieti ...
s 136.0; cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B.&nb ...
72.7; apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
s 26.1; plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
s 18.0; strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
8.8.
Mining and minerals
Bulgaria's mining industry has declined in the post-communist era. Many deposits have remained underdeveloped because of a lack of modern equipment and low funding. Mining has contributed less than 2 percent of GDP and engaged less than 3 percent of the workforce in the early 2000s. Bulgaria has the following estimated deposits of metallic minerals: 207 million tons of iron ore, 127 million tons of manganese ore, 936 million tons of copper ore, 238 million tons of chromium ore, and 150 million tons of gold ore. Several of Bulgaria's minerals are extracted commercially; 80 percent of mining is done by open-pit excavation. Iron extraction at Kremikovtsi and elsewhere is not sufficient to support the domestic steel industry, but copper, lead, and zinc deposits fully supply the nonferrous metallurgy industries. A British firm has exploratory gold mines at Dikanyite and Gornoseltsi, and a domestic copper and gold mine operates at Chelopech. About 50 nonmetallic minerals are present in significant amounts. Substantial amounts of uranium are present in the Rhodope Mountains, but no extraction has occurred in the last 10 years. Despite the poor performance of the mining sector, productivity has increased in recent years. Mining remains one of the most important sources of export earnings and is still a significant contributor to economic growth. The mining industry is worth $760 mln, and, along with related industries, employs 120,000 people. The rising global prices ofgold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, lead and copper in 2010, as well as investments in zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and coal production, have boosted economic growth in the mining sector after the Financial crisis of 2007–2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fi ...
. As of 2010 Bulgaria ranks as the 19th largest coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
producer in the world, 9th largest bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental ...
producer, 19th largest copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
producer, and the 26th largest zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
producer. In Europe, the country ranks fourth in gold production and sixth in coal production.
The "Elatsite" copper mine and reprocessing facility, built during Vulko Chervenkov
Valko Velyov Chervenkov ...
's rule, takes its place as one of the largest in South-Eastern Europe. It extracts 13 million tonnes of ore annually, producing about 42,000 tonnes of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, 1.6 tonnes of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
and 5.5 tonnes of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
.
Ferrous metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
has major importance. Much of the production of steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
and pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silic ...
takes place in Kremikovtsi
Kremikovtsi ( bg, Кремиковци ) is an industrial district of Sofia, Bulgaria. It is located to the northeast of the capital. The Kremikovtsi Steel Complex which is close to the neighbourhood is one of the largest industrial enterprises i ...
and Stomana steel in Pernik
Pernik ( bg, Перник ) is a town in western Bulgaria (about south-west of Sofia) with a population of 70,285 . Pernik is the most populated town in western Bulgaria after Sofia. It is the main town of Pernik Province and lies on both bank ...
, with a third metallurgical base in Debelt
Debelt (Bulgarian: Дебелт) is a village in Burgas Province in southeastern Bulgaria. It is located in the municipality of Sredets.
History
Debelt is located near the ruins of the city of Develtos. During the Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829, ...
. In production of steel and steel products per capita the country heads the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. the fate of Kremikovtsi steel factories has come under debate because of serious pollution in the capital, Sofia.
The largest refineries for lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
operate in Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
, Kardzhali
Kardzhali ( bg, Кърджали , ''Kărdžali''; tr, Kırcaali; gr, Κάρτζαλι, ''Kártzali''), sometimes spelt Kardžali or Kurdzhali, is a town in the Eastern Rhodopes in Bulgaria, centre of Kardzhali Municipality and Kardzhali Provi ...
and Novi Iskar
Novi Iskar ( bg, Нови Искър ) is a town in Western Bulgaria, located in Sofia City Province, which is a part of the Municipality of Sofia (the capital of Bulgaria).
It is often regarded as a northern suburb of Bulgarian capital Sofia and ...
; for copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
in Pirdop
Pirdop ( bg, Пирдоп ) is a town located in South-West Bulgaria in Pirdop Municipality of Sofia Province in the southeastern part of the Zlatitsa - Pirdop Valley at 670 m above sea level. It is surrounded by the Balkan Range (also known as t ...
and Eliseina (now defunct); for aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
in Shumen
Shumen ( bg, Шумен, also romanized as ''Shoumen'' or ''Šumen'', ) is the tenth largest city in Bulgaria and the administrative and economic capital of Shumen Province.
Etymology
The city was first mentioned as ''Šimeonis'' in 1153 by t ...
. In production of many metals ''per capita'', such as zinc and iron, Bulgaria ranks first in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
.
Infrastructure
motorways in Bulgaria
Highways in Bulgaria are dual carriageways, grade separated with controlled-access, designed for high speeds. In 2012, legislation amendments defined two types of highways: motorways (, ) and expressways (, ). The main differences are that motorway ...
, such as Trakia, Hemus Hemus may refer to:
* ''Hemus'' (crab), a genus of spider crabs
* Haemus, a Thracian king in Greek mythology
* Haemus Mons, ancient name of the Balkan Mountains (Bulgaria)
* Hemus Air, a Bulgarian airline
* Hemus (publishing house), a Bulgaria ...
, Struma and Maritsa
Maritsa or Maritza ( bg, Марица ), also known as Meriç ( tr, Meriç ) and Evros ( ell, Έβρος ), is a river that runs through the Balkans in Southeast Europe. With a length of , Bulgaria also has of railway track and plans to construct a
 In 2010, Bulgaria spent 0.25% of its GDP on scientific research, which represents one of the lowest scientific budgets in Europe.
Chronic underinvestment in the sector since 1990 forced many scientific professionals to leave the country. As a result, Bulgaria's economy scores low in terms of innovation, competitiveness and high added value exports. Nevertheless, Bulgaria ranked 8th in the world in 2002 by total number of ICT specialists, outperforming countries with far larger populations, and it operates the only supercomputer in the Balkan region, an IBM
In 2010, Bulgaria spent 0.25% of its GDP on scientific research, which represents one of the lowest scientific budgets in Europe.
Chronic underinvestment in the sector since 1990 forced many scientific professionals to leave the country. As a result, Bulgaria's economy scores low in terms of innovation, competitiveness and high added value exports. Nevertheless, Bulgaria ranked 8th in the world in 2002 by total number of ICT specialists, outperforming countries with far larger populations, and it operates the only supercomputer in the Balkan region, an IBM
 In 2005 the labour force was estimated at 3.3 million; in 2004, 11 percent worked in agriculture, 33 percent in industry, and 56 percent in services. The unemployment rate has been in double digits throughout the post-communist era, reaching a high point of 19 percent in 2000. Since then, the rate has decreased substantially with the creation of new jobs in private and state enterprises. In 2005 the official figure was 11.5 percent, compared with 16.9 percent at the end of 2002. However, in 2003 an estimated 500,000 Bulgarians were unemployed but not officially counted because they were not seeking work. In January 2005, the government raised the minimum wage by 25 percent, to US$90 per month. The largest labour unions are Podkrepa (Support) and the Confederation of Independent Trade Unions in Bulgaria. They represent labour in the National Council for Tripartite Partnership, in which they join government and business representatives to discuss issues of labour, social security, and living standards. The unions were an important political force in the fall of the Zhivkov regime. In late autumn of 2016 reported an unemployment rate of 7%. In 2016, the government increased the minimum wage to 215 euros per month. At the end of 2016 the average monthly salary is about 480 euros a month, but there are differences in the regions of the country.
The average monthly gross salary has reached the value of 1,036 leva (530 euro) in March 2017. According to the latest Annual report of the Institute of Economic Studies at the
In 2005 the labour force was estimated at 3.3 million; in 2004, 11 percent worked in agriculture, 33 percent in industry, and 56 percent in services. The unemployment rate has been in double digits throughout the post-communist era, reaching a high point of 19 percent in 2000. Since then, the rate has decreased substantially with the creation of new jobs in private and state enterprises. In 2005 the official figure was 11.5 percent, compared with 16.9 percent at the end of 2002. However, in 2003 an estimated 500,000 Bulgarians were unemployed but not officially counted because they were not seeking work. In January 2005, the government raised the minimum wage by 25 percent, to US$90 per month. The largest labour unions are Podkrepa (Support) and the Confederation of Independent Trade Unions in Bulgaria. They represent labour in the National Council for Tripartite Partnership, in which they join government and business representatives to discuss issues of labour, social security, and living standards. The unions were an important political force in the fall of the Zhivkov regime. In late autumn of 2016 reported an unemployment rate of 7%. In 2016, the government increased the minimum wage to 215 euros per month. At the end of 2016 the average monthly salary is about 480 euros a month, but there are differences in the regions of the country.
The average monthly gross salary has reached the value of 1,036 leva (530 euro) in March 2017. According to the latest Annual report of the Institute of Economic Studies at the
 As of 1 January 2008 the income tax for all citizens is set to a flat rate of 10%. This flat tax is one of the lowest income rates in the world and the lowest income rate in the
As of 1 January 2008 the income tax for all citizens is set to a flat rate of 10%. This flat tax is one of the lowest income rates in the world and the lowest income rate in the
Starting a Business in Bulgaria
 ''This article incorporates public domain, public domain material]
''This article incorporates public domain, public domain material]
Bulgaria country profile
(October 2006) from websites or documents of the Library of Congress Federal Research Division.
CIA World Factbook
{{DEFAULTSORT:Economy of Bulgaria Economy of Bulgaria, European Union member economies, Bulgaria World Trade Organization member economies, Bulgaria Economies of Europe by country, Bulgaria
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
way by 2017, at a cost of €3 bln. Sofia and Plovdiv are major air travel hubs, while Varna and Burgas are the principal maritime trade ports.
Bulgaria has an extensive, but antiquated telecommunications network which requires substantial modernization. Telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
service is available in most villages, and a central digital trunk line connects most regions. Currently there are three active mobile phone operators - A1 Bulgaria
A1 Bulgaria (previously known as Mtel or Mobiltel) is a telecommunications company in Bulgaria ownedy by A1 Telekom Austria Group.
History
A1 Bulgaria was founded in March 1994 but was not launched commercially until September 1995 (as ''Citron'' ...
, Telenor
Telenor ASA ( or ) is a Norwegian majority state-owned multinational telecommunications company headquartered at Fornebu in Bærum, close to Oslo. It is one of the world's largest mobile telecommunications companies with operations worldwide, ...
and Vivacom
Vivacom ( bg, Виваком) is the largest telecommunications company in Bulgaria and a former state-owned incumbent operator. The company is headquartered in the capital city Sofia and employs around 5,900 people, owning a mature distribution ne ...
. Since 2000, a rapid increase in the number of Internet users has occurred – from 430,000 they grew to 1,545,100 in 2004, and 3.4 million (48% penetration rate) in 2010. In 2017, the Internet users in Bulgaria are 4.2 million people (59.8% penetration rate).
Bulgaria had the 3rd fastest Average Broadband Internet Speed in the world, after Romania and South Korea, in 2011.
In 2017, Bulgaria ranks 27th in the world in the Mean Download Speed chart with 17.54 Mbit/s, ranks 31st in the world in the Average Monthly Broadband Cost chart with $28.81, and holds the 18th position in the world in the Speed/Cost Ratio with as much as 0.61.
Science and technology
 In 2010, Bulgaria spent 0.25% of its GDP on scientific research, which represents one of the lowest scientific budgets in Europe.
Chronic underinvestment in the sector since 1990 forced many scientific professionals to leave the country. As a result, Bulgaria's economy scores low in terms of innovation, competitiveness and high added value exports. Nevertheless, Bulgaria ranked 8th in the world in 2002 by total number of ICT specialists, outperforming countries with far larger populations, and it operates the only supercomputer in the Balkan region, an IBM
In 2010, Bulgaria spent 0.25% of its GDP on scientific research, which represents one of the lowest scientific budgets in Europe.
Chronic underinvestment in the sector since 1990 forced many scientific professionals to leave the country. As a result, Bulgaria's economy scores low in terms of innovation, competitiveness and high added value exports. Nevertheless, Bulgaria ranked 8th in the world in 2002 by total number of ICT specialists, outperforming countries with far larger populations, and it operates the only supercomputer in the Balkan region, an IBM Blue Gene
Blue Gene is an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with low power consumption.
The project created three generations of supercomputers, Blue Gene/L, Blue Gene/P, ...
/P, which entered service in September 2008.
The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences
The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (abbreviated BAS; bg, Българска академия на науките, ''Balgarska akademiya na naukite'', abbreviated ''БАН'') is the National Academy of Bulgaria, established in 1869.
The Academy ...
(BAS) is the leading scientific institution in the country and employs most of Bulgaria's researchers in its numerous branches. The principal areas of research and development are energy, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal o ...
, archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
and medicine.
With major-general
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Georgi Ivanov flying on Soyuz 33
Soyuz 33 (russian: Союз 33, ''Union 33'') was an April, 1979, Soviet crewed space flight to the Salyut 6 space station.The mission report is available here: http://www.spacefacts.de/mission/english/soyuz-33.htm It was the ninth mission to the ...
in 1979, Bulgaria became the 6th country in the world to have an astronaut in space. Bulgaria has deployed its own experiments on various missions, such as the RADOM-7 RADOM is a Bulgarian Liulin-type instruments-type spectrometry-dosimetry instrument, designed to precisely measure cosmic radiation around the Moon. It is installed on the Indian satellite Chandrayaan-1. Another three instruments were deployed on ...
dosimeters on the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ...
and Chandrayaan-1
Chandrayaan-1 (, ) was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program. It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008, and operated until August 2009. The mission included a lunar orbiter and an impact ...
and the space greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
(a Bulgarian invention) on the Mir space station
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to&n ...
. In 2011 the government announced plans to reboot the space program by producing a new microsatellite and joining the European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
.
From June 2017, Bulgaria will have its first geostationary
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude ...
communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
. BulgariaSat-1
BulgariaSat-1 is a geostationary communications satellite operated by Bulgaria Sat and manufactured by SSL. The satellite will provide high definition and ultra-high-definition television, very-small-aperture terminal (VSAT) communications, sate ...
is a geostationary communications satellite operated by Bulgaria Sat and manufactured by SSL, based on the space-proven SSL 1300
The SSL 1300, previously the LS-1300 and the FS-1300, is a satellite bus produced by Maxar Technologies. Total broadcast power ranges from 5 to 25 kW, and the platform can accommodate from 12 to 150 transponders. The SSL 1300 is a modular platf ...
satellite platform.
BulgariaSat-1 is the first in the history of the country geostationary communications satellite at the Bulgarian orbital position and it is designed to provide Direct-to-Home (DTH) television service and data communications services to the Balkans and other European regions.
In this way, Bulgaria will be among other European countries with their satellites, namely Belarus, France, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, Norway, Russia, Spain, Sweden, Turkey and the United Kingdom.
Due to its large-scale computing technology exports to COMECON
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (, ; English abbreviation COMECON, CMEA, CEMA, or CAME) was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc along wi ...
states, in the 1980s Bulgaria became known as the Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo County ...
of the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
.
Labour
Bulgarian Academy of Sciences
The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (abbreviated BAS; bg, Българска академия на науките, ''Balgarska akademiya na naukite'', abbreviated ''БАН'') is the National Academy of Bulgaria, established in 1869.
The Academy ...
, the average salary in Bulgaria is only a quarter (1/4) of the average salary in the EU, and should be two times higher when the labour productivity is calculated in the formula.
Currency and inflation
Bulgaria's unit of currency is thelev
Lev may refer to:
Common uses
*Bulgarian lev, the currency of Bulgaria
*an abbreviation for Leviticus, the third book of the Hebrew Bible and the Torah
People and fictional characters
*Lev (given name)
*Lev (surname)
Places
*Lev, Azerbaijan, a ...
(pl., leva). In October 2006, the U.S. dollar was worth 1.57 leva. In 1999 the value of the lev was pegged to that of the German Deutschmark
The Deutsche Mark (; English: ''German mark''), abbreviated "DM" or "D-Mark" (), was the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later the unified Germany from 1990 until the adoption of the euro in 2002. In English, it was ...
, which was replaced by the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
in 2001. Following Bulgaria's admission to the EU, the lev is scheduled to be replaced by the euro.Bulgaria country profile, p. 14.
In 2003 Bulgaria's inflation rate was estimated at between 2.3 and 3 percent. The rate was 6 percent in 2004 and 5 percent in 2005. In 2015 and 2016 it was recorded minimum level of deflation.
Taxation, state budget and debt
 As of 1 January 2008 the income tax for all citizens is set to a flat rate of 10%. This flat tax is one of the lowest income rates in the world and the lowest income rate in the
As of 1 January 2008 the income tax for all citizens is set to a flat rate of 10%. This flat tax is one of the lowest income rates in the world and the lowest income rate in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
. The reform was done in pursue for higher GDP growth and greater tax collection rates. Some called it a "revolution" in taxation, but the changes were met with mild discussions and some protests by affected working classes. The proposal was modified to allow for compensating the perceived losers from the changes in the tax formula. The corporate income tax is also 10% as of 1 January 2007 which is also among the lowest in Europe. Currently this taxation is kept while other countries raised their taxes during the crisis. However, most of the state revenues come from Value-added tax, VAT and excises, but share of income and corporate taxes in the revenues is increasing.
For 2005 Bulgaria's estimated state revenues totaled US$11.2 billion, and its estimated state expenditures, including capital expenditures, were US$10.9 billion, yielding a surplus of US$300 million. In 2004 revenues totaled US$10.1 billion and expenditures US$9.7 billion, for a surplus of US$400 million.
After the political changes, in 1991, Bulgaria had a US$11.25 billion state debt, which represented 180% of the GDP. The state debt peaked in 1994, when it reached US$14.4 billion. During 1998-2008 Bulgaria maintained policy of Government budget balance, budget surpluses, which reduced the state debt to 5.07 billion euro. Combined with the economic growth in that period, the state debt dropped to a record low of 13.7% of GDP, one of the lowest in the European Union. In 2008 Bulgaria also maintained 4.286 billion euro fiscal reserve, meaning that net state debt at this moment was only 0.784 billion euro. After the Financial crisis of 2007–08, 2008 financial crisis Bulgaria turned to policy of Deficit spending, budget deficits and at the end of 2013 the state debt rose up to 7.219 billion euro, representing 18.1% of the GDP. In 2015, the debt rate increased further to 26.7% of the GDP, still remaining the third lowest in EU after Estonia and Luxembourg. Part of the increase was driven by the collapse of Corporate Commercial Bank in 2014, the fourth largest bank in the country, and the subsequent paying out of Deposit insurance, guaranteed deposits.
Foreign economic relations
In the 1990s, Bulgaria moved gradually away from dependence on markets in the former Soviet sphere, increasing its exports to the European Union (EU). In 1999 Bulgaria joined the Central European Free-Trade Agreement (CEFTA), with whose members (Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia; Macedonia was added in 2006) it has established important trade relations. The admission of all but Croatia and Romania to the EU in 2004 reduced the significance of CEFTA trade, however. In 2004 some 54 percent of Bulgaria's import trade and 58 percent of its export trade was with EU member countries. Bulgaria has bilateral free-trade agreements with Albania, Croatia, Estonia, Israel, Latvia, Lithuania, Macedonia, Moldova, and Turkey. In the early 2000s, hydrocarbon fuels remained an important import, although beginning in the late 1990s those commodities' share of total imports decreased significantly, from 29 percent in 1996 to 13 percent in 2004. During that period, the diversification of imported products improved as the volume of machinery and equipment, consumer products, and automobiles increased. A large percentage of imports is accounted for by raw materials such as cloth, metal ore, and petroleum, which are processed and re-exported. The most important imports in 2005 were machinery and equipment, metals and ores, chemicals and plastics, fuels, and minerals. The major sources of imports, in order of volume, were Germany, Russia, Italy, Turkey, and Greece. In 2005 Bulgaria's largest export markets, in order of volume, were Italy, Germany, Turkey, Greece, and Belgium. The most important export commodities were clothing, footwear, iron and steel, machinery and equipment, and fuels. In 2005 Bulgaria's exports totaled US$11.7 billion and its imports totaled US$15.9 billion, incurring a trade deficit of US$4.2 billion. The trade deficit is especially severe with Russia, where markets for Bulgarian goods have shrunk drastically in the early 2000s. In the first half of 2006, Bulgaria had a current account deficit of US$2.3 billion, a substantial increase over the deficit for the same period of 2005, which was some US$1.4 billion. Its trade deficit was US$2.78 billion, foreign direct investment totaled US$1.8 billion, and the financial account balance was US$2.29 billion. In mid-2006 the overall balance of payments was US$883 million, compared with US$755 million for the same period of 2005.Bulgaria country profile, p. 13. Bulgaria's large foreign debt has been an economic burden throughout the postcommunist era. At the end of 2005, Bulgaria reported an external debt of US$15.2 billion, an increase in value but a decrease as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) compared with 2002 and previous years. As a percentage of GDP, the external debt remained constant between 2004 and 2005. Beginning in the late 1990s, investment from the West and from Russia has contributed significantly to recovery from the economic crisis of 1996–97, but the rate of investment has remained lower than that in other countries of Eastern Europe. In 2003 the largest national sources of foreign direct investment, in order of volume, were Austria, Greece, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. In 1997 the Belgian Solve company bought the Deny Soda Combine, and in 1999 LUKoil of Russia bought the Neftochim Oil Refinery at Burgas. Union Minière, a Belgian mining company, bought the large Pirdop copper-smelting plant, giving an important boost to Bulgarian nonferrous metallurgy. A number of foreign companies have invested in the chemical fertilizer and food-processing industries in the early 2000s, China invested in the Bulgarian electronics industry. Some cooperative agreements have been made for manufacture of vehicle components. Daimler-Chrysler of Germany has a contract to update Bulgaria's military transport vehicles between 2003 and 2015. The French Eurocopter company has a bilateral protocol involving a variety of machinery, computer software, and other industrial products. In 2004 Bulgarian oil reserves attracted interest from Melrose Resources of Edinburgh. Russia's natural gas giant, Gazprom, has pledged investment in Bulgaria's natural gas infrastructure in exchange for increased purchase of its product. A three-company Israeli consortium agreed in 2004 to work with the domestic Overgas company (which is half-owned by Gazprom) on a major natural-gas distribution network in Bulgaria. In 2005 three European consortia submitted bids for construction of the Belene nuclear power plant. One such investor is the Italian ENEL energy consortium, which also owns the Maritsa–Iztok–3 thermal power plant. In 2006 Russia's Gazprom company bid against several European energy companies for ownership of newly privatized regional heating utilities, and the Austrian Petromaxx Energy Group invested US$120 million in a new oil refinery at Silistra. In December 1996, Bulgaria joined theWorld Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
. In the early 1990s Bulgaria's slow pace of privatization, contradictory government tax and investment policies, and bureaucratic red tape kept foreign investment among the lowest in the region. Total direct foreign investment from 1991 through 1996 was $831 million. In the years since 1997, however, Bulgaria has begun to attract substantial foreign investment. In 2004 alone over 2.72 billion Euro (3.47 billion US dollars) were invested by foreign companies. In 2005 economists observed a slowdown to about 1.8 billion euros (2.3 billion US dollars) in FDI which is attributed mainly to the end of the privatization of the major state owned companies. After joining the EU in 2007 Bulgaria registered a peak in foreign investment of about 6 billion euros.
Miscellaneous data
Bulgarian households with Internet access at home The data on ICT usage in households and by individuals are based on an annual sample survey which is part of the European Community Statistical Programme. The methodology and the statistical tools are completely harmonized to Eurostat requirements and Regulation No.808/2004 of the European Parliament and the council. The aim of the survey is to collect and disseminate reliable and comparable information on the use of Information and Communication Technologies in households at European level and covers the following subjects: * access to and use of ICT systems by individuals and/or in households; * use of internet for different purposes by individuals and/or in households; * ICT security; * ICT competence; * e-Commerce; * barriers to use of ICT and the internet; * perceived effects of ICT usage on individuals and/or in households.See also
* List of Bulgarian provinces by GDP *Bulgarian National Bank
The Bulgarian National Bank ( bg, Българска народна банка, Bohlgarska narodna banka, ), or BNB, is the central bank of the Republic of Bulgaria. Headquartered in Sofia, the bank was established in 1879. It is the 13th oldest ...
* Bulgarian Stock Exchange
* Economy of Europe
Starting a Business in Bulgaria
References
Bulgaria country profile
(October 2006) from websites or documents of the Library of Congress Federal Research Division.
External links
CIA World Factbook
{{DEFAULTSORT:Economy of Bulgaria Economy of Bulgaria, European Union member economies, Bulgaria World Trade Organization member economies, Bulgaria Economies of Europe by country, Bulgaria