DrGeo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
GNU Dr. Geo is interactive geometry software that allows its users to design & manipulate interactive geometric sketches. It is free software (source code, translations, icons and installer are released under
 A script is a first class object defined along Dr. Geo code. It comes with zero, one or several arguments, from types selected when defining the script. When an instance of a script is plugged in a canvas, the user first selects its arguments in the canvas with mouse clicks, then the position in the canvas of the script output. The script is updated at each canvas computation. Scripts can be used in cascade, with one as the argument of another one.
A script is a first class object defined along Dr. Geo code. It comes with zero, one or several arguments, from types selected when defining the script. When an instance of a script is plugged in a canvas, the user first selects its arguments in the canvas with mouse clicks, then the position in the canvas of the script output. The script is updated at each canvas computation. Scripts can be used in cascade, with one as the argument of another one.
 Script are designed to be used in two different ways:
# To output an object (i.e. a numeric value) and to show its result in the canvas. This result can be used when building subsequent objects (geometric or script).
# To access objects in the canvas: model (MathItem) or view (Costume) for arbitrary uses and modifications. For example to modify the colour of an object given the result to a computation.
From the script, the arguments model are reached with the methods #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the methods #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, the script
Script are designed to be used in two different ways:
# To output an object (i.e. a numeric value) and to show its result in the canvas. This result can be used when building subsequent objects (geometric or script).
# To access objects in the canvas: model (MathItem) or view (Costume) for arbitrary uses and modifications. For example to modify the colour of an object given the result to a computation.
From the script, the arguments model are reached with the methods #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the methods #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, the script
compute
"returns the square of a number"
^ self arg1 valueItem squared
creates a numeric object, whose value is the square of the argument number object. Whenever the first number is changed, the script returned value changes too.
Video demonstration on programmed sketch
/ref>
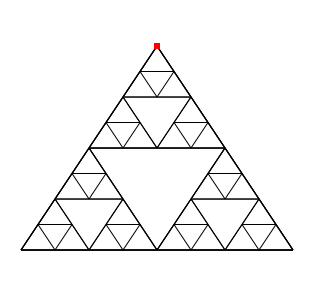
, triangle c ,
c := DrGeoSketch new.
triangle := [].
triangle := [:s1 :s2 :s3 :n ,
c segment: s1 to: s2; segment: s2 to: s3; segment: s3 to: s1.
n >0 ifTrue: [
triangle
value: s1
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s2) hide
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s3) hide
value: n-1.
triangle
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s2) hide
value: s2
value: (c middleOf: s2 and: s3) hide
value: n-1.
triangle
value: (c middleOf: s1 and: s3) hide
value: (c middleOf: s2 and: s3) hide
value: s3
value: n-1.
triangle value: 0@3 value: 4@ -3 value: -4@ -3 value: 3.
(c point: 0@3) show
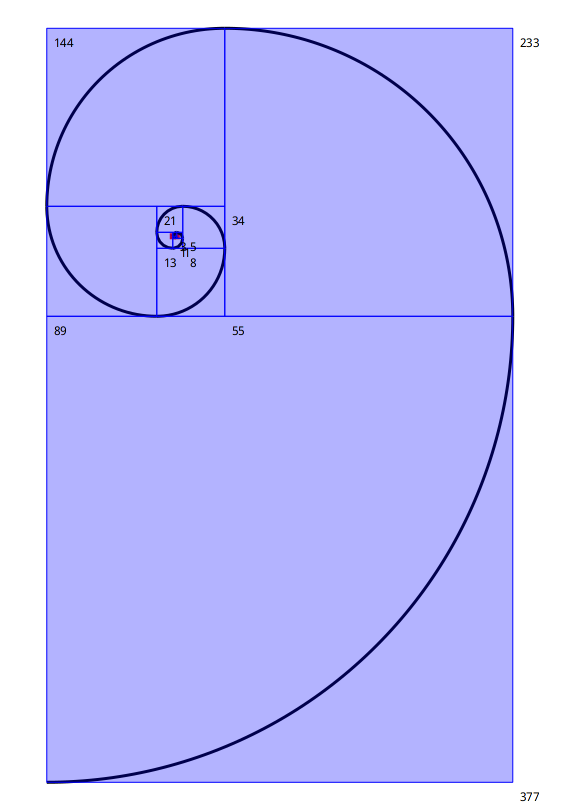
, canvas shape alfa fibo a b m s,
canvas := DrGeoSketch new fullscreen.
alfa := (canvas freeValue: -90 degreesToRadians) hide.
shape := [:c :o :f, , e p ,
e := (canvas rotate: o center: c angle: alfa) hide.
(canvas arcCenter: c from: o to: e) large.
p := canvas translate: e vector: (canvas vector: c to: o) hide.
(canvas polygon: ) name: f.
e].
fibo := [ ].
fibo := [ :f :o :c :k , , e f1 f2 f3 c2,
"f1: term Fn-1, f2: term Fn, o & c: origin and center of spiral arm
e: extremity of the spiral arm"
f1 := f first.
f2 := f second.
f3 := f1 + f2.
e := shape value: c value: o value: f3.
c2 := (canvas scale: c center: e factor: f3 / f2) hide.
k > 0 ifTrue: fibo value: value: e value: c2 value: k - 1 .
a := canvas point: 1@0.
b := canvas point: -1 @0.
m := (canvas middleOf: a and: b) hide.
s := shape value: m value: a value: 1.
shape value: m value: s value: 1.
fibo value: value: b value: a value: 10

, sketch f df xn ptA ptB,
sketch := DrGeoSketch new axesOn.
xn := 2.
f := x cos + x
"Derivate number"
df := (f value: x + 1e-8) - (f value: x) * 1e8
sketch plot: f from: -20 to: 20.
ptA := (sketch point: xn@0) large; name: 'Drag me'.
5 timesRepeat: pt point x @ (f value: pt point x)
parent: ptA.
ptB hide.
(sketch segment: ptA to: ptB) dotted forwardArrow .
ptA := sketch point:
"> x ,
x := pt point x.
x - ( (f value: x) / (df value: x) ) @ 0 parent: ptB.
ptA hide.
(sketch segment: ptB to: ptA) dotted forwardArrow
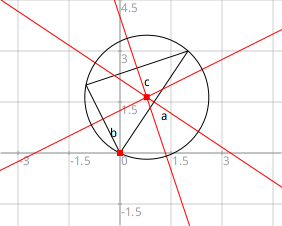
, figure a b c m1 m2,
figure := DrGeoSketch nouveau.
figure pleinEcran; afficherGrille; afficherAxes.
a := figure segmentDe: 2@ 3 a: 0@0.
a nommer: 'a'.
b := figure segmentDe: 0@0 a: -1@2.
b nommer: 'b'.
c := figure segmentDe: -1@2 a: 2@3.
c nommer: 'c'.
m1 := (figure mediatrice: a) couleur: Color red.
m2 := (figure mediatrice: b) couleur: Color red.
(figure mediatrice: c) couleur: Color red.
figure cercleCentre: (figure intersectionDe: m1 et: m2) passantPar: 0@0.
(figure point: 0@0) montrer
ESUG Innovation Technology Awards
(Amsterdam, 2008)
(Paris, 2000)
Official websiteUser guideDownload source code and Windows, Linux and Mac versionsPharo official web site
Educational software for Linux Free educational software Free interactive geometry software
GNU GPL
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general ...
license), created by Hilaire Fernandes, it is part of the GNU
GNU () is an extensive collection of free software
Free software or libre software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any ...
project.
It runs over a Morphic graphic system (which means that it runs on Linux, Mac OS, Windows, Android). Current version of Dr. Geo is also called Dr. Geo II. Historically Dr. Geo was developed in C++ and Dr. Geo II is a complete rewrite using Pharo that happened in 2005. This article refers to the most recent version.
Objects
Dr. Geo manipulates different kinds of objects such as points, lines, circles, block of code.Points
Dr. Geo has several kinds of points: a free point, which can be moved with the mouse (but may be attached to a curve) and a point given by its coordinates. Points can also be created as theintersection
In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another object consisting of everything that is contained in all of the objects simultaneously. For example, in Euclidean geometry, when two lines in a plane are not parallel, thei ...
of 2 curves or as the midpoint
In geometry, the midpoint is the middle point of a line segment. It is equidistant from both endpoints, and it is the centroid both of the segment and of the endpoints. It bisects the segment.
Formula
The midpoint of a segment in ''n''-dimens ...
of a segment.
Lines
Dr. Geo is equipped with the classicline
Line most often refers to:
* Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity
* Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system
Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to:
Art ...
, ray
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (g ...
, segment and vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
.
Other curvilinear objects include circles (defined by 2 points, a center and segment or a radius), arcs (defined by three points or center and angle), polygons (regular or not, defined by end points), and loci
Locus (plural loci) is Latin for "place". It may refer to:
Entertainment
* Locus (comics), a Marvel Comics mutant villainess, a member of the Mutant Liberation Front
* ''Locus'' (magazine), science fiction and fantasy magazine
** '' Locus Award ...
.
Transformations
Besides the parallel and perpendicular line through a point, Dr. Geo can apply to a point or a line one of these transformations: # reflexion # symmetry # translation # rotation # homothetyMacro-construction
Dr. Geo comes with macro-construction: a way to teach Dr. Geo new constructions. It allows to add new objects to Dr. Geo: new transformations likecircle inversion
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is cons ...
, tedious constructions involving a lot of intermediate objects or constructions involving script (also named macro-script).
When some objects, called ''final'' depend on other objects, called ''initial'', it is possible to create a complex construction deducing the final objects from the user-given initial objects. This is a macro-construction, a graph of interdependent objects.
Programming
Access to user programming is at the essence of Dr. Geo: from the software, the user can directly read, study, modify and redistribute modified version of Dr. Geo. Additionally, scripting embedded in sketch is proposed. Dr. Geo source code is Pharo. It is also the language used for user programming: to extend Dr. Geo with arbitrary computing operations (Pharo script) and to define a geometric sketch entirely with programming instructions (Pharo sketch). Dr. Geo is shipped with its source code and the developer tools. Therefore its code can be edited and recompiled from Dr. Geo while it is functioning. This design, inherited from Pharo, makes easy to test new ideas and new designs.Pharo script
 A script is a first class object defined along Dr. Geo code. It comes with zero, one or several arguments, from types selected when defining the script. When an instance of a script is plugged in a canvas, the user first selects its arguments in the canvas with mouse clicks, then the position in the canvas of the script output. The script is updated at each canvas computation. Scripts can be used in cascade, with one as the argument of another one.
A script is a first class object defined along Dr. Geo code. It comes with zero, one or several arguments, from types selected when defining the script. When an instance of a script is plugged in a canvas, the user first selects its arguments in the canvas with mouse clicks, then the position in the canvas of the script output. The script is updated at each canvas computation. Scripts can be used in cascade, with one as the argument of another one.
 Script are designed to be used in two different ways:
# To output an object (i.e. a numeric value) and to show its result in the canvas. This result can be used when building subsequent objects (geometric or script).
# To access objects in the canvas: model (MathItem) or view (Costume) for arbitrary uses and modifications. For example to modify the colour of an object given the result to a computation.
From the script, the arguments model are reached with the methods #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the methods #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, the script
Script are designed to be used in two different ways:
# To output an object (i.e. a numeric value) and to show its result in the canvas. This result can be used when building subsequent objects (geometric or script).
# To access objects in the canvas: model (MathItem) or view (Costume) for arbitrary uses and modifications. For example to modify the colour of an object given the result to a computation.
From the script, the arguments model are reached with the methods #arg1, #arg2, etc. The arguments view are reached with the methods #costume1, #costume2, etc.
The computation of the script is done in its #compute method. For example, to calculate the square of a number, the script
Pharo sketch
Dr. Geo Pharo sketches are sketches entirely defined in the Pharo language. This is not about constructing a sketch with the Dr. Geo graphical interface, but about describing a sketch with the Pharo language. A programming interface with an easy and light syntax is provided./ref>
Sierpinski triangle
Here is how to program a Sierpinski triangle recursively:
Fibonacci spiral
A Fibonacci spiral programmed with geometric transformations (rotation, translation and homothety):
Newton-Raphson algorithm
Pharo sktech can be used to design interactive sketch demonstrating numerical analysis method:
Circumscribed circle in French
A French version of the Pharo sketch API makes possible writing source code in this language:
Awards
ESUG Innovation Technology Awards
(Amsterdam, 2008)
(Paris, 2000)
See also
*Compass-and-straightedge construction
In geometry, straightedge-and-compass construction – also known as ruler-and-compass construction, Euclidean construction, or classical construction – is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an Idealiz ...
* Interactive geometry software
Interactive geometry software (IGS) or dynamic geometry environments (DGEs) are computer programs which allow one to create and then manipulate geometric constructions, primarily in plane geometry. In most IGS, one starts construction by putting a ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Official website
Educational software for Linux Free educational software Free interactive geometry software