Doncaster - The Hub From Friars Gate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Doncaster (, ) is a

The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. It was certainly an In 1248, a charter was granted for Doncaster Market to be held in the area surrounding the Church of St Mary Magdalene, which was built in Norman times. In the 16th century, the church was adapted for use as the
In 1248, a charter was granted for Doncaster Market to be held in the area surrounding the Church of St Mary Magdalene, which was built in Norman times. In the 16th century, the church was adapted for use as the
 Access to the town was restricted and some officeholders secured charters to collect tolls. In 1605, King James I granted to William Levett of Doncaster, brother of York merchant
Access to the town was restricted and some officeholders secured charters to collect tolls. In 1605, King James I granted to William Levett of Doncaster, brother of York merchant  Doncaster has traditionally been prosperous within the wapentake of Stafford and Tickhill. The borough was known for rich landowners and huge stately homes such as Brodsworth Hall,
Doncaster has traditionally been prosperous within the wapentake of Stafford and Tickhill. The borough was known for rich landowners and huge stately homes such as Brodsworth Hall,  Perhaps the most striking building to survive is
Perhaps the most striking building to survive is

 The Doncaster skyline is dominated by the minster in the middle of the town. The
The Doncaster skyline is dominated by the minster in the middle of the town. The
 In the 2011 census the town of Doncaster (identified as the "built-up area subdivision") had a population of 109,805, while the wider " Built-up area" had a population of 158,141. The Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster had a 2011 population of 302,402, while a mid-2019 estimate was 310,000.
The 2011 census figure makes Doncaster's population very slightly larger than that of Rotherham (pop 109,691).
In the 2011 census the town of Doncaster (identified as the "built-up area subdivision") had a population of 109,805, while the wider " Built-up area" had a population of 158,141. The Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster had a 2011 population of 302,402, while a mid-2019 estimate was 310,000.
The 2011 census figure makes Doncaster's population very slightly larger than that of Rotherham (pop 109,691).

 Doncaster emerged as an industrial centre in the late 18th to 20th centuries. Its communications, particularly its waterways, meant that it became extremely busy and experienced migration to its centre. Underneath Doncaster lies a huge natural resource by way of deep seam coal.
Doncaster emerged as an industrial centre in the late 18th to 20th centuries. Its communications, particularly its waterways, meant that it became extremely busy and experienced migration to its centre. Underneath Doncaster lies a huge natural resource by way of deep seam coal.

 On 5 March 2004, Doncaster was granted Fairtrade Town status. Over the last few years the Doncaster Lakeside, as home to the Doncaster Rovers ground, has undergone modernisation. Doncaster has a bowling alley and a cinema near Lakeside. The Dome, opened in 1989 by Princess Diana, contains a swimming pool, gym, ice rink and café.
The Frenchgate Centre is a shopping centre and transport interchange. Opened in June 2006, it connects with the railway and bus stations.
Lakeside Village, a retail outlet with some 45 retail shops and restaurants lies along the A6182 dual carriageway. The Waterdale area of the town centre is currently undergoing rejuvenation, with a new theatre (known as CAST), new civic offices and a new public square having been completed on the site of the Waterdale car park. The old council house and civic theatre have been demolished and new housing is being built in the town itself, opposite Doncaster Racecourse, and in out-of-town suburbs.
On 5 March 2004, Doncaster was granted Fairtrade Town status. Over the last few years the Doncaster Lakeside, as home to the Doncaster Rovers ground, has undergone modernisation. Doncaster has a bowling alley and a cinema near Lakeside. The Dome, opened in 1989 by Princess Diana, contains a swimming pool, gym, ice rink and café.
The Frenchgate Centre is a shopping centre and transport interchange. Opened in June 2006, it connects with the railway and bus stations.
Lakeside Village, a retail outlet with some 45 retail shops and restaurants lies along the A6182 dual carriageway. The Waterdale area of the town centre is currently undergoing rejuvenation, with a new theatre (known as CAST), new civic offices and a new public square having been completed on the site of the Waterdale car park. The old council house and civic theatre have been demolished and new housing is being built in the town itself, opposite Doncaster Racecourse, and in out-of-town suburbs.
 Today, Doncaster railway station, on the
Today, Doncaster railway station, on the
 In 1909,
In 1909,
 In 1930, International Harvester (IH) started the production of agricultural implements at a factory on Wheatley Hall Road and later at another in the Carr Hill area of Doncaster. The first tractor built at the factory was a
In 1930, International Harvester (IH) started the production of agricultural implements at a factory on Wheatley Hall Road and later at another in the Carr Hill area of Doncaster. The first tractor built at the factory was a
 From around the 16th century, Doncaster embraced the wealthy
From around the 16th century, Doncaster embraced the wealthy
 Founded in 1951, Doncaster (formerly known as Doncaster Dragons RLFC and Doncaster Lakers) have played consistently in rugby league's
Founded in 1951, Doncaster (formerly known as Doncaster Dragons RLFC and Doncaster Lakers) have played consistently in rugby league's

Doncaster cuts ties with Russian twin-town of Ozyorsk as Mansion House lights up for Ukraine
 *
*
The Doncaster Council website
Doncaster in Yorkshire.com website
{{Authority control Doncaster, Doncaster Towns in South Yorkshire Railway towns in England Unparished areas in South Yorkshire Geography of the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in South Yorkshire, England. Named after the River Don, it is the administrative centre of the larger City of Doncaster. It is the second largest settlement in South Yorkshire after Sheffield. Doncaster is situated in the Don Valley on the western edge of the Humberhead Levels and east of the Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commo ...
. At the 2021 census, the city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
had a population of 308,100, while its built-up area had a population of 158,141 at the 2011 census.
Sheffield lies south-west, Leeds north-west, York to the north, Hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
north-east, and Lincoln south-east. Doncaster's suburbs include Armthorpe
Armthorpe is a large village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. Historically within the West Riding of Yorkshire, it had a population of 12,630, increasing to 14,457 at the 2011 Census.
Histor ...
, Bessacarr and Sprotbrough. The towns of Bawtry
Bawtry is a market town and civil parish in the City of Doncaster in South Yorkshire, England. It lies between Doncaster, Gainsborough and Retford, on the border with Nottinghamshire and close to Lincolnshire. The town is historically part of ...
, Mexborough, Conisbrough, Hatfield and Stainforth, among others, are only a short distance away within the metropolitan borough. The towns of Epworth Epworth originally referred to Epworth, Lincolnshire, a town in England that was the birthplace of John Wesley and Charles Wesley, early leaders of the Methodist religious movement. The town's name has since been used for other places and instituti ...
and Haxey are a short distance to the east in Lincolnshire, and directly south is the town of Harworth Bircotes in Nottinghamshire. Also, within the city's vicinity are Barnsley
Barnsley () is a market town in South Yorkshire, England. As the main settlement of the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley and the fourth largest settlement in South Yorkshire. In Barnsley, the population was 96,888 while the wider Borough has ...
, Wakefield, Pontefract, Selby, Goole, Scunthorpe, Gainsborough, Retford, Worksop and Rotherham, to which Doncaster is linked by road and rail.
As part of the Platinum Jubilee Civic Honours, Doncaster received city status by Letters Patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, titl ...
. A ceremony to confer city status took place at Mansion House on 9 November 2022 as part of a tour of Yorkshire by King Charles III and Queen Camilla.
History
Roman
Possibly inhabited earlier, Doncaster grew up on the site of aRoman fort
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
of the 1st century CE, at a crossing of the River Don. The 2nd-century Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary ( la, Itinerarium Antonini Augusti, "The Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is a famous ''itinerarium'', a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly ...
and early-5th-century ''Notitia Dignitatum
The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (Latin for "The List of Offices") is a document of the late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very few surviving documents of ...
'' (''Register of Dignitaries'') called the fort . The first section of road to the Doncaster fort had probably been built since the early 50s, while a route through the north Derbyshire hills was opened in the later 1st century, possibly by Governor Gn. Julius Agricola in the late 70s. Doncaster provided an alternative land route between Lincoln and York, while the main route Ermine Street involved parties breaking up to cross the Humber in boats. As this was not always practical, the Romans saw Doncaster as an important staging post. The Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
appears on two routes recorded in the Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary ( la, Itinerarium Antonini Augusti, "The Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is a famous ''itinerarium'', a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly ...
. The itinerary includes the same section of road between Lincoln and York and lists three stations between these two coloniae. Routes 7 and 8 ('' VII & VIII'') are entitled "the route from York to London".
Several areas of intense archaeological interest have been identified in the town, although many such as St Sepulchre Gate
St Sepulchre Gate is a pedestrianised street in the city centre of Doncaster, in South Yorkshire, England.
History
The street lay outside the Roman and Saxon settlements of Doncaster. It emerged as the main route into the town from the south-w ...
remain hidden under buildings. The Roman fort is thought to have lain on the site now taken by St George's Minster
Doncaster Minster, formally the Minster and Parish Church of St George, is the Anglican minster church of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It is a grade I listed building and was designed by architect designer George Gilbert Scott. The church ...
, beside the River Don. The Doncaster garrison units are named in a ''Register'' produced near the end of Roman rule in Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew tr ...
: it was the home of the Crispinian Horse, presumably named after the tribes living near Crispiana in Pannonia Superior (near present-day Zirc in western Hungary), but possibly after Crispus, son of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
, who was headquartered there while his father was based in nearby York. The ''Register'' names the unit as under the command of the " Duke of the Britons".
In 1971 the Danum shield
The Danum shield was a Roman shield found in the Danum Roman fort at Doncaster in 1971. It was discovered amid the remains of a bonfire and may have been intentionally disposed of during the partial abandonment of the fort. The shield was rect ...
, a rectangular Roman shield dating to the 1st or 2nd century CE, was recovered from the site of the Danum fort.
An inscribed altar, dedicated to the Matres by Marcus Nantonius Orbiotalus, was found at St Sepulchre Gate in 1781. This was donated to the Yorkshire Museum in 1856.

Medieval
Doncaster is generally identified with Cair DaunNennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
(). Theodor Mommsen (). ''Historia Brittonum'', VI. Composed after AD 830. Hosted at Latin Wikisource. listed as one of 28 British cities in the 9th-century '' History of the Britons'' traditionally ascribed to Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
.David Nash FordThe 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. It was certainly an
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
burh, and in that period received its present name: "Don-" ( ang, Donne) from the settlement and river and "-caster" (') from an Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
version of the Latin ''castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
'' (military camp; fort). It was mentioned in the 1003 will
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and will
...
of Wulfric Spott
Wulfric (died ''circa'' 1004), called Wulfric Spot or Spott, was an Anglo-Saxon nobleman. His will is an important document from the reign of King Æthelred the Unready. Wulfric was a patron of the Burton Abbey, around which the modern town of B ...
. Shortly after the Norman Conquest, Nigel Fossard refortified the town and built Conisbrough Castle. By the time of Domesday Book, Hexthorpe
Hexthorpe is a suburb of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, the area's shape resembles a rhombus, with borders with Balby and Doncaster town centre, separated by railway lines and the river se ...
in the wapentake of Strafforth was said to have a church and two mills. The historian David Hey says these facilities represent the settlement at Doncaster. He also suggests that the street name Frenchgate indicates that Fossard invited fellow Normans to trade in the town. Doncaster was ceded to Scotland in the Treaty of Durham and never formally returned to England.
With the 13th century, Doncaster matured into a busy town. In 1194 King Richard I granted it national recognition with a town charter. It suffered a disastrous fire in 1204, from which it slowly recovered. At the time, buildings were built of wood, and open fireplaces used for cooking and heating.
 In 1248, a charter was granted for Doncaster Market to be held in the area surrounding the Church of St Mary Magdalene, which was built in Norman times. In the 16th century, the church was adapted for use as the
In 1248, a charter was granted for Doncaster Market to be held in the area surrounding the Church of St Mary Magdalene, which was built in Norman times. In the 16th century, the church was adapted for use as the town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
. It was finally demolished in 1846. Some 750 years on, the market continues to operate, with busy traders located under cover, at the 19th-century Corn Exchange building (1873) and in outside stalls. The Corn Exchange was much rebuilt in 1994 after a major fire.
During the 14th century, numerous friars arrived in Doncaster who were known for their religious enthusiasm and preaching. In 1307 the Franciscan friars (Greyfriar
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
s) arrived, as did Carmelites (Whitefriars) in the mid-14th century. Other major medieval features included the Hospital of St Nicholas and the leper colony
A leper colony, also known by many other names, is an isolated community for the quarantining and treatment of lepers, people suffering from leprosy. '' M. leprae'', the bacterium responsible for leprosy, is believed to have spread from East Af ...
of the Hospital of St James, a moot hall, a grammar school and a five-arched stone town bridge with a chapel dedicated to Our Lady of the Bridge. By 1334, Doncaster was the wealthiest town in southern Yorkshire and the sixth in Yorkshire as a whole, even boasting its own banker. By 1379, it was recovering from the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, which had reduced its population to 1,500. In October 1536, the Pilgrimage of Grace ended in Doncaster. This rebellion led by the lawyer Robert Aske Robert Aske may refer to:
* Robert Aske (political leader) (1500–1537), leader of the Pilgrimage of Grace, against the dissolution of the monasteries
*Robert Aske (merchant)
Robert Aske (24 February 1619 – 27 January 1689) was a merchant an ...
commanded 40,000 Yorkshire people against Henry VIII, in protest at the Dissolution of the Monasteries. Many of Doncaster's streets are named with the suffix "-gate", after the old Danish
The Danish language developed during the Middle Ages out of Old East Norse, the common predecessor of Danish and Swedish. It was a late form of common Old Norse. The Danish philologist Johannes Brøndum-Nielsen divided the history of Danish into ...
word ''gata'', meaning street. In medieval times, craftsmen or tradesmen with similar skills tended to live in the same street. Baxter is an ancient word for baker: Baxtergate was the bakers' street. Historians believe that Frenchgate may be named after French-speaking Normans who settled there.
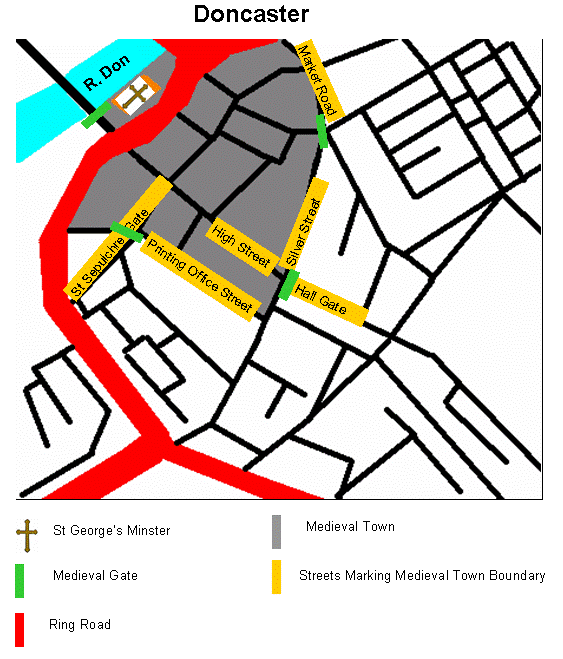
The medieval township is known to have been protected by earthen ramparts and ditches, with four substantial gates as entrances to the town. These were located at Hall Gate, St Mary's Bridge (old), St Sepulchre Gate and Sunny Bar. Today the gates at Sunny Bar are commemorated by huge "Boar Gates"; similarly, the entrance to St Sepulchre Gate is commemorated by white marble "Roman Gates". The boundary of the town mainly extended from the Don along a route known now Market Road, Silver Street, Cleveland Street and Printing Office Street.
Modern
Percival Levett
Percival Levett (1560–1625) was an early merchant and innkeeper of York, England, Sheriff of the city, member of the Eastland Company and father of English explorer Capt. Christopher Levett.
Levett was born in Harewood, Yorkshire, and rem ...
, the right to levy tolls at Friar's and St Mary's bridges. Having served as mayors and aldermen of Doncaster, the Levetts probably believed they could control a monopoly. In 1618 the family began enforcing it, but by 1628 the populace revolted. Capt. Christopher Levett, Percival's son, petitioned Parliament to enforce the tolls, but Parliament disagreed, calling them "a grievance to the subjects, both in creation and execution," and axing the Levett monopoly. Doncaster's Levet Road is named after the family, as are nearby hamlets of Hooton Levitt and the largely extinct Levitt Hagg, where much of the town's early limestone was quarried.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, Doncaster continued to expand, but it suffered several outbreaks of plague between 1562 and 1606. Each struck down significant numbers of victims.
During the First English Civil War
The First English Civil War took place in England and Wales from 1642 to 1646, and forms part of the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. They include the Bishops' Wars, the Irish Confederate Wars, the Second English Civil War, the Ang ...
, King Charles I marched by Bridgnorth, Lichfield and Ashbourne to Doncaster, where on 18 August 1645 he was met by numbers of Yorkshire gentlemen who had rallied to his cause. On 2 May 1664, Doncaster was rewarded with the title of Free Borough as a way for the King (Charles I's son, King Charles II) to express gratitude for the allegiance.
Doncaster was connected to the rail network in 1848 and a plant and carriage works for Great Northern Railway was constructed in the town in 1853.The Doncaster Carr rail depot was opened in 1876.
The area to the east of Doncaster started developing settlements where coal miners lived from the 1850s onwards, exploiting coal near Barnsley
Barnsley () is a market town in South Yorkshire, England. As the main settlement of the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley and the fourth largest settlement in South Yorkshire. In Barnsley, the population was 96,888 while the wider Borough has ...
. One such settment is Deneby.
Doncaster and surrounding settlements became part of the West Riding of Yorkshire in 1899. Under the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
it was drawn into a new metropolitan borough
A metropolitan borough (or metropolitan district) is a type of local government district in England. Created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972, metropolitan boroughs are defined in English law as metropolitan districts within metropolitan ...
in 1974 and became part of the new county of South Yorkshire.
 Doncaster has traditionally been prosperous within the wapentake of Stafford and Tickhill. The borough was known for rich landowners and huge stately homes such as Brodsworth Hall,
Doncaster has traditionally been prosperous within the wapentake of Stafford and Tickhill. The borough was known for rich landowners and huge stately homes such as Brodsworth Hall, Cantley Hall
Cantley Hall is a grade II* listed Georgian mansion set in , in the village of Old Cantley in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England.
It is constructed in two storeys of stuccoed brick with a graduated Westmorland slate roof.
Early history
Cantley ...
, Cusworth Hall, Hickleton Hall, Nether Hall and Wheatley Hall (demolished 1934). This wealth appears in the luxurious, historic gilded 18th-century Mansion House in High Street. This land ownership developed over what is an ancient market place and large buildings were erected in the 19th century, including the Market Hall and Corn Exchange. The old Doncaster Guildhall in Frenchgate was designed by John Butterfield with a tetrastyle portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
and completed in 1847: it was demolished in the redevelopment of the 1960s.
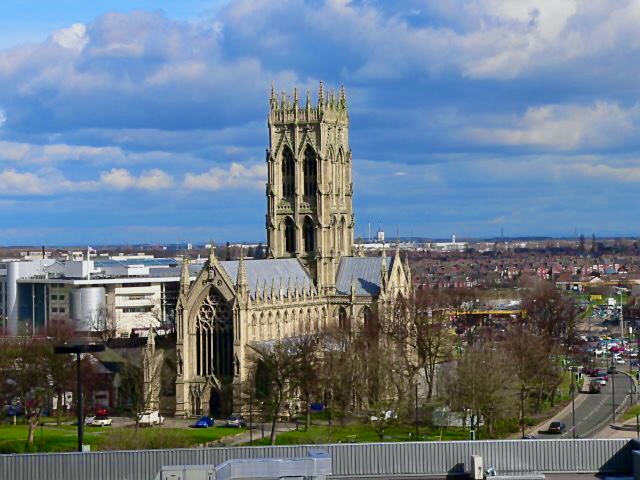
 Perhaps the most striking building to survive is
Perhaps the most striking building to survive is St George's Minster
Doncaster Minster, formally the Minster and Parish Church of St George, is the Anglican minster church of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It is a grade I listed building and was designed by architect designer George Gilbert Scott. The church ...
, built in the 19th century and promoted from a parish church in 2004. Doncaster was already a communication centre by this time. It straddled the Great North Road or A1, gaining strategic importance, as this was the main route for traffic between London and Edinburgh.
Governance and politics
National politics
Doncaster is represented in the House of Commons by three Members of Parliament (MPs); two from Labour and one from the Conservatives.Rosie Winterton
Dame Rosalie Winterton, (born 10 August 1958) is a British Labour Party politician who has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Doncaster Central since 1997. In June 2017, Winterton became one of three Deputy Speakers in the House of Comm ...
represents Doncaster Central, as a former Labour Party leader, Ed Miliband represents Doncaster North, and Nick Fletcher the Don Valley.
In September 2014, UKIP held an annual party conference at Doncaster Racecourse
Doncaster Racecourse (also known as the Town Moor course) is a racecourse in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It hosts two of Great Britain's 36 annual Group 1 flat races, the St Leger Stakes and the Racing Post Trophy.
History
Doncas ...
. UKIP party leader Nigel Farage claimed that by holding the conference in Doncaster, UKIP were "now parking our tanks on the Labour Party's lawn", referring to Labour leader Ed Miliband's Doncaster North constituency. Shortly afterwards in the seat, at the 2015 general election, UKIP won 8,928 votes to Labour's 20,708. In the 2016 EU Referendum
The United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, commonly referred to as the EU referendum or the Brexit referendum, took place on 23 June 2016 in the United Kingdom (UK) and Gibraltar to ask the electorate whether the country shoul ...
, however, Doncaster voted 69 per cent to leave the European Union.

Local politics
Doncaster forms part of theSouth Yorkshire Combined Authority
The South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority is the combined authority for South Yorkshire in England, with powers over transport (public transport and major trunk roads only), economic development and regeneration. It covers a total area of ...
, which elects a mayor every four years.
Additionally, the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster is one of twelve districts in the United Kingdom to have a directly elected mayor, currently Ros Jones, who was re-elected in 2021.
City status
The town applied several times, unsuccessfully, for city status. Its borough population greater than 300,000 is larger than many cities' such asHull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, Southampton and Newcastle. Its town centre alone, with over 109,000 population, is larger than 25 cities across the UK. On 28 October 2021, Doncaster Metropolitan Borough Council announced its bid for Doncaster City for the Queen's Platinum Jubilee. This has been supported by the Doncaster Labour Group and the Doncaster Conservative Association. All three MPs for Doncaster expressed support for city status, with Don Valley's Nick Fletcher speaking for it in Parliament.
Alongside seven other towns, Doncaster was announced to have succeeded in its bid to gain city status on 20 May 2022 as part of the Platinum Jubilee of Elizabeth II. It formally received the letters patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, titl ...
and became a city when a ceremony took place on 9 November 2022 as part of a royal visit.
Geography
Human geography
Doncaster is the second largest settlement in South Yorkshire and the largest metropolitan district in England by area. It expanded dramatically in population with the development of coal mining. Closure of coal mines in the 1970s and early 1980s caused economic difficulties; the town then developed its service industry, drawing on the good communication links with the rest of the UK.Frenchgate Shopping Centre
The Frenchgate Shopping Centre (formerly Arndale Centre) is a large shopping centre located in the city centre of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It is named after the street of the same name that formed one of the old gates of medieval D ...
holds an important position in the skyline, along with the Doncaster College Hub building.
After the old Doncaster College and surrounding buildings were demolished, a new Doncaster Civic Office designed by Cartwright Pickard was built for Doncaster Council at a cost of £20 million and completed in 2012.
Topography
Doncaster lies in a lowland valley in southern Yorkshire. To the west are low rolling hills eventually reaching thePennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commo ...
. To the east are the low-lying Isle of Axholme and Humberhead Levels. The south is relatively low-lying, with a large forested area including Sherwood Forest in Nottinghamshire. The Vale of York lies to the north. The floodplains of the River Don lie to Doncaster's north-east; this area is regularly flooded, notably in 2007 and 2019.
Conservation
Nature reserves
Thorne and Hatfield Moors, east of Doncaster, is the largest area of low-lying peat bog in the United Kingdom. It is protected as a national nature reserve. Potteric Carr, including Potteric Carr Nature Reserve, lies to the south.Green belt
Doncaster is within a green belt that extends into the surrounding counties. First defined in 1966, the policy is controlled throughout the town by the local planning authority, Doncaster Council. It reduces urban sprawl, prevent areas in the conurbation from further convergence, protects outlying communities, encourages brownfield reuse, and protects nearby countryside by restricting development in the designated areas and imposing stricter conditions on permitted building. It surrounds the side of the urban area west of the East Coast Line, preventing suburbs such as Sprotbrough,New Edlington
New Edlington is an area of the town of Edlington, Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England, lying close to Warmsworth and the A630 road.
Churches and places of worship
Warmsworth and New Edlington Church lies on the border o ...
, Old Edlington
Edlington is a town and civil parish in the City of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England, lying to the south west of Doncaster and Warmsworth. It has a population of 8,276. The original parish town of Edlington is now known as ''Old Edlington ...
, Scawsby and New Rossington
Rossington is a civil parish and former mining village in the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster in South Yorkshire, England and is surrounded by countryside and the market towns of Bawtry and Tickhill.
Geography
Historically part of the West ...
merging. As a result, open rural land can be very close to the town centre at some points (for example the wide undeveloped valley of the River Don is adjacent to the town centre), while at other points the urban sprawl rolls on for up to five miles. Another aim of the green belt is to encourage recreation and leisure interests, with rural landscape features, greenfield areas and facilities including the River Don and valley west of Hexthorpe; Hexthorpe Park; Cusworth Hall, museum and country park; Potteric Carr and Huxter Well Marsh; and the Trans Pennine Trail.
Climate
Doncaster has a maritime climate lacking extreme temperatures, like much of the British Isles. Its low elevation in the Don Valley, in the lee of the Pennines, and inland from the North Sea, mean daytime summer temperatures are no lower than parts of South East England, despite the more northerly location. The nearest weather station is RAF Finningley, now known as Doncaster Sheffield Airport, about to the south-east of Doncaster town centre and at a similar elevation. The Doncaster area is about as far north as the average July/August maximum temperature isotherm reaches – Indeed, the August 1990 record high of is the most northerly temperature above in the British Isles. The nearby town of Bawtry, slightly further south, still holds the UK's September monthly record high temperature of , set in 1906. Typically, the warmest day of the year reaches and 12 or 13 days report a daytime maximum of or above. The absolute minimum temperature stands at , set during December 1981. However, online records only relate to the period 1960–2000, so that lower temperatures may have been recorded earlier. During the 1971–2000 period, an average of 51.9 nights of the year recorded an air frost. Typically 106.9 days of the year report 1 mm or more of rainfall. Total annual precipitation is slightly below , which is comparable to the driest parts of the UK, due to Doncaster's location in therain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
of the Pennines.
Demography
 In the 2011 census the town of Doncaster (identified as the "built-up area subdivision") had a population of 109,805, while the wider " Built-up area" had a population of 158,141. The Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster had a 2011 population of 302,402, while a mid-2019 estimate was 310,000.
The 2011 census figure makes Doncaster's population very slightly larger than that of Rotherham (pop 109,691).
In the 2011 census the town of Doncaster (identified as the "built-up area subdivision") had a population of 109,805, while the wider " Built-up area" had a population of 158,141. The Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster had a 2011 population of 302,402, while a mid-2019 estimate was 310,000.
The 2011 census figure makes Doncaster's population very slightly larger than that of Rotherham (pop 109,691).
Economy

Distribution centres
Doncaster's proximity to major urban centres and motorway/rail infrastructure gives it a number of major distribution centres, including the 420-acre Doncaster International Railport, which dispatches goods to Europe. It also has large warehousing and logistic capabilities for retailers such as Next, Tesco,IKEA
IKEA (; ) is a Dutch multinational conglomerate based in the Netherlands that designs and sells , kitchen appliances, decoration, home accessories, and various other goods and home services. Started in 1943 by Ingvar Kamprad, IKEA has been t ...
, Amazon.com, Lidl and Faberge. A marked proportion of fresh and frozen goods for northern supermarkets is dispatched by road from Doncaster.
Regeneration initiatives

 On 5 March 2004, Doncaster was granted Fairtrade Town status. Over the last few years the Doncaster Lakeside, as home to the Doncaster Rovers ground, has undergone modernisation. Doncaster has a bowling alley and a cinema near Lakeside. The Dome, opened in 1989 by Princess Diana, contains a swimming pool, gym, ice rink and café.
The Frenchgate Centre is a shopping centre and transport interchange. Opened in June 2006, it connects with the railway and bus stations.
Lakeside Village, a retail outlet with some 45 retail shops and restaurants lies along the A6182 dual carriageway. The Waterdale area of the town centre is currently undergoing rejuvenation, with a new theatre (known as CAST), new civic offices and a new public square having been completed on the site of the Waterdale car park. The old council house and civic theatre have been demolished and new housing is being built in the town itself, opposite Doncaster Racecourse, and in out-of-town suburbs.
On 5 March 2004, Doncaster was granted Fairtrade Town status. Over the last few years the Doncaster Lakeside, as home to the Doncaster Rovers ground, has undergone modernisation. Doncaster has a bowling alley and a cinema near Lakeside. The Dome, opened in 1989 by Princess Diana, contains a swimming pool, gym, ice rink and café.
The Frenchgate Centre is a shopping centre and transport interchange. Opened in June 2006, it connects with the railway and bus stations.
Lakeside Village, a retail outlet with some 45 retail shops and restaurants lies along the A6182 dual carriageway. The Waterdale area of the town centre is currently undergoing rejuvenation, with a new theatre (known as CAST), new civic offices and a new public square having been completed on the site of the Waterdale car park. The old council house and civic theatre have been demolished and new housing is being built in the town itself, opposite Doncaster Racecourse, and in out-of-town suburbs.
Confectionery
During the 19th and 20th centuries, confectioners based in Doncaster included Parkinson's the Butterscotch inventors, Nuttalls Mintoes and Murray Mints. In August 2011, Parkinson's put its 190-year-old trademark up for sale on eBay.Coal and industrial expansion
The waterways, River Don and Don Navigation were used to transport coal from Doncaster to the steel production centres at Rotherham, Scunthorpe and Sheffield. A large number of mining jobs were lost in the late 1980s. Today coal mining has ceased. Rockware Glass is a specialist glass manufacturer. A production facility for chemical polymers was built in Wheatley Hall Road. It changed hands during its existence, untilDuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
closed it in the mid-1990s.
Steel foundries, rolling mills and wire mills were built close to the railways that brought steel from Rotherham and Sheffield. Bridon Ropes produces wire rope, including the ropes used at coal mines to haul coal and miners. It is claimed to be the largest wire rope manufacturing plant in Europe. Bridon supplied wire rope for the Olympic Stadium for the 2012 Olympic Games
The 2012 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012) was an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
.
During the First and Second World Wars, the town became involved in munitions manufacture.
The railways and locomotive works
During the Industrial Revolution, the Great Northern Railway established the Doncaster Locomotive and Carriage Building Works to meet Doncaster's communication needs, the necessity to transport coal quickly and efficiently, and Doncaster's expertise in specialist metal products. An extensive housing programme was undertaken for the increased population. The Chairman of the Great Northern, anxious about the workers and their families' spiritual welfare, persuaded the directors to contribute towards the building of St James's Church, which became known as the "Plant Church". The railway also built St James's School. The Doncaster Plant became famous for building LNER locomotives '' Flying Scotsman'' and ''Mallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Arge ...
'', as well as many thousands more locomotives. By August 2008, the whole Plant complex had been razed to make way for a very large housing development. The current plant owner Wabtec continues to do refurbishment in Doncaster.
 Today, Doncaster railway station, on the
Today, Doncaster railway station, on the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
, is linked to towns and cities across the UK such as Wakefield, Leeds, Hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, Sheffield, Manchester, Birmingham, London, York, Darlington
Darlington is a market town in the Borough of Darlington, County Durham, England. The River Skerne flows through the town; it is a tributary of the River Tees. The Tees itself flows south of the town.
In the 19th century, Darlington underwen ...
, Newcastle upon Tyne, Berwick-upon-Tweed, Edinburgh, Motherwell
Motherwell ( sco, Mitherwall, gd, Tobar na Màthar) is a town and former burgh in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, United Kingdom, south east of Glasgow. It has a population of around 32,120. Historically in the parish of Dalziel and part of Lanarks ...
, Glasgow, and Lincoln. Doncaster PSB is one of the largest signalling centres on the UK network, controlling hundreds of route-miles of railway. Doncaster International Railport and Doncaster iPort are important road-rail intermodal terminals.
The rail freight company DB Cargo UK has its headquarters in Doncaster.
Also nearby is one of the two National College for Advance Transport and Infrastructure Campuses that specialises in courses relating to the railways and transport systems.
Aviation
 In 1909,
In 1909, Doncaster Racecourse
Doncaster Racecourse (also known as the Town Moor course) is a racecourse in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It hosts two of Great Britain's 36 annual Group 1 flat races, the St Leger Stakes and the Racing Post Trophy.
History
Doncas ...
was chosen as the venue for an airshow, after the world's first international air display in Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
, France in 1909. Around a dozen aviators were present, the most famous being Léon Delagrange and Roger Sommer. Samuel Cody (no relation to William F. Cody) in an attempt to win a prize offered by the ''Daily Mail
The ''Daily Mail'' is a British daily middle-market tabloid newspaper and news websitePeter Wilb"Paul Dacre of the Daily Mail: The man who hates liberal Britain", ''New Statesman'', 19 December 2013 (online version: 2 January 2014) publish ...
'' for the first British pilot in a British aeroplane to fly a circular mile signed British naturalisation papers in front of the crowd with the band playing both '' God Save the King'' and the ''Star Spangled Banner
"The Star-Spangled Banner" is the national anthem of the United States. The lyrics come from the "Defence of Fort M'Henry", a poem written on September 14, 1814, by 35-year-old lawyer and amateur poet Francis Scott Key after witnessing the bo ...
''. Unfortunately, he crashed his aeroplane on the first day of the meeting and made no significant flights.
During the First World War, fighters based first on the racecourse, then at a temporary airstrip near Finningley (later RAF Finningley and now Doncaster Sheffield Airport) and finally, in 1916, on a newly built airfield alongside the racecourse, were deployed to defend the east coast against Zeppelins. On several occasions fighters took off to search for intruders but none were ever seen. The Royal Flying Corps
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colors =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, decorations ...
station trained pilots for the war in France. Within months of the war ending the station was put up for sale and two of its three Belfast hangars, the same type that now forms the basis for the Royal Air Force Museum at Hendon
Hendon is an urban area in the Borough of Barnet, North-West London northwest of Charing Cross. Hendon was an ancient manor and parish in the county of Middlesex and a former borough, the Municipal Borough of Hendon; it has been part of Great ...
, were sold to a Sheffield motor manufacturing company for storage and assembly at Finningley. The third of the hangars stayed in place, mainly housing buses, until the 1970s, when it was knocked down and replaced with modern buildings.
In 1920, the government asked local authorities to assist in forming a chain of airfields for civil air services. Doncaster, with expert advice from Alan Cobham, opened its aviation centre on 26 May 1934. Development of the airfield continued and on 1 July 1936 an international service was opened to Amsterdam. On 1 November 1938, after discussions with the Air Ministry, 616 (South Yorkshire) Squadron of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force
The Royal Auxiliary Air Force (RAuxAF), formerly the Auxiliary Air Force (AAF), together with the Air Force Reserve, is a component of His Majesty's Reserve Air Forces (Reserve Forces Act 1996, Part 1, Para 1,(2),(c)). It provides a primary rein ...
was formed. Shortly after the outbreak of war in 1939 the squadron went to its battle station and played a part in the Battle of Britain. After the departure of 616 squadron, its place was taken by the formation of 271 (Transport) Squadron composed mainly of requisitioned civilian aircraft and obsolescent twin-engined bombers. 616 squadron was the first Allied jet fighter squadron, equipped with the Gloster Meteor, famed for using their wingtips to throw German V-1 flying bombs off course. In 1944, after being equipped with American-made Douglas DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner
manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper version ...
Dakotas, the squadron moved south to take part in Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operat ...
and later in the airborne invasion at Arnhem, where Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the India ...
David Lord was awarded a posthumous Victoria Cross.
After the war the airfield reverted to civilian flying, and finally closed in 1992.
Tractor production
 In 1930, International Harvester (IH) started the production of agricultural implements at a factory on Wheatley Hall Road and later at another in the Carr Hill area of Doncaster. The first tractor built at the factory was a
In 1930, International Harvester (IH) started the production of agricultural implements at a factory on Wheatley Hall Road and later at another in the Carr Hill area of Doncaster. The first tractor built at the factory was a Farmall M
The Farmall M is a large three-plow row crop tractor produced by International Harvester under the Farmall brand from 1939 to 1953. It was of International Harvester's "List of International Harvester vehicles#Farmall F and Letter Series (1924� ...
, which came off the production line on 13 September 1949. Tractors were initially built from parts shipped from the US. The Wheatley Hall Road factory was extended after the war with a new foundry to make the heavy castings. The factory started Crawler tractor production in 1953. By 1960, the factory was making a range of tractors from scratch, designed specifically for British and European markets and sold under the 'McCormick International' name. Assembly moved in 1965 to the Carr Hill plant. In 1983, tractor production was moved to IH's other Doncaster factory at Wheatley Hall. In 1985, International Harvester sold its agricultural division to Tenneco, Inc. which then merged it with its subsidiary J.I. Case to form Case IH, which continued to design and build its European tractor range in Doncaster, but shutting the David Brown Ltd.
David Brown Engineering Limited is an English engineering company, principally engaged in the manufacture of gears and Transmission (mechanics), gearboxes. Their major gear manufacturing plant is in Swan Lane, Lockwood, West Yorkshire, Lockwoo ...
tractor factory near Huddersfield. The 350,000th tractor came off the production line in 1999.
In 2000, the factory was purchased by ARGO SpA, an Italian-based agricultural equipment builder. Doncaster was the sole production site of the McCormick Tractors brand, and the factory employed around 380 people (although about 1,100 people are employed in the worldwide McCormick group). In December 2006, the parent company, ARGO Spa, announced that the Doncaster facility would close in 2007, with the loss of around 325 jobs. The announcement was made only a week before Christmas. Sixty-one years of tractor production in Doncaster ended in 2007.
Culture and tourism
Doncaster Museum and Art Gallery
Doncaster Museum and Art Gallery is a museum in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England.
History
The first Doncaster Museum opened in 1909 at Beechfield House, utilising only the ground floor of the building, and operated a small zoo at the site fr ...
opened as the town's main museum in 1964. It covers natural history, archaeology, local history and fine and decorative art. It has a major exhibition of silverware and trophies won at Doncaster Racecourse
Doncaster Racecourse (also known as the Town Moor course) is a racecourse in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It hosts two of Great Britain's 36 annual Group 1 flat races, the St Leger Stakes and the Racing Post Trophy.
History
Doncas ...
. It also houses the Regimental Museum of the King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry
The King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry (KOYLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army. It officially existed from 1881 to 1968, but its predecessors go back to 1755. In 1968, the regiment was amalgamated with the Somerset and Cornwall ...
.
Doncaster is home to Yorkshire Wildlife Park, which has over 400 animals and over 70 different species, including the only polar bears in England .
The South Yorkshire Aircraft Museum (formerly AeroVenture) is based on the old site of RAF Doncaster at Doncaster Lakeside. The Trolleybus Museum in the nearby village of Sandtoft specialises in preserving trolleybuses, and claims to have the largest collection of them in Europe, with over 60 examples. Markham Grange Steam Museum, in a garden centre in the nearby village of Brodsworth, has a private collection of steam engines. Ashworth Barracks Museum is a military museum in Balby telling the story of the men awarded the Victoria Cross. It also houses a First World War exhibit including a "Weekers Helmet", one of only two known that exist in the UK.
Since 1973, Doncaster has been the home of the Doncaster Youth Jazz Association (DYJA). Founded by John Ellis, DYJA has been a training ground for generations of amateur and professional jazz musicians including, Andy Cato (of Groove Armada), Denis Rollins, John Escreet, Nadim Teimoori and Reuben Fowler.
In 1956, Tish the goldfish was won at a funfair in Doncaster. Tish lived till the age of 43 becoming the world's oldest known goldfish.
Theatre and cinemas
*Cast is a £22 million venue opened officially on Monday 2 September 2013. Cast includes a 620-seat auditorium, a flexible studio space, drama studio, dance studio, education and ancillary space, and a large foyer with a café. Its director was Kully Thiarai, formerly of the Contact Theatre, Manchester. *The Doncaster Little Theatre is a 99-seat community theatre which puts on 12 of its own in-house shows including a pantomime, along with two Afternoon Cabarets a month during the day. Hire companies also use the theatre space for their own shows. *The town has an 11-screen multiplex Vue which was expanded as part of a £5 million upgrade. *Events and concerts take place atDoncaster Racecourse
Doncaster Racecourse (also known as the Town Moor course) is a racecourse in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It hosts two of Great Britain's 36 annual Group 1 flat races, the St Leger Stakes and the Racing Post Trophy.
History
Doncas ...
and The Dome Leisure Centre.
Nightlife
The Silver Street, Cleveland Street and High Street areas have over 40 bars and clubs within a 2–3-minute walk of each other and other bars can be found on Priory Walk, Lazarus Court, Bradford Row and around the Market Place. Various restaurants serving food from around the world can also be found in the town centre, especially in the Netherhall and Copley Road areas.Transport
Road
Doncaster sits on the European route E15 and is the starting point of European route E13. The E13 connects Doncaster, Sheffield and Nottingham to London. In the United Kingdom, European route designators are not displayed on road signs. The intended motorway design is evidenced in road maps. The M1 was extended northward to Leeds, which is why the E13 starts at Doncaster and follows the path of the M18 and the M1. Doncaster is situated on the A1(M) and M18 motorways, within 20 minutes of the key M1 and M62 motorways. The A1(M) motorway bypass cost £6 million and was opened by Ernest Marples in 1961. The former route is now the A638 and partly the A614 toBlyth Blyth may refer to:
People
* Blyth (surname)
* Blythe (given name)
Places Australia
* Blyth, South Australia, a small town
Canada
* Blyth, Ontario, a village
United Kingdom
* Blyth, Northumberland, a town
** Blyth Valley (UK Parliament ...
.
Air
Until 2022, Doncaster was a European hub with n international airport. Doncaster Sheffield Airport opened in 2005, closing in November 2022 after the Peel Group cited it was unlikely to return to profitability.Rail
Doncaster is also an important railway town with astation
Station may refer to:
Agriculture
* Station (Australian agriculture), a large Australian landholding used for livestock production
* Station (New Zealand agriculture), a large New Zealand farm used for grazing by sheep and cattle
** Cattle statio ...
on the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
.
Doncaster International Railport facilities link to the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
.
Bus
New developments include campus facilities for Doncaster College and theFrenchgate Interchange
The Frenchgate Interchange (also known as Doncaster Interchange) is a rail and bus transport interchange located within the Frenchgate Shopping Centre in the city centre of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It has 30 bus stands, with a large ...
(a unification of bus and railway stations with the Frenchgate Centre). The extension to the shopping centre and the new bus station opened on 8 June 2006, when all Doncaster bus routes started to use the station.
Cycling
Cycling in Doncaster is increasingly more popular. Its situation on the Trans Pennine Trail means it is connected to other surrounding towns. Additionally, cycle lanes are being installed across the borough allowing for safer road commuter cycling.Media
Television
Doncaster is served by BBC Yorkshire from Leeds which broadcasts the flagship nightly news programmeLook North
''BBC Look North'' is a name used by the BBC for its regional news programmes in three regions in the North of England:
*''BBC Look North'' for the BBC North East and Cumbria region
*''BBC Look North'' for the BBC Yorkshire region
*''BBC Look No ...
. ITV Yorkshire is the local ITV franchise.
Radio
Doncaster is served by several commercial and community radio stations. For 22 years,Trax FM
Trax FM was a local radio station serving Doncaster in South Yorkshire and the Bassetlaw district of north Nottinghamshire. The station was folded into Greatest Hits Radio Yorkshire, as part of a rebrand, on 1 September 2020.
History
The stati ...
was arguably the most popular station based in the city. It was rebranded as Greatest Hits Radio Yorkshire
Greatest Hits Radio Yorkshire is a radio station regional sub-network serving Yorkshire, Lincolnshire & the North Midlands as part of Bauer’s Greatest Hits Radio network. Whilst all programming is shared either across the region, or nationall ...
in 2020, along with numerous other stations in the region. TX1 Radio
TX1 Radio is an Independent Local Radio station broadcasting to the Doncaster and Bassetlaw districts of South Yorkshire and Nottinghamshire, England. It launched on September 14, 2020 following the re-branding of Trax FM and other stations ...
was set up following the closure of Trax FM and broadcasts exclusively on DAB radio to Doncaster and Bassetlaw.
Additionally, BBC Radio Sheffield and Hallam FM broadcast to South Yorkshire from Sheffield.
Sine FM
Sine FM, sometimes known simply as Sine, is a community radio station based near the Eco-Power Stadium in Doncaster. It broadcasts 24/7 to the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster on 102.6 FM and to the world on its website''Sine FM.com''
History
S ...
is a community radio station broadcasting to Doncaster's central business district
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business centre of a city. It contains commercial space and offices, and in larger cities will often be described as a financial district. Geographically, it often coincides with the "city ...
and inner suburbs on FM. TMCR 95.3
TMCR or Today's More Choice Radio is a community radio station in Thorne, near Doncaster in South Yorkshire.
TMCR was set up as a Restricted Service Licence or 'trial station' to see how it would be received by the communities of Thorne and ...
is a community radio station based in Thorne serving North East Doncaster on FM.
Print media
The '' Doncaster Free Press'' is a weekly newspaper distributed across the greater Doncaster region. Doncaster has its own edition of the '' Sheffield Star'' printed daily. '' The Yorkshire Post'' is the local daily broadsheet newspaper from Leeds. The ''Dearne Valley Weekender'' is a weekly newspaper targeted towards the Dearne Valley, which includes some parts of South West Doncaster, although it is widely available across the town.Sport
Racecourse
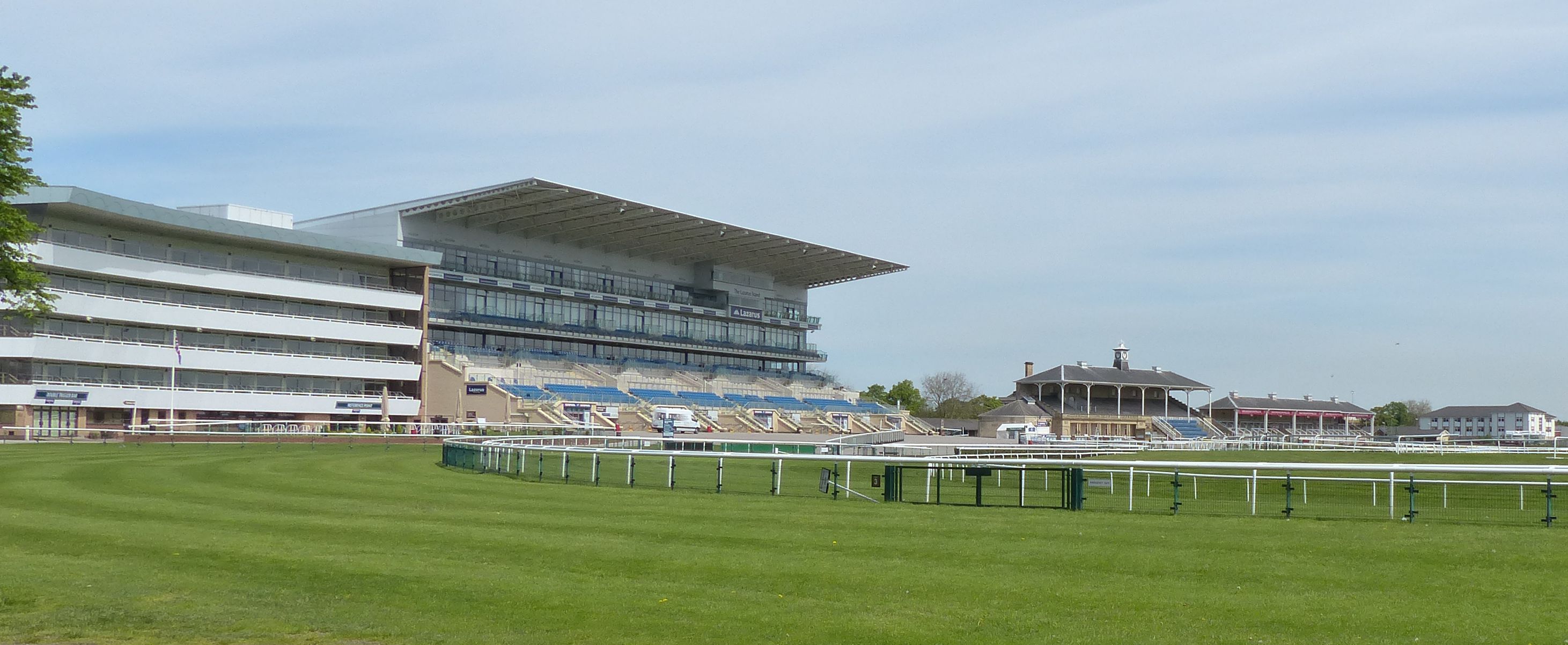
 From around the 16th century, Doncaster embraced the wealthy
From around the 16th century, Doncaster embraced the wealthy stagecoach
A stagecoach is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are draw ...
trade. This led to horse breeding in Doncaster, which in turn led to the start of horseraces there. The earliest important race in Doncaster's history was the Doncaster Gold Cup, first run over Cantley Common in 1766. The Doncaster Cup is the oldest continuing regulated horserace in the world.
Rugby football
 Founded in 1951, Doncaster (formerly known as Doncaster Dragons RLFC and Doncaster Lakers) have played consistently in rugby league's
Founded in 1951, Doncaster (formerly known as Doncaster Dragons RLFC and Doncaster Lakers) have played consistently in rugby league's National League One
National One (last season known as National League 1 and previously known before September 2009 as National Division Two), is the third of three national leagues in the domestic rugby union competition of England. It was known as Courage Leagu ...
and its successor the RFL Championship
The Championship, known as the Betfred Championship for sponsorship reasons, is a professional rugby league competition. It is the Rugby Football League Championship Second Division, second-tier competition organised by the Rugby Football Lea ...
, with its home at the Keepmoat Stadium.
Doncaster Knights currently play in rugby union's RFU Championship, with their home at Castle Park.
Football

Doncaster Rovers F.C.
Doncaster Rovers Football Club is a professional association football club based in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. The team compete in League Two, the fourth tier of the English football league system. The club play their home games at T ...
, and one of the most successful women's football Women's football most often refers to:
* Women's association football (hannah jones ).
Women's football may also refer to:
* Women's gridiron football
* Women's Australian rules football
* Ladies' Gaelic football
* Women's rugby league
* Women's ...
clubs in the country, Doncaster Rovers Belles, play at the Keepmoat Stadium. It is also the home of the British professional wrestling promotion
A professional wrestling promotion is a company or business that regularly performs shows involving professional wrestling that has little relationship to the rules of the amateur olympic form. "Promotion" also describes a role which entails man ...
One Pro Wrestling.
Others
Speedway racing was staged at Doncaster Greyhound Stadium in 1969 and 1970. The team was known as the Stallions and then the Dragons. The team raced in the British League Second Division. Doncaster has a men's basketball team called the Doncaster Danum Eagles who compete in National League Division 2. Doncaster additionally has an American football team called the Doncaster Mustangs, who are in Division 1 of the British American Football League. The town also has regular involvement in the Tour de Yorkshire cycling event, having the finish line of stage two, of the 2016 Tour de Yorkshire hosted in Doncaster, as well as the finish line of stage one of the2018 Tour de Yorkshire
The 2018 Tour de Yorkshire was a four day cycling stage race held in Yorkshire over 3–6 May 2018. It was the fourth edition of the Tour de Yorkshire, organised by Welcome to Yorkshire and the Amaury Sport Organisation. The 2018 TDY differed ...
hosted in the town as well.
International links
Doncaster istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Avion, France
* Herten
Herten (; Westphalian: ''Hiätten'') is a town and a municipality in the district of Recklinghausen, in North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ks ...
, Germany
* Camden
Camden may refer to:
People
* Camden (surname), a surname of English origin
* Camden Joy (born 1964), American writer
* Camden Toy (born 1957), American actor
Places Australia
* Camden, New South Wales
* Camden, Rosehill, a heritage res ...
, England, United Kingdom
* Gliwice, Poland
* Wilmington, North Carolina, United States
Several roads in the Lakeside area are named after Doncaster's twin towns, such as Gliwice Way, Herten Way, Wilmington Drive and Carolina Way, named after the state where Wilmington lies.
Former
* Ozyorsk, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia (ceased following the2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
Doncaster cuts ties with Russian twin-town of Ozyorsk as Mansion House lights up for Ukraine
Notable people
David Firth David Firth may refer to:
* David Firth (actor), English actor and writer
* David Firth (animator), creator of the British animated web series ''Salad Fingers''
* David Firth (statistician), British statistician
See also
* David Frith
David E ...
, animator and filmmaker.
* John McLaughlin, highly reputed guitarist and frontman of Mahavishnu Orchestra
* Jeremy Clarkson, famous for being the presenter of '' Top Gear'' and face of the show '' The Grand Tour''.
* Louis Tomlinson
Louis William Tomlinson (; born Louis Troy Austin; 24 December 1991) is an English singer and songwriter. He rose to fame as a member of the boy band One Direction. Tomlinson began his career appearing in television dramas before he auditioned ...
, English singer, songwriter and model, former member of the band One Direction.
* Kevin Keegan
Joseph Kevin Keegan (born 14 February 1951) is an English former footballer and manager. A forward, he played for several professional clubs from 1968 to 1984. Having begun his career at Scunthorpe United, he moved to Liverpool in 1971 and ...
, football manager and former player.
* Emma Chambers, actress, famous for her role of Alice Horton in '' The Vicar of Dibley'' and Honey Thacker in '' Notting Hill''.
* Yungblud, singer, songwriter and musician.
* Sarah Stevenson, 2011 world champion of Taekwondo.
* James Toseland, a former motocyclist, currently vocalist in a band with his own name.
* Thomas Howes, known for playing the role of William Mason in the famous British TV series '' Downton Abbey''.
* Roy Clarke, a writer, famous for his '' Last of the Summer Wine'' and '' Keeping Up Appearances''.
* Diana Rigg, actress
* Tan France, one of the hosts of ''Queer Eye (2003 TV series), Queer Eye''.
* Andrew White (presenter), Andrew White, presenter and producer of ''Walks Around Britain (TV series), Walks Around Britain'' and writer of ''The Walker Mysteries'' novels.
* Danny Schofield, a professional football coach and a former player.
See also
*Listed buildings in Doncaster (Town Ward) *Doncaster Education City *List of people from Doncaster *Doncaster Pride, gay pride event *Trolleybuses in Doncaster *Doncaster Caledonian SocietyNotes
References
External links
*The Doncaster Council website
Doncaster in Yorkshire.com website
{{Authority control Doncaster, Doncaster Towns in South Yorkshire Railway towns in England Unparished areas in South Yorkshire Geography of the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster