Donbas Status Referendums, 2014 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The Donbas (, ; ) or Donbass ( ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern
The Donbas (, ; ) or Donbass ( ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern
 The
The  It was at this point that the name ''Donbas'' came into use, derived from the term "Donets Coal Basin" (; ), referring to the area along the
It was at this point that the name ''Donbas'' came into use, derived from the term "Donets Coal Basin" (; ), referring to the area along the
 In April 1918 troops loyal to the
In April 1918 troops loyal to the
 In the 1991 referendum on Ukrainian independence, 83.9% of voters in Donetsk Oblast and 83.6% in Luhansk Oblast supported independence from the
In the 1991 referendum on Ukrainian independence, 83.9% of voters in Donetsk Oblast and 83.6% in Luhansk Oblast supported independence from the
n Ukrainian ''www.bbc.com'' A total of 3,576 delegates from 16
The initial protests in the Donbas were largely native expressions of discontent with the new Ukrainian government. Russian involvement at this stage was limited to its voicing of support for the demonstrations. The emergence of the separatists in Donetsk and Luhansk began as a small fringe group of the protesters, independent of Russian control. This unrest, however, only evolved into an armed conflict because of Russian military backing for what had been a marginal group as part of the

 The Donbas (, ; ) or Donbass ( ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern
The Donbas (, ; ) or Donbass ( ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
. The majority of the Donbas is occupied by Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
as a result of the Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
.
The word ''Donbas'' is a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
formed from "Donets Basin", an abbreviation of "Donets Coal Basin" (; ). The name of the coal basin is a reference to the Donets Ridge
The Donets Ridge is a highland that is the highest north-eastern part of the Donets upland. The ridge is in the Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts of Ukraine and partially in the Rostov Oblast of Russia. The highest point on the ridge is a hill — Mohyl ...
; the latter is associated with the Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets (), is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv ...
river.
There are numerous definitions of the region's extent. The ''Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine
''Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine'' () is an illustrated encyclopedia on history of Ukraine in 10 volumes. It was published in Ukrainian language in 2003–2013 and 2019Ihor Syundyukov. Ukraine and Ukrainians: Eternal search (Україна ...
'' defines the "small Donbas" as the northern part of Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; ; ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin, and Stalino, is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine located on the Kalmius River in Donetsk Oblast, which is currently occupied by Russia as the capita ...
and the southern part of Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; , ), also known as Lugansk (, ; , ), is a city in the Donbas in eastern Ukraine. As of 2022, the population was estimated to be making Luhansk the Cities in Ukraine, 12th-largest city in Ukraine.
Luhansk served as the administra ...
regions of Ukraine, and the attached part of Rostov
Rostov-on-Don is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, from the Sea of Azov, directly north of t ...
region of Russia. The historical coal mining
Coal mining is the process of resource extraction, extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its Energy value of coal, energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to Electricity generation, generate electr ...
region excluded parts of Donetsk and Luhansk oblast
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
s, and included areas in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
Dnipropetrovsk Oblast (), is an administrative divisions of Ukraine, oblast (province) in simultaneously southern, eastern and central Ukraine, the most important industrial region of the country. It was created on February 27, 1932. Dnipropetro ...
and Southern Russia
Southern Russia or the South of Russia ( rus, Юг России, p=juk rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a Colloquialism, colloquial term for the southernmost geographic portion of European Russia. The term is generally used to refer to the region of Russia's So ...
. A Euroregion
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two (or more) contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border regio ...
of the same name is composed of Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts in Ukraine and Rostov Oblast
Rostov Oblast ( rus, Росто́вская о́бласть, r=Rostovskaya oblastʹ, p=rɐˈstofskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in the Southern Federal District. The oblast ...
in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
.
The Donbas formed the historical border between the Zaporizhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich (, , ; also ) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of Zaporozhian Cossacks that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, for the latter part of that period as an autonomous stratocratic state within the Cossa ...
and the Don Cossack Host
Don Cossacks (, ) or Donians (, ), are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (, ), which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic republic in present-da ...
. It has been an important coal mining area since the late 19th century, when it became a heavily industrialised territory.
In March 2014, following the Euromaidan
Euromaidan ( ; , , ), or the Maidan Uprising, was a wave of Political demonstration, demonstrations and civil unrest in Ukraine, which began on 21 November 2013 with large protests in Maidan Nezalezhnosti (Independence Square) in Kyiv. The p ...
protest movement and the resulting Revolution of Dignity
The Revolution of Dignity (), also known as the Maidan Revolution or the Ukrainian Revolution, took place in Ukraine in February 2014 at the end of the Euromaidan protests, when deadly clashes between protesters and state forces in the capit ...
, large swaths of the Donbas became gripped by pro-Russian and anti-government unrest. This unrest later grew into a war
''A War'' () is a 2015 Danish war drama film written and directed by Tobias Lindholm, and starring Pilou Asbæk, Tuva Novotny and Søren Malling. It tells the story of a Danish military company in Afghanistan that is fighting the Taliban while t ...
between Ukrainian government forces and pro-Russian separatists affiliated with the self-proclaimed Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; ; ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin, and Stalino, is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine located on the Kalmius River in Donetsk Oblast, which is currently occupied by Russia as the capita ...
and Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; , ), also known as Lugansk (, ; , ), is a city in the Donbas in eastern Ukraine. As of 2022, the population was estimated to be making Luhansk the Cities in Ukraine, 12th-largest city in Ukraine.
Luhansk served as the administra ...
"People's Republics", who were supported by Russia as part of the broader Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
. The conflict split the Donbas into Ukrainian-held territory, constituting about two-thirds of the region, and separatist-held territory, constituting about one-third. The region remained this way for years until Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022. On 30 September 2022, Russia unilaterally declared its annexation of Donbas together with two other Ukrainian oblasts, Kherson and Zaporizhzhia.
The city of Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; ; ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin, and Stalino, is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine located on the Kalmius River in Donetsk Oblast, which is currently occupied by Russia as the capita ...
(the fifth largest city in Ukraine) is considered the unofficial capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
of the Donbas. Other large cities (over 100,000 inhabitants) include Mariupol
Mariupol is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast (Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius, Kalmius River. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, it was the tenth-largest city in the coun ...
, Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; , ), also known as Lugansk (, ; , ), is a city in the Donbas in eastern Ukraine. As of 2022, the population was estimated to be making Luhansk the Cities in Ukraine, 12th-largest city in Ukraine.
Luhansk served as the administra ...
, Makiivka
Makiivka (, ), formerly Dmytriivsk () until 1931, is an industrial city in Donetsk Oblast, eastern Ukraine, located east from Donetsk. The two cities are practically a conurbation. It has a population of It hosts the administration of Makiivka ...
, Horlivka
Horlivka ( ; , ), also known as Gorlovka (, ), is a city in Donetsk Oblast of Ukraine. Its population is
Economic activity is predominantly coal mining and the chemical industry. The Horlivka Institute for Foreign Languages has a two-building ...
, Kramatorsk
Kramatorsk (, ; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Kramatorsk Raion in Donetsk Oblast of the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine. Prior to 2020, Kramatorsk was a city of oblast significance. Since October 2014, Kramatorsk has been the ...
, Sloviansk
Sloviansk is a city in Donetsk Oblast, northern part of the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine. The city was known as ''Tor'' until 1784. While it did not actually belong to the raion itself, Sloviansk served as the administrative center of the S ...
, Alchevsk
Alchevsk (; ) is a city and the nominal administrative center of Alchevsk Raion in Luhansk Oblast, in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine. It is located from the administrative center of the oblast, Luhansk. Population:
Alchevsk is one of t ...
, Sievierodonetsk
Sievierodonetsk or Severodonetsk, officially since 2024 Siverskodonetsk, is a city in Luhansk Oblast, eastern Ukraine. It is located to the northeast of the left bank of the Donets river and approximately to the northwest from the administrati ...
, and Lysychansk
Lysychansk ( , ; , ; , ) is a city in Sievierodonetsk Raion, Luhansk Oblast, eastern Ukraine. It is located on the high right bank of the Donets River, approximately from the administrative center of the oblast, Luhansk. It faces Sievierodonet ...
.
History
Ancient, medieval and imperial Russian periods
 The
The Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and part ...
places the Pontic steppes
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from nor ...
of Ukraine and southern Russia as the linguistic homeland
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ( , from German 'original' and 'home') of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the reconstructed or historically ...
of the Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric ethnolinguistic group of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family.
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from t ...
. The Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya ( ) or Yamna culture ( ), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, is a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic–C ...
is identified with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans.
The region has been inhabited for centuries by various nomadic tribes, such as Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
, Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
, Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
, Kipchaks
The Kipchaks, also spelled Qipchaqs, known as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Russian annals, were Turkic nomads and then a confederation that existed in the Middle Ages inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe.
First mentioned in the eighth cent ...
, Turco-Mongols, Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
and in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Nogais
The Nogais ( ) are a Kipchaks, Kipchak people who speak a Turkic languages, Turkic language and live in Southeastern Europe, North Caucasus, Volga region, Central Asia and Turkey. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well ...
. The region now known as the Donbas was largely unpopulated until the second half of the 17th century, when Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (, ) or Donians (, ), are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don River (Russia), Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (, ), which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic rep ...
established the first permanent settlements in the region.
The first town in the region was founded in 1676, called Solanoye (now Soledar
Soledar (, ; , ; ) is a destroyed city in Bakhmut Raion, Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. Situated in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine, the city was formerly highly important for its salt mining industry, from which its name Soledar is derived. The ...
), which was built for the profitable business of exploiting newly discovered rock-salt reserves. Known for being a Cossack
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Rus ...
land, the "Wild Fields
The Wild Fields is a historical term used in the Polish–Lithuanian documents of the 16th to 18th centuries to refer to the Pontic steppe in the territory of present-day Eastern and Southern Ukraine and Western Russia, north of the Black Sea ...
" (, ), the area that is now called the Donbas was largely under the control of the Ukrainian Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate (; Cossack Hetmanate#Name, see other names), officially the Zaporozhian Host (; ), was a Ukrainian Cossacks, Cossack state. Its territory was located mostly in central Ukraine, as well as in parts of Belarus and southwest ...
and the Turkic Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of th ...
until the mid-late 18th century, when the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
conquered the Hetmanate and annexed the Khanate.
In the second half of the 17th century, settlers and fugitives from Hetman's Ukraine and Muscovy Muscovy or Moscovia () is an alternative name for the Principality of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721).
It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
*Muscovy duck (''Cairina mosch ...
settled the lands north of the Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets (), is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv ...
river. At the end of the 18th century, many Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
and Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
migrated to lands along the southern course of the Donets river, into an area previously inhabited by nomadic Nogais
The Nogais ( ) are a Kipchaks, Kipchak people who speak a Turkic languages, Turkic language and live in Southeastern Europe, North Caucasus, Volga region, Central Asia and Turkey. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well ...
, who were nominally subject to the Crimean Khanate. Tsarist Russia named the conquered territories "New Russia
Novorossiya rus, Новороссия, Novorossiya, p=nəvɐˈrosʲːɪjə, a=Ru-Новороссия.ogg; , ; ; ; "New Russia". is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later becom ...
" (, ). As the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
took hold across Europe, the vast coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
resources of the region, discovered in 1721, began to be exploited in the mid-late 19th century.
 It was at this point that the name ''Donbas'' came into use, derived from the term "Donets Coal Basin" (; ), referring to the area along the
It was at this point that the name ''Donbas'' came into use, derived from the term "Donets Coal Basin" (; ), referring to the area along the Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets (), is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv ...
river where most of the coal reserves were found. The rise of the coal industry led to a population boom in the region, largely driven by Russian settlers.
Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; ; ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin, and Stalino, is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine located on the Kalmius River in Donetsk Oblast, which is currently occupied by Russia as the capita ...
, the most important city in the region today, was founded in 1869 by Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, of or about Wales
* Welsh language, spoken in Wales
* Welsh people, an ethnic group native to Wales
Places
* Welsh, Arkansas, U.S.
* Welsh, Louisiana, U.S.
* Welsh, Ohio, U.S.
* Welsh Basin, during t ...
businessman John Hughes John Hughes may refer to:
Arts and Entertainment Literature
*John Hughes (poet) (1677–1720), English poet
*John Hughes (1790–1857), English author
*John Ceiriog Hughes (1832–1887), Welsh poet
*John Hughes (writer) (born 1961), Australian au ...
on the site of the old Zaporozhian Cossack
The Zaporozhian Cossacks (in Latin ''Cossacorum Zaporoviensis''), also known as the Zaporozhian Cossack Army or the Zaporozhian Host (), were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids. Along with Registered Cossac ...
town of Oleksandrivka. Hughes built a steel mill and established several collieries
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extrac ...
in the region. The city was named after him as Yuzivka () or Yuzovka (). With the development of Yuzovka and similar cities, large numbers of landless peasants from peripheral governorates of the Russian Empire
A governorate (, , ) was a major and principal administrative subdivision of the Russian Empire. After the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917, governorates remained as subdivisions in the Byelorussian, Russian and Ukrainian Soviet republics, and ...
came looking for work.
According to the Russian Imperial Census of 1897, Ukrainians ("Little Russia
Little Russia, also known as Lesser Russia, Malorussia, or Little Rus', is a geographical and historical term used to describe Ukraine.
At the beginning of the 14th century, the patriarch of Constantinople accepted the distinction between wha ...
ns", in the official imperial language) accounted for 52.4% of the population of the region, whilst ethnic Russians constituted 28.7%. Ethnic Greeks, Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
and Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
also had a significant presence in the Donbas, particularly in the in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
district
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
of Mariupol
Mariupol is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast (Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius, Kalmius River. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, it was the tenth-largest city in the coun ...
, where they constituted 36.7% of the population. Despite this, Russians constituted the majority of the industrial workforce. Ukrainians dominated rural areas, but cities were often inhabited solely by Russians who had come seeking work in the region's heavy industries. Those Ukrainians who did move to the cities for work were quickly assimilated into the Russian-speaking worker class.
Russian Civil War and Soviet period (1918–1941)
 In April 1918 troops loyal to the
In April 1918 troops loyal to the Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) was a short-lived state in Eastern Europe. Prior to its proclamation, the Central Council of Ukraine was elected in March 1917 Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, as a result of the February Revolution, ...
took control of large parts of the region. For a while, its government bodies operated in the Donbas alongside their Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
equivalents. The Ukrainian State
The Ukrainian State (), sometimes also called the Second Cossack Hetmanate, Hetmanate (), was an Anti-communism, anti-Bolshevik government that existed on most of the modern territory of Ukraine (except for Western Ukraine) from 29 April to 14 ...
, the successor of the Ukrainian People's Republic, was able in May 1918 to bring the region under its control for a short time with the help of its German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
and Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consist ...
allies.Lessons for the Donbas from two warsThe Ukrainian Week
''The Ukrainian Week'' (, ) is an illustrated weekly magazine and news outlet covering politics, economics and the arts and aimed at the socially engaged Ukrainian-language reader. It provides a range of analysis, opinion, interviews, feature p ...
(16 January 2019)
During the 1917–22 Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
, Nestor Makhno
Nestor Ivanovych Makhno (, ; 7 November 1888 – 25 July 1934), also known as Bat'ko Makhno ( , ), was a Ukrainians, Ukrainian anarchist revolutionary and the commander of the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine during the Ukrainian War o ...
, who commanded the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine
The Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine (; RIAU), also known as ''Makhnovtsi'' (), named after their founder Nestor Makhno, was an Anarchism, anarchist army formed largely of Ukrainians, Ukrainian peasants and workers during the Russian C ...
, was the most popular leader in the Donbas.
Along with other territories inhabited by Ukrainians, the Donbas was incorporated into the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
in the aftermath of the Russian Civil War. Cossacks in the region were subjected to decossackisation during 1919–1921. Ukrainians in the Donbas were greatly affected by the 1932–33 Holodomor
The Holodomor, also known as the Ukrainian Famine, was a mass famine in Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1930–193 ...
famine and the Russification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
policy of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
. As most ethnic Ukrainians were rural peasant farmers, they bore the brunt of the famine.
Nazi occupation (1941–1943)
The Donbas was greatly affected by theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. In the lead-up to the war, the region was racked by poverty and food shortages. War preparations resulted in an extension of the working day for factory labourers, whilst those who deviated from the heightened standards were arrested. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
's leader Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
viewed the resources of the Donbas as critical to Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
. As such, the Donbas suffered under Nazi occupation during 1941 and 1942.
Thousands of industrial labourers were deported to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
for use in factories. In what was then called Stalino Oblast
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
, now Donetsk Oblast
Donetsk Oblast, also referred to as Donechchyna (, ), is an Oblasts of Ukraine, oblast in eastern Ukraine. It is Ukraine's most populous province, with around 4.1 million residents. Its capital city, administrative centre is Donetsk, though d ...
, 279,000 civilians were killed over the course of the occupation. In Voroshilovgrad Oblast, now Luhansk Oblast
Luhansk Oblast (; ), also referred to as Luhanshchyna (), is the easternmost Administrative divisions of Ukraine, oblast (province) of Ukraine. Its administrative center is the city of Luhansk. The oblast was established in 1938 and bore the n ...
, 45,649 were killed.
In 1943 the Operation Little Saturn
Operation Little Saturn () was a Red Army offensive on the Eastern Front of World War II that led to battles in Don and Chir rivers region in German-occupied Soviet Union territory in 16–30 December 1942.
The success of Operation Uranus, lau ...
and Donbas strategic offensive by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
resulted in the return of Donbas to Soviet control. The war had taken its toll, leaving the region both destroyed and depopulated.
Soviet period (1943–1991)
During the reconstruction of the Donbas after the end of the Second World War, large numbers of Russian workers arrived to repopulate the region, further altering the population balance. In 1926, 639,000 ethnic Russians resided in the Donbas, and Ukrainians made up 60% of the population. As a result of theRussification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
policy, the Ukrainian population of the Donbass then declined drastically as ethnic Russians settled in the region in large numbers. By 1959, the ethnic Russian population was 2.55 million. Russification was further advanced by the 1958–59 Soviet educational reforms, which led to the near elimination of all Ukrainian-language schooling in the Donbas. By the time of the Soviet Census of 1989, 45% of the population of the Donbas reported their ethnicity as Russian. In 1990, the Interfront of the Donbass was founded as a movement against Ukrainian independence.
In independent Ukraine (from 1991)
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. Turnout was 76.7% in Donetsk Oblast and 80.7% in Luhansk Oblast. In October 1991, a congress of South-Eastern deputies from all levels of government took place in Donetsk, where delegates demanded federalisation.
The region's economy deteriorated severely in the ensuing years. By 1993, industrial production had collapsed, and average wages had fallen by 80% since 1990. The Donbas fell into crisis, with many accusing the new central government in Kyiv
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
of mismanagement and neglect. Donbas coal miners went on strike in 1993, causing a conflict that was described by historian Lewis Siegelbaum as "a struggle between the Donbas region and the rest of the country". One strike leader said that Donbas people had voted for independence because they wanted "power to be given to the localities, enterprises, cities", not because they wanted heavily centralised power moved from "Moscow to Kyiv".
This strike was followed by a 1994 consultative referendum on various constitutional questions in Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts, held concurrently with the first parliamentary elections in independent Ukraine. These questions included whether Russian should be declared an official language of Ukraine, whether Russian should be the language of administration in Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts, whether Ukraine should federalise, and whether Ukraine should have closer ties with the Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional organization, regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an ar ...
.
Close to 90% of voters voted in favour of these propositions. None of them were adopted since the vote was nationwide. Ukraine remained a unitary state
A unitary state is a (Sovereign state, sovereign) State (polity), state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or ...
, Ukrainian was retained as the sole official language, and the Donbas gained no autonomy. Nevertheless, the Donbas strikers gained many economic concessions from Kyiv, allowing for an alleviation of the economic crisis in the region.
Small strikes continued throughout the 1990s, though demands for autonomy faded. Some subsidies to Donbas heavy industries were eliminated, and many mines were closed by the Ukrainian government because of liberalising reforms pushed for by the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
. Leonid Kuchma
Leonid Danylovych Kuchma (, ; born 9 August 1938) is a Ukrainian politician who was the second president of Ukraine, serving from 19 July 1994 to 23 January 2005. The only president of Ukraine to serve two terms, his presidency was marked by demo ...
, who had won the 1994 presidential election with support from the Donbas and other areas in eastern Ukraine, was re-elected as president of Ukraine
The president of Ukraine (, ) is the head of state of Ukraine. The president represents the nation in international relations, administers the foreign political activity of the state, conducts negotiations and concludes international treaties. ...
in 1999
1999 was designated as the International Year of Older Persons.
Events January
* January 1 – The euro currency is established and the European Central Bank assumes its full powers.
* January 3 – The Mars Polar Lander is launc ...
. President Kuchma gave economic aid to the Donbas, using development money to gain political support in the region.
Power in the Donbas became concentrated in a regional political elite, known as oligarchs, during the early 2000s. Privatisation of state industries led to rampant corruption. Regional historian Hiroaki Kuromiya described this elite as the "Donbas clan", a group of people that controlled economic and political power in the region. Prominent members of the "clan" included Viktor Yanukovych
Viktor Fedorovych Yanukovych (born 9 July 1950) is a Ukrainian politician who served as the fourth president of Ukraine from 2010 to 2014. He also served as the prime minister of Ukraine several times between 2002 and 2007 and was a member of t ...
and Rinat Akhmetov
Rinat Leonidovych Akhmetov (born 21 September 1966) is a Ukrainian billionaire and businessman. He is the founder and president of international investment group System Capital Management (SCM), and is the wealthiest man in Ukraine. Akhmetov i ...
.
A brief attempt at gaining autonomy by pro-Viktor Yanukovych politicians and officials was made in 2004 during the Orange Revolution
The Orange Revolution () was a series of protests that led to political upheaval in Ukraine from late November 2004 to January 2005. It gained momentum primarily due to the initiative of the general population, sparked by the aftermath of the ...
. The so-called South-East Ukrainian Autonomous Republic was intended to consist out of nine South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
-Eastern
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:
Transportation
Airlines
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 192 ...
regions of Ukraine. The project was initiated on 26 November 2004 by the Luhansk Oblast Council, and was discontinued the next month by the Donetsk Oblast Council. On 28 November 2004, in Sievierodonetsk
Sievierodonetsk or Severodonetsk, officially since 2024 Siverskodonetsk, is a city in Luhansk Oblast, eastern Ukraine. It is located to the northeast of the left bank of the Donets river and approximately to the northwest from the administrati ...
, the so-called took place, organised by the supporters of Viktor Yanukovych.The Congress of the Victors ("Съезд победителей")Zerkalo Nedeli
''Dzerkalo Tyzhnia'' (, ), usually referred to in English as the ''Mirror of the week'', is a Ukrainian online newspaper; it was one of Ukraine's most influential analytical weekly-publisher newspapers, founded in 1994.n Russian
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages, and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
''zn.ua''"The Congress of Regions" took place in Sievierodonetskn Ukrainian ''www.bbc.com'' A total of 3,576 delegates from 16
oblasts
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
of Ukraine, Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
and Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
took part in the congress, claiming to represent over 35 million citizens. Moscow Mayor Yurii Luzhkov and an advisor from the Russian Embassy were present in the presidium. There were calls for the appointment of Viktor Yanukovych as president of Ukraine or prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
, for declaring of martial law in Ukraine, dissolution of the Verkhovna Rada
The Verkhovna Rada ( ; VR), officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameralism, unicameral parliament of Ukraine. It consists of 450 Deputy (legislator), deputies presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovn ...
, creation of self-defence forces, and for the creation of a federative South-Eastern state with its capital in Kharkiv
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.
.
Donetsk Mayor Oleksandr Lukyanchenko
Oleksandr Oleksiyovych Lukyanchenko (, ; born 30 August 1947) is the '' de facto'' former mayor of the city of Donetsk, Ukraine. Under Ukrainian law, he is the ''de jure'' Mayor since 2014.
Life
He was born to a Russian-speaking Ukrainian fa ...
, however, stated that no one wanted autonomy, but rather sought to stop the Orange Revolution demonstrations going on at the time in Kyiv and negotiate a compromise. After the Orange Revolution's victory, some of the organisers of the congress were charged with "encroachment upon the territorial integrity and inviolability of Ukraine", but no convictions were made.
In other parts of Ukraine during the 2000s, the Donbas was often perceived as having a "thug culture", as being a "Soviet cesspool", and as "backward". Writing in the ''Narodne slovo'' newspaper in 2005, commentator Viktor Tkachenko said that the Donbas was home to "fifth column
A fifth column is a group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize ...
s", and that speaking Ukrainian in the region was "not safe for one's health and life". It was also portrayed as being home to pro-Russian separatism. The Donbas is home to a significantly higher number of cities and villages that were named after Communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
figures compared to the rest of Ukraine. Despite this portrayal, surveys taken across that decade and during the 1990s showed strong support for remaining within Ukraine and insignificant support for separatism.
Russo-Ukrainian War (2014–present)
War in Donbas
From the beginning of March 2014, demonstrations bypro-Russian
Russophilia is the identification or solidarity with, appreciation of, or support for the Russia, country, Russians, people, Russian language, language, and history of Russia. One who espouses Russophilia is called a russophile. Its Opposite ...
and anti-government groups took place in the Donbas, as part of the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity
The Revolution of Dignity (), also known as the Maidan Revolution or the Ukrainian Revolution, took place in Ukraine in February 2014 at the end of the Euromaidan protests, when deadly clashes between protesters and state forces in the capit ...
and the Euromaidan
Euromaidan ( ; , , ), or the Maidan Uprising, was a wave of Political demonstration, demonstrations and civil unrest in Ukraine, which began on 21 November 2013 with large protests in Maidan Nezalezhnosti (Independence Square) in Kyiv. The p ...
movement. These demonstrations, which followed the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula, part of Ukraine, and then annexed it. This took place in the relative power vacuum immediately following the Revolution of Dignity. It marked the beginning of the Russ ...
, and which were part of a wider group of concurrent pro-Russian protests across southern and eastern Ukraine, escalated in April 2014 into a war
''A War'' () is a 2015 Danish war drama film written and directed by Tobias Lindholm, and starring Pilou Asbæk, Tuva Novotny and Søren Malling. It tells the story of a Danish military company in Afghanistan that is fighting the Taliban while t ...
between the Russian-backed separatist forces of the self-declared Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; ; ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin, and Stalino, is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine located on the Kalmius River in Donetsk Oblast, which is currently occupied by Russia as the capita ...
and Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; , ), also known as Lugansk (, ; , ), is a city in the Donbas in eastern Ukraine. As of 2022, the population was estimated to be making Luhansk the Cities in Ukraine, 12th-largest city in Ukraine.
Luhansk served as the administra ...
People's Republics (DPR and LPR respectively), and the Ukrainian government
The Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine (), commonly referred to as the Government of Ukraine (), is the highest body of state executive power in Ukraine. As the Cabinet of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR, it was formed on 18 April 1991, by the Law ...
.
Amid that conflict, the self-proclaimed republics held referendums
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a direct vote by the electorate (rather than their representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either binding (resulting in the adoption of a new policy) or advis ...
on the status of Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts on 11 May 2014. In the referendums, viewed as illegal by Ukraine and undemocratic by the international community, about 90% voted for the independence of the DPR and LPR.The initial protests in the Donbas were largely native expressions of discontent with the new Ukrainian government. Russian involvement at this stage was limited to its voicing of support for the demonstrations. The emergence of the separatists in Donetsk and Luhansk began as a small fringe group of the protesters, independent of Russian control. This unrest, however, only evolved into an armed conflict because of Russian military backing for what had been a marginal group as part of the
Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
. The conflict was thus, in the words of historian Hiroaki Kuromiya, "secretly engineered and cleverly camouflaged by outsiders".
There was limited support for separatism in the Donbas before the outbreak of the war, and little evidence of support for an armed uprising. Russian claims that Russian speakers in the Donbas were being persecuted or even subjected to "genocide
Genocide is violence that targets individuals because of their membership of a group and aims at the destruction of a people. Raphael Lemkin, who first coined the term, defined genocide as "the destruction of a nation or of an ethnic group" by ...
" by the Ukrainian government, forcing its hand to intervene, were deemed false by Voice of America
Voice of America (VOA or VoA) is an international broadcasting network funded by the federal government of the United States that by law has editorial independence from the government. It is the largest and oldest of the American internation ...
.
Fighting continued through the summer of 2014, and by August 2014, the Ukrainian "Anti-Terrorist Operation" was able to vastly shrink the territory under the control of the pro-Russian forces, and came close to regaining control of the Russo-Ukrainian border. In response to the deteriorating situation in the Donbas, Russia abandoned what has been called its "hybrid war
Hybrid warfare was defined by Frank Hoffman in 2007 as the emerging simultaneous use of multiple types of warfare by flexible and sophisticated adversaries who understand that successful conflict requires a variety of forms designed to fit the goa ...
" approach, and began a conventional invasion of the region. As a result of the Russian invasion, DPR and LPR insurgents regained much of the territory they had lost during the Ukrainian government's preceding military offensive.
Only this Russian intervention prevented an immediate Ukrainian resolution to the conflict. This forced the Ukrainian side to seek the signing of a ceasefire agreement. Called the Minsk Protocol
The Minsk agreements were a series of international agreements which sought to end the Donbas war fought between armed Russian separatist groups and Armed Forces of Ukraine, with Russian regular forces playing a central part. After a defe ...
, this was signed on 5 September 2014. As this failed to stop the fighting, another agreement, called Minsk II
The Minsk agreements were a series of international agreements which sought to end the Donbas war fought between armed Russian separatist groups and Armed Forces of Ukraine, with Russian regular forces playing a central part. After a defe ...
was signed on 12 February 2015. This agreement called for the eventual reintegration of the Donbas republics into Ukraine, with a level of autonomy. The aim of the Russian intervention in the Donbas was to establish pro-Russian governments that, upon reincorporation into Ukraine, would facilitate Russian interference in Ukrainian politics. The Minsk agreements were thus highly favourable to the Russian side, as their implementation would accomplish these goals.
The conflict led to a vast exodus from the Donbas: half the region's population were forced to flee their homes. A UN OHCHR report released on 3 March 2016 stated that, since the conflict broke out in 2014, the Ukrainian government registered 1.6 million internally displaced people who had fled the Donbas to other parts of Ukraine. Over 1 million were said to have fled elsewhere, mostly to Russia. At the time of the report, 2.7 million people were said to continue to live in areas under DPR and LPR control, comprising about one-third of the Donbas.
Despite the Minsk agreements, low-intensity fighting along the line of contact between Ukrainian government and Russian-controlled areas continued until 2022. Since the start of the conflict there have been 29 ceasefires, each intended to remain in force indefinitely, but none of them stopped the violence.New Year ceasefire enters into force in DonbassTASS
The Russian News Agency TASS, or simply TASS, is a Russian state-owned news agency founded in 1904. It is the largest Russian news agency and one of the largest news agencies worldwide.
TASS is registered as a Federal State Unitary Enterpri ...
(29 December 2018) This led the war to be referred to as a "frozen conflict
In international relations, a frozen conflict is a situation in which active armed conflict has been brought to an end, but no peace treaty or other political framework resolves the conflict to the satisfaction of the combatants. Therefore, ...
".
On 11 January 2017, the Ukrainian government approved a plan to reintegrate the occupied part of the Donbas and its population into Ukraine. The plan would give Russian-backed political entities partial control of the electorate and has been described by ''Zerkalo Nedeli
''Dzerkalo Tyzhnia'' (, ), usually referred to in English as the ''Mirror of the week'', is a Ukrainian online newspaper; it was one of Ukraine's most influential analytical weekly-publisher newspapers, founded in 1994.Sociological Group "Rating" of residents of the Ukrainian-controlled parts of the Donbas found that 82% of respondents believed there was no discrimination against Russian-speaking people in Ukraine. Only 11% saw some evidence of discrimination. The same survey also found that 71% of respondents did not support Russia's military intervention to "protect" the Russian-speaking population, with only 9% offering support for that action. Another survey by Rating, conducted in 2019, found that only 23% of those Ukrainians polled supported granting the Donbas autonomous status, whilst 34% supported a ceasefire and "freezing" the conflict, 23% supported military action to recover the occupied Donbas territories, and 6% supported separating these territories from Ukraine.
 According to the 2001 census, ethnic Ukrainians form 58% of the population of Luhansk Oblast and 56.9% of Donetsk Oblast.
According to the 2001 census, ethnic Ukrainians form 58% of the population of Luhansk Oblast and 56.9% of Donetsk Oblast.  According to linguist George Shevelov, in the early 1920s the proportion of secondary schools teaching in the Ukrainian language was lower than the proportion of ethnic Ukrainians in the DonbasGames from the Past: The continuity and change of the identity dynamic in Donbas from a historical perspective
According to linguist George Shevelov, in the early 1920s the proportion of secondary schools teaching in the Ukrainian language was lower than the proportion of ethnic Ukrainians in the DonbasGames from the Past: The continuity and change of the identity dynamic in Donbas from a historical perspective
Södertörn University (19 May 2014) – even though the Soviet Union had ordered that all schools in the Ukrainian SSR should be Ukrainian-speaking (as part of its Ukrainization policy). Surveys of regional identities in Ukraine have shown that around 40% of Donbas residents claim to have a "Soviet people, Soviet identity". Roman Horbyk of Södertörn University wrote that in the 20th century, "[a]s peasants from all surrounding regions were flooding its then busy mines and plants on the border of ethnically Ukrainian and Russian territories", "incomplete and archaic institutions" prevented Donbas residents from "acquiring a notably strong modern urban – and also national – new identity".

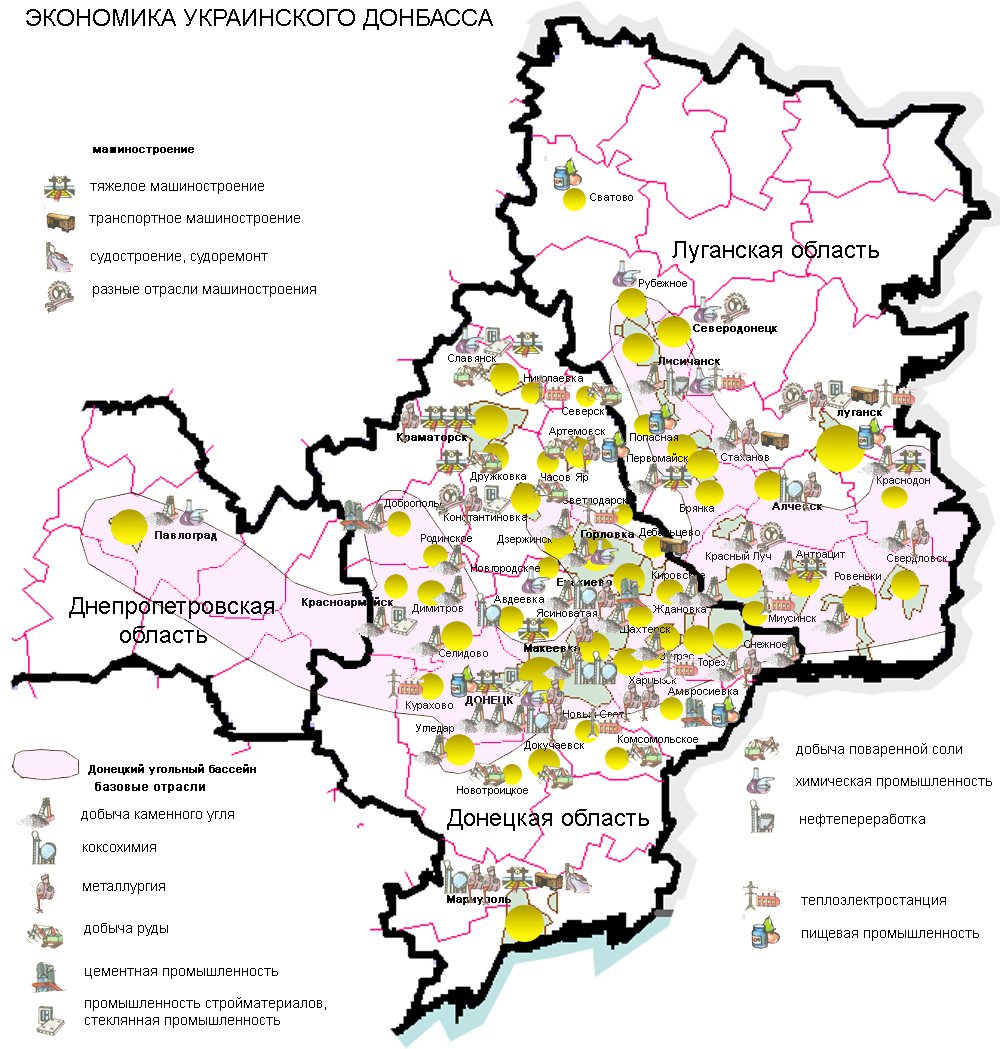
 The Gross regional product of Donbas was ₴335 billion (EUR, €10 billion) in 2021.
In 2013 (before war) GDP of Donbas was ₴220 billion (€20 billion).
The Donbas' economy is dominated by heavy industry, such as
The Gross regional product of Donbas was ₴335 billion (EUR, €10 billion) in 2021.
In 2013 (before war) GDP of Donbas was ₴220 billion (€20 billion).
The Donbas' economy is dominated by heavy industry, such as
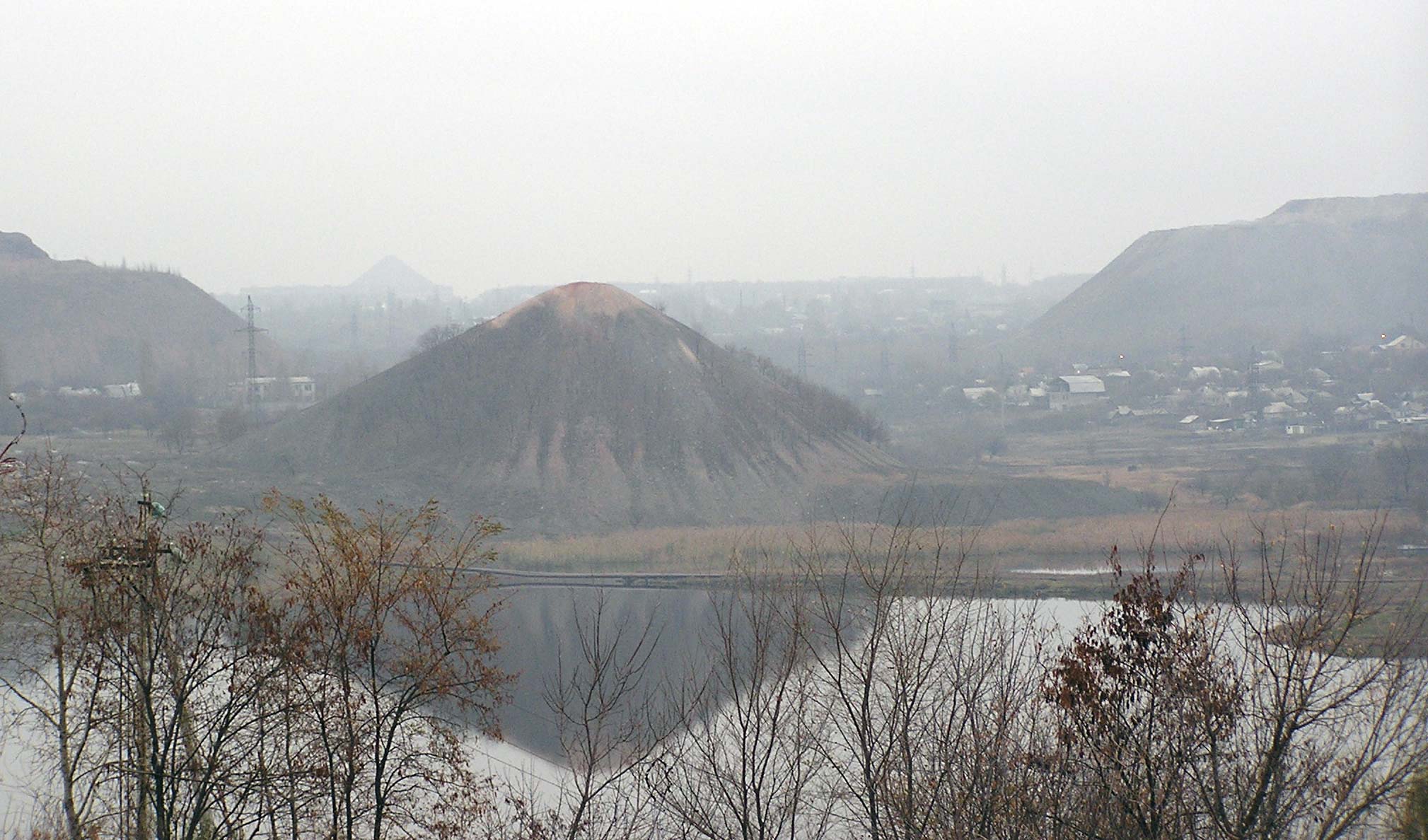 Intensive coal-mining and steel industry, smelting in the Donbas have led to severe damage to the local environment. The most common problems throughout the region include:
*water-supply disruption and flooding due to the mine water
*visible air pollution around Coke (fuel), coke and steel mills
*air/water contamination and mudslide threat from spoil tips
Additionally, several chemical waste-disposal sites in the Donbas have not been maintained, and pose a constant threat to the environment. One unusual threat is the result of the Soviet-era to test experimental Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy, nuclear mining in Yenakiieve. For example, on 16 September 1979, at the Yunkom coal mine, known today as the Young Communard mine in Yenakiyeve, a 300kt nuclear test explosion was conducted at 900m to free methane gas or to degasified coal seams into a sandstone oval dome known as the Klivazh [Rift] Site so that methane would not pose a hazard or threat to life. Before Glasnost, no miners were informed of the presence of radioactivity at the mine, however.
Intensive coal-mining and steel industry, smelting in the Donbas have led to severe damage to the local environment. The most common problems throughout the region include:
*water-supply disruption and flooding due to the mine water
*visible air pollution around Coke (fuel), coke and steel mills
*air/water contamination and mudslide threat from spoil tips
Additionally, several chemical waste-disposal sites in the Donbas have not been maintained, and pose a constant threat to the environment. One unusual threat is the result of the Soviet-era to test experimental Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy, nuclear mining in Yenakiieve. For example, on 16 September 1979, at the Yunkom coal mine, known today as the Young Communard mine in Yenakiyeve, a 300kt nuclear test explosion was conducted at 900m to free methane gas or to degasified coal seams into a sandstone oval dome known as the Klivazh [Rift] Site so that methane would not pose a hazard or threat to life. Before Glasnost, no miners were informed of the presence of radioactivity at the mine, however.
"Deconstructing the Donbass", overview of the 2014–2015 conflict
''midwestdiplomacy.com''
"The coal-mining racket threatening Ukraine's economy"
by BBC News
Bulletin board "Объявления Донбасса"
''donbass.men'' {{Authority control Donbas, Regions of Russia Geographic regions of Ukraine Economy of Ukraine Geography of Donetsk Oblast Geography of Luhansk Oblast Geography of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Geography of Rostov Oblast
Full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 21 February 2022, Russia officially recognised the independence of the Donetsk and Luhansk republics, effectively killing theMinsk agreements
The Minsk agreements were a series of international agreements which sought to end the Donbas war fought between armed Russian separatist groups and Armed Forces of Ukraine, with Russian regular forces playing a central part. After a defe ...
. Russia subsequently launched a new, full-scale invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022, which Russian president Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
said was intended to "protect" the people of the Donbas from the "abuse" and "genocide" of the Ukrainian government. However, Putin's claims have been refuted. The DPR and LPR joined Russia's operation; the separatists stated that an operation to capture the entirety of Donetsk Oblast and Luhansk Oblast had begun.
On 18 April 2022, the battle of Donbas began, a Russian offensive in mid-2022 within the larger eastern Ukraine campaign
Ukraine's easternmost oblasts, Donetsk, Luhansk, and Kharkiv, have been the site of an ongoing theatre of operation since the start of the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
The battle of Donbas was a major offensive in the easter ...
.
By September 2024, Russia had control of about 80% of the region.
Demographics and politics
 According to the 2001 census, ethnic Ukrainians form 58% of the population of Luhansk Oblast and 56.9% of Donetsk Oblast.
According to the 2001 census, ethnic Ukrainians form 58% of the population of Luhansk Oblast and 56.9% of Donetsk Oblast. Ethnic Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
form the largest minority, accounting for 39% and 38.2% of the two oblasts respectively. In the present day, the Donbas is a predominately Russophone region. According to the 2001 census, Russian is the main language of 74.9% of residents in Donetsk Oblast and 68.8% in Luhansk Oblast.
Residents of Russian origin are mainly concentrated in the larger urban centers. Russian became the main language and ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
'' in the course of industrialization, boosted by the immigration of many Russians, particularly from Kursk Oblast
Kursk Oblast (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Kursk. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, Kursk Oblast had a pop ...
, to newly founded cities in the Donbas. A subject of continuing research controversies, and often denied in these two oblasts, is the extent of forced emigration and deaths during the Soviet period, which particularly affected rural Ukrainians during the Holodomor which resulted as a consequence of early Soviet industrialization policies combined with two years of drought throughout southern Ukraine and the Volga region.
Nearly all Ukrainian Jews either fled or were murdered in the Holocaust in Ukraine
The Holocaust saw the systematic mass murder of Jews in the '' Reichskommissariat Ukraine'', the General Government, the Crimean General Government and some areas which were located to the east of ''Reichskommissariat Ukraine'' (all of those ar ...
during the German occupation in World War II. The Donbas is about 6% Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
according to the official censuses of 1926
In Turkey, the year technically contained only 352 days. As Friday, December 18, 1926 ''(Julian Calendar)'' was followed by Saturday, January 1, 1927 '' (Gregorian Calendar)''. 13 days were dropped to make the switch. Turkey thus became the ...
and Ukrainian Census (2001), 2001.
Prior to the Revolution of Dignity, the politics of the region were dominated by the pro-Russian Party of Regions, which gained about 50% of Donbas votes in the 2008 Ukrainian parliamentary election. Prominent members of that party, such as former Ukrainian president Viktor Yanukovych, were from the Donbas.
 According to linguist George Shevelov, in the early 1920s the proportion of secondary schools teaching in the Ukrainian language was lower than the proportion of ethnic Ukrainians in the DonbasGames from the Past: The continuity and change of the identity dynamic in Donbas from a historical perspective
According to linguist George Shevelov, in the early 1920s the proportion of secondary schools teaching in the Ukrainian language was lower than the proportion of ethnic Ukrainians in the DonbasGames from the Past: The continuity and change of the identity dynamic in Donbas from a historical perspective Södertörn University (19 May 2014) – even though the Soviet Union had ordered that all schools in the Ukrainian SSR should be Ukrainian-speaking (as part of its Ukrainization policy). Surveys of regional identities in Ukraine have shown that around 40% of Donbas residents claim to have a "Soviet people, Soviet identity". Roman Horbyk of Södertörn University wrote that in the 20th century, "[a]s peasants from all surrounding regions were flooding its then busy mines and plants on the border of ethnically Ukrainian and Russian territories", "incomplete and archaic institutions" prevented Donbas residents from "acquiring a notably strong modern urban – and also national – new identity".
Religion
According to a 2016 survey of religion in Ukraine held by the Razumkov Center, 65.0% of the population in the Donbas believe in Christianity (including 50.6% Orthodox, 11.9% who declared themselves to be "simply Christians", and 2.5% who belonged to Protestant churches). Islam is the religion of 6% of the population of the Donbas and Hinduism of the 0.6%, both the religions with a share of the population that is higher compared to other regions of Ukraine. People who declared to be not believers or believers in some other religions, not identifying in one of those listed, were 28.3% of the population.Economy

 The Gross regional product of Donbas was ₴335 billion (EUR, €10 billion) in 2021.
In 2013 (before war) GDP of Donbas was ₴220 billion (€20 billion).
The Donbas' economy is dominated by heavy industry, such as
The Gross regional product of Donbas was ₴335 billion (EUR, €10 billion) in 2021.
In 2013 (before war) GDP of Donbas was ₴220 billion (€20 billion).
The Donbas' economy is dominated by heavy industry, such as coal mining
Coal mining is the process of resource extraction, extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its Energy value of coal, energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to Electricity generation, generate electr ...
and metallurgy. The region takes its name from an abbreviation of the term "Donets Coal Basin" (, ), and while annual extraction of coal has decreased since the 1970s, the Donbas remains a significant producer. The Donbas represents one of the largest coal reserves in Ukraine, with estimated reserves of 60 billion tonnes of coal.
Coal mining in the Donbas is conducted at very deep depths. Lignite mining takes place at around below the surface, whilst mining for the more valuable anthracite and bituminous coal takes place at depths of around . Prior to the start of the region's war in April 2014, Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts together produced about 30 percent of Ukraine's exports.
Other industries in the Donetsk region include blast-furnace and steel-making equipment, railway freight-cars, metal-cutting machine-tools, tunneling machines, agricultural harvesters and ploughing systems, railway tracks, mining cars, electric locomotives, military vehicles, tractors and excavators. The region also produces consumer goods like household washing-machines, refrigerators, freezers, TV sets, leather footwear, and toilet soap. Over half its production is exported, and about 22% is exported to Russia.
In mid-March 2017, Ukrainian president Petro Poroshenko signed a decree on a temporary ban on the movement of goods to and from territory controlled by the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic, so since then Ukraine does not buy coal from the Donets Coal Basin.
Shale gas reserves, part of the larger Dnieper–Donets basin, are present in the Donbas, most notably the Yuzivska gas field. In an effort to reduce Ukrainian dependence on Russian gas imports, the Ukrainian government reached an agreement with Royal Dutch Shell in 2012 to develop the Yuzivska field. Shell was forced to freeze operations after the outbreak of war in the region in 2014, and officially withdrew from the project in June 2015.
Occupational safety in the coal industry
The coal mines of the Donbas are some of the most Mining accident, hazardous in the world because of the deep depths of mines, as well as frequent methane, methane explosions, coal dust, coal-dust explosions, rock burst dangers, and outdated infrastructure.Grumau, S. (2002). Coal mining in Ukraine. Economic Review. 44. Even more hazardous illegal coal mines became very common across the region in the late 2000s.Environmental problems
 Intensive coal-mining and steel industry, smelting in the Donbas have led to severe damage to the local environment. The most common problems throughout the region include:
*water-supply disruption and flooding due to the mine water
*visible air pollution around Coke (fuel), coke and steel mills
*air/water contamination and mudslide threat from spoil tips
Additionally, several chemical waste-disposal sites in the Donbas have not been maintained, and pose a constant threat to the environment. One unusual threat is the result of the Soviet-era to test experimental Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy, nuclear mining in Yenakiieve. For example, on 16 September 1979, at the Yunkom coal mine, known today as the Young Communard mine in Yenakiyeve, a 300kt nuclear test explosion was conducted at 900m to free methane gas or to degasified coal seams into a sandstone oval dome known as the Klivazh [Rift] Site so that methane would not pose a hazard or threat to life. Before Glasnost, no miners were informed of the presence of radioactivity at the mine, however.
Intensive coal-mining and steel industry, smelting in the Donbas have led to severe damage to the local environment. The most common problems throughout the region include:
*water-supply disruption and flooding due to the mine water
*visible air pollution around Coke (fuel), coke and steel mills
*air/water contamination and mudslide threat from spoil tips
Additionally, several chemical waste-disposal sites in the Donbas have not been maintained, and pose a constant threat to the environment. One unusual threat is the result of the Soviet-era to test experimental Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy, nuclear mining in Yenakiieve. For example, on 16 September 1979, at the Yunkom coal mine, known today as the Young Communard mine in Yenakiyeve, a 300kt nuclear test explosion was conducted at 900m to free methane gas or to degasified coal seams into a sandstone oval dome known as the Klivazh [Rift] Site so that methane would not pose a hazard or threat to life. Before Glasnost, no miners were informed of the presence of radioactivity at the mine, however.
Culture and religion
Sviatohirsk () is the main religious sanctuary of the region. The Sviatohirsk Lavra is located near the city. The monastery was restored following the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the independence of Ukraine. In 2004 the monastery was granted the status of lavra. In 1997 area around the monastery was turned into the Holy Mountains National Nature Park.See also
* Donbas Arena * HC Donbass, an ice hockey team based inDonetsk
Donetsk ( , ; ; ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin, and Stalino, is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine located on the Kalmius River in Donetsk Oblast, which is currently occupied by Russia as the capita ...
bearing the name of the region
* Russians in Ukraine
* Kryvbas
Notes
References
External links
"Deconstructing the Donbass", overview of the 2014–2015 conflict
''midwestdiplomacy.com''
"The coal-mining racket threatening Ukraine's economy"
by BBC News
Bulletin board "Объявления Донбасса"
''donbass.men'' {{Authority control Donbas, Regions of Russia Geographic regions of Ukraine Economy of Ukraine Geography of Donetsk Oblast Geography of Luhansk Oblast Geography of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Geography of Rostov Oblast