Diamantinasaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Diamantinasaurus'' is a genus of
 The
The
 As is typical for
As is typical for
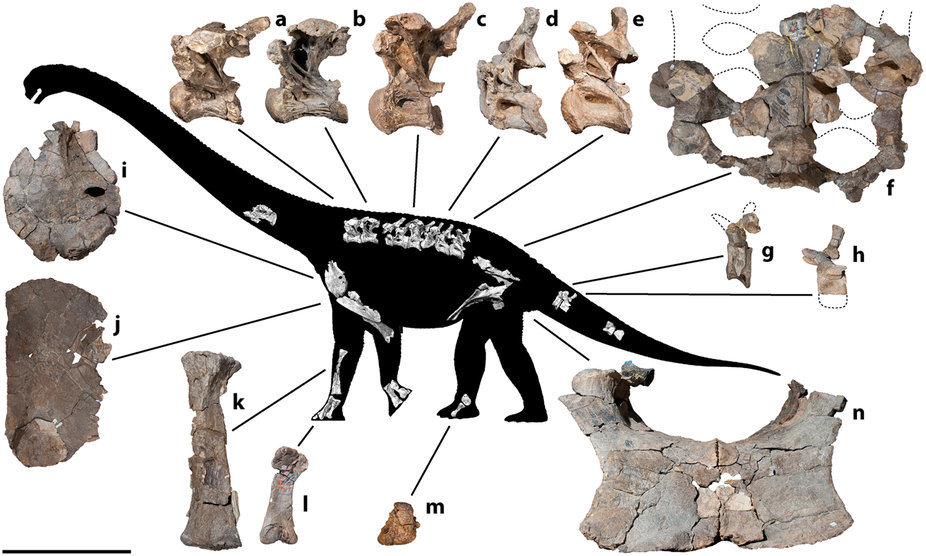
 Almost all the right forelimb is known from ''Diamantinasaurus'', although the left humerus is known in addition to the right, and the left first metacarpal is known while the right is unpreserved. Diagnostic of ''Diamantinasaurus'', the
Almost all the right forelimb is known from ''Diamantinasaurus'', although the left humerus is known in addition to the right, and the left first metacarpal is known while the right is unpreserved. Diagnostic of ''Diamantinasaurus'', the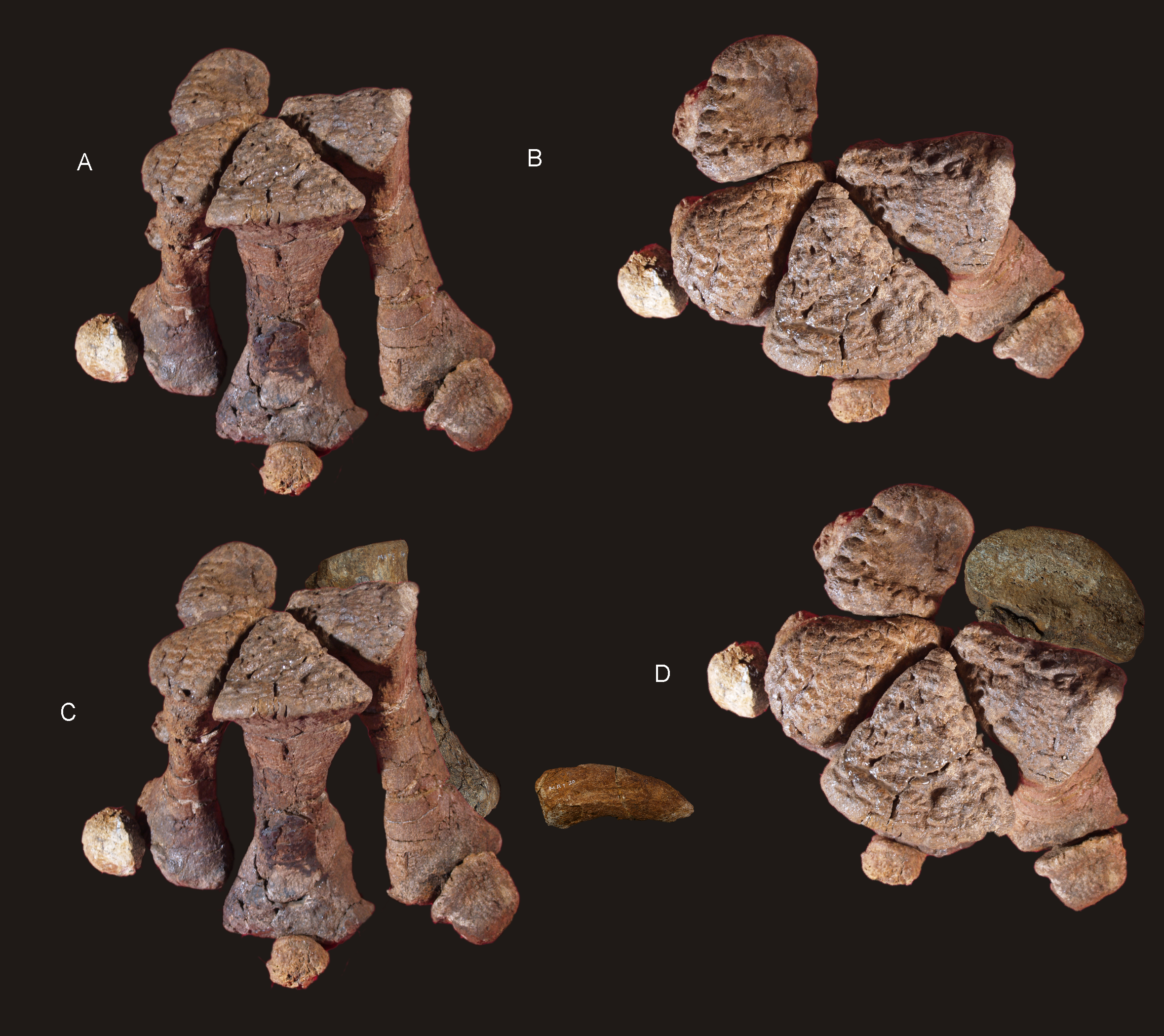  Because of the completeness of the forelimb material, the absence of
Because of the completeness of the forelimb material, the absence of
 The left ilium, left and right pubes, left and right
The left ilium, left and right pubes, left and right 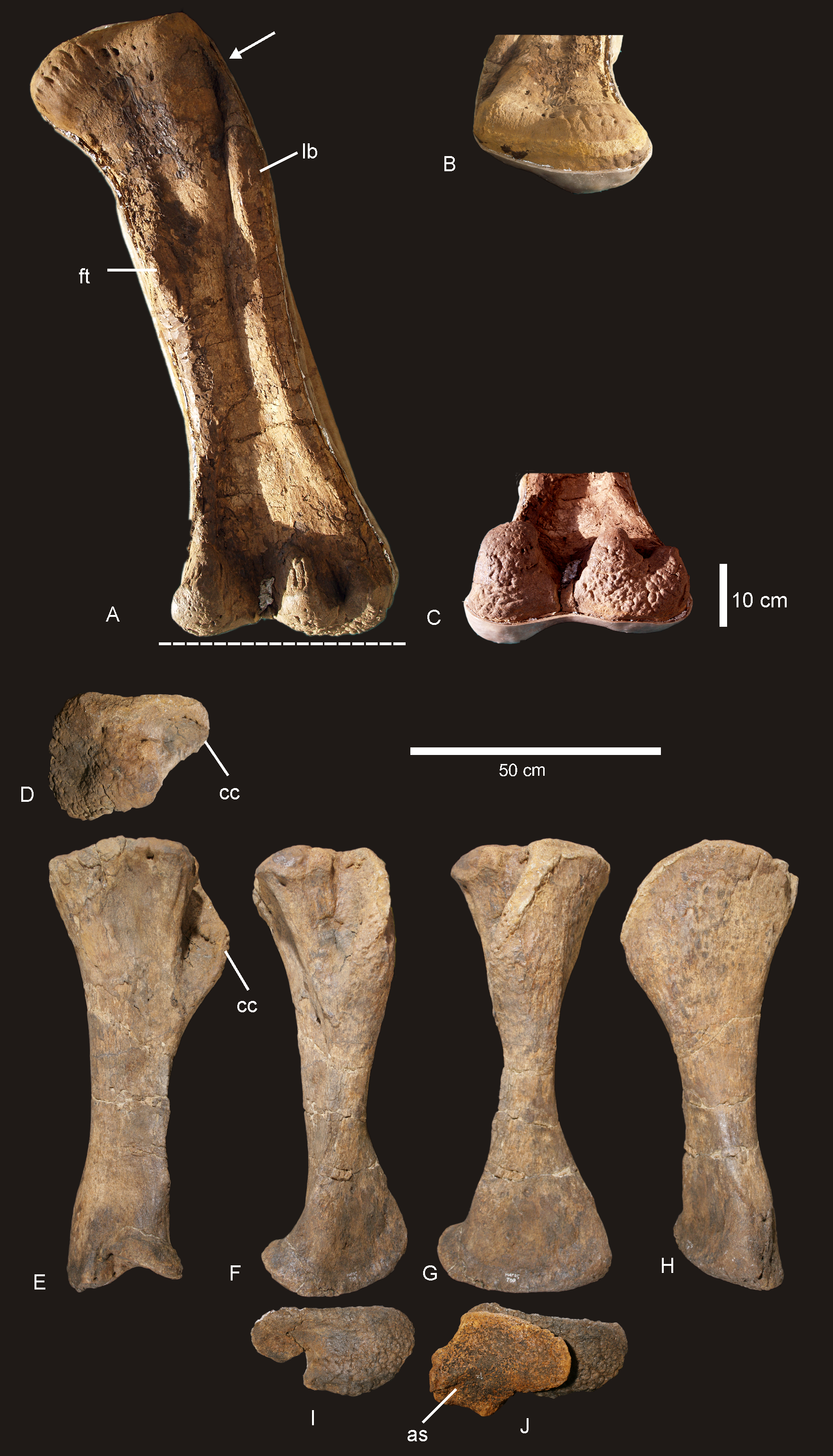 The femur, long, is roughly twice as wide as it is long, as in other derived sauropods, although it has been slightly crushed. The crushing did not prevent the preservation of the ''linea intermuscularis cranialis'' ridge, also present in ''Saltasaurus'', ''Neuquensaurus'', ''
The femur, long, is roughly twice as wide as it is long, as in other derived sauropods, although it has been slightly crushed. The crushing did not prevent the preservation of the ''linea intermuscularis cranialis'' ridge, also present in ''Saltasaurus'', ''Neuquensaurus'', ''

 In the same study, the relationships using the Mannion ''et al.'' (2013) matrix were tested. These resolved with ''Diamantinasaurus'' as a saltasaurid, sister to ''
In the same study, the relationships using the Mannion ''et al.'' (2013) matrix were tested. These resolved with ''Diamantinasaurus'' as a saltasaurid, sister to '' The 2021 study recovered a similar topology, finding a close relationship with ''Savannasaurus'' as well as ''
The 2021 study recovered a similar topology, finding a close relationship with ''Savannasaurus'' as well as ''
 ''Diamantinasaurus'' was found about northwest of Winton, near Elderslie Station. It was recovered from the fossil-rich section of the
''Diamantinasaurus'' was found about northwest of Winton, near Elderslie Station. It was recovered from the fossil-rich section of the
titanosaur
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still th ...
ian sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their bo ...
from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
that lived during the early Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5ŌĆō66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
, about 94 million years ago. The type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
of the genus is ''D. matildae'', first described and named in 2009
File:2009 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The vertical stabilizer of Air France Flight 447 is pulled out from the Atlantic Ocean; Barack Obama becomes the first African American to become President of the United States; 2009 Iran ...
by Scott Hocknull
Scott Hocknull (born 1977) is a vertebrate palaeontologist and Senior Curator in Geology at the Queensland Museum in Brisbane. He was the 2002 recipient of the Young Australian of the Year Award.
He is the youngest Australian to date to hold a ...
and colleagues based on fossil finds in the Winton Formation
The Winton Formation is a Cretaceous geological formation in central-western Queensland, Australia. It is late Albian to early Turonian in age. The formation blankets large areas of central-western Queensland. It consists of sedimentary rocks suc ...
. Meaning "Diamantina lizard", the name is derived from the location of the nearby Diamantina River
The Diamantina River is a major river located in Central West Queensland and the far north of South Australia.
The river was named by William Landsborough in 1866 for Lady Diamantina Bowen (n├®e Roma), wife of Sir George Bowen, the first Govern ...
and the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word ''sauros'', "lizard". The specific epithet is from the Australian song Waltzing Matilda, also the locality of the holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
and paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype nor a syntype). Of ...
. The known skeleton includes most of the forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial ( anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. ...
, shoulder girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of t ...
, pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, hindlimb
A hindlimb or back limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the caudal ( posterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso.http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hind%20limb, Merriam Webster Dictionary-Hindl ...
and rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s of the holotype, and one shoulder bone, a radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
and some vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic i ...
of the paratype.
History of discovery
 The
The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
of ''Diamantinasaurus'' was first uncovered over four seasons of excavations near Winton, Queensland
Winton is a town and Suburbs and localities (Australia), locality in the Shire of Winton in Central West Queensland, Australia. It is northwest of Longreach, Queensland, Longreach. The main industries of the area are sheep and cattle raising. Th ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
. The bones were found alongside the holotype of ''Australovenator
''Australovenator'' (meaning "southern hunter") is a genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation (dated to 95 million years ago) of Australia. It is known from partial cranial and postcranial rem ...
'' and crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction.
During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, cro ...
s and mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
s. The two dinosaurs found, known from specimens catalogued as AODF 603 and 604 were described in 2009 by Scott Hocknull
Scott Hocknull (born 1977) is a vertebrate palaeontologist and Senior Curator in Geology at the Queensland Museum in Brisbane. He was the 2002 recipient of the Young Australian of the Year Award.
He is the youngest Australian to date to hold a ...
and his colleagues. Specimen AODF 603 became the basis for the genus ''Diamantinasaurus'', and the species ''D. matildae''. The species name is a reference to the song "Waltzing Matilda", written by Banjo Paterson
Andrew Barton "Banjo" Paterson, (17 February 18645 February 1941) was an Australian bush poet, journalist and author. He wrote many ballads and poems about Australian life, focusing particularly on the rural and outback areas, including the ...
in Winton, while the generic name is derived from the Diamantina River
The Diamantina River is a major river located in Central West Queensland and the far north of South Australia.
The river was named by William Landsborough in 1866 for Lady Diamantina Bowen (n├®e Roma), wife of Sir George Bowen, the first Govern ...
, running nearby the type locality combined with the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''sauros'', meaning "lizard". AODF 603, the holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
, includes the right scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
, both humeri
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a round ...
, right ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
, both incomplete hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
s, dorsal rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s and gastralia
Gastralia (singular gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these ...
, partial pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, and the right hindlimb missing the foot. The paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype nor a syntype). Of ...
, under the same specimen, includes dorsal and sacral vertebrae, the right sternal plate now thought to represent the remainder of a coracoid
A coracoid (from Greek ╬║ŽīŽü╬▒╬Š, ''koraks'', raven) is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is prese ...
, a radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
, and one manual phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, Žå╬¼╬╗╬▒╬│╬Š; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly use ...
. All these bones come from AODL 85, nicknamed the "Matilda Site" at Elderslie Sheep Station, located about west-northwest from Winton in central Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
. This locality is in the upper midsection of the Winton Formation
The Winton Formation is a Cretaceous geological formation in central-western Queensland, Australia. It is late Albian to early Turonian in age. The formation blankets large areas of central-western Queensland. It consists of sedimentary rocks suc ...
, which dates to the Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the s ...
of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5ŌĆō66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
.
The discovery of ''Diamantinasaurus'' ended a pause in the discovery of new dinosaurs in Australia, as the first sauropod named in over 75 years. Along with ''Australovenator'', ''Diamantinasaurus'' has been nicknamed after the Australian song "Waltzing Matilda", with ''Australovenator'' being called "Banjo" and ''Diamantinasaurus'' being nicknamed "Matilda". ''Wintonotitan
''Wintonotitan'' (meaning " Winton titan") is a genus of titanosauriform dinosaur from late Albian (Early Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation of Australia. It is known from partial postcranial remains.
Description and history
Fossils that are ...
'', also from the site, was dubbed "Clancy". The find was apparently the largest dinosaur discovery in Australia that was documented since that of ''Muttaburrasaurus
''Muttaburrasaurus'' was a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian ornithopod dinosaur, which lived in what is now northeastern Australia sometime between 110 and 103 million years agoHoltz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-D ...
'' in 1981.
An additional specimen, AODF 836, was described in 2016. It includes portions of the skull, including a left squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including ...
, nearly complete braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
, right surangular
The suprangular or surangular is a jaw bone found in most land vertebrates, except mammals. Usually in the back of the jaw, on the upper edge, it is connected to all other jaw bones: dentary, angular, splenial and articular
The articular bone i ...
, and various fragments. Additionally, the specimen also includes the atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
, axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
*Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinate ...
, five other cervical vertebrae, three dorsal vertebrae, additional dorsal ribs, portions of the hip, and another right scapula. In 2021 the referred material was thoroughly described.
Description
''Diamantinasaurus'' was relatively small for a titanosaurian, possibly reaching in length and in weight. Some of its relatives are known possessed armourosteoderms
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct ...
although it is unknown whether ''Diamantinasaurus'' had these. Like other sauropods, ''Diamantinasaurus'' would have been a large quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor' ...
al herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
. Since the original description, the only major revisions include the misidentification of the "sternal plate", misplacement of manual phalanges III-1 and IV-1 as III-1 and V-1 respectively, and the identification of the missing portion of the fibula.
The skull of ''Diamantinasaurus'' is incompletely known, with only the posterior skull roof and braincase being preserved. Similarly to ''Saltasaurus
''Saltasaurus'' (which means "lizard from Salta") is a genus of saltasaurid dinosaur of the Late Cretaceous period of Argentina. Small among sauropods, though still heavy by the standards of modern creatures, ''Saltasaurus'' was characterized by ...
'' and ''Rapetosaurus
''Rapetosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur that lived in Madagascar from 70 to 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period. Only one species, ''Rapetosaurus krausei'', has been identified.
Like other sauropod ...
'' and unlike ''Nemegtosaurus
''Nemegtosaurus'' (meaning 'Reptile from the Nemegt') was a sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now Mongolia. It was named after the Nemegt Basin in the Gobi Desert, where the remains ŌĆö a single skull ŌĆö were found. Th ...
'', the was bordered by the frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, par ...
. Contrasting from both latter genera, ''Diamantinasaurus'' has a low above the cranial foramen, which is subsequently less than 1.5 times the height of the (which has a foramen). All of these traits are however shared with ''Saltasaurus''. Multiple other traits are found throughout derived titanosaurs, including downward angling of the skull, prong shaped lateral braincase processes, an undisturbed pituitary fossa
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric la ...
, and a more centrally located opening for the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these b ...
.
 As is typical for
As is typical for Titanosauriformes
Macronaria is a clade of sauropod dinosaurs. Macronarians are named after the large diameter of the nasal opening of their skull, known as the external naris, which exceeded the size of the orbit, the skull opening where the eye is located (hence ...
, all cervical and dorsal vertebrae of ''Diamantinasaurus'' are and camellate (many small internal chambers). The axis vertebra of the genus is short, a potential characteristic of Saltasauridae
Saltasauridae (named after the Salta region of Argentina where they were first found) is a family of armored herbivorous sauropods from the Upper Cretaceous. They are known from fossils found in South America, Asia, North America, and Europe. Th ...
. Contrasting ''Saltasaurus'' and ''Rapetosaurus'' however, the of ''Diamantinasaurus'' extend in front of the centrum. Only certain in the known middle dorsals, the (ridge on posterior surface of spine) extends below the spine itself. Like more basal sauropods ''Europasaurus
''Europasaurus'' is a basal macronarian sauropod, a form of quadrupedal herbivorous dinosaur. It lived during the Late Jurassic (middle Kimmeridgian, about 154 million years ago) of northern Germany, and has been identified as an example of insul ...
'' and ''Euhelopus
''Euhelopus'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived between 145 and 133 million years ago during the Berriasian and Valanginian stages of the Early Cretaceous in what is now Shandong Province in China. It was a large quadrupedal herbivore. U ...
'', the dorsal vertebrae have a notch on the top of the posterior centrum face, giving it a heart-shaped appearance, contrasting more derived titanosaurs or ''Giraffatitan
''Giraffatitan'' (name meaning "titanic giraffe") is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the late Jurassic Period (geology), Period (KimmeridgianŌĆōTithonian stages) in what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania. It was originally named as an ...
'' which possess flattened centra. Although differing in centrum shape, ''Opisthocoelicaudia
''Opisthocoelicaudia'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur of the late Cretaceous, Late Cretaceous Period discovered in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. The type species is ''Opisthocoelicaudia skarzynskii''. A well-preserved skeleton lacking only the ...
'' and ''Diamantinasaurus'' are the only titanosaurs to share a ventral keel set within a sharply defined depression under the dorsals. Dorsal prezygapophyses are linked to the spine by a , which is absent in ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' and most dorsals of ''Rapetosaurus'', and the found in ''Diamantinasaurus'' is also absent in most derived titanosaurs. There is no indication of a , a diagnostic feature of derived titanosaurs. Shared with ''Opisthocoelicaudia'', ''Alamosaurus
''Alamosaurus'' (; meaning "Ojo Alamo lizard") is a genus of opisthocoelicaudiine titanosaurian sauropod dinosaurs, containing a single known species, ''Alamosaurus sanjuanensis'', from the late Cretaceous Period of what is now southern North Am ...
'' and ''Lirainosaurus
''Lirainosaurus'' (meaning "slender lizard"; from the Basque ''lirain'', meaning "slender", and the Greek ''sauros'', meaning "lizard")is a genus of titanosaur sauropod which lived in what is now Spain. The type species, ''Lirainosaurus astibiae ...
'' to the exclusion of other titanosaurs, ''Diamantinasaurus'' has a simple undivided ridge between the posterior centrum and diapophysis (). A poorly preserved feature between the prezygapophysis and centrum may be the , found in some brachiosaurids, basal titanosaurs, and ''Opisthocoelicaudia''. ''Diamantinasaurus'' possessed at least five, possibly six, sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
.
Forelimb
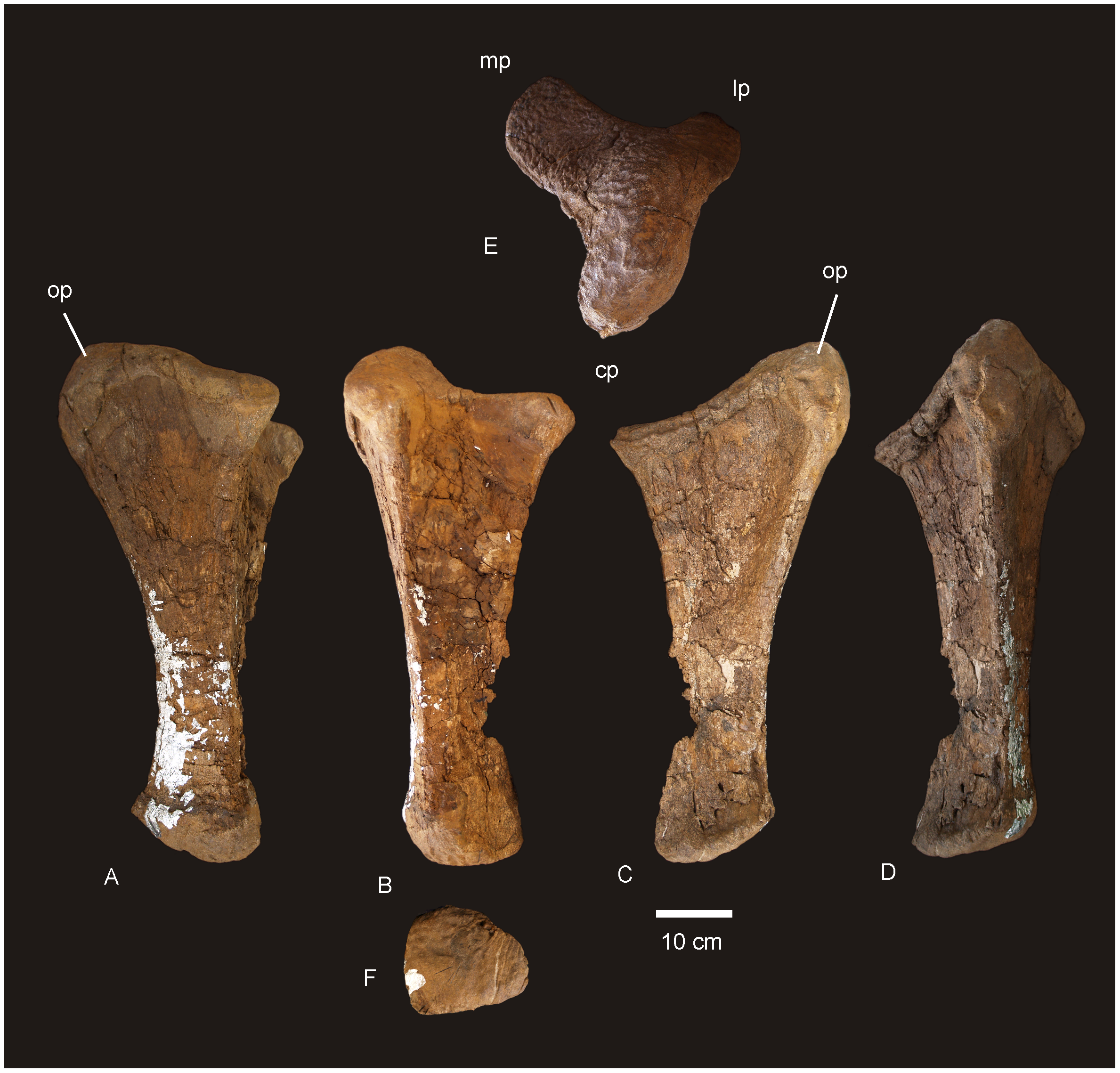
 Almost all the right forelimb is known from ''Diamantinasaurus'', although the left humerus is known in addition to the right, and the left first metacarpal is known while the right is unpreserved. Diagnostic of ''Diamantinasaurus'', the
Almost all the right forelimb is known from ''Diamantinasaurus'', although the left humerus is known in addition to the right, and the left first metacarpal is known while the right is unpreserved. Diagnostic of ''Diamantinasaurus'', the glenoid
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from el, gl├®ne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a sha ...
(humerus) articulation of the scapula is rotated to the outside, differing from all other somphospondylans. Similar to ''Alamosaurus'' and taxa around the base of Titanosauria, at least a single ventral process is known, although it is poorly preserved. The scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
of ''Diamantinasaurus'' is robust, having a more round cross-section than other somphospondylans. The coracoid, misidentified as a sternal in the original description, is plain and unfeatured, contrasting ''Huabeisaurus
''Huabeisaurus'' (, meaning " North China lizard") was a genus of dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous ( Cenomanian to Maastrichtian stages, around 99.7ŌĆō70.6 million years ago). It was a sauropod which lived in what is present-day northern Chin ...
'', ''Lirainosaurus'' and ''Opisthocoelicaudia''. The proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
surface of the humerus is prominently curved as in the derived titanosaurs ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' and ''Saltasaurus''. The lateral corner is also squared, placing it within Somphospondyli. Like with most somphospondylans but unlike ''Euhelopus'' and ''Rapetosaurus'', ''Diamantinasaurus'' has a middle-shifted . Ridges for muscle attachment are less developed than in ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' and ''Magyarosaurus
''Magyarosaurus'' (" Magyar lizard") is a genus of dwarf sauropod dinosaur from late Cretaceous Period (early to late Maastrichtian) in Romania. It is one of the smallest-known adult sauropods, measuring only in length and in body mass. The t ...
''. Differing from derived titanosaurs, the condyles to articulate with the forearm are not pronounced. ''Diamantinasaurus'' has an ulna comparing to derived titanosaurs in the level of robustness, as well as having a very pronounced olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony eminence of the ulna, a long bone in the forearm that projects behind the elbow. It forms the most pointed portion of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit. The olecranon ...
. Similarly, the radius of ''Diamantinasaurus'' is more robust than all titanosaurs except ''Opisthocoelicaudia''. The ulna is long, while the radius is .
 Because of the completeness of the forelimb material, the absence of
Because of the completeness of the forelimb material, the absence of carpal bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek ╬║╬▒ŽüŽĆŽīŽé (karp├│s), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, th ...
among the preserved material was presumed by Poropat ''et al.'' (2014) to be related to their genuine absence in life, as in ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' and ''Alamosaurus''. The manus of ''Diamantinasaurus'' comparatively displays some plesiomorphic features, including: the middle metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones ...
being the longest ( Mc III compared to next longest Mc II); the presence of a thumb claw; and the presence of multiple phalanges, having the phalangeal formula 2–1–1–1–1. However, the manus of ''Diamantinasaurus'' is completely cylindrical and vertical like other titanosaurs. The presence of large numbers of phalanges in ''Diamantinasaurus'' was used by Poropat ''et al.'' (2014) to suggest that all titanosaurs actually had ossified phalanges contrasting earlier studies. Following this logic, they suggested that for ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' and ''Epachthosaurus
''Epachthosaurus'' (meaning "heavy lizard") was a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It was a basal lithostrotian titanosaur. Its fossils have been found in Central and Northern Patagonia in South America.
Discov ...
'', which both preserve a single phalanx from the fourth finger, the absence of others was due to them being lost before fossilization for the preceding digits, instead of absence. The complete absence of preserved phalanges in ''Alamosaurus'', ''Rapetosaurus'', ''Neuquensaurus
''Neuquensaurus'' (meaning "Neuqu├®n lizard") is a genus of saltasaurid sauropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 80 million years ago in Argentina and Uruguay in South America. Its fossils were recovered from outcrops of the Ana ...
'' and ''Saltasaurus'' potentially being due to disarticulation instead of absence of ossification.
Hindlimb
 The left ilium, left and right pubes, left and right
The left ilium, left and right pubes, left and right ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to west ...
, and entire right leg lacking the foot are preserved for ''Diamantinasaurus'', although some bones are highly fragmented and poorly preserved. The ilium has the outside well preserved, but its size and fragility mean the internal side cannot be seen for anatomical features. The top edge of the ilium is broken, revealing numerous small internal camerae, as present in the titanosaurs ''Alamosaurus'', ''Epachthosaurus'', ''Lirainosaurus'', ''Saltasaurus'' and ''Sonidosaurus
''Sonidosaurus'' (meaning "Sonid lizard", after Sonid, the large geographical area that includes the type locality ) is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It was a titanosaur which lived in what is now Inner Mongolia. The type ...
''. Shared with other derived titanosaurs, the anterior process of the ilium flares to the side and rotates so the vertical ilium body becomes a horizontal shelf. ''Diamantinasaurus'' also displays the derived sauropod traits of a rounded ilium, reduced articular surface for the ischium, and a protuberance above the ischiatic articulation (only shared with ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' among Titanosauriformes). The pubis, as in advanced sauropods, is a flattened bone, lacking the anterior hook of diplodocoids, but with potentially autapomorphic grooves surrounding the obturator foramen
The obturator foramen (Latin foramen obturatum) is the large opening created by the ischium and pubis (bone), pubis bones of the pelvis through which nerves and blood vessels pass.
Structure
It is bounded by a thin, uneven margin, to which a str ...
. Articulation with the ischium takes up 46% of the pubic length, as in most macronarians but contrasting with ''Alamosaurus'' and ''Opisthocoelicaudia'', where it is reduced. The entire ischium is only 68% of the length of the pubis as in other titanosaurs, and also expands medially so the entire floor of the pelvis is closed. Unlike some titanosaurs, the ischium of ''Diamantinasaurus'' displays no constriction of its width, nor a flange projecting internally. ''Diamantinasaurus'' also lacks a notable muscle scar for the ''M. flexor tibialis internus 3'' on the side of the distal ischium, which is diagnostic for the taxon amongst Neosauropoda
Neosauropoda is a clade within Dinosauria, coined in 1986 by Argentine paleontologist Jos├® Bonaparte and currently described as ''Saltasaurus loricatus'', ''Diplodocus longus'', and all animals directly descended from their most recent common ...
.
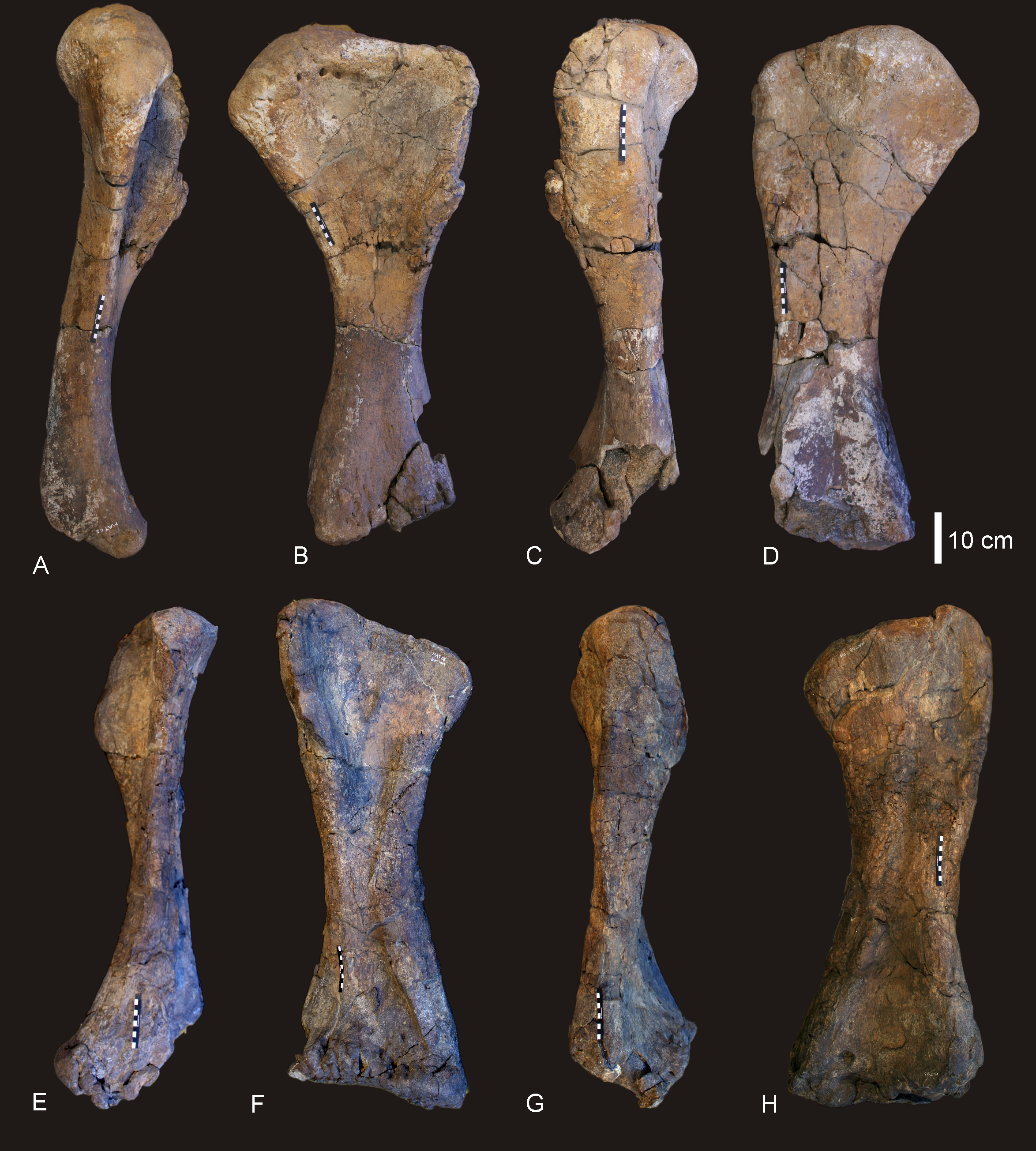
 The femur, long, is roughly twice as wide as it is long, as in other derived sauropods, although it has been slightly crushed. The crushing did not prevent the preservation of the ''linea intermuscularis cranialis'' ridge, also present in ''Saltasaurus'', ''Neuquensaurus'', ''
The femur, long, is roughly twice as wide as it is long, as in other derived sauropods, although it has been slightly crushed. The crushing did not prevent the preservation of the ''linea intermuscularis cranialis'' ridge, also present in ''Saltasaurus'', ''Neuquensaurus'', ''Bonatitan
''Bonatitan'' is a genus of titanosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Allen Formation of Argentina. It was named in 2004.
Description
The type species is ''Bonatitan reigi'', first described by Martinelli and Forasiepi in 2004. The speci ...
'', ''Rocasaurus
''Rocasaurus'' (meaning "General Roca lizard") is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod that lived in South America. ''Rocasaurus'' was discovered in Argentina in 2000, within the Allen Formation which is dated to be middle Campanian to early Maastr ...
'' and ''Alamosaurus''. As is typical for a sauropod, the head of the femur is slightly above the greater trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system.
It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2ŌĆō4 cm lower than the femoral head.Stan ...
, and there is a mild trochanteric shelf. A moderate lateral bulge is present, above which the femur is shifted medially, like most macronarians except ''Opisthocoelicaudia'', ''Saltasaurus'' and ''Rapetosaurus''. The condyles for articulation with the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
and fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is ...
extend high onto the posterior surface of the femur, but unlike ''Neuquensaurus'' and ''Opisthocoelicaudia'' do not extend onto the anterior surface. A depression subdivides the fibular condyle, which bears a slight ridge also found in ''Magyarosaurus'' and other titanosaurs, although the prominence of it is unique to ''Diamantinasaurus''. The fibular condyle is larger than the tibial, and extends farther down, giving the femur a bevelled appearance, potentially diagnostic of Saltasauridae but also found in ''Rapetosaurus'' and the non-titanosaur ''Dongbeititan
''Dongbeititan'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous-age Yixian Formation of Beipiao, Liaoning, China. It is based on holotype DNHM D2867, a partial postcranial skeleton including bones from the limbs, shoulder and pelvic gi ...
''.
The tibia is 59% of the length of the femur, and as is normal for neosauropods is wider than it is long on the proximal surface. ''Diamantinasaurus'' bears multiple fossae and ridges on the tibia that have not been observed in other sauropods, making them a suite of diagnostic traits. As in many titanosaurs, the distal end of the tibia is flared to over double the midshaft width, although a thin flange along the midshaft may be diagnostic to ''Diamantinasaurus''. Originally reconstructed missing part of the shaft, the fibula is long, and is intermediately robust, although close to gracile. The bone is poorly preserved, but still displays a diagnostic widening of the fibular muscle scar, and a diagnostic medial ridge with surrounding grooves. As in many titanosauriforms, the astragalus
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to tempe ...
of ''Diamantinasaurus'' is less than 1.5 times as wide as long, and the proximal surface is divided into the ascending process and the fossa for the tibia. There is also a shallow fossa for the fibula on the outside face of the astragalus, giving the bone a subtriangular shape. No depressions or foramina are present at the anterior base of the ascending process, a condition typical of Eusauropoda
Eusauropoda (meaning "true sauropods") is a derived clade of sauropod dinosaurs. Eusauropods represent the node-based group that includes all descendant sauropods starting with the basal eusauropods of ''Shunosaurus'', and possibly ''Barapasaur ...
. A process on the posterior side of the astragalar body is unique among all sauropods, making it an autapomorphy of ''Diamantinasaurus''.
Classification
When it was originally described, ''Diamantinasaurus'' was assigned to Lithostrotia ''incertae sedis''. In both phylogenies it was placed in, ''Diamantinasaurus'' was either just outsideSaltasauridae
Saltasauridae (named after the Salta region of Argentina where they were first found) is a family of armored herbivorous sauropods from the Upper Cretaceous. They are known from fossils found in South America, Asia, North America, and Europe. Th ...
or the sister taxon of ''Opisthocoelicaudia
''Opisthocoelicaudia'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur of the late Cretaceous, Late Cretaceous Period discovered in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. The type species is ''Opisthocoelicaudia skarzynskii''. A well-preserved skeleton lacking only the ...
'' within the family. In a 2014 study, it was found that the genus was placed as a lithostrotian in both large phylogenies, in a relatively derived position in Titanosauria. Their first phylogeny was modified from that of Carbadillo and Sander (2014), the matrix being indirectly based on Wilson's 2002 phylogeny. In that cladogram, ''Diamantinasaurus'' was found to be sister taxon to ''Tapuiasaurus
''Tapuiasaurus'' (meaning " Tapuia lizard") is a genus of titanosaur which lived during the Lower Cretaceous period (Aptian age) in what is now Minas Gerais, Brazil. Its fossils, including a partial skeleton with a nearly complete skull, ha ...
'', their relationship outside of Saltasauridae
Saltasauridae (named after the Salta region of Argentina where they were first found) is a family of armored herbivorous sauropods from the Upper Cretaceous. They are known from fossils found in South America, Asia, North America, and Europe. Th ...
. In this phylogeny, the Bremer support for each group was at most 1. Five features of the skeleton supported the placement of ''Diamantinasaurus'' in Lithostrotia.

 In the same study, the relationships using the Mannion ''et al.'' (2013) matrix were tested. These resolved with ''Diamantinasaurus'' as a saltasaurid, sister to ''
In the same study, the relationships using the Mannion ''et al.'' (2013) matrix were tested. These resolved with ''Diamantinasaurus'' as a saltasaurid, sister to ''Opisthocoelicaudia
''Opisthocoelicaudia'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur of the late Cretaceous, Late Cretaceous Period discovered in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. The type species is ''Opisthocoelicaudia skarzynskii''. A well-preserved skeleton lacking only the ...
'', with ''Dongyangosaurus
''Dongyangosaurus'' is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. The only species is ''Dongyangosaurus sinensis'', from which only a single fragmentary skeleton is known, coming from the Zhejiang province of eastern Chin ...
'' as the next closest. Two characters were found to support the placement of ''Diamantinasaurus'' in Lithostrotia, and a third could not be evaluated.
Another phylogenetic analysis in 2016, partially reproduced below, found it as a non-lithostrotian titanosaur and the sister taxon of the contemporary ''Savannasaurus
''Savannasaurus'' is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Winton Formation of Queensland, Australia. It contains one species, ''Savannasaurus elliottorum'', named in 2016 by Stephen Poropat and colleagues. The holot ...
''.
 The 2021 study recovered a similar topology, finding a close relationship with ''Savannasaurus'' as well as ''
The 2021 study recovered a similar topology, finding a close relationship with ''Savannasaurus'' as well as ''Sarmientosaurus
''Sarmientosaurus'' is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur belonging to the Titanosauria. It lived in what is now South America, specifically Argentina, during the Upper Cretaceous Period about 95 million years ago. The type species is ' ...
'' from the early Late Cretaceous of Patagonia, which skull had similarities to the referred cranial material of ''Diamantinasaurus''. The clade containing these taxa was dubbed Diamantinasauria
Diamantinasauria is an extinct clade of non- lithostrotian titanosaurian sauropod dinosaurs, known from the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) of South America and Australia. It was named by Poropat and colleagues in 2021, and contains f ...
.
Paleobiology
Growth
In 2011, the smallest positively identified titanosaur embryo was described. Although it was uncovered inMongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, the embryo shares the most features with ''Diamantinasaurus'' and ''Rapetosaurus''. The embryo, from a relatively spherical egg, was identified as persisting to a lithostrotian. The embryo was slightly robust, intermediate between the robustness of ''Rapetosaurus'' and ''Diamantinasaurus''. The egg is part of an entire nesting site for lithostrotian titanosaurs. Dating of the region also suggests that this egg predates those of Auca Mahuevo Auca Mahuevo is a Cretaceous lagerst├żtte in the eroded badlands of the Patagonian province of Neuqu├®n, Argentina. The sedimentary layers of the Anacleto Formation at Auca Mahuevo were deposited between 83.5 and 79.5 million years before present a ...
in Argentina, and the eggs were laid in the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
.
Paleoecology
 ''Diamantinasaurus'' was found about northwest of Winton, near Elderslie Station. It was recovered from the fossil-rich section of the
''Diamantinasaurus'' was found about northwest of Winton, near Elderslie Station. It was recovered from the fossil-rich section of the Winton Formation
The Winton Formation is a Cretaceous geological formation in central-western Queensland, Australia. It is late Albian to early Turonian in age. The formation blankets large areas of central-western Queensland. It consists of sedimentary rocks suc ...
, which can be dated to approximately 93 million years ago. ''Diamantinasaurus'' was found in a clay layer between sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
layers, interpreted as an oxbow lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called '' resacas''. In Australia, oxbow lakes are call ...
deposit. Also found at the site was ''Australovenator
''Australovenator'' (meaning "southern hunter") is a genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation (dated to 95 million years ago) of Australia. It is known from partial cranial and postcranial rem ...
'', which was directly associated with ''Diamantinasaurus'', bivalves
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bival ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
s, crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
ns, and various plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s. The Winton Formation had a faunal assemblage including bivalves, gastropods
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. Ther ...
, insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s, the lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
''Metaceratodus
''Metaceratodus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric lungfish in the family Ceratodontidae, with an indeterminate specimen known from the Late Triassic (Norian)-aged Lissauer Breccia of Poland and more complete specimens known from the Late Cre ...
'', turtles, the crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
n '' Isisfordia'', pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to ...
s, and several types of dinosaurs, such as the aforementioned ''Australovenator'', the sauropods ''Wintonotitan
''Wintonotitan'' (meaning " Winton titan") is a genus of titanosauriform dinosaur from late Albian (Early Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation of Australia. It is known from partial postcranial remains.
Description and history
Fossils that are ...
'', ''Savannasaurus
''Savannasaurus'' is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Winton Formation of Queensland, Australia. It contains one species, ''Savannasaurus elliottorum'', named in 2016 by Stephen Poropat and colleagues. The holot ...
'', and ''Austrosaurus
''Austrosaurus'' (; ) was an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Allaru Formation, from the early Cretaceous (112-105 million years ago) of Central-Western Queensland in Australia.
Discovery and species
The holotype, QM ...
'', and unnamed ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. ...
ns and hypsilophodont
Hypsilophodontidae (or Hypsilophodontia) is a traditionally used family of ornithopod dinosaurs, generally considered invalid today. It historically included many small bodied bipedal neornithischian taxa from around the world, and spanning from ...
s. ''Diamantinasaurus'' bones can be distinguished from other sauropods because of the overall robusticity as well as multiple specific features. Plants known from the formation include fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except t ...
s, ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus within ...
es, gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, ╬│Žģ╬╝╬ĮŽīŽ ...
s, and angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s.
References
External links
{{Taxonbar, from=Q132881 Titanosaurs Late Cretaceous dinosaurs Cretaceous dinosaurs of Australia Cenomanian life Paleontology in Queensland Fossil taxa described in 2009 Taxa named by Scott Hocknull Sauropods of Australia