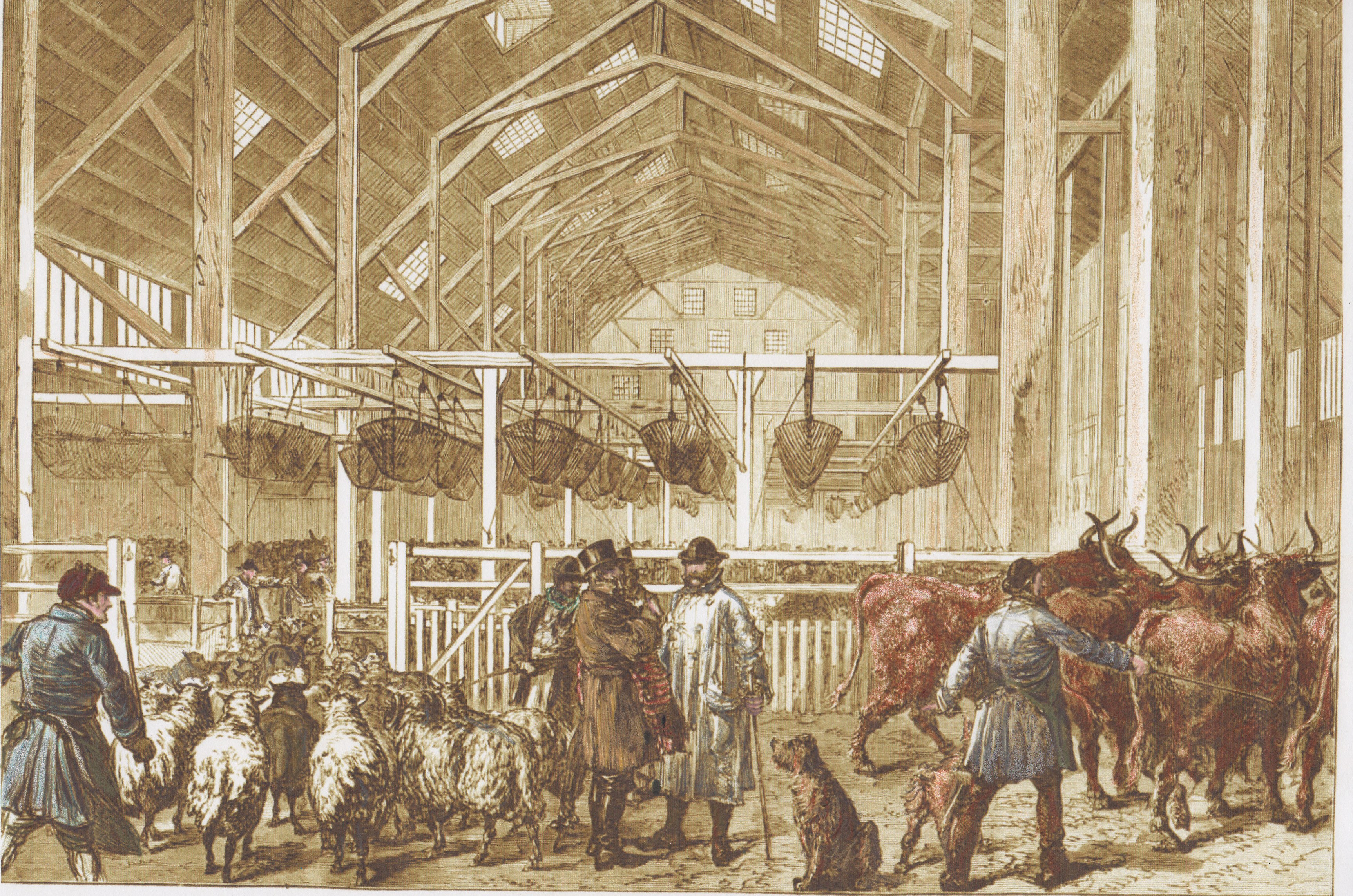

The Foreign Cattle Market,
Deptford
Deptford is an area on the south bank of the River Thames in southeast London, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It is named after a ford of the River Ravensbourne. From the mid 16th century to the late 19th it was home to Deptford Dock ...
(1872-1913) was one of the two great
livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
markets of London; from it came about half the capital's supply of freshly killed meat. Situated at the former royal
Deptford Dockyard
Deptford Dockyard was an important naval dockyard and base at Deptford on the River Thames, operated by the Royal Navy from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It built and maintained warships for 350 years, and many significant events a ...
on a bend of the River Thames and owned by the
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London fr ...
, all animals came from overseas, were landed by cattle boat, kept under quarantine conditions, and had to be slaughtered within 10 days of disembarkation. None could leave the market alive: the purpose was to stop the importation of animal diseases. Besides cattle, the market handled sheep, pigs and a few others. It could shelter 8,500 cattle and 20,000 sheep at a time, and had 70 slaughterhouses.
More than a set of buildings in Deptford, it had trading links with four continents: part of what has been called the
first globalisation. Cattle were brought there from the great
grasslands
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natural ...
of the world: initially, from Western Europe,
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
and the steppes of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
30° to the east; but later, and mostly, from the
Great Plains of America, literally being rounded up by
cowboys
A cowboy is a professional pastoralist or mounted livestock herder, usually from the Americas or Australia.
Cowboy(s) or The Cowboy(s) may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''Cowboy'' (1958 film), starring Glenn Ford
* ''Cowboy'' (1966 film), ...
. Such was the volume and quality of the trade that it had a appreciable impact on the livestock industry of the American and Canadian West. Boats also brought live animals across the equator from the
pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazil ...
of Argentina, and even from the other side of the globe: Australia and New Zealand.
In stormy weather numbers of animals were fatally injured, washed overboard, or
jettisoned to save the vessel; others were stifled to death under closed hatches. Prior to the sea voyages most had endured long journeys on tightly packed cattle trains. Both on trains and ships severe methods were used to make recumbent cattle stand up — in case they were trampled to death. The intercontinental traffic in live animals was not actually necessary, because it was cheaper to import chilled meat, which was of good quality. Yet the Foreign Cattle Market survived for 40 years; possibly because of irrational prejudice, possibly because butchers could pass off Deptford-killed meat as Scotch or English meat, which sold at a premium.
Background: London's cattle markets
The end of Smithfield as a livestock market

For centuries the main cattle market for London had been held at
Smithfield. There being no refrigeration, butchers bought an animal at the market, and slaughtered it themselves. The site was small and by the Victorian era the volume of trade had increased to the point that it was badly overcrowded and a public health nuisance. Driving cattle to Smithfield through the thoroughfares of the metropolis e.g. Oxford Street was bad for traffic congestion and endangered life and limb.
Hence in 1855 Parliament moved London's livestock market to a site in
Islington
Islington () is a district in the north of Greater London, England, and part of the London Borough of Islington. It is a mainly residential district of Inner London, extending from Islington's High Street to Highbury Fields, encompassing the ar ...
. Later, Smithfield was rebuilt as a dead meat market: the one that stands today.
The Metropolitan Cattle Market

The new
Metropolitan Cattle Market
The Metropolitan Cattle Market (later Caledonian Market), just off the Caledonian Road in the parish of Islington (now the London Borough of Islington) was built by the City of London Corporation and was opened in June 1855 by Prince Albert. ...
was in Copenhagen Fields, Islington.
A growing population and increasing money wages created a demand for more meat. The British farming industry, protected from competition, could not satisfy the demand. In 1842-6 the Conservative government of Sir
Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet, (5 February 1788 – 2 July 1850) was a British Conservative statesman who served twice as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1834–1835 and 1841–1846) simultaneously serving as Chancellor of the Exchequer ...
— as in its repeal of the
Corn Laws
The Corn Laws were tariffs and other trade restrictions on imported food and corn enforced in the United Kingdom between 1815 and 1846. The word ''corn'' in British English denotes all cereal grains, including wheat, oats and barley. They were ...
— had legislated to allow all foreign cattle to be imported
duty free
A duty-free shop (or store) is a retail outlet whose goods are exempt from the payment of certain local or national taxes and duties, on the requirement that the goods sold will be sold to travelers who will take them out of the country, who ...
. It was the beginning of the
free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold econo ...
era ("the
first globalisation").
By railway the Metropolitan Cattle Market received livestock not only from most parts of Great Britain and Ireland, but increasingly from the Continent.
John Gamgee
John Gamgee (1831–1894) was a British veterinarian and inventor. He specialised in the contagious diseases of larger animals: primarily cattle and horses.
Life
Gamgee was born in 1831 in Florence, Italy, the son of Joseph Gamgee (1801–1895), ...
, a veterinary scientist, warned that free trade in animals was dangerous because it would import diseases — had already done so. But the commercial interests were too powerful, and the trade continued.
As European rail links improved, these cattle came from as far away as the plains of Hungary and, eventually, Russia. That country had never been free from cattle plague (
rinderpest
Rinderpest (also cattle plague or steppe murrain) was an infectious viral disease of cattle, domestic buffalo, and many other species of even-toed ungulates, including gaurs, buffaloes, large antelope, deer, giraffes, wildebeests, and warthogs ...
), an infectious disease highly mortal to immunologically naïve cattle. It got into the Metropolitan Cattle Market and rapidly spread to most parts of Great Britain.
The 1865 cattle plague: need for a second, quarantine market


The cattle plague epidemic of 1865-7 has been described as the most dramatic event in 19th century agricultural history. Believing it to be a divine retribution for the sins of society, the Archbishop of Canterbury demanded a day of national humiliation.
Little was known about rinderpest in Great Britain and it took two years to eradicate. It did not help that the
germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade h ...
had yet to be established. Quarantines and the mass slaughter of infected herds led to agitation against the foreign cattle trade.
Wrote
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
:
New laws followed. They encouraged the
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London fr ...
to open and run a second metropolitan livestock market exclusively for imported animals, to be known as the Foreign Cattle Market. It was appreciated that, not only rinderpest, but
pleuro-pneumonia
Pleuropneumonia is inflammation of the lungs and pleura, pleurisy being the inflammation of the pleura alone.
See also
* Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia – a disease in cattle
* Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia
Contagious caprine pleurop ...
and
foot-and-mouth
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild bovids. The virus causes a high fever lasting two to six days, follow ...
disease were contagious threats.
Unless convinced that a foreign country was disease-free, the
Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
(later, the
Board of Agriculture
The Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (MAFF) was a United Kingdom government department created by the Board of Agriculture Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict. c.30) and at that time called the Board of Agriculture, and then from 1903 the Board ...
) was authorised to "schedule" it, which meant put it on a greylist. Animals from that country, while not banned outright, must be landed at this new market, and nowhere else. It was to operate under quarantine conditions, and no animal was to leave it alive, but had to be slaughtered within 10 days.
The Foreign Cattle Market: location, design and opening

Since the new market must be in a port, a suitable site on the Thames had to be chosen. There was lobbying for the market to be on the river's north bank, since many traders, especially the butchers of
Whitechapel
Whitechapel is a district in East London and the future administrative centre of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is a part of the East End of London, east of Charing Cross. Part of the historic county of Middlesex, the area formed ...
, did not want to have to travel to south London to buy their meat; but there were few adequate sites and access to these was poor. Eventually the defunct royal dockyard at Deptford was chosen. Here in times past
Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
had come to knight
Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
aboard the
Golden Hind
''Golden Hind'' was a galleon captained by Francis Drake in his circumnavigation of the world between 1577 and 1580. She was originally known as ''Pelican,'' but Drake renamed her mid-voyage in 1578, in honour of his patron, Sir Christopher Hat ...
, and
Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
of Russia had studied shipbuilding.
The Deptford site comprised 22 acres (afterwards increased to 30, bigger than
Les Halles
Les Halles (; 'The Halls') was Paris' central fresh food market. It last operated on January 12, 1973, after which it was "left to the demolition men who will knock down the last three of the eight iron-and-glass pavilions""Les Halles Dead at 200 ...
in Paris) and had a river frontage of 1,012 feet. It was situated on a bend in the Thames, at the bottom of
Limehouse Reach. It was designed to receive up to three cattle boats at once, which might conceivably arrive at any time, day or night. Hence three large, immensely strong, timber piers were constructed for disembarking cattle. Piers were provided with platforms at two levels, so that animals could be discharged no matter what the state of the tide. At low tides the water depth was at least 12 feet, thought to be sufficient for most steamers. These piers still stand today, though they have been interconnected.
The architect was Sir
Horace Jones, designer of Smithfield Market and
Tower Bridge
Tower Bridge is a Listed building#Grade I, Grade I listed combined Bascule bridge, bascule and Suspended-deck suspension bridge, suspension bridge in London, built between 1886 and 1894, designed by Horace Jones (architect), Horace Jones and e ...
. Since time was short, Jones took a minimalist approach. The site was not cleared: the existing dockyard buildings were preserved and adapted as necessary. The dockyard had a tidal basin surrounded by three ship-building sheds, each as lofty as Charing Cross station (see title image). By connecting these together Jones obtained a cattle
lairage building comprising a pentagonal horseshoe with open sides facing the river and the landing piers (see Layout). To the east another lairage shed had its own pier. Animals were provided with water troughs and hay racks, and the lairs were brilliantly lighted at night by gas lamps. There was enough covered accommodation for 5,000 cattle and 14,000 sheep. Later it was enlarged, and could accommodate 8,500 cattle and 20,000 sheep. Admiralty storehouses were converted into abattoirs, comprising some 70 slaughterhouses.
The demise of the old naval dockyard was regretted by many, and some features dating to Henry VIII were preserved. By order of the City officials, a board was put up bearing the following inscription: "Here worked as a ship-carpenter Peter, Czar of all the Russias, afterwards Peter the Great, 1698."
File:Edward Stanford 1904.jpg, Location
File:Edward Stanford 1904 (detail).jpg, Layout
The market was opened for business in January 1872. In 1871 nearly half of cattle and sheep imported into the UK had been sold live at Islington, but by 1880 most were slaughtered at Deptford.
Market life
The market was surrounded by a high boundary wall. Services inside included bank branches, a postal telegraph office, and the market's own pub, the ''Peter the Great''.
File:Foreign Cattle Market.jpg, The main gate, Foreign Cattle Market, Deptford
File:Deptford sheepskins.jpg, Sheepskins had to be disinfected before leaving
Trading

It was not an auction market. Trading was by private bargain, and in live animals only. Exporters consigned cattle, sheep and pigs to salesmen who worked on commission. Salesmen and buyers intermingled around the animal pens. Market days were Mondays and Thursdays, but there was nothing to stop animals being sold in their lairs on other days, and this was often done, especially when a shipload arrived late.
Weighbridges were seldom used: it was a matter of professional pride that cattle weights were
guesstimated. A journalist described it for Australian readers:The buyers were wholesale (and sometimes retail) butchers, who had access to slaughterhouse space on the premises, generally renting it by the year. Slaughtermen, paid by results, killed and butchered their purchases for them within the 10 days required by law; the buyers took away the meat, offal, hides and fleeces: most of the meat they resold at Smithfield. By the end of 1887 some 9.4 million animals had been landed at Deptford.
Statistics
The volume of trade fluctuated considerably, but from modest beginnings in 1872 it increased until, by about 1890, more (foreign) cattle were sent to Deptford than (British) to Islington. By 1907, according to the
Westminster Gazette
''The Westminster Gazette'' was an influential Liberal newspaper based in London. It was known for publishing sketches and short stories, including early works by Raymond Chandler, Anthony Hope, D. H. Lawrence, Katherine Mansfield, and Saki, an ...
78% of London's live cattle trade went to Deptford. The largest number of cattle ever landed in one year was 224,831 (1897); of sheep, 783,440 (1882). Detailed statistics are set out in tables in this note.
In the Edwardian era a combination of Chicago meatpackers took advantage of the loophole in the regulations — that animals need not be put up for sale on market days — to bypass the marketing system altogether. See The Beef Trust, below.
Altogether 16.5 million animals were slaughtered at Deptford.
Cattle boats

Cattle boats from the Continent — over a thousand a year — came up the Thames on Sundays and Wednesdays.
As the transatlantic cattle trade developed (see below), large ocean-going cattle steamers came into use, but these were reluctant to come alongside. Accordingly the market purchased three paddle steamers (named ''Racoon'', ''Taurus'' and ''Claude Hamilton'') into which cattle were
transshipped at
Gravesend
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the Bank (geography), south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Ro ...
. Between them, those vessels conveyed more than 1.6 million animals to Deptford.
Jack the Ripper, Deptford cattle boat man
One of the many theories about
Jack the Ripper
Jack the Ripper was an unidentified serial killer active in and around the impoverished Whitechapel district of London, England, in the autumn of 1888. In both criminal case files and the contemporaneous journalistic accounts, the killer wa ...
was that he was a Portuguese cattle attendant on a boat from
Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropol ...
. When it docked at Deptford, a Whitechapel murder ensued, or so insisted a customs official who claimed to see a statistical correlation. His persistence irritated the police, but his theory was noticed by Queen Victoria. "The Queen fears the Detective Department is not as efficient as it might be... Have the cattle boats & passenger boats been examined?"
Veterinary
On landing, animals were examined by a veterinary surgeon who took their pulse and temperature. Suspects were set aside for observation. If one animal in a cargo was found to be contagious, it was slaughtered at once and its carcase sterilised by steam in an iron digester; its companions were put with the suspects. Drovers wore protective clothing, afterwards disinfected in a sulphur chamber. Hides, horns, fleeces and offal were also disinfected; manure and litter were sterilised. A correspondent from ''The Times'' thought the market was very clean and by the standards of the day animals were slaughtered humanely.
Foreign veterinarians observed for their governments. American cattle bore ear tags and, if one was found to be diseased, the American vet would telegraph the serial number to his government: the animal's home farm could be traced within hours and a quarantine imposed if necessary. The Argentine government sent a vet too, in 1903.
The quarantine rules could minimise, but could not altogether prevent, the importation of contagious diseases. The government accepted that cattle plague (1877) and foot-and-mouth disease (1880 and 1882) had escaped from Deptford market.
Besides cattle, sheep and pigs, there was a small trade in horses and donkeys. The rule that no animal could leave the market alive was strictly enforced. A country bumpkin from Essex brought a complaint before magistrate
Montagu Williams
Montagu Stephen Williams Q.C. (30 September 1835 – 23 December 1892) was an English teacher, British Army officer, actor, playwright, barrister and magistrate.
Williams was educated at Eton College and started his career as a schoolmaster at ...
. The Essex man, needing a good steed, had been induced by a glowing advertisement to pay £30 for a horse, viewable at Deptford Market. He did not realise it was in no condition to be ridden away.
George Philcox


To find a superintendent for the market the City interviewed 25 candidates, and chose a 28-year old Southend station-master, George Philcox. Philcox was in charge of the market for the next 40 years; when he died in 1912, it soon closed. Apparently an able and popular man, it was said "The market made him, and in turn he made it".
Employment conditions
Employment conditions in Deptford Foreign Cattle Market were investigated by social researcher
Charles Booth and are described in his
Life and Labour of the People in London
''Life and Labour of the People in London'' was a multi-volume book by Charles Booth which provided a survey of the lives and occupations of the working class of late 19th century London. The first edition was published in two volumes as ''Lif ...
(1896).
The market had about 110 direct employees. In addition 1500 casual workers, mostly drovers and
slaughtermen, were paid on
piecework
Piece work (or piecework) is any type of employment in which a worker is paid a fixed piece rate for each unit produced or action performed, regardless of time.
Context
When paying a worker, employers can use various methods and combinations of ...
, and at times could earn high wages, but the hours were irregular and employment was precarious. They were irregular because they depended on when ships arrived. It was precarious because the volume of trade was driven by the animal disease regulations, which kept changing. As was common in high-wage, insecure jobs that attracted improvident men, there was much insobriety, said Booth's researchers.
Unemployment at the market might cause severe hardship in Deptford, where it was already high because people migrated to the district to find work. There is a record of market workers sending a wreath to the funeral of
George Joseph Cooper MP, admired because at one time Argentina was put on the blacklist and he had tried very hard to get it removed. In 1924, years after the market had closed, efforts were still being made to get it re-opened.
Drovers

It was their job to drive the animals off the boats, or to transship them from the transatlantic steamers at Gravesend.
Drovers at Deptford market were paid a lump sum per vessel, George Philcox told Booth. They could unload a cattle boat in as little as 15 minutes. Some cattle, especially from Argentina, were very wild, and were best given "a wide berth". A man in regular employment could earn as much as £4 a week (about £520 purchasing power in 2018 money).
Slaughtermen
These men, who killed and butchered the animals, worked in gangs of four, and earned very high wages for the era: £5 (≅ £650
2018) a week was not uncommon. No slaughtering was done on Saturdays; on other days it varied according to demand, and for a rush order might last up to 20 hours on end. The work was said to be brutalising "and conducive to drink".
A carefully aimed blow at the head with a poleaxe was the usual method of stunning used in Britain. While ''The Times'' reported favourably on the relative humanity practised at Deptford, it came from the skill acquired by regular repetition; it was not infallible. A
tanner, examining the lesions on a sample 100 cattle hides — albeit not from Deptford — noted that 45% showed signs of more than one blow i.e., they were not stunned by the first stroke. An advocate of the Jewish ''
shechita
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''.
Sources
states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtered ...
'' method (which was also used at the market) said that he had observed that it often took five blows to fell an ox at Deptford.
That women slaughtered animals at Deptford is not supported by reliable sources.
Women: the gut girls

One of the most unpleasant jobs was cleaning cattle and sheep intestines, which were used for making sausage skins (and, according to a later source, condoms). Originally men's work, in about 1891 they went on strike for more pay: management responded by assigning the work to women.
Some 80-100 women and girls, aged 14 to 40, were employed daily; they worked for two firms that had contracted to buy all the gut offal from the market's slaughterhouses. Writing for the ''Daily Telegraph'', "A Lady Visitor", who claimed to have smelled some vile odours in her time, said the stink was insupportable. Tubs of unwashed entrails were coarsely de-fatted by men. This work was done by a first group who cleaned off the outside, made the gut into a figure of eight rope, and tossed it to a second. The second group, armed with a powerful watercock, turned the gut inside out and washed it ready for the sausage makers. In winter the water nearly froze the hands.
They made 12''s'' to 14''s'' (≅ £77 to £89
2018) a week which, for women's work, was good pay.
For some reason
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
took an interest in the Deptford market, and she asked her daughter-in-law,
the Duchess of Albany, to look into the working conditions of the girls there. The Duchess of Albany went down to Deptford, saw the work, was horrified, and complained in high places. It turned out that the gut firms had been processing, not just the entrails from Deptford market, but huge quantities brought in from outside. The City's markets committee, finding out, banned it as a health risk. The result was that the women became unemployed, and a charity, the Deptford Fund, had to be started to support them. The stage play ''The Gut Girls'' by
Sarah Daniels is a fictionalised version of this incident.
Years later
the Duchess of Albany's daughter (aged 95) told the BBC:
Despite this, it appears that most women tried to conceal their employment at the market.
Deptford as an international livestock market
Over the years roughly half of London's meat came from the Foreign Cattle Market. As a consumer of meat, the London of the era has been described as the greatest market in the world. "The British were beef hungry. They had the money to buy meat in any market, and as the great creditor nation they were at a distinct advantage in purchasing livestock in America and in the rest of the world". It was described as the first globalisation.
Hence Deptford market was much more than a set of buildings on the Thames. From it radiated a web of commercial relationships that went out to livestock producers in distant parts of the planet. For example a salesman at Deptford could be representing a cattle buyer in (say) Chicago, who might get his supplies from finishers in the American Cornbelt, who were supplied by Western ranchers, and so on.
From Europe
Early days



Describing the pull of London as a meat market for European farmers,
Richard Peet
J. Richard Peet (born 16 April 1940 in Southport, England) is a retired professor of human geography at the Graduate School of Geography at Clark University in Worcester MA, USA. Peet received a BSc (Economics) from the London School of Economics, ...
said "It was as though a city of several million people were located just off the Dutch coast". A journalist, visiting Deptford market in 1889, reported:
The Spanish cattle were "beautiful chestnut brown in colour, sleek and well-built, though rather depressed in look, as Spanish cattle always are".
Some animals had more distant origins.
Forrest Capie and Richard Perren said that, although most European animals were shipped from
Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
and
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
,
Several Deptford shipments arrived directly from the port of
Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for "crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city of ...
, in Russia, and were known to have been purchased in the cattle market of
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. The Russian capital was more than 30° to the east of Deptford, and these animals may have come from much further still, since Saint Petersburg
oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdom of ...
raised few export-grade cattle. They may have been driven to market from south Russia. In 1872 the Russian Empire was blacklisted for cattle plague and no more Russian cattle could be landed, even at Deptford.
Demise of European cattle trade
The European livestock trade was gradually stopped by the late 1880s — except for Iceland — after the British authorities faced the fact that too much livestock was really coming from places where disease was endemic "and the provincial authorities made no attempt to stamp it out". For example
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
had stringent laws against animal disease but "the profits from smuggling cattle from Poland are too enticing.
By then the United States had become the main supplier.
From the United States
Of all the cattle ever landed at Deptford market, the largest proportion came from the U.S.A. The practice started in 1878 when American cattle and pigs were "scheduled" for port slaughter. By 1913, when Deptford had closed, 3,144,400 American cattle had been landed there, besides sheep and pigs.
Nearly all American livestock exports went to England. Americans sent livestock to England because they had a surplus that could not be absorbed by local demand. When, eventually, it was, which happened by 1913, exportation ceased. Writing in 1915, two senior American officials said: "Our beef surplus has vanished and our own people now require all that our farms and ranches produce".
Upgrading livestock in the American West
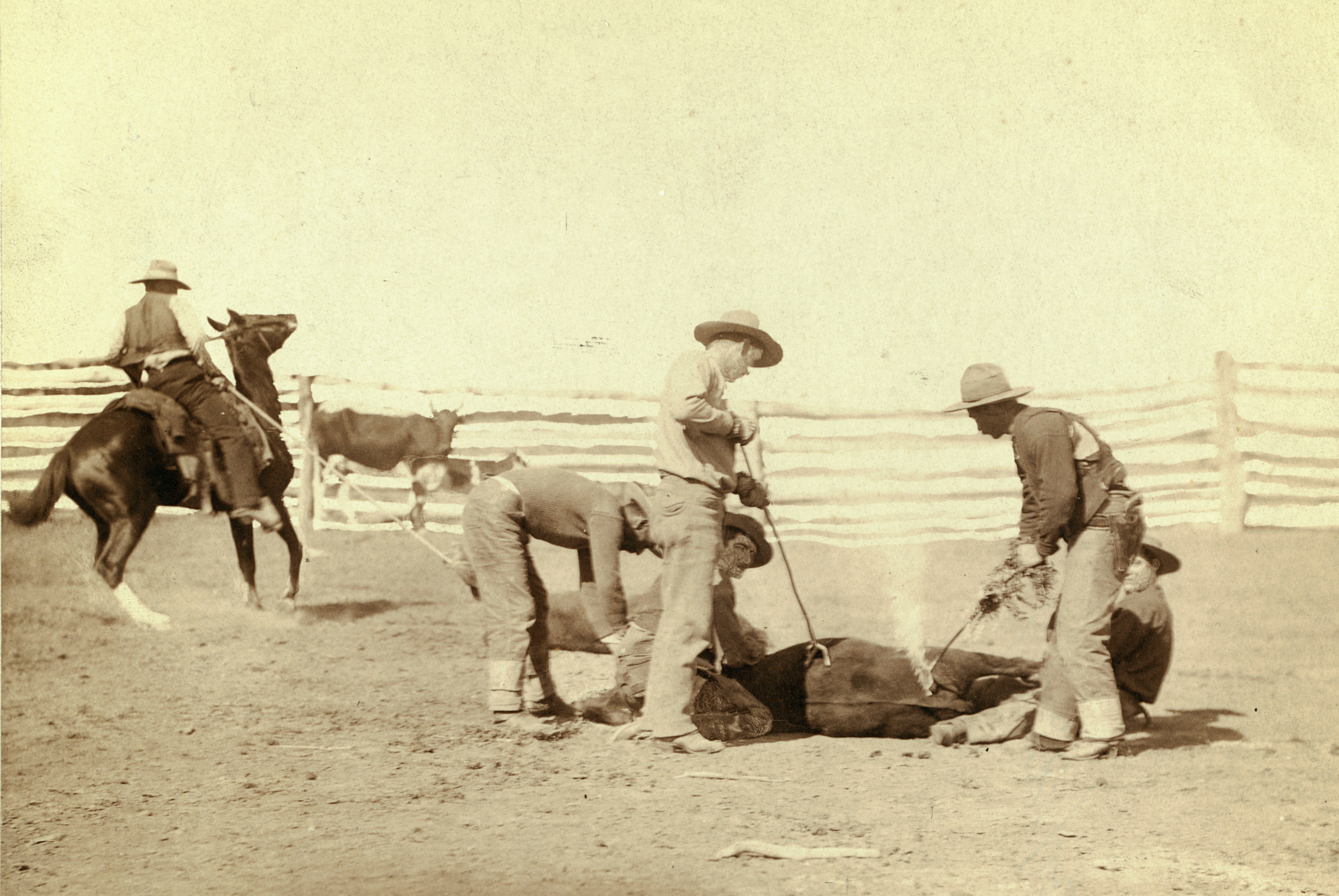





The surplus came from the new, teeming lands of the American West. But early Western cattle e.g. Texas longhorns, though hardy, made tough eating. It cost exactly the same to ship a top quality steer from New York to London as a gristly one. Consequently, it made economic sense for American shippers to export their best animals, as better able to absorb the cost of carriage.
At first, export-grade cattle were to be found in the East only, where cattle breeds were similar to those of the British Isles. British farmers were advised not to worry about imported Western livestock for the present, because it would not compete on quality. But (as predicted) Western cattlemen realised they could capture lucrative markets by improving their stock — and did so. The English export trade contributed to the demand for more and better cattle. Progressive American cattlemen imported prize British bulls, sometimes paying fabulous prices. "On the western plains the ranches that succeeded the open range bought high priced sires with which to upgrade their old stock. The upturn in the quality of beef animals, with younger cattle going to the feedlot, meant better beef from the slaughter house and on the family table, all part of a general improvement".
Comparable improvements were made in sheep. By 1884, 95% of cattle exported came from the West.
Distances
Already in 1880 ''The Times'' was advising its readers that a 1,200 lb steer from (say)
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
,
Wyoming
Wyoming () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the south ...
or
Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
could be conveyed to Deptford market — over 2,000 miles of land and 3,000 of ocean — for £10 or £12. It included cowboys' wages, rail fare, shipping freight and the landing charges at Deptford (which, thought the author, were rather extortionate). All this added only 4''d'' a pound to the carcase price of beef (≅£4.40 a kilo
2018).
''Scientific American'' reported that, recently, five cattle-laden steamers had sailed from New York to England in one day. The cattle in this new trade "come principally from
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
,
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
,
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
,
Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
,
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
,
Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
,
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
and Colorado".
Some cattle came to Deptford from as far away as
Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, though this was sporadic. The English adventurer
Moreton Frewen
Moreton Frewen (8 May 1853 – 2 September 1924) was and entrepreneur, an Anglo-Irish writer on monetary reform, who served briefly as a Member of Parliament (MP).
Early life
Frewen was born the 8 May 1853 in England. He was the fifth son of T ...
, writing to ''The Times'', said
Significance to the West
The exportation of cattle to England had a discernible impact on the American livestock industry. While not all American exports went to Deptford, London was the most important market. Wrote John P. Huttman:As noted, the trade became a factor in improving the quality of American cattle.
Further, some British agriculturalists, shielded until recently from American competition — first by distance, then by quality issues — found it attractive to go in for American ranching themselves. They "fought competition at its source and engaged directly in American ranching, until by 1884 it was estimated that 'one-sixth of all our herds are now owned by Englishmen'". And British investors, attracted by the fabulous profits sometimes realised in the West, made an important contribution to its development.
From Canada
A major export industry at the time, range cattle came from
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
and
Assiniboia
Assiniboia District refers to two historical districts of Canada's Northwest Territories. The name is taken from the Assiniboine First Nation.
Historical usage
''For more information on the history of the provisional districts, see also Distric ...
and went east on the
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadi ...
. The
St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
route meant that cattle started the voyage in calm waters and comparatively cool weather. "Most of the losses of cattle in shipments from Atlantic ports were due to delay and neglect prior to shipping and occurred during the first few days of the crossing". For many years Canadian livestock was considered disease-free and could be landed freely, but it was scheduled for slaughter at Deptford from 1892 on. It did western ranchers little harm:Exports to England rose from 115,000 cattle in 1900 to 160,000 in 1905, but petered out after a severe winter depleted half the range-cattle industry's working capital.
From Argentina
As the North American surplus dwindled, Deptford's main supply of animals came from Argentina. Formerly, Argentine cattle "were of an inferior breed, their chief characteristics being thick hides and well-developed horns"; they were slaughtered locally for their hides, bones and tallow. Two things transformed the Argentine beef industry into the greatest exporter in the world: selective breeding and
alfalfa
Alfalfa () (''Medicago sativa''), also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as w ...
(lucerne)
forage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also used m ...
.
From about 1888 live cattle and sheep were shipped as deck cargo from Buenos Aires, carpenters knocking up temporary stalls and pens. Animals were brought to Buenos Aires e.g. 450 to 750 miles by rail and hoisted aboard vessels by steam crane. The voyage to London took about 30 days. Progressive Argentine cattlemen were keenly aware that quality was important, and they paid large prices for Shorthorn bulls to improve their herds. Such was the demand for export-grade cattle in 1903 that an American agent told his government "it is extremely difficult to get a good piece of beef in the city of Buenos Aires". "Wild, untamed brutes" did badly on the sea journey, and had to be tamed in advance and taught to eat hay.
Deptford was closed to Argentine cattle and sheep in 1900 for foot-and-mouth, and briefly re-opened in 1903. Thereafter there was scant incentive to revive the live meat trade on these very long journeys. From about 1900 good chilled Argentine beef was a more satisfactory alternative. Severe unemployment came to Deptford.
From Australia and New Zealand

At the end of the Victorian era cattle and sheep were shipped to Deptford Market from as far away as
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state with a land area of , the second most populated state (after New South Wales) with a population of over 6.5 million, and the most densely populated state in ...
,
New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
,
Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
, and
Dunedin
Dunedin ( ; mi, Ōtepoti) is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand (after Christchurch), and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from , the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. Th ...
, New Zealand.
The first commercial (though experimental) shipment was from
Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
on the steamer ''Maori King'', a 67-day voyage which went around
Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramírez ...
in winter — presumably to avoid the heat of the
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
. The cattle landed at Deptford in September 1894, but sold at a heavy loss. Next year there was a much more successful voyage by ''Port Pirie'': one animal died of heat in the Red Sea, but the others arrived in excellent condition (see illustration). Another success was 250 sheep per ''Banffshire'' from Dunedin; only one was lost.
However, as shipments continued there were "terrible" losses. For these ambitious voyages more than halfway round the world, excellent planning and execution were essential, but were wanting.
Altogether in the Australasian live trade, 607 cattle were lost out of 2,654 shipped, and 57 out of 3,882 sheep.
The Beef Trust

The
Beef Trust was a
cartel
A cartel is a group of independent market participants who collude with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate the market. Cartels are usually associations in the same sphere of business, and thus an alliance of rivals. Mos ...
of the large Chicago meat packers. Acting in collusion they allocated market shares and fixed meat prices in the United States, eventually coming under attack by "trust buster" president
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
. As described in the next section, by 1900 the Beef Trust controlled the business of shipping live cattle to England from America.
In the Edwardian era reputable newspapers claimed that
*the Trust had bought up many shops in Smithfield Market;
*they met every morning to fix the price of British beef;
*they practically controlled the lairages at Deptford Market; but
*instead of selling their Deptford cattle to buyers at that market, they sent the meat directly to Smithfield; with the result that, on a numerous occasions, market days at Deptford were cancelled for lack of support.
As a result of persistent questioning by
C. W. Bowerman
Charles William Bowerman (22 January 1851 – 11 June 1947), often known as C. W. Bowerman, was a prominent British trade unionist and politician.
Life
Born in Honiton, Bowerman moved to Clerkenwell in London at an early age. On leaving educ ...
, Labour MP for Deptford,
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
(the President of the Board of Trade) set up an inquiry into "how far and in what manner the general supply, distribution and price of Meat in the United Kingdom are controlled or affected by any combination of firms or companies". The inquiry reported in 1909. The allegations were generally true, except that the Trust was not powerful enough to fix the price of beef in the United Kingdom. This was because, although it did indeed control the North Atlantic meat trade, American beef exports had declined, and large shipments of refrigerated beef were coming from Argentina.
Animal welfare: journeys

Animals were sent from the grasslands of the world to be slaughtered at Deptford market. Even today, when animal welfare is a consideration and the average journey from feedlot to slaughter plant lasts just a few hours, transport-related stress and injury are major sources of loss to the American meat industry. According to
Temple Grandin
Mary Temple Grandin (born August 29, 1947) is an American academic and animal behaviorist. She is a prominent proponent for the humane treatment of livestock for slaughter and the author of more than 60 scientific papers on animal behavior. Gra ...
, fear, which motivates animals to avoid predators, is a very strong stressor during transport. Animals unaccustomed to human beings are liable to be stressed more, and in that era of range cattle there were many. An American special agent, reporting on the overseas shipping of untamed Argentine cattle (1904), said:
In the Victorian era there was much publicity about the iniquities of transatlantic cattle ships. Before crossing the Atlantic, however, most animals had endured journeys in cattle trains, sometimes travelling for a week or more. A paper read before the
American Veterinary Medical Association
The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), founded in 1863, is a not-for-profit association representing more than 99,500 veterinarians in the US.
The AVMA provides information resources, continuing education opportunities, publicatio ...
claimed that the train journeys had been overlooked, being as bad as the sea voyages if not worse.
Transatlantic cattle ships
American cattle most often sailed from New York; also Boston, Philadelphia, Baltimore and
Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
. Canadian cattle were shipped from the port of Montreal; Argentine cattle and sheep from the port of Buenos Aires.
Early days

Sending cattle safely across the Atlantic demanded forward planning and knowhow. Quite often these were lacking, especially in the early days, when conditions were "very bad", or "little better than the horrors of "the middle passage" of the old slave trading days". According to a government inquiry the worst culprits were
tramp steamers
A boat or ship engaged in the tramp trade is one which does not have a fixed schedule, itinerary nor published ports of call, and trades on the spot market as opposed to freight liners. A steamship engaged in the tramp trade is sometimes calle ...
, neither specialising in the trade nor built for it. When freights were high these vessels were hastily rigged up with temporary decks and crammed tightly with cattle.
Risk was greatest in winter, when insurance rates soared to 10% "as a heavy storm may make it necessary to lighten the ship by throwing the entire deck load of cattle overboard".
In 1879 the British government's chief veterinary officer reported on animals jettisoned from transatlantic cattle ships or dying on board from injury or suffocation. Describing the losses as "terrible", he said 10,667 animals were thrown overboard, 1,210 were landed dead, and 718 were so badly injured or exhausted that they had to be slaughtered on landing.
Samuel Plimsoll
In 1890
Samuel Plimsoll
Samuel Plimsoll (10 February 1824 – 3 June 1898) was a British politician and social reformer, now best remembered for having devised the Plimsoll line (a line on a ship's hull indicating the maximum safe draught, and therefore the minimum fr ...
, having successfully campaigned for his
Plimsoll line
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indi ...
, turned to the transatlantic cattle trade. He said it ought to be abolished. In ''Cattle Ships'' he seized the reader's attention thus:

Plimsoll wrote that cattle ships were dangerously unstable in stormy weather, cruel to animals, and unnecessary. They were unstable if cattle were carried on the upper deck or (worse) on a temporary, higher platform that raised the ship's centre of gravity even further, and obstructed the crew in their duties. Animals were washed overboard by heavy seas, or were deliberately jettisoned to save the vessel. If carried down in the holds they could stifle to death after the hatches were battened down in bad weather. Knowing this, captains sometimes took risks in leaving the hatches open. Further, animals stood on their own dung, which could not be cleared away; on this slippery surface they fell about helplessly and were injured, often fatally.
Plimsoll alleged that cattle attendants were not allowed to
euthanise badly injured livestock, because the insurance companies would refuse to pay up. Animals were left to die a lingering death. Plimsoll was probably wrong about the insurance companies; but it made no difference, because the cattle attendants thought it was so and behaved accordingly.
Another accusation was that cattle attendants used cruel methods to make animals get on their feet, such as piercing them with pitchforks, twisting their tails, beating them about the head with iron buckets, or pouring paraffin in their ears. "Some of the men in charge, who are paid a percentage on the number of cattle they bring alive into Deptford, tortured the animals most fiendishly into a semblance of animation". It was indignantly denied by cattle shippers, who asked what they had to gain by such practices: cattle were free to lie down if they wanted to.
File:Plimsoll image.jpg, Cattle ship according to Samuel Plimsoll and his campaign to abolish them
File:Catttle steamer image Chadwick.jpg, A better class of steamer, good weather, adequate ventilation
The cattle attendants included foremen known as "cowboys of the seas", "big burly fellows who are used to rough living and facing danger"; also a despised class called "stiffs" who did the work for little or no pay just to get across the Atlantic. Sometimes educated men e.g. Harvard students travelled as stiffs. The poet
W.H. Davies
William Henry Davies (3 July 1871 – 26 September 1940) was a Welsh poet and writer, who spent much of his life as a tramp or hobo in the United Kingdom and the United States, yet became one of the most popular poets of his time. His themes inc ...
was a stiff and wrote about the harsh methods used to make the cattle stand up; so did an English solicitor returning from a working holiday to Canada. It was done to stop animals tangling their head ropes, or being trampled to death by their fellows.
Improvements
A government inquiry tended to confirm many of Plimsoll's allegations. Although he did not succeed in abolishing the trade, British and American regulations prohibited some of the worst practices.
When the export trade became well organised it was dominated by four American meat packers:
Swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, ...
,
Armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
,
Hammond and
Morris
Morris may refer to:
Places
Australia
*St Morris, South Australia, place in South Australia
Canada
* Morris Township, Ontario, now part of the municipality of Morris-Turnberry
* Rural Municipality of Morris, Manitoba
** Morris, Manitob ...
: members of the "Beef Trust". They were not shipowners, but they established a liner system. (A liner is a ship that sails to a schedule; a tramp, when she has a cargo.) It was essential to organise a regular liner trade because cattle transportation required close coordination, regularity and long-term contractual relationships. For example, to make sure of shipping space it had to be bought in advance without knowing if London spot meat prices were going to make it worthwhile. It was to the business advantage of shippers (hence, liners) that livestock arrive in the Thames on time and in excellent condition. By 1892 North Atlantic animal losses were reduced to less than 1%, ten times better than on the Buenos Aires run.
Even in the good liners, however, the dung and urine were left to accumulate in the holds; the ammoniacal stench was said to be unbearable. According to ''
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it i ...
'' The average run from New York to the Thames was 11 days. Cattle could scent land, sometimes setting up "a united bellow" when thirty or forty hours from shore.
Cattle trains

From the livestock-raising regions animals were taken to market by train, mostly to Chicago. onto which 17 railroads converged. At the
Chicago stockyards
The Union Stock Yard & Transit Co., or The Yards, was the meatpacking district in Chicago for more than a century, starting in 1865. The district was operated by a group of railroad companies that acquired marshland and turned it into a central ...
there was a special market for "export grade" cattle; these were railed to ports on the eastern seaboard for shipment to England. The map also shows the Canadian Pacific Railway that took livestock from the foothills of the Rocky mountains to Montreal.
Lengthy journeys
Animals were not supposed to travel more than 28 hours at a time, according to a U.S. federal law of 1873, after which they must be got off the train for water, food and 5 hours rest. Quite often at these stops, however, the railroad companies, who were not very enthusiastic about the cattle trade, neglected to provide proper water or food, or there was nowhere to rest because the station stockyard was a sea of mud or a drift of snow.
The 28-hour limit was widely ignored, and there was even something to be said for that, because repeatedly unloading and reloading the animals could do them more harm than leaving them on the train. Thus in 1906 the law was amended to allow animals to be carried for up to 36 hours at a time if the owners agreed, and from now on the law was enforced
'Palace' or "parlor" stock cars were special vehicles supposed to furnish water and hay for animals to consume en route, and hence exempted from the 28-hour law. Thus they could and did run for 60 or even 100 hours at a time. It seems that in reality, however, water and food were seldom supplied to these vehicles: some thought they were a sham.
Overcrowding and injury
Shipping space was usually sold by the carload, so there was an incentive to cram in as many animals as possible to save freight charges, which were high. Some held that tight packing was good for the animals because it stopped them fighting or lying down, or falling over when the engine jerked the train or when it went round a tight curve.

If a steer did fall, or lay down to rest, there was a risk that it might never get up again. Consequently cattle attendants, who travelled in the
caboose
A caboose is a crewed North American railroad car coupled at the end of a freight train. Cabooses provide shelter for crew at the end of a train, who were formerly required in switching and shunting, keeping a lookout for load shifting, damag ...
, went round at intervals and, if they spotted a recumbent animal, tried to make it stand up. For this purpose there was a special tool called a cattle prod which, if the steer was not actually dying, usually worked. A stockman recalled:
He described how:
A government official wrote: "Under the present system not a train is brought to any great market without having many crippled
beeves
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ma ...
, and several dead ones".
In Canada
There was no 28-hour law in Canada and rail journeys were immense. The Canadian Live Stock Commissioner said the method of exporting western range cattle was "sinfully wasteful, unbusinesslike and unprofitable to the producer", so that Canadian cattle arrived in Britain "gaunt and shrunken".
Whether economic justification for live cattle trade
Plimsoll's case

Samuel Plimsoll argued that the transatlantic cattle trade had no rational commercial purpose except to enrich dishonest traders. He asked: And he answered:
Was Plimsoll right?
An alternative to the live cattle trade
An alternative to the live cattle trade was American chilled meat. Already imported into London in 1875, before the Foreign Cattle Market was doing much business, it was a commercial success. Pound for pound, it was much cheaper to send chilled meat across the Atlantic than on the hoof; it required refrigerating plant, but it took up less space and only the edible parts were shipped.
Imported dead vs. alive
Further, butchers could easily tell that wholesale meat was American if it was imported dead, but not if imported alive. Meat slaughtered in America was cut ("dressed") according to American butchering practices, which were visibly different. Also, the chilling process slightly discoloured the product. In contrast, American meat killed at Deptford was dressed by British butchers, hence looked the same as British-fed beef.



Why the price premium?
At Smithfield Market a wholesale quantity of Deptford-killed American beef sold for 10-15% more than the same weight of American chilled beef. Was this because it was thought to be better; or was it because it could be resold fraudulently — as Scotch or English beef? That was the question debated in the Victorian era. The British farming industry had no doubt: the butchers were cheating. The butchers riposted that the farmers were just trying to protect themselves against competition: customers were not really bothered and rarely asked if a joint was English or foreign.
As for palatability, Plimsoll argued that chilled meat (not be confused with frozen meat, an inferior product) was as good as, indeed was better than Deptford-killed beef. It was better because chilling and keeping were equivalent to well-hung meat. Cattle slaughtered at Deptford were tired, stressed and bruised from the journey.
What Victorian and Edwardian consumers really thought of chilled beef is difficult to tell: taste, prejudice and snobbery came into it. A writer to ''The Times'' said: By the Edwardian era two authors said "the West-End folk are very large customers for chilled beef of the highest quality", which suggests it could be quite palatable. However that may be, Plimsoll argued it was up to the customer to decide. She might be prejudiced, but if she was willing to pay more for British-grown beef, she was entitled to get the real thing.
Another theory
Richard Perren of Aberdeen University in an 1971 essay argued that the live meat trade survived because the chilled meat trade was riskier. A consignment, having arrived at the London docks, would not keep much longer and had to be sold at Smithfield promptly — even if the market was glutted. There was less urgency about disposing of the live beasts. However, Perren accepted that, once cold-storage was available at ports, chilled meat would keep for another 14 days after arrival; that livestock had to be slaughtered within 10 days of arrival; that the live animal trade was also risky; and that the chilled trade was the bigger of the two. He also acknowledged that some butchers fraudulently sold Deptford-killed meat as English, the price being higher.
Incentives to fraud
If fraud there was, it was easy to perpetrate: truly effective compulsory marking of origin was not introduced until 1933. It seems no prosecutions were attempted, and it could be argued the City of London itself encouraged the practice.
Plimsoll calculated that the fraud was worth a penny the pound of meat, or £4 per head of cattle (≝ £500
2018). A 2010 study found that but the gains declined as time went by, and had ceased to exist by 1911. By then, Deptford Market's trade was fading away.
Examples
In the Victorian era it was reported that "foreign merino sheep are slaughtered at Deptford, sent to Cardiff, the hind quarters there cut off, sent to London again, and there sold as Welsh mutton". It is corroborated by reliable sources.
''Scientific American'' said (1904):
A writer for a Chicago livestock magazine in 1912 tried and failed to find any American meat for sale at Smithfield, though he knew hundreds of American cattle had recently been butchered at Deptford. At last a stallholder admitted their meat was being sold as English.
An English port medical officer, generally sympathetic to the live cattle trade, remarked on the disparity between port-killed wholesale prices and butchers' retail prices.
Unexpected benefit
Paradoxically, the transatlantic cattle trade made for cheaper bread. The reason was spotted by economic historian
Knick Harley
Charles Knickerbocker Harley is an academic economic historian who has written on a wide range of topics including the British industrial revolution, the late nineteenth century international economy, and the impact of technological change. He is ...
.
Vessels laden with cattle were too
buoyant
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pr ...
, and needed to be
ballasted. An easy way to do it was to fill their deep holds with American grain. On some routes it was carried free — it was cheaper than buying ballast. Thus, inexpensive and abundant American wheat was conveyed to England for very low rates. Effectively, the beef eaters were subsidising the bread eaters.
The end of the Foreign Cattle Market
With the 1903 embargo on Argentine cattle, and diminishing American and Canadian supplies, the market went into a decline. In 1912 George Philcox died, borne to the grave by market employees: the ''City Press'' wrote that it was of a broken heart, caused by the decay of the market to which he had devoted his life. In 1913 the City of London decided to close it down.
At the outbreak of World War I the site was occupied by the War Office. It became a supply base, sending rations to the troops in France. After the War the City sold it to the government. In time the site became known as
Convoys Wharf
Convoys Wharf, formerly called the King's Yard, is the site of Deptford Dockyard, the first of the Royal Dockyards, built on a riverside site in Deptford, by the River Thames in London, England. It was first developed in 1513 by Henry VIII to bui ...
.
["Convoys" was the trading name of a firm that stored paper. In the 1920s and 1930s they had a newsprint warehouse near the old Foreign Cattle Market; its wharf became known as Convoys Wharf. See ''The Times'', 2 October 1928, page xxvii (advertisement).]
Some remains of the old Market (and former dockyard), such as boundary walls, were made
listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
s, and stand today.
References and notes
Sources
General
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Newspapers
*
*
*
*
*, content reprinted in ''The Farmer's Magazine'
retrieved 5 September 2022.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Purchasing power
:''Where historic money values have been re-expressed in £ of 2018 purchasing power (e.g. £1,234
2018) they been estimated with this tool:''
*{{cite web
, title=Inflation Calculator
, website=Bank of England
, url=https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/monetary-policy/inflation/inflation-calculator
External links
Samuel Plimsoll's ''Cattle Ships'' (1890) his campaigning pamphlet.
''Five Thousand Miles With Range-Cattle'' (1891) An English solicitor on a working holiday in Canada takes a trainload of cattle from the foothills of the Rocky Mountains to England.
Animal trade
Buildings and structures in the London Borough of Lewisham
Cattle
Cruelty to animals
Deptford
Economic history of London
Food markets in the United Kingdom
History of globalization
History of international trade
History of the American West
History of the River Thames
Meat industry
Port of London
 The Foreign Cattle Market,
The Foreign Cattle Market,  For centuries the main cattle market for London had been held at Smithfield. There being no refrigeration, butchers bought an animal at the market, and slaughtered it themselves. The site was small and by the Victorian era the volume of trade had increased to the point that it was badly overcrowded and a public health nuisance. Driving cattle to Smithfield through the thoroughfares of the metropolis e.g. Oxford Street was bad for traffic congestion and endangered life and limb.
Hence in 1855 Parliament moved London's livestock market to a site in
For centuries the main cattle market for London had been held at Smithfield. There being no refrigeration, butchers bought an animal at the market, and slaughtered it themselves. The site was small and by the Victorian era the volume of trade had increased to the point that it was badly overcrowded and a public health nuisance. Driving cattle to Smithfield through the thoroughfares of the metropolis e.g. Oxford Street was bad for traffic congestion and endangered life and limb.
Hence in 1855 Parliament moved London's livestock market to a site in  The new
The new 
 The cattle plague epidemic of 1865-7 has been described as the most dramatic event in 19th century agricultural history. Believing it to be a divine retribution for the sins of society, the Archbishop of Canterbury demanded a day of national humiliation.
Little was known about rinderpest in Great Britain and it took two years to eradicate. It did not help that the
The cattle plague epidemic of 1865-7 has been described as the most dramatic event in 19th century agricultural history. Believing it to be a divine retribution for the sins of society, the Archbishop of Canterbury demanded a day of national humiliation.
Little was known about rinderpest in Great Britain and it took two years to eradicate. It did not help that the 
 Since the new market must be in a port, a suitable site on the Thames had to be chosen. There was lobbying for the market to be on the river's north bank, since many traders, especially the butchers of
Since the new market must be in a port, a suitable site on the Thames had to be chosen. There was lobbying for the market to be on the river's north bank, since many traders, especially the butchers of  It was not an auction market. Trading was by private bargain, and in live animals only. Exporters consigned cattle, sheep and pigs to salesmen who worked on commission. Salesmen and buyers intermingled around the animal pens. Market days were Mondays and Thursdays, but there was nothing to stop animals being sold in their lairs on other days, and this was often done, especially when a shipload arrived late.
Weighbridges were seldom used: it was a matter of professional pride that cattle weights were guesstimated. A journalist described it for Australian readers:The buyers were wholesale (and sometimes retail) butchers, who had access to slaughterhouse space on the premises, generally renting it by the year. Slaughtermen, paid by results, killed and butchered their purchases for them within the 10 days required by law; the buyers took away the meat, offal, hides and fleeces: most of the meat they resold at Smithfield. By the end of 1887 some 9.4 million animals had been landed at Deptford.
It was not an auction market. Trading was by private bargain, and in live animals only. Exporters consigned cattle, sheep and pigs to salesmen who worked on commission. Salesmen and buyers intermingled around the animal pens. Market days were Mondays and Thursdays, but there was nothing to stop animals being sold in their lairs on other days, and this was often done, especially when a shipload arrived late.
Weighbridges were seldom used: it was a matter of professional pride that cattle weights were guesstimated. A journalist described it for Australian readers:The buyers were wholesale (and sometimes retail) butchers, who had access to slaughterhouse space on the premises, generally renting it by the year. Slaughtermen, paid by results, killed and butchered their purchases for them within the 10 days required by law; the buyers took away the meat, offal, hides and fleeces: most of the meat they resold at Smithfield. By the end of 1887 some 9.4 million animals had been landed at Deptford.
 Cattle boats from the Continent — over a thousand a year — came up the Thames on Sundays and Wednesdays.
As the transatlantic cattle trade developed (see below), large ocean-going cattle steamers came into use, but these were reluctant to come alongside. Accordingly the market purchased three paddle steamers (named ''Racoon'', ''Taurus'' and ''Claude Hamilton'') into which cattle were transshipped at
Cattle boats from the Continent — over a thousand a year — came up the Thames on Sundays and Wednesdays.
As the transatlantic cattle trade developed (see below), large ocean-going cattle steamers came into use, but these were reluctant to come alongside. Accordingly the market purchased three paddle steamers (named ''Racoon'', ''Taurus'' and ''Claude Hamilton'') into which cattle were transshipped at 
 To find a superintendent for the market the City interviewed 25 candidates, and chose a 28-year old Southend station-master, George Philcox. Philcox was in charge of the market for the next 40 years; when he died in 1912, it soon closed. Apparently an able and popular man, it was said "The market made him, and in turn he made it".
To find a superintendent for the market the City interviewed 25 candidates, and chose a 28-year old Southend station-master, George Philcox. Philcox was in charge of the market for the next 40 years; when he died in 1912, it soon closed. Apparently an able and popular man, it was said "The market made him, and in turn he made it".
 It was their job to drive the animals off the boats, or to transship them from the transatlantic steamers at Gravesend.
Drovers at Deptford market were paid a lump sum per vessel, George Philcox told Booth. They could unload a cattle boat in as little as 15 minutes. Some cattle, especially from Argentina, were very wild, and were best given "a wide berth". A man in regular employment could earn as much as £4 a week (about £520 purchasing power in 2018 money).
It was their job to drive the animals off the boats, or to transship them from the transatlantic steamers at Gravesend.
Drovers at Deptford market were paid a lump sum per vessel, George Philcox told Booth. They could unload a cattle boat in as little as 15 minutes. Some cattle, especially from Argentina, were very wild, and were best given "a wide berth". A man in regular employment could earn as much as £4 a week (about £520 purchasing power in 2018 money).
 One of the most unpleasant jobs was cleaning cattle and sheep intestines, which were used for making sausage skins (and, according to a later source, condoms). Originally men's work, in about 1891 they went on strike for more pay: management responded by assigning the work to women.
Some 80-100 women and girls, aged 14 to 40, were employed daily; they worked for two firms that had contracted to buy all the gut offal from the market's slaughterhouses. Writing for the ''Daily Telegraph'', "A Lady Visitor", who claimed to have smelled some vile odours in her time, said the stink was insupportable. Tubs of unwashed entrails were coarsely de-fatted by men. This work was done by a first group who cleaned off the outside, made the gut into a figure of eight rope, and tossed it to a second. The second group, armed with a powerful watercock, turned the gut inside out and washed it ready for the sausage makers. In winter the water nearly froze the hands.
They made 12''s'' to 14''s'' (≅ £77 to £892018) a week which, for women's work, was good pay.
For some reason
One of the most unpleasant jobs was cleaning cattle and sheep intestines, which were used for making sausage skins (and, according to a later source, condoms). Originally men's work, in about 1891 they went on strike for more pay: management responded by assigning the work to women.
Some 80-100 women and girls, aged 14 to 40, were employed daily; they worked for two firms that had contracted to buy all the gut offal from the market's slaughterhouses. Writing for the ''Daily Telegraph'', "A Lady Visitor", who claimed to have smelled some vile odours in her time, said the stink was insupportable. Tubs of unwashed entrails were coarsely de-fatted by men. This work was done by a first group who cleaned off the outside, made the gut into a figure of eight rope, and tossed it to a second. The second group, armed with a powerful watercock, turned the gut inside out and washed it ready for the sausage makers. In winter the water nearly froze the hands.
They made 12''s'' to 14''s'' (≅ £77 to £892018) a week which, for women's work, was good pay.
For some reason 

 Describing the pull of London as a meat market for European farmers,
Describing the pull of London as a meat market for European farmers, 



 The surplus came from the new, teeming lands of the American West. But early Western cattle e.g. Texas longhorns, though hardy, made tough eating. It cost exactly the same to ship a top quality steer from New York to London as a gristly one. Consequently, it made economic sense for American shippers to export their best animals, as better able to absorb the cost of carriage.
At first, export-grade cattle were to be found in the East only, where cattle breeds were similar to those of the British Isles. British farmers were advised not to worry about imported Western livestock for the present, because it would not compete on quality. But (as predicted) Western cattlemen realised they could capture lucrative markets by improving their stock — and did so. The English export trade contributed to the demand for more and better cattle. Progressive American cattlemen imported prize British bulls, sometimes paying fabulous prices. "On the western plains the ranches that succeeded the open range bought high priced sires with which to upgrade their old stock. The upturn in the quality of beef animals, with younger cattle going to the feedlot, meant better beef from the slaughter house and on the family table, all part of a general improvement".
Comparable improvements were made in sheep. By 1884, 95% of cattle exported came from the West.
The surplus came from the new, teeming lands of the American West. But early Western cattle e.g. Texas longhorns, though hardy, made tough eating. It cost exactly the same to ship a top quality steer from New York to London as a gristly one. Consequently, it made economic sense for American shippers to export their best animals, as better able to absorb the cost of carriage.
At first, export-grade cattle were to be found in the East only, where cattle breeds were similar to those of the British Isles. British farmers were advised not to worry about imported Western livestock for the present, because it would not compete on quality. But (as predicted) Western cattlemen realised they could capture lucrative markets by improving their stock — and did so. The English export trade contributed to the demand for more and better cattle. Progressive American cattlemen imported prize British bulls, sometimes paying fabulous prices. "On the western plains the ranches that succeeded the open range bought high priced sires with which to upgrade their old stock. The upturn in the quality of beef animals, with younger cattle going to the feedlot, meant better beef from the slaughter house and on the family table, all part of a general improvement".
Comparable improvements were made in sheep. By 1884, 95% of cattle exported came from the West.
 At the end of the Victorian era cattle and sheep were shipped to Deptford Market from as far away as
At the end of the Victorian era cattle and sheep were shipped to Deptford Market from as far away as  The Beef Trust was a
The Beef Trust was a  Animals were sent from the grasslands of the world to be slaughtered at Deptford market. Even today, when animal welfare is a consideration and the average journey from feedlot to slaughter plant lasts just a few hours, transport-related stress and injury are major sources of loss to the American meat industry. According to
Animals were sent from the grasslands of the world to be slaughtered at Deptford market. Even today, when animal welfare is a consideration and the average journey from feedlot to slaughter plant lasts just a few hours, transport-related stress and injury are major sources of loss to the American meat industry. According to  Sending cattle safely across the Atlantic demanded forward planning and knowhow. Quite often these were lacking, especially in the early days, when conditions were "very bad", or "little better than the horrors of "the middle passage" of the old slave trading days". According to a government inquiry the worst culprits were
Sending cattle safely across the Atlantic demanded forward planning and knowhow. Quite often these were lacking, especially in the early days, when conditions were "very bad", or "little better than the horrors of "the middle passage" of the old slave trading days". According to a government inquiry the worst culprits were  Plimsoll wrote that cattle ships were dangerously unstable in stormy weather, cruel to animals, and unnecessary. They were unstable if cattle were carried on the upper deck or (worse) on a temporary, higher platform that raised the ship's centre of gravity even further, and obstructed the crew in their duties. Animals were washed overboard by heavy seas, or were deliberately jettisoned to save the vessel. If carried down in the holds they could stifle to death after the hatches were battened down in bad weather. Knowing this, captains sometimes took risks in leaving the hatches open. Further, animals stood on their own dung, which could not be cleared away; on this slippery surface they fell about helplessly and were injured, often fatally.
Plimsoll alleged that cattle attendants were not allowed to euthanise badly injured livestock, because the insurance companies would refuse to pay up. Animals were left to die a lingering death. Plimsoll was probably wrong about the insurance companies; but it made no difference, because the cattle attendants thought it was so and behaved accordingly.
Another accusation was that cattle attendants used cruel methods to make animals get on their feet, such as piercing them with pitchforks, twisting their tails, beating them about the head with iron buckets, or pouring paraffin in their ears. "Some of the men in charge, who are paid a percentage on the number of cattle they bring alive into Deptford, tortured the animals most fiendishly into a semblance of animation". It was indignantly denied by cattle shippers, who asked what they had to gain by such practices: cattle were free to lie down if they wanted to.
Plimsoll wrote that cattle ships were dangerously unstable in stormy weather, cruel to animals, and unnecessary. They were unstable if cattle were carried on the upper deck or (worse) on a temporary, higher platform that raised the ship's centre of gravity even further, and obstructed the crew in their duties. Animals were washed overboard by heavy seas, or were deliberately jettisoned to save the vessel. If carried down in the holds they could stifle to death after the hatches were battened down in bad weather. Knowing this, captains sometimes took risks in leaving the hatches open. Further, animals stood on their own dung, which could not be cleared away; on this slippery surface they fell about helplessly and were injured, often fatally.
Plimsoll alleged that cattle attendants were not allowed to euthanise badly injured livestock, because the insurance companies would refuse to pay up. Animals were left to die a lingering death. Plimsoll was probably wrong about the insurance companies; but it made no difference, because the cattle attendants thought it was so and behaved accordingly.
Another accusation was that cattle attendants used cruel methods to make animals get on their feet, such as piercing them with pitchforks, twisting their tails, beating them about the head with iron buckets, or pouring paraffin in their ears. "Some of the men in charge, who are paid a percentage on the number of cattle they bring alive into Deptford, tortured the animals most fiendishly into a semblance of animation". It was indignantly denied by cattle shippers, who asked what they had to gain by such practices: cattle were free to lie down if they wanted to.
 From the livestock-raising regions animals were taken to market by train, mostly to Chicago. onto which 17 railroads converged. At the
From the livestock-raising regions animals were taken to market by train, mostly to Chicago. onto which 17 railroads converged. At the  If a steer did fall, or lay down to rest, there was a risk that it might never get up again. Consequently cattle attendants, who travelled in the
If a steer did fall, or lay down to rest, there was a risk that it might never get up again. Consequently cattle attendants, who travelled in the  Samuel Plimsoll argued that the transatlantic cattle trade had no rational commercial purpose except to enrich dishonest traders. He asked: And he answered:
Samuel Plimsoll argued that the transatlantic cattle trade had no rational commercial purpose except to enrich dishonest traders. He asked: And he answered:


