Depression (differential Diagnoses) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Depression, one of the most commonly diagnosed psychiatric disorders, is being diagnosed in increasing numbers in various segments of the population worldwide. Depression in the United States alone affects 17.6 million Americans each year or 1 in 6 people. Depressed patients are at increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and suicide. Within the next twenty years depression is expected to become the second leading cause of disability worldwide and the leading cause in high-income nations, including the United States. In approximately 75% of suicides, the individuals had seen a physician within the prior year before their death, 45–66% within the prior month. About a third of those who died by suicide had contact with mental health services in the prior year, a fifth within the preceding month.
There are many psychiatric and medical conditions that may mimic some or all of the symptoms of depression or may occur
Depression, one of the most commonly diagnosed psychiatric disorders, is being diagnosed in increasing numbers in various segments of the population worldwide. Depression in the United States alone affects 17.6 million Americans each year or 1 in 6 people. Depressed patients are at increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and suicide. Within the next twenty years depression is expected to become the second leading cause of disability worldwide and the leading cause in high-income nations, including the United States. In approximately 75% of suicides, the individuals had seen a physician within the prior year before their death, 45–66% within the prior month. About a third of those who died by suicide had contact with mental health services in the prior year, a fifth within the preceding month.
There are many psychiatric and medical conditions that may mimic some or all of the symptoms of depression or may occur
/ref>
 *
*
 *
*
Strategies for Reducing the Misdiagnosis of Bipolar Depression-Charles M. Bowden M.D.
* ttps://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/03/090311085151.htm Toxoplasmosis Parasite May Trigger Schizophrenia And Bipolar Disorders
10 Signs of depression
{{DEFAULTSORT:Depression, differential diagnoses of Neuropsychology Major depressive disorder
 Depression, one of the most commonly diagnosed psychiatric disorders, is being diagnosed in increasing numbers in various segments of the population worldwide. Depression in the United States alone affects 17.6 million Americans each year or 1 in 6 people. Depressed patients are at increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and suicide. Within the next twenty years depression is expected to become the second leading cause of disability worldwide and the leading cause in high-income nations, including the United States. In approximately 75% of suicides, the individuals had seen a physician within the prior year before their death, 45–66% within the prior month. About a third of those who died by suicide had contact with mental health services in the prior year, a fifth within the preceding month.
There are many psychiatric and medical conditions that may mimic some or all of the symptoms of depression or may occur
Depression, one of the most commonly diagnosed psychiatric disorders, is being diagnosed in increasing numbers in various segments of the population worldwide. Depression in the United States alone affects 17.6 million Americans each year or 1 in 6 people. Depressed patients are at increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and suicide. Within the next twenty years depression is expected to become the second leading cause of disability worldwide and the leading cause in high-income nations, including the United States. In approximately 75% of suicides, the individuals had seen a physician within the prior year before their death, 45–66% within the prior month. About a third of those who died by suicide had contact with mental health services in the prior year, a fifth within the preceding month.
There are many psychiatric and medical conditions that may mimic some or all of the symptoms of depression or may occur comorbid
In medicine, comorbidity - from Latin morbus ("sickness"), co ("together"), -ity (as if - several sicknesses together) - is the presence of one or more additional conditions often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary ...
to it. A disorder either psychiatric or medical that shares symptoms and characteristics of another disorder, and may be the true cause of the presenting symptoms is known as a differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
.
Many psychiatric disorders such as depression are diagnosed by allied health
Allied health professions are health care professions distinct from optometry, dentistry, nursing, medicine, and pharmacy. They provide a range of diagnostic, technical, therapeutic, and support services in connection with health care.
Definitio ...
professionals with little or no medical training, and are made on the basis of presenting symptoms without proper consideration of the underlying cause, adequate screening of differential diagnoses is often not conducted. According to one study, "non-medical mental health care providers may be at increased risk of not recognizing masked medical illnesses in their patients."
Misdiagnosis or missed diagnoses may lead to lack of treatment or ineffective and potentially harmful treatment which may worsen the underlying causative disorder. A conservative estimate is that 10% of all psychological symptoms may be due to medical reasons, with the results of one study suggesting that about half of individuals with a serious mental illness "have general medical conditions that are largely undiagnosed and untreated and may cause or exacerbate psychiatric symptoms".
In a case of misdiagnosed depression recounted in ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print m ...
'', a writer received treatment for depression for years; during the last 10 years of her depression the symptoms worsened, resulting in multiple suicide attempts and psychiatric hospitalizations. When an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
finally was performed, it showed the presence of a tumor. However, she was told by a neurologist that it was benign. After a worsening of symptoms, and upon the second opinion of another neurologist, the tumor was removed. After the surgery, she no longer had depressive symptoms.Is It Depression--or a Tumor? - Newsweek Nov 21, 2007/ref>
Autoimmune disorders
*Celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barl ...
; is an autoimmune disorder in which the body is unable to digest gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grain ...
which is found in various food grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and l ...
s, most notably wheat, and also rye and barley. Current research has shown its neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest without the gastrointestinal symptoms.
:"However, more recent studies have emphasized that a wider spectrum of neurologic syndromes may be the presenting extraintestinal manifestation of gluten sensitivity with or without intestinal pathology."
* Lupus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". P ...
connective tissue disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
that can affect any part of the body.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Lupus can cause or worsen depression.
Bacterial-viral-parasitic infection
 *
* Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
; is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus ''Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it make ...
, a spirochete bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
transmitted by the Deer tick (Ixodes scapularis
''Ixodes scapularis'' is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick (although some people reserve the latter term for ''Ixodes pacificus'', which is found on the west coast of the US), and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It wa ...
). Lyme disease is one of a group of diseases which have earned the name the "great imitator" for their propensity to mimic the symptoms of a wide variety of medical and neuropsychiatric disorders. Lyme disease is an underdiagnosed illness, partially as a result of the complexity and unreliability of serologic testing.
:"Because of the rapid rise of Lyme borreliosis nationwide and the need for antibiotic treatment to prevent severe neurologic damage, mental health professionals need to be aware of its possible psychiatric presentations.
* Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
; the prevalence of which is on the rise, is another of the "great imitators", which if left untreated can progress to neurosyphilis
Neurosyphilis refers to infection of the central nervous system in a patient with syphilis. In the era of modern antibiotics the majority of neurosyphilis cases have been reported in HIV-infected patients. Meningitis is the most common neurologic ...
and affect the brain, can present with solely neuropsychiatric symptoms. "This case emphasises that neurosyphilis still has to be considered in the differential diagnosis within the context of psychiatric conditions and diseases. Owing to current epidemiological data and difficulties in diagnosing syphilis, routine screening tests in the psychiatric field are necessary."
* Neurocysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis is a specific form of the infectious parasitic disease cysticercosis that is caused by the infection with ''Taenia solium'', a tapeworm found in pigs. Neurocysticercosis occurs when cysts formed by the infection take hold with ...
(NCC): is an infection of the brain or spinal cord caused by the larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
l stage of the pork tapeworm
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass is Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodar ...
, ''Taenia solium
''Taenia solium'', the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans as its definitive host and pigs ...
''. NCC is the most common helminthic (parasitic worm) infestation of the central nervous system worldwide. Humans develop cysticercosis when they ingest eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
of the pork tapeworm via contact with contaminated fecal matter or eating infected vegetables or undercooked pork. "While cysticercosis is endemic in Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
, it is an emerging disease with increased prevalence in the United States." "The rate of depression in those with neurocysticercosis is higher than in the general population."
* Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months ...
; is an infection caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan (specifically an apicomplexan) that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as d ...
'' an intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
protozoan
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
. Humans can be infected in 3 different ways: ingestion of tissue cysts
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble) ...
, ingestion of oocysts
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism i ...
, or in utero
''In Utero'' is the third and final studio album by American rock band Nirvana. It was released on September 21, 1993, by DGC Records. After breaking into the mainstream with their second album, ''Nevermind'' (1991), Nirvana hired Steve Albini t ...
infection with tachyzoites
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism i ...
. One of the prime methods for transmission to humans is contact with the feces of the host species, the domesticated cat. Toxoplasma gondii infects approximately 30% of the world's human population, but causes overt clinical symptoms in only a small segment of those infected. Exposure to Toxoplasma gondii ( seropositivity) without developing Toxoplasmosis has been proven to alter various characteristics of human behavior as well as being a causative factor in some cases of depression, in addition, studies have linked seropositivity with an increased rate of suicide
* West Nile virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae'', from the genus ''Flavivirus'', which also contains the Zika virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus. The virus ...
(WNV); which can cause encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, ...
has been reported to be a causal factor in developing depression in 31% of those infected in a study conducted in Houston, Texas and reported to the Center for Disease Control (CDC). The primary vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
s for disease transmission to humans are various species of mosquito. WNV which is endemic to Southern Europe, Africa the Middle East and Asia was first identified in the United States in 1999. Between 1999 and 2006, 20,000 cases of confirmed symptomatic WNV were reported in the United States, with estimates of up to 1 million being infected. "WNV is now the most common cause of epidemic viral encephalitis in the United States, and it will likely remain an important cause of neurological disease for the foreseeable future."
Blood disorders
*Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
: is a decrease in normal number of red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s (RBCs) or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
in the blood. Depressive symptoms are associated with anemia in a general population of older persons living in the community.
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Between 1 and 4 million Americans are believed to havechronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) or ME/CFS, is a complex, debilitating, long-term medical condition. The causes and mechanisms of the disease are not fully understood. Distinguishing core symptoms are ...
(CFS), yet only 50% have consulted a physician for symptoms of CFS. In addition individuals with CFS symptoms often have an undiagnosed medical or psychiatric disorder such as diabetes, thyroid disease or substance abuse. CFS, at one time considered to be psychosomatic in nature, is now considered to be a valid medical condition in which early diagnosis and treatment can aid in alleviating or completely resolving symptoms. While frequently misdiagnosed as depression, differences have been noted in rate of cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arterie ...
.
CFS is underdiagnosed in more than 80% of the people who have it; at the same time, it is often misdiagnosed as depression.
Dietary disorders
*Fructose malabsorption
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a ketonic simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed ...
and lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pa ...
; deficient fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
transport by the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
, or by the deficiency of the enzyme, lactase
Lactase is an enzyme produced by many organisms. It is located in the brush border of the small intestine of humans and other mammals. Lactase is essential to the complete digestion of whole milk; it breaks down lactose, a sugar which gives m ...
in the mucosal lining, respectively. As a result of this malabsorption the saccharide
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may ...
s reach the colon and are digested by bacteria which convert them to short chain fatty acids Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are fatty acids with fewer than six carbon atoms. Derived from intestinal microbial fermentation of indigestible foods, SCFAs are the main energy source of colonocytes, making them crucial to gastrointestinal health. ...
, , and H2. Approximately 50% of those affected exhibit the physical signs of irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
.
:"Fructose malabsorption may play a role in the development of depressed mood. Fructose malabsorption should be considered in patients with symptoms of major depression...."
:"Fructose and sorbitol
Sorbitol (), less commonly known as glucitol (), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alcohol g ...
reduced diet in subjects with fructose malabsorption does not only reduce gastrointestinal symptoms but also improves mood and early signs of depression."
Endocrine system disorders
Dysregulation of theendocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
may present with various neuropsychiatric symptoms; irregularities in the hypothalamic
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus i ...
-pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypop ...
- adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
(HPA) axis and the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
(HPT) axis have been shown in patients with primary depression.
Adrenal gland
*Addison's disease
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrenal ...
: also known as chronic adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androge ...
, hypocortisolism, and hypocorticism) is a rare endocrine disorder wherein the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
s, located above the kidneys, produce insufficient steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wi ...
s (glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s and often mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary mi ...
s). "Addison's disease presenting with psychiatric features in the early stage has the tendency to be overlooked and misdiagnosed."
* Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, ...
, also known as hypercortisolism
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a ...
, is an endocrine disorder characterized by an excess of cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland ...
. In the absence of prescribed steroid medications, it is caused by a tumor on the pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypop ...
or adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
glands, or more rarely, an ectopic hormone-secreting tumor. Depression is a common feature in diagnosed patients and it often improves with treatment.
Thyroid and parathyroid glands
 *
* Graves' disease
Graves' disease (german: Morbus Basedow), also known as toxic diffuse goiter, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyr ...
: an autoimmune disease where the thyroid is overactive, resulting in hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism ...
and thyrotoxicosis
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. ...
.
* Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarg ...
: also known chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed by a variety of cell and antibody mediated immune processes. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is associated with thyroid peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine re ...
and thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric glycoprotein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Tg is secreted and accumulated at hundreds of grams per litre in the extracellular compartment o ...
autoantibodies
* Hashitoxicosis
Hashitoxicosis, which can be abbreviated "Htx", is a transient hyperthyroidism caused by inflammation associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis disturbing the thyroid follicles, resulting in excess release of thyroid hormone. Robins Basic Pathology ...
* Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
* Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism ...
* Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany (involuntary musc ...
; can affect calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
, supplementation of which has completely resolved cases of depression in which hypoparathyroidism is the sole causative factor.
Pituitary tumors
Tumors of thepituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The ...
are fairly common in the general population with estimates ranging as high as 25%. Most tumors are considered to be benign and are often an incidental finding discovered during autopsy or as of neuroimaging in which case they are dubbed "incidentaloma
In medical or research imaging, an incidental imaging finding (also called an incidentaloma) is an unanticipated finding which is not related to the original diagnostic inquiry. As with other types of incidental medical findings, they may represe ...
s". Even in benign cases, pituitary tumors can affect cognitive, behavioral and emotional changes. Pituitary microadenomas are smaller than 10 mm in diameter and are generally considered benign, yet the presence of a microadenoma has been positively identified as a risk factor for suicide.
"... patients with pituitary disease were diagnosed and treated for depression and showed little response to the treatment for depression".
Pancreas
*Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
: an overproduction of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
causes reduced blood levels of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
. In one study of patients recovering from acute lung injury in intensive care, those patients who developed hypoglycemia while hospitalized showed an increased rate of depression.
Neurological
CNS Tumors
In addition to pituitary tumors, tumors in various locations in thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
may cause depressive symptoms and be misdiagnosed as depression.
Post concussion syndrome
Post-concussion syndrome
Post-concussion syndrome (PCS) is a set of symptoms that may continue for weeks, months, or a year or more after a concussion – medically classified as a so-called mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). About 34 to 35% of people with concussi ...
(PCS), is a set of symptoms that a person may experience for weeks, months, or occasionally years after a concussion
A concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. Symptoms may include loss of consciousness (LOC); memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking, concentration, ...
with a prevalence rate of 38–80% in mild traumatic brain injuries, it may also occur in moderate and severe cases of traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic b ...
. A diagnosis may be made when symptoms resulting from concussion, depending on criteria, last for more than three to six months after the injury, in which case it is termed persistent postconcussive syndrome (PPCS). In a study of the prevalence of post concussion syndrome symptoms in patients with depression utilizing the British Columbia Postconcussion Symptom Inventory
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
: "Approximately 9 out of 10 patients with depression met liberal self-report criteria for a postconcussion syndrome and more than 5 out of 10 met conservative criteria for the diagnosis." These self reported rates were significantly higher than those obtained in a scheduled clinical interview. Normal controls have exhibited symptoms of PCS as well as those seeking psychological services. There is considerable debate over the diagnosis of PCS in part because of the medico-legal and thus monetary ramifications of receiving the diagnosis.
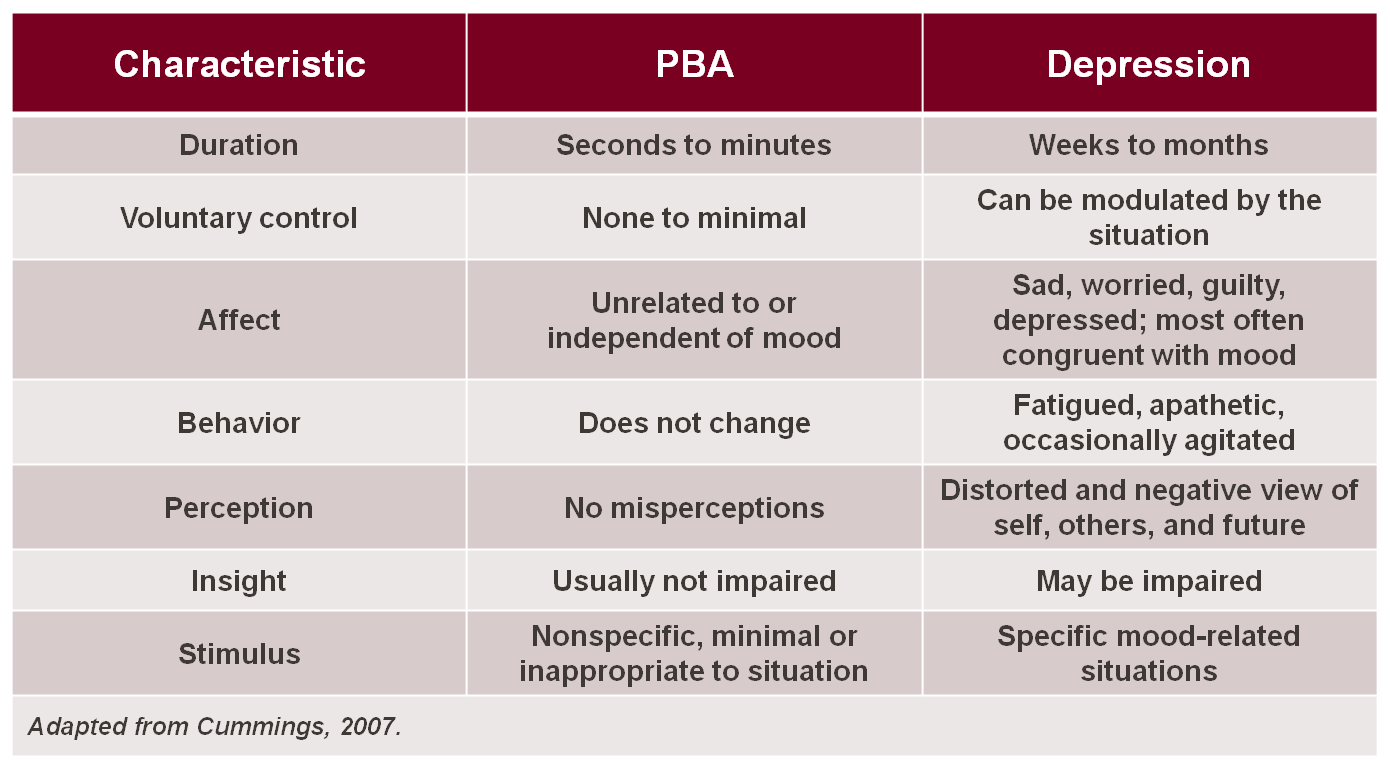
Pseudobulbar affect

Pseudobulbar affect
Pseudobulbar affect (PBA), or emotional incontinence, is a type of emotional disturbance characterized by uncontrollable episodes of crying, laughing, anger or other emotional displays. PBA occurs secondary to a neurologic disorder or brain inj ...
(PBA) is an affective disinhibition syndrome that is largely unrecognized in clinical settings and thus often untreated due to ignorance of the clinical manifestations of the disorder; it may be misdiagnosed as depression. It often occurs secondary to various neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most comm ...
, and also can result from head trauma. PBA is characterized by involuntary and inappropriate outbursts of laughter and/or crying. PBA has a high prevalence rate with estimates of 1.5–2 million cases in the United States alone.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This d ...
is a chronic demyelinating disease
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency i ...
in which the myelin sheaths
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to Insulator (electricity), insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The ...
of cells in the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spi ...
are irreparably damaged. Symptoms of depression are very common in patients at all stages of the disease and may be exacerbated by medical treatments, notably interferon beta-1a
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified '' E. coli''. Some research indic ...
.
Neurotoxicity
Various compounds have been shown to have neurotoxic effects many of which have been implicated as having a causal relationship in the development of depression.Cigarette smoking
There has been research which suggests a correlation between cigarette smoking and depression. The results of one recent study suggest that smoking cigarettes may have a direct causal effect on the development of depression. There have been various studies done showing a positive link between smoking, suicidal ideation and suicide attempts. In a study conducted among nurses, those smoking between 1-24 cigarettes per day had twice the suicide risk; 25 cigarettes or more, 4 times the suicide risk, than those who had never smoked. In a study of 300,000 male U.S. Army soldiers, a definitive link between suicide and smoking was observed with those smoking over a pack a day having twice the suicide rate of non-smokers.Medication
Various medications have been suspected of having a causal relation in the development of depression; this has been classified as "organic mood syndrome". Some classes of medication such as those used to treathypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, have been recognized for decades as having a definitive relationship with the development of depression.
Monitoring of those taking medications which have shown a relationship with depression is often indicated, as well as the necessity of factoring in the use of such medications in the diagnostic process.
* Topical Tretinoin
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth ...
(Retin-A); derived from Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably bet ...
and used for various medical conditions such as in topical solutions used to treat acne vulgaris
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and po ...
. Although applied externally to the skin, it may enter the bloodstream and cross the blood brain barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the Cell (biology), cells, and transports Metabolic waste, metabolic waste products away from th ...
where it may have neurotoxic effects.
* Interferons
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten the ...
; proteins produced by the human body, three types have been identified ''alpha, beta'' and ''gamma''. Synthetic versions are utilized in various medications used to treat different medical conditions such as the use of interferon-alpha in cancer treatment
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. ...
and hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
treatment. All three classes of interferons may cause depression and suicidal ideation.
Chronic exposure to organophosphates
The neuropsychiatric effects of chronicorganophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered a ...
exposure include mood disorders, suicidal thinking and behaviour, cognitive impairment and chronic fatigue.
Neuropsychiatric
Bipolar disorder
*Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
is frequently misdiagnosed as major depression, and is thus treated with antidepressants alone which is not only not efficacious it is often contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
as it may exacerbate hypomania, mania, or cycling between moods. There is ongoing debate about whether this should be classified as a separate disorder because individuals diagnosed with major depression often experience some hypomanic symptoms, indicating a continuum between the two.
Nutritional deficiencies
Nutrition plays a key role in every facet of maintaining proper physical and psychological wellbeing. Insufficient or inadequate nutrition can have a profound effect on mental health. The emerging field ofnutritional neuroscience
Nutritional neuroscience is the scientific discipline that studies the effects various components of the diet such as minerals, vitamins, protein, carbohydrates, fats, dietary supplements, synthetic hormones, and food additives have on neuroch ...
explores the various connections between diet, neurological functioning and mental health.
* Vitamin B6: pyridoxal phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent ac ...
(PLP), the active form of B6, is a cofactor in the dopamine serotonin pathway, a deficiency in vitamin B6 may cause depressive symptoms.
* Folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
(vitamin B9) – Vitamin B
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. Though these vitamins share similar names (B1, B2, B3, etc.), they are chemically distinct compounds that often coexist ...
cobalamin: Low blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intra ...
and particularly red cell folate and diminished levels of vitamin B have been found in patients with depressive disorders. " suggest that oral doses of both folic acid (800 μg/(mcg) daily) and vitamin B12 (1 mg daily) should be tried to improve treatment outcome in depression."
* Long chain fatty acids: higher levels of omega-6
Omega-6 fatty acids (also referred to as ω-6 fatty acids or ''n''-6 fatty acids) are a family of polyunsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon-carbon double bond in the ''n''-6 position, that is, the sixth bond, counting from ...
and lower levels of omega-3
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chem ...
fatty acids has been associated with depression and behavioral change.
* Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D defic ...
is associated with depression
Sleep disorders
*Insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
: While the inability to fall asleep is often a symptom of depression, it can also in some instances serve as the trigger for developing a depressive disorder. It can be transient, acute or chronic. It can be a primary disorder or a co-morbid one.
* Restless legs syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis-Ekbom disease (WED), is generally a long-term disorder that causes a strong urge to move one's legs. There is often an unpleasant feeling in the legs that improves somewhat by moving them. This ...
(RLS), also known as Wittmaack-Ekbom's syndrome, is characterized by an irresistible urge to move one's body to stop uncomfortable or odd sensations. It most commonly affects the legs, but can also affect the arms or torso, and even phantom limb
A phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. Approximately 80 to 100% of individuals with an amputation experience sensations in their amputated limb. However, only a small percentage will experience painf ...
s. Restless Leg syndrome has been associated with Major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
. "Adjusted odds ratio for diagnosis of major depressive disorder... suggested a strong association between restless legs syndrome and major depressive disorder and/or panic disorder."
* Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea, also spelled sleep apnoea, is a sleep disorder in which pauses in breathing or periods of shallow breathing during sleep occur more often than normal. Each pause can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and they happen many times ...
is a sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of an individual's sleep patterns. Some sleep disorders are severe enough to interfere with normal physical, mental, social and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are test ...
characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a de ...
. Each episode, called an apnea
Apnea, BrE: apnoea, is the temporal cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the airways are ( patency), there ...
, lasts long enough for one or more breaths to be missed; such episodes occur repeatedly throughout the sleep cycle. Undiagnosed sleep apnea may cause or contribute to the severity of depression.
* Circadian rhythm sleep disorders
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSD), also known as circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders (CRSWD), are a family of sleep disorders which affect the timing of sleep. CRSDs arise from a persistent pattern of sleep/wake disturbances that can be ...
, of which few clinicians are aware, often go untreated or are treated inappropriately, as when misdiagnosed as either primary insomnia or as a psychiatric condition.
See also
*Rosenhan experiment
The Rosenhan experiment or Thud experiment was an experiment conducted to determine the validity of psychiatric diagnosis. The participants feigned hallucinations to enter psychiatric hospitals but acted normally afterwards. They were diagnosed w ...
* Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire
The Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire, or SPAQ, is a simple, self-administered screening test for Seasonal Affective Disorder, first developed in 1984. Though some aspects of its accuracy have been questioned since then, it is widely used t ...
References
Bibliography
* ''A Dose of Sanity: Mind, Medicine, and Misdiagnosis'' by Sydney Walker.John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in p ...
, 1997.
External links
Strategies for Reducing the Misdiagnosis of Bipolar Depression-Charles M. Bowden M.D.
* ttps://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/03/090311085151.htm Toxoplasmosis Parasite May Trigger Schizophrenia And Bipolar Disorders
10 Signs of depression
{{DEFAULTSORT:Depression, differential diagnoses of Neuropsychology Major depressive disorder