
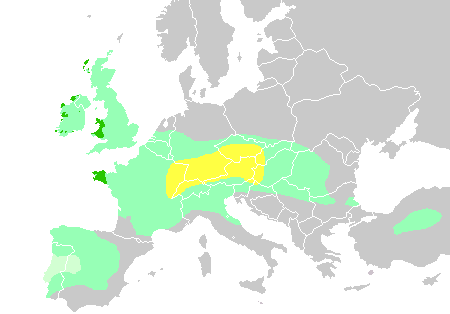
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
inhabitants of the cultural region of
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
, located in the area near the
Carpathian Mountains and west of the
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. They are often considered a subgroup of the
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and
Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
, as well as parts of
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
,
Eastern Serbia,
Northern Bulgaria
Northern Bulgaria ( bg, Северна България, Severna Bylgarija), also called Moesia ( bg, Мизия, ''Mizija'') is the northern half of Bulgaria, located to the north of the main ridge of the Balkan Mountains which conventionally s ...
,
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
,
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
and Southern
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. The Dacians and the related
Getae spoke the
Dacian language
Dacian is an extinct language, generally believed to be Indo-European, that was spoken in the Carpathian region in antiquity.
In the 1st century, it was probably the predominant language of the ancient regions of Dacia and Moesia and possib ...
, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring
Thracian language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it wa ...
and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
and by the
Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC.
Name and etymology
Name
The Dacians were known as ''Geta'' (plural ''Getae'') in
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
writings, and as ''Dacus'' (plural ''Daci'') or ''Getae'' in
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
documents, but also as ''Dagae'' and ''Gaete'' as depicted on the late Roman map ''
Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
''. It was
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
who first used the
ethnonym ''Getae'' in his ''
Histories''. In Greek and Latin, in the writings of
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
,
Strabo, and
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
, the people became known as 'the Dacians'. Getae and Dacians were interchangeable terms, or used with some confusion by the Greeks. Latin poets often used the name ''Getae''.
Vergil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
called them ''Getae'' four times, and ''Daci'' once,
Lucian ''Getae'' three times and ''Daci'' twice,
Horace named them ''Getae'' twice and ''Daci'' five times, while
Juvenal
Decimus Junius Juvenalis (), known in English as Juvenal ( ), was a Roman poet active in the late first and early second century CE. He is the author of the collection of satirical poems known as the '' Satires''. The details of Juvenal's life ...
one time ''Getae'' and two times ''Daci''. In AD 113,
Hadrian used the poetic term ''Getae'' for the Dacians. Modern historians prefer to use the name ''Geto-Dacians''.
Strabo describes the Getae and Dacians as distinct but cognate tribes. This distinction refers to the regions they occupied. Strabo and Pliny the Elder also state that Getae and Dacians spoke the same language.
By contrast, the name of ''Dacians'', whatever the origin of the name, was used by the more western tribes who adjoined the
Pannonians
This is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria ( grc-gre, Ἰλλυρία; la, Illyria). The name ''Illyrians'' seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greeks ...
and therefore first became known to the Romans. According to Strabo's ''
Geographica'', the original name of the Dacians was "''Daoi''". The name Daoi (one of the ancient Geto-Dacian tribes) was certainly adopted by foreign observers to designate all the inhabitants of the countries north of
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
that had not yet been conquered by
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
or Rome.
The ethnographic name ''Daci'' is found under various forms within ancient sources. Greeks used the forms "''Dakoi''" (
Strabo,
Dio Cassius, and
Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of '' De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vo ...
) and "Daoi" (singular Daos).
[Garašanin, Benac (1973) 243] The form "Daoi" was frequently used according to
Stephan of Byzantium.
Latins used the forms ''Davus'', ''Dacus'', and a derived form ''Dacisci'' (Vopiscus and inscriptions).
There are similarities between the ethnonyms of the Dacians and those of
Dahae
The Dahae, also known as the Daae, Dahas or Dahaeans (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , , , ; Latin: ; Chinese: ; Persian: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian nomadic tribal confederation, who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia.
Ident ...
(Greek ''Dáoi'', ''Dáai'', ''Dai'', ''Dasai''; Latin ''Dahae'', ''Daci''), an Indo-European people located east of the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
, until the 1st millennium BC. Scholars have suggested that there were links between the two peoples since ancient times. The historian
David Gordon White
David Gordon White (born September 3, 1953) is an American Indologist.
Academic career
David Gordon White took his B.A. in South Asian Studies at the University of Wisconsin in 1975. He obtained an M.A. in Religion at the University of Chicago ...
has, moreover, stated that the "Dacians ... appear to be related to the Dahae". (Likewise White and other scholars also believe that the names Dacii and Dahae may also have a shared etymology – see the section following for further details.)
By the end of the first century AD, all the inhabitants of the lands which now form Romania were known to the Romans as Daci, with the exception of some
Celtic and
Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
who infiltrated from the west, and
Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
and related people from the east.
Etymology
The name ''Daci'', or "Dacians" is a collective
ethnonym. Dio Cassius reported that the Dacians themselves used that name, and the Romans so called them, while the Greeks called them Getae. Opinions on the origins of the name ''Daci'' are divided. Some scholars consider it to originate in the Indo-European *''dha-k''-, with the stem *''dhe''- 'to put, to place', while others think that the name ''Daci'' originates in *''daca'' 'knife, dagger' or in a word similar to ''dáos,'' meaning 'wolf' in the related language of the
Phrygians.'
One hypothesis is that the name ''Getae'' originates in Indo-European *''guet-'' 'to utter, to talk'. Another hypothesis is that ''Getae'' and ''Daci'' are the Iranian names of two Iranian-speaking
Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
groups that had been assimilated into the larger Thracian-speaking population of the later "Dacia".
Early history of etymological approaches
In the 1st century AD, Strabo suggested that its stem formed a name previously borne by slaves: Greek Daos, Latin Davus (-k- is a known suffix in Indo-European ethnic names). In the 18th century, Grimm proposed the
Gothic ''dags'' or "day" that would give the meaning of "light, brilliant". Yet ''dags'' belongs to the Sanskrit word-root ''dah-'', and a derivation from ''Dah'' to "Daci" is difficult. In the 19th century, Tomaschek (1883) proposed the form "Dak", meaning ''those who understand and can speak'', by considering "Dak" as a derivation of the root ''da'' ("k" being a suffix); cf.
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
''dasa'', Bactrian ''daonha''. Tomaschek also proposed the form "Davus", meaning "members of the clan/countryman" cf.
Bactrian ''daqyu'', ''danhu'' "canton".
Modern theories
Since the 19th century, many scholars have proposed an
etymological
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words a ...
link between the
endonym of the Dacians and wolves.
* A possible connection with the
Phrygians was proposed by
Dimitar Dechev (in a work not published until 1957). The
Phrygian language
The Phrygian language () was the Indo-European language of the Phrygians, spoken in Anatolia (modern Turkey), during classical antiquity (c. 8th century BC to 5th century AD).
Phrygian ethno-linguistic homogeneity is debatable. Ancient Greek aut ...
word ''daos'' meant "wolf", and ''Daos'' was also a Phrygian deity. In later times,
Roman auxiliaries
The (, lit. "auxiliaries") were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 30 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of inf ...
recruited from the Dacian area were also known as ''Phrygi''. Such a connection was supported by material from
Hesychius of Alexandria
Hesychius of Alexandria ( grc, Ἡσύχιος ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς, Hēsýchios ho Alexandreús, lit=Hesychios the Alexandrian) was a Greek grammarian who, probably in the 5th or 6th century AD,E. Dickey, Ancient Greek Scholarship (2007 ...
(5th/6th century), as well as by the 20th century historian
Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanian historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. He was a leading interpreter of religious experience, who established paradigms in religiou ...
.
* The German linguist
Paul Kretschmer Paul Kretschmer (2 May 1866 – 9 March 1956) was a German linguist who studied the earliest history and interrelations of the Indo-European languages and showed how they were influenced by non-Indo-European languages, such as Etruscan.
Biograph ...
linked ''daos'' to wolves via the root ''dhau'', meaning to press, to gather, or to strangle – i.e. it was believed that wolves would often use a neck bite to kill their prey.
* Endonyms linked to wolves have been demonstrated or proposed for other
Indo-European tribes, including the
Luvians
The Luwians were a group of Anatolian peoples who lived in central, western, and southern Anatolia, in present-day Turkey, during the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. They spoke the Luwian language, an Indo-European language of the Anatolian sub-fam ...
,
Lycians
Lycians is the name of various peoples who lived, at different times, in Lycia, a geopolitical area in Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor).
History
The earliest known inhabitants of the area were the ''Solymoi'' (or ''Solymi''), also kno ...
,
Lucanians,
Hyrcanians and, in particular, the
Dahae
The Dahae, also known as the Daae, Dahas or Dahaeans (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , , , ; Latin: ; Chinese: ; Persian: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian nomadic tribal confederation, who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia.
Ident ...
(of the south-east Caspian region), who were known in Old Persian as ''Daos''. Scholars such as
David Gordon White
David Gordon White (born September 3, 1953) is an American Indologist.
Academic career
David Gordon White took his B.A. in South Asian Studies at the University of Wisconsin in 1975. He obtained an M.A. in Religion at the University of Chicago ...
have explicitly linked the endonyms of the Dacians and the Dahae.
* Hungarian linguist and historian Dr. Viktor Padányi writes "By all indications their name comes from the
Sumerian "dag, tag" word meaning two handed axe, battle axe."
* The ''
Draco
Draco is the Latin word for serpent or dragon.
Draco or Drako may also refer to:
People
* Draco (lawgiver) (from Greek: Δράκων; 7th century BC), the first lawgiver of ancient Athens, Greece, from whom the term ''draconian'' is derived
* ...
'', a standard flown by the Dacians, also prominently featured a wolf head.
However, according to Romanian historian and archaeologist
Alexandru Vulpe, the Dacian etymology explained by ''daos'' ("wolf") has little plausibility, as the transformation of ''daos'' into ''dakos'' is phonetically improbable and the ''Draco'' standard was not unique to Dacians. He thus dismisses it as
folk etymology.
Another etymology, linked to the
Proto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
roots ''*dhe-'' meaning "to set, place" and ''dheua'' → ''dava'' ("settlement") and ''dhe-k'' → ''daci'' is supported by Romanian historian
Ioan I. Russu (1967).
Mythological theories

Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanian historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. He was a leading interpreter of religious experience, who established paradigms in religiou ...
attempted, in his book ''From Zalmoxis to Genghis Khan'', to give a mythological foundation to an alleged special relation between Dacians and the wolves:
* Dacians might have called themselves "wolves" or "ones the same with wolves", suggesting religious significance.
* Dacians draw their name from a god or a legendary ancestor who appeared as a wolf.
* Dacians had taken their name from a group of fugitive immigrants arrived from other regions or from their own young outlaws, who acted similarly to the wolves circling villages and living from looting. As was the case in other societies, those young members of the community went through an initiation, perhaps up to a year, during which they lived as a "wolf". Comparatively,
Hittite laws referred to fugitive outlaws as "wolves".
* The existence of a ritual that provides one with the ability to turn into a wolf. Such a transformation may be related either to
lycanthropy itself, a widespread phenomenon, but attested especially in the
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
-
Carpathian region, or a ritual imitation of the behavior and appearance of the wolf. Such a ritual was presumably a military initiation, potentially reserved to a secret brotherhood of warriors (or
Männerbünde). To become formidable warriors they would assimilate behavior of the wolf, wearing wolf skins during the ritual. Traces related to wolves as a cult or as totems were found in this area since the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
period, including the
Vinča culture
The Vinča culture (), also known as Turdaș culture or Turdaș–Vinča culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5700–4500 BC or 5300–4700/4500 BC.. Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo, ...
artifacts: wolf statues and fairly rudimentary figurines representing dancers with a wolf mask. The items could indicate warrior initiation rites, or ceremonies in which young people put on their seasonal wolf masks. The element of unity of beliefs about
werewolves
In folklore, a werewolf (), or occasionally lycanthrope (; ; uk, Вовкулака, Vovkulaka), is an individual that can shapeshift into a wolf (or, especially in modern film, a therianthropic hybrid wolf-like creature), either purposely ...
and lycanthropy exists in the magical-religious experience of mystical solidarity with the wolf by whatever means used to obtain it. But all have one original myth, a primary event.
Origins and ethnogenesis
Evidence of proto-Thracians or proto-Dacians in the prehistoric period depends on the remains of
material culture. It is generally proposed that a proto-Dacian or proto-Thracian people developed from a mixture of
indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
and
Indo-Europeans from the time of
Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
expansion in the
Early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
(3,300–3,000 BC) when the latter, around 1500 BC, conquered the indigenous peoples. The indigenous people were Danubian farmers, and the invading people of the BC 3rd millennium were Kurgan warrior-herders from the Ukrainian and Russian steppes.
Indo-Europeanization was complete by the beginning of the Bronze Age. The people of that time are best described as proto-Thracians, which later developed in the Iron Age into Danubian-Carpathian Geto-Dacians as well as Thracians of the eastern Balkan Peninsula.
Between 15th–12th century BC, the Dacian-Getae culture was influenced by the Bronze Age Tumulus-Urnfield warriors who were on their way through the Balkans to Anatolia.
In the 8th to 7th centuries BCE, the migration of the
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
from the east into the Pontic Steppe pushed westwards and away from the steppes the related
Scythic Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
people who had previously dwelt on the
Pontic Steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from no ...
around the
Lake Maeotis
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
, following which the Agathyrsi settled in the territories of present-day
Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
,
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, and possibly
Oltenia
Oltenia (, also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions, with the alternative Latin names ''Wallachia Minor'', ''Wallachia Alutana'', ''Wallachia Caesarea'' between 1718 and 1739) is a historical province and geographical region of Romania ...
where they mingled with the indigenous population which was of
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
origins, and having later become completely assimilated by the Geto-Thracian populations; the fortified settlements of the Agathyrsi became the centres of the Getic groups who would later transform into the Dacian culture, and an important part of the Dacian people was descended from the Agathyrsi. When the La Tène Celts arrived in the 4th century BC, the Dacians were under the influence of the Scythians.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
attacked the Getae in 335 BC on the lower Danube, but by 300 BC they had formed a state founded on a military democracy, and began a period of conquest. More Celts arrived during the 3rd century BC, and in the 1st century BC the people of
Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul ( Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom ...
tried to conquer some of the Dacian territory on the eastern side of the Teiss river. The Dacians drove the Boii south across the Danube and out of their territory, at which point the Boii abandoned any further plans for invasion.
Some Hungarian historians consider the Dacians and Getae the same as the Scythian tribes of the
Dahae
The Dahae, also known as the Daae, Dahas or Dahaeans (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , , , ; Latin: ; Chinese: ; Persian: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian nomadic tribal confederation, who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia.
Ident ...
,
Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translati ...
, also the exonym
Daxia
Daxia, Ta-Hsia, or Ta-Hia (; literally: 'Great Xia') was apparently the name given in antiquity by the Han Chinese to Tukhara or Tokhara: the main part of Bactria, in what is now northern Afghanistan, and parts of southern Tajikistan and Uzbek ...
one with Dacia.
Identity and distribution
North of the Danube, Dacians occupied a larger territory than Ptolemaic Dacia, stretching between Bohemia in the west and the
Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
in the east, and up to the
Pripyat
Pripyat ( ; russian: При́пять), also known as Prypiat ( uk, При́пʼять, , ), is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1 ...
,
Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
, and
Oder rivers in the north and northwest. In BC 53,
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
stated that the Dacian territory was on the eastern border of the
Hercynian forest. According to Strabo's ''
Geographica'', written around AD 20, the Getes (Geto-Dacians) bordered the
Suevi who lived in the
Hercynian Forest, which is somewhere in the vicinity of the river Duria, the present-day
Váh
The Váh (; german: Waag, ; hu, Vág; pl, WagWag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów ...
(Waag). Dacians lived on both sides of the Danube. According to
Strabo, Moesians also lived on both sides of the Danube. According to
Agrippa Agrippa may refer to:
People Antiquity
* Agrippa (mythology), semi-mythological king of Alba Longa
* Agrippa (astronomer), Greek astronomer from the late 1st century
* Agrippa the Skeptic, Skeptic philosopher at the end of the 1st century
* Agri ...
, Dacia was limited by the Baltic Ocean in the North and by the Vistula in the West. The names of the people and settlements confirm Dacia's borders as described by Agrippa. Dacian people also lived south of the Danube.
Linguistic affiliation
The Dacians and Getae were always considered as Thracians by the ancients (Dio Cassius, Trogus Pompeius,
Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
, Strabo and Pliny the Elder), and were both said to speak the same
Thracian language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it wa ...
. The linguistic affiliation of Dacian is uncertain, since the ancient
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
language in question became extinct (?) and left very limited traces (?), usually in the form of place names, plant names and personal names. Thraco-Dacian (or Thracian and Daco-Mysian) seems to belong to the eastern (satem) group of Indo-European languages. There are two contradictory theories: some scholars (such as Tomaschek 1883; Russu 1967; Solta 1980; Crossland 1982; Vraciu 1980) consider Dacian to be a Thracian language or a dialect thereof. This view is supported by R. G. Solta, who says that Thracian and Dacian are very closely related languages. Other scholars (such as Georgiev 1965, Duridanov 1976) consider that Thracian and Dacian are two different and specific Indo-European languages which cannot be reduced to a common language (?). Linguists such as
Polomé and
Katičić expressed reservations about both theories.
The Dacians are generally considered to have been Thracian speakers, representing a cultural continuity from earlier Iron Age communities loosely termed Getic, Since in one interpretation, Dacian is a variety of Thracian, for the reasons of convenience, the generic term ‘Daco-Thracian" is used, with "Dacian" reserved for the language or dialect that was spoken north of Danube, in present-day Romania and eastern Hungary, and "Thracian" for the variety spoken south of the Danube. There is no doubt that the Thracian language was related to the Dacian language which was spoken in what is today Romania, before some of that area was occupied by the Romans. Also, both Thracian and Dacian have one of the main satem characteristic changes of Indo-European language, *k and *g to *s and *z. With regard to the term "Getic" (Getae), even though attempts have been made to distinguish between Dacian and Getic, there seems no compelling reason to disregard the view of the Greek geographer Strabo that the Daci and the Getae, Thracian tribes dwelling north of the Danube (the Daci in the west of the area and the Getae further east), were one and the same people and spoke the same language.
Another variety that has sometimes been recognized is that of
Moesian
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
(or Mysian) for the language of an intermediate area immediately to the south of Danube in Serbia, Bulgaria and Romanian Dobruja: this and the dialects north of the Danube have been grouped together as Daco-Moesian. The language of the indigenous population has left hardly any trace in the anthroponymy of Moesia, but the toponymy indicates that the Moesii on the south bank of the Danube, north of the Haemus Mountains, and the Triballi in the valley of the Morava, shared a number of characteristic linguistic features with the Dacii south of the Carpathians and the Getae in the Wallachian plain, which sets them apart from the Thracians though their languages are undoubtedly related.
Dacian culture is mostly followed through Roman sources. Ample evidence suggests that they were a regional power in and around the city of
Sarmizegetusa. Sarmizegetusa was their political and spiritual capital. The ruined city lies high in the mountains of central Romania.
Vladimir Georgiev disputes that Dacian and Thracian were closely related for various reasons, most notably that Dacian and Moesian town names commonly end with the suffix ''-
DAVA'', while towns in
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
proper (i.e. South of the
Balkan mountains) generally end in ''-PARA'' (see
Dacian language
Dacian is an extinct language, generally believed to be Indo-European, that was spoken in the Carpathian region in antiquity.
In the 1st century, it was probably the predominant language of the ancient regions of Dacia and Moesia and possib ...
). According to Georgiev, the language spoken by the ethnic Dacians should be classified as "Daco-Moesian" and regarded as distinct from Thracian. Georgiev also claimed that names from approximately Roman Dacia and Moesia show different and generally less extensive changes in Indo-European consonants and vowels than those found in Thrace itself. However, the evidence seems to indicate divergence of a Thraco-Dacian language into northern and southern groups of dialects, not so different as to qualify as separate languages. Polomé considers that such lexical differentiation ('' -dava'' vs. ''para'') would, however, be hardly enough evidence to separate Daco-Moesian from Thracian.
Tribes

An extensive account of the native tribes in Dacia can be found in the ninth tabula of Europe of Ptolemy's Geography. The Geography was probably written in the period AD 140–150, but the sources were often earlier; for example, Roman Britain is shown before the building of Hadrian's Wall in the AD 120s. Ptolemy's Geography also contains a physical map probably designed before the Roman conquest, and containing no detailed nomenclature. There are references to the
Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
, but it appears that the Dacian map of the Tabula was completed after the final triumph of Roman nationality. Ptolemy's list includes no fewer than twelve tribes with Geto-Dacian names.
The fifteen tribes of Dacia as named by Ptolemy, starting from the northernmost ones, are as follows. First, the
Anartes
The Anartes (or Anarti, Anartii or Anartoi)Jan Czarnecki (1975) 120 were Celtic tribes, or, in the case of those sub-groups of Anartes which penetrated the ancient region of Dacia (roughly modern Romania), Celts culturally assimilated by the Dacian ...
, the
Teurisci
Teurisci was a Dacian tribe at the time of Ptolemy (140 AD). They were originally considered a branch of the Celtic Taurisci (Noricum), who moved to Upper Tisza. However, the archaeology shows that Celts have been absorbed by Dacians, at some poi ...
and the Coertoboci/
Costoboci
The Costoboci (; lat, Costoboci, Costobocae, Castabocae, Coisstoboci, grc, Κοστωβῶκοι, Κοστουβῶκοι or Κοιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains a ...
. To the south of them are the Buredeense (
Buri/
Burs), the
Cotenses/
Cotini The Gotini (in Tacitus), who are generally equated to the Cotini in other sources, were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland,
and Slovakia.
The spelling "Got ...
and then the
Albocenses, the
Potulatenses and the
Sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
, while the southernmost were the
Saldenses, the
Ciaginsi and the
Piephigi. To the south of them were
Predasenses/Predavenses, the
Rhadacenses/Rhatacenses, the
Caucoenses (Cauci) and
Biephi
Biephi was a Dacian tribe.Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
*List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around ...
. Twelve out of these fifteen tribes listed by Ptolemy are ethnic Dacians, and three are Celts: Anarti, Teurisci, and Cotenses. There are also previous brief mentions of other Getae or Dacian tribes on the left and right banks of the Danube, or even in Transylvania, to be added to the list of
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
. Among these other tribes are the
Trixae,
Crobidae and
Appuli.
Some peoples inhabiting the region generally described in Roman times as "Dacia" were not ethnic Dacians. The true Dacians were a people of Thracian descent. German elements (Daco-Germans), Celtic elements (Daco-Celtic) and Iranian elements (Daco-Sarmatian) occupied territories in the north-west and north-east of Dacia. This region covered roughly the same area as modern
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
plus
Bessarabia (Republic of
Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
) and eastern
Galicia (south-west Ukraine), although Ptolemy places Moldavia and Bessarabia in ''Sarmatia Europaea'', rather than ''Dacia''. After the
Dacian Wars (AD 101-6), the Romans occupied only about half of the wider Dacian region. The
Roman province of Dacia covered just western
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
as far as the ''
Limes Transalutanus
''Limes Transalutanus''Technological challenges on the Limes Transalutanus,
Eugen S. Teodor, Dan Ştefan, https://www.antiquity.ac.uk/projgall/teodor342 is the modern name given to a fortified frontier system of the Roman Empire, built on the west ...
'' (East of the river ''Alutus'', or
Olt
Olt or OLT may refer to:
People:
* Károly Olt (1904–1985), Hungarian politician
* Mike Olt (born 1988), American baseball player
Places:
* Olt County, a county (județ) of Romania
* Olt (river), a river in Romania
** Olt Defile, a defile that ...
) and
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, as bordered by the Carpathians.
The impact of the Roman conquest on these people is uncertain. One hypothesis was that they were effectively eliminated. An important clue to the character of Dacian casualties is offered by the ancient sources Eutropius and Crito. Both speak about men when they describe the losses suffered by the Dacians in the wars. This suggests that both refer to losses due to fighting, not due to a process of extermination of the whole population. A strong component of the Dacian army, including the Celtic Bastarnae and the Germans, had withdrawn rather than submit to Trajan.
[Wilcox (2000)27] Some scenes on Trajan's Column represent acts of obedience of the Dacian population, and others show the refugee Dacians returning to their own places. Dacians trying to buy amnesty are depicted on
Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
(one offers to Trajan a tray of three gold ingots). Alternatively, a substantial number may have survived in the province, although were probably outnumbered by the Romanised immigrants. Cultural life in Dacia became very mixed and decidedly cosmopolitan because of the colonial communities. The Dacians retained their names and their own ways in the midst of the newcomers, and the region continued to exhibit Dacian characteristics. The Dacians who survived the war are attested as revolting against the Roman domination in Dacia at least twice, in the period of time right after the Dacian Wars, and in a more determined manner in 117 AD. In 158 AD, they revolted again, and were put down by M. Statius Priscus. Some Dacians were apparently expelled from the occupied zone at the end of each of the two Dacian Wars or otherwise emigrated. It is uncertain where these refugees settled. Some of these people might have mingled with the existing ethnic Dacian tribes beyond the Carpathians (the Costoboci and Carpi).
After Trajan's conquest of Dacia, there was recurring trouble involving Dacian groups excluded from the Roman province, as finally defined by Hadrian. By the early third century the "Free Dacians", as they were earlier known, were a significantly troublesome group, then identified as the Carpi, requiring imperial intervention on more than one occasion. In 214
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
dealt with their attacks. Later,
Philip the Arab
Philip the Arab ( la, Marcus Julius Philippus "Arabs"; 204 – September 249) was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. He was born in Aurantis, Arabia, in a city situated in modern-day Syria. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Philip, ...
came in person to deal with them; he assumed the triumphal title Carpicus Maximus and inaugurated a new era for the province of Dacia (July 20, 246). Later both Decius and Gallienus assumed the titles Dacicus Maximus. In 272, Aurelian assumed the same title as Philip.
In about 140 AD, Ptolemy lists the names of several tribes residing on the fringes of the
Roman Dacia (west, east and north of the Carpathian range), and the ethnic picture seems to be a mixed one. North of the Carpathians are recorded the Anarti, Teurisci and Costoboci. The
Anarti (or Anartes) and the Teurisci were originally probably Celtic peoples or mixed Dacian-Celtic. The Anarti, together with the Celtic
Cotini The Gotini (in Tacitus), who are generally equated to the Cotini in other sources, were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland,
and Slovakia.
The spelling "Got ...
, are described by
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
as vassals of the powerful
Quadi Germanic people. The Teurisci were probably a group of Celtic
Taurisci
The Taurisci were a federation of Celtic tribes who dwelt in today's Carinthia and northern Slovenia (Carniola) before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC). According to Pliny the Elder, they are the same as the people known as the Norici.
Etym ...
from the eastern
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
. However, archaeology has revealed that the Celtic tribes had originally spread from west to east as far as Transylvania, before being absorbed by the Dacians in the 1st century BC.
Costoboci
The main view is that the ''
Costoboci
The Costoboci (; lat, Costoboci, Costobocae, Castabocae, Coisstoboci, grc, Κοστωβῶκοι, Κοστουβῶκοι or Κοιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains a ...
'' were ethnically Dacian. Others considered them a Slavic or Sarmatian tribe. There was also a Celtic influence, so that some consider them a mixed Celtic and Thracian group that appear, after Trajan's conquest, as a Dacian group within the Celtic superstratum. The Costoboci inhabited the southern slopes of the Carpathians. Ptolemy named the Coestoboci (Costoboci in Roman sources) twice, showing them divided by the Dniester and the Peucinian (Carpathian) Mountains. This suggests that they lived on both sides of the Carpathians, but it is also possible that two accounts about the same people were combined. There was also a group, the Transmontani, that some modern scholars identify as Dacian Transmontani Costoboci of the extreme north. The name Transmontani was from the Dacians' Latin, literally "people over the mountains". Mullenhoff identified these with the Transiugitani, another Dacian tribe north of the Carpathian mountains.
Based on the account of
Dio Cassius, Heather (2010) considers that Hasding Vandals, around 171 AD, attempted to take control of lands which previously belonged to the free Dacian group called the Costoboci. Hrushevskyi (1997) mentions that the earlier widespread view that these Carpathian tribes were Slavic has no basis. This would be contradicted by the Coestobocan names themselves that are known from the inscriptions, written by a Coestobocan and therefore presumably accurately. These names sound quite unlike anything Slavic. Scholars such as Tomaschek (1883), Shutte (1917) and Russu (1969) consider these Costobocian names to be Thraco-Dacian. This inscription also indicates the Dacian background of the wife of the Costobocian king "Ziais Tiati filia Daca". This indication of the socio-familial line of descent seen also in other inscriptions (i.e. Diurpaneus qui Euprepes Sterissae f(ilius) Dacus) is a custom attested since the historical period (beginning in the 5th century BC) when Thracians were under Greek influence. It may not have originated with the Thracians, as it could be just a fashion borrowed from Greeks for specifying ancestry and for distinguishing homonymous individuals within the tribe. Shutte (1917), Parvan, and Florescu (1982) pointed also to the Dacian characteristic place names ending in '–dava' given by Ptolemy in the Costoboci's country.
Carpi
The Carpi were a sizeable group of tribes, who lived beyond the north-eastern boundary of Roman Dacia. The majority view among modern scholars is that the Carpi were a North Thracian tribe and a subgroup of the Dacians. However, some historians classify them as Slavs.
According to Heather (2010), the Carpi were Dacians from the eastern foothills of the Carpathian range – modern Moldavia and Wallachia – who had not been brought under direct Roman rule at the time of Trajan's conquest of Transylvania Dacia. After they generated a new degree of political unity among themselves in the course of the third century, these Dacian groups came to be known collectively as the Carpi.

The ancient sources about the Carpi, before 104 AD, located them on a territory situated between the western side of Eastern European Galicia and the mouth of the Danube. The name of the tribe is homonymous with the Carpathian mountains. Carpi and Carpathian are Dacian words derived from the root ''(s)ker''- "cut" cf. Albanian ''karp'' "stone" and Sanskrit ''kar''- "cut".
A quote from the 6th-century Byzantine chronicler
Zosimus Zosimus, Zosimos, Zosima or Zosimas may refer to:
People
*
* Rufus and Zosimus (died 107), Christian saints
* Zosimus (martyr) (died 110), Christian martyr who was executed in Umbria, Italy
* Zosimos of Panopolis, also known as ''Zosimus Alchem ...
referring to the
Carpo-Dacians (Greek: Καρποδάκαι, Latin: ''Carpo-Dacae''), who attacked the Romans in the late 4th century, is seen as evidence of their Dacian ethnicity. In fact, Carpi/Carpodaces is the term used for Dacians outside of Dacia proper.
However, that the Carpi were Dacians is shown not so much by the form Καρποδάκαι in
Zosimus Zosimus, Zosimos, Zosima or Zosimas may refer to:
People
*
* Rufus and Zosimus (died 107), Christian saints
* Zosimus (martyr) (died 110), Christian martyr who was executed in Umbria, Italy
* Zosimos of Panopolis, also known as ''Zosimus Alchem ...
as by their characteristic place-names in –''dava'', given by Ptolemy in their country. The origin and ethnic affiliations of the Carpi have been debated over the years; in modern times they are closely associated with the Carpathian Mountains, and a good case has been made for attributing to the Carpi a distinct material culture, "a developed form of the Geto-Dacian La Tene culture", often known as the Poienesti culture, which is characteristic of this area.
Physical characteristics

Dacians are represented in the statues surmounting the
Arch of Constantine
The Arch of Constantine ( it, Arco di Costantino) is a triumphal arch in Rome dedicated to the emperor Constantine the Great. The arch was commissioned by the Roman Senate to commemorate Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the Battle of Milv ...
and on
Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
. The artist of the Column took some care to depict, in his opinion, a variety of Dacian people—from high-ranking men, women, and children to the near-savage. Although the artist looked to models in Hellenistic art for some body types and compositions, he does not represent the Dacians as generic barbarians.
Classical authors applied a generalized stereotype when describing the "barbarians"Celts, Scythians, Thraciansinhabiting the regions to the north of the Greek world. In accordance with this stereotype, all these peoples are described, in sharp contrast to the "civilized" Greeks, as being much taller, their skin lighter and with straight light-coloured hair and blue eyes. For instance,
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
wrote that "the Scythians on the Black Sea and the Thracians are straight-haired, for both they themselves and the environing air are moist"; according to
Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria ( grc , Κλήμης ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς; – ), was a Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen an ...
,
Xenophanes
Xenophanes of Colophon (; grc, Ξενοφάνης ὁ Κολοφώνιος ; c. 570 – c. 478 BC) was a Greek philosopher, theologian, poet, and critic of Homer from Ionia who travelled throughout the Greek-speaking world in early Classical ...
described the Thracians as "ruddy and tawny". On Trajan's column, Dacian soldiers' hair is depicted longer than the hair of Roman soldiers and they had trimmed beards.
Body-painting was customary among the Dacians. It is probable that the tattooing originally had a religious significance. They practiced symbolic-ritual tattooing or body painting for both men and women, with hereditary symbols transmitted up to the fourth generation.
History
Early history

In the absence of historical records written by the Dacians (and Thracians) themselves, analysis of their origins depends largely on the remains of material culture. On the whole, the Bronze Age witnessed the evolution of the ethnic groups which emerged during the
Eneolithic
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often v ...
period, and eventually the syncretism of both autochthonous and Indo-European elements from the steppes and the Pontic regions. Various groups of Thracians had not separated out by 1200 BC, but there are strong similarities between the ceramic types found at Troy and the ceramic types from the Carpathian area. About the year 1000 BC, the Carpatho-Danubian countries were inhabited by a northern branch of the Thracians. At the time of the arrival of the Scythians (c. 700 BC), the Carpatho-Danubian Thracians were developing rapidly towards the Iron Age civilization of the West. Moreover, the whole of the fourth period of the Carpathian Bronze Age had already been profoundly influenced by the first Iron Age as it developed in Italy and the Alpine lands. The Scythians, arriving with their own type of Iron Age civilization, put a stop to these relations with the West. From roughly 500 BC (the second Iron Age), the Dacians developed a distinct civilization, which was capable of supporting large centralised kingdoms by 1st BC and 1st AD.
Since the very first detailed account by Herodotus, Getae are acknowledged as belonging to the Thracians. Still, they are distinguished from the other Thracians by particularities of religion and custom. The first written mention of the name "Dacians" is in Roman sources, but classical authors are unanimous in considering them a branch of the Getae, a Thracian people known from Greek writings.
Strabo specified that the Daci are the Getae who lived in the area towards the
Pannonian plain
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the ...
(
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
), while the Getae proper gravitated towards the Black Sea coast (
Scythia Minor
Scythia Minor or Lesser Scythia (Greek: , ) was a Roman province in late antiquity, corresponding to the lands between the Danube and the Black Sea, today's Dobruja divided between Romania and Bulgaria. It was detached from Moesia Inferior by th ...
).
Relations with Thracians
Since the writings of Herodotus in the 5th century BC, Getae/Dacians are acknowledged as belonging to the Thracian sphere of influence. Despite this, they are distinguished from other Thracians by particularities of religion and custom. Geto-Dacians and Thracians were kin people but they were not the same. The differences from the southern Thracians or from the neighbouring Scythians were probably faint, as several ancient authors make confusions of identification with both groups. Linguist
Vladimir Georgiev says that based on the absence of toponyms ending in ''dava'' in
Southern Bulgaria
Southern Bulgaria ( bg, Южна България, ''Yuzhna Balgariya'') is the southern half of the territory of Bulgaria, located to the south of the main ridge of the Balkan Mountains which conventionally separates the country into a northern an ...
, the
Moesians
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
and Dacians (or as he calls them Daco-Mysians) couldn't be related to the
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
.
In the 19th century,
Tomaschek considered a close affinity between the Besso-Thracians and Getae-Dacians, an original kinship of both people with Iranian peoples. They are
Aryan tribes, several centuries before
Scolotes of the Pont and
Sauromatae
The Sauromatian culture (russian: Савроматская культура, Savromatskaya kulʹtura) was a Iron Age culture of horse nomads in the area of the lower Volga River in southern Russia, dated to the 6th to 4th centuries BCE. The name o ...
left the Aryan homeland and settled in the Carpathian chain, in the
Haemus (Balkan) and
Rhodope mountains. The Besso-Thracians and Getae-Dacians separated very early from Aryans, since their language still maintains roots that are missing from Iranian and it shows non-Iranian phonetic characteristics (i.e. replacing the Iranian "l" with "r").
Relations with Celts

Geto-Dacians inhabited both sides of the
Tisa River
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza b ...
before the rise of the Celtic
Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul ( Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom ...
, and again after the latter were defeated by the Dacians under king Burebista. During the second half of the 4th century BC, Celtic cultural influence appears in the archaeological records of the middle Danube, Alpine region, and north-western Balkans, where it was part of the Middle
La Tène material culture. This material appears in north-western and central Dacia, and is reflected especially in burials. The Dacians absorbed the Celtic influence from the northwest in the early third century BC. Archaeological investigation of this period has highlighted several Celtic warrior graves with military equipment. It suggests the forceful penetration of a military Celtic elite within the region of Dacia, now known as Transylvania, that is bounded on the east by the Carpathian range. The archaeological sites of the third and second centuries BC in Transylvania revealed a pattern of co-existence and fusion between the bearers of La Tène culture and indigenous Dacians. These were domestic dwellings with a mixture of Celtic and Dacian pottery, and several graves in the Celtic style containing vessels of Dacian type. There are some seventy Celtic sites in Transylvania, mostly cemeteries, but most if not all of them indicate that the native population imitated Celtic art forms that took their fancy, but remained obstinately and fundamentally Dacian in their culture.
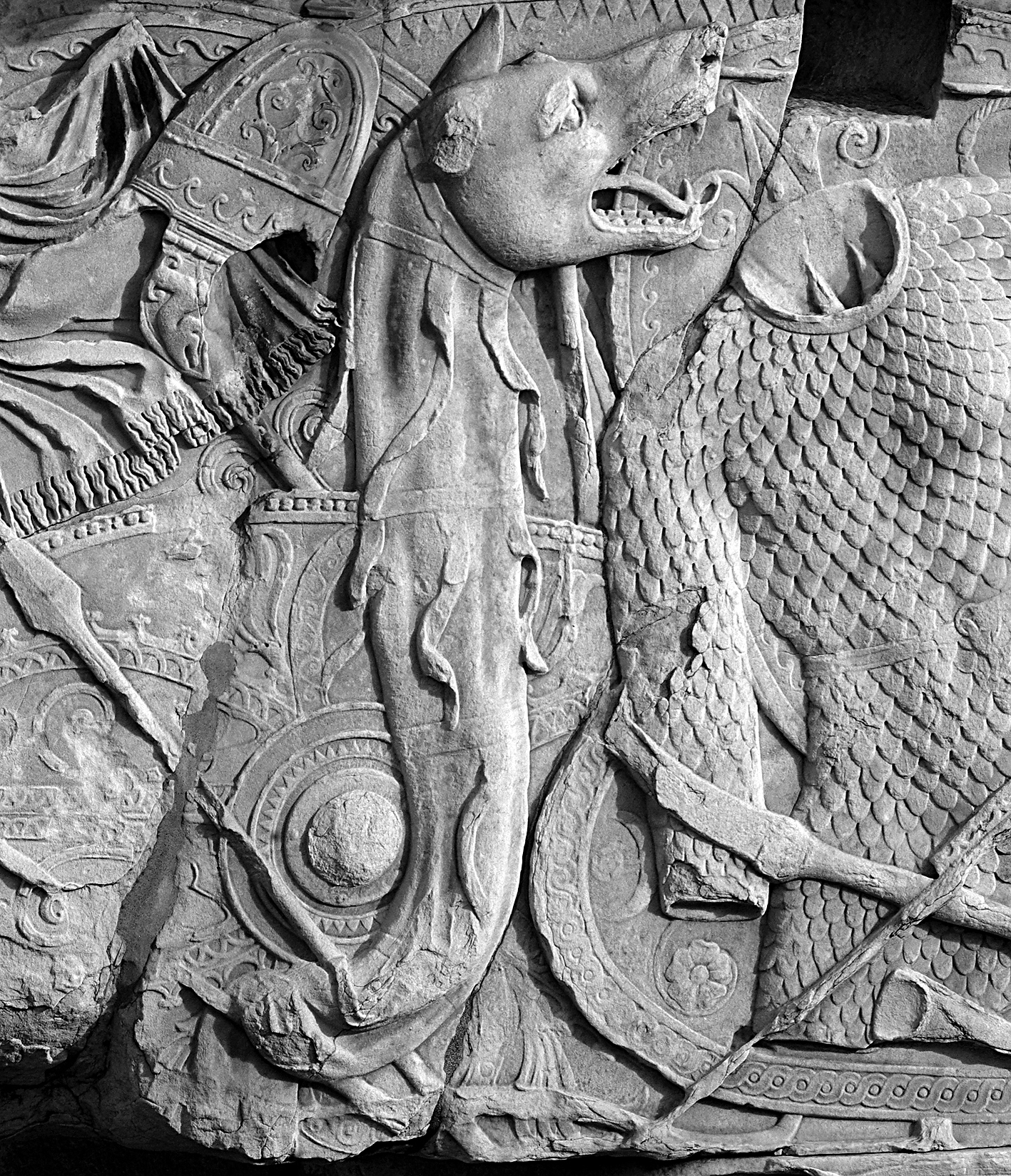
The Celtic Helmet from
Ciumeşti,
Satu Mare, Romania (northern Dacia), an Iron Age raven totem helmet, dated around the 4th century BC. A similar helmet is depicted on the Thraco-Celtic
Gundestrup cauldron
The Gundestrup cauldron is a richly decorated silver vessel, thought to date from between 200 BC and 300 AD,Nielsen, S; Andersen, J; Baker, J; Christensen, C; Glastrup, J; et al. (2005). "The Gundestrup cauldron: New scientific and technical ...
, being worn by one of the mounted warriors (detail tagge
here. See also a
illustration of Brennos wearing a similar helmet
Around 150 BC, La Tène material disappears from the area. This coincides with the ancient writings which mention the rise of Dacian authority. It ended the Celtic domination, and it is possible that Celts were driven out of Dacia. Alternatively, some scholars have proposed that the
Transylvanian Celts remained, but merged into the local culture and thus ceased to be distinctive.
Archaeological discoveries in the settlements and fortifications of the Dacians in the period of their kingdoms (1st century BC and 1st century AD) included imported Celtic vessels and others made by Dacian potters imitating Celtic prototypes, showing that relations between the Dacians and the Celts from the regions north and west of Dacia continued. In present-day
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, archaeology has revealed evidence for mixed Celtic-Dacian populations in the
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of about 78,353, it is the fifth l ...
and
Hron
The Hron ( sk, Hron; german: Gran; hu, Garam; la, Granus) is a long left tributary of the Danube[Cotini The Gotini (in Tacitus), who are generally equated to the Cotini in other sources, were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland,
and Slovakia.
The spelling "Got ...]
stayed in the mountains of Central Slovakia, where they took up mining and metalworking. Together with the original domestic population, they created the
Puchov culture that spread into central and northern Slovakia, including
Spis, and penetrated northeastern
Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
and southern Poland. Along the
Bodrog
The Bodrog is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary. It is a tributary to the river Tisza. The Bodrog is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ondava and Latorica near Zemplín in eastern Slovakia. It crosses the Slovak–H ...
River in
Zemplin they created Celtic-Dacian settlements which were known for the production of painted ceramics.
Relations with Greeks
Greek and Roman chroniclers record the defeat and capture of the Macedonian general
Lysimachus in the 3rd century BC by the Getae (Dacians) ruled by
Dromihete, their military strategy, and the release of Lysimachus following a debate in the assembly of the Getae.
Relations with Persians
Herodotus says: "before
Darius reached the Danube, the first people he subdued were the Getae, who believed that they never die". It is possible that the Persian expedition and the subsequent occupation may have altered the way in which the Getae expressed the immortality belief. The influence of thirty years of
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
presence may be detected in the emergence of an explicit iconography of the "Royal Hunt" that influenced Dacian and Thracian metalworkers, and of the practice of
hawking
Hawking may refer to:
People
* Stephen Hawking (1942–2018), English theoretical physicist and cosmologist
* Hawking (surname), a family name (including a list of other persons with the name)
Film
* ''Hawking'' (2004 film), about Stephen Ha ...
by their upper class.
Relations with Scythians
Agathyrsi Transylvania
The Scythians' arrival in the Carpathian mountains is dated to 700 BC. The
Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
of Transylvania had been mentioned by Herodotus (fifth century BC), who regarded them as not a Scythian people, but closely related to them. In other respects, their customs were close to those of the Thracians. The Agathyrsi were completely denationalized at the time of Herodotus and absorbed by the native Thracians.
The opinion that the Agathyrsi were almost certainly Thracians results also from the writings preserved by
Stephen of Byzantium, who explains that the Greeks called the
Trausi the
Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
, and we know that the
Trausi lived in the
Rhodope Mountains. Certain details from their way of life, such as tattooing, also suggest that the Agathyrsi were Thracians. Their place was later taken by the Dacians. That the Dacians were of Thracian stock is not in doubt, and it is safe to assume that this new name also encompassed the Agathyrsi, and perhaps other neighbouring Thracian people as well, as a result of some political upheaval.
Relations with Germanic tribes

The
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, a confederation of east German peoples, arrived in southern Ukraine no later than 230. During the next decade, a large section of them moved down the Black Sea coast and occupied much of the territory north of the lower Danube. The Goths' advance towards the area north of the Black Sea involved competing with the indigenous population of Dacian-speaking Carpi, as well as indigenous Iranian-speaking Sarmatians and Roman garrison forces. The Carpi, often called "Free Dacians", continued to dominate the anti-Roman coalition made up of themselves, Taifali,
Astringi, Vandals, Peucini, and Goths until 248, when the Goths assumed the hegemony of the loose coalition. The first lands taken over by the
Thervingi
The Thervingi, Tervingi, or Teruingi (sometimes pluralised Tervings or Thervings) were a Gothic people of the plains north of the Lower Danube and west of the Dniester River in the 3rd and the 4th centuries.
They had close contacts with the G ...
Goths were in Moldavia, and only during the fourth century did they move in strength down into the Danubian plain. The Carpi found themselves squeezed between the advancing Goths and the Roman province of Dacia. In 275 AD,
Aurelian surrendered the Dacian territory to the Carpi and the Goths. Over time, Gothic power in the region grew, at the Carpi's expense. The Germanic-speaking Goths replaced native Dacian-speakers as the dominant force around the Carpathian mountains. Large numbers of Carpi, but not all of them, were admitted into the Roman empire in the twenty-five years or so after 290 AD. Despite this evacuation of the Carpi around 300 AD, considerable groups of the natives (non-Romanized Dacians, Sarmatians and others) remained in place under Gothic domination.
In 330 the Gothic Thervingi contemplated moving to the Middle Danube region, and from 370 relocated with their fellow Gothic Greuthungi to new homes in the Roman Empire. The
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
were still more isolated, but even the
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
preferred to live among their own kind. As a result, the Goths settled in pockets. Finally, although Roman towns continued on a reduced level, there is no question as to their survival.
In 336 AD, Constantine took the
title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify either generation, an official position, or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may be inserted between the f ...
''Dacicus Maximus'' 'great victor in Dacia', implying at least partial reconquest of Trajan Dacia. In an inscription of 337, Constantine was commemorated officially as Germanicus Maximus, Sarmaticus, Gothicus Maximus, and Dacicus Maximus, meaning he had defeated the Germans, Sarmatians, Goths, and Dacians.
Dacian kingdoms

Dacian polities arose as confederacies that included the Getae, the Daci, the Buri, and the Carpi (cf. Bichir 1976, Shchukin 1989), united only periodically by the leadership of Dacian kings such as
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
and
Decebal. This union was both military-political and ideological-religious on ethnic basis. The following are some of the attested Dacian kingdoms:
The kingdom of
Cothelas, one of the Getae, covered an area near the Black Sea, between northern Thrace and the Danube, today Bulgaria, in the 4th century BC. The kingdom of
Rubobostes controlled a region in Transylvania in the 2nd century BC.
Gaius Scribonius Curio (proconsul 75–73 BC) campaigned successfully against the Dardani and the
Moesi
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
, becoming the first Roman general to reach the river Danube with his army. His successor,
Marcus Licinius Lucullus, brother of the famous
Lucius Lucullus, campaigned against the Thracian
Bessi tribe and the Moesi, ravaging the whole of
Moesia, the region between the Haemus (Balkan) mountain range and the Danube. In 72 BC, his troops occupied the Greek coastal cities of Scythia Minor (the modern
Dobrogea region in Romania and Bulgaria), which had sided with Rome's
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
arch-enemy, king
Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
of
Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
, in the
Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
. Greek geographer Strabo claimed that the Dacians and Getae had been able to muster a combined army of 200,000 men during Strabo's era, the time of Roman emperor
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
.
The kingdom of Burebista
The Dacian kingdom reached its maximum extent under king
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
(ruled 82 – 44 BC). The capital of the kingdom was possibly the city of
Argedava
Argedava (''Argedauon'', ''Sargedava'', ''Sargedauon'', ''Zargedava'', ''Zargedauon'', grc, Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον) was an important Dacians, Dacian town mentioned in the Decree of Dionysopolis (48 BC), and potentially ...
, also called Sargedava in some historical writings, situated close to the river Danube. The kingdom of Burebista extended south of the Danube, in what is today Bulgaria, and the Greeks believed their king was the greatest of all Thracians. During his reign, Burebista transferred the Geto-Dacians' capital from Argedava to
Sarmizegetusa. For at least one and a half centuries,
Sarmizegethusa was the Dacian capital, reaching its peak under king
Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invas ...
. Burebista annexed the Greek cities on the Pontus.(55–48 BC). Augustus wanted to avenge the defeat of
Gaius Antonius Hybrida
Gaius Antonius Hybrida (flourished 1st century BC) was a politician of the Roman Republic. He was the second son of Marcus Antonius and brother of Marcus Antonius Creticus; his mother is unknown. He was also the uncle of the famed triumvir Mark ...
at
Histria (Sinoe)
Histria or Istros ( grc, Ἰστρίη, Thracian river god, Danube), was a Greek colony or ''polis'' (πόλις, city) near the mouths of the Danube (known as Ister in Ancient Greek), on the western coast of the Black Sea. It was the first urba ...
32 years before, and to recover the lost standards. These were held in a powerful fortress called
Genucla (Isaccea, near modern Tulcea, in the Danube delta region of Romania), controlled by
Zyraxes, the local Getan petty king.
[Dio LI.26.5] The man selected for the task was
Marcus Licinius Crassus, grandson of
Crassus the
triumvir
A triumvirate ( la, triumvirātus) or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs ( la, triumviri). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are ...
, and an experienced general at 33 years of age, who was appointed proconsul of Macedonia in 29 BC.
The kingdom of Decebalus 87 – 106
By the year AD 100, more than 400,000 square kilometres were dominated by the Dacians, who numbered two million. Decebalus was the last king of the Dacians, and despite his fierce resistance against the Romans was defeated, and committed suicide rather than being marched through Rome in a
triumph
The Roman triumph (Latin triumphus) was a celebration for a victorious military commander in ancient Rome. For later imitations, in life or in art, see Trionfo. Numerous later uses of the term, up to the present, are derived directly or indirectl ...
as a captured enemy leader.
Conflict with Rome
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
's Dacian state was powerful enough to threaten Rome, and
Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
contemplated campaigning against the Dacians. Despite this, the formidable Dacian power under
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
lasted only until his death in 44 BC. The subsequent division of Dacia continued for about a century until the reign of
Scorilo
Scorilo (died 70) was a Dacian king who may have been the father of Decebalus. Evidence for his life and reign is fragmentary.
Sources
The Roman historian Jordanes lists a series of Dacian kings before Decebalus, placing a ruler called "Coryll ...
. This was a period of only occasional attacks on the Roman Empire's border, with some local significance.
The unifying actions of the last Dacian king
Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invas ...
(ruled 87–106 AD) were seen as dangerous by Rome. Despite the fact that the Dacian army could now gather only some 40,000 soldiers, Decebalus' raids south of the Danube proved unstoppable and costly. In the Romans' eyes, the situation at the border with Dacia was out of control, and Emperor
Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(ruled 81 to 96 AD) tried desperately to deal with the danger through military action. But the outcome of Rome's disastrous campaigns into Dacia in AD 86 and AD 88 pushed Domitian to settle the situation through diplomacy.
Emperor
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
(ruled 98–117 AD) opted for a different approach and decided to conquer the Dacian kingdom, partly in order to seize its vast
gold mines
Gold mining is the extraction of gold resources by mining. Historically, mining gold from alluvial deposits used manual separation processes, such as gold panning. However, with the expansion of gold mining to ores that are not on the surface, ...
wealth. The effort required two major wars (the Dacian Wars), one in 101–102 AD and the other in 105–106 AD. Only fragmentary details survive of the Dacian war: a single sentence of Trajan's own Dacica; little more of the Getica written by his doctor,
T. Statilius Crito;
nothing whatsoever of the poem proposed by
Caninius Rufus (if it was ever written),
Dio Chrysostom
Dio Chrysostom (; el, Δίων Χρυσόστομος ''Dion Chrysostomos''), Dion of Prusa or Cocceianus Dio (c. 40 – c. 115 AD), was a Greek orator, writer, philosopher and historian of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD. Eighty of his ...
's Getica or
Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
's Dacica. Nonetheless, a reasonable account can be pieced together.
In the first war, Trajan invaded Dacia by crossing the river Danube with a boat-bridge and inflicted a crushing defeat on the Dacians at the
Second Battle of Tapae
The Second Battle of Tapae (101) was the decisive battle of the first Dacian War, in which Roman Emperor Trajan defeated the Dacian King Decebalus's army. Other setbacks in the campaign delayed its completion until 102. The battle is most ...
in 101 AD. The Dacian king Decebalus was forced to sue for peace. Trajan and Decebalus then concluded a peace treaty which was highly favourable to the Romans. The peace agreement required the Dacians to cede some territory to the Romans and to demolish their fortifications. Decebalus' foreign policy was also restricted, as he was prohibited from entering into alliances with other tribes.
However, both Trajan and Decebalus considered this only a temporary truce and readied themselves for renewed war. Trajan had Greek engineer
Apollodorus of Damascus
Apollodorus of Damascus ( grc, Ἀπολλόδωρος ὁ Δαμασκηνός) was a Nabataean architect and engineer from Damascus, Roman Syria, who flourished during the 2nd century AD. As an engineer he authored several technical treatises, ...
construct a stone bridge over the Danube river, while Decebalus secretly plotted alliances against the Romans. In 105, Trajan crossed the Danube river and besieged Decebalus' capital,
Sarmizegetusa, but the siege failed because of Decebalus' allied tribes. However, Trajan was an optimist. He returned with a newly constituted army and took Sarmizegetusa by treachery. Decebalus fled into the mountains, but was cornered by pursuing Roman cavalry. Decebalus committed suicide rather than being captured by the Romans and be paraded as a slave, then be killed. The Roman captain took his head and right hand to Trajan, who had them displayed in the
Forums.
Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
in Rome was constructed to celebrate the conquest of Dacia.
The Roman people hailed Trajan's triumph in Dacia with the longest and most expensive celebration in their history, financed by a part of the gold taken from the Dacians. For his triumph, Trajan gave a 123-day festival (
ludi
''Ludi'' (Latin plural) were public games held for the benefit and entertainment of the Roman people (''populus Romanus''). ''Ludi'' were held in conjunction with, or sometimes as the major feature of, Roman religious festivals, and were also ...
) of celebration, in which approximately 11,000 animals were slaughtered and 11,000 gladiators fought in combats. This surpassed Emperor Titus's celebration in AD 70, when a 100-day festival included 3,000 gladiators and 5,000 to 9,000 wild animals.
Roman rule
Only about half part of Dacia then became a Roman province, with a newly built capital at
Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa
Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa was the capital and the largest city of Roman Dacia, later named ''Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa'' after the former Dacian capital, located some 40 km away. Built on the ground of a camp of t ...
, 40 km away from the site of Old Sarmisegetuza Regia, which was razed to the ground. The name of the Dacians' homeland, Dacia, became the name of a Roman province, and the name Dacians was used to designate the people in the region. ''Roman Dacia'', also ''
Dacia Traiana
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today ...
'' or ''Dacia Felix'', was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271 or 275 AD.
Its territory consisted of eastern and southeastern
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, and the regions of
Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
and
Oltenia
Oltenia (, also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions, with the alternative Latin names ''Wallachia Minor'', ''Wallachia Alutana'', ''Wallachia Caesarea'' between 1718 and 1739) is a historical province and geographical region of Romania ...
(located in modern Romania).
Dacia was organised from the beginning as an
imperial province
An imperial province was a Roman province during the Principate where the Roman Emperor had the sole right to appoint the governor (''legatus Augusti pro praetore''). These provinces were often the strategically located border provinces.
The pro ...
, and remained so throughout the Roman occupation. It was one of the empire's
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
provinces; official
epigraphs attest that the language of administration was Latin.
Historian estimates of the population of Roman Dacia range from 650,000 to 1,200,000.
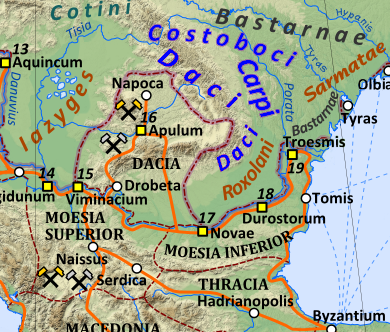
Dacians that remained outside the Roman Empire after the Dacian wars of AD 101–106 had been named Dakoi prosoroi (Latin ''Daci limitanei''), "neighbouring Dacians".
Modern historians use the generic name "Free Dacians" or ''Independent Dacians''. The tribes Daci Magni (Great Dacians), Costoboci (generally considered a Dacian subtribe), and Carpi remained outside the Roman empire, in what the Romans called ''Dacia Libera'' (Free Dacia). By the early third century the "Free Dacians" were a significantly troublesome group, by now identified as the Carpi. Bichir argues that the Carpi were the most powerful of the Dacian tribes who had become the principal enemy of the Romans in the region. In 214 AD,
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
campaigned against the Free Dacians. There were also campaigns against the Dacians recorded in 236 AD.
Roman Dacia was evacuated by the Romans under emperor Aurelian (ruled 271–5 AD). Aurelian made this decision on account of counter-pressures on the Empire there caused by the
Carpi,
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
,
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
, and
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
; the lines of defence needed to be shortened, and Dacia was deemed not defensible given the demands on available resources. Roman power in Thracia rested mainly with the legions stationed in Moesia. The rural nature of Thracia's populations, and the distance from Roman authority, encouraged the presence of local troops to support Moesia's legions. Over the next few centuries, the province was periodically and increasingly attacked by migrating Germanic tribes. The reign of
Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
saw the construction of over 100
legionary fortresses to supplement the defence. Thracians in Moesia and Dacia were
Romanized, while those within the
Byzantine empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
were their Hellenized descendants that had mingled with the Greeks.
After the Aurelian Retreat

Roman Dacia was never a uniformly or fully Romanized area. Post-Aurelianic Dacia fell into three divisions: the area along the river, usually under some type of Roman administration even if in a highly localized form; the zone beyond this area, from which Roman military personnel had withdrawn, leaving a sizable population behind that was generally Romanized; and finally what is now the northern parts of Moldavia, Crisana, and Maramures, which were never occupied by the Romans. These last areas were always peripheral to the Roman province, not militarily occupied but nonetheless influenced by Rome as part of the Roman economic sphere. Here lived the free, unoccupied Carpi, often called "Free Dacians".
The Aurelian retreat was a purely military decision to withdraw the Roman troops to defend the Danube. The inhabitants of the old province of Dacia displayed no awareness of impending dissolution. There were no sudden flights or dismantling of property. It is not possible to discern how many civilians followed the army out of Dacia; it is clear that there was no mass emigration, since there is evidence of continuity of settlement in Dacian villages and farms; the evacuation may not at first have been intended to be a permanent measure. The Romans left the province, but they didn't consider that they lost it. Dobrogea was not abandoned at all, but continued as part of the Roman Empire for over 350 years. As late as AD 300, the
tetrarchic emperors had resettled tens of thousands of Dacian
Carpi inside the empire, dispersing them in communities the length of the Danube, from Austria to the Black Sea.
Society
Dacians were divided into two classes: the aristocracy (''tarabostes'') and the common people (''comati''). Only the aristocracy had the right to cover their heads, and wore a
felt hat. The common people, who comprised the rank and file of the army, the
peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasant ...
s and artisans, might have been called ''capillati'' in Latin. Their appearance and clothing can be seen on
Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
.
Occupations

The chief occupations of the Dacians were
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
,
apiculture
Beekeeping (or apiculture) is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in man-made beehives. Honey bees in the genus '' Apis'' are the most-commonly-kept species but other honey-producing bees such as ''Melipona'' stingless bees are also kept. ...
,
viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for '' vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of '' Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ...
,
livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animal ...
,
ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
and
metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scal ...
. They also worked the gold and silver mines of Transylvania. At Pecica,
Arad, a Dacian workshop was discovered, along with equipment for minting coins and evidence of bronze, silver, and iron-working that suggests a broad spectrum of smithing. Evidence for the mass production of iron is found on many Dacian sites, indicating guild-like specialization. Dacian ceramic manufacturing traditions continue from the pre-Roman to the Roman period, both in provincial and unoccupied Dacia, and well into the fourth and even early fifth centuries. They engaged in considerable external trade, as is shown by the number of foreign coins found in the country (see also
Decebalus Treasure
The Decebalus Treasure is written by Cassius Dio concerning events said to have happened in the Roman world during the 2nd century AD.
The story
During the Second Dacian War many Dacian nobles surrendered or were caught. One of them, Bicilis, ...
). On the northernmost frontier of "free Dacia", coin circulation steadily grew in the first and second centuries, with a decline in the third and a rise again in the fourth century; the same pattern as observed for the Banat region to the southwest. What is remarkable is the extent and increase in coin circulation after Roman withdrawal from Dacia, and as far north as Transcarpathia.
Currency

The first coins produced by the Geto-Dacians were imitations of
silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
coins of the
Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. Th ...
ian kings
Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
and
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. Early in the 1st century BC, the Dacians replaced these with silver
denarii
The denarius (, dēnāriī ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very ...
of the Roman Republic, both official coins of Rome exported to Dacia, as well as locally made imitations of them. The Roman province Dacia is represented on the Roman
sestertius
The ''sestertius'' (plural ''sestertii''), or sesterce (plural sesterces), was an ancient Roman coin. During the Roman Republic it was a small, silver coin issued only on rare occasions. During the Roman Empire it was a large brass coin.
The n ...
coin as a woman seated on a rock, holding an
aquila, a small child on her knee. The aquila holds ears of grain, and another small child is seated before her holding grapes.
Construction
Dacians had developed the
murus dacicus (double-skinned ashlar-masonry with rubble fill and tie beams) characteristic to their complexes of fortified cities, like their capital
Sarmisegetuza Regia in what is today
Hunedoara County
Hunedoara County () is a county ('' județ'') of Romania, in Transylvania, with its capital city at Deva. The county is part of the Danube–Criș–Mureș–Tisa Euroregion.
Name
In Hungarian, it is known as , in German as , and in Slovak ...
, Romania. This type of wall has been discovered not only in the Dacian citadel of the Orastie mountains, but also in those at
Covasna,
Breaza
Breaza () is a town in Prahova County, Muntenia, Romania. The town center consists of at least two former villages, ''Podu Vadului'' and ''Breaza de Sus'', which were later merged. Today, ten villages are administratively part of the town: Breaza ...
near
Făgăraș
Făgăraș (; german: Fogarasch, Fugreschmarkt, hu, Fogaras) is a city in central Romania, located in Brașov County. It lies on the Olt River and has a population of 28,330 as of 2011. It is situated in the historical region of Transylvania, and ...
,
Tilișca near
Sibiu
Sibiu ( , , german: link=no, Hermannstadt , la, Cibinium, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Härmeschtat'', hu, Nagyszeben ) is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. Located some north-west of Bucharest, the city straddles the Ci ...
,
Căpâlna
Căpâlna ( hu, Feketekápolna) is a commune in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania with a population of 1,663 people (2011). It is composed of five villages: Căpâlna, Ginta (''Gyanta''), Rohani (''Rohány''), Săldăbagiu Mic (''Körösszáldobág ...
in the
Sebeș
Sebeș (; German: ''Mühlbach''; Hungarian: ''Szászsebes''; Transylvanian Saxon dialect: ''Melnbach'') is a city in Alba County, central Romania, southern Transylvania.
Geography
The city lies in the Mureș River valley and straddles the rive ...
valley,
Bănița not far from
Petroșani
Petroșani (; Hungarian: ''Petrozsény''; German: ''Petroschen'') is a city in Hunedoara County, Transylvania, Romania, with a population of 34,331 (2011). The city has been associated with mining since the 19th century.
History
"Pietros" means ...
, and
Piatra Craivii to the north of
Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
. The degree of their urban development was displayed on
Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
and in the account of how Sarmizegetusa Regia was defeated by the Romans. The Romans were given by treachery the locations of
aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
and
pipelines of the Dacian capital, only after destroying the water supply being able to end the long siege of Sarmisegetuza.
Material culture
According to Romanian nationalist archaeology, the cradle of the Dacian culture is considered to be north of the Danube towards the Carpathian mountains, in the historical Romanian province of
Muntenia. It is identified as an evolution of the
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Basarabi culture. Such narrative believe that the earlier Iron Age Basarabi evidence in the northern lower Danube area connects to the iron-using Ferigile-Birsesti group. This is an archaeological manifestation of the historical Getae who, along with the Agathyrsae, are one of a number of tribal formations recorded by Herodotus. In archaeology, "free Dacians" are attested by the
Puchov culture (in which there are Celtic elements) and
Lipiţa culture to the east of the Carpathians. The Lipiţa culture has a Dacian/North Thracian origin. This North Thracian population was dominated by strong Celtic influences, or had simply absorbed Celtic ethnic components. Lipiţa culture has been linked to the Dacian tribe of
Costoboci
The Costoboci (; lat, Costoboci, Costobocae, Castabocae, Coisstoboci, grc, Κοστωβῶκοι, Κοστουβῶκοι or Κοιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains a ...
.
These standpoints are highly problematic, as there is no linear continuity between aforementioned cultures. in reality, the creation of the Dacian ethnos was foreshadowed by migratory movements from the lower Danube region following the collapse of the Celtic cultural circle c. 300 BCE (The grave with a helmet from Ciumeşti – 50 years from its discovery. Comments on the greaves. 2. The Padea-Panagjurski kolonii group in Transylvania. Old and new discoveries)
Specific Dacian material culture includes: wheel-turned pottery that is generally plain but with distinctive elite wares, massive silver dress
fibulae
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is ...
, precious metal plate, ashlar masonry, fortifications, upland sanctuaries with horseshoe-shaped precincts, and decorated clay heart altars at settlement sites. Among many discovered artifacts, the
Dacian bracelets stand out, depicting their cultural and aesthetic sense. There are difficulties correlating funerary monuments chronologically with Dacian settlements; a small number of burials are known, along with cremation pits, and isolated rich burials as at Cugir. Dacian burial ritual continued under Roman occupation and into the post-Roman period.
Language
The Dacians are generally considered to have been Thracian speakers, representing a cultural continuity from earlier Iron Age communities. Some historians and linguists consider Dacian language to be a dialect of or the same language as
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
. The vocalism and consonantism differentiate the Dacian and Thracian languages. Others consider that Dacian and
Illyrian form regional varieties (dialects) of a common language. (Thracians inhabited modern southern Bulgaria and northern Greece. Illyrians lived in modern Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia.)
The ancient languages of these people became extinct, and their cultural influence highly reduced, after the repeated invasions of the Balkans by Celts,
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, Goths, and Sarmatians, accompanied by persistent
hellenization
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the H ...
, romanisation and later
slavicisation
Slavicisation or Slavicization, is the acculturation of something Slavic into a non-Slavic culture, cuisine, region, or nation. To a lesser degree, it also means acculturation or adoption of something non-Slavic into Slavic culture or terms. Th ...
. Therefore, in the study of the toponomy of Dacia, one must take account of the fact that some place-names were taken by the Slavs from as yet unromanised Dacians. A number of Dacian words are preserved in ancient sources, amounting to about 1150 anthroponyms and 900 toponyms, and in Discorides some of the rich plant lore of the Dacians is preserved along with the names of 42 medicinal plants.
Symbols
The Dacians knew about writing. Permanent contacts with the Graeco-Roman world had brought the use of the Greek and later the Latin alphabet. It is also certainly not the case that writing with Greek and Latin letters and knowledge of Greek and Latin were known in all the settlements scattered throughout Dacia, but there is no doubt about the existence of such knowledge in some circles of Dacian society. However, the most revealing discoveries concerning the use of the writing by the Dacians occurred in the citadels on the Sebes mountains. Some groups of letters from stone blocks at Sarmisegetuza might express personal names; these cannot now be read because the wall is ruined, and because it is impossible to restore the original order of the blocks in the wall.
Religion

Dacian religion was considered by the classic sources as a key source of authority, suggesting to some that Dacia was a predominantly theocratic state led by priest-kings. However, the layout of the Dacian capital Sarmizegethusa indicates the possibility of co-rulership, with a separate high king and high priest. Ancient sources recorded the names of several Dacian high priests (Deceneus, Comosicus and Vezina) and various orders of priests: "god-worshipers", "smoke-walkers" and "founders". Both Hellenistic and Oriental influences are discernible in the religious background, alongside
chthonic and solar motifs.
According to Herodotus' account of the story of
Zalmoxis
Zalmoxis ( grc-gre, Ζάλμοξις) also known as Salmoxis (Σάλμοξις), Zalmoxes (Ζάλμοξες), Zamolxis (Ζάμολξις), Samolxis (Σάμολξις), Zamolxes (Ζάμολξες), or Zamolxe (Ζάμολξε) is a divinity of the ...
or Zamolxis, the Getae (speaking the same language as the Dacians and the Thracians, according to
Strabo) believed in the immortality of the soul, and regarded death as merely a change of country. Their chief priest held a prominent position as the representative of the supreme deity, Zalmoxis, who is called also Gebeleizis by some among them. Strabo wrote about the high priest of King Burebista
Deceneus: "a man who not only had wandered through
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, but also had thoroughly learned certain prognostics through which he would pretend to tell the divine will; and within a short time he was set up as god (as I said when relating the story of Zamolxis)."

The Goth
Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') a ...
in his ''
Getica
''De origine actibusque Getarum'' (''The Origin and Deeds of the Getae oths'), commonly abbreviated ''Getica'', written in Late Latin by Jordanes in or shortly after 551 AD, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the o ...
'' (''
The origin and deeds of the Goths
''De origine actibusque Getarum'' (''The Origin and Deeds of the Getae oths'), commonly abbreviated ''Getica'', written in Late Latin by Jordanes in or shortly after 551 AD, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the o ...
''), also gives an account of Deceneus the highest priest, and considered Dacians a nation related to the Goths. Besides Zalmoxis, the Dacians believed in other deities, such as Gebeleizis, the god of storm and lightning, possibly related to the Thracian god
Zibelthiurdos
Zibelthiurdos is a Thracian god of heaven, lightning and rain, whose name is known mainly from epigraphic monuments. The only known reference to this god so far in ancient literature is in Cicero's speech against Pizon, where he is mentioned unde ...
. He was represented as a handsome man, sometimes with a beard. Later Gebeleizis was equated with Zalmoxis as the same god. According to Herodotus, Gebeleizis (*Zebeleizis/Gebeleizis who is only mentioned by Herodotus) is just another name of Zalmoxis.
Another important deity was
Bendis
Bendis ( grc, Βένδις) was a Thracian goddess associated with hunting and the moon. Goddess worship seems to have been introduced into Attica around 430 BC. Some writers identified Bendis in Attica with the goddess Artemis, but the temple ...
, goddess of the moon and the hunt.
By a decree of the
oracle of Dodona, which required the Athenians to grant land for a shrine or temple, her cult was introduced into
Attica
Attica ( el, Αττική, Ancient Greek ''Attikḗ'' or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the city of Athens, the capital of Greece and its countryside. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean S ...
by immigrant Thracian residents, and, though Thracian and Athenian processions remained separate, both cult and festival became so popular that in Plato's time (c. 429–13 BC) its festivities were naturalised as an official ceremony of the Athenian city-state, called the Bendideia.
Known Dacian theonyms include ''Zalmoxis'', ''Gebeleïzis'' and ''
Darzalas Derzelas (''Darzalas'') was a Dacian or Thracian chthonic god of abundance and the underworld, health and human spirit's vitality.
Darzalas was the god of Hellenistic period Odessos (modern Varna) and was frequently depicted on itcoinagefrom the t ...
''. Gebeleizis is probably cognate to the Thracian god Zibelthiurdos (also ''Zbelsurdos'', ''Zibelthurdos''), wielder of lightning and thunderbolts. Derzelas (also ''Darzalas'') was a chthonic god of health and human vitality. The pagan religion survived longer in Dacia than in other parts of the empire; Christianity made little headway until the fifth century.
Pottery

Fragments of pottery with different "inscriptions" with Latin and Greek letters incised before and after firing have been discovered in the settlement at Ocnita – Valcea. An inscription carries the word Basileus (Βασιλεύς in Greek, meaning "king") and seems to have been written before the vessel was hardened by fire. Other inscriptions contain the name of the king, believed to be Thiemarcus, and Latin groups of letters (BVR, REB). BVR indicates the name of the tribe or union of tribes, the Buridavensi Dacians who lived at Buridava and who were mentioned by Ptolemy in the second century AD under the name of Buridavensioi.
Clothing and science
The typical dress of Dacians, both men and women, can be seen on
Trajan's column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
.
Dio Chrysostom
Dio Chrysostom (; el, Δίων Χρυσόστομος ''Dion Chrysostomos''), Dion of Prusa or Cocceianus Dio (c. 40 – c. 115 AD), was a Greek orator, writer, philosopher and historian of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD. Eighty of his ...
described the Dacians as
natural philosophers
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wor ...
.

Warfare
The history of Dacian warfare spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 2nd century AD in the region typically referred to by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Dacia. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Dacian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Dacians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Dacian tribes as well.
Weapons
The weapon most associated with the Dacian forces that fought against Trajan's army during his invasions of Dacia was the
falx
The ''falx'' was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans.
Etymology
''Falx'' is a Latin word originally meaning 'sickle' b ...
, a single-edged scythe-like weapon. The falx was able to inflict horrible wounds on opponents, easily disabling or killing the heavily armored Roman legionaries that they faced. This weapon, more so than any other single factor, forced the Roman army to adopt previously unused or modified equipment to suit the conditions on the Dacian battlefield.
Notable individuals
This is a list of several important Dacian individuals or those of partly Dacian origin.
*
Zalmoxis
Zalmoxis ( grc-gre, Ζάλμοξις) also known as Salmoxis (Σάλμοξις), Zalmoxes (Ζάλμοξες), Zamolxis (Ζάμολξις), Samolxis (Σάμολξις), Zamolxes (Ζάμολξες), or Zamolxe (Ζάμολξε) is a divinity of the ...
, a semi-legendary social and religious reformer, eventually deified by the Getae and Dacians and regarded as
the only true god.
*
Zoltes
*
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
was a king of Dacia, 70–44 BC, who united under his rule Thracians in a large territory, from today's
Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
in the West, to the
Southern Bug river (
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
) in the East, and from the Northern
Carpathian Mountains to Southern
Dionysopolis. The Greeks considered him the first and greatest king of Thrace.
*
Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invas ...
, a king of Dacia who was ultimately defeated by the forces of
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
.
*
Diegis
Diegis was a Dacian chief, general and brother of Decebalus. He served as his representative at the peace negotiations held with Domitian in 89AD. After the peace negotiation, Domitian placed a diadem upon Diegis' head, symbolically saying that he ...
was a Dacian chief, general and brother of Decebalus, and his representative at the peace negotiations held with Domitian (89 CE)
Trivia
"The ducks come from the trucks" – Romanian language pun about a mistranslation (duck and truck sound like dac and trac, the ethnonyms for Dacian and Thracian).
In Romanian nationalism

Study of the Dacians, their culture, society and religion is not purely a subject of ancient history, but has present day implications in the context of
Romanian nationalism
Romanian nationalism is the nationalism which asserts that Romanians are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Romanians. Its extremist variation is the Romanian ultranationalism.Aristotle KallisGenocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Drive ...
. Positions taken on the vexed question of the
origin of the Romanians
Several theories address the issue of the origin of the Romanians. The Romanian language descends from the Vulgar Latin dialects spoken in the Roman provinces north of the "Jireček Line" (a proposed notional line separating the predominantly ...
and to what degree are present-day Romanians descended from the Dacians might have contemporary political implications. For example, the government of
Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( , ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian communist politician and dictator. He was the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 to 1989, and the second and last Communist leader of Romania. He ...
claimed an uninterrupted continuity of a Dacian-Romanian state, from King
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
to Ceaușescu himself.
[Boia, L., ''History and Myth in Romanian Consciousness'', Central European University Press, Budapest, 2001, p. 78; 125] The Ceaușescu government conspicuously commemorated the supposed 2,050th anniversary of the founding of the "unified and centralized" country that was to become Romania, on which occasion the historical film ''
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
'' was produced.
See also
*
Moesi
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
*
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
*
Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, a ...
*
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
*
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
*
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
*
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
**
List of rulers of Thrace and Dacia
This article lists rulers of Thrace and Dacia, and includes Thracian, Paeonian, Celtic, Dacian, Scythian, Persian or Ancient Greek up to the point of its fall to the Roman Empire, with a few figures from Greek mythology.
Mythological
*Haemus, bec ...
**
List of cities in Thrace and Dacia
**
Dacian language
Dacian is an extinct language, generally believed to be Indo-European, that was spoken in the Carpathian region in antiquity.
In the 1st century, it was probably the predominant language of the ancient regions of Dacia and Moesia and possib ...
***
List of Dacian names
*
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
**
Thracology
**
Odrysian kingdom
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria an ...
**
Thracian language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it wa ...
**
Thracian mythology
The Thracian religion refers to the mythology, ritual practices and beliefs of the Thracians, a collection of closely related ancient Indo-European peoples who inhabited eastern and southeastern Europe and northwestern Anatolia throughout antiqui ...
**
Thraco-Dacian
**
Thraco-Cimmerian
Thraco-Cimmerian is a historiographical and archaeological term, composed of the names of the Thracians and the Cimmerians. It refers to 8th to 7th century BC cultures that are linked in Eastern Central Europe and in the area west of the Black Se ...
**
Thraco-Illyrian
The term Thraco-Illyrian refers to a hypothesis according to which the Daco-Thracian and Illyrian languages comprise a distinct branch of Indo-European. Thraco-Illyrian is also used as a term merely implying a Thracian- Illyrian interference, m ...
**
Thraex
The Thraex (pl. Thraeces), or Thracian, was a type of Roman gladiator, armed in the Thracian style with a small rectangular, square or circular shield called a '' parmula'' (about 60 x 65 cm) and a very short sword with a slightly curved blade ...
Notes
References
Sources
Ancient
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Modern
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Dacian reenactor with falxDacian Enciclopedia
{{Authority control
Ancient tribes in Dacia
Iron Age peoples of Europe
Thracians
Ancient peoples of Serbia
Ancient Bulgaria
Ancient history of Romania
 The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient 
 An extensive account of the native tribes in Dacia can be found in the ninth tabula of Europe of Ptolemy's Geography. The Geography was probably written in the period AD 140–150, but the sources were often earlier; for example, Roman Britain is shown before the building of Hadrian's Wall in the AD 120s. Ptolemy's Geography also contains a physical map probably designed before the Roman conquest, and containing no detailed nomenclature. There are references to the
An extensive account of the native tribes in Dacia can be found in the ninth tabula of Europe of Ptolemy's Geography. The Geography was probably written in the period AD 140–150, but the sources were often earlier; for example, Roman Britain is shown before the building of Hadrian's Wall in the AD 120s. Ptolemy's Geography also contains a physical map probably designed before the Roman conquest, and containing no detailed nomenclature. There are references to the  Dacians are represented in the statues surmounting the
Dacians are represented in the statues surmounting the 
 Geto-Dacians inhabited both sides of the
Geto-Dacians inhabited both sides of the  Dacian polities arose as confederacies that included the Getae, the Daci, the Buri, and the Carpi (cf. Bichir 1976, Shchukin 1989), united only periodically by the leadership of Dacian kings such as
Dacian polities arose as confederacies that included the Getae, the Daci, the Buri, and the Carpi (cf. Bichir 1976, Shchukin 1989), united only periodically by the leadership of Dacian kings such as  Dacians that remained outside the Roman Empire after the Dacian wars of AD 101–106 had been named Dakoi prosoroi (Latin ''Daci limitanei''), "neighbouring Dacians". Modern historians use the generic name "Free Dacians" or ''Independent Dacians''. The tribes Daci Magni (Great Dacians), Costoboci (generally considered a Dacian subtribe), and Carpi remained outside the Roman empire, in what the Romans called ''Dacia Libera'' (Free Dacia). By the early third century the "Free Dacians" were a significantly troublesome group, by now identified as the Carpi. Bichir argues that the Carpi were the most powerful of the Dacian tribes who had become the principal enemy of the Romans in the region. In 214 AD,
Dacians that remained outside the Roman Empire after the Dacian wars of AD 101–106 had been named Dakoi prosoroi (Latin ''Daci limitanei''), "neighbouring Dacians". Modern historians use the generic name "Free Dacians" or ''Independent Dacians''. The tribes Daci Magni (Great Dacians), Costoboci (generally considered a Dacian subtribe), and Carpi remained outside the Roman empire, in what the Romans called ''Dacia Libera'' (Free Dacia). By the early third century the "Free Dacians" were a significantly troublesome group, by now identified as the Carpi. Bichir argues that the Carpi were the most powerful of the Dacian tribes who had become the principal enemy of the Romans in the region. In 214 AD,  Roman Dacia was never a uniformly or fully Romanized area. Post-Aurelianic Dacia fell into three divisions: the area along the river, usually under some type of Roman administration even if in a highly localized form; the zone beyond this area, from which Roman military personnel had withdrawn, leaving a sizable population behind that was generally Romanized; and finally what is now the northern parts of Moldavia, Crisana, and Maramures, which were never occupied by the Romans. These last areas were always peripheral to the Roman province, not militarily occupied but nonetheless influenced by Rome as part of the Roman economic sphere. Here lived the free, unoccupied Carpi, often called "Free Dacians".
The Aurelian retreat was a purely military decision to withdraw the Roman troops to defend the Danube. The inhabitants of the old province of Dacia displayed no awareness of impending dissolution. There were no sudden flights or dismantling of property. It is not possible to discern how many civilians followed the army out of Dacia; it is clear that there was no mass emigration, since there is evidence of continuity of settlement in Dacian villages and farms; the evacuation may not at first have been intended to be a permanent measure. The Romans left the province, but they didn't consider that they lost it. Dobrogea was not abandoned at all, but continued as part of the Roman Empire for over 350 years. As late as AD 300, the tetrarchic emperors had resettled tens of thousands of Dacian Carpi inside the empire, dispersing them in communities the length of the Danube, from Austria to the Black Sea.
Roman Dacia was never a uniformly or fully Romanized area. Post-Aurelianic Dacia fell into three divisions: the area along the river, usually under some type of Roman administration even if in a highly localized form; the zone beyond this area, from which Roman military personnel had withdrawn, leaving a sizable population behind that was generally Romanized; and finally what is now the northern parts of Moldavia, Crisana, and Maramures, which were never occupied by the Romans. These last areas were always peripheral to the Roman province, not militarily occupied but nonetheless influenced by Rome as part of the Roman economic sphere. Here lived the free, unoccupied Carpi, often called "Free Dacians".
The Aurelian retreat was a purely military decision to withdraw the Roman troops to defend the Danube. The inhabitants of the old province of Dacia displayed no awareness of impending dissolution. There were no sudden flights or dismantling of property. It is not possible to discern how many civilians followed the army out of Dacia; it is clear that there was no mass emigration, since there is evidence of continuity of settlement in Dacian villages and farms; the evacuation may not at first have been intended to be a permanent measure. The Romans left the province, but they didn't consider that they lost it. Dobrogea was not abandoned at all, but continued as part of the Roman Empire for over 350 years. As late as AD 300, the tetrarchic emperors had resettled tens of thousands of Dacian Carpi inside the empire, dispersing them in communities the length of the Danube, from Austria to the Black Sea.
 The chief occupations of the Dacians were
The chief occupations of the Dacians were  The first coins produced by the Geto-Dacians were imitations of
The first coins produced by the Geto-Dacians were imitations of  Dacian religion was considered by the classic sources as a key source of authority, suggesting to some that Dacia was a predominantly theocratic state led by priest-kings. However, the layout of the Dacian capital Sarmizegethusa indicates the possibility of co-rulership, with a separate high king and high priest. Ancient sources recorded the names of several Dacian high priests (Deceneus, Comosicus and Vezina) and various orders of priests: "god-worshipers", "smoke-walkers" and "founders". Both Hellenistic and Oriental influences are discernible in the religious background, alongside chthonic and solar motifs.
According to Herodotus' account of the story of
Dacian religion was considered by the classic sources as a key source of authority, suggesting to some that Dacia was a predominantly theocratic state led by priest-kings. However, the layout of the Dacian capital Sarmizegethusa indicates the possibility of co-rulership, with a separate high king and high priest. Ancient sources recorded the names of several Dacian high priests (Deceneus, Comosicus and Vezina) and various orders of priests: "god-worshipers", "smoke-walkers" and "founders". Both Hellenistic and Oriental influences are discernible in the religious background, alongside chthonic and solar motifs.
According to Herodotus' account of the story of  The Goth
The Goth  Fragments of pottery with different "inscriptions" with Latin and Greek letters incised before and after firing have been discovered in the settlement at Ocnita – Valcea. An inscription carries the word Basileus (Βασιλεύς in Greek, meaning "king") and seems to have been written before the vessel was hardened by fire. Other inscriptions contain the name of the king, believed to be Thiemarcus, and Latin groups of letters (BVR, REB). BVR indicates the name of the tribe or union of tribes, the Buridavensi Dacians who lived at Buridava and who were mentioned by Ptolemy in the second century AD under the name of Buridavensioi.
Fragments of pottery with different "inscriptions" with Latin and Greek letters incised before and after firing have been discovered in the settlement at Ocnita – Valcea. An inscription carries the word Basileus (Βασιλεύς in Greek, meaning "king") and seems to have been written before the vessel was hardened by fire. Other inscriptions contain the name of the king, believed to be Thiemarcus, and Latin groups of letters (BVR, REB). BVR indicates the name of the tribe or union of tribes, the Buridavensi Dacians who lived at Buridava and who were mentioned by Ptolemy in the second century AD under the name of Buridavensioi.
 Study of the Dacians, their culture, society and religion is not purely a subject of ancient history, but has present day implications in the context of
Study of the Dacians, their culture, society and religion is not purely a subject of ancient history, but has present day implications in the context of