la, Constantinopolis
ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (
Old Norse), Tsargrad (
Slavic), Qustantiniya (
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis (
Turkish)
, image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png
, alt =
, caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day
Fatih district of
Istanbul
, map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey
, map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul.
, map_size = 275
, map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the
Greek colony of
Byzantion
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
, which today is known as
Istanbul in
Turkey.
, coordinates =
, location =
Fatih,
İstanbul,
Turkey
, region =
Marmara Region
, type = Imperial city
, part_of =
, length =
, width =
, area = enclosed within Constantinian Walls
enclosed within Theodosian Walls
, height =
, builder =
Constantine the Great
, material =
, built = 11 May 330
, abandoned =
, epochs =
Late antiquity to
Late Middle Ages
, cultures =
, event =
Sieges of Constantinople
The following is a list of sieges of Constantinople, a historic city located in an area which is today part of Istanbul, Turkey. The city was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the ...
, including fall of the city (
1204
Year 1204 ( MCCIV) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
* January 27-28 – Byzantine emperor Alexios IV Angelos is overthrown in a revolution.
* February 5 – Ale ...
and
1453
Year 1453 ( MCDLIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 1453rd year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 453rd year of the 2nd millennium, the 53rd year of the 15th century, and the 4 ...
)
, depende =
, occupants =
, designation1 = WHS
, designation1_offname =
Historic Areas of Istanbul
The Historic Areas of Istanbul are a group of sites in the capital district of Fatih in the city of Istanbul, Turkey. These areas were added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1985.
This World Heritage Site includes buildings and structures s ...
, designation1_type = Cultural
, designation1_criteria = (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
, designation1_date = 1985
(9th session)
, designation1_number
356bis, designation1_free1name = Extension
, designation1_free1value = 2017
, designation1_free2name = Area
, designation1_free2value = 765.5 ha
, designation1_free3name = UNESCO region
, designation1_free3value =
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
}
Constantinople ''Kōnstantinoúpolis'', ; la,
Cōnstantīnopolis, ; ota, قسطنطينيه, Ḳosṭanṭīnīye (
see other names) was the capital of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, and later, the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the
Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the
Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the
Turkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
, the Turkish capital then moved to
Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, mak ...
. Officially renamed
Istanbul in 1930, the city is today the largest city and financial centre of the
Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
(1923–present). It is also the
largest city in Europe.
In 324, the ancient city of
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' con ...
was renamed "New Rome" and declared the new capital of the Roman Empire by Emperor
Constantine the Great. On 11 May 330, it was renamed to Constantinople, and dedicated to Constantine.
Constantinople is generally considered to be the center and the "cradle of Orthodox
Christian civilization
Christianity has been intricately intertwined with the History of Western civilization, history and formation of Western society. Throughout history of Christianity, its long history, the Christian Church, Church has been a major source of socia ...
". From the mid-5th century to the early 13th century, Constantinople was the largest and wealthiest city in Europe. The city became famous for its architectural masterpieces, such as
Hagia Sophia, the cathedral of the
Eastern Orthodox Church, which served as the seat of the
Ecumenical Patriarchate
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
, the sacred
Imperial Palace where the emperors lived, the
Hippodrome, the
Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by th ...
of the Land Walls, and opulent aristocratic palaces. The
University of Constantinople was founded in the fifth century and contained artistic and literary treasures before it was sacked in 1204 and 1453, including its vast
Imperial Library which contained the remnants of the
Library of Alexandria and had 100,000 volumes. The city was the home of the
Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople and guardian of
Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwin ...
's holiest relics such as the
Crown of thorns
According to the New Testament, a woven crown of thorns ( or grc, ἀκάνθινος στέφανος, akanthinos stephanos, label=none) was placed on the head of Jesus during the events leading up to his crucifixion. It was one of the inst ...
and the
True Cross.

Constantinople was famous for its massive and complex fortifications, which ranked among the most sophisticated defensive architecture of
antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
. The
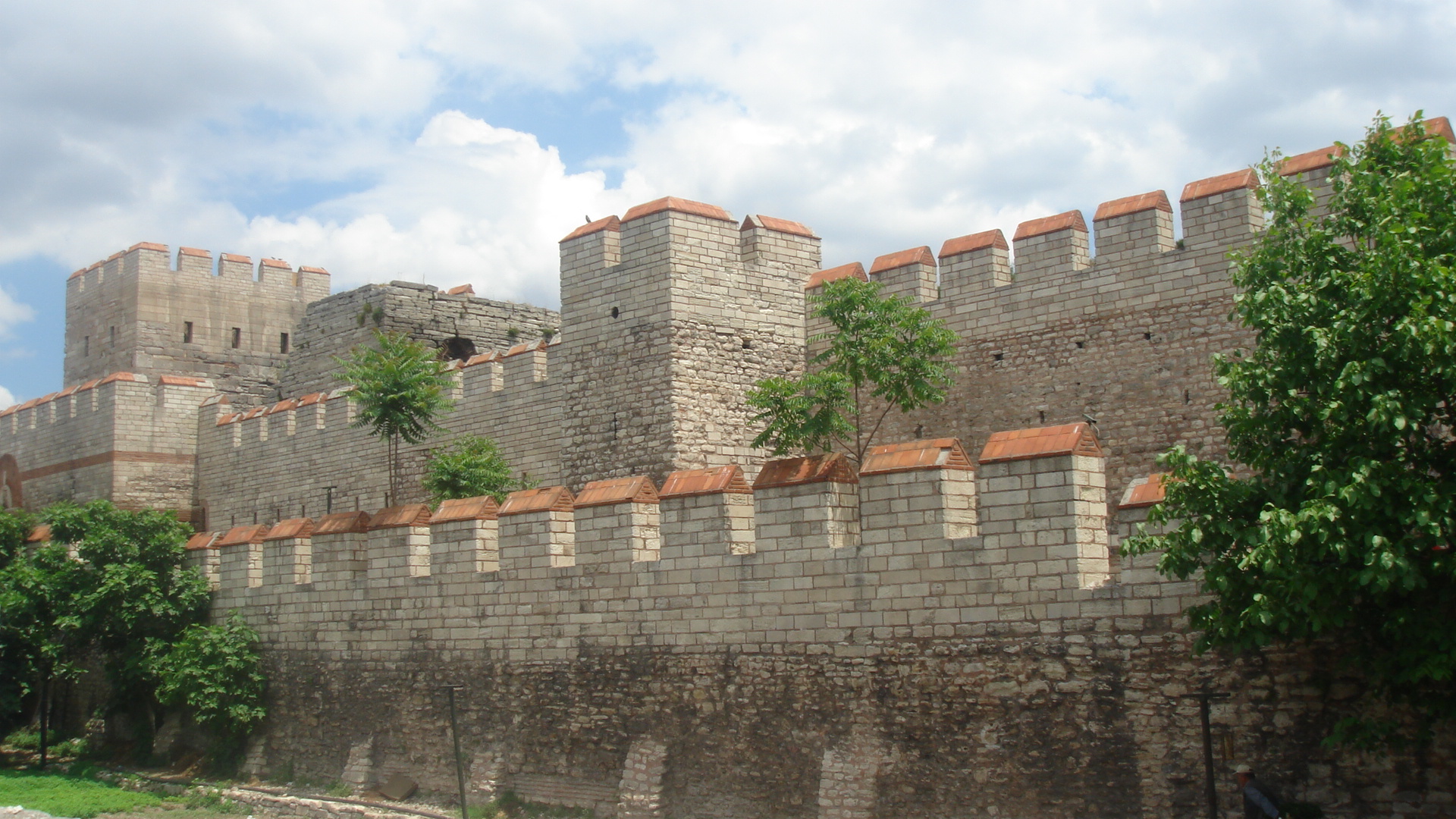
Theodosian Walls
The Walls of Constantinople ( el, Τείχη της Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) are a series of defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (today Istanbul in Turkey) since its founding as the ...
consisted of a double wall lying about to the west of the first wall and a moat with palisades in front. Constantinople's location between the
Golden Horn and the
Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the B ...
reduced the land area that needed defensive walls. The city was built intentionally to rival
Rome, and it was claimed that several elevations within its walls matched Rome's 'seven hills'. The impenetrable defenses enclosed magnificent palaces, domes, and towers, the result of prosperity Constantinople achieved as the gateway between two continents (
Europe and
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
) and two seas (the Mediterranean and the Black Sea). Although besieged on numerous occasions by various armies, the defenses of Constantinople proved impenetrable for nearly nine hundred years.
In 1204, however, the armies of the
Fourth Crusade took and devastated the city and, for several decades, its inhabitants resided under Latin occupation in a dwindling and depopulated city. In 1261 the Byzantine Emperor
Michael VIII Palaiologos liberated the city, and after the restoration under the
Palaiologos dynasty, it enjoyed a partial recovery. With the advent of the
Ottoman Empire in 1299, the Byzantine Empire began to lose territories and the city began to lose population. By the early 15th century, the Byzantine Empire was reduced to just Constantinople and its environs, along with
Morea
The Morea ( el, Μορέας or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used for the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman ...
in Greece, making it an enclave inside the Ottoman Empire. The city was finally
besieged and conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1453, remaining under its control until the early 20th century, after which it was renamed Istanbul under the Empire's
successor state, Turkey.
Names

Before Constantinople
According to
Pliny the Elder in his ''
Natural History'', the first known name of a settlement on the site of Constantinople was ''Lygos'', a settlement likely of
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
origin founded between the 13th and 11th centuries BC. The site, according to the founding myth of the city, was abandoned by the time Greek settlers from the city-state of
Megara founded ''
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' con ...
'' ( grc, Βυζάντιον, ''Byzántion'') in around 657 BC,
across from the town of
Chalcedon
Chalcedon ( or ; , sometimes transliterated as ''Chalkedon'') was an ancient maritime town of Bithynia, in Asia Minor. It was located almost directly opposite Byzantium, south of Scutari (modern Üsküdar) and it is now a district of the city ...
on the Asiatic side of the Bosphorus.
The origins of the name of ''
Byzantion
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
'', more commonly known by the later Latin ''Byzantium'', are not entirely clear, though some suggest it is of
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
origin.
[Georgacas, Demetrius John (1947). "The Names of Constantinople". ''Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association'' (The Johns Hopkins University Press) 78: 347–67. . .] The founding myth of the city has it told that the settlement was named after the leader of the Megarian colonists,
Byzas
Byzas ( Ancient Greek: Βύζας, ''Býzas'') was the legendary founder of Byzantium (Ancient Greek: Βυζάντιον, ''Byzántion''), the city later known as Constantinople and then Istanbul.
Background
The legendary history of the foundin ...
. The later Byzantines of Constantinople themselves would maintain that the city was named in honor of two men, Byzas and Antes, though this was more likely just a play on the word
Byzantion
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
.
The city was briefly renamed ''Augusta Antonina'' in the early 3rd century AD by the Emperor
Septimius Severus (193–211), who razed the city to the ground in 196 for supporting a
rival contender in the
civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policie ...
and had it rebuilt in honor of his son Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (who succeeded him as Emperor), popularly known as
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
.
[Necdet Sakaoğlu (1993/94a): "İstanbul'un adları" The names of Istanbul" In: 'Dünden bugüne İstanbul ansiklopedisi', ed. Türkiye Kültür Bakanlığı, Istanbul.] The name appears to have been quickly forgotten and abandoned, and the city reverted to Byzantium/Byzantion after either the assassination of Caracalla in 217 or, at the latest, the fall of the
Severan dynasty in 235.
Names of Constantinople

Byzantium took on the name of ''Kōnstantinoupolis'' ("city of Constantine", ''Constantinople'') after its refoundation under
Roman emperor Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterrane ...
, who transferred the capital of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
to Byzantium in 330 and designated his new capital officially as ''
Nova Roma'' () 'New Rome'. During this time, the city was also called 'Second Rome', 'Eastern Rome', and ''Roma Constantinopolitana'' (
Latin for "Constantinople Rome").
As the city became the sole remaining capital of the Roman Empire after the fall of the West, and its wealth, population, and influence grew, the city also came to have a multitude of nicknames.

As the largest and wealthiest city in Europe during the 4th–13th centuries and a center of culture and education of the Mediterranean basin, Constantinople came to be known by prestigious titles such as ''Basileuousa'' (Queen of Cities) and ''Megalopolis'' (the Great City) and was, in colloquial speech, commonly referred to as just ''Polis'' () 'the City' by Constantinopolitans and provincial Byzantines alike.
In the language of other peoples, Constantinople was referred to just as reverently. The medieval Vikings, who had contacts with the empire through their expansion in eastern Europe (
Varangians
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';[Varangian]
" Online Etymo ...
) used the Old Norse name ''Miklagarðr'' (from ''mikill'' 'big' and ''garðr'' 'city'), and later ''Miklagard'' and ''Miklagarth''.
In Arabic, the city was sometimes called ''Rūmiyyat al-Kubra'' (Great City of the Romans) and in Persian as ''Takht-e Rum'' (Throne of the Romans).
In East and South Slavic languages, including in
Kievan Rus', Constantinople has been referred to as ''
Tsargrad
''Tsargrad'' is a Slavic name for the city or land of Constantinople (present-day Istanbul in Turkey), the capital of the Byzantine Empire. It is rendered in several ways depending on the language, for instance Old Church Slavonic Цѣсарь� ...
'' (''Царьград'') or ''Carigrad'', 'City of the Caesar (Emperor)', from the Slavonic words ''tsar'' ('Caesar' or 'King') and ''grad'' ('city'). This was presumably a
calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language w ...
on a Greek phrase such as (''Vasileos Polis''), 'the city of the emperor
ing
Ing, ING or ing may refer to:
Art and media
* '' ...ing'', a 2003 Korean film
* i.n.g, a Taiwanese girl group
* The Ing, a race of dark creatures in the 2004 video game '' Metroid Prime 2: Echoes''
* "Ing", the first song on The Roches' 1992 ...
.
Modern names of the city

The modern Turkish name for the city, ''
İstanbul'', derives from the
Greek phrase ''eis tin Polin'' (), meaning "(in)to the city".
This name was used in
Turkish alongside ''Kostantiniyye'', the more formal adaptation of the original ''Constantinople'', during the period of
Ottoman rule, while western languages mostly continued to refer to the city as Constantinople until the early 20th century. In 1928,
the Turkish alphabet was changed from Arabic script to Latin script. After that, as part of the 1920s
Turkification
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization ( tr, Türkleştirme) describes a shift whereby populations or places received or adopted Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly ...
movement, Turkey started to urge other countries to use
Turkish names for Turkish cities, instead of other transliterations to Latin script that had been used in Ottoman times.
[Stanford and Ezel Shaw (1977): History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Vol II, p. 386; Robinson (1965), The First Turkish Republic, p. 298] In time the city came to be known as Istanbul and its variations in most world languages.
The name "Constantinople" is still used by members of the
Eastern Orthodox Church in the title of one of their most important leaders, the Orthodox
patriarch based in the city, referred to as "His Most Divine All-Holiness the Archbishop of Constantinople New Rome and Ecumenical Patriarch." In Greece today, the city is still called ''Konstantinoúpoli(s)'' () or simply just "the City" ().
History

Foundation of Byzantium
Constantinople was founded by the Roman emperor
Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterrane ...
(272–337) in 324
on the site of an already-existing city,
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' con ...
, which was settled in the early days of
Greek colonial expansion, in around 657 BC, by colonists of the city-state of
Megara. This is the first major settlement that would develop on the site of later Constantinople, but the first known settlements was that of ''Lygos'', referred to in Pliny's Natural Histories. Apart from this, little is known about this initial settlement. The site, according to the founding myth of the city, was abandoned by the time Greek settlers from the city-state of Megara founded Byzantium () in around 657 BC,
across from the town of Chalcedon on the Asiatic side of the Bosphorus.
Hesychius of Miletus
Hesychius of Miletus ( el, Ἡσύχιος ὁ Μιλήσιος, translit=Hesychios o Milesios), Greek chronicler and biographer, surnamed Illustrius, son of an advocate, lived in Constantinople in the 6th century AD during the reign of Justinian. ...
wrote that some "claim that people from Megara, who derived their descent from Nisos, sailed to this place under their leader Byzas, and invent the fable that his name was attached to the city." Some versions of the founding myth say Byzas was the son of a local
nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are typ ...
, while others say he was conceived by one of Zeus' daughters and
Poseidon. Hesychius also gives alternate versions of the city's founding legend, which he attributed to old poets and writers:
It is said that the first Argives, after having received this prophecy from Pythia,
Blessed are those who will inhabit that holy city,
a narrow strip of the Thracian shore at the mouth of the Pontos,
where two pups drink of the gray sea,
where fish and stag graze on the same pasture,
set up their dwellings at the place where the rivers Kydaros and Barbyses have their estuaries, one flowing from the north, the other from the west, and merging with the sea at the altar of the nymph called Semestre"
The city maintained independence as a city-state until it was annexed by
Darius I in 512 BC into the
Persian Empire, who saw the site as the optimal location to construct a
pontoon bridge crossing into Europe as Byzantium was situated at the narrowest point in the Bosphorus strait. Persian rule lasted until 478 BC when as part of the Greek counterattack to the
Second Persian invasion of Greece, a Greek army led by the Spartan general
Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to:
* Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of ...
captured the city which remained an independent, yet subordinate, city under the Athenians, and later to the Spartans after 411 BC. A farsighted treaty with the emergent power of Rome in which stipulated tribute in exchange for independent status allowed it to enter Roman rule unscathed. This treaty would pay dividends retrospectively as Byzantium would maintain this independent status, and prosper under peace and stability in the
Pax Romana, for nearly three centuries until the late 2nd century AD.

Byzantium was never a major influential city-state like that of
Athens,
Corinth or
Sparta, but the city enjoyed relative peace and steady growth as a prosperous trading city lent by its remarkable position. The site lay astride the land route from
Europe to
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
and the
seaway from the
Black Sea to the
Mediterranean, and had in the
Golden Horn an excellent and spacious harbor. Already then, in Greek and early Roman times, Byzantium was famous for the strategic geographic position that made it difficult to besiege and capture, and its position at the crossroads of the Asiatic-European trade route over land and as the gateway between the Mediterranean and Black Seas made it too valuable a settlement to abandon, as Emperor
Septimius Severus later realized when he razed the city to the ground for supporting
Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was Roman Emperor from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a riv ...
's
claimancy. It was a move greatly criticized by the contemporary consul and historian
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
who said that Severus had destroyed "a strong Roman outpost and a base of operations against the barbarians from Pontus and Asia". He would later rebuild Byzantium towards the end of his reign, in which it would be briefly renamed ''Augusta Antonina'', fortifying it with a new city wall in his name, the Severan Wall.
324–337: The refoundation as Constantinople



Constantine had altogether more colourful plans. Having restored the unity of the Empire, and, being in the course of major governmental reforms as well as of
sponsoring the consolidation of the Christian church, he was well aware that Rome was an unsatisfactory capital. Rome was too far from the frontiers, and hence from the armies and the imperial courts, and it offered an undesirable playground for disaffected politicians. Yet it had been the capital of the state for over a thousand years, and it might have seemed unthinkable to suggest that the capital be moved to a different location. Nevertheless, Constantine identified the site of Byzantium as the right place: a place where an emperor could sit, readily defended, with easy access to the
Danube or the
Euphrates frontiers, his court supplied from the rich gardens and sophisticated workshops of Roman Asia, his treasuries filled by the wealthiest provinces of the Empire.
Constantinople was built over six years, and consecrated on 11 May 330.
Constantine divided the expanded city, like Rome, into 14 regions, and ornamented it with public works worthy of an imperial metropolis. Yet, at first, Constantine's new Rome did not have all the dignities of old Rome. It possessed a
proconsul, rather than an
urban prefect. It had no
praetors,
tribunes, or
quaestors
A ( , , ; "investigator") was a public official in Ancient Rome. There were various types of quaestors, with the title used to describe greatly different offices at different times.
In the Roman Republic, quaestors were elected officials w ...
. Although it did have senators, they held the title ''clarus'', not ''
clarissimus
The constitution of the late Roman Empire was an unwritten set of guidelines and principles passed down, mainly through precedent, which defined the manner in which the late Roman Empire was governed. As a matter of historical convention, the late ...
'', like those of Rome. It also lacked the panoply of other administrative offices regulating the food supply, police, statues, temples, sewers, aqueducts, or other public works. The new programme of building was carried out in great haste: columns, marbles, doors, and tiles were taken wholesale from the temples of the empire and moved to the new city. In similar fashion, many of the greatest works of Greek and Roman art were soon to be seen in its squares and streets. The emperor stimulated private building by promising householders gifts of land from the imperial estates in
Asiana and
Pontica and on 18 May 332 he announced that, as in Rome, free distributions of food would be made to the citizens. At the time, the amount is said to have been 80,000 rations a day, doled out from 117 distribution points around the city.
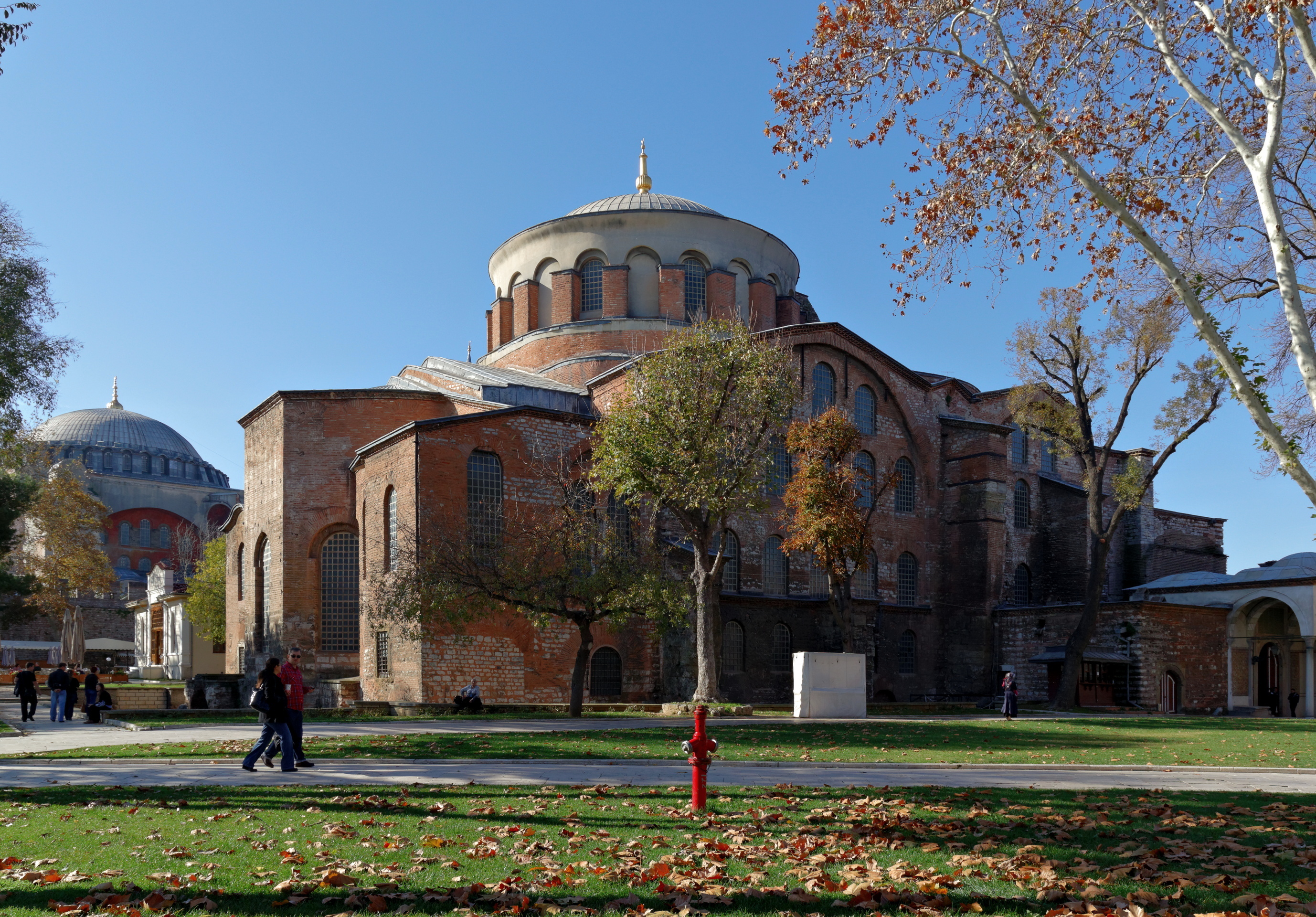

Constantine laid out a new square at the centre of old Byzantium, naming it the
Augustaeum. The new senate-house (or Curia) was housed in a basilica on the east side. On the south side of the great square was erected the
Great Palace of the Emperor with its imposing entrance, the
Chalke
The Chalke Gate ( el, ), was the main ceremonial entrance (vestibule) to the Great Palace of Constantinople in the Byzantine period. The name, which means "the Bronze Gate", was given to it either because of the bronze portals or from the gild ...
, and its ceremonial suite known as the
Palace of Daphne. Nearby was the vast
Hippodrome for chariot-races, seating over 80,000 spectators, and the famed
Baths of Zeuxippus
The Baths of Zeuxippus were popular public baths in the city of Constantinople. They took their name because they were built on a site previously occupied by a temple of Zeus,Gilles, P. p. 70 on the earlier Greek Acropolis in Byzantion. Constructe ...
. At the western entrance to the Augustaeum was the
Milion
The Milion ( grc-gre, Μίλιον or , ''Míllion''; tr, Milyon taşı) was a monument erected in the early 4th century AD in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). It was the Byzantine zero-mile marker, the starting-place for the measu ...
, a vaulted monument from which distances were measured across the Eastern Roman Empire.
From the Augustaeum led a great street, the
Mese, lined with colonnades. As it descended the First Hill of the city and climbed the Second Hill, it passed on the left the
Praetorium or law-court. Then it passed through the oval
Forum of Constantine where there was a second Senate-house and a
high column with a statue of Constantine himself in the guise of
Helios, crowned with a halo of seven rays and looking toward the rising sun. From there, the Mese passed on and through the
Forum Tauri
The Forum of Theodosius ( el, φόρος Θεοδοσίου, today Beyazıt Square) was probably the largest square in Constantinople and stood on the Mese, the major road that ran west from Hagia Sophia ( Turkish: Ayasofya). It was originally bu ...
and then the
Forum Bovis
The Forum of the Ox ( la, Forum Bovis, gr, ὁ Bοῦς, meaning "the Ox") was a public square ( la, Forum) in the city of Constantinople (today's Istanbul). Used also a place for public executions and torture, it disappeared completely after t ...
, and finally up the Seventh Hill (or Xerolophus) and through to the Golden Gate in the
Constantinian Wall. After the construction of the
Theodosian Walls
The Walls of Constantinople ( el, Τείχη της Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) are a series of defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (today Istanbul in Turkey) since its founding as the ...
in the early 5th century, it was extended to the new
Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by th ...
, reaching a total length of seven
Roman miles. After the construction of the Theodosian Walls, Constantinople consisted of an area approximately the size of Old Rome within the Aurelian walls, or some 1,400 ha.
337–529: Constantinople during the Barbarian Invasions and the fall of the West

The importance of Constantinople increased, but it was gradual. From the death of Constantine in 337 to the accession of Theodosius I, emperors had been resident only in the years 337–338, 347–351, 358–361, 368–369. Its status as a capital was recognized by the appointment of the first known Urban Prefect of the City Honoratus, who held office from 11 December 359 until 361. The urban prefects had concurrent jurisdiction over three provinces each in the adjacent dioceses of Thrace (in which the city was located), Pontus and Asia comparable to the 100-mile extraordinary jurisdiction of the prefect of Rome. The emperor
Valens, who hated the city and spent only one year there, nevertheless built the Palace of
Hebdomon on the shore of the
Propontis near the
Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by th ...
, probably for use when reviewing troops. All the emperors up to
Zeno
Zeno ( grc, Ζήνων) may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 BC), ...
and
Basiliscus
Basiliscus ( grc-gre, Βασιλίσκος, Basilískos; died 476/477) was Eastern Roman emperor from 9 January 475 to August 476. He became in 464, under his brother-in-law, Emperor Leo (457–474). Basiliscus commanded the army for an inva ...
were crowned and acclaimed at the Hebdomon.
Theodosius I founded the
Church of John the Baptist to house the skull of the saint (today preserved at the
Topkapı Palace), put up a memorial pillar to himself in the Forum of Taurus, and turned the ruined temple of
Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include ...
into a coach house for the
Praetorian Prefect;
Arcadius
Arcadius ( grc-gre, Ἀρκάδιος ; 377 – 1 May 408) was Roman emperor from 383 to 408. He was the eldest son of the ''Augustus'' Theodosius I () and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla, and the brother of Honorius (). Arcadius ruled the e ...
built a new forum named after himself on the Mese, near the walls of Constantine.
After the shock of the
Battle of Adrianople
The Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels (largely Thervings as well as Greutungs, non-Gothic ...
in 378, in which the emperor
Valens with the flower of the Roman armies was destroyed by the
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is kno ...
within a few days' march, the city looked to its defences, and in 413–414
Theodosius II built the 18-metre (60-foot)-tall
triple-wall fortifications, which were not to be breached until the coming of gunpowder. Theodosius also founded a
University near the Forum of Taurus, on 27 February 425.
Uldin, a prince of the
Huns, appeared on the Danube about this time and advanced into Thrace, but he was deserted by many of his followers, who joined with the Romans in driving their king back north of the river. Subsequent to this, new walls were built to defend the city and the fleet on the Danube improved.

After the
barbarians overran the Western Roman Empire, Constantinople became the indisputable capital city of the Roman Empire. Emperors were no longer peripatetic between various court capitals and palaces. They remained in their palace in the Great City and sent generals to command their armies. The wealth of the eastern Mediterranean and western Asia flowed into Constantinople.
527–565: Constantinople in the Age of Justinian

The emperor
Justinian I (527–565) was known for his successes in war, for his legal reforms and for his public works. It was from Constantinople that his expedition for the reconquest of the former Diocese of Africa set sail on or about 21 June 533. Before their departure, the ship of the commander
Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean terri ...
was anchored in front of the Imperial palace, and the Patriarch offered prayers for the success of the enterprise. After the victory, in 534, the
Temple treasure of Jerusalem, looted by the Romans in
AD 70 and taken to
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
by the
Vandals after their sack of Rome in 455, was brought to Constantinople and deposited for a time, perhaps in the
Church of St Polyeuctus, before being returned to
Jerusalem in either the
Church of the Resurrection or the New Church.
Chariot-racing had been important in Rome for centuries. In Constantinople, the hippodrome became over time increasingly a place of political significance. It was where (as a shadow of the popular elections of old Rome) the people by acclamation showed their approval of a new emperor, and also where they openly criticized the government, or clamoured for the removal of unpopular ministers. In the time of Justinian, public order in Constantinople became a critical political issue.

Throughout the late Roman and early Byzantine periods, Christianity was resolving fundamental questions of identity, and the dispute between the
orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
and the
monophysites
Monophysitism ( or ) or monophysism () is a Christological term derived from the Greek (, "alone, solitary") and (, a word that has many meanings but in this context means "nature"). It is defined as "a doctrine that in the person of the incarn ...
became the cause of serious disorder, expressed through allegiance to the chariot-racing parties of the Blues and the Greens. The partisans of the Blues and the Greens were said to affect untrimmed facial hair, head hair shaved at the front and grown long at the back, and wide-sleeved tunics tight at the wrist; and to form gangs to engage in night-time muggings and street violence. At last these disorders took the form of a major rebellion of 532, known as the
"Nika" riots (from the battle-cry of "Conquer!" of those involved).
Fires started by the Nika rioters consumed the Theodosian basilica of Hagia Sophia (Holy Wisdom), the city's cathedral, which lay to the north of the Augustaeum and had itself replaced the Constantinian basilica founded by Constantius II to replace the first Byzantine cathedral,
Hagia Irene
Hagia Irene ( el, Αγία Ειρήνη) or Hagia Eirene ( grc-x-byzant, Ἁγία Εἰρήνη , "Holy Peace", tr, Aya İrini), sometimes known also as Saint Irene, is an Eastern Orthodox church located in the outer courtyard of Topkapı Palac ...
(Holy Peace). Justinian commissioned
Anthemius of Tralles and
Isidore of Miletus
Isidore of Miletus ( el, Ἰσίδωρος ὁ Μιλήσιος; Medieval Greek pronunciation: ; la, Isidorus Miletus) was one of the two main Byzantine Greek architects (Anthemius of Tralles was the other) that Emperor Justinian I commissioned ...
to replace it with a new and incomparable
Hagia Sophia. This was the great cathedral of the city, whose dome was said to be held aloft by God alone, and which was directly connected to the palace so that the imperial family could attend services without passing through the streets. The dedication took place on 26 December 537 in the presence of the emperor, who was later reported to have exclaimed, "O
Solomon, I have outdone thee!" Hagia Sophia was served by 600 people including 80 priests, and cost 20,000 pounds of gold to build.
Justinian also had Anthemius and Isidore demolish and replace the original
Church of the Holy Apostles
The Church of the Holy Apostles ( el, , ''Agioi Apostoloi''; tr, Havariyyun Kilisesi), also known as the ''Imperial Polyándreion'' (imperial cemetery), was a Byzantine Eastern Orthodox church in Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman ...
and Hagia Irene built by Constantine with new churches under the same dedication. The Justinianic Church of the Holy Apostles was designed in the form of an equal-armed cross with five domes, and ornamented with beautiful mosaics. This church was to remain the burial place of the emperors from Constantine himself until the 11th century. When the city fell to the Turks in 1453, the church was demolished to make room for the tomb of
Mehmet II
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
the Conqueror. Justinian was also concerned with other aspects of the city's built environment, legislating against the abuse of laws prohibiting building within of the sea front, in order to protect the view.
During Justinian I's reign, the city's population reached about 500,000 people. However, the social fabric of Constantinople was also damaged by the onset of the
Plague of Justinian between 541 and 542 AD. It killed perhaps 40% of the city's inhabitants.

Survival, 565–717: Constantinople during the Byzantine Dark Ages
In the early 7th century, the
Avars and later the
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
overwhelmed much of the
Balkans, threatening Constantinople with attack from the west. Simultaneously, the
Persian
Sassanids overwhelmed the Prefecture of the East and penetrated deep into
Anatolia.
Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
, son of the
exarch of Africa, set sail for the city and assumed the throne. He found the military situation so dire that he is said to have contemplated withdrawing the imperial capital to Carthage, but relented after the people of Constantinople begged him to stay. The citizens lost their right to free grain in 618 when Heraclius realized that the city could no longer be supplied from Egypt as a result of the Persian wars: the population fell substantially as a result.

While the city withstood a
siege by the Sassanids and Avars in 626, Heraclius campaigned deep into Persian territory and briefly restored the ''status quo'' in 628, when the Persians surrendered all their conquests. However, further sieges followed the
Arab conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, first from
674 to 678 and then in
717 to 718. The
Theodosian Walls
The Walls of Constantinople ( el, Τείχη της Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) are a series of defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (today Istanbul in Turkey) since its founding as the ...
kept the city impenetrable from the land, while a newly discovered incendiary substance known as
Greek Fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon used by the Eastern Roman Empire beginning . Used to set fire to enemy ships, it consisted of a combustible compound emitted by a flame-throwing weapon. Some historians believe it could be ignited on contact w ...
allowed the
Byzantine navy
The Byzantine navy was the naval force of the East Roman or Byzantine Empire. Like the empire it served, it was a direct continuation from its Imperial Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state tha ...
to destroy the Arab fleets and keep the city supplied. In the second siege, the second ruler of
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
,
Khan Tervel
Khan Tervel ( bg, Тервел) also called ''Tarvel'', or ''Terval'', or ''Terbelis'' in some Byzantine sources, was the khan of Bulgaria during the First Bulgarian Empire at the beginning of the 8th century. In 705 Emperor Justinian II named ...
, rendered decisive help. He was called ''Saviour of Europe''.
717–1025: Constantinople during the Macedonian Renaissance

In the 730s
Leo III carried out extensive repairs of the Theodosian walls, which had been damaged by frequent and violent attacks; this work was financed by a special tax on all the subjects of the Empire.
Theodora, widow of the Emperor
Theophilus
Theophilus is a male given name with a range of alternative spellings. Its origin is the Greek word Θεόφιλος from θεός (God) and φιλία (love or affection) can be translated as "Love of God" or "Friend of God", i.e., it is a theoph ...
(died 842), acted as regent during the minority of her son
Michael III, who was said to have been introduced to dissolute habits by her brother Bardas. When Michael assumed power in 856, he became known for excessive drunkenness, appeared in the hippodrome as a charioteer and burlesqued the religious processions of the clergy. He removed Theodora from the Great Palace to the Carian Palace and later to the
monastery of Gastria, but, after the death of Bardas, she was released to live in the palace of St Mamas; she also had a rural residence at the Anthemian Palace, where Michael was assassinated in 867.
In 860, an
attack was made on the city by a new principality set up a few years earlier at
Kyiv by
Askold and Dir
Askold and Dir (''Haskuldr'' or ''Hǫskuldr'' and ''Dyr'' or ''Djur'' in Old Norse; died in 882), mentioned in both the Primary Chronicle and the Nikon Chronicle, were the earliest known ''purportedly Norse'' rulers of Kiev.
Primary Chronicle
Th ...
, two
Varangian chiefs: Two hundred small vessels passed through the Bosporus and plundered the monasteries and other properties on the suburban
Princes' Islands
The Princes' Islands ( tr, Prens Adaları; the word "princes" is plural, because the name means "Islands of the Princes", el, Πριγκηπονήσια, ''Pringiponisia''), officially just Adalar ( en, Islands); alternatively the Princes' Arch ...
.
Oryphas, the admiral of the Byzantine fleet, alerted the emperor Michael, who promptly put the invaders to flight; but the suddenness and savagery of the onslaught made a deep impression on the citizens.
In 980, the emperor
Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar ...
received an unusual gift from Prince
Vladimir of Kyiv: 6,000
Varangian warriors, which Basil formed into a new bodyguard known as the
Varangian Guard. They were known for their ferocity, honour, and loyalty. It is said that, in 1038, they were dispersed in winter quarters in the
Thracesian Theme when one of their number attempted to violate a countrywoman, but in the struggle she seized his sword and killed him; instead of taking revenge, however, his comrades applauded her conduct, compensated her with all his possessions, and exposed his body without burial as if he had committed suicide. However, following the death of an Emperor, they became known also for plunder in the Imperial palaces. Later in the 11th century the Varangian Guard became dominated by
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
who preferred this way of life to subjugation by the
new Norman kings of England.

The ''
Book of the Eparch
The ''Book of the Prefect'' or ''Eparch'' ( gr, Τὸ ἐπαρχικὸν βιβλίον, To eparchikon biblion) is a Byzantine commercial manual or guide addressed to the eparch of Constantinople (the governor of the city with supreme judicial ju ...
'', which dates to the 10th century, gives a detailed picture of the city's commercial life and its organization at that time. The corporations in which the tradesmen of Constantinople were organised were supervised by the Eparch, who regulated such matters as production, prices, import, and export. Each guild had its own monopoly, and tradesmen might not belong to more than one. It is an impressive testament to the strength of tradition how little these arrangements had changed since the office, then known by the Latin version of its title, had been set up in 330 to mirror the urban prefecture of Rome.
In the 9th and 10th centuries, Constantinople had a population of between 500,000 and 800,000.

Iconoclast controversy in Constantinople
In the 8th and 9th centuries, the
iconoclast
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be conside ...
movement caused serious political unrest throughout the Empire. The emperor
Leo III issued a decree in 726 against images, and ordered the destruction of a statue of Christ over one of the doors of the Chalke, an act that was fiercely resisted by the citizens.
Constantine V
Constantine V ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantīnos; la, Constantinus; July 718 – 14 September 775), was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able ...
convoked a
church council in 754, which condemned the worship of images, after which many treasures were broken, burned, or painted over with depictions of trees, birds or animals: One source refers to the
church of the Holy Virgin at
Blachernae
Blachernae ( gkm, Βλαχέρναι) was a suburb in the northwestern section of Constantinople, the capital city of the Byzantine Empire. It is the site of a water source and a number of prominent churches were built there, most notably the grea ...
as having been transformed into a "fruit store and aviary". Following the death of her husband
Leo IV in 780, the empress
Irene
Irene is a name derived from εἰρήνη (eirēnē), the Greek for "peace".
Irene, and related names, may refer to:
* Irene (given name)
Places
* Irene, Gauteng, South Africa
* Irene, South Dakota, United States
* Irene, Texas, United State ...
restored the veneration of images through the agency of the
Second Council of Nicaea
The Second Council of Nicaea is recognized as the last of the first seven ecumenical councils by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. In addition, it is also recognized as such by the Old Catholics, the Anglican Communion, an ...
in 787.
The iconoclast controversy returned in the early 9th century, only to be resolved once more in 843 during the regency of Empress
Theodora
Theodora is a given name of Greek origin, meaning "God's gift".
Theodora may also refer to:
Historical figures known as Theodora
Byzantine empresses
* Theodora (wife of Justinian I) ( 500 – 548), saint by the Orthodox Church
* Theodora o ...
, who restored the icons. These controversies contributed to the deterioration of relations between the
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and the
Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
* Eastern Air ...
Churches.
1025–1081: Constantinople after Basil II

In the late 11th century catastrophe struck with the unexpected and calamitous defeat of the imperial armies at the
Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and t ...
in Armenia in 1071. The Emperor
Romanus
Romanus (Latin for "Roman"), hellenized as Romanos (Ῥωμανός) was a Roman cognomen and may refer to:
People
* Adrianus Romanus, Flemish mathematician (1561–1615)
*Aquila Romanus, Latin grammarian
*Giles of Rome, Aegidius Romanus, medieva ...
Diogenes was captured. The peace terms demanded by
Alp Arslan
Alp Arslan was the second Sultan of the Seljuk Empire and great-grandson of Seljuk, the eponymous founder of the dynasty. He greatly expanded the Seljuk territory and consolidated his power, defeating rivals to the south and northwest, and his ...
, sultan of the Seljuk Turks, were not excessive, and Romanus accepted them. On his release, however, Romanus found that enemies had placed their own candidate on the throne in his absence; he surrendered to them and suffered death by torture, and the new ruler,
Michael VII
Michael VII Doukas or Ducas ( gr, Μιχαήλ Δούκας), nicknamed Parapinakes ( gr, Παραπινάκης, lit. "minus a quarter", with reference to the devaluation of the Byzantine currency under his rule), was the senior Byzantine e ...
Ducas, refused to honour the treaty. In response, the Turks began to move into Anatolia in 1073. The collapse of the old defensive system meant that they met no opposition, and the empire's resources were distracted and squandered in a series of civil wars. Thousands of
Turkoman tribesmen crossed the unguarded frontier and moved into Anatolia. By 1080, a huge area had been lost to the Empire, and the Turks were within striking distance of Constantinople.
1081–1185: Constantinople under the Comneni
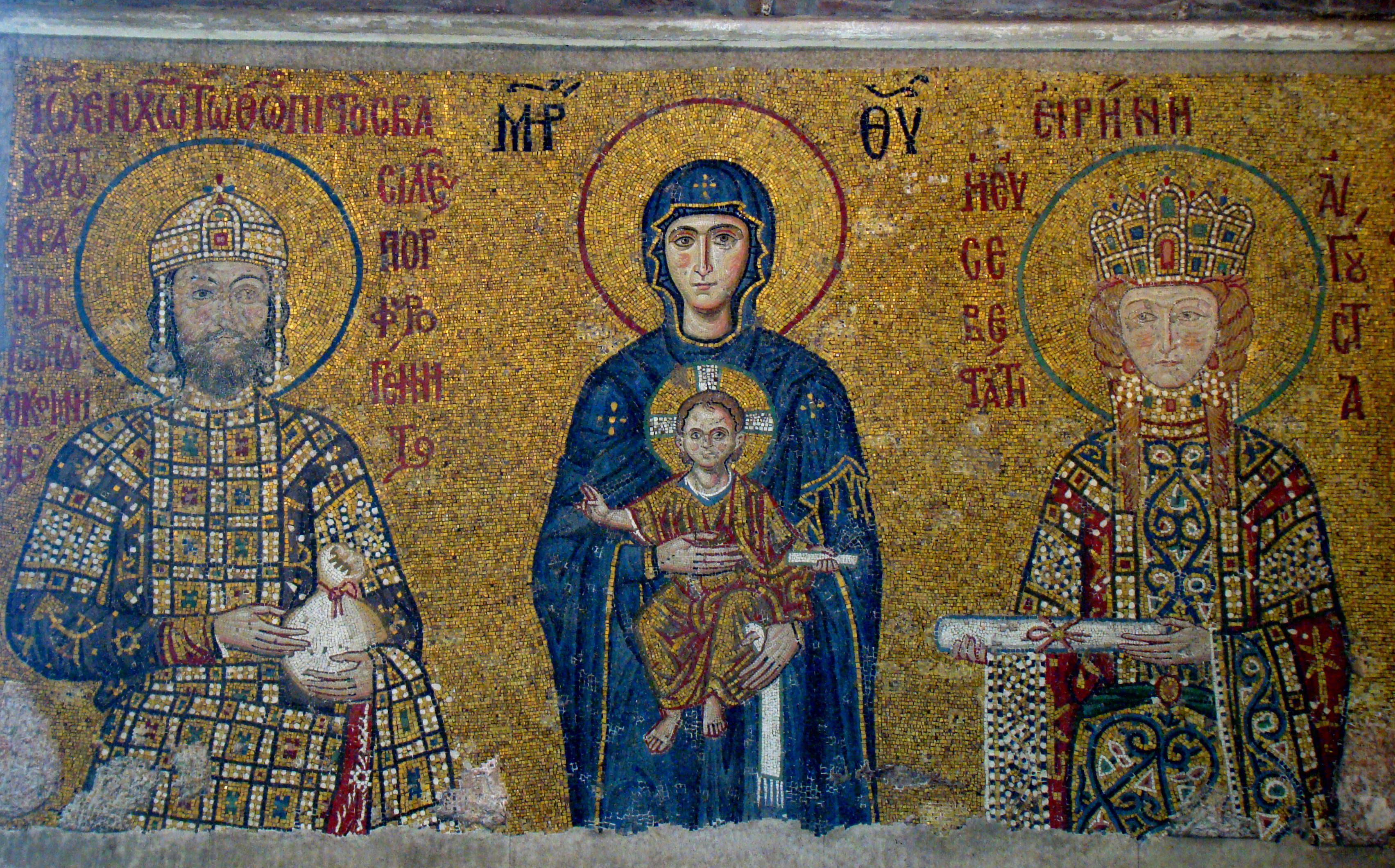


Under the Comnenian dynasty (1081–1185), Byzantium staged a remarkable recovery. In 1090–91, the nomadic
Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
reached the walls of Constantinople, where Emperor Alexius I with the aid of the
Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the Sec ...
annihilated their army. In response to a call for aid from
Alexius, the
First Crusade assembled at Constantinople in 1096, but declining to put itself under Byzantine command set out for
Jerusalem on its own account.
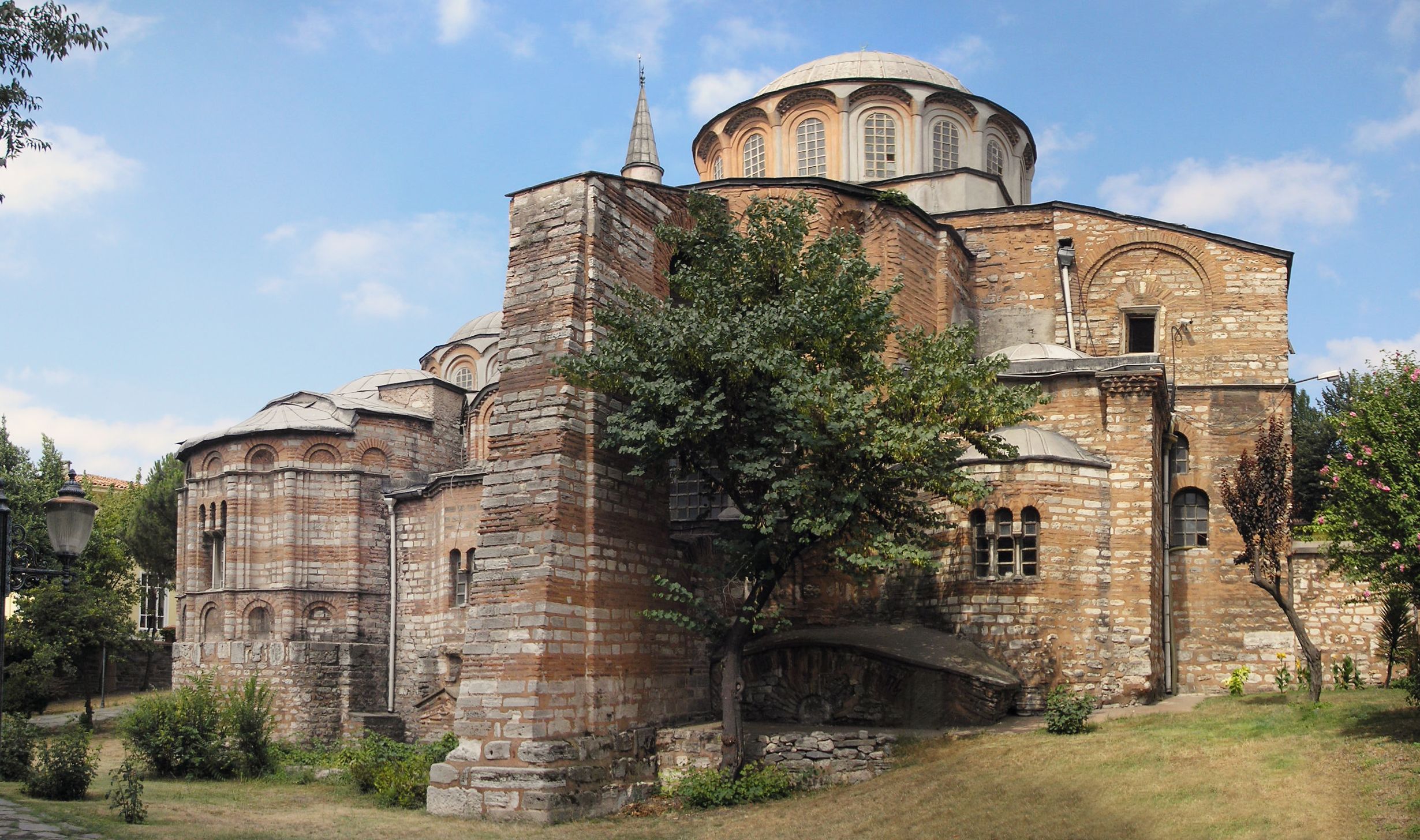
John II built the monastery of the Pantocrator (Almighty) with a hospital for the poor of 50 beds.
With the restoration of firm central government, the empire became fabulously wealthy. The population was rising (estimates for Constantinople in the 12th century vary from some 100,000 to 500,000), and towns and cities across the realm flourished. Meanwhile, the volume of money in circulation dramatically increased. This was reflected in Constantinople by the construction of the Blachernae palace, the creation of brilliant new works of art, and general prosperity at this time: an increase in trade, made possible by the growth of the Italian city-states, may have helped the growth of the economy. It is certain that the
Venetians and others were active traders in Constantinople, making a living out of shipping goods between the Crusader Kingdoms of
Outremer and the West, while also trading extensively with Byzantium and
Egypt. The Venetians had factories on the north side of the Golden Horn, and large numbers of westerners were present in the city throughout the 12th century. Toward the end of
Manuel I Komnenos's reign, the number of foreigners in the city reached about 60,000–80,000 people out of a total population of about 400,000 people.
[J. Phillips, ''The Fourth Crusade and the Sack of Constantinople'', 144.] In 1171, Constantinople also contained a small community of 2,500 Jews.
[J. Phillips, ''The Fourth Crusade and the Sack of Constantinople'', 155.] In 1182, most Latin (Western European) inhabitants of Constantinople
were massacred.
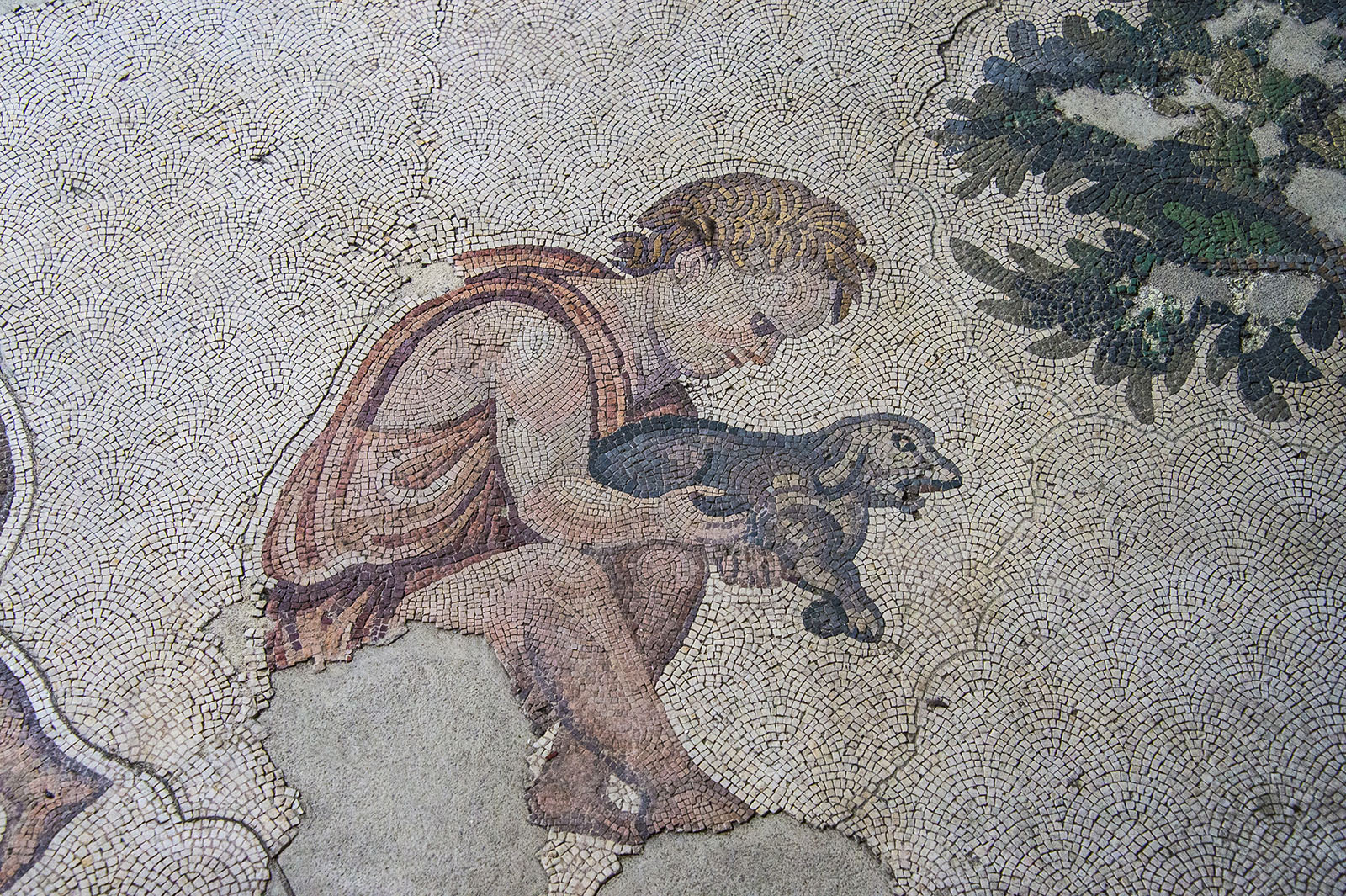
In artistic terms, the 12th century was a very productive period. There was a revival in the
mosaic art, for example: Mosaics became more realistic and vivid, with an increased emphasis on depicting three-dimensional forms. There was an increased demand for art, with more people having access to the necessary wealth to commission and pay for such work. According to N.H. Baynes (''Byzantium, An Introduction to East Roman Civilization''):
1185–1261: Constantinople during the Imperial Exile


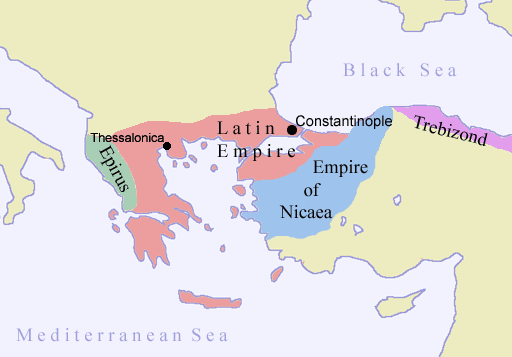
On 25 July 1197, Constantinople was struck by a
severe fire which burned the Latin Quarter and the area around the Gate of the Droungarios ( tr, Odun Kapısı) on the Golden Horn.
Nevertheless, the destruction wrought by the 1197 fire paled in comparison with that brought by the Crusaders. In the course of a plot between
Philip of Swabia,
Boniface of Montferrat
Boniface I, usually known as Boniface of Montferrat ( it, Bonifacio del Monferrato, link=no; el, Βονιφάτιος Μομφερρατικός, ''Vonifatios Momferratikos'') (c. 1150 – 4 September 1207), was the ninth Marquis of Montferrat ...
and the
Doge of Venice, the
Fourth Crusade was, despite papal excommunication, diverted in 1203 against Constantinople, ostensibly promoting the claims of
Alexios IV Angelos
Alexios IV Angelos or Alexius IV Angelus ( el, Ἀλέξιος Ἄγγελος) (c. 1182 – February 1204) was Byzantine Emperor from August 1203 to January 1204. He was the son of Emperor Isaac II Angelos and his first wife, an unknown Palai ...
brother-in-law of Philip, son of the deposed emperor
Isaac II Angelos. The reigning emperor
Alexios III Angelos
Alexios III Angelos ( gkm, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός Ἄγγελος, Alexios Komnēnos Angelos; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnen ...
had made no preparation. The Crusaders occupied
Galata, broke the
defensive chain protecting the
Golden Horn, and entered the harbour, where on 27 July they breached the sea walls: Alexios III fled. But the new Alexios IV Angelos found the Treasury inadequate, and was unable to make good the rewards he had promised to his western allies. Tension between the citizens and the Latin soldiers increased. In January 1204, the ''
protovestiarius
''Protovestiarios'' ( el, πρωτοβεστιάριος, "first ''vestiarios''") was a high Byzantine court position, originally reserved for eunuchs. In the late Byzantine period (12th–15th centuries), it denoted the Empire's senior-most fina ...
''
Alexios Murzuphlos provoked a riot, it is presumed, to intimidate Alexios IV, but whose only result was the destruction of the great statue of
Athena Promachos
The ''Athena Promachos'' (, "Athena who fights in the front line") was a colossal bronze statue of Athena sculpted by Pheidias, which stood between the Propylaea and the Parthenon on the Acropolis of Athens. Athena was the tutelary deity of Athen ...
, the work of
Phidias, which stood in the principal forum facing west.
In February 1204, the people rose again: Alexios IV was imprisoned and executed, and Murzuphlos took the purple as
Alexios V Doukas
Alexios V Doukas ( gr, Ἀλέξιος Δούκας; – December 1204), in Latinised spelling Alexius V Ducas, was Byzantine emperor from February to April 1204, just prior to the sack of Constantinople by the participants of the Fourth C ...
. He made some attempt to repair the walls and organise the citizenry, but there had been no opportunity to bring in troops from the provinces and the guards were demoralised by the revolution. An attack by the Crusaders on 6 April failed, but a second from the Golden Horn on 12 April succeeded, and the invaders poured in. Alexios V fled. The Senate met in
Hagia Sophia and offered the crown to
Theodore Lascaris, who had married into the
Angelos dynasty
The House of Angelos (; gr, Ἄγγελος), feminine form Angelina (), plural Angeloi (), was a Byzantine Greek noble lineage which rose to prominence through the marriage of its founder, Constantine Angelos, with Theodora Komnene, the young ...
, but it was too late. He came out with the Patriarch to the
Golden Milestone
The ''Milliarium Aureum'' (; it, Miliario Aureo), also known by the translation Golden Milestone, was a monument, probably of marble or gilded bronze, erected by the Emperor Augustus near the Temple of Saturn in the central Forum of Ancient R ...
before the Great Palace and addressed the
Varangian Guard. Then the two of them slipped away with many of the nobility and embarked for Asia. By the next day the Doge and the leading Franks were installed in the Great Palace, and the city was given over to pillage for three days.
Sir Steven Runciman
Sir James Cochran Stevenson Runciman ( – ), known as Steven Runciman, was an English historian best known for his three-volume '' A History of the Crusades'' (1951–54).
He was a strong admirer of the Byzantine Empire. His history's negativ ...
, historian of the Crusades, wrote that the sack of Constantinople is "unparalleled in history".
For the next half-century, Constantinople was the seat of the
Latin Empire. Under the rulers of the Latin Empire, the city declined, both in population and the condition of its buildings. Alice-Mary Talbot cites an estimated population for Constantinople of 400,000 inhabitants; after the destruction wrought by the Crusaders on the city, about one third were homeless, and numerous courtiers, nobility, and higher clergy, followed various leading personages into exile. "As a result Constantinople became seriously depopulated," Talbot concludes.
[Talbot]
"The Restoration of Constantinople under Michael VIII"
, ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers'', 47 (1993), p. 246

The Latins took over at least 20 churches and 13 monasteries, most prominently the Hagia Sophia, which became the cathedral of the Latin Patriarch of Constantinople. It is to these that E.H. Swift attributed the construction of a series of flying buttresses to shore up the walls of the church, which had been weakened over the centuries by earthquake tremors. However, this act of maintenance is an exception: for the most part, the Latin occupiers were too few to maintain all of the buildings, either secular and sacred, and many became targets for vandalism or dismantling. Bronze and lead were removed from the roofs of abandoned buildings and melted down and sold to provide money to the chronically under-funded Empire for defense and to support the court; Deno John Geanokoplos writes that "it may well be that a division is suggested here: Latin laymen stripped secular buildings, ecclesiastics, the churches." Buildings were not the only targets of officials looking to raise funds for the impoverished Latin Empire: the monumental sculptures which adorned the Hippodrome and fora of the city were pulled down and melted for coinage. "Among the masterpieces destroyed, writes Talbot, "were a Herakles attributed to the fourth-century B.C. sculptor
Lysippos
Lysippos (; grc-gre, Λύσιππος) was a Greek sculptor of the 4th century BC. Together with Scopas and Praxiteles, he is considered one of the three greatest sculptors of the Classical Greek era, bringing transition into the Hellenistic ...
, and monumental figures of Hera, Paris, and Helen."
[Talbot, "Restoration of Constantinople", p. 248]
The Nicaean emperor
John III Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes ( el, Ιωάννης Δούκας Βατάτζης, ''Iōannēs Doukas Vatatzēs'', c. 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known ...
reportedly saved several churches from being dismantled for their valuable building materials; by sending money to the Latins "to buy them off" (''exonesamenos''), he prevented the destruction of several churches. According to Talbot, these included the churches of Blachernae,
Rouphinianai
Rouphinianai ( grc, Ρουφινιαναί), also known as Drys ( grc, Δρῦς), was a coastal town of ancient Bithynia located on the road from Libyssa to Chalcedon on the north coast of the Propontis. Its church was reportedly saved by Nicae ...
, and St. Michael at Anaplous. He also granted funds for the restoration of the
Church of the Holy Apostles
The Church of the Holy Apostles ( el, , ''Agioi Apostoloi''; tr, Havariyyun Kilisesi), also known as the ''Imperial Polyándreion'' (imperial cemetery), was a Byzantine Eastern Orthodox church in Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman ...
, which had been seriously damaged in an earthquake.
The Byzantine nobility scattered, many going to
Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
, where Theodore Lascaris set up an imperial court, or to
Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinric ...
, where Theodore Angelus did the same; others fled to
Trebizond, where one of the Comneni had already with Georgian support established an independent seat of empire. Nicaea and Epirus both vied for the imperial title, and tried to recover Constantinople. In 1261, Constantinople was
captured from its last Latin ruler,
Baldwin II, by the forces of the
Nicaean emperor
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse ...
Michael VIII Palaiologos under the command of Caesar
Alexios Strategopoulos
Alexios Komnenos Strategopoulos ( gr, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνὸς Στρατηγόπουλος) was a Byzantine aristocrat and general who rose to the rank of '' megas domestikos'' and ''Caesar''. Distantly related to the Komnenian dynasty ...
.
1261–1453: Palaiologan Era and the Fall of Constantinople

Although Constantinople was retaken by
Michael VIII Palaiologos, the Empire had lost many of its key economic resources, and struggled to survive. The
palace of Blachernae
The Palace of Blachernae ( el, ). was an imperial Byzantine residence in the suburb of Blachernae, located in the northwestern section of Constantinople (today located in the quarter of Ayvansaray in Fatih, Istanbul, Turkey). The area of the pal ...
in the north-west of the city became the main Imperial residence, with the old Great Palace on the shores of the
Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
going into decline. When Michael VIII captured the city, its population was 35,000 people, but, by the end of his reign, he had succeeded in increasing the population to about 70,000 people.
[T. Madden, ''Crusades: The Illustrated History'', 113.] The Emperor achieved this by summoning former residents who had fled the city when the crusaders captured it, and by relocating Greeks from the recently reconquered
Peloponnese to the capital.
Military defeats, civil wars, earthquakes and natural disasters were joined by the
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causing ...
, which in 1347 spread to Constantinople, exacerbated the people's sense that they were doomed by God. In 1453, when the
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
captured the city, it contained approximately 50,000 people.
Constantinople was conquered by the
Ottoman Empire on 29 May 1453. The Ottomans were commanded by 21-year-old Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II. The conquest of Constantinople followed a seven-week siege which had begun on 6 April 1453.
1453–1922: Ottoman Kostantiniyye

The Christian Orthodox city of Constantinople was now under Ottoman control. When
Mehmed II
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
finally entered Constantinople through the Gate of Charisius (today known as
Edirnekapı or Adrianople Gate), he immediately rode his horse to the
Hagia Sophia, where after the doors were axed down, the thousands of citizens hiding within the sanctuary were raped and enslaved, often with slavers fighting each other to the death over particularly beautiful and valuable slave girls.
[Ibrahim, Raymond. '']Sword and Scimitar
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip ...
''. Da Capo Press, New York, . p. 244. Moreover, symbols of Christianity were everywhere vandalized or destroyed, including the crucifix of Hagia Sophia which was paraded through the sultan's camps.
[Ibrahim, Raymond. '']Sword and Scimitar
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip ...
''. Da Capo Press, New York, . p. 245. Afterwards he ordered his soldiers to stop hacking at the city's valuable marbles and 'be satisfied with the booty and captives; as for all the buildings, they belonged to him'.
[Mansel, Philip. '' Constantinople: City of the World's Desire''. Penguin History Travel, . p. 1.] He ordered that an
imam meet him there in order to chant the
adhan
Adhan ( ar, أَذَان ; also variously transliterated as athan, adhane (in French), azan/azaan (in South Asia), adzan (in Southeast Asia), and ezan (in Turkish), among other languages) is the Islamic call to public prayer ( salah) in a mo ...
thus transforming the
Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
cathedral into a Muslim
mosque,
solidifying
Islamic rule in Constantinople.
Mehmed's main concern with Constantinople had to do with solidifying control over the city and rebuilding its defenses. After 45,000 captives were marched from the city, building projects were commenced immediately after the conquest, which included the repair of the walls, construction of the citadel, and building a new palace.
[Inalcik, Halil. "The Policy of Mehmed II toward the Greek Population of Istanbul and the Byzantine Buildings of the City." Dumbarton Oaks Papers 23, (1969): 229–249. p. 236] Mehmed issued orders across his empire that Muslims, Christians, and Jews should resettle the city, with Christians and Jews required to pay ''jizya'' and Muslims pay Zakat; he demanded that five thousand households needed to be transferred to Constantinople by September.
From all over the Islamic empire, prisoners of war and deported people were sent to the city: these people were called "Sürgün" in Turkish ( gr, σουργούνιδες).
[Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 28] Two centuries later, Ottoman traveler
Evliya Çelebi gave a list of groups introduced into the city with their respective origins. Even today, many quarters of
Istanbul, such as
Aksaray,
Çarşamba, bear the names of the places of origin of their inhabitants.
However, many people escaped again from the city, and there were several outbreaks of plague, so that in 1459 Mehmed allowed the deported Greeks to come back to the city.
Culture


Constantinople was the largest and richest urban center in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea during the late Eastern Roman Empire, mostly as a result of its strategic position commanding the trade routes between the Aegean Sea and the Black Sea. It would remain the capital of the eastern, Greek-speaking empire for over a thousand years. At its peak, roughly corresponding to the Middle Ages, it was one of the richest and largest cities in Europe. It exerted a powerful cultural pull and dominated much of the economic life in the Mediterranean. Visitors and merchants were especially struck by the beautiful monasteries and churches of the city, in particular the
Hagia Sophia, or the Church of Holy Wisdom. According to Russian 14th-century traveler
Stephen of Novgorod Stephen of Novgorod ( 14th century) was a Russian traveller to Constantinople who wrote an account of the city called the ''Wanderer''.
Stephen was a layman. He arrived in Constantinople on Holy Thursday in 1348 or 1349. He probably travelled on o ...
: "As for Hagia Sophia, the human mind can neither tell it nor make description of it."
It was especially important for preserving in its libraries manuscripts of Greek and Latin authors throughout a period when instability and disorder caused their mass-destruction in western Europe and north Africa: On the city's fall, thousands of these were brought by refugees to Italy, and played a key part in stimulating the Renaissance, and the transition to the modern world. The cumulative influence of the city on the west, over the many centuries of its existence, is incalculable. In terms of technology, art and culture, as well as sheer size, Constantinople was without parallel anywhere in Europe for a thousand years. Many languages were spoken in Constantinople. A 16th century Chinese geographical treatise specifically recorded that there were translators living in the city, indicating this was a multilingual, multicultural cosmopolitan.

Women in literature
Constantinople was home to the first known Western
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
journal published and edited by a woman (Elpis Kesaratsian). Entering circulation in 1862, ''Kit'arr'' or ''Guitar'' stayed in print for only seven months. Female writers who openly expressed their desires were viewed as immodest, but this changed slowly as journals began to publish more "women's sections". In the 1880s, Matteos Mamurian invited
Srpouhi Dussap
Srpouhi Dussap (Armenian: Սրբուհի Տիւսաբ; 1840–1901) was an Armenian feminist writer and the first female Armenian novelist. She was the sister of famed Ottoman Armenian politician Hovhannes Vahanian.
Biography
Dussap was born ...
to submit essays for ''Arevelian Mamal''. According to Zaruhi Galemkearian's autobiography, she was told to write about women's place in the family and home after she published two volumes of poetry in the 1890s. By 1900, several Armenian journals had started to include works by female contributors including the Constantinople-based ''Tsaghik''.
Markets
Even before Constantinople was founded, the markets of
Byzantion
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
were mentioned first by
Xenophon and then by
Theopompus
Theopompus ( grc-gre, Θεόπομπος, ''Theópompos''; c. 380 BCc. 315 BC) was an ancient Greek historian and rhetorician.
Biography
Theopompus was born on the Aegean island of Chios. In early youth, he seems to have spent some time at Athen ...
who wrote that Byzantians "spent their time at the market and the harbour". In
Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized '' renov ...
's age the ''Mese'' street running across the city from east to west was a daily market.
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gener ...
claimed "more than 500 prostitutes" did business along the market street.
Ibn Batutta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim wor ...
who traveled to the city in 1325 wrote of the bazaars "Astanbul" in which the "majority of the artisans and salespeople in them are women".
Architecture

The Byzantine Empire used Roman and Greek architectural models and styles to create its own unique type of architecture. The influence of Byzantine architecture and art can be seen in the copies taken from it throughout Europe. Particular examples include
St Mark's Basilica in Venice, the basilicas of
Ravenna, and many churches throughout the Slavic East. Also, alone in Europe until the 13th-century Italian
florin, the Empire continued to produce sound gold coinage, the
solidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; ''solidi'') or nomisma ( grc-gre, νόμισμα, ''nómisma'', 'coin') was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Late Roman Empire and By ...
of
Diocletian becoming the
bezant
In the Middle Ages, the term bezant ( Old French ''besant'', from Latin ''bizantius aureus'') was used in Western Europe to describe several gold coins of the east, all derived ultimately from the Roman ''solidus''. The word itself comes from t ...
prized throughout the Middle Ages. Its
city walls
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
were much imitated (for example, see
Caernarfon Castle
Caernarfon Castle ( cy, Castell Caernarfon ) – often anglicised as Carnarvon Castle or Caernarvon Castle – is a medieval fortress in Caernarfon, Gwynedd, north-west Wales cared for by Cadw, the Welsh Government's historic environ ...
) and its urban infrastructure was moreover a marvel throughout the Middle Ages, keeping alive the art, skill and technical expertise of the Roman Empire. In the Ottoman period Islamic architecture and symbolism were used.
Great
bathhouses were built in
Byzantine centers such as Constantinople and
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
.
Religion
Constantine's foundation gave prestige to the Bishop of Constantinople, who eventually came to be known as the
Ecumenical Patriarch, and made it a prime center of Christianity alongside Rome. This contributed to cultural and theological differences between Eastern and Western Christianity eventually leading to the
Great Schism that divided
Western Catholicism
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
from
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical" ...
from 1054 onwards. Constantinople is also of great religious importance to
Islam, as the conquest of Constantinople is one of the signs of the
End time in Islam.
Education
In 1909, in Constantinople there were 626 primary schools and 12 secondary schools. Of the primary schools, 561 were of the lower grade and 65 were of the higher grade; of the latter, 34 were public and 31 were private. There was one secondary college and eleven secondary preparatory schools.
["Report of the Commissioner of Education for the Year Ended June 30, 1912." Whole Number 525. Volume 1. Washington Government Printing Office, 1913. In: '']Congressional Edition
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
'', Volume 6410. U.S. Government Printing Office
The United States Government Publishing Office (USGPO or GPO; formerly the United States Government Printing Office) is an agency of the legislative branch of the United States Federal government. The office produces and distributes information ...
, 1913. p
570
.
Media
In the past the Bulgarian newspapers in the late Ottoman period were ''Makedoniya'', ''Napredŭk'', and ''Pravo''.
[Strauss, Johann. "Twenty Years in the Ottoman capital: the memoirs of Dr. Hristo Tanev Stambolski of Kazanlik (1843–1932) from an Ottoman point of view." In: Herzog, Christoph and Richard Wittmann (editors). ''Istanbul – Kushta – Constantinople: Narratives of Identity in the Ottoman Capital, 1830–1930''. Routledge, 10 October 2018. , 9781351805223. p. 267.]
International status

The city provided a defence for the eastern provinces of the old Roman Empire against the barbarian invasions of the 5th century. The 18-meter-tall walls built by
Theodosius II were, in essence, impregnable to the barbarians coming from south of the
Danube river, who found easier targets to the west rather than the richer provinces to the east in Asia. From the 5th century, the city was also protected by the
Anastasian Wall
The Anastasian Wall (Greek: , ; tr, Anastasius Suru) or the Long Walls of Thrace (Greek: , ; Turkish: ''Uzun Duvar'') is an ancient stone and turf fortification located west of Istanbul, Turkey, built by the Eastern Roman Empire during the late ...
, a 60-kilometer chain of walls across the
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
peninsula. Many scholars argue that these sophisticated fortifications allowed the east to develop relatively unmolested while
Ancient Rome and
the west
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.
West or The West may also refer to:
Geography and locations
Global context
* The Western world
* Western culture and Western civilization in general
* The Western Bloc, countries allied with NAT ...
collapsed.
Constantinople's fame was such that
it was described even in contemporary
Chinese histories, the ''
Old
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
* Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, M ...
'' and ''
New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
'', which mentioned its massive walls and gates as well as a purported
clepsydra mounted with a golden statue of a man.
[Hirth (2000) ]885
Year 885 ( DCCCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* Summer – Emperor Charles the Fat summons a meeting of officials at Lobith (modern ...
br>East Asian History Sourcebook
. Retrieved 24 September 2016. The Chinese histories even related how the city
had been besieged in the 7th century by
Muawiyah I
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
and how he exacted
tribute in a peace settlement.
See also
People from Constantinople
*
List of people from Constantinople
This is a list of notable people from the city of Constantinople (present-day Istanbul) between the third century and 1453 CE. For a list of people born before the third century CE, see Notable people from Byzantium. For a list of people born af ...
Secular buildings and monuments
*
Augustaion
The ''Augustaion'' ( el, ) or, in Latin, ''Augustaeum'', was an important ceremonial square in ancient and medieval Constantinople (modern Istanbul, Turkey), roughly corresponding to the modern ''Aya Sofya Meydanı'' ( Turkish, "Hagia Sophia Squa ...
**
Column of Justinian
The Column of Justinian was a Roman triumphal column erected in Constantinople by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I in honour of his victories in 543. It stood in the western side of the great square of the Augustaeum, between the Hagia Sophia a ...
*
Basilica Cistern
The Basilica Cistern, or Cisterna Basilica ( el, βασιλική κινστέρνή, tr, Yerebatan Sarnıcı or tr, Yerebatan Saray, label=none, "Subterranean Cistern" or "Subterranean Palace"), is the largest of several hundred ancient ciste ...
*
Column of Marcian
The Column of Marcian ( tr, Kıztaşı) is a Roman honorific column erected in Constantinople by the ''praefectus urbi'' Tatianus (450-c.452) and dedicated to the Emperor Marcian (450-57). It is located in the present-day Fatih district of Ist ...
*
Bucoleon Palace
The Palace of Boukoleon ( el, Βουκολέων) or Bucoleon was one of the Byzantine palaces in Constantinople (present-day Istanbul in Turkey.) The palace is located on the shore of the Sea of Marmara, to the south of the Hippodrome and ea ...
*
Horses of Saint Mark
*
Obelisk of Theodosius
The Obelisk of Theodosius ( tr, Dikilitaş) is the Ancient Egyptian obelisk of Pharaoh Thutmose III re-erected in the Hippodrome of Constantinople (known today as ''At Meydanı'' or ''Sultanahmet Meydanı'', in the modern city of Istanbul, ...
*
Serpent Column
The Serpent Column ( grc, Τρικάρηνος Ὄφις ''Τrikarenos Οphis'' "Three-headed Serpent";, i.e. "the bronze three-headed serpent"; see
See also , . tr, Yılanlı Sütun "Serpentine Column"), also known as the Serpentine Column, ...
*
Walled Obelisk
The Walled Obelisk or Masonry Obelisk ( tr, Örme Dikilitaş) is a Roman monument in the form of an obelisk in the former Hippodrome of Constantinople, now Sultanahmet Square in Istanbul, Turkey. It is situated west of the Sultan Ahmed Mosque, ...
*
Palace of Lausus
The Palace of Lausus or Lausos, also known as the Lauseion ( el, Λαυσεῖον), was a 5th-century building located in Constantinople that was acquired and owned by the eunuch Lausus.
Lausus
Lausus, who had formerly served as a eunuch in ...
*
Cistern of Philoxenos
The Cistern of Philoxenos ( el, Κινστέρνα Φιλοξένου), or Binbirdirek Cistern, is a man-made subterranean reservoir in Istanbul, situated between the Forum of Constantine and the Hippodrome of Constantinople in the Sultanahmet dis ...
*
Palace of the Porphyrogenitus
The Palace of the Porphyrogenitus ( el, τὸ Παλάτιον τοῦ Πορφυρογεννήτου), known in Turkish as the ''Tekfur Sarayı'' ("Palace of the Sovereign"), is a late 13th-century Byzantine palace in the north-western part of ...
*
Prison of Anemas
The Prison of Anemas ( tr, Anemas Zindanları) is a large Byzantine building attached to the walls of the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). It is traditionally identified with the prisons named after Michael Anemas, a Byzantin ...
*
Valens Aqueduct
Churches, monasteries and mosques
*
Atik Mustafa Pasha Mosque
Atik Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( tr, Atik Mustafa Paşa Camii; more commonly known as ''Hazreti Cabir Camii'') is a former Eastern Orthodox church in Istanbul, converted into a mosque by the Ottomans. In Çember Sokak in the neighbourhood of Ayvansaray, ...
*
Bodrum Mosque
Bodrum Mosque ( tr, Bodrum Camii, or ''Mesih Paşa Camii'' named after its converter) in Istanbul, Turkey, is a former Eastern Orthodox church converted into a mosque by the Ottomans. The church was known under the Greek name of Myrelaion ( el, E� ...
*
Chora Church
'' '' tr, Kariye Mosque''
, image = Chora Church Constantinople 2007 panorama 002.jpg
, caption = Exterior rear view
, map_type = Istanbul Fatih
, map_size = 220px
, map_caption ...
*
Church of Saints Sergius and Bacchus
*
Church of the Holy Apostles
The Church of the Holy Apostles ( el, , ''Agioi Apostoloi''; tr, Havariyyun Kilisesi), also known as the ''Imperial Polyándreion'' (imperial cemetery), was a Byzantine Eastern Orthodox church in Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman ...
*
Church of St. Polyeuctus
*
Eski Imaret Mosque
*
Fenari Isa Mosque
Fenâri Îsâ Mosque (full name in tr, Molla Fenâri Îsâ Câmîi), in Byzantine times known as the Lips Monastery ( el, Μονὴ τοῦ Λιβός), is a mosque in Istanbul, made of two former Eastern Orthodox churches.
Location
The complex ...
*
Gül Mosque
Gül Mosque ( tr, Gül Camii, meaning Rose Mosque' in English) is a former Byzantine church in Istanbul, Turkey, converted into a mosque by the Ottomans.
It is in Vakıf Mektebi Sokak in the district of Fatih, Istanbul, in the neighbourhood of ...
*
Hagia Irene
Hagia Irene ( el, Αγία Ειρήνη) or Hagia Eirene ( grc-x-byzant, Ἁγία Εἰρήνη , "Holy Peace", tr, Aya İrini), sometimes known also as Saint Irene, is an Eastern Orthodox church located in the outer courtyard of Topkapı Palac ...
*
Hirami Ahmet Pasha Mosque
*
Kalenderhane Mosque
*
Koca Mustafa Pasha Mosque
Koca Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( tr, Koca Mustafa Paşa Camii; also named ''Sünbül Efendi Camii'') is a former Eastern Orthodox church converted into a mosque by the Ottomans, located in Istanbul, Turkey. The church, as the adjoining monastery, was d ...
*
Nea Ekklesia
The Nea Ekklēsia ( gkm, Νέα Ἐκκλησία, "New Church"; known in English as "The Nea") was a church built by Byzantine Emperor Basil I the Macedonian in Constantinople between 876 and 880. It was the first monumental church built in the ...
*
Pammakaristos Church
The Pammakaristos Church, also known as the Church of Theotokos Pammakaristos ( el, , "All-Blessed Mother of God"), is one of the most famous Byzantine churches in Istanbul, Turkey, and was the last pre- Ottoman building to house the Ecumenica ...
*
Stoudios Monastery
*
Toklu Dede Mosque
''Toklu Dede Mosque'' ( tr, Toklu Dede Mescidi, where ''mescit'' is the Turkish word for a small mosque), was an Ottoman mosque in Istanbul, Turkey.Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 206. The building was originally a Byzantine Eastern Orthodox church of ...
*
Vefa Kilise Mosque
Church-Mosque of Vefa ( tr, Vefa Kilise Camii, meaning "the church mosque of Vefa", to distinguish it from the other ''kilise camiler'' of Istanbul: also known as ''Molla Gürani Camii'' after the name of his founder) is a former Eastern Orthodox ...
*
Zeyrek Mosque
'' '' tr, Zeyrek Camii''
, image = Molla Zeyrek Camii.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption =The mosque viewed from north east. From left to right, one can see the apses of the ''Church of Christ Pantocrato ...
* Unnamed Mosque established during Byzantine times for visiting Muslim dignitaries.
Miscellaneous
*
Ahmed Bican Yazıcıoğlu
*
Byzantine calendar
The Byzantine calendar, also called the Roman calendar, the Creation Era of Constantinople or the Era of the World ( grc, Ἔτη Γενέσεως Κόσμου κατὰ Ῥωμαίους, also or , abbreviated as ε.Κ.; literal translation of ...
*
Byzantine silk
*
Eparch of Constantinople
The ''praefectus urbanus'', also called ''praefectus urbi'' or urban prefect in English, was prefect of the city of Rome, and later also of Constantinople. The office originated under the Roman kings, continued during the Republic and Empire, and ...
(
List of eparchs)
*
Sieges of Constantinople
The following is a list of sieges of Constantinople, a historic city located in an area which is today part of Istanbul, Turkey. The city was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the ...
*
Third Rome
The continuation, succession and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the Mediterranean Basin. It reflects the lasting memories of power and prestige associated with the Roman Empire itself.
Several politi ...
*
Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek ...
*
Timeline of Istanbul history
The following is a timeline of the history of the town of Istanbul, Turkey.
Prior to 4th century
* 1000 BCE - Thracian tribes find the settlements of Lygos and Semistra.
* 657 BCE – Byzantium founded by Greeks.
* 513 BCE – City taken by P ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
Ball, Warwick (2016). ''Rome in the East: Transformation of an Empire'', 2nd edition. London & New York: Routledge, .
*
*
*
* Emerson, Charles. ''1913: In Search of the World Before the Great War'' (2013) compares Constantinople to 20 major world cities; pp 358–80.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
online review
*
*
*
*
Ibrahim, Raymond (2018). ''Sword and Scimitar'', 1st edition. New York, .
*
* Klein, Konstantin M.: Wienand, Johannes (2022) (eds.): ''City of Caesar, City of God: Constantinople and Jerusalem in Late Antiquity.'' De Gruyter, Berlin 2022, ISBN 978-3-11-071720-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110718447.
* Korolija Fontana-Giusti, Gordana 'The Urban Language of Early Constantinople: The Changing Roles of the Arts and Architecture in the Formation of the New Capital and the New Consciousness' in ''Intercultural Transmission in the Medieval Mediterranean'', (2012), Stephanie L. Hathaway and David W. Kim (eds), London: Continuum, pp 164–202. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Yule, Henry (1915). Henri Cordier (ed.)
''Cathay and the Way Thither: Being a Collection of Medieval Notices of China, Vol I: Preliminary Essay on the Intercourse Between China and the Western Nations Previous to the Discovery of the Cape Route'' London: Hakluyt Society. Accessed 21 September 2016.
External links
from ''History of the Later Roman Empire'', by
J. B. Bury
History of Constantinoplefrom the "New Advent Catholic Encyclopedia".
Monuments of Byzantium– Pantokrator Monastery of Constantinople
Constantinoupolis on the webSelect internet resources on the history and culture
from the Foundation for the Advancement of Sephardic Studies and Culture
* , documenting the monuments of Byzantine Constantinople
Byzantium 1200 a project aimed at creating computer reconstructions of the Byzantine monuments located in Istanbul in 1200 AD.
Constantine and ConstantinopleHow and why Constantinople was founded
Hagia Sophia MosaicsThe Deesis and other Mosaics of Hagia Sophia in Constantinople
{{Authority control
320s establishments in the Roman Empire
330 establishments
1453 disestablishments in the Ottoman Empire
15th-century disestablishments in the Byzantine Empire
Capitals of former nations
Constantine the Great
*
Holy cities
Populated places along the Silk Road
Populated places established in the 4th century
Populated places disestablished in the 15th century
Populated places of the Byzantine Empire
Roman towns and cities in Turkey
Thrace
 Constantinople was famous for its massive and complex fortifications, which ranked among the most sophisticated defensive architecture of
Constantinople was famous for its massive and complex fortifications, which ranked among the most sophisticated defensive architecture of 
 Byzantium took on the name of ''Kōnstantinoupolis'' ("city of Constantine", ''Constantinople'') after its refoundation under Roman emperor
Byzantium took on the name of ''Kōnstantinoupolis'' ("city of Constantine", ''Constantinople'') after its refoundation under Roman emperor  The modern Turkish name for the city, '' İstanbul'', derives from the Greek phrase ''eis tin Polin'' (), meaning "(in)to the city". This name was used in Turkish alongside ''Kostantiniyye'', the more formal adaptation of the original ''Constantinople'', during the period of Ottoman rule, while western languages mostly continued to refer to the city as Constantinople until the early 20th century. In 1928, the Turkish alphabet was changed from Arabic script to Latin script. After that, as part of the 1920s
The modern Turkish name for the city, '' İstanbul'', derives from the Greek phrase ''eis tin Polin'' (), meaning "(in)to the city". This name was used in Turkish alongside ''Kostantiniyye'', the more formal adaptation of the original ''Constantinople'', during the period of Ottoman rule, while western languages mostly continued to refer to the city as Constantinople until the early 20th century. In 1928, the Turkish alphabet was changed from Arabic script to Latin script. After that, as part of the 1920s 
 Byzantium was never a major influential city-state like that of Athens, Corinth or Sparta, but the city enjoyed relative peace and steady growth as a prosperous trading city lent by its remarkable position. The site lay astride the land route from Europe to
Byzantium was never a major influential city-state like that of Athens, Corinth or Sparta, but the city enjoyed relative peace and steady growth as a prosperous trading city lent by its remarkable position. The site lay astride the land route from Europe to 

 Constantine had altogether more colourful plans. Having restored the unity of the Empire, and, being in the course of major governmental reforms as well as of sponsoring the consolidation of the Christian church, he was well aware that Rome was an unsatisfactory capital. Rome was too far from the frontiers, and hence from the armies and the imperial courts, and it offered an undesirable playground for disaffected politicians. Yet it had been the capital of the state for over a thousand years, and it might have seemed unthinkable to suggest that the capital be moved to a different location. Nevertheless, Constantine identified the site of Byzantium as the right place: a place where an emperor could sit, readily defended, with easy access to the Danube or the Euphrates frontiers, his court supplied from the rich gardens and sophisticated workshops of Roman Asia, his treasuries filled by the wealthiest provinces of the Empire.
Constantinople was built over six years, and consecrated on 11 May 330. Constantine divided the expanded city, like Rome, into 14 regions, and ornamented it with public works worthy of an imperial metropolis. Yet, at first, Constantine's new Rome did not have all the dignities of old Rome. It possessed a proconsul, rather than an urban prefect. It had no praetors, tribunes, or
Constantine had altogether more colourful plans. Having restored the unity of the Empire, and, being in the course of major governmental reforms as well as of sponsoring the consolidation of the Christian church, he was well aware that Rome was an unsatisfactory capital. Rome was too far from the frontiers, and hence from the armies and the imperial courts, and it offered an undesirable playground for disaffected politicians. Yet it had been the capital of the state for over a thousand years, and it might have seemed unthinkable to suggest that the capital be moved to a different location. Nevertheless, Constantine identified the site of Byzantium as the right place: a place where an emperor could sit, readily defended, with easy access to the Danube or the Euphrates frontiers, his court supplied from the rich gardens and sophisticated workshops of Roman Asia, his treasuries filled by the wealthiest provinces of the Empire.
Constantinople was built over six years, and consecrated on 11 May 330. Constantine divided the expanded city, like Rome, into 14 regions, and ornamented it with public works worthy of an imperial metropolis. Yet, at first, Constantine's new Rome did not have all the dignities of old Rome. It possessed a proconsul, rather than an urban prefect. It had no praetors, tribunes, or  Constantine laid out a new square at the centre of old Byzantium, naming it the Augustaeum. The new senate-house (or Curia) was housed in a basilica on the east side. On the south side of the great square was erected the Great Palace of the Emperor with its imposing entrance, the
Constantine laid out a new square at the centre of old Byzantium, naming it the Augustaeum. The new senate-house (or Curia) was housed in a basilica on the east side. On the south side of the great square was erected the Great Palace of the Emperor with its imposing entrance, the  After the barbarians overran the Western Roman Empire, Constantinople became the indisputable capital city of the Roman Empire. Emperors were no longer peripatetic between various court capitals and palaces. They remained in their palace in the Great City and sent generals to command their armies. The wealth of the eastern Mediterranean and western Asia flowed into Constantinople.
After the barbarians overran the Western Roman Empire, Constantinople became the indisputable capital city of the Roman Empire. Emperors were no longer peripatetic between various court capitals and palaces. They remained in their palace in the Great City and sent generals to command their armies. The wealth of the eastern Mediterranean and western Asia flowed into Constantinople.
 The emperor Justinian I (527–565) was known for his successes in war, for his legal reforms and for his public works. It was from Constantinople that his expedition for the reconquest of the former Diocese of Africa set sail on or about 21 June 533. Before their departure, the ship of the commander
The emperor Justinian I (527–565) was known for his successes in war, for his legal reforms and for his public works. It was from Constantinople that his expedition for the reconquest of the former Diocese of Africa set sail on or about 21 June 533. Before their departure, the ship of the commander  Throughout the late Roman and early Byzantine periods, Christianity was resolving fundamental questions of identity, and the dispute between the
Throughout the late Roman and early Byzantine periods, Christianity was resolving fundamental questions of identity, and the dispute between the  While the city withstood a siege by the Sassanids and Avars in 626, Heraclius campaigned deep into Persian territory and briefly restored the ''status quo'' in 628, when the Persians surrendered all their conquests. However, further sieges followed the
While the city withstood a siege by the Sassanids and Avars in 626, Heraclius campaigned deep into Persian territory and briefly restored the ''status quo'' in 628, when the Persians surrendered all their conquests. However, further sieges followed the  In the 730s Leo III carried out extensive repairs of the Theodosian walls, which had been damaged by frequent and violent attacks; this work was financed by a special tax on all the subjects of the Empire.
Theodora, widow of the Emperor
In the 730s Leo III carried out extensive repairs of the Theodosian walls, which had been damaged by frequent and violent attacks; this work was financed by a special tax on all the subjects of the Empire.
Theodora, widow of the Emperor 
 In the late 11th century catastrophe struck with the unexpected and calamitous defeat of the imperial armies at the
In the late 11th century catastrophe struck with the unexpected and calamitous defeat of the imperial armies at the 


 On 25 July 1197, Constantinople was struck by a severe fire which burned the Latin Quarter and the area around the Gate of the Droungarios ( tr, Odun Kapısı) on the Golden Horn. Nevertheless, the destruction wrought by the 1197 fire paled in comparison with that brought by the Crusaders. In the course of a plot between Philip of Swabia,
On 25 July 1197, Constantinople was struck by a severe fire which burned the Latin Quarter and the area around the Gate of the Droungarios ( tr, Odun Kapısı) on the Golden Horn. Nevertheless, the destruction wrought by the 1197 fire paled in comparison with that brought by the Crusaders. In the course of a plot between Philip of Swabia,  The Latins took over at least 20 churches and 13 monasteries, most prominently the Hagia Sophia, which became the cathedral of the Latin Patriarch of Constantinople. It is to these that E.H. Swift attributed the construction of a series of flying buttresses to shore up the walls of the church, which had been weakened over the centuries by earthquake tremors. However, this act of maintenance is an exception: for the most part, the Latin occupiers were too few to maintain all of the buildings, either secular and sacred, and many became targets for vandalism or dismantling. Bronze and lead were removed from the roofs of abandoned buildings and melted down and sold to provide money to the chronically under-funded Empire for defense and to support the court; Deno John Geanokoplos writes that "it may well be that a division is suggested here: Latin laymen stripped secular buildings, ecclesiastics, the churches." Buildings were not the only targets of officials looking to raise funds for the impoverished Latin Empire: the monumental sculptures which adorned the Hippodrome and fora of the city were pulled down and melted for coinage. "Among the masterpieces destroyed, writes Talbot, "were a Herakles attributed to the fourth-century B.C. sculptor
The Latins took over at least 20 churches and 13 monasteries, most prominently the Hagia Sophia, which became the cathedral of the Latin Patriarch of Constantinople. It is to these that E.H. Swift attributed the construction of a series of flying buttresses to shore up the walls of the church, which had been weakened over the centuries by earthquake tremors. However, this act of maintenance is an exception: for the most part, the Latin occupiers were too few to maintain all of the buildings, either secular and sacred, and many became targets for vandalism or dismantling. Bronze and lead were removed from the roofs of abandoned buildings and melted down and sold to provide money to the chronically under-funded Empire for defense and to support the court; Deno John Geanokoplos writes that "it may well be that a division is suggested here: Latin laymen stripped secular buildings, ecclesiastics, the churches." Buildings were not the only targets of officials looking to raise funds for the impoverished Latin Empire: the monumental sculptures which adorned the Hippodrome and fora of the city were pulled down and melted for coinage. "Among the masterpieces destroyed, writes Talbot, "were a Herakles attributed to the fourth-century B.C. sculptor  Although Constantinople was retaken by Michael VIII Palaiologos, the Empire had lost many of its key economic resources, and struggled to survive. The
Although Constantinople was retaken by Michael VIII Palaiologos, the Empire had lost many of its key economic resources, and struggled to survive. The  The Christian Orthodox city of Constantinople was now under Ottoman control. When
The Christian Orthodox city of Constantinople was now under Ottoman control. When 
 Constantinople was the largest and richest urban center in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea during the late Eastern Roman Empire, mostly as a result of its strategic position commanding the trade routes between the Aegean Sea and the Black Sea. It would remain the capital of the eastern, Greek-speaking empire for over a thousand years. At its peak, roughly corresponding to the Middle Ages, it was one of the richest and largest cities in Europe. It exerted a powerful cultural pull and dominated much of the economic life in the Mediterranean. Visitors and merchants were especially struck by the beautiful monasteries and churches of the city, in particular the Hagia Sophia, or the Church of Holy Wisdom. According to Russian 14th-century traveler
Constantinople was the largest and richest urban center in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea during the late Eastern Roman Empire, mostly as a result of its strategic position commanding the trade routes between the Aegean Sea and the Black Sea. It would remain the capital of the eastern, Greek-speaking empire for over a thousand years. At its peak, roughly corresponding to the Middle Ages, it was one of the richest and largest cities in Europe. It exerted a powerful cultural pull and dominated much of the economic life in the Mediterranean. Visitors and merchants were especially struck by the beautiful monasteries and churches of the city, in particular the Hagia Sophia, or the Church of Holy Wisdom. According to Russian 14th-century traveler 
 The Byzantine Empire used Roman and Greek architectural models and styles to create its own unique type of architecture. The influence of Byzantine architecture and art can be seen in the copies taken from it throughout Europe. Particular examples include St Mark's Basilica in Venice, the basilicas of Ravenna, and many churches throughout the Slavic East. Also, alone in Europe until the 13th-century Italian florin, the Empire continued to produce sound gold coinage, the
The Byzantine Empire used Roman and Greek architectural models and styles to create its own unique type of architecture. The influence of Byzantine architecture and art can be seen in the copies taken from it throughout Europe. Particular examples include St Mark's Basilica in Venice, the basilicas of Ravenna, and many churches throughout the Slavic East. Also, alone in Europe until the 13th-century Italian florin, the Empire continued to produce sound gold coinage, the  The city provided a defence for the eastern provinces of the old Roman Empire against the barbarian invasions of the 5th century. The 18-meter-tall walls built by Theodosius II were, in essence, impregnable to the barbarians coming from south of the Danube river, who found easier targets to the west rather than the richer provinces to the east in Asia. From the 5th century, the city was also protected by the
The city provided a defence for the eastern provinces of the old Roman Empire against the barbarian invasions of the 5th century. The 18-meter-tall walls built by Theodosius II were, in essence, impregnable to the barbarians coming from south of the Danube river, who found easier targets to the west rather than the richer provinces to the east in Asia. From the 5th century, the city was also protected by the