Cholesterol Test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic

 This molecule is then reduced to
This molecule is then reduced to  Mevalonate is finally converted to
Mevalonate is finally converted to 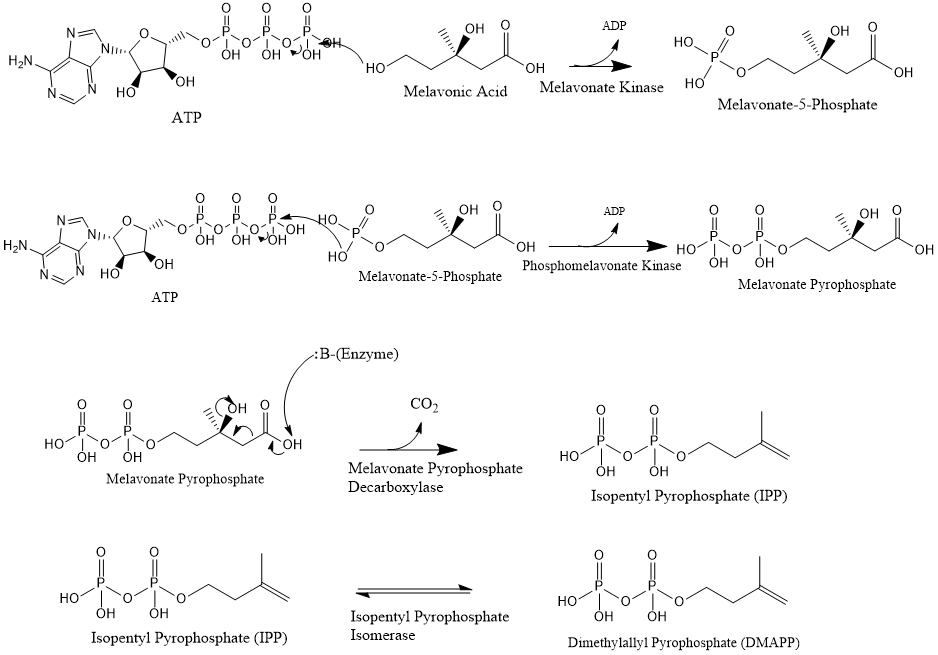 Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form farnesyl pyrophosphate through the action of geranyl transferase.
Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form farnesyl pyrophosphate through the action of geranyl transferase.

 Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate then condense to form
Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate then condense to form 
 Oxidosqualene cyclase then cyclizes squalene to form
Oxidosqualene cyclase then cyclizes squalene to form 

 Finally, lanosterol is converted to cholesterol via either of two pathways, the Bloch pathway, or the Kandutsch-Russell pathway.
The final 19 steps to cholesterol contain NADPH and oxygen to help oxidize
Finally, lanosterol is converted to cholesterol via either of two pathways, the Bloch pathway, or the Kandutsch-Russell pathway.
The final 19 steps to cholesterol contain NADPH and oxygen to help oxidize 

 As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in
As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in
 According to the lipid hypothesis, elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood lead to atherosclerosis which may increase the risk of myocardial infarction, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Since higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes to this process more than the cholesterol content of the HDL particles, LDL particles are often termed "bad cholesterol". High concentrations of functional HDL, which can remove cholesterol from cells and atheromas, offer protection and are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol". These balances are mostly genetically determined, but can be changed by body composition, medications, diet, and other factors. A 2007 study demonstrated that blood total cholesterol levels have an exponential effect on cardiovascular and total mortality, with the association more pronounced in younger subjects. Because cardiovascular disease is relatively rare in the younger population, the impact of high cholesterol on health is larger in older people.
Elevated levels of the lipoprotein fractions, LDL, IDL and VLDL, rather than the total cholesterol level, correlate with the extent and progress of atherosclerosis. Conversely, the total cholesterol can be within normal limits, yet be made up primarily of small LDL and small HDL particles, under which conditions atheroma growth rates are high. A ''post hoc'' analysis of the IDEAL and the EPIC prospective studies found an association between high levels of HDL cholesterol (adjusted for apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein B) and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, casting doubt on the cardioprotective role of "good cholesterol".
About one in 250 individuals can have a genetic mutation for the LDL cholesterol receptor that causes them to have familial hypercholesterolemia. Inherited high cholesterol can also include genetic mutations in the PCSK9 gene and the gene for apolipoprotein B.
Elevated cholesterol levels are treated with a strict diet consisting of low saturated fat, trans fat-free, low cholesterol foods, often followed by one of various Lipid-lowering agent, hypolipidemic agents, such as
According to the lipid hypothesis, elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood lead to atherosclerosis which may increase the risk of myocardial infarction, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Since higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes to this process more than the cholesterol content of the HDL particles, LDL particles are often termed "bad cholesterol". High concentrations of functional HDL, which can remove cholesterol from cells and atheromas, offer protection and are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol". These balances are mostly genetically determined, but can be changed by body composition, medications, diet, and other factors. A 2007 study demonstrated that blood total cholesterol levels have an exponential effect on cardiovascular and total mortality, with the association more pronounced in younger subjects. Because cardiovascular disease is relatively rare in the younger population, the impact of high cholesterol on health is larger in older people.
Elevated levels of the lipoprotein fractions, LDL, IDL and VLDL, rather than the total cholesterol level, correlate with the extent and progress of atherosclerosis. Conversely, the total cholesterol can be within normal limits, yet be made up primarily of small LDL and small HDL particles, under which conditions atheroma growth rates are high. A ''post hoc'' analysis of the IDEAL and the EPIC prospective studies found an association between high levels of HDL cholesterol (adjusted for apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein B) and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, casting doubt on the cardioprotective role of "good cholesterol".
About one in 250 individuals can have a genetic mutation for the LDL cholesterol receptor that causes them to have familial hypercholesterolemia. Inherited high cholesterol can also include genetic mutations in the PCSK9 gene and the gene for apolipoprotein B.
Elevated cholesterol levels are treated with a strict diet consisting of low saturated fat, trans fat-free, low cholesterol foods, often followed by one of various Lipid-lowering agent, hypolipidemic agents, such as  Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a Low-density lipoprotein#Estimation of LDL particles via cholesterol content, variant): estimated LDL = [total cholesterol] − [total HDL] − [estimated VLDL]. Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the Framingham Heart Study, each 10 mg/dL (0.6 Mole (unit), mmol/L) increase in total cholesterol levels increased 30-year overall mortality by 5% and CVD mortality by 9%. While subjects over the age of 50 had an 11% increase in overall mortality, and a 14% increase in cardiovascular disease mortality per 1 mg/dL (0.06 Mole (unit), mmol/L) year drop in total cholesterol levels. The researchers attributed this phenomenon to Correlation does not imply causation#B causes A (reverse causation or reverse causality), reverse causation, whereby the disease itself increases risk of death, as well as changes a myriad of factors, such as weight loss and the inability to eat, which lower serum cholesterol. This effect was also shown in men of all ages and women over 50 in the Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Programme. These groups were more likely to die of cancer, liver diseases, and mental diseases with very low total cholesterol, of 186 mg/dL (10.3 Mole (unit), mmol/L) and lower. This result indicates the low-cholesterol effect occurs even among younger respondents, contradicting the previous assessment among cohorts of older people that this is a marker for frailty occurring with age.
Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a Low-density lipoprotein#Estimation of LDL particles via cholesterol content, variant): estimated LDL = [total cholesterol] − [total HDL] − [estimated VLDL]. Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the Framingham Heart Study, each 10 mg/dL (0.6 Mole (unit), mmol/L) increase in total cholesterol levels increased 30-year overall mortality by 5% and CVD mortality by 9%. While subjects over the age of 50 had an 11% increase in overall mortality, and a 14% increase in cardiovascular disease mortality per 1 mg/dL (0.06 Mole (unit), mmol/L) year drop in total cholesterol levels. The researchers attributed this phenomenon to Correlation does not imply causation#B causes A (reverse causation or reverse causality), reverse causation, whereby the disease itself increases risk of death, as well as changes a myriad of factors, such as weight loss and the inability to eat, which lower serum cholesterol. This effect was also shown in men of all ages and women over 50 in the Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Programme. These groups were more likely to die of cancer, liver diseases, and mental diseases with very low total cholesterol, of 186 mg/dL (10.3 Mole (unit), mmol/L) and lower. This result indicates the low-cholesterol effect occurs even among younger respondents, contradicting the previous assessment among cohorts of older people that this is a marker for frailty occurring with age.
 Cholesterol has 256 stereoisomers that arise from its eight stereocenters, although only two of the stereoisomers are of biochemical significance (''nat''-cholesterol and ''ent''-cholesterol, for ''natural'' and ''enantiomer'', respectively), and only one occurs naturally (''nat''-cholesterol).
Cholesterol has 256 stereoisomers that arise from its eight stereocenters, although only two of the stereoisomers are of biochemical significance (''nat''-cholesterol and ''ent''-cholesterol, for ''natural'' and ''enantiomer'', respectively), and only one occurs naturally (''nat''-cholesterol).
File:ConversColest.png, Cholesterol units conversion
File:Steroidogenesis.svg, Steroidogenesis, using cholesterol as building material
File:Cholesterol Spacefill.jpeg, Space-filling model of the Cholesterol molecule
File:Steroid numbering.svg, Numbering of the steroid nuclei
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s called lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids includ ...
s. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules ...
by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
solid.
Cholesterol also serves as a precursor
Precursor or Precursors may refer to:
* Precursor (religion), a forerunner, predecessor
** The Precursor, John the Baptist
Science and technology
* Precursor (bird), a hypothesized genus of fossil birds that was composed of fossilized parts of u ...
for the biosynthesis of steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Withi ...
s, bile acid and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Conne ...
s (bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth.
François Poulletier de la Salle François Poulletier de la Salle (September 30, 1719 in Lyon – March 20, 1788 in Paris) was a French doctor and chemist. In about 1758, he isolated for the first time the crystals from cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain org ...
first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
s in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine".
Etymology
The word "cholesterol" comes from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
''chole-'' ( bile) and ''stereos'' (solid), followed by the chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
suffix ''-ol'' for an alcohol.
Physiology
Cholesterol is essential for all animal life, with each cell capable of synthesizing it by way of a complex 37-step process. This begins with themevalonate
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate ...
or HMG-CoA reductase pathway, the target of statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
drugs, which encompasses the first 18 steps. This is followed by 19 additional steps to convert the resulting lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
into cholesterol.
A human male weighing 68 kg (150 lb) normally synthesizes about 1 gram (1,000 mg) of cholesterol per day, and his body contains about 35 g, mostly contained within the cell membranes. Typical daily cholesterol dietary intake for a man in the United States is 307 mg.
Most ingested cholesterol is esterified
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
, which causes it to be poorly absorbed by the gut. The body also compensates for absorption of ingested cholesterol by reducing its own cholesterol synthesis. For these reasons, cholesterol in food, seven to ten hours after ingestion, has little, if any effect on concentrations of cholesterol in the blood. However, during the first seven hours after ingestion of cholesterol, as absorbed fats are being distributed around the body within extracellular water by the various lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, su ...
s (which transport all fats in the water outside cells), the concentrations increase.
Plants make cholesterol in very small amounts. In larger quantities they produce phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phy ...
s, chemically similar substances which can compete with cholesterol for reabsorption in the intestinal tract, thus potentially reducing cholesterol reabsorption. When intestinal lining cells absorb phytosterols, in place of cholesterol, they usually excrete the phytosterol molecules back into the GI tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
, an important protective mechanism. The intake of naturally occurring phytosterols, which encompass plant sterols and stanols, ranges between ≈200–300 mg/day depending on eating habits. Specially designed vegetarian experimental diets have been produced yielding upwards of 700 mg/day.
Function
Membranes
Cholesterol composes about 30% of all animalcell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s. It is required to build and maintain membranes and modulates membrane fluidity
In biology, membrane fluidity refers to the viscosity of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane or a synthetic lipid membrane. Lipid packing can influence the fluidity of the membrane. Viscosity of the membrane can affect the rotation and diffusion ...
over the range of physiological temperatures. The hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
group of each cholesterol molecule interacts with water molecules surrounding the membrane, as do the polar heads of the membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. ...
phospholipids and sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because o ...
s, while the bulky steroid and the hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
chain are embedded in the membrane, alongside the nonpolar
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
fatty-acid chain of the other lipids. Through the interaction with the phospholipid fatty-acid chains, cholesterol increases membrane packing, which both alters membrane fluidity and maintains membrane integrity so that animal cells do not need to build cell walls (like plants and most bacteria). The membrane remains stable and durable without being rigid, allowing animal cells to change shape and animals to move.
The structure of the tetracyclic ring of cholesterol contributes to the fluidity of the cell membrane, as the molecule is in a ''trans'' conformation making all but the side chain of cholesterol rigid and planar. In this structural role, cholesterol also reduces the permeability of the plasma membrane to neutral solutes, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
ions, and sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
ions.
Substrate presentation
Cholesterol regulates the biological process of substrate presentation and the enzymes that use substrate presentation as a mechanism of their activation. (PLD2
Phospholipase D2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLD2'' gene.
Function
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)-specific phospholipases D (PLDs) catalyze the hydrolysis of PC to produce phosphatidic acid and choline. Activation of PC-specifi ...
) is a well-defined example of an enzyme activated by substrate presentation. The enzyme is palmitoylated causing the enzyme to traffic to cholesterol dependent lipid domains sometimes called "lipid rafts
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein receptors organised in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular membranes remains somewhat controversial. ...
". The substrate of phospholipase D is phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.
They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybea ...
(PC) which is unsaturated and is of low abundance in lipid rafts. PC localizes to the disordered region of the cell along with the polyunsaturated lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number o ...
(PIP2). PLD2 has a PIP2 binding domain
In molecular biology, binding domain is a protein domain which binds to a specific atom or molecule, such as calcium or DNA. A protein domain is a part of a protein sequence and a tertiary structure that can change or evolve, function, and liv ...
. When PIP2 concentration in the membrane increases, PLD2 leaves the cholesterol-dependent domains and binds to PIP2 where it then gains access to its substrate PC and commences catalysis based on substrate presentation.

Signaling
Cholesterol is also implicated in cell signaling processes, assisting in the formation oflipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein receptors organised in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular membranes remains somewhat controversial ...
s in the plasma membrane, which brings receptor proteins in close proximity with high concentrations of second messenger molecules.
In multiple layers, cholesterol and phospholipids, both electrical insulators, can facilitate speed of transmission of electrical impulses along nerve tissue. For many neuron fibers, a myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
sheath, rich in cholesterol since it is derived from compacted layers of Schwann cell
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory ens ...
membrane, provides insulation for more efficient conduction of impulses. Demyelination
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency i ...
(loss of some of these Schwann cells) is believed to be part of the basis for multiple sclerosis.
Cholesterol binds to and affects the gating of a number of ion channels such as the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral ner ...
, GABAA receptor, and the inward-rectifier potassium channel
Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are activated by phosphatidylino ...
. Cholesterol also activates the estrogen-related receptor alpha
Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), also known as NR3B1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group B, member 1), is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''ESRRA'' (Estrogen Related Receptor Alpha) gene. ERRα was originally cloned b ...
(ERRα), and may be the endogenous ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elec ...
for the receptor. The constitutively active nature of the receptor may be explained by the fact that cholesterol is ubiquitous in the body. Inhibition of ERRα signaling by reduction of cholesterol production has been identified as a key mediator of the effects of statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
s and bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis. They are called bisphosphonates because they ...
s on bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
, muscle, and macrophages. On the basis of these findings, it has been suggested that the ERRα should be de-orphanized and classified as a receptor for cholesterol.
Chemical precursor
Within cells, cholesterol is also a precursor molecule for several biochemical pathways. For example, it is the precursor molecule for the synthesis ofvitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
in the calcium metabolism
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and ...
and all steroid hormones
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Withi ...
, including the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex whic ...
hormones cortisol and aldosterone, as well as the sex hormones progesterone, estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s, and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
, and their derivatives.
Epidermis
The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis. It is composed of terminally differentiated and enucleated corneocytes that reside within a lipid matrix, like "bricks and mortar." Together with ceramides and free fatty acids, cholesterol forms the lipid mortar, a water-impermeable barrier that prevents evaporative water loss. As a general rule of thumb, the epidermal lipid matrix is composed of an equimolar mixture of ceramides (~50% by weight), cholesterol (~ 25% by weight), and free fatty acids (~15% by weight), with smaller quantities of other lipids also being present. Cholesterol sulfate reaches its highest concentration in the granular layer of the epidermis. Steroid sulfate sulfatase then decreases its concentration in the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis. The relative abundance of cholesterol sulfate in the epidermis varies across different body sites with the heel of the foot having the lowest concentration.Metabolism
Cholesterol is recycled in the body. The liver excretes cholesterol intobiliary
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.
Bile is required for the digestion of food and is secreted by the liver into passages that carry bile toward the hepatic duct. It ...
fluids, which are then stored in the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
, which then excretes them in a non-ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides a ...
ified form (via bile) into the digestive tract. Typically, about 50% of the excreted cholesterol is reabsorbed by the small intestine back into the bloodstream.
Biosynthesis and regulation
Biosynthesis
All animal cells (exceptions exist within the invertebrates) manufacture cholesterol, for both membrane structure and other uses, with relative production rates varying by cell type and organ function. About 80% of total daily cholesterol production occurs in theliver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
and the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
; other sites of higher synthesis rates include the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
, the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex whic ...
s, and the reproductive organs.
Synthesis within the body starts with the mevalonate pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl ...
where two molecules of acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
condense to form acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion ...
. This is followed by a second condensation between acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
and acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion ...
to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA
β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of ...
).
 This molecule is then reduced to
This molecule is then reduced to mevalonate
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate ...
by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Production of mevalonate
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate ...
is the rate-limiting and irreversible step in cholesterol synthesis and is the site of action for statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
s (a class of cholesterol-lowering drugs).
 Mevalonate is finally converted to
Mevalonate is finally converted to isopentenyl pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of i ...
(IPP) through two phosphorylation steps and one decarboxylation step that requires ATP.
 Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form farnesyl pyrophosphate through the action of geranyl transferase.
Three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate condense to form farnesyl pyrophosphate through the action of geranyl transferase.

squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
by the action of squalene synthase in the endoplasmic reticulum.

 Oxidosqualene cyclase then cyclizes squalene to form
Oxidosqualene cyclase then cyclizes squalene to form lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
.


 Finally, lanosterol is converted to cholesterol via either of two pathways, the Bloch pathway, or the Kandutsch-Russell pathway.
The final 19 steps to cholesterol contain NADPH and oxygen to help oxidize
Finally, lanosterol is converted to cholesterol via either of two pathways, the Bloch pathway, or the Kandutsch-Russell pathway.
The final 19 steps to cholesterol contain NADPH and oxygen to help oxidize methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in ma ...
s for removal of carbons, mutases to move alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
groups, and NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an aden ...
to help reduce ketones.


Konrad Bloch
Konrad Emil Bloch (; 21 January 1912 – 15 October 2000) was a German-American biochemist. Bloch received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1964 (joint with Feodor Lynen) for discoveries concerning the mechanism and regulation of the ...
and Feodor Lynen
Feodor Felix Konrad Lynen (; 6 April 19116 August 1979) was a German biochemist. In 1964 he won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine together with Konrad Bloch for their discoveries concerning the mechanism and regulation of cholesterol an ...
shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
in 1964 for their discoveries concerning some of the mechanisms and methods of regulation of cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism.
Regulation of cholesterol synthesis
Biosynthesis of cholesterol is directly regulated by the cholesterol levels present, though thehomeostatic
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and ...
mechanisms involved are only partly understood. A higher intake of food leads to a net decrease in endogenous production, whereas a lower intake of food has the opposite effect. The main regulatory mechanism is the sensing of intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum by the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
SREBP
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes '' SREBF1'' and ''SREBF2''. SREBPs belong to the basic- ...
(sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 and 2). In the presence of cholesterol, SREBP is bound to two other proteins: SCAP (SREBP cleavage-activating protein) and INSIG-1
Insulin induced gene 1, also known as INSIG1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''INSIG1'' gene.
INSIG1 is short for insulin-induced gene 1; it is located on chromosome 7 (7q36). This human gene encodes for a transmembrane protein of ...
. When cholesterol levels fall, INSIG-1 dissociates from the SREBP-SCAP complex, which allows the complex to migrate to the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
. Here SREBP is cleaved by S1P and S2P (site-1 protease and site-2 protease), two enzymes that are activated by SCAP when cholesterol levels are low.
The cleaved SREBP then migrates to the nucleus and acts as a transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
to bind to the sterol regulatory element (SRE), which stimulates the transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
of many genes. Among these are the low-density lipoprotein (LDL
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall densit ...
) receptor and HMG-CoA reductase. The LDL receptor scavenges circulating LDL from the bloodstream, whereas HMG-CoA reductase leads to an increase in endogenous production of cholesterol. A large part of this signaling pathway was clarified by Dr. Michael S. Brown and Dr. Joseph L. Goldstein in the 1970s. In 1985, they received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
for their work. Their subsequent work shows how the SREBP pathway regulates the expression of many genes that control lipid formation and metabolism and body fuel allocation.
Cholesterol synthesis can also be turned off when cholesterol levels are high. HMG-CoA reductase contains both a cytosolic domain (responsible for its catalytic function) and a membrane domain. The membrane domain senses signals for its degradation. Increasing concentrations of cholesterol (and other sterols) cause a change in this domain's oligomerization state, which makes it more susceptible to destruction by the proteasome. This enzyme's activity can also be reduced by phosphorylation by an AMP-activated protein kinase. Because this kinase is activated by AMP, which is produced when ATP is hydrolyzed, it follows that cholesterol synthesis is halted when ATP levels are low.
Plasma transport and regulation of absorption
 As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in
As an isolated molecule, cholesterol is only minimally soluble in water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
, or hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are ...
. Because of this, it dissolves in blood at exceedingly small concentrations. To be transported effectively, cholesterol is instead packaged within lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, su ...
s, complex discoidal particles with exterior amphiphilic
An amphiphile (from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα philia, love, friendship), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'') properties. Such a compo ...
proteins and lipids, whose outward-facing surfaces are water-soluble and inward-facing surfaces are lipid-soluble. This allows it to travel through the blood via emulsification
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Altho ...
. Unbound cholesterol, being amphipathic, is transported in the monolayer surface of the lipoprotein particle along with phospholipids and proteins. Cholesterol esters bound to fatty acid, on the other hand, are transported within the fatty hydrophobic core of the lipoprotein, along with triglyceride.
There are several types of lipoproteins in the blood. In order of increasing density, they are chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85 ...
s, very-low-density lipoprotein
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, low-density lipo ...
(VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein
Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs) belong to the lipoprotein particle family and are formed from the degradation of very low-density lipoproteins as well as high-density lipoproteins. IDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chyl ...
(IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Lower protein/lipid ratios make for less dense lipoproteins. Cholesterol within different lipoproteins is identical, although some is carried as its native "free" alcohol form (the cholesterol-OH group facing the water surrounding the particles), while others as fatty acyl esters, known also as cholesterol esters, within the particles.
Lipoprotein particles are organized by complex apolipoproteins, typically 80–100 different proteins per particle, which can be recognized and bound by specific receptors on cell membranes, directing their lipid payload into specific cells and tissues currently ingesting these fat transport particles. These surface receptors serve as unique molecular signatures, which then help determine fat distribution delivery throughout the body.
Chylomicrons, the least dense cholesterol transport molecules, contain apolipoprotein B-48, apolipoprotein C, and apolipoprotein E (the principal cholesterol carrier in the brain) in their shells. Chylomicrons carry fats from the intestine to muscle and other tissues in need of fatty acids for energy or fat production. Unused cholesterol remains in more cholesterol-rich chylomicron remnants, and taken up from here to the bloodstream by the liver.
VLDL molecules are produced by the liver from Triglyceride, triacylglycerol and cholesterol which was not used in the synthesis of bile acids. These molecules contain apolipoprotein B100 and apolipoprotein E in their shells, and can be degraded by lipoprotein lipase on the artery wall to IDL. This arterial wall cleavage allows absorption of Triglyceride, triacylglycerol and increases the concentration of circulating cholesterol. IDL molecules are then consumed in two processes: half is metabolized by HTGL and taken up by the LDL receptor on the liver cell surfaces, while the other half continues to lose triacylglycerols in the bloodstream until they become cholesterol-laden LDL particles.
LDL particles are the major blood cholesterol carriers. Each one contains approximately 1,500 molecules of cholesterol ester. LDL molecule shells contain just one molecule of apolipoprotein B100, recognized by LDL receptors in peripheral tissues. Upon binding of apolipoprotein B100, many LDL receptors concentrate in clathrin-coated pits. Both LDL and its receptor form vesicles within a cell via endocytosis. These vesicles then fuse with a lysosome, where the Lysosomal lipase, lysosomal acid lipase enzyme hydrolyzes the cholesterol esters. The cholesterol can then be used for membrane biosynthesis or esterified and stored within the cell, so as to not interfere with the cell membranes.
LDL receptors are used up during cholesterol absorption, and its synthesis is regulated by SREBP, the same protein that controls the synthesis of cholesterol ''de novo'', according to its presence inside the cell. A cell with abundant cholesterol will have its LDL receptor synthesis blocked, to prevent new cholesterol in LDL molecules from being taken up. Conversely, LDL receptor synthesis proceeds when a cell is deficient in cholesterol.
When this process becomes unregulated, LDL molecules without receptors begin to appear in the blood. These LDL molecules are oxidized and taken up by macrophages, which become engorged and form foam cells. These foam cells often become trapped in the walls of blood vessels and contribute to atheroma, atherosclerotic plaque formation. Differences in cholesterol homeostasis affect the development of early atherosclerosis (carotid intima-media thickness). These plaques are the main causes of heart attacks, strokes, and other serious medical problems, leading to the association of so-called LDL cholesterol (actually a lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, su ...
) with "bad" cholesterol.
HDL particles are thought to transport cholesterol back to the liver, either for excretion or for other tissues that synthesize hormones, in a process known as reverse cholesterol transport (RCT). Large numbers of HDL particles correlates with better health outcomes, whereas low numbers of HDL particles is associated with atheromatous disease progression in the arteries.
Metabolism, recycling and excretion
Cholesterol is susceptible to oxidation and easily forms oxygenated derivatives called oxysterols. Three different mechanisms can form these: autoxidation, secondary oxidation to lipid peroxidation, and cholesterol-metabolizing enzyme oxidation. A great interest in oxysterols arose when they were shown to exert inhibitory actions on cholesterol biosynthesis. This finding became known as the "oxysterol hypothesis". Additional roles for oxysterols in human physiology include their participation in bile acid biosynthesis, function as transport forms of cholesterol, and regulation of gene transcription. In biochemical experiments radiolabelled forms of cholesterol, such as tritiated-cholesterol are used. These derivatives undergo degradation upon storage and it is essential to purify cholesterol prior to use. Cholesterol can be purified using small Sephadex LH-20 columns. Cholesterol is oxidized by the liver into a variety of bile acids. These, in turn, are phase 2 reaction, conjugated with glycine, taurine, glucuronic acid, or sulfate. A mixture of conjugated and nonconjugated bile acids, along with cholesterol itself, is excreted from theliver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
into the bile. Approximately 95% of the bile acids are reabsorbed from the intestines, and the remainder are lost in the feces. The excretion and reabsorption of bile acids forms the basis of the enterohepatic circulation, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Under certain circumstances, when more concentrated, as in the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
, cholesterol crystallises and is the major constituent of most gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
s (lecithin and bilirubin gallstones also occur, but less frequently). Every day, up to 1 g of cholesterol enters the colon. This cholesterol originates from the diet, bile, and desquamated intestinal cells, and can be metabolized by the colonic bacteria. Cholesterol is converted mainly into coprostanol, a nonabsorbable sterol that is excreted in the feces.
Although cholesterol is a steroid generally associated with mammals, the human pathogen ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' is able to completely degrade this molecule and contains a large number of genes that are regulated by its presence. Many of these cholesterol-regulated genes are Homology (biology), homologues of fatty acid β-oxidation genes, but have evolved in such a way as to bind large steroid substrates like cholesterol.
Dietary sources
Animal fats are complex mixtures of triglycerides, with lesser amounts of both the phospholipids and cholesterol molecules from which all animal (and human) cell membranes are constructed. Since all animal cells manufacture cholesterol, all animal-based foods contain cholesterol in varying amounts. Major dietary sources of cholesterol include red meat, Yolk, egg yolks and whole Egg as food, eggs,liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, kidney, giblets, fish oil, and butter. Human breast milk also contains significant quantities of cholesterol.
Plant cells synthesize cholesterol as a precursor for other compounds, such as phytosterols and steroidal glycoalkaloids, with cholesterol remaining in plant foods only in minor amounts or absent. Some plant foods, such as avocado, flax seeds and peanuts, contain phytosterols, which compete with cholesterol for absorption in the intestines, and reduce the absorption of both dietary and bile cholesterol. A typical diet contributes on the order of 0.2 gram of phytosterols, which is not enough to have a significant impact on blocking cholesterol absorption. Phytosterols intake can be supplemented through the use of phytosterol-containing functional foods or dietary supplements that are recognized as having potential to reduce levels of low-density lipoprotein, LDL-cholesterol.
Medical guidelines and recommendations
In 2015, the United States Department of Agriculture Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) recommended that Americans eat as little dietary cholesterol as possible, because most foods that are rich in cholesterol are also high in saturated fat and thereby may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. A 2013 report by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology recommended focusing on healthy dietary patterns rather than specific cholesterol limits, as they are hard for clinicians and consumers to implement. They recommend the DASH diet, DASH and Mediterranean diet, which are low in cholesterol. A 2017 review by the American Heart Association recommends switching saturated fats for polyunsaturated fats to reduce cardiovascular disease risk. Some supplemental guidelines have recommended doses of phytosterols in the 1.6–3.0 grams per day range (Health Canada, EFSA, ATP III, FDA). A recent meta-analysis demonstrating a 12% reduction in LDL-cholesterol at a mean dose of 2.1 grams per day. However, the benefits of a diet supplemented with phytosterols have also been questioned.Clinical significance
Hypercholesterolemia
 According to the lipid hypothesis, elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood lead to atherosclerosis which may increase the risk of myocardial infarction, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Since higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes to this process more than the cholesterol content of the HDL particles, LDL particles are often termed "bad cholesterol". High concentrations of functional HDL, which can remove cholesterol from cells and atheromas, offer protection and are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol". These balances are mostly genetically determined, but can be changed by body composition, medications, diet, and other factors. A 2007 study demonstrated that blood total cholesterol levels have an exponential effect on cardiovascular and total mortality, with the association more pronounced in younger subjects. Because cardiovascular disease is relatively rare in the younger population, the impact of high cholesterol on health is larger in older people.
Elevated levels of the lipoprotein fractions, LDL, IDL and VLDL, rather than the total cholesterol level, correlate with the extent and progress of atherosclerosis. Conversely, the total cholesterol can be within normal limits, yet be made up primarily of small LDL and small HDL particles, under which conditions atheroma growth rates are high. A ''post hoc'' analysis of the IDEAL and the EPIC prospective studies found an association between high levels of HDL cholesterol (adjusted for apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein B) and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, casting doubt on the cardioprotective role of "good cholesterol".
About one in 250 individuals can have a genetic mutation for the LDL cholesterol receptor that causes them to have familial hypercholesterolemia. Inherited high cholesterol can also include genetic mutations in the PCSK9 gene and the gene for apolipoprotein B.
Elevated cholesterol levels are treated with a strict diet consisting of low saturated fat, trans fat-free, low cholesterol foods, often followed by one of various Lipid-lowering agent, hypolipidemic agents, such as
According to the lipid hypothesis, elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood lead to atherosclerosis which may increase the risk of myocardial infarction, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Since higher blood LDL – especially higher LDL concentrations and smaller LDL particle size – contributes to this process more than the cholesterol content of the HDL particles, LDL particles are often termed "bad cholesterol". High concentrations of functional HDL, which can remove cholesterol from cells and atheromas, offer protection and are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol". These balances are mostly genetically determined, but can be changed by body composition, medications, diet, and other factors. A 2007 study demonstrated that blood total cholesterol levels have an exponential effect on cardiovascular and total mortality, with the association more pronounced in younger subjects. Because cardiovascular disease is relatively rare in the younger population, the impact of high cholesterol on health is larger in older people.
Elevated levels of the lipoprotein fractions, LDL, IDL and VLDL, rather than the total cholesterol level, correlate with the extent and progress of atherosclerosis. Conversely, the total cholesterol can be within normal limits, yet be made up primarily of small LDL and small HDL particles, under which conditions atheroma growth rates are high. A ''post hoc'' analysis of the IDEAL and the EPIC prospective studies found an association between high levels of HDL cholesterol (adjusted for apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein B) and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, casting doubt on the cardioprotective role of "good cholesterol".
About one in 250 individuals can have a genetic mutation for the LDL cholesterol receptor that causes them to have familial hypercholesterolemia. Inherited high cholesterol can also include genetic mutations in the PCSK9 gene and the gene for apolipoprotein B.
Elevated cholesterol levels are treated with a strict diet consisting of low saturated fat, trans fat-free, low cholesterol foods, often followed by one of various Lipid-lowering agent, hypolipidemic agents, such as statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
s, fibrates, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, monoclonal antibody therapy (PCSK9 inhibitors), nicotinic acid derivatives or bile acid sequestrants. There are several international guidelines on the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia.
Human trials using HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, known as statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
s, have repeatedly confirmed that changing lipoprotein transport patterns from unhealthy to healthier patterns significantly lowers cardiovascular disease event rates, even for people with cholesterol values currently considered low for adults. Studies have shown that reducing LDL cholesterol levels by about 38.7 mg/dL with the use of statins can reduce cardiovascular disease and stroke risk by about 21%. Studies have also found that statins reduce atheroma progression. As a result, people with a history of cardiovascular disease may derive benefit from statins irrespective of their cholesterol levels (total cholesterol below 5.0 mmol/L [193 mg/dL]), and in men without cardiovascular disease, there is benefit from lowering abnormally high cholesterol levels ("primary prevention"). Primary prevention in women was originally practiced only by extension of the findings in studies on men, since, in women, none of the large statin trials conducted prior to 2007 demonstrated a significant reduction in overall mortality or in cardiovascular endpoints. Meta-analyses have demonstrated significant reductions in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, without significant heterogeneity by sex.
The 1987 report of National Cholesterol Education Program, Adult Treatment Panels suggests the total blood cholesterol level should be: < 200 mg/dL normal blood cholesterol, 200–239 mg/dL borderline-high, > 240 mg/dL high cholesterol. The American Heart Association provides a similar set of guidelines for total (fasting) blood cholesterol levels and risk for heart disease: Statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol and widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease.
More current testing methods determine LDL ("bad") and HDL ("good") cholesterol separately, allowing cholesterol analysis to be more nuanced. The desirable LDL level is considered to be less than 100 mg/dL (2.6 Mole (unit), mmol/L), although a newer upper limit of 70 mg/dL (1.8 mmol/L) can be considered in higher-risk individuals based on some of the above-mentioned trials. A ratio of total cholesterol to HDL—another useful measure—of far less than 5:1 is thought to be healthier.
 Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a Low-density lipoprotein#Estimation of LDL particles via cholesterol content, variant): estimated LDL = [total cholesterol] − [total HDL] − [estimated VLDL]. Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the Framingham Heart Study, each 10 mg/dL (0.6 Mole (unit), mmol/L) increase in total cholesterol levels increased 30-year overall mortality by 5% and CVD mortality by 9%. While subjects over the age of 50 had an 11% increase in overall mortality, and a 14% increase in cardiovascular disease mortality per 1 mg/dL (0.06 Mole (unit), mmol/L) year drop in total cholesterol levels. The researchers attributed this phenomenon to Correlation does not imply causation#B causes A (reverse causation or reverse causality), reverse causation, whereby the disease itself increases risk of death, as well as changes a myriad of factors, such as weight loss and the inability to eat, which lower serum cholesterol. This effect was also shown in men of all ages and women over 50 in the Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Programme. These groups were more likely to die of cancer, liver diseases, and mental diseases with very low total cholesterol, of 186 mg/dL (10.3 Mole (unit), mmol/L) and lower. This result indicates the low-cholesterol effect occurs even among younger respondents, contradicting the previous assessment among cohorts of older people that this is a marker for frailty occurring with age.
Total cholesterol is defined as the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Usually, only the total, HDL, and triglycerides are measured. For cost reasons, the VLDL is usually estimated as one-fifth of the triglycerides and the LDL is estimated using the Friedewald formula (or a Low-density lipoprotein#Estimation of LDL particles via cholesterol content, variant): estimated LDL = [total cholesterol] − [total HDL] − [estimated VLDL]. Direct LDL measures are used when triglycerides exceed 400 mg/dL. The estimated VLDL and LDL have more error when triglycerides are above 400 mg/dL.
In the Framingham Heart Study, each 10 mg/dL (0.6 Mole (unit), mmol/L) increase in total cholesterol levels increased 30-year overall mortality by 5% and CVD mortality by 9%. While subjects over the age of 50 had an 11% increase in overall mortality, and a 14% increase in cardiovascular disease mortality per 1 mg/dL (0.06 Mole (unit), mmol/L) year drop in total cholesterol levels. The researchers attributed this phenomenon to Correlation does not imply causation#B causes A (reverse causation or reverse causality), reverse causation, whereby the disease itself increases risk of death, as well as changes a myriad of factors, such as weight loss and the inability to eat, which lower serum cholesterol. This effect was also shown in men of all ages and women over 50 in the Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Programme. These groups were more likely to die of cancer, liver diseases, and mental diseases with very low total cholesterol, of 186 mg/dL (10.3 Mole (unit), mmol/L) and lower. This result indicates the low-cholesterol effect occurs even among younger respondents, contradicting the previous assessment among cohorts of older people that this is a marker for frailty occurring with age.
Hypocholesterolemia
Abnormally low levels of cholesterol are termed ''hypocholesterolemia''. Research into the causes of this state is relatively limited, but some studies suggest a link with depression (mood), depression, cancer, and cerebral hemorrhage. In general, the low cholesterol levels seem to be a consequence, rather than a cause, of an underlying illness. A genetic defect in cholesterol synthesis causes Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome, which is often associated with low plasma cholesterol levels. Hyperthyroidism, or any other endocrine disturbance which causes upregulation of the LDL receptor, may result in hypocholesterolemia.Cholesterol testing
The American Heart Association recommends testing cholesterol every 4–6 years for people aged 20 years or older. A separate set of American Heart Association guidelines issued in 2013 indicates that people takingstatin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
medications should have their cholesterol tested 4–12 weeks after their first dose and then every 3–12 months thereafter. For men ages 45 to 65 and women ages 55 to 65, a cholesterol test should occur every 1-2 years, and for seniors over age 65, an annual test should be performed.
A blood sample after 12-hours of fasting is taken by a Health professional, healthcare professional from an arm vein to measure a lipid profile for a) total cholesterol, b) HDL cholesterol, c) LDL cholesterol, and d) triglycerides. Results may be expressed as "calculated", indicating a calculation of total cholesterol, HDL, and triglycerides.
Cholesterol is tested to determine for "normal" or "desirable" levels if a person has a total cholesterol of 5.2 mmol/L or less (200 mg/dL), an HDL value of more than 1 mmol/L (40 mg/dL, "the higher, the better"), an LDL value of less than 2.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL), and a triglycerides level of less than 1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dL). Blood cholesterol in people with lifestyle, aging, or cardiovascular risk factors, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, family history of coronary artery disease, or angina, are evaluated at different levels.
Interactive pathway map
Cholesteric liquid crystals
Some cholesterol derivatives (among other simple cholesteric lipids) are known to generate the liquid crystalline "cholesteric phase". The cholesteric phase is, in fact, a chirality (chemistry), chiral Liquid crystal, nematic phase, and it changes colour when its temperature changes. This makes cholesterol derivatives useful for indicating temperature in liquid-crystal display thermometers and in temperature-sensitive paints.Stereoisomers
Additional images
See also
* Arcus senilis "Cholesterol ring" in the eyes * Cardiovascular disease * Cholesterol embolism * Cholesterol total synthesis * Familial hypercholesterolemia * Hypercholesterolemia "High Cholesterol" * Hypocholesterolemia "Low Cholesterol" * Janus-faced molecule * List of cholesterol in foods * Niemann–Pick disease Type C * Oxycholesterol * Remnant cholesterolReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Cholestanes GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Lipid disorders Neurosteroids Nutrition Receptor agonists Sterols