Cultural Depictions Of Professional Wrestlers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the
 Culture is considered a central concept in
Culture is considered a central concept in



 Cultures are internally affected by both forces encouraging change and forces resisting change. These forces are related to both
Cultures are internally affected by both forces encouraging change and forces resisting change. These forces are related to both
As applied to the computational universe
 In 1795, the Prussian linguist and philosopher
In 1795, the Prussian linguist and philosopher
social behavior
Social behavior is behavior among two or more organisms within the same species, and encompasses any behavior in which one member affects the other. This is due to an interaction among those members. Social behavior can be seen as similar to an ...
, institution
Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions a ...
s, and norms found in human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
societies
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societ ...
, as well as the knowledge
Knowledge can be defined as awareness of facts or as practical skills, and may also refer to familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often defined as true belief that is distin ...
, belief
A belief is an attitude that something is the case, or that some proposition is true. In epistemology, philosophers use the term "belief" to refer to attitudes about the world which can be either true or false. To believe something is to tak ...
s, arts, law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
s, customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs ...
, capabilities, and habit
A habit (or wont as a humorous and formal term) is a routine of behavior that is repeated regularly and tends to occur subconsciously.
s of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location.
Humans acquire culture through the learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of lea ...
processes of enculturation
Enculturation is the process by which people learn the dynamics of their surrounding culture and acquire values and norms appropriate or necessary to that culture and its worldviews.Grusec, Joan E.; Hastings, Paul D. ''Handbook of Socialization: ...
and socialization
In sociology, socialization or socialisation (see spelling differences) is the process of internalizing the norms and ideologies of society. Socialization encompasses both learning and teaching and is thus "the means by which social and cul ...
, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies.
A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group.
Accepting only a monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monoculture is widely used in intensive farming and in organic farming: both a 1,000-hectare/acre cornfield and a 10-ha/acre field of organic kale are ...
in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change.
Thus in military culture, valor
Valor, valour, or valorous may mean:
* Courage, a similar meaning
* Virtue ethics, roughly "courage in defense of a noble cause"
Entertainment
* Valor (band), a Christian gospel music group
* Valor Kand, a member of the band Christian Death
* ' ...
is counted a typical behavior for an individual and duty, honor, and loyalty to the social group are counted as virtues or functional responses in the continuum of conflict
A conflict continuum is a model or concept various social science researchers use when modeling conflict on a continuum from low to high-intensity, such as from aggression to irritation to explosiveness.
The mathematical model of game theory ori ...
. In the practice of religion, analogous attributes can be identified in a social group.
Cultural change, or repositioning, is the reconstruction of a cultural concept of a society. Cultures are internally affected by both forces encouraging change and forces resisting change. Cultures are externally affected via contact between societies.
Organizations like UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
attempt to preserve culture and cultural heritage.
Description
 Culture is considered a central concept in
Culture is considered a central concept in anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
, encompassing the range of phenomena that are transmitted through social learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of lea ...
in human societies
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societ ...
. Cultural universals
A cultural universal (also called an anthropological universal or human universal) is an element, pattern, trait, or institution that is common to all known human cultures worldwide. Taken together, the whole body of cultural universals is known ...
are found in all human societies. These include expressive forms like art, music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, dance
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoire ...
, ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized ...
, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
, and technologies
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
like tool usage, cooking
Cooking, cookery, or culinary arts is the art, science and craft of using heat to prepare food for consumption. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric stoves, to baking in vario ...
, shelter
Shelter is a small building giving temporary protection from bad weather or danger.
Shelter may also refer to:
Places
* Port Shelter, Hong Kong
* Shelter Bay (disambiguation), various locations
* Shelter Cove (disambiguation), various locatio ...
, and clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natura ...
. The concept of material culture
Material culture is the aspect of social reality grounded in the objects and architecture that surround people. It includes the usage, consumption, creation, and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms, and rituals that the objects crea ...
covers the physical expressions of culture, such as technology, architecture and art, whereas the immaterial aspects of culture such as principles of social organization
In sociology, a social organization is a pattern of relationships between and among individuals and social groups.
Characteristics of social organization can include qualities such as sexual composition, spatiotemporal cohesion, leadership, s ...
(including practices of political organization
A political organization is any organization that involves itself in the political process, including political parties, non-governmental organizations, and special interest advocacy groups. Political organizations are those engaged in poli ...
and social institutions
Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions a ...
), mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
(both written
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
and oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
** Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or or ...
), and science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
comprise the intangible cultural heritage
An intangible cultural heritage (ICH) is a practice, representation, expression, knowledge, or skill considered by UNESCO to be part of a place's cultural heritage. Buildings, historic places, monuments, and artifacts are cultural property. I ...
of a society.
In the humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at t ...
, one sense of culture as an attribute of the individual has been the degree to which they have cultivated a particular level of sophistication in the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
, sciences, education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
, or manners. The level of cultural sophistication has also sometimes been used to distinguish civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
s from less complex societies. Such hierarchical perspectives on culture are also found in class-based distinctions between a high culture
High culture is a subculture that emphasizes and encompasses the cultural objects of aesthetic value, which a society collectively esteem as exemplary art, and the intellectual works of philosophy, history, art, and literature that a society con ...
of the social elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (french: élite, from la, eligere, to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. ...
and a low culture
In sociology, the term Low culture identifies the forms of popular culture that have Commoner, mass appeal, which is in contrast to High culture, which has a limited appeal to a smaller proportion of the populace. Culture theory proposes that b ...
, popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
, or folk culture
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging fro ...
of the lower classes, distinguished by the stratified access to cultural capital
In the field of sociology, cultural capital comprises the social assets of a person (education, intellect, style of speech, style of dress, etc.) that promote social mobility in a stratified society. Cultural capital functions as a social relatio ...
. In common parlance, culture is often used to refer specifically to the symbolic markers used by ethnic groups
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
to distinguish themselves visibly from each other such as body modification
Body modification (or body alteration) is the deliberate altering of the human anatomy or human physical appearance. In its broadest definition it includes skin tattooing, socially acceptable decoration (''e.g.'', common ear piercing in many so ...
, clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natura ...
or jewelry
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
. Mass culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in ...
refers to the mass-produced
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and ba ...
and mass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
ted forms of consumer culture that emerged in the 20th century. Some schools of philosophy, such as Marxism
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
and critical theory
A critical theory is any approach to social philosophy that focuses on society and culture to reveal, critique and challenge power structures. With roots in sociology and literary criticism, it argues that social problems stem more from s ...
, have argued that culture is often used politically as a tool of the elites to manipulate the proletariat
The proletariat (; ) is the social class of wage-earners, those members of a society whose only possession of significant economic value is their labour power (their capacity to work). A member of such a class is a proletarian. Marxist philo ...
and create a false consciousness
In Marxist theory, false consciousness is a term describing the ways in which material, ideological, and institutional processes are said to mislead members of the proletariat and other class actors within capitalist societies, concealing the ...
. Such perspectives are common in the discipline of cultural studies
Cultural studies is an interdisciplinary field that examines the political dynamics of contemporary culture (including popular culture) and its historical foundations. Cultural studies researchers generally investigate how cultural practices re ...
. In the wider social sciences
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of so ...
, the theoretical perspective of cultural materialism holds that human symbolic culture arises from the material conditions of human life, as humans create the conditions for physical survival, and that the basis of culture is found in evolved biological dispositions.
When used as a count noun
In linguistics, a count noun (also countable noun) is a noun that can be modified by a quantity and that occurs in both singular and plural forms, and that can co-occur with quantificational determiners like ''every'', ''each'', ''several'', e ...
, a "culture" is the set of customs, tradition
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or ...
s, and values of a society or community, such as an ethnic group or nation. Culture is the set of knowledge acquired over time. In this sense, multiculturalism
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for " ethnic pluralism", with the two terms often used interchang ...
values the peaceful coexistence and mutual respect between different cultures inhabiting the same planet. Sometimes "culture" is also used to describe specific practices within a subgroup of a society, a subculture
A subculture is a group of people within a culture that differentiates itself from the parent culture to which it belongs, often maintaining some of its founding principles. Subcultures develop their own norms and values regarding cultural, poli ...
(e.g. "bro culture
Bro culture is a subculture of young people (originally young men, hence "brother culture") who spend time partying with others like themselves. Although the original image of the bro lifestyle is associated with sports apparel and fraternities, ...
"), or a counterculture
A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores.Eric Donald Hirsch. ''The Dictionary of Cultural Literacy''. H ...
. Within cultural anthropology
Cultural anthropology is a branch of anthropology focused on the study of cultural variation among humans. It is in contrast to social anthropology, which perceives cultural variation as a subset of a posited anthropological constant. The portma ...
, the ideology and analytical stance of cultural relativism
Cultural relativism is the idea that a person's beliefs and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture. Proponents of cultural relativism also tend to argue that the norms and values of one culture should not be evaluated ...
hold that cultures cannot easily be objectively ranked or evaluated because any evaluation is necessarily situated within the value system of a given culture.
Etymology
The modern term "culture" is based on a term used by theancient Roman
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–50 ...
orator Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
in his ''Tusculanae Disputationes
The ''Tusculanae Disputationes'' (also ''Tusculanae Quaestiones''; English: ''Tusculan Disputations'') is a series of five books written by Cicero, around 45 BC, attempting to popularise Greek philosophy in Ancient Rome, including Stoicism. It is s ...
'', where he wrote of a cultivation of the soul or ''"cultura animi,"'' using an agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wi ...
for the development of a philosophical soul, understood teleologically as the highest possible ideal for human development. Samuel Pufendorf
Samuel Freiherr von Pufendorf (8 January 1632 – 26 October 1694) was a German jurist, political philosopher, economist and historian. He was born Samuel Pufendorf and ennobled in 1694; he was made a baron by Charles XI of Sweden a few months b ...
took over this metaphor in a modern context, meaning something similar, but no longer assuming that philosophy was man's natural perfection. His use, and that of many writers after him, "''refers to all the ways in which human beings overcome their original barbarism
Barbarism, barbarity, or barbarous may refer to:
* Barbarism (linguistics), a non-standard word, expression, or pronunciation
** Hybrid words, formerly called "barbarisms"
* Any society construed as barbarian
** Barbarian invasions, a period of ...
, and through artifice, become fully human."''
In 1986, philosopher Edward S. Casey wrote, "The very word ''culture'' meant 'place tilled' in Middle English, and the same word goes back to Latin ''colere'', 'to inhabit, care for, till, worship' and ''cultus'', 'A cult, especially a religious one.' To be cultural, to have a culture, is to inhabit a place sufficiently intensely to cultivate it—to be responsible for it, to respond to it, to attend to it caringly."
Culture described by Richard Velkley: ... originally meant the cultivation of the soul or mind, acquires most of its later modern meaning in the writings of the 18th-century German thinkers, who were on various levels developingIn the words of anthropologist E.B. Tylor, it is "that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, art, morals, law, custom and any other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society." Alternatively, in a contemporary variant, "Culture is defined as a social domain that emphasizes the practices, discourses and material expressions, which, over time, express the continuities and discontinuities of social meaning of a life held in common. The ''Rousseau Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...'s criticism of "modern Modern may refer to: History *Modern history ** Early Modern period ** Late Modern period *** 18th century *** 19th century *** 20th century ** Contemporary history * Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century Philosophy ...liberalism Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostilit ...and Enlightenment." Thus a contrast between "culture" and "civilization A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system). ..." is usually implied in these authors, even when not expressed as such.
Cambridge English Dictionary
The ''Cambridge Advanced Learner's Dictionary'' (abbreviated ''CALD'') was first published in 1995 under the name ''Cambridge International Dictionary of English'', by the Cambridge University Press. The dictionary has over 140,000 words, ...
'' states that culture is "the way of life, especially the general customs and beliefs, of a particular group of people at a particular time." Terror management theory posits that culture is a series of activities and worldviews that provide humans with the basis for perceiving themselves as "person of worth within the world of meaning"—raising themselves above the merely physical aspects of existence, in order to deny the animal insignificance and death that ''Homo sapiens'' became aware of when they acquired a larger brain.
The word is used in a general sense as the evolved ability to categorize and represent experiences with symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
s and to act imaginatively and creatively. This ability arose with the evolution of behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current '' Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterize ...
in humans around 50,000 years ago and is often thought to be unique to human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s. However, some other species have demonstrated similar, though much less complicated, abilities for social learning. It is also used to denote the complex networks of practices and accumulated knowledge and ideas that are transmitted through social interaction
Interaction is action that occurs between two or more objects, with broad use in philosophy and the sciences. It may refer to:
Science
* Interaction hypothesis, a theory of second language acquisition
* Interaction (statistics)
* Interaction ...
and exist in specific human groups, or cultures, using the plural form.
Change

Raimon Panikkar
Raimon Panikkar Alemany, also known as Raimundo Panikkar and Raymond Panikkar (November 2, 1918 – August 26, 2010), was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and a proponent of Interfaith dialogue. As a scholar, he specialized in comparative reli ...
identified 29 ways in which cultural change Culture change is a term used in public policy making that emphasizes the influence of cultural capital on individual and community behavior. It has been sometimes called repositioning of culture, which means the reconstruction of the cultural conce ...
can be brought about, including growth, development, evolution, involution
Involution may refer to:
* Involute, a construction in the differential geometry of curves
* '' Agricultural Involution: The Processes of Ecological Change in Indonesia'', a 1963 study of intensification of production through increased labour inpu ...
, renovation, reconception, reform, innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed enti ...
, revivalism, revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
, mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
, progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension w ...
, diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical ...
, osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region ...
, borrowing, eclecticism
Eclecticism is a conceptual approach that does not hold rigidly to a single paradigm or set of assumptions, but instead draws upon multiple theories, styles, or ideas to gain complementary insights into a subject, or applies different theories i ...
, syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
, modernization, indigenization
Indigenization is the act of making something more native; transformation of some service, idea, etc. to suit a local culture, especially through the use of more indigenous people in public administration, employment and other fields.
The term i ...
, and transformation. In this context, modernization could be viewed as adoption of Enlightenment era beliefs and practices, such as science, rationalism, industry, commerce, democracy, and the notion of progress. Rein Raud
Rein Raud (born 21 December 1961) is an Estonian scholar and author.
Early life
He was born in 1961 in the family of Eno Raud and Aino Pervik, both children's authors. He is the eldest of three children. His younger brother Mihkel Raud is a ...
, building on the work of Umberto Eco
Umberto Eco (5 January 1932 – 19 February 2016) was an Italian medievalist, philosopher, semiotician, novelist, cultural critic, and political and social commentator. In English, he is best known for his popular 1980 novel ''The Name of th ...
, Pierre Bourdieu
Pierre Bourdieu (; 1 August 1930 – 23 January 2002) was a French sociologist and public intellectual. Bourdieu's contributions to the sociology of education, the theory of sociology, and sociology of aesthetics have achieved wide influence ...
and Jeffrey C. Alexander, has proposed a model of cultural change based on claims and bids, which are judged by their cognitive adequacy
Rein Raud (born 21 December 1961) is an Estonian scholar and author.
Early life
He was born in 1961 in the family of Eno Raud and Aino Pervik, both children's authors. He is the eldest of three children. His younger brother Mihkel Raud is a ...
and endorsed or not endorsed by the symbolic authority of the cultural community in question.


Cultural invention A cultural invention is any innovation developed by people. Cultural inventions include sets of behaviour adopted by groups of people. They are perpetuated by being passed on to others within the group or outside it. They are also passed on to futur ...
has come to mean any innovation that is new and found to be useful to a group of people and expressed in their behavior but which does not exist as a physical object. Humanity is in a global "accelerating culture change period," driven by the expansion of international commerce, the mass media, and above all, the human population
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
explosion, among other factors. Culture repositioning means the reconstruction of the cultural concept of a society.
 Cultures are internally affected by both forces encouraging change and forces resisting change. These forces are related to both
Cultures are internally affected by both forces encouraging change and forces resisting change. These forces are related to both social structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
s and natural events, and are involved in the perpetuation of cultural ideas and practices within current structures, which themselves are subject to change.
Social conflict and the development of technologies can produce changes within a society by altering social dynamics and promoting new cultural models, and spurring or enabling generative action. These social shifts may accompany ideological
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied prim ...
shifts and other types of cultural change. For example, the U.S. feminist movement
The feminist movement (also known as the women's movement, or feminism) refers to a series of social movements and political campaigns for Radical politics, radical and Liberalism, liberal reforms on women's issues created by the inequality b ...
involved new practices that produced a shift in gender relations, altering both gender and economic structures. Environmental conditions may also enter as factors. For example, after tropical forests returned at the end of the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
, plants suitable for domestication were available, leading to the invention of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, which in turn brought about many cultural innovations and shifts in social dynamics.
Cultures are externally affected via contact between societies, which may also produce—or inhibit—social shifts and changes in cultural practices. War or competition over resources may impact technological development or social dynamics. Additionally, cultural ideas may transfer from one society to another, through diffusion or acculturation. In diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
, the form of something (though not necessarily its meaning) moves from one culture to another. For example, Western restaurant chains and culinary brands sparked curiosity and fascination to the Chinese as China opened its economy to international trade in the late 20th-century. "Stimulus diffusion" (the sharing of ideas) refers to an element of one culture leading to an invention or propagation in another. "Direct borrowing," on the other hand, tends to refer to technological or tangible diffusion from one culture to another. Diffusion of innovations
Diffusion of innovations is a theory that seeks to explain how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread. Everett Rogers, a professor of communication studies, popularized the theory in his book ''Diffusion of Innovations''; the book ...
theory presents a research-based model of why and when individuals and cultures adopt new ideas, practices, and products.Stephen Wolfram (May 16, 2017) A New Kind of Science: A 15-Year ViewAs applied to the computational universe
Acculturation
Acculturation is a process of social, psychological, and cultural change that stems from the balancing of two cultures while adapting to the prevailing culture of the society. Acculturation is a process in which an individual adopts, acquires and ...
has different meanings. Still, in this context, it refers to the replacement of traits of one culture with another, such as what happened to certain Native American tribes and many indigenous peoples across the globe during the process of colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
. Related processes on an individual level include assimilation (adoption of a different culture by an individual) and transculturation
Transculturation is a term coined by Cuban anthropologist Fernando Ortiz in 1940 (from the article Our America by José Martí) to describe the phenomenon of merging and converging cultures. Transculturation encompasses more than transition from ...
. The transnational flow of culture has played a major role in merging different cultures and sharing thoughts, ideas, and beliefs.
Early modern discourses
German Romanticism
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (, , ; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and ...
(1724–1804) formulated an individualist definition of "enlightenment" similar to the concept of ''bildung
''Bildung'' (, "education", "formation", etc.) refers to the German tradition of self-cultivation (as related to the German for: creation, image, shape), wherein philosophy and education are linked in a manner that refers to a process of both pe ...
'': "Enlightenment is man's emergence from his self-incurred immaturity." He argued that this immaturity comes not from a lack of understanding, but from a lack of courage to think independently. Against this intellectual cowardice, Kant urged: "" ("Dare to be wise!"). In reaction to Kant, German scholars such as Johann Gottfried Herder
Johann Gottfried von Herder ( , ; 25 August 174418 December 1803) was a German philosopher, theologian, poet, and literary critic. He is associated with the Enlightenment, ''Sturm und Drang'', and Weimar Classicism.
Biography
Born in Mohrun ...
(1744–1803) argued that human creativity, which necessarily takes unpredictable and highly diverse forms, is as important as human rationality. Moreover, Herder proposed a collective form of : "For Herder, was the totality of experiences that provide a coherent identity, and sense of common destiny, to a people."
 In 1795, the Prussian linguist and philosopher
In 1795, the Prussian linguist and philosopher Wilhelm von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Christian Karl Ferdinand von Humboldt (, also , ; ; 22 June 1767 – 8 April 1835) was a Prussian philosopher, linguist, government functionary, diplomat, and founder of the Humboldt University of Berlin, which was named after ...
(1767–1835) called for an anthropology that would synthesize Kant's and Herder's interests. During the Romantic era
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
, scholars in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, especially those concerned with nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
movements—such as the nationalist struggle to create a "Germany" out of diverse principalities, and the nationalist struggles by ethnic minorities against the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
—developed a more inclusive notion of culture as "worldview
A worldview or world-view or ''Weltanschauung'' is the fundamental cognitive orientation of an individual or society encompassing the whole of the individual's or society's knowledge, culture, and point of view. A worldview can include natural p ...
" (). According to this school of thought, each ethnic group has a distinct worldview that is incommensurable with the worldviews of other groups. Although more inclusive than earlier views, this approach to culture still allowed for distinctions between "civilized" and "primitive" or "tribal" cultures.
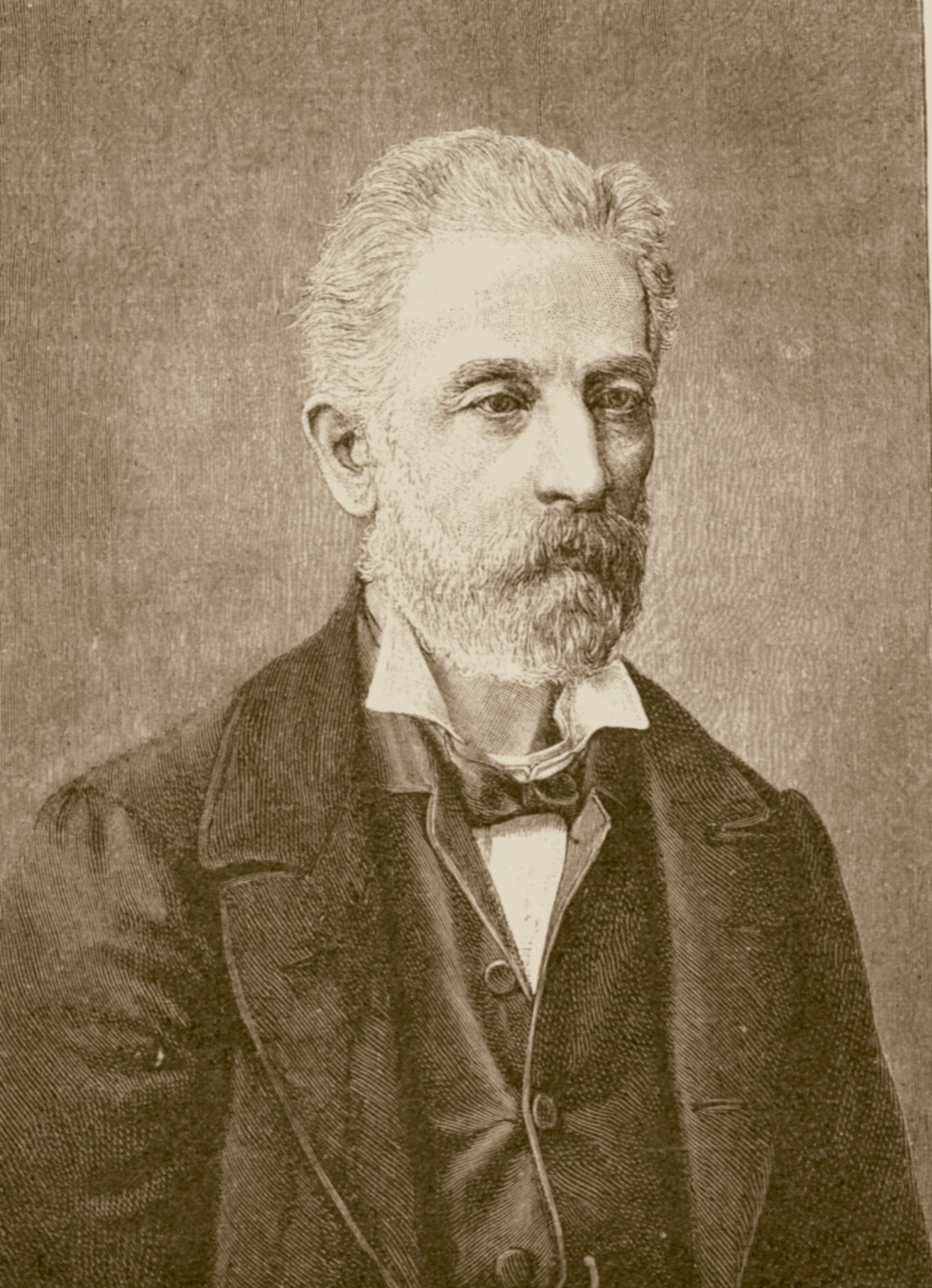
In 1860, Adolf Bastian
Adolf Philipp Wilhelm Bastian (26 June 18262 February 1905) was a 19th-century polymath best remembered for his contributions to the developm