Croatia–Hungary Relations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Diplomatic relations between
 Trade between Croatia and Hungary amounted to €625,083 in 2009, a decrease from €894,270 in 2008. In 2009 Croatian exports to Hungary reached €132,474, while Hungarian exports to Croatia were worth €492,609. Overall, the 2009 trade volume represented 2.75 percent of total Croatian
Trade between Croatia and Hungary amounted to €625,083 in 2009, a decrease from €894,270 in 2008. In 2009 Croatian exports to Hungary reached €132,474, while Hungarian exports to Croatia were worth €492,609. Overall, the 2009 trade volume represented 2.75 percent of total Croatian  Croatia and Hungary coordinate the development of infrastructure, especially transportation routes. Pan-European corridors Vb and Vc connect Budapest to the
Croatia and Hungary coordinate the development of infrastructure, especially transportation routes. Pan-European corridors Vb and Vc connect Budapest to the

 According to the 2001 census there are 16,595
According to the 2001 census there are 16,595

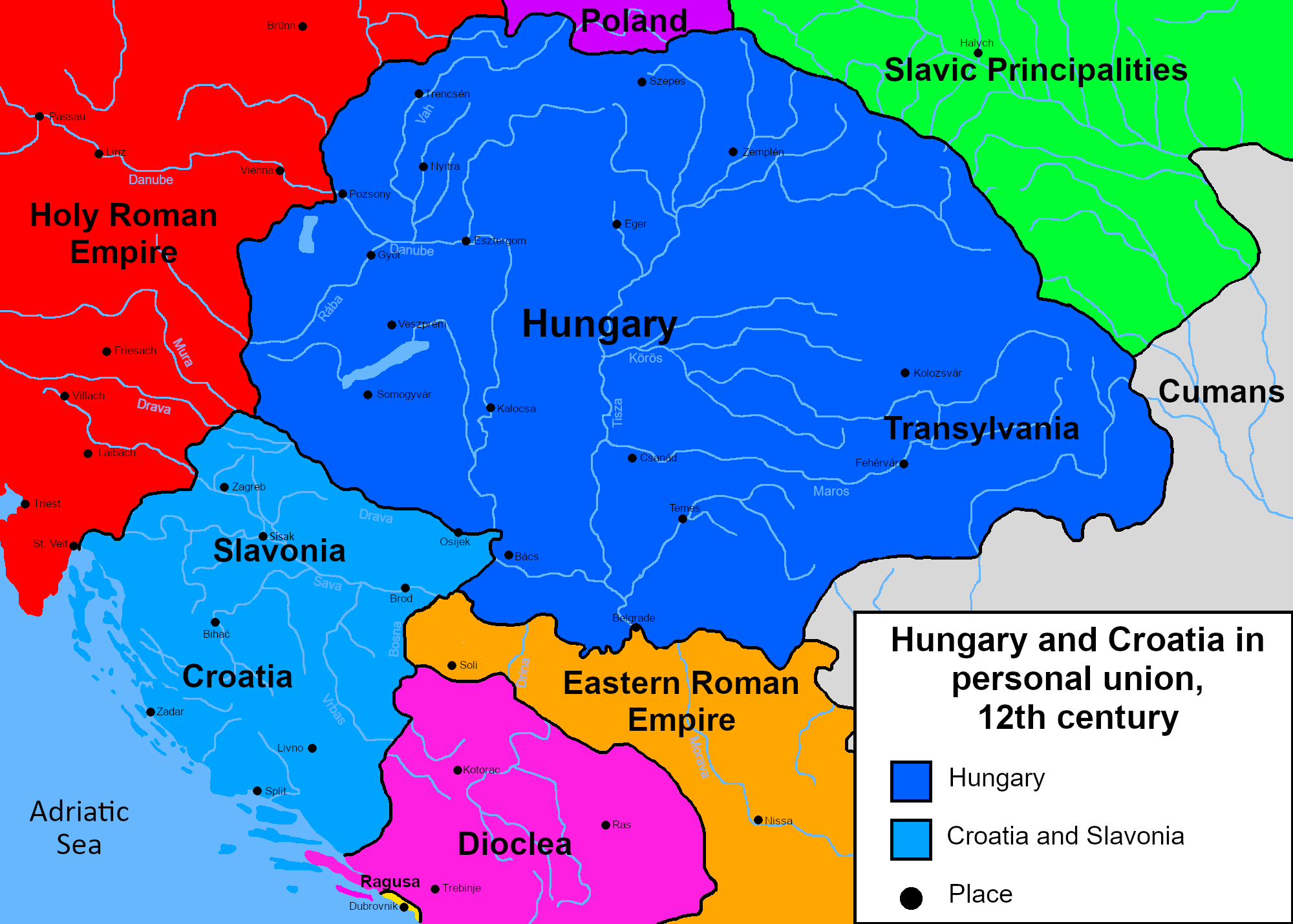 When Stjepan II died in 1091, ending the Trpimirović dynasty rule in the medieval kingdom of Croatia,
When Stjepan II died in 1091, ending the Trpimirović dynasty rule in the medieval kingdom of Croatia,
 During the 1830s and 1840s
During the 1830s and 1840s
 The
The
Croatian Minister of Foreign Affairs and European Integration: list of bilateral treaties with Hungary
Croatian embassy in Budapest (in Croatian and Hungarian only)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Croatia-Hungary relations
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
were established on 18 January 1992 following Croatia's independence from SFR Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yug ...
.
Croatia has an embassy in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
a general consulate in Pécs
Pécs ( , ; hr, Pečuh; german: Fünfkirchen, ; also known by other #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the countr ...
and a consulate in Nagykanizsa
Nagykanizsa (; hr, Velika Kaniža/Velika Kanjiža, or just ''Kaniža/Kanjiža''; german: Großkirchen, Groß-Kanizsa; it, Canissa; sl, Velika Kaniža; tr, Kanije), known colloquially as Kanizsa, is a medium-sized city in Zala County in southw ...
, while Hungary has an embassy in Zagreb
Zagreb ( , , , ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Croatia#List of cities and towns, largest city of Croatia. It is in the Northern Croatia, northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slop ...
, a general consulate in Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja ...
and honorary consulates in Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
, Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enterta ...
and Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
.
In 1102 the previously-independent Kingdom of Croatia Kingdom of Croatia may refer to:
* Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), an independent medieval kingdom
* Croatia in personal union with Hungary (1102–1526), a kingdom in personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary
* Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg) (152 ...
and Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
entered personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
and the two were henceforth ruled by the same monarch. Following the Ottoman conquests and a disastrous defeat at the Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and thos ...
in 1526, Croatian nobility elected the Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand I as the new king of Croatia. The Hungarian nobility was divided but the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
annexed the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, keeping Croatia and Hungary under a single crown. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 or fully Hungarian Civic Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas. Although th ...
Croatia sided with the Austrians so Croatian Ban Josip Jelačić
Count Josip Jelačić von Bužim (16 October 180120 May 1859; also spelled ''Jellachich'', ''Jellačić'' or ''Jellasics''; hr, Josip grof Jelačić Bužimski; hu, Jelasics József) was a Croatian lieutenant field marshal in the Imperial-Roy ...
helped Austria to defeat the Hungarian forces in 1849 and ushering in a period of Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationa ...
. By the 1860s the failure of this policy became apparent, leading to the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867
The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 (german: Ausgleich, hu, Kiegyezés) established the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary. The Compromise only partially re-established the former pre-1848 sovereignty and status of the Kingdom of Hungary ...
and the creation of a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
between the crowns of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
. The issue of Croatia's status was resolved by the Croatian–Hungarian Settlement
The Croatian–Hungarian Settlement ( hr, Hrvatsko-ugarska nagodba, hu, magyar–horvát kiegyezés, german: Kroatisch-Ungarischer Ausgleich) was a pact signed in 1868 that governed Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia's political status in th ...
of 1868, when the kingdoms of Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
and Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja ...
were united into Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia
The Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia ( hr, Kraljevina Hrvatska i Slavonija; hu, Horvát-Szlavónország or ; de-AT, Königreich Kroatien und Slawonien) was a nominally autonomous kingdom and constitutionally defined separate political nation with ...
. Following the breakup of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
after its defeat in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Croatian Parliament
The Croatian Parliament ( hr, Hrvatski sabor) or the Sabor is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Croatia. Under the terms of the Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the people and is vested with legislative power. The Sabor ...
declared independence on 29 October 1918 and decided to join the newly formed State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( sh, Država Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba / ; sl, Država Slovencev, Hrvatov in Srbov) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( ...
, ending Habsburg rule and the personal union with Hungary after 816 years. Through the Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in ...
, Hungary lost Međimurje County
Međimurje County (; hr, Međimurska županija ; hu, Muraköz megye) is a triangle-shaped Counties of Croatia, county in the northernmost part of Croatia, roughly corresponding to the historical and geographical region of Međimurje (region), ...
and the southern part of Baranya Baranya or Baranja may refer to:
* Baranya (region) or Baranja, a region in Hungary and Croatia
* Baranya County, a county in modern Hungary
* Baranya County (former), a county in the historic Kingdom of Hungary
* Baranya, Hungarian name of villag ...
to Croatia. Since World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, relations between two states have been defined by cooperation with Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
, Soviets
Soviet people ( rus, сове́тский наро́д, r=sovyétsky naród), or citizens of the USSR ( rus, гра́ждане СССР, grázhdanye SSSR), was an umbrella demonym for the population of the Soviet Union.
Nationality policy in th ...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
until the revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Natio ...
and the breakup of Yugoslavia
The breakup of Yugoslavia occurred as a result of a series of political upheavals and conflicts during the early 1990s. After a period of political and economic crisis in the 1980s, constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
. Hungary recognised Croatian independence with the rest of the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
in 1992, and supported Croatia during the Croatian War of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serb-controlled Yugosl ...
.
Croatian and Hungarian high-ranking officials usually meet several times a year. Trade between Croatia and Hungary amounted $1.020 bln in 2012, largely consisting of Hungarian exports to Croatia. Hungarian tourists contribute significantly to Croatian tourism; in 2009, a total of 323,000 visited Croatia, including the Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán
Viktor Mihály Orbán (; born 31 May 1963) is a Hungarian politician who has served as prime minister of Hungary since 2010, previously holding the office from 1998 to 2002. He has presided over Fidesz since 1993, with a brief break between 20 ...
who spends his summer holidays in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
for last few decades. Both countries coordinate the development of cross-border infrastructure. Pan-European corridors Vb and Vc connect Budapest to the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
via Zagreb
Zagreb ( , , , ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Croatia#List of cities and towns, largest city of Croatia. It is in the Northern Croatia, northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slop ...
and Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja ...
. Both countries have sizable minorities living across their common border, and both have passed laws to protect their minority rights
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
Civil-rights movements ofte ...
.
Croatia and Hungary are parties to 96 bilateral treaties and members of a number of multinational organizations, including NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
.
Country comparison
Present
Diplomatic relations
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
established diplomatic relations on 16 and 18 January 1992, after Hungary recognised the independence of Croatia
The independence of Croatia was a process started with the changes in the political system and the constitutional changes in 1990 that transformed the Socialist Republic of Croatia into the Republic of Croatia, which in turn proclaimed the Chris ...
on 15 January 1992. As of December 2011 Croatia maintains an embassy in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
(headed by ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sov ...
Ivan Bandić), a consulate
A consulate is the office of a consul. A type of diplomatic mission, it is usually subordinate to the state's main representation in the capital of that foreign country (host state), usually an embassy (or, only between two Commonwealth coun ...
general in Pécs
Pécs ( , ; hr, Pečuh; german: Fünfkirchen, ; also known by other #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the countr ...
and a consulate in Nagykanizsa
Nagykanizsa (; hr, Velika Kaniža/Velika Kanjiža, or just ''Kaniža/Kanjiža''; german: Großkirchen, Groß-Kanizsa; it, Canissa; sl, Velika Kaniža; tr, Kanije), known colloquially as Kanizsa, is a medium-sized city in Zala County in southw ...
. The Nagykanizsa consulate is led by an honorary consul
A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, as well as to facilitate trade and friendship between the people ...
. Hungary maintains an embassy in Zagreb
Zagreb ( , , , ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Croatia#List of cities and towns, largest city of Croatia. It is in the Northern Croatia, northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slop ...
and consulates in Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
and Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enterta ...
. The embassy is headed by ambassador Gábor Iván; the offices also include an army and air attaché office in the Republic of Croatia (headed by László Hajas) and the Office for Economic Affairs of the Embassy of the Republic of Hungary in the Republic of Croatia (headed by András Péter Závoczky, Counsellor for Economy and Trade).
Croatian and Hungarian high-ranking officials (including heads of state, prime ministers and foreign ministers) meet several times a year. In addition, Croatian and Hungarian governments have occasionally held joint sessions since January 2006.
Economy and infrastructure
 Trade between Croatia and Hungary amounted to €625,083 in 2009, a decrease from €894,270 in 2008. In 2009 Croatian exports to Hungary reached €132,474, while Hungarian exports to Croatia were worth €492,609. Overall, the 2009 trade volume represented 2.75 percent of total Croatian
Trade between Croatia and Hungary amounted to €625,083 in 2009, a decrease from €894,270 in 2008. In 2009 Croatian exports to Hungary reached €132,474, while Hungarian exports to Croatia were worth €492,609. Overall, the 2009 trade volume represented 2.75 percent of total Croatian foreign trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significant s ...
. Croatian–Hungarian trade comprises only a small fraction of total Hungarian foreign trade, reaching 0.54 percent of the total in 2009. Hungarian investments in Croatia rose sharply in 2003, reaching the fourth ranking in that year following investments exceeding US$630 million, largely in tourism and manufacturing. The largest single investment that year was the purchase of more than 25 percent of the stock of INA for US$500 million by the MOL Group
MOL Plc. ( hu, Magyar OLaj- és Gázipari Részvénytársaság, lit=Hungarian Oil and Gas Public Limited Company), also commonly known as MOL Group, is a Hungarian multinational oil and gas company headquartered in Budapest, Hungary. Members of M ...
. By 2011, the MOL Group increased its stake in INA to 47.16 percent.
Hungarian tourists contribute significantly to the Croatian tourist industry; in 2009, a total of 323,000 Hungarians visited Croatia as tourists. A total of 1.644 million overnight stays were made by Hungarian tourists in that year alone, ranking Hungarian tourists seventh in the number of nights spent in Croatia (behind the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their n ...
, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Austrians
, pop = 8–8.5 million
, regions = 7,427,759
, region1 =
, pop1 = 684,184
, ref1 =
, region2 =
, pop2 = 345,620
, ref2 =
, region3 =
, pop3 = 197,990
, ref3 ...
, Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, c ...
and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
). At the same time, the Hungarian tourists spent more than 143 million kuna
Kuna may refer to:
Places
* Kuna, Idaho, a town in the United States
** Kuna Caves, a lava tube in Idaho
* Kuna Peak, a mountain in California
* , a village in the Orebić municipality, Croatia
* , a village in the Konavle municipality, Croatia ...
( €19 million) in Croatia, representing a sharp increase from 69.5 million kuna ( €9.3 million) spent in 2008. In 2009, 103,000 Croatians visited Hungary (excluding family and friend visits) in 356,000 overnight stays, spending 204,000 kuna ( €27,000). This spending represented a 250-percent increase from 2008.
 Croatia and Hungary coordinate the development of infrastructure, especially transportation routes. Pan-European corridors Vb and Vc connect Budapest to the
Croatia and Hungary coordinate the development of infrastructure, especially transportation routes. Pan-European corridors Vb and Vc connect Budapest to the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
via Zagreb and Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
(Vb) and to Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja ...
and Ploče
Ploče (; it, Porto Tolero) is a town and seaport in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia.
Geography
Ploče is located on the Adriatic coast in Dalmatia just north of the Neretva Delta and is the natural seaside endpoint of most north-south ...
(Vc). The Pan-European corridor Vb comprises road and rail links between the Hungarian and Croatian capitals and the Port of Rijeka
The Port of Rijeka ( hr, Luka Rijeka, ) is a seaport in Rijeka, Croatia, located on the shore of the Kvarner Gulf in the Adriatic Sea. The first records of the port date to 1281. It was the main port of the History of Hungary 1700–1919, Kingdom ...
. The corridor's road component primarily consists of the M7, the A4 and the A6 motorways (as well as several other connecting motorway sections) completed on 22 October 2008. The rail component of the corridor largely uses the route completed in 1873, but it is planned to be rebuilt to increase its capacity. The Pan-European corridor Vc primarily consists of the M6 and the A5 motorways; however, as of December 2011 the motorway is not completed. Other infrastructure jointly developed by Croatia and Hungary includes a €395 million gas pipeline and two electric-power lines. On the border between Croatia and Hungary there are six international-road border crossings, three rail border crossings and five local-traffic border crossings. Citizens of Croatia and Hungary may cross the border with a valid passport or an identity card
An identity document (also called ID or colloquially as papers) is any documentation, document that may be used to prove a person's identity. If issued in a small, standard credit card size form, it is usually called an identity card (IC, ID c ...
for stays of up to 90 days.
Minorities and migrations

Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
living in Croatia, representing 0.37 percent of the population. In 2000, there were 15,597 Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, G ...
living in Hungary, accounting for 0.15 percent of the total population. The Hungarian minority in Croatia is recognised by the Constitution of Croatia
The Constitution of the Republic of Croatia ( hr, Ustav Republike Hrvatske) is promulgated by the Croatian Parliament.
History
While it was part of the socialist Yugoslavia, the Socialist Republic of Croatia had its own Constitution under the ...
; minority rights
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
Civil-rights movements ofte ...
(including official use of Hungarian by local governments
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
and education in Hungarian) are safeguarded by legislation enacted by the Sabor
The Croatian Parliament ( hr, Hrvatski sabor) or the Sabor is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Croatia. Under the terms of the Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the people and is vested with legislative power. The Sabor ...
. Seven municipalities in Croatia introduced Hungarian for official use (either in part of their territory or the entire municipality), depending on the distribution of the Hungarian population there. There are five Hungarian minority organizations in Croatia, and the Hungarian minority is guaranteed one seat in the Croatian Parliament
The Croatian Parliament ( hr, Hrvatski sabor) or the Sabor is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Croatia. Under the terms of the Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the people and is vested with legislative power. The Sabor ...
.
The Hungarian government recognised Croats as a minority native to Hungary; it has decided to implement the optional regulations of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, the ...
with respect to Croatian and establish a minority self-government for the Croatian minority in Hungary, guaranteeing cultural autonomy
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
Civil-rights movements oft ...
. The Croatian minority set up 127 local and 7 county self-governments in Hungary. There are concerns that Croatian minority rights in Hungary are being diminished, but the president of Croatia has assessed that both Croatian and Hungarian minority policies were appropriate. The Croatian minority in Hungary is particularly active in Pécs
Pécs ( , ; hr, Pečuh; german: Fünfkirchen, ; also known by other #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the countr ...
, where the Scientific Institute of Croats in Hungary and the Croatian Theatre have been established.
The number of migrants between Croatia and Hungary is very low; in 2009, only 22 people emigrated from Hungary to Croatia while a single person emigrated from Croatia to Hungary.
Cultural and scientific cooperation
Croatia and Hungary have agreed to the Cultural Cooperation Programme, which defines cooperation and cultural exchange in the fields of music, theatre and dance, and with respect to the arts, museums, galleries, literature, publishing, libraries, archives, film and cultural-heritage protection. The programme was agreed to on 7 November 2011 in Budapest by secretaries of theCroatian Ministry of Culture
The Ministry of Culture and Media ( hr, Ministarstvo kulture i medija) is a ministry of the Croatian government in charge of preserving the country's natural and cultural heritage and overseeing its development. The ministry in its present form w ...
and the Hungarian Ministry of National Resources. The programme pertains to the 2012–2014 period and represents a continuation of cultural cooperation through cultural exchange, outside the framework of formal agreements. Cultural, educational and scientific cooperation between the two countries is covered by a treaty of 16 March 1994, with additional treaties regulating diploma recognitions since 16 June 1997 and additional treaties and protocols on scientific and technological cooperation signed in 2002 and 2009. The scientific and educational cooperation entails the awarding of scholarships and bilateral research projects.
Bilateral treaties and multinational organizations
Croatia and Hungary have either signed or succeeded 133 different treaties and other agreements. Some were originally signed by Hungary andSFR Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yug ...
, while Croatia succeeded relevant documents pursuant to decisions of the Badinter Arbitration Committee The Arbitration Commission of the Conference on Yugoslavia (commonly known as Badinter Arbitration Committee) was an arbitration body set up by the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community (EEC) on 27 August 1991 to provide the confer ...
.
As of December 2011 96 remain in force, regulating various aspects of relations between the countries (including minority rights, diplomatic relations, cultural and scientific cooperation, trade and economic relations, river navigation, border control and air transport). Free-trade agreements were signed, but have since been repealed through adoption of similar agreements with the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
. There were also agreements made with a limited period of application, pertaining to sporting-event security.
Croatia and Hungary are members of several multinational organizations, including the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
and the Central European Initiative
The Central European Initiative (CEI) is a forum of regional cooperation in Central and Eastern Europe, counting 18 member states. It was formed in Budapest in 1989. The body was developed on the basis of earlier experiences with The Alps-Adriatic ...
. In addition, Hungary is a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EU). On 9 December 2011, Croatia signed an EU accession treaty and is expected to become a member on 1 July 2013. Both countries are also taking part in the formulation and implementation of the Danube Strategy
The Danube Strategy of the European Union aimed at closer cooperation between the states along the Danube. The focus is on the areas of infrastructure, environmental protection, wealth creation and good governance.
History of the Danube Strategy ...
, focusing on transport, environmental and economic development of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
area and involving all countries along its banks.
History
Personal union

 When Stjepan II died in 1091, ending the Trpimirović dynasty rule in the medieval kingdom of Croatia,
When Stjepan II died in 1091, ending the Trpimirović dynasty rule in the medieval kingdom of Croatia, Ladislaus I of Hungary
Ladislaus I ( hu, László, hr, Ladislav, sk, Ladislav, pl, Władysław; 1040 – 29 July 1095), also known as Saint Ladislas, was King of Hungary from 1077 and King of Croatia from 1091. He was the second son of King Béla I of Hungary and ...
claimed the Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
n crown. Opposition to the claim led to a war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
and the personal union of Croatia and Hungary
The Kingdom of Croatia ( la, Regnum Croatiae; hr, Kraljevina Hrvatska, ''Hrvatsko kraljevstvo'', ''Hrvatska zemlja'') entered a personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary in 1102, after a period of rule of kings from the Trpimirović and Svetosl ...
in 1102, ruled by Coloman Coloman, es, Colomán (german: Koloman (also Slovak, Czech, Croatian), it, Colomanno, ca, Colomà; hu, Kálmán)
The Germanic origin name Coloman used by Germans since the 9th century.
* Coloman, King of Hungary
* Coloman of Galicia-Lodomeria ...
. For the next four centuries, Croatia was ruled by the Sabor
The Croatian Parliament ( hr, Hrvatski sabor) or the Sabor is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Croatia. Under the terms of the Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the people and is vested with legislative power. The Sabor ...
(parliament) and a Ban of Croatia
Ban of Croatia ( hr, Hrvatski ban) was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) an ...
(viceroy) appointed by the king. This period saw an increasing threat of Ottoman conquest and a struggle against the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
for control of coastal areas. The Venetians gained control over most of Dalmatia by 1428 except for the city-state of Dubrovnik
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubr ...
, which became independent. Ottoman conquests led to the 1493 Battle of Krbava Field
The Battle of Krbava Field ( hr, Bitka na Krbavskom polju, Krbavska bitka; hu, Korbávmezei csata; tr, Krbava Muharebesi) was fought between the Ottoman Empire of Bayezid II and an army of the Kingdom of Croatia, at the time in personal unio ...
and the 1526 Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and thos ...
, both ending in decisive Ottoman victories against Hungarian and Croatian armies. King Louis II died at Mohács; in 1527, the assembly of Croatian nobility meeting at Cetin chose Ferdinand I of Habsburg
Ferdinand I ( es, Fernando I; 10 March 1503 – 25 July 1564) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564.Milan Kruhek: Cetin, grad izbornog sabo ...
as the new ruler of Croatia under the conditions that he provide protection to Croatia against the Ottoman Empire and respect its political rights. In political disarray, the divided Hungarian nobility
The Hungarian nobility consisted of a privileged group of individuals, most of whom owned landed property, in the Kingdom of Hungary. Initially, a diverse body of people were described as noblemen, but from the late 12th century only high- ...
elected two kings simultaneously: János Szapolyai
János or Janos may refer to:
* János, male Hungarian given name, a variant of John
Places
* Janos Municipality, a municipality of Chihuahua
** Janos, Chihuahua, town in Mexico
** Janos Biosphere Reserve, a nature reserve in Chihuahua
* Janos ...
and Ferdinand I. With the conquest of Buda
Buda (; german: Ofen, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Budim, Будим, Czech and sk, Budín, tr, Budin) was the historic capital of the Kingdom of Hungary and since 1873 has been the western part of the Hungarian capital Budapest, on the ...
by the Ottomans in 1541, the remaining part of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
not ruled by the Ottomans (known as the Royal Hungary
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
) was annexed by the Habsburgs; they ruled as Kings of Hungary, thus keeping the kingdoms of Hungary and Croatia under a single crown.
Habsburg rule
 During the 1830s and 1840s
During the 1830s and 1840s romantic nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
appeared in Croatia, inspiring the Croatian National Revival
The Illyrian movement ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Ilirski pokret, Илирски покрет; sl, Ilirsko gibanje) was a pan-South-Slavic cultural and political campaign with roots in the early modern period, and revived by a group of young Croatian inte ...
(a political and cultural campaign advocating the unity of all South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hu ...
in the empire). Its primary focus was the establishment of a standard language as a counterweight to Hungarian and the promotion of Croatian literature and culture. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 or fully Hungarian Civic Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas. Although th ...
, Croatia sided with the Austrians; Ban Josip Jelačić
Count Josip Jelačić von Bužim (16 October 180120 May 1859; also spelled ''Jellachich'', ''Jellačić'' or ''Jellasics''; hr, Josip grof Jelačić Bužimski; hu, Jelasics József) was a Croatian lieutenant field marshal in the Imperial-Roy ...
helped defeat the Hungarian forces in 1849, ushering in a period of Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
. By the 1860s the policy's failure became apparent, leading to the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867
The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 (german: Ausgleich, hu, Kiegyezés) established the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary. The Compromise only partially re-established the former pre-1848 sovereignty and status of the Kingdom of Hungary ...
and the creation of a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
between the crowns of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
. The treaty left the issue of Croatia's status to Hungary; this was resolved by the Croatian–Hungarian Settlement
The Croatian–Hungarian Settlement ( hr, Hrvatsko-ugarska nagodba, hu, magyar–horvát kiegyezés, german: Kroatisch-Ungarischer Ausgleich) was a pact signed in 1868 that governed Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia's political status in th ...
of 1868, when the kingdoms of Croatia and Slavonia were united. The Kingdom of Dalmatia remained under ''de facto'' Austrian control, while Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
retained its status of ''Corpus separatum
''Corpus separatum'' is a Latin term referring to a city or region which is given a special legal and political status different from its environment, but which falls short of being sovereign, or an independent city state. The term may refer to:
* ...
'' introduced in 1779. After Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
occupied Bosnia and Herzegovina following the 1878 Treaty of Berlin
The Treaty of Berlin (formally the Treaty between Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Great Britain and Ireland, Italy, Russia, and the Ottoman Empire for the Settlement of Affairs in the East) was signed on 13 July 1878. In the aftermath of the R ...
, the Croatian Military Frontier
The Croatian Military Frontier ( hr, Vojna krajina or ') was a district of the Military Frontier, a territory in the Habsburg monarchy, first during the period of the Austrian Empire and then during Austria-Hungary.
History
Founded in the late 16 ...
was abolished and the territory returned to Croatia in 1881. Renewed efforts to reform Austria-Hungary
The United States of Greater Austria (german: Vereinigte Staaten von Groß-Österreich) was an unrealized proposal made in 1906 to federalize Austria-Hungary to help resolve widespread ethnic and nationalist tensions. It was conceived by a group ...
, entailing federalisation
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments (Province, provincial, State (sub-national), state, Canton (administrative division), can ...
with Croatia as a federal unit, were halted by World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. On 29 October 1918 the Croatian Sabor declared independence and decided to join the newly formed State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( sh, Država Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba / ; sl, Država Slovencev, Hrvatov in Srbov) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( ...
, ending Habsburg rule and the personal union with Hungary after 816 years.
Treaty of Trianon and World War II
 The
The Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in ...
was signed in 1920, at the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, between the Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Em ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
(as one of the successor states of Austria-Hungary). The treaty regulated the status of the independent Hungarian state and defined its borders. Compared to the prewar Kingdom of Hungary (as a part of Austria-Hungary), post-Trianon Hungary lost 72 percent of its territory. The principal beneficiaries of the territorial division of the prewar Kingdom of Hungary were Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
. The treaty established the southern border of Hungary along the and Mura rivers (except in Baranya Baranya or Baranja may refer to:
* Baranya (region) or Baranja, a region in Hungary and Croatia
* Baranya County, a county in modern Hungary
* Baranya County (former), a county in the historic Kingdom of Hungary
* Baranya, Hungarian name of villag ...
, where only the northern part of the county was retained by Hungary). On 4 December 1918 the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (comprising present-day Croatia) joined the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
to form the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
.
The invasion of Yugoslavia
The invasion of Yugoslavia, also known as the April War or Operation 25, or ''Projekt 25'' was a German-led attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II. The order for the invasion was p ...
by the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
began on 6 April 1941, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and ended with the unconditional surrender of the Royal Yugoslav Army
The Yugoslav Army ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Jugoslovenska vojska, JV, Југословенска војска, ЈВ), commonly the Royal Yugoslav Army, was the land warfare military service branch of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia (originally Kingdom of Serbs ...
on 17 April 1941. During that time, a genocide of Serbs happened. Many Jews and Roma people were murdered too. Also, during that time, on 12 April the Hungarian Third Army
The Hungarian Third Army ( hu, 3. magyar hadsereg) was a field army in the Royal Hungarian Army that saw action during World War II.
Commanders
* Lieutenant General Elemér Gorondy-Novák from 1 March 1940 to 1 November 1941
* Lieutenant General ...
crossed the border (advancing into Međimurje and southern Baranya Baranya or Baranja may refer to:
* Baranya (region) or Baranja, a region in Hungary and Croatia
* Baranya County, a county in modern Hungary
* Baranya County (former), a county in the historic Kingdom of Hungary
* Baranya, Hungarian name of villag ...
). Those territorial gains were reversed by Yugoslav partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослобод ...
and the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
in 1944 and 1945, and confirmed by the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947
The Paris Peace Treaties (french: Traités de Paris) were signed on 10 February 1947 following the end of World War II in 1945.
The Paris Peace Conference lasted from 29 July until 15 October 1946. The victorious wartime Allied powers (princi ...
. As World War II was replaced by the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, Hungarian–Croatian relations were substantially dictated by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
; it dominated the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
, which included Hungary and Communist-ruled Yugoslavia (which in turn comprised Croatia as its constituent part), as defined by the Tito–Stalin split
The Tito–Stalin split or the Yugoslav–Soviet split was the culmination of a conflict between the political leaderships of Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union, under Josip Broz Tito and Joseph Stalin, respectively, in the years following World W ...
. This situation ended with the revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Natio ...
, the end of Communism in Hungary and the breakup of Yugoslavia
The breakup of Yugoslavia occurred as a result of a series of political upheavals and conflicts during the early 1990s. After a period of political and economic crisis in the 1980s, constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
.
Fall of Communism and Croatian independence
Hungary recognised Croatian independence on 15 January 1992 (with the rest of theEuropean Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
member states), and established diplomatic relations with Croatia three days later. During the Croatian War of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serb-controlled Yugosl ...
, Croatia obtained arms from several countries (including Hungary), despite a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
-imposed arms embargo
An arms embargo is a restriction or a set of sanctions that applies either solely to weaponry or also to "dual-use technology." An arms embargo may serve one or more purposes:
* to signal disapproval of the behavior of a certain actor
* to maintain ...
. As of December 2011, Hungary and Croatia have 96 treaties and agreements in force regulating a wide range of activities and relations (including diplomatic, cultural, economic, energy, transport, education, minority and other issues). Furthermore, Hungary supported the Croatian NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
membership request and Croatian accession to the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
.
Economy
Hungary → Croatia
Most important Hungarian investors in Croatia: MOL- INA,OTP Bank
OTP Bank Group is the largest commercial bank of Hungary and one of the largest independent financial service providers in Central and Eastern Europe and with banking services for private individuals and corporate clients. The OTP Group comprise ...
, TriGránit
TriGranit is one of the largest privately owned real estate platforms in Central Europe, focusing primarily on retail and office buildings in urban locations. TriGranit manages investment, acquisition, development, and construction. In its two d ...
, AdriaticHolidays
See also
*Foreign relations of Croatia
The Republic of Croatia is a sovereign country at the crossroads of Central Europe, Southeast Europe, and the Mediterranean that declared its independence from Yugoslavia on 25 June 1991. Croatia is a member of the European Union (EU), United N ...
* Foreign relations of Hungary
Hungary wields considerable influence in Central and Eastern Europe and is a middle power in international affairs.Solomon S (1997South African Foreign Policy and Middle Power Leadership, ''ISS'' The foreign policy of Hungary is based on four basi ...
* Hungarians of Croatia
Hungarians are a recognized ethnic minority in Croatia. According to the 2011 census there are 14,048 people of Hungarian ethnicity living in Croatia (or 0.33% of total population). Around two thirds of them (8,249) live in Osijek-Baranja County i ...
* Croats of Hungary
The Hungarian Croats ( Croatian: ''Hrvati u Mađarskoj''; hu, Magyarországi horvátok) are an ethnic minority in Hungary. According to the 2011 census, there were 26,774 Croats in Hungary or 0.3% of population.
Croats of Hungary belong to seve ...
References
External links
Croatian Minister of Foreign Affairs and European Integration: list of bilateral treaties with Hungary
Croatian embassy in Budapest (in Croatian and Hungarian only)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Croatia-Hungary relations
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
Bilateral relations of Hungary