Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=,
Modern
Modern may refer to:
History
* Modern history
** Early Modern period
** Late Modern period
*** 18th century
*** 19th century
*** 20th century
** Contemporary history
* Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century
Phil ...
: ,
Ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian language, Sumerian c ...
: ) is the largest and most populous of the
Greek islands
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227.
The largest Greek island by a ...
, the
88th largest island in the world and the
fifth largest island in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, after
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
,
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
,
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, and
Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
, with the
Sea of Crete
300px, Map of the Sea of Crete
The Sea of Crete (, ''Kritiko Pelagos''), or Cretan Sea, is a sea, part of the Aegean Sea, located in its southern extremity, with a total surface area of . The sea stretches to the north of the island of Crete, eas ...
(or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the
Libyan Sea
The Libyan Sea (Greek , Latin ''Libycum Mare'', Arabic البحر الليبي) is the portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of the African coast of ancient ''Libya'', i.e. Cyrenaica, and Marmarica
(the coast of what is now eastern Libya and ...
(or South Cretan Sea) to the south.
Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13
top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The
Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. ...
are located to the northeast of Crete, while the
Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The nam ...
are situated to the north, separated by the
Sea of Crete
300px, Map of the Sea of Crete
The Sea of Crete (, ''Kritiko Pelagos''), or Cretan Sea, is a sea, part of the Aegean Sea, located in its southern extremity, with a total surface area of . The sea stretches to the north of the island of Crete, eas ...
. The
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
is to the region's northwest.
Humans have inhabited the island since at least 130,000 years ago, during the
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
age. Crete was the centre of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
's first advanced civilization, the
Minoans, from 2700 to 1420 BC. The Minoan civilization was overrun by the
Mycenaean civilization
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
from mainland Greece. Crete was later ruled by Rome, then successively by the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
,
Andalusian Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
, the
Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
, and the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. In 1898 Crete, whose people had for some time wanted to join the Greek state, achieved independence from the Ottomans, formally becoming the
Cretan State
The Cretan State ( el, Κρητική Πολιτεία, Kritiki Politeia; ota, كريد دولتى, Girid Devleti) was established in 1898, following the intervention by the Great Powers (United Kingdom, France, Italy, Austria-Hungary, Germany ...
. Crete became part of Greece in December 1913.
The island is mostly mountainous, and its character is defined by a high mountain range crossing from west to east. It includes Crete's highest point,
Mount Ida
In Greek mythology, two sacred mountains are called Mount Ida, the "Mountain of the Goddess": Mount Ida in Crete, and Mount Ida in the ancient Troad region of western Anatolia (in modern-day Turkey), which was also known as the '' Phrygian Ida'' ...
, and the range of the
White Mountains (Lefka Ori) with 30 summits above in altitude and the
Samaria Gorge
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first-ce ...
, a
World Biosphere Reserve
The UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) covers internationally designated protected areas, known as biosphere reserves, which are meant to demonstrate a balanced relationship between people and nature (e.g. encourage sustainable dev ...
. Crete forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece, while retaining its own local cultural traits (such as its own
poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
and
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
). The
Nikos Kazantzakis
Nikos Kazantzakis ( el, ; 2 March ( OS 18 February) 188326 October 1957) was a Greek writer. Widely considered a giant of modern Greek literature, he was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in nine different years.
Kazantzakis's no ...
airport at Heraklion and the
Daskalogiannis
Ioannis Vlachos (), better known as Daskalogiannis (; 1722/30 – 17 June 1771) was a wealthy shipbuilder and shipowner who led a Cretan revolt against Ottoman rule in the 18th century.Detorakis, Turkish rule in Crete, p. 357
Life and career
...
airport at
Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
serve international travelers. The palace of
Knossos
Knossos (also Cnossos, both pronounced ; grc, Κνωσός, Knōsós, ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and has been called Europe's oldest city.
Settled as early as the Neolithic period, the na ...
, a Bronze Age settlement and ancient Minoan city, is also located in Heraklion.
[Ancient Crete](_blank)
Oxford Bibliographies Online: Classics
Name
The earliest references to the island of Crete come from texts from the
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
n city of
Mari dating from the 18th century BC, where the island is referred to as ''Kaptara''. This is repeated later in
Neo-Assyrian
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
records and the
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
(''
Caphtor
Caphtor ( he, ''Kaftōr'') is a locality mentioned in the Bible, in which its people are called Caphtorites or Caphtorim and are named as a division of the ancient Egyptians. Caphtor is also mentioned in ancient inscriptions from Egypt, Mari, a ...
''). It was known in ancient
Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
as or , strongly suggesting a similar
Minoan
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
name for the island.
The current name ''Crete'' is first attested in the 15th century BC in
Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the most ancient attested form of the Greek language, on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC), before the hypothesised Dorian invasion, often cited as the ''terminus ad quem'' for the ...
texts, written in
Linear B
Linear B was a syllabic script used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of Greek. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from ...
, through the words (, ; later Greek: , plural of ) and (, ; later Greek: , 'Cretan'). In
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
, the name Crete () first appears in
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's ''
Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
''. Its etymology is unknown. One proposal derives it from a hypothetical
Luwian
The Luwians were a group of Anatolian peoples who lived in central, western, and southern Anatolia, in present-day Turkey, during the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. They spoke the Luwian language, an Indo-European language of the Anatolian sub-fa ...
word (compare 'island', 'cutting, sliver'). Another proposal suggests that it derives from the
ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
word ''"κραταιή" (krataie̅)'', meaning strong or powerful, the reasoning being that Crete was the strongest
thalassocracy
A thalassocracy or thalattocracy sometimes also maritime empire, is a state with primarily maritime realms, an empire at sea, or a seaborne empire. Traditional thalassocracies seldom dominate interiors, even in their home territories. Examples ...
during ancient times.
In
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, the name of the island became . The original Arabic name of Crete was ( ar, اقريطش < , but after the
Emirate of Crete
The Emirate of Crete ( ar, إقريطش, Iqrīṭish or , ''Iqrīṭiya''; gr, Κρήτη, Krētē) was an Islamic state that existed on the Mediterranean island of Crete from the late 820s to the reconquest of the island by the Byzantine Empir ...
's establishment of its new capital at (modern
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
; el, Ηράκλειο, ), both the city and the island became known as () or (), which gave Latin, Italian, and Venetian , from which were derived French and English ''Candy'' or ''Candia''. Under
Ottoman rule
Ottoman is the Turkish spelling of the Arabic masculine given name Uthman ( ar, عُثْمان, ‘uthmān). It may refer to:
Governments and dynasties
* Ottoman Caliphate, an Islamic caliphate from 1517 to 1924
* Ottoman Empire, in existence fro ...
, in
Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, لِسانِ عُثمانى, Lisân-ı Osmânî, ; tr, Osmanlı Türkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extens ...
, Crete was called (). In the Hebrew Bible, Crete is referred to as () "kretim".
Physical geography




Crete is the largest island in Greece and the fifth largest island in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. It is located in the southern part of the
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
separating the Aegean from the
Libyan Sea
The Libyan Sea (Greek , Latin ''Libycum Mare'', Arabic البحر الليبي) is the portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of the African coast of ancient ''Libya'', i.e. Cyrenaica, and Marmarica
(the coast of what is now eastern Libya and ...
.
Island morphology
The island has an elongated shape: it spans from east to west, is at its widest point, and narrows to as little as (close to
Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete.
History
The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is loc ...
). Crete covers an area of , with a coastline of ; to the north, it broaches the
Sea of Crete
300px, Map of the Sea of Crete
The Sea of Crete (, ''Kritiko Pelagos''), or Cretan Sea, is a sea, part of the Aegean Sea, located in its southern extremity, with a total surface area of . The sea stretches to the north of the island of Crete, eas ...
( el, Κρητικό Πέλαγος, links=no); to the south, the
Libyan Sea
The Libyan Sea (Greek , Latin ''Libycum Mare'', Arabic البحر الليبي) is the portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of the African coast of ancient ''Libya'', i.e. Cyrenaica, and Marmarica
(the coast of what is now eastern Libya and ...
( el, links=no, Λιβυκό Πέλαγος); in the west, the
Myrtoan Sea
The Myrtoan Sea (also Mirtoan Sea; el, Mυρτώο Πέλαγος, ''Myrtoo Pelagos'' ) is a subdivision of the Mediterranean Sea that lies between the Cyclades and Peloponnese. It is described as the part of the Aegean Sea south of Euboea, Att ...
, and toward the east the Carpathian Sea. It lies approximately south of the Greek mainland.
Mountains and valleys
Crete is mountainous, and its character is defined by a high mountain range crossing from west to east, formed by six different groups of mountains:
*The White Mountains or
Lefka Ori
Lefka Ori ( el, Λευκά Όρη, meaning 'White Mountains') or Madares ( from the Cretan Greek meaning 'without coverage, bald, bare of any vegetation for high mountain areas') is a mountain range located in Western Crete, in the Chania prefect ...
*The Idi Range (
Psiloritis
Mount Ida ( el, Ἴδα), known variously as Idha, Ídhi, Idi, and Ita (the massif including the mountain is called Psiloritis, el, Ψηλορείτης), is the highest mountain on the island of Crete, with an elevation of . It has the highest ...
)
*
Asterousia Mountains
The Asterousia Mountains are a range in southern Crete separating the Messara Plain from the Libyan Sea. Evidence of ancient Cretan cultures have been found in excavations performed within sites contained in this range; moreover, one of the most ...
*
Kedros
*The
Dikti Mountains
*Thripti
These mountains lavish Crete with valleys, such as
Amari valley The Amari Valley is a fertile valley on the foothills of Mount Ida and Mount Kedros in Crete. The valley was known as a center of resistance to the Germans during the Battle of Crete and the German occupation. After the abduction of General Heinrich ...
, fertile plateaus, such as
Lasithi plateau
The Lasithi Plateau ( el, Οροπέδιο Λασιθίου, ''Oropedio Lasithiou''), sometimes spelt Lassithi Plateau, is a high endorheic plateau, located in the Lasithi regional unit in eastern Crete, Greece. Since the 1997 Kapodistrias reform, ...
,
Omalos
Omalos ( el, Ομαλός) is a small village in western Crete, in the Mousouroi unit of the Chania region. The Greek word Ομαλός means even, plain, regular, or smooth, referring to the plateau.
Description
Omalos is situated at the nort ...
and
Nidha; caves, such as
Gourgouthakas
Gourgouthakas ( el, Γουργούθακας; from "small cutting on rocks, in which rain water is collected and from which animals drink water") is a cave located in the Lefka Ori mountains on the Greek island of Crete. It is the deepest cave in G ...
,
Diktaion, and
Idaion (the birthplace of the ancient Greek god
Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
); and a number of gorges.
Mountains in Crete are the object of tremendous fascination both for locals and tourists. The mountains have been seen as a key feature of the island's distinctiveness, especially since the time of Romantic travellers' writing. Contemporary Cretans distinguish between highlanders and lowlanders; the former often claim to reside in places affording a higher/better climatic but also moral environment. In keeping with the legacy of Romantic authors, the mountains are seen as having determined their residents' 'resistance' to past invaders which relates to the oft-encountered idea that highlanders are 'purer' in terms of less intermarriages with occupiers. For residents of mountainous areas, such as Sfakia in western Crete, the aridness and rockiness of the mountains is emphasised as an element of pride and is often compared to the alleged soft-soiled mountains of others parts of Greece or the world.
Gorges, rivers and lakes
The island has a number of gorges, such as the
Samariá Gorge
The Samariá Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι Σαμαριάς or just ''Φάραγγας'') is a
National Park of Greece since 1962 on the island of Crete – a major tourist attraction of the island – and a World's Biosphere Reserve.
The gorg ...
,
Imbros Gorge Imbros Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι Ίμπρου, Faragi Imbrou) is an 11 km long canyon located near Hora Sfakion in southern Crete, the Mediterranean island. It runs parallel to Samariá Gorge, its narrowest part has 1.60 m and it ends at ...
,
Kourtaliotiko Gorge,
Ha Gorge
Ha Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι Χά) is a narrow gorge, at the Monasteraki Dakos, on the eastern part of the island of Crete in Greece. It is located in the west slope of Thrypti mountain range, and exits east
of Vasiliki village in the plain of ...
,
Platania Gorge, the Gorge of the Dead (at
Kato Zakros Zakros ( el, Ζάκρος; Linear B: zakoro) is a site on the eastern coast of the island of Crete, Greece, containing ruins from the Minoan civilization. The site is often known to archaeologists as Zakro or Kato Zakro. It is believed to have been ...
,
Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
) and
Richtis Gorge
Richtis Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι του Ρίχτη, Faraggi tou Richti) is a gorge in Crete, GreeceMap of Richtis Gorge here. It is a state protected park near Exo Mouliana, Sitia, eastern Crete (Greece) that starts at the traditional village ...
and (Richtis) waterfall at Exo Mouliana in
Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
.
The rivers of Crete include the
Ieropotamos River
The Geropotamos ( el, Γεροπόταμος or Ιερός Ποταμός) is a watercourse in southern Crete in Greece. Its drainage area is . It rises on the north slope of the Asterousia Mountains, near the village Sternes. It flows west throug ...
, the Koiliaris, the Anapodiaris, the Almiros, the Giofyros, and Megas Potamos. There are only two freshwater lakes in Crete: Lake
Kournas
Kournas is a mountainous village of Municipality of Apokoronas, Chania, on the Greek island of Crete. It has a population of 500 citizens. It is located at 200 meters altitude and south-east of the mountain named Dafnomadara (1680 meters).
Kourn ...
and Lake Agia, which are both in Chania regional unit.
Lake Voulismeni
Lake Voulismeni (Greek: Λίμνη Βουλισμένη, ''Límni Voulisméni'') is a small, formerly freshwater lake, later connected to the sea, located at the centre of the town of Agios Nikolaos on the Greek island of Crete. It has a circula ...
at the coast, at Aghios Nikolaos, was formerly a freshwater lake but is now connected to the sea, in Lasithi. Three artificial lakes created by dams also exist in Crete: the lake of
Aposelemis Dam, the lake of Potamos Dam, and the lake of Mpramiana Dam.
File:HaGorgeExit.jpg, Ha Gorge
Ha Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι Χά) is a narrow gorge, at the Monasteraki Dakos, on the eastern part of the island of Crete in Greece. It is located in the west slope of Thrypti mountain range, and exits east
of Vasiliki village in the plain of ...
File:Samaria Gorge 09.jpg, Samariá Gorge
The Samariá Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι Σαμαριάς or just ''Φάραγγας'') is a
National Park of Greece since 1962 on the island of Crete – a major tourist attraction of the island – and a World's Biosphere Reserve.
The gorg ...
File:Crete Aradaina3 tango7174.jpg, Aradaina Gorge
File:Venetian Bridge over Megalopótamos River, Préveli, Crete.jpg, Venetian Bridge over Megalopotamos River
Surrounding islands

A large number of islands, islets, and rocks hug the coast of Crete. Many are visited by tourists, some are only visited by
archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
and
biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
s. Some are
environmentally protected. A small sample of the islands includes:
*
Gramvousa
Gramvousa also Grampousa ( el, Γραμβούσα or Γραμπούσα, further names include ''Akra'', ''Cavo Buso'', ''Cavo Bouza'', ''Garabusa'' and ''Grabusa'') refers to two small uninhabited islands off the coast of a peninsula also known ...
(
Kissamos
Kissamos ( el, Κίσσαμος) is a town and a municipality in the west of the island of Crete, Greece. It is part of the Chania regional unit and of the former Kissamos Province which covers the northwest corner of the island. The town of Kissam ...
, Chania) the pirate island opposite the Balo lagoon
*
Elafonisi
Elafonisi ( el, Ελαφονήσι "deer island") is an island located close to the southwestern corner of the Mediterranean island of Crete, of which it is administratively a part, in the regional unit of Chania. When the weather is fine it is ...
(Chania), which commemorates a shipwreck and an Ottoman massacre
*
Chrysi island (
Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete.
History
The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is loc ...
,
Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thr ...
), which hosts the largest natural ''
Juniperus macrocarpa
''Juniperus macrocarpa'' (large-fruited juniper, syn. ''J. oxycedrus'' subsp. ''macrocarpa'' (Sibth. & Sm.) Ball) is a species of juniper, native across the northern Mediterranean region from southwestern Spain east to western Turkey and Cyprus, ...
'' forest in Europe
*
Paximadia
Paximadia ( el, Παξιμάδια, "rusks") are two small uninhabited islands in the gulf of Mesara located approximately south of Agia Galini in Rethymno regional unit. They are in the Libyan Sea next to the southern coast of Crete. Due to ...
island (Agia Galini,
Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
) where the god Apollo and the goddess Artemis were born
*The Venetian fort and leper colony at
Spinalonga
Spinalonga ( el, Σπιναλόγκα) is an island located in the Gulf of Elounda in north-eastern Crete, in Lasithi, next to the town of Plaka. The island is further assigned to the area of Kalydon.
It is near the Spinalonga peninsula ("large ...
opposite the beach and shallow waters of
Elounda
Elounda ( el, Ελούντα, Elúnda), alternatively transliterated as Elounta or Elouda, is a small town on the northern coast of the island of Crete, Greece. It is part of the municipality of Agios Nikolaos.
Settlement structure
Elounda is f ...
(
Agios Nikolaos, Lasithi)
*
Dionysades
The Dionysades ( el, Διονυσάδες, also Γιανυσάδες - ''Gianysades'') is a small, northward-trending archipelago off the north coast of the island of Crete, mid-way between the Cape Sidero lighthouse to the southeast (from whi ...
islands which are in an environmentally protected region together the Palm Beach Forest of
Vai in the municipality of
Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
, Lasithi
Off the south coast, the island of
Gavdos
Gavdos ( el, Γαύδος, ) is the southernmost Greek island, located to the south of its much larger neighbour, Crete, of which it is administratively a part, in the regional unit of Chania. It forms a community with surrounding islets and was ...
is located south of
Hora Sfakion
Image:Chora Sfakion 1941 evacuation monument.jpg, 200px, Monument commemorating the evacuation during WW2 of British and ANZAC forces from Hora Sfakion in May 1941. ''Click on the left plaque for a closer view''
rect 198 536 320 1082
rect 0 0 900 ...
and is the
southernmost
The most southerly geographical features of various types are listed here.
Cities and settlements
Geography
Islands
Berkner Island is further south than any of these, but its bedrock lies entirely below sea level, with only its ice cov ...
point of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
Climate
Crete straddles two climatic zones, the Mediterranean and the
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
n, mainly falling within the former. As such, the climate in Crete is primarily
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
. The atmosphere can be quite humid, depending on the proximity to the sea, while winter is fairly mild. Snowfall is common on the mountains between November and May, but rare in the low-lying areas. While some mountain tops are snow-capped for most of the year, near the coast snow only stays on the ground for a few minutes or hours. However, a truly exceptional cold snap swept the island in February 2004, during which period the whole island was blanketed with snow. During the Cretan summer, average temperatures reach the high 20s-low 30s Celsius (mid 80s to mid 90s Fahrenheit), with maxima touching the upper 30s-mid 40s.
The south coast, including the
Mesara Plain
The Messara Plain or simply Messara ( el, Μεσσαρά) is an alluvial plain in southern Crete, stretching about 50 km west-to-east and 7 km north-to-south, making it the largest plain in Crete.
On a hill at its west end are the ruin ...
and
Asterousia Mountains
The Asterousia Mountains are a range in southern Crete separating the Messara Plain from the Libyan Sea. Evidence of ancient Cretan cultures have been found in excavations performed within sites contained in this range; moreover, one of the most ...
, falls in the North African climatic zone, and thus enjoys significantly more sunny days and high temperatures throughout the year. There,
date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
s bear fruit, and
swallows
The swallows, martins, and saw-wings, or Hirundinidae, are a family of passerine songbirds found around the world on all continents, including occasionally in Antarctica. Highly adapted to aerial feeding, they have a distinctive appearance. The ...
remain year-round rather than migrate to
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The fertile region around
Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete.
History
The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is loc ...
, on the southeastern corner of the island, is renowned for its exceptional year-round agricultural production, with all kinds of summer vegetables and fruit produced in
greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
s throughout the winter. Western Crete (Chania province) receives more rain and the soils there suffer more erosion compared to the Eastern part of Crete.
According to the data of the
Hellenic National Meteorological Service
The Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) ( el, Εθνική Μετεωρολογική Υπηρεσία (ΕΜΥ)) is a government agency responsible for making weather forecasts and observations for Greece. HNMS was founded in 1931 under ...
, South Crete receives the highest sunshine in
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
with locally more than 3,257 hours of sunshine per year.
Human geography
Crete is the most populous island in Greece with a population of more than 600,000 people. Approximately 42% live in Crete's main cities and towns whilst 45% live in rural areas.
Administration
Crete with its nearby islands form the Crete Region ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, translit=, , ), one of the 13
regions of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, περιφέρειες, translit=periféries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional u ...
which were established in the 1987 administrative reform. Under the 2010
Kallikratis plan
The Kallikratis Programme ( el, Πρόγραμμα Καλλικράτης, Prógramma Kallikrátis) is the common name of Greek law 3852/2010 of 2010, a major administrative reform in Greece. It brought about the second major reform of the count ...
, the powers and authority of the regions were redefined and extended. The region is based at
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
and is divided into four
regional units (pre-Kallikratis
prefectures
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
). From west to east these are:
Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
,
Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
,
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
, and
Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thr ...
. These are further subdivided into 24
municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
.
The region's governor is, since 1 January 2011,
Stavros Arnaoutakis, who was elected in the
November 2010 local administration elections for the
Panhellenic Socialist Movement
The Panhellenic Socialist Movement ( el, Πανελλήνιο Σοσιαλιστικό Κίνημα, Panellínio Sosialistikó Kínima, ), known mostly by its acronym PASOK, (; , ) is a social-democratic political party in Greece. Until 2012, it ...
.
Cities
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
is the largest city and capital of Crete, holding more than a fourth of the island's population.
Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
was the capital until 1971. The principal cities are:
*
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
(''Iraklion'' or ''Candia'') (144,422 inhabitants)
[2011 Census]
*
Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
(''Haniá'') (53,910 inhabitants)
[
* ]Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
(34,300 inhabitants)[
* ]Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete.
History
The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is loc ...
(23,707 inhabitants)
* Agios Nikolaos (20,679 inhabitants)
* Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
(14,338 inhabitants)
File:Venetian Fortress in Heraklion Crete NE side.jpg, Venetian fortress in Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
File:Kreta - Chania - Kathedrale der drei Märtyrer.jpg, Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
cathedral
File:Rethymno Fortezza Mosque 02.JPG, Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
Fortezza Mosque
Demographics
The region has shrunk by 5,705 people between 2011 and 2021, experiencing a population loss of 0.9%.
Economy
The economy of Crete is predominantly based on services and tourism. However, agriculture also plays an important role and Crete is one of the few Greek islands that can support itself independently without a tourism industry. The economy began to change visibly during the 1970s as tourism gained in importance. Although an emphasis remains on agriculture and stock breeding, because of the climate and terrain of the island, there has been a drop in manufacturing, and an observable expansion in its service industries (mainly tourism-related). All three sectors of the Cretan economy (agriculture/farming, processing-packaging, services), are directly connected and interdependent. The island has a per capita income much higher than the Greek average, whereas unemployment is at approximately 4%, one-sixth of that of the country overall.
As in many regions of Greece, viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
and olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
groves are significant; oranges
An orange is a fruit of various citrus species in the family Rutaceae (see list of plants known as orange); it primarily refers to ''Citrus'' × ''sinensis'', which is also called sweet orange, to distinguish it from the related ''Citrus × ...
, citrons and avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Then as now it was prized for i ...
es are also cultivated. Until recently there were restrictions on the import of bananas to Greece, therefore bananas were grown on the island, predominantly in greenhouses. Dairy products are important to the local economy and there are a number of speciality cheeses such as mizithra
Mizithra or myzithra ( ) is a Greek whey cheese or mixed milk- whey cheese from sheep or goats, or both. Barron, Rosemary (1991). ''Flavors of Greece.'' William Morrow, It is sold both as a fresh cheese, similar to Italian ''ricotta'', and as a ...
, anthotyros
Anthotyros () (Anthotyro in modern Greek, "flowery cheese") is a traditional fresh cheese. There are dry Anthotyros and fresh Anthotyros. Dry Anthotyros is a matured cheese similar to Mizithra. Anthotyros is made with milk and whey from sheep or ...
, and kefalotyri
Kefalotyri or kefalotiri ( el, κεφαλοτύρι, tr, talar peyniri) is a hard, salty white cheese made from sheep milk or goat's milk (or both) in Greece and Cyprus. A similar cheese Kefalograviera, also made from sheep or goat milk (or both ...
.
The Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
(GDP) of the region was €9.4 billion in 2018, accounting for 5.1% of Greek economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was €17,800 or 59% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 68% of the EU average. Crete is the region in Greece with the fifth highest GDP per capita.
Transport infrastructure

Airports
The island has three significant airports, Nikos Kazantzakis
Nikos Kazantzakis ( el, ; 2 March ( OS 18 February) 188326 October 1957) was a Greek writer. Widely considered a giant of modern Greek literature, he was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in nine different years.
Kazantzakis's no ...
at Heraklion, the Daskalogiannis
Ioannis Vlachos (), better known as Daskalogiannis (; 1722/30 – 17 June 1771) was a wealthy shipbuilder and shipowner who led a Cretan revolt against Ottoman rule in the 18th century.Detorakis, Turkish rule in Crete, p. 357
Life and career
...
airport at Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
and a smaller one in Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
. The first two serve international routes, acting as the main gateways to the island for travellers. There is a long-standing plan to replace Heraklion airport with a completely new airport at Kastelli, where there is presently an air force base.
Ferries
The island is well served by ferries, mostly from Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; el, Πειραιάς ; grc, Πειραιεύς ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens' city centre, along the east coast of the Saronic ...
, by ferry companies such as Minoan Lines
Minoan Lines is one of the largest passenger ferry companies in Europe, and one of the dominant passenger ferry companies in Greece, sailing between Piraeus and Crete and in the Adriatic Sea, between Patras and various Italian ports. The company ...
and ANEK Lines
ANEK Lines (Ανώνυμη Ναυτιλιακή Εταιρεία Κρήτης, ''Anonymi Naftiliaki Eteria Kritis'', Anonymous Shipping Company of Crete) is one of the largest passenger shipping companies in Greece. It was founded in 1967 by nu ...
. Seajets
Seajets is a Greek/ Cypriot ferry company operating passenger and freight ferry services in the Aegean Sea.
History
Seajets was established in 1989. Today, it operates a fleet of 14 high speed vessels, and 3 conventional Ro-Ro ferries which serv ...
operates routes to Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The nam ...
.
Road network
Although almost everywhere is covered by the road network, there is a lack of modern highways
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
, although this is gradually changing with the completion of the northern coastal spine highway. In addition, a European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
study has been devised to promote a modern highway to connect the northern and southern parts of the island via a tunnel
A tunnel is an underground passageway, dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, and enclosed except for the entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A pipeline is not a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube cons ...
. The study proposal includes a section of road between the villages of Agia Varvara and Agia Deka in central Crete. It is hoped to benefit both tourists and locals by improving the connections to the southern part of the island and by reducing accidents. The new road section forms part of the route between Messara in the south and Crete's largest city Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
, which houses the island's airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface ...
and principal ferry links with mainland Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
. Traffic speeds on the new road will increase by 19 km/hour (from 29 km/hour to 48 km/hour), which should reduce journey times between Messara and Heraklion by 55 minutes. The scheme is also expected to improve road safety by cutting the number of accidents along the route. Building works include construction of three road tunnels, five bridges and three junctions. This project is expected to create 44 jobs during the implementation phase.
The investment falls under Greece's "Improvement of Accessibility" Operational Programme, which aims to improve the country's transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, an ...
infrastructures as well as its international connections. The Operational Programme works to link Greece's more prosperous and less developed regions, and thus help to promote greater territorial cohesion.
Total investment for the project "Completion of construction of the section of Ag. Varvara - Ag. Deka (Kasteli
Kastelli ( el, Καστέλλι, ''Kastélli''; also Καστέλι, ''Kastéli''), often called Kastelli Pediadas (Greek: Καστέλλι Πεδιάδας) to differentiate it from Kissamos (also occasionally called Kastelli-Kissamos) is a villa ...
) (22+170 km to 37+900 km) of the vertical road axis Irakleio – Messara in the prefecture of Irakleio, Kriti" is EUR 102 273 321, of which the EU's European Regional Development Fund
The European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) is one of the European Structural and Investment Funds allocated by the European Union. Its purpose is to transfer money from richer regions (not countries), and invest it in the infrastructure and se ...
is contributing EUR 86 932 323 from the Operational Programme "Improvement of Accessibility" for the 2007 to 2013 programming period. Work falls under the priority "Road Transport – trans-European and trans-regional route network of the regions on the Convergence objective".
Railway
Also, during the 1930s there was a narrow-gauge industrial railway in Heraklion, from Giofyros in the west side of the city to the port. There are now no railway lines on Crete. The government is planning the construction of a line from Chania to Heraklion via Rethymno.[Rackham, O. & Moody, J., 1996]
The Making of the Cretan Landscape
Manchester University Press,
Development
Newspapers have reported that the Ministry of Mercantile Marine is ready to support the agreement between Greece, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, Dubai Ports World
DP World is an Emirati multinational logistics company based in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It specialises in cargo logistics, port terminal operations, maritime services and free trade zones. Formed in 2005 by the merger of Dubai Ports Auth ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
for the construction of a large international container
A container is any receptacle or enclosure for holding a product used in storage, packaging, and transportation, including shipping.
Things kept inside of a container are protected on several sides by being inside of its structure. The term ...
port and free trade zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re- exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to cus ...
in southern Crete near Tympaki
Tympaki ( el, Τυμπάκι) is a town and a former municipality in the Heraklion regional unit, Crete, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reforms it is part of the municipality of Faistos, of which it is a municipal unit, the unit has an ar ...
; the plan is to expropriate of land. The port would handle two million containers per year, but the project has not been universally welcomed because of its environmental, economic and cultural impact.[No Container Transshipment Hub in Timbaki]
. Retrieved 27 May 2007. As of January 2013, the project has still not been confirmed, although there is mounting pressure to approve it, arising from Greece's difficult economic situation.
There are plans for underwater cables going from mainland Greece to Israel and Egypt passing by Crete and Cyprus: EuroAfrica Interconnector
EuroAfrica Interconnector is a HVDC interconnector and submarine power cable between the Greek, Cypriot, and Egypt power grids.[EuroAsia Interconnector
The EuroAsia Interconnector is a HVDC interconnector between the Greek, Cypriot, and Israeli power grids via the world's longest submarine power cable ( from Israel to Cyprus and from Cyprus to Greece, for a total of ).
Connecting Kofinou, Cypru ...](_blank)
.
History
 Hominids settled in Crete at least 130,000 years ago. In the later Neolithic and Bronze Age periods, under the Minoans, Crete had a highly developed, literate civilization. It has been ruled by various ancient Greek entities, the
Hominids settled in Crete at least 130,000 years ago. In the later Neolithic and Bronze Age periods, under the Minoans, Crete had a highly developed, literate civilization. It has been ruled by various ancient Greek entities, the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the Emirate of Crete
The Emirate of Crete ( ar, إقريطش, Iqrīṭish or , ''Iqrīṭiya''; gr, Κρήτη, Krētē) was an Islamic state that existed on the Mediterranean island of Crete from the late 820s to the reconquest of the island by the Byzantine Empir ...
, the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. After a brief period of independence (1897–1913) under a provisional Cretan government, it joined the Kingdom of Greece. It was occupied by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Prehistory
In 2002, the paleontologist Gerard Gierlinski discovered fossil footprints possibly left by ancient human relatives 5,600,000 years ago.
The first human settlement in Crete dates to more than 130,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
age. Settlements dating to the aceramic Aceramic is defined as "not producing pottery". In archaeology, the term means "without pottery".
Aceramic societies usually used bark, basketry, gourds and leather for containers. It is sometimes used to refer to a specific early Neolithic period ...
Neolithic in the 7th millennium BC, used cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
, sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated s ...
, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s, pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus s ...
s and dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Do ...
s as well as domesticated cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
s and legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock f ...
s; ancient Knossos
Knossos (also Cnossos, both pronounced ; grc, Κνωσός, Knōsós, ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and has been called Europe's oldest city.
Settled as early as the Neolithic period, the na ...
was the site of one of these major Neolithic (then later Minoan) sites. Other neolithic settlements include those at Kephala Kephala is a hill landform in northern Crete, Greece. This location was chosen by ancient settlers for the site of the Palace of Knossos; the footprint of the Neolithic settlement at Kephala Hill was actually larger than the Bronze Age
T ...
, Magasa Magasa may refer to places in:
;Greece
* Magasa, Crete
Magasa ( el, Μαγκασά) is a Neolithic settlement on the eastern part of the island of Crete in present-day Greece. Magasa is notable as a Neolithic Cretan settlement for some use of lar ...
, and Trapeza.
Minoan civilization
During the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, Crete was the centre of the Minoan
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
, notable for its art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, its writing systems such as Linear A
Linear A is a writing system that was used by the Minoans of Crete from 1800 to 1450 BC to write the hypothesized Minoan language or languages. Linear A was the primary script used in palace and religious writings of the Minoan civil ...
, and for its massive building complexes including the palace at Knossos
Knossos (also Cnossos, both pronounced ; grc, Κνωσός, Knōsós, ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and has been called Europe's oldest city.
Settled as early as the Neolithic period, the na ...
. Its economy benefited from a network of trade around much of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
, and Minoan cultural influence extended to Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, and the Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. Some scholars have speculated that legends
A legend is a historical narrative, a symbolic representation of folk belief.
Legend(s) or The Legend(s) may also refer to:
Narrative
* Urban legend, a widely repeated story of dubious truth
* A fictitious identity used in espionage
Books, co ...
such as that of the minotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur ( , ;. grc, ; in Latin as ''Minotaurus'' ) is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "pa ...
have a historical basis in Minoan times.
Mycenaean civilization
In 1420 BC, the Minoan civilization was subsumed by the Mycenaean civilization
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
from mainland Greece. The oldest samples of writing in the Greek language, as identified by Michael Ventris
Michael George Francis Ventris, (; 12 July 1922 – 6 September 1956) was an English architect, classicist and philologist who deciphered Linear B, the ancient Mycenaean Greek script. A student of languages, Ventris had pursued deciphermen ...
, is the Linear B archive from Knossos, dated approximately to 1425–1375 BC.
Archaic and Classical period
After the Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near Ea ...
, Crete was settled by new waves of Greeks from the mainland. A number of city states developed in the Archaic period. There was very limited contact with mainland Greece, and Greek historiography
Hellenic historiography (or Greek historiography) involves efforts made by Greeks to track and record historical events. By the 5th century BC, it became an integral part of ancient Greek literature and held a prestigious place in later Roman hist ...
shows little interest in Crete, and as a result, there are very few literary sources.
During the 6th to 4th centuries BC, Crete was comparatively free from warfare. The Gortyn code
The Gortyn code (also called the Great Code) was a legal code that was the codification of the civil law of the ancient Greek city-state of Gortyn in southern Crete.
History
Our sole source of knowledge of the code is the fragmentary boustro ...
(5th century BC) is evidence for how codified civil law established a balance between aristocratic power and civil rights.
In the late 4th century BC, the aristocratic order began to collapse due to endemic infighting among the elite, and Crete's economy was weakened by prolonged wars between city states. During the 3rd century BC, Gortyn
Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna ( el, Γόρτυν, , or , ) is a municipality, and an archaeological site, on the Mediterranean island of Crete away from the island's capital, Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka. Gortyn ...
, Kydonia (Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
), Lyttos
Lyctus or Lyttos (Greek: or ), was one of the most considerable cities in ancient Crete, which appears in the Homeric catalogue. Lyttos is now a village in the municipality of Minoa Pediada.
Lyctus in mythology
According to Hesiod, ''Theogony' ...
and Polyrrhenia
Polyrrhenia or Polyrrenia ( grc, Πολυρρηνία; modern el, Πολυρρηνία, Polyrrinia), Polyrrhen or Polyrren (Πολύρρην) or Polyren (Πολύρην), or Pollyrrhenia or Pollyrrenia (Πολλύρρηνα),''Periplus of Pseudo- ...
challenged the primacy of ancient Knossos.
While the cities continued to prey upon one another, they invited into their feuds mainland powers like Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
and its rivals Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the So ...
and Ptolemaic Egypt. In 220 BC the island was tormented by a war between two opposing coalitions of cities. As a result, the Macedonian king Philip V Philip V may refer to:
* Philip V of Macedon (221–179 BC)
* Philip V of France (1293–1322)
* Philip II of Spain, also Philip V, Duke of Burgundy (1526–1598)
* Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was ...
gained hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
over Crete which lasted to the end of the Cretan War (205–200 BC)
The Cretan War (205–200 BC) was fought by King Philip V of Macedon, the Aetolian League, many Cretan cities (of which Olous and Hierapytna were the most important) and Spartan pirates against the forces of Rhodes and later Attalus I of Perga ...
, when the Rhodians
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the So ...
opposed the rise of Macedon and the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
started to interfere in Cretan affairs.
In the 2nd century BC Ierapytna (Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete.
History
The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is loc ...
) gained supremacy on eastern Crete.
Roman rule
Crete was involved in the Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman provinc ...
, initially repelling an attack by Roman general Marcus Antonius Creticus
Marcus Antonius Creticus (flourished 1st century BC), a member of the Antonius family, was a Roman politician during the Late Roman Republic. He is best known for his failed pirate hunting career and being the father of the general Mark Antony.
Bi ...
in 71 BC. Nevertheless, a ferocious three-year campaign soon followed under Quintus Caecilius Metellus, equipped with three legions and Crete was finally conquered by Rome in 69 BC, earning for Metellus the title "''Creticus''". Gortyn
Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna ( el, Γόρτυν, , or , ) is a municipality, and an archaeological site, on the Mediterranean island of Crete away from the island's capital, Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka. Gortyn ...
was made capital of the island, and Crete became a Roman province, along with Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
that was called Creta et Cyrenaica
Crete and Cyrenaica ( la, Provincia Creta et Cyrenaica, Ancient Greek ) was a senatorial province of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC. It comprised the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in present-day L ...
. Archaeological remains suggest that Crete under Roman rule witnessed prosperity and increased connectivity with other parts of the Empire. In the 2nd century AD, at least three cities in Crete (Lyttos, Gortyn, Hierapytna) joined the Panhellenion
The Panhellenion ( el, Πανελλήνιον) or Panhellenium was a league of Greek city-states established in the year 131–132 AD by the Roman Emperor Hadrian while he was touring the Roman Greece, Roman provinces of Greece.
Hadrian was Philh ...
, a league of Greek cities founded by the emperor Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
. When Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
redivided the Empire, Crete was placed, along with Cyrene, under the diocese of Moesia
The Diocese of Moesia ( la, Dioecesis Moesiarum, el, Διοίκησις Μοισίας) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, in the area of modern western Bulgaria, central Serbia, Montenegro, Albania, North Macedonia, and Greece.
History
...
, and later by Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
to the diocese of Macedonia
The Diocese of Macedonia ( la, Dioecesis Macedoniae; el, Διοίκησις Μακεδονίας) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, forming part of the praetorian prefecture of Illyricum. Its administrative centre was Thessaloniki.
Histo ...
.
Byzantine Empire – first period
 Crete was separated from Cyrenaica . It remained a province within the eastern half of the Roman Empire, usually referred to as the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire after the establishment of a second capital in Constantinople by Constantine in 330. Crete was subjected to an attack by
Crete was separated from Cyrenaica . It remained a province within the eastern half of the Roman Empire, usually referred to as the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire after the establishment of a second capital in Constantinople by Constantine in 330. Crete was subjected to an attack by Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
in 467, the great earthquakes of 365 and 415, a raid by Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
in 623, Arab raids in 654 and the 670s, and again in the 8th century. In , the Emperor Leo III the Isaurian
Leo III the Isaurian ( gr, Λέων ὁ Ἴσαυρος, Leōn ho Isauros; la, Leo Isaurus; 685 – 18 June 741), also known as the Syrian, was Byzantine Emperor from 717 until his death in 741 and founder of the Isaurian dynasty. He put an en ...
transferred the island from the jurisdiction of the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
to that of the Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
.
Andalusian Arab rule
 In the 820s, after 900 years as a Roman island, Crete was captured by Andalusian Muwallads led by
In the 820s, after 900 years as a Roman island, Crete was captured by Andalusian Muwallads led by Abu Hafs Abu Hafs may refer to:
* Abu Hafs Umar al-Nasafi, a Muslim scholar of 11th/12th century
* Mohammed Atef (Abu Hafs al-Masri), past military chief of al-Qaeda
* Abu Hafs Umar al-Iqritishi, early ninth-century Andalusian pirate and founder of the Emir ...
,[Reinhart Dozy, ''Histoire des Musulmans d'Espagne: jusqu'à la conquête de l'Andalousie par les Almoravides'' (French) pg. 711–1110, Leiden, 1861 & 1881, 2nd edition] who established the Emirate of Crete
The Emirate of Crete ( ar, إقريطش, Iqrīṭish or , ''Iqrīṭiya''; gr, Κρήτη, Krētē) was an Islamic state that existed on the Mediterranean island of Crete from the late 820s to the reconquest of the island by the Byzantine Empir ...
. The Byzantines launched a campaign that took most of the island back in 842 and 843 under Theoktistos
Theoktistos or Theoctistus (; died November 20, 855) was a leading Byzantine official during the second quarter of the 9th century and the ''de facto'' head of the regency for the underage emperor Michael III from 842 until his dismissal and mu ...
. Further Byzantine campaigns in 911 and 949 failed. In 960–61, Nikephoros Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
' campaign
Campaign or The Campaign may refer to:
Types of campaigns
* Campaign, in agriculture, the period during which sugar beets are harvested and processed
*Advertising campaign, a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme
* Bl ...
completely restored Crete to the Byzantine Empire, after a century and a half of Arab control.
Byzantine Empire – second period
In 961, Nikephoros Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
returned the island to Byzantine rule after expelling the Arabs. Extensive efforts at conversion of the populace were undertaken, led by John Xenos and Nikon "the Metanoeite". The reconquest of Crete was a major achievement for the Byzantines, as it restored Byzantine control over the Aegean littoral and diminished the threat of Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia Pe ...
pirates, for which Crete had provided a base of operations.
In 1204, the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
seized and sacked the imperial capital of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. Crete was initially granted to leading Crusader Boniface of Montferrat
Boniface I, usually known as Boniface of Montferrat ( it, Bonifacio del Monferrato, link=no; el, Βονιφάτιος Μομφερρατικός, ''Vonifatios Momferratikos'') (c. 1150 – 4 September 1207), was the ninth Marquis of Montferrat ( ...
in the partition of spoils that followed. However, Boniface sold his claim to the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
, whose forces made up the majority of the Crusade. Venice's rival the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the Lat ...
immediately seized the island and it was not until 1212 that Venice secured Crete as a colony.
Venetian rule
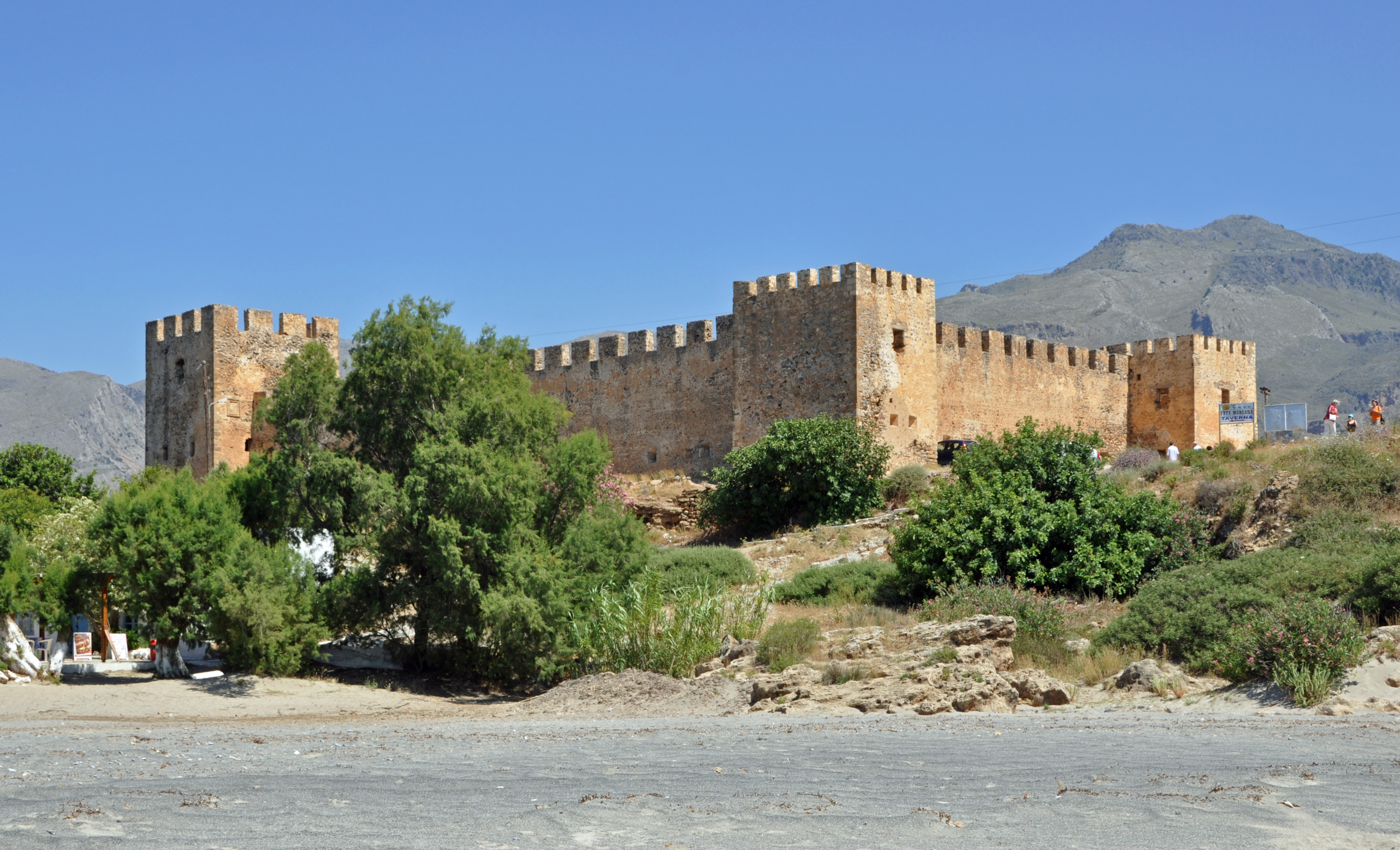 From 1212, during
From 1212, during Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
's rule, which lasted more than four centuries, a Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
swept through the island as is evident from the plethora of artistic works dating to that period. Known as The Cretan School
Cretan School describes an important school of icon painting, under the umbrella of post-Byzantine art, which flourished while Crete was under Venetian rule during the late Middle Ages, reaching its climax after the Fall of Constantinople, beco ...
or Post-Byzantine Art
Cretan School describes an important school of icon painting, under the umbrella of post-Byzantine art, which flourished while Crete was under Venetian rule during the late Middle Ages, reaching its climax after the Fall of Constantinople, becom ...
, it is among the last flowerings of the artistic traditions of the fallen empire. The most notable representatives of this Cretan renaissance were the painter El Greco
Domḗnikos Theotokópoulos ( el, Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος ; 1 October 1541 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco ("The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. "El G ...
and the writers Nicholas Kalliakis
Nicholas Kalliakis ( el, Νικόλαος Καλλιάκης, ''Nikolaos Kalliakis''; la, Nicolaus Calliachius; it, Niccolò Calliachi; c. 1645 - 8 May 1707) was a Cretan Greek scholar and philosopher who flourished in Italy in the 17th century ...
(1645–1707), Georgios Kalafatis (professor) (–1720), Andreas Musalus
Andreas Musalus ( la, Andreas Musalus, it, Andrea Musalo, gr, Ανδρέας Μουσάλος; ca. 1665/6 – ca. 1721) was a Greek professor of mathematics, philosopher and architectural theorist who was largely active in Venice during the 1 ...
(–1721) and Vitsentzos Kornaros
Vitsentzos or Vikentios Kornaros ( el, Βιτσέντζος or ) or Vincenzo Cornaro (March 29, 1553 – 1613/1614) was a Cretan poet, who wrote the romantic epic poem ''Erotokritos''. He wrote in vernacular Cretan dialect (Cretan Greek), and was ...
.Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
Venetians, the city of Candia was reputed to be the best fortified city of the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
.[M. Greene. 2001. Ruling an island without a navy: A comparative view of Venetian and Ottoman Crete. ''Oriente moderno'', 20(81), 193–207] The three main forts were located at Gramvousa
Gramvousa also Grampousa ( el, Γραμβούσα or Γραμπούσα, further names include ''Akra'', ''Cavo Buso'', ''Cavo Bouza'', ''Garabusa'' and ''Grabusa'') refers to two small uninhabited islands off the coast of a peninsula also known ...
, Spinalonga
Spinalonga ( el, Σπιναλόγκα) is an island located in the Gulf of Elounda in north-eastern Crete, in Lasithi, next to the town of Plaka. The island is further assigned to the area of Kalydon.
It is near the Spinalonga peninsula ("large ...
, and Fortezza
Fortezza is an information security system that uses the Fortezza Crypto Card, a PC Card-based security token. It was developed for the U.S. government's Clipper chip project and has been used by the U.S. Government in various applications.
Ea ...
at Rethymnon. Other fortifications include the Kazarma fortress
Kazarma ( el, Καζάρμα) (from it, Casa di arma, "the guard barracks") is the Venetian-era fortress of the city of Sitia in Crete, Greece. This fortress was built in the 13th Century during Venetian rule on Crete. The Venetians abandoned t ...
at Sitia. In 1492, Jews expelled from Spain settled on the island. In 1574–77, Crete was under the rule of Giacomo Foscarini as Proveditor General, Sindace and Inquisitor
An inquisitor was an official (usually with judicial or investigative functions) in an inquisition – an organization or program intended to eliminate heresy and other things contrary to the doctrine or teachings of the Catholic faith. Literal ...
. According to Starr's 1942 article, the rule of Giacomo Foscarini was a Dark Age for Jews and Greeks. Under his rule, non-Catholics had to pay high taxes with no allowances. In 1627, there were 800 Jews in the city of Candia, about seven percent of the city's population. Marco Foscarini was the Doge of Venice during this time period.
Ottoman rule


 The
The Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
conquered Crete (Girit Eyâleti) in 1669, after the siege of Candia
The siege of Candia (modern Heraklion, Crete) was a military conflict in which Ottoman forces besieged the Venetian-ruled city. Lasting from 1648 to 1669, or a total of 21 years, it is the second-longest siege in history after the siege of Ce ...
. Many Greek Cretans fled to other regions of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
after the Ottoman–Venetian Wars, some even prospering such as the family of Simone Stratigo
Simone Stratigo ( gr, Συμεών Φίλιππος Στρατηγός, ''Symeon Filippos Stratigos''; it, Simone Filippo Stratico; 1733–1824) was an Italian Greek mathematician and a nautical science expert who studied and lived in Padua and ...
(c. 1733 – c. 1824) who migrated to Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
from Crete in 1669.Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
presence on the island, aside from the interlude of the Arab occupation, was cemented by the Ottoman conquest. Most Cretan Muslims
The Cretan Muslims ( el, Τουρκοκρητικοί or , or ; tr, Giritli, , or ; ar, أتراك كريت) or Cretan Turks were the Muslim inhabitants of the island of Crete. Their descendants settled principally in Turkey, the Dodecanese ...
were local Greek converts who spoke Cretan Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, but in the island's 19th-century political context they came to be viewed by the Christian population as Turks. Contemporary estimates vary, but on the eve of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
(1830), as much as 45% of the population of the island may have been Muslim. A number of Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
orders were widespread throughout the island, the Bektashi order being the most prevalent, possessing at least five tekkes. Many Cretan Turks fled Crete because of the unrest, settling in Turkey, Rhodes, Syria, Libya and elsewhere. By 1900, 11% of the population was Muslim. Those remaining were relocated in the 1924 population exchange between Greece and Turkey.
During Easter of 1770, a notable revolt against Ottoman rule, in Crete, was started by Daskalogiannis, a shipowner from Sfakia who was promised support by Orlov Revolt, Orlov's fleet which never arrived. Daskalogiannis eventually surrendered to the Ottoman authorities. Today, the airport at Chania is named after him.
During the Greek war of independence, Sultan Mahmud II granted rule over Crete to Egypt's ruler Muhammad Ali Pasha in exchange for his military support. Crete was subsequently left out of the new Greek state established under the London Protocol of 1830. Its administration by Muhammad Ali was confirmed in the Convention of Kütahya of 1833, but direct Ottoman rule was re-established by the Convention of London (1840), Convention of London of 3 July 1840.
Heraklion was surrounded by high walls and bastions and extended westward and southward by the 17th century. The most opulent area of the city was the northeastern quadrant where all the elite were gathered together. The city had received another name under the rule of the Ottomans, "the deserted city".
Cretan State 1898–1908
 Following the repeated uprisings in 1841, 1858, 1889, 1895 and 1897 by the Cretan people, who wanted to join Greece, the Great powers#History, Great Powers decided to restore order and in February 1897 sent in troops. The island was subsequently garrisoned by troops from Great Britain, France, Italy and Russia; Germany and Austro-Hungary withdrawing from the occupation in early 1898. During this period Crete was governed through a committee of admirals from the remaining four Powers. In March 1898 the Powers decreed, with the very reluctant consent of the Sultan, that the island would be granted autonomy under Ottoman suzerainty in the near future.
In September 1898 the Candia massacre in Candia, modern Heraklion, left over 500 Cretan Christians and 14 British servicemen dead at the hands of Muslim irregulars. As a result, the Admirals ordered the expulsion of all Ottoman troops and administrators from the island, a move that was ultimately completed by early November. The decision to grant autonomy to the island was enforced and a High Commissioner, Prince George of Greece, appointed, arriving to take up his post in December 1898.
Following the repeated uprisings in 1841, 1858, 1889, 1895 and 1897 by the Cretan people, who wanted to join Greece, the Great powers#History, Great Powers decided to restore order and in February 1897 sent in troops. The island was subsequently garrisoned by troops from Great Britain, France, Italy and Russia; Germany and Austro-Hungary withdrawing from the occupation in early 1898. During this period Crete was governed through a committee of admirals from the remaining four Powers. In March 1898 the Powers decreed, with the very reluctant consent of the Sultan, that the island would be granted autonomy under Ottoman suzerainty in the near future.
In September 1898 the Candia massacre in Candia, modern Heraklion, left over 500 Cretan Christians and 14 British servicemen dead at the hands of Muslim irregulars. As a result, the Admirals ordered the expulsion of all Ottoman troops and administrators from the island, a move that was ultimately completed by early November. The decision to grant autonomy to the island was enforced and a High Commissioner, Prince George of Greece, appointed, arriving to take up his post in December 1898.[Robert Holland and Diane Markides, ''The British and the Hellenes: Struggles for Mastery in the Eastern Mediterranean 1850–1960''. p. 81. Oxford University Press, 2005.] The flag of the Cretan State
The Cretan State ( el, Κρητική Πολιτεία, Kritiki Politeia; ota, كريد دولتى, Girid Devleti) was established in 1898, following the intervention by the Great Powers (United Kingdom, France, Italy, Austria-Hungary, Germany ...
was chosen by the Powers, with the white star representing the Ottoman suzerainty over the island.
 In 1905, disagreements between Prince George and minister Eleftherios Venizelos
over the question of the ''enosis'' (union with Greece), such as the Prince's autocratic style of government, resulted in the Theriso revolt, one of the leaders being Eleftherios Venizelos.
Prince George resigned as High Commissioner and was replaced by Alexandros Zaimis, a former Greek prime minister, in 1906. In 1908, taking advantage of domestic turmoil in Turkey as well as the timing of Zaimis's vacation away from the island, the Cretan deputies unilaterally declared union with Greece.
With the breakout of the First Balkan War, the Greek government declared that Crete was now Greek territory. This was not recognised internationally until 1 December 1913.
In 1905, disagreements between Prince George and minister Eleftherios Venizelos
over the question of the ''enosis'' (union with Greece), such as the Prince's autocratic style of government, resulted in the Theriso revolt, one of the leaders being Eleftherios Venizelos.
Prince George resigned as High Commissioner and was replaced by Alexandros Zaimis, a former Greek prime minister, in 1906. In 1908, taking advantage of domestic turmoil in Turkey as well as the timing of Zaimis's vacation away from the island, the Cretan deputies unilaterally declared union with Greece.
With the breakout of the First Balkan War, the Greek government declared that Crete was now Greek territory. This was not recognised internationally until 1 December 1913.[
]
Second World War
 During World War II, the island was the scene of the famous Battle of Crete in May 1941. The initial 11-day battle was bloody and left more than 11,000 soldiers and civilians killed or wounded. As a result of the fierce resistance from both Allied forces and civilian Cretan locals, the invasion force suffered heavy casualties, and Adolf Hitler forbade further large-scale paratroop operations for the rest of the war. During the initial and subsequent occupation, German firing squads routinely executed male civilians in reprisal for the death of German soldiers; civilians were rounded up randomly in local villages for the mass killings, such as at the Massacre of Kondomari and the Viannos massacres. Two German generals were later tried and executed for their roles in the killing of 3,000 of the island's inhabitants.
During World War II, the island was the scene of the famous Battle of Crete in May 1941. The initial 11-day battle was bloody and left more than 11,000 soldiers and civilians killed or wounded. As a result of the fierce resistance from both Allied forces and civilian Cretan locals, the invasion force suffered heavy casualties, and Adolf Hitler forbade further large-scale paratroop operations for the rest of the war. During the initial and subsequent occupation, German firing squads routinely executed male civilians in reprisal for the death of German soldiers; civilians were rounded up randomly in local villages for the mass killings, such as at the Massacre of Kondomari and the Viannos massacres. Two German generals were later tried and executed for their roles in the killing of 3,000 of the island's inhabitants.
Civil War
In the aftermath of the Dekemvriana in Athens, Cretan leftists were targeted by the right-wing paramilitary organization National Organization of Rethymno (EOR), which engaged in attacks in the villages of Koxare and Melampes, as well as Rethymno in January 1945. Those attacks did not escalate into a full-scale insurgency as they did in the Greek mainland and the Cretan ELAS did not surrender its weapons after the Treaty of Varkiza. An uneasy truce was maintained until 1947, with a series of arrests of notable communists in Chania and Heraklion. Encouraged by orders from the central organization in Athens, KKE launched an insurgency in Crete; marking the beginning of the Greek Civil War on the island. In eastern Crete the Democratic Army of Greece (DSE) struggled to establish its presence in Dikti and Psilorites. On 1 July 1947, the surviving 55 fighters of DSE were ambushed south of Psilorites, the few surviving members of the unit managed to join the rest of DSE in Lefka Ori
Lefka Ori ( el, Λευκά Όρη, meaning 'White Mountains') or Madares ( from the Cretan Greek meaning 'without coverage, bald, bare of any vegetation for high mountain areas') is a mountain range located in Western Crete, in the Chania prefect ...
.
The Lefka Ori region in the west offered more favourable conditions for DSE's insurgency. In the summer of 1947 DSE raided and looted the Maleme Airport and motor depot at Chrysopigi. Its numbers swelled to approximately 300 fighters, the rise of DSE numbers compounded with crop failure on the island created serious logistical issues for the insurgents. The communists resorted to Cattle raiding, cattle rustling and crop confiscations which solved the problem only temporarily. In the autumn of 1947, the Greek government offered generous amnesty terms to Cretan DSE fighters and mountain bandits, many of whom opted to abandon armed struggle or even defect to the nationalists. On 4 July 1948, government troops launched a large scale offensive on Samariá Gorge
The Samariá Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι Σαμαριάς or just ''Φάραγγας'') is a
National Park of Greece since 1962 on the island of Crete – a major tourist attraction of the island – and a World's Biosphere Reserve.
The gorg ...
. Many DSE soldiers were killed in the fighting while the survivors broke into small armed bands. In October 1948, the secretary of the Cretan KKE Giorgos Tsitilos was killed in an ambush. By the following month only 34 DSE fighters remained active in Lefka Ori. The insurgency in Crete gradually withered away, with the last two hold outs surrendering in 1974, 25 years after the conclusion of the war in mainland Greece.
Tourism
 Crete is one of the most popular holiday destinations in Greece. 15% of all arrivals in Greece come through the city of Heraklion (port and airport), while charter journeys to Heraklion make up abou
Crete is one of the most popular holiday destinations in Greece. 15% of all arrivals in Greece come through the city of Heraklion (port and airport), while charter journeys to Heraklion make up abou
20% of all charter flights in Greece
The number of hotel beds on the island increased by 53% in the period between 1986 and 1991.
Today, the island's tourism infrastructure caters to all tastes, including a very wide range of accommodation; the island's facilities take in large luxury hotels with their complete facilities, swimming pools, sports and recreation, smaller family-owned apartments, camping facilities and others. Visitors reach the island via two international airports in Heraklion and Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
and a smaller airport in Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
(international charter and domestic flights starting May 2012) or by boat to the main ports of Heraklion, Chania, Rethimno, Agios Nikolaos and Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
.
Popular tourist attractions include the archaeological sites of the Minoan civilisation, the Venetian old city and port of Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
, the Venetian castle at Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
, the gorge of Samariá Gorge, Samaria, the islands of Chrysi, Elafonisi
Elafonisi ( el, Ελαφονήσι "deer island") is an island located close to the southwestern corner of the Mediterranean island of Crete, of which it is administratively a part, in the regional unit of Chania. When the weather is fine it is ...
, Gramvousa
Gramvousa also Grampousa ( el, Γραμβούσα or Γραμπούσα, further names include ''Akra'', ''Cavo Buso'', ''Cavo Bouza'', ''Garabusa'' and ''Grabusa'') refers to two small uninhabited islands off the coast of a peninsula also known ...
, Spinalonga
Spinalonga ( el, Σπιναλόγκα) is an island located in the Gulf of Elounda in north-eastern Crete, in Lasithi, next to the town of Plaka. The island is further assigned to the area of Kalydon.
It is near the Spinalonga peninsula ("large ...
and the Palm Beach of Vai, which is the largest natural palm forest in Europe.
Transportation
Crete has an extensive bus system with regular services across the north of the island and from north to south. There are two regional bus stations in Heraklion. Bus routes and timetables can be found on KTEL website.
Holiday homes and immigration
Crete's mild climate attracts interest from northern Europeans who want a holiday home or residence on the island. European Union, EU citizens have the right to freely buy property and reside with little formality. In the cities of Heraklion and Chania, the average price per square metre of apartments ranges from €1,670 to €1,700. A growing number of real estate companies cater mainly to British immigrants, followed by Netherlands, Dutch, Germany, German, Scandinavian and other European nationalities wishing to own a home in Crete. The United Kingdom, British immigrants are concentrated in the western regional units of Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
and Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
and to a lesser extent in Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
and Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thr ...
.
Archaeological sites and museums
The area has a large number of archaeological sites, including the Minoan sites of Knossos
Knossos (also Cnossos, both pronounced ; grc, Κνωσός, Knōsós, ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and has been called Europe's oldest city.
Settled as early as the Neolithic period, the na ...
, Malia, Crete#History, Malia (not to be confused with the town of the same name), Petras and Phaistos, the classical site of Gortys, and the diverse archaeology of the island of Koufonisi, which includes Minoan, Roman, and World War II era ruins (nb. due to conservation concerns, access to Koufonisi has been restricted for the last few years, so it is best to check before heading to a port).
There are a number of museums throughout Crete. The Heraklion Archaeological Museum displays most of the archaeological finds from the Minoan era and was reopened in 2014.
Harmful effects
Helen Briassoulis, in a qualitative analysis, proposed in the ''Journal of Sustainable Tourism'' that Crete is affected by tourism applying pressure to it to develop at an unhealthy rate, and that informal, internal systems within the country are forced to adapt. According to her, these forces have strengthened in three stages: from the period from 1960 to 1970, 1970–1990, and 1990 to the present. During this first period, tourism was a largely positive force, pushing modern developments like running water and electricity onto the largely rural countryside. However, beginning in the second period and especially in the third period leading up to the present day, tourist companies became more pushy with deforestation and pollution of Crete's natural resources. The country is then pulled into an interesting parity, where these companies only upkeep those natural resources that are directly essential to their industry.
File:Gortys R02.jpg, View of Gortyn
Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna ( el, Γόρτυν, , or , ) is a municipality, and an archaeological site, on the Mediterranean island of Crete away from the island's capital, Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka. Gortyn ...
File:Festos1(js).jpg, Archaeological site of Phaistos
File:Knossos south propylaeum.jpg, Ruins of the Knossos, Palace of Knossos
File:Archaeological Museum of Chania.jpg, Archeological Museum of Chania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion.
The muni ...
File:AMC Intern of Museum of Chania (Crete) 2.jpg, Archaeological Museum of Chania
File:Chania naval museum.jpg, Crete Naval museum
File:Pluto Serapis and Persephone Isis Heraklion museum.jpg, Pluto (mythology), Pluto and Persephone in Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
Museum
File:Jars in Malia Crete the two.jpg, Jars in Malia, Crete, Malia, Crete
Fauna and flora
Fauna
Crete is isolated from mainland Europe, Asia, and Africa, and this is reflected in the diversity of the fauna and flora. As a result, the fauna and flora of Crete have many clues to the evolution of species. There are no animals that are dangerous to humans on the island of Crete in contrast to other parts of Greece. Indeed, the ancient Greeks attributed the lack of large mammals such as bears, wolves, jackals, and venomous snakes, to the labour of Hercules (who took a live Cretan bull to the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
). Hercules wanted to honor the birthplace of Zeus by removing all "harmful" and "venomous" animals from Crete. Later, Cretans believed that the island was cleared of dangerous creatures by the Apostle Paul, who lived on the island of Crete for two years, with his exorcisms and blessings. There is a natural history museum, the Natural History Museum of Crete, operating under the direction of the University of Crete and two aquariums – Aquaworld Aquarium, Aquaworld in Hersonissos and Cretaquarium in Gournes, displaying sea creatures common in Cretan waters.
Prehistoric fauna
Dwarf elephants, Hippopotamus creutzburgi, dwarf hippopotamus, dwarf mammoths, Candiacervus, dwarf deer, and Cretan owl, giant flightless owls were native to Pleistocene Crete.
Mammals
Mammals of Crete include the vulnerable kri-kri, ''Capra aegagrus cretica'' that can be seen in the national park of the Samaria Gorge
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first-ce ...
and on Thodorou, Dia (island), Dia and Agioi Pantes (islets off the north coast), the Cretan wildcat and the Cretan spiny mouse.[Thodorou Islands off Platanias]
ExploreCrete.com Other terrestrial mammals include subspecies of the Cretan marten, the Cretan weasel, the Cretan badger, the long-eared hedgehog, and the edible dormouse.
The Cretan shrew, a type of white-toothed shrew is considered endemic species, endemic to the island of Crete because this species of shrew is unknown elsewhere. It is a relic species of the ''Crocidura'' shrews of which fossils have been found that can be dated to the Pleistocene era. In the present day it can only be found in the highlands of Crete. It is considered to be the only surviving remnant of the endemic species of the Pleistocene Mediterranean islands.
Bat species include: Blasius's horseshoe bat, the lesser horseshoe bat, the greater horseshoe bat, the lesser mouse-eared bat, Geoffroy's bat, the whiskered bat, Kuhl's pipistrelle, the common pipistrelle, Savi's pipistrelle, the serotine bat, the long-eared bat, Schreibers' bat and the European free-tailed bat.[Wildlife on Crete]
IntoCrete.com
File:Kri-kri 1.jpg, The Kri-kri (the Cretan ibex) lives in protected natural parks at the gorge of Samaria and the island of Agios Theodoros.
File:Male Cretan ibex.jpg, Male Cretan ibex
File:Kritikos Lagonikos 02.jpg, ''Cretan Hound'' or Kritikos Lagonikos, one of Europe's oldest hunting dog breeds
Birds
A large variety of birds includes eagles (can be seen in Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thr ...
), swallows (throughout Crete in the summer and year-round in the south of the island), pelicans (along the coast), and common cranes (including Gavdos
Gavdos ( el, Γαύδος, ) is the southernmost Greek island, located to the south of its much larger neighbour, Crete, of which it is administratively a part, in the regional unit of Chania. It forms a community with surrounding islets and was ...
and Gavdopoula). The Cretan mountains and gorges are refuges for the endangered lammergeier vulture. Bird species include: the golden eagle, Bonelli's eagle, the bearded vulture or lammergeier, the griffon vulture, Eleonora's falcon, peregrine falcon, lanner falcon, European kestrel, tawny owl, little owl, hooded crow, alpine chough, red-billed chough, and the Eurasian hoopoe. The population of griffon vultures in Crete is the largest insular one of the species in the world and consists the majority of griffon vulture population in Greece.
Reptiles and amphibians
Tortoises can be seen throughout the island. Snakes can be found hiding under rocks. Toads and frogs reveal themselves when it rains.
Reptiles include the Aegean wall lizard, Balkan green lizard, common chameleon, Chalcides ocellatus, ocellated skink, snake-eyed skink, moorish gecko, Turkish gecko, Kotschy's gecko, spur-thighed tortoise, and the Caspian turtle.[Native Reptiles of Crete at Aquaworld]
Aquaworld Aquarium.
There are four species of snake on the island and these are not dangerous to humans. The four species include the leopard snake (locally known as Ochendra), the Balkan whip snake (locally called Dendrogallia), the dice snake (called Nerofido in Greek), and the only venomous snake is the nocturnal European cat snake, cat snake which has evolved to deliver a weak venom at the back of its mouth to paralyse geckos and small lizards, and is not dangerous to humans.[The Snakes of Crete by John McClaren]
CreteGazette.com
Sea turtles include the green turtle and the loggerhead turtle which are both threatened species.[ The loggerhead turtle nests and hatches on north-coast beaches around Rethymno and Chania, and south-coast beaches along the gulf of Mesara.][Crete p. 69]
by Victoria Kyriakopoulos
Amphibians include the European green toad, American bullfrog (introduced), European tree frog, and the Cretan marsh frog (Endemism, endemic).[
]
Arthropods
Crete has an unusual variety of insects. Cicadas, known locally as ''Tzitzikia'', make a distinctive repetitive ''tzi tzi'
sound
that becomes louder and more frequent on hot summer days. Butterfly species include the swallowtail butterfly.[ Moth species include the hummingbird moth. There are several species of scorpion such as Euscorpius carpathicus whose venom is generally no more potent than a mosquito bite.
]
Crustaceans and molluscs
River crabs include the semi-terrestrial ''Potamon potamios'' crab.[ Edible snails are widespread and can cluster in the hundreds waiting for rainfall to reinvigorate them.
]
Sealife
 Apart from terrestrial mammals, the seas around Crete are rich in large marine mammals, a fact unknown to most Greeks at present, although reported since ancient times. Indeed, the Minoan frescoes depicting dolphins in Queen's Megaron at Knossos indicate that Minoans were well aware of and celebrated these creatures. Apart from the famous endangered Mediterranean monk seal, which lives in almost all the coasts of the country, Greece hosts whales, sperm whales, dolphins and porpoises. These are either permanent residents of the Mediterranean or just occasional visitors. The area south of Crete, known as the Greek Abyss, hosts many of them. Squid and octopus can be found along the coast and sea turtles and hammerhead sharks swim in the sea around the coast. The Cretaquarium and the Aquaworld Aquarium, are two of only three aquariums in the whole of Greece. They are located in Gournes and Hersonissos respectively. Examples of the local sealife can be seen there.
Apart from terrestrial mammals, the seas around Crete are rich in large marine mammals, a fact unknown to most Greeks at present, although reported since ancient times. Indeed, the Minoan frescoes depicting dolphins in Queen's Megaron at Knossos indicate that Minoans were well aware of and celebrated these creatures. Apart from the famous endangered Mediterranean monk seal, which lives in almost all the coasts of the country, Greece hosts whales, sperm whales, dolphins and porpoises. These are either permanent residents of the Mediterranean or just occasional visitors. The area south of Crete, known as the Greek Abyss, hosts many of them. Squid and octopus can be found along the coast and sea turtles and hammerhead sharks swim in the sea around the coast. The Cretaquarium and the Aquaworld Aquarium, are two of only three aquariums in the whole of Greece. They are located in Gournes and Hersonissos respectively. Examples of the local sealife can be seen there.[Great Britons in Crete, John Bryce McLaren]
BritsinCrete.net
Some of the fish that can be seen in the waters around Crete include: scorpion fish, dusky grouper, east Atlantic peacock wrasse, five-spotted wrasse, weever fish, common stingray, brown ray, mediterranean black goby, pearly razorfish, star-gazer, painted comber, damselfish, and the flying gurnard.
Flora
The Minoans contributed to the deforestation of Crete. Further deforestation occurred in the 1600s "so that no more local supplies of firewood were available".
Common wildflowers include: camomile, daisy, gladiolus, hyacinth, Iris flower, iris, poppy, cyclamen and tulip, among others.[Fielding, J. and Turland, N. "Flowers of Crete", Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, , 2008] There are more than 200 different species of wild orchid on the island and this includes 14 varieties of ''Ophrys cretica''.[Crete p.68]
by Victoria Kyriakopoulos Crete has a rich variety of indigenous herbs including common Salvia officinalis, sage, rosemary, thyme, and oregano.[The Flora of Crete]
ExploreCrete.com Rare herbs include the endemic Origanum dictamus, Cretan dittany.[ and ironwort, ''Sideritis syriaca'', known as Malotira (Μαλοτήρα). Varieties of cactus include the edible Opuntia, prickly pear. Common trees on the island include the chestnut tree, chestnut, cypress tree, cypress, oak tree, oak, Olea europaea, olive tree, pine tree, pine, plane tree, plane, and tamarisk tree, tamarisk.][ Trees tend to be taller to the west of the island where water is more abundant.
File:044 Dracunculus vulgaris at Akrotiri peninsula, Crete, Greece.jpg, Snake lily (''Dracunculus vulgaris'')
File:Ophrys cretica-001.jpg, The ''Ophrys cretica'' orchid.
]
Environmentally protected areas
There are a number of environmentally protected areas. One such area is located at the island of Elafonisi
Elafonisi ( el, Ελαφονήσι "deer island") is an island located close to the southwestern corner of the Mediterranean island of Crete, of which it is administratively a part, in the regional unit of Chania. When the weather is fine it is ...
on the coast of southwestern Crete. Also, the palm forest of Vai in eastern Crete and the Dionysades
The Dionysades ( el, Διονυσάδες, also Γιανυσάδες - ''Gianysades'') is a small, northward-trending archipelago off the north coast of the island of Crete, mid-way between the Cape Sidero lighthouse to the southeast (from whi ...
(both in the municipality of Sitia
Sitia ( el, Σητεία) is a port town and a municipality in Lasithi, Crete, Greece. The town has 9,912 inhabitants (2011) and the municipality has 18,318 (2011). It lies east of Agios Nikolaos and northeast of Ierapetra. Sitia port is on the ...
, Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thr ...
), have diverse animal and plant life. Vai has a palm beach and is the largest natural palm forest in Europe. The island of Chrysi, south of Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete.
History
The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is loc ...
, has the largest naturally-grown ''Juniperus macrocarpa
''Juniperus macrocarpa'' (large-fruited juniper, syn. ''J. oxycedrus'' subsp. ''macrocarpa'' (Sibth. & Sm.) Ball) is a species of juniper, native across the northern Mediterranean region from southwestern Spain east to western Turkey and Cyprus, ...
'' forest in Europe. Samaria Gorge
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first-ce ...
is a Man and the Biosphere Programme, World Biosphere Reserve and Richtis Gorge
Richtis Gorge ( el, Φαράγγι του Ρίχτη, Faraggi tou Richti) is a gorge in Crete, GreeceMap of Richtis Gorge here. It is a state protected park near Exo Mouliana, Sitia, eastern Crete (Greece) that starts at the traditional village ...
is protected for its landscape diversity.
Mythology
 Crete has a strong association with ancient Greek gods but is also connected with the Minoan civilization.
According to Greek mythology, the Psychro Cave, Diktaean Cave at Mount Dikti was the birthplace of the god
Crete has a strong association with ancient Greek gods but is also connected with the Minoan civilization.
According to Greek mythology, the Psychro Cave, Diktaean Cave at Mount Dikti was the birthplace of the god Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
. The Paximadia
Paximadia ( el, Παξιμάδια, "rusks") are two small uninhabited islands in the gulf of Mesara located approximately south of Agia Galini in Rethymno regional unit. They are in the Libyan Sea next to the southern coast of Crete. Due to ...
islands were the birthplace of the goddess Artemis and the god Apollo. Their mother, the goddess Leto, was worshipped at Phaistos. The goddess Athena bathed in Lake Voulismeni. Zeus launched a lightning bolt at a giant lizard that was threatening Crete. The lizard immediately turned to stone and became the lizard-shaped island of Dia (island), Dia, which can be seen from Knossos. The islets of Souda (island), Lefkai were the result of a musical contest between the Siren (mythology), Sirens and the Muses. The Muses were so anguished to have lost that they plucked the feathers from the wings of their rivals; the Sirens turned white and fell into the sea at Aptera, Greece, Aptera ("featherless"), where they formed the islands in the bay that were called Lefkai (the islands of Souda (island), Souda and Leon (Souda Bay), Leon). Heracles, in one of his labors, took the Cretan bull to the Peloponnese. Europa (consort of Zeus), Europa and Zeus made love at Gortys and conceived the kings of Crete: Rhadamanthys, Sarpedon (brother of Minos), Sarpedon, and Minos.
The labyrinth of the Palace of Knossos was the setting for the myth of Theseus#Minotaur, Theseus and the Minotaur in which the Minotaur was slain by Theseus. Icarus and Daedalus were captives of King Minos and crafted wings to escape. After his death, King Minos became a judge of the dead in Hades, while Rhadamanthys became the ruler of the Elysium, Elysian fields.
Culture
Crete has its own distinctive Mantinada, Mantinades poetry. The island is known for its Mantinades-based Music of Crete, music (typically performed with the Lyra (Cretan), Cretan lyra and the laouto) and has many indigenous dances, the most noted of which is the Pentozali. Since the 1980s and certainly in the 1990s onwards there has been a proliferation of Cultural Associations that teach dancing (in Western Crete many focus on rizitiko singing). These Associations often perform in official events but also become stages for people to meet up and engage in traditionalist practices. The topic of tradition and the role of Cultural Associations in reviving it is very often debated throughout Crete.
Cretan authors have made important contributions to Greek literature throughout the modern period; major names include Vikentios Kornaros, creator of the 17th-century epic romance ''Erotokritos'' (Greek Ερωτόκριτος), and, in the 20th century, Nikos Kazantzakis. In the Renaissance, Crete was the home of the Cretan School of icon painting, which influenced El Greco
Domḗnikos Theotokópoulos ( el, Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος ; 1 October 1541 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco ("The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. "El G ...
and through him subsequent European painting.
Cretans are fiercely proud of their island and customs, and men often don elements of traditional dress in everyday life: knee-high black riding boots (''stivania''), Breeches#Types of breeches, ''vráka'' breeches tucked into the boots at the knee, black shirt and black headdress consisting of a fishnet-weave kerchief worn wrapped around the head or draped on the shoulders (''sariki''). Men often grow large mustaches as a mark of masculinity.
Cretan society is known in Greece and internationally for family and clan feud, vendettas which persist on the island to date.[Brian Murphy]
Vendetta Victims: People, A Village – Crete's `Cycle Of Blood' Survives The Centuries
at ''The Seattle Times'', 14 January 1999. Cretans also have a tradition of keeping firearms at home, a tradition lasting from the era of resistance against the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. Nearly every rural household on Crete has at least one unregistered gun.
Sports
Crete has many football clubs playing in the local leagues. During the 2011–12 season, OFI Crete, which plays at Theodoros Vardinogiannis Stadium (Iraklion), and Ergotelis F.C., which plays at the Pankritio Stadium (Iraklion) were both members of the Superleague Greece, Greek Superleague. During the 2012–13 season, OFI Crete, which plays at Theodoros Vardinogiannis Stadium (Iraklion), and Platanias F.C., which plays at the Perivolia Municipal Stadium, near Chania, are both members of the Superleague Greece, Greek Superleague.
Notable people

 Notable people from Crete include:
*Nikos Kazantzakis, author, born in Heraklion, 7 times suggested for the Nobel Prize
*Odysseas Elytis, poet, awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1979, born in
Notable people from Crete include:
*Nikos Kazantzakis, author, born in Heraklion, 7 times suggested for the Nobel Prize
*Odysseas Elytis, poet, awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1979, born in Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
*Georgios Chortatzis, Renaissance author
*Vitsentzos Kornaros
Vitsentzos or Vikentios Kornaros ( el, Βιτσέντζος or ) or Vincenzo Cornaro (March 29, 1553 – 1613/1614) was a Cretan poet, who wrote the romantic epic poem ''Erotokritos''. He wrote in vernacular Cretan dialect (Cretan Greek), and was ...
, Renaissance author from Sitia, who lived in Heraklion (then Candia)
*Domenikos Theotokopoulos (El Greco), Renaissance artist, born in Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
*Nikos Xilouris, famous composer and singer.
*Psarantonis, Cretan folk singer and Cretan lyra player and brother of Nikos Xilouris.
*Nana Mouskouri, singer, born in Chania
*Eleftherios Venizelos, former Greek Prime Minister, born in Chania Prefecture
*Konstantinos Mitsotakis, nephew of Eleftherios Venizelos and Prime Minister of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
.
*Daskalogiannis, leader of the Orlov Revolt in Crete in 1770
*Michalis Kourmoulis, leader of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
from Messara.
*Eleni Daniilidou, tennis player, born in Chania
*Louis Tikas, Greek-American labor union leader
*Tess Fragoulis, Greek-Canadian writer, born in Heraklion
*Nick Dandolos, a.k.a. Nick the Greek, professional gambler and high roller
*Joseph Sifakis, a computer scientist, laureate of the 2007 Turing Award, born in Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
in 1946
*Constantinos Daskalakis, Associate Professor at MIT's Electrical Engineering and Computer Science department.
*George Karniadakis, Professor of Applied Mathematics at Brown University; also Research Scientist at MIT
*John Aniston (Giannis Anastasakis), Greek-American actor, father of Jennifer Aniston
*George Psychoundakis, a shepherd, a war hero and an author.
* Ahmed Resmî Efendi: 18th-century Ottoman statesman, diplomat and author (notably of two sefâretnâme). Turkey's first-ever ambassador in Berlin (during the reign of Frederick the Great). He was born into a Muslim family of Greek people, Greek descent in the Cretan town of Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants ( ...
in 1700.Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thr ...
.
* Ismail Fazil Pasha (1856–1921): descended from the rooted Cebecioğlu family of Söke who had settled in Crete. He has been the first Minister of Public Works in the government of Grand National Assembly of Turkey, Grand National Assembly in 1920. He was the father of Ali Fuat Cebesoy, Ali Fuad and Mehmet Ali Cebesoy, Mehmed Ali.
* Mehmet Atıf Ateşdağlı (1876–1947): Turkish officer.
* Mustafa Ertuğrul Aker (1892–1961): Turkish officer who sank HMS Ben-my-Chree.
* Cevat Şakir Kabaağaçlı, alias ''Halikarnas Balıkçısı'' (The Fisherman of Halicarnassus), writer, although born in Crete and has often let himself be cited as Cretan, descends from a family of Ottoman aristocracy with roots in Afyonkarahisar. His father had been an Ottoman High Commissioner in Crete and later ambassador in Athens. *Likewise, as stated above, Mustafa Naili Pasha was Albanians, Albanian/Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
ian.
* Bülent Arınç (born 25 May 1948) has been a Deputy Prime Minister of Turkey since 2009. He is of Cretan Muslim heritage with his ancestors arriving to Turkey as Cretan refugees during the population exchange between Greece and Turkey at the time of Sultan Abdul Hamid II and is fluent in Cretan Greek. Arınç is a proponent of wanting to reconvert the Hagia Sophia into a mosque, which has caused diplomatic protestations from Greece.Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
, Crete.
See also
* Cretan Greek
* Cretan lyra
* Cretan Turks
* Cretan wine
* List of novels set in Crete
* List of rulers of Crete
* Mantinada, Mantinades
Citations
General and citied sources
*
* Francis, Jane and Anna Kouremenos (eds.) 2016. ''Roman Crete: New Perspectives''. Oxford: Oxbow.
*
*
*
*
External links
*
Natural History Museum of Crete
at the University of Crete.
Cretaquarium Thalassocosmos
in Heraklion.
Aquaworld Aquarium
in Hersonissos.
Ancient Crete
at Oxford Bibliographies Online: Classics.
Official Greek National Tourism Organisation website
Interactive Virtual Tour of Crete
{{Authority control
Crete,
Aegean islands
Crete and Cyrenaica
Islands of Greece
Mediterranean islands
Minoan geography
Territories of the Republic of Venice



 Crete is the largest island in Greece and the fifth largest island in the
Crete is the largest island in Greece and the fifth largest island in the  A large number of islands, islets, and rocks hug the coast of Crete. Many are visited by tourists, some are only visited by
A large number of islands, islets, and rocks hug the coast of Crete. Many are visited by tourists, some are only visited by 
 Hominids settled in Crete at least 130,000 years ago. In the later Neolithic and Bronze Age periods, under the Minoans, Crete had a highly developed, literate civilization. It has been ruled by various ancient Greek entities, the
Hominids settled in Crete at least 130,000 years ago. In the later Neolithic and Bronze Age periods, under the Minoans, Crete had a highly developed, literate civilization. It has been ruled by various ancient Greek entities, the  Crete was separated from Cyrenaica . It remained a province within the eastern half of the Roman Empire, usually referred to as the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire after the establishment of a second capital in Constantinople by Constantine in 330. Crete was subjected to an attack by
Crete was separated from Cyrenaica . It remained a province within the eastern half of the Roman Empire, usually referred to as the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire after the establishment of a second capital in Constantinople by Constantine in 330. Crete was subjected to an attack by  In the 820s, after 900 years as a Roman island, Crete was captured by Andalusian Muwallads led by
In the 820s, after 900 years as a Roman island, Crete was captured by Andalusian Muwallads led by  From 1212, during
From 1212, during 


 Following the repeated uprisings in 1841, 1858, 1889, 1895 and 1897 by the Cretan people, who wanted to join Greece, the Great powers#History, Great Powers decided to restore order and in February 1897 sent in troops. The island was subsequently garrisoned by troops from Great Britain, France, Italy and Russia; Germany and Austro-Hungary withdrawing from the occupation in early 1898. During this period Crete was governed through a committee of admirals from the remaining four Powers. In March 1898 the Powers decreed, with the very reluctant consent of the Sultan, that the island would be granted autonomy under Ottoman suzerainty in the near future.
In September 1898 the Candia massacre in Candia, modern Heraklion, left over 500 Cretan Christians and 14 British servicemen dead at the hands of Muslim irregulars. As a result, the Admirals ordered the expulsion of all Ottoman troops and administrators from the island, a move that was ultimately completed by early November. The decision to grant autonomy to the island was enforced and a High Commissioner, Prince George of Greece, appointed, arriving to take up his post in December 1898.Robert Holland and Diane Markides, ''The British and the Hellenes: Struggles for Mastery in the Eastern Mediterranean 1850–1960''. p. 81. Oxford University Press, 2005. The flag of the
Following the repeated uprisings in 1841, 1858, 1889, 1895 and 1897 by the Cretan people, who wanted to join Greece, the Great powers#History, Great Powers decided to restore order and in February 1897 sent in troops. The island was subsequently garrisoned by troops from Great Britain, France, Italy and Russia; Germany and Austro-Hungary withdrawing from the occupation in early 1898. During this period Crete was governed through a committee of admirals from the remaining four Powers. In March 1898 the Powers decreed, with the very reluctant consent of the Sultan, that the island would be granted autonomy under Ottoman suzerainty in the near future.
In September 1898 the Candia massacre in Candia, modern Heraklion, left over 500 Cretan Christians and 14 British servicemen dead at the hands of Muslim irregulars. As a result, the Admirals ordered the expulsion of all Ottoman troops and administrators from the island, a move that was ultimately completed by early November. The decision to grant autonomy to the island was enforced and a High Commissioner, Prince George of Greece, appointed, arriving to take up his post in December 1898.Robert Holland and Diane Markides, ''The British and the Hellenes: Struggles for Mastery in the Eastern Mediterranean 1850–1960''. p. 81. Oxford University Press, 2005. The flag of the  During World War II, the island was the scene of the famous Battle of Crete in May 1941. The initial 11-day battle was bloody and left more than 11,000 soldiers and civilians killed or wounded. As a result of the fierce resistance from both Allied forces and civilian Cretan locals, the invasion force suffered heavy casualties, and Adolf Hitler forbade further large-scale paratroop operations for the rest of the war. During the initial and subsequent occupation, German firing squads routinely executed male civilians in reprisal for the death of German soldiers; civilians were rounded up randomly in local villages for the mass killings, such as at the Massacre of Kondomari and the Viannos massacres. Two German generals were later tried and executed for their roles in the killing of 3,000 of the island's inhabitants.
During World War II, the island was the scene of the famous Battle of Crete in May 1941. The initial 11-day battle was bloody and left more than 11,000 soldiers and civilians killed or wounded. As a result of the fierce resistance from both Allied forces and civilian Cretan locals, the invasion force suffered heavy casualties, and Adolf Hitler forbade further large-scale paratroop operations for the rest of the war. During the initial and subsequent occupation, German firing squads routinely executed male civilians in reprisal for the death of German soldiers; civilians were rounded up randomly in local villages for the mass killings, such as at the Massacre of Kondomari and the Viannos massacres. Two German generals were later tried and executed for their roles in the killing of 3,000 of the island's inhabitants.
 Crete is one of the most popular holiday destinations in Greece. 15% of all arrivals in Greece come through the city of Heraklion (port and airport), while charter journeys to Heraklion make up abou
Crete is one of the most popular holiday destinations in Greece. 15% of all arrivals in Greece come through the city of Heraklion (port and airport), while charter journeys to Heraklion make up abou Apart from terrestrial mammals, the seas around Crete are rich in large marine mammals, a fact unknown to most Greeks at present, although reported since ancient times. Indeed, the Minoan frescoes depicting dolphins in Queen's Megaron at Knossos indicate that Minoans were well aware of and celebrated these creatures. Apart from the famous endangered Mediterranean monk seal, which lives in almost all the coasts of the country, Greece hosts whales, sperm whales, dolphins and porpoises. These are either permanent residents of the Mediterranean or just occasional visitors. The area south of Crete, known as the Greek Abyss, hosts many of them. Squid and octopus can be found along the coast and sea turtles and hammerhead sharks swim in the sea around the coast. The Cretaquarium and the Aquaworld Aquarium, are two of only three aquariums in the whole of Greece. They are located in Gournes and Hersonissos respectively. Examples of the local sealife can be seen there.Great Britons in Crete, John Bryce McLaren
Apart from terrestrial mammals, the seas around Crete are rich in large marine mammals, a fact unknown to most Greeks at present, although reported since ancient times. Indeed, the Minoan frescoes depicting dolphins in Queen's Megaron at Knossos indicate that Minoans were well aware of and celebrated these creatures. Apart from the famous endangered Mediterranean monk seal, which lives in almost all the coasts of the country, Greece hosts whales, sperm whales, dolphins and porpoises. These are either permanent residents of the Mediterranean or just occasional visitors. The area south of Crete, known as the Greek Abyss, hosts many of them. Squid and octopus can be found along the coast and sea turtles and hammerhead sharks swim in the sea around the coast. The Cretaquarium and the Aquaworld Aquarium, are two of only three aquariums in the whole of Greece. They are located in Gournes and Hersonissos respectively. Examples of the local sealife can be seen there.Great Britons in Crete, John Bryce McLaren Crete has a strong association with ancient Greek gods but is also connected with the Minoan civilization.
According to Greek mythology, the Psychro Cave, Diktaean Cave at Mount Dikti was the birthplace of the god
Crete has a strong association with ancient Greek gods but is also connected with the Minoan civilization.
According to Greek mythology, the Psychro Cave, Diktaean Cave at Mount Dikti was the birthplace of the god 
 Notable people from Crete include:
*Nikos Kazantzakis, author, born in Heraklion, 7 times suggested for the Nobel Prize
*Odysseas Elytis, poet, awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1979, born in
Notable people from Crete include:
*Nikos Kazantzakis, author, born in Heraklion, 7 times suggested for the Nobel Prize
*Odysseas Elytis, poet, awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1979, born in