Cranioplasty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cranioplasty is a
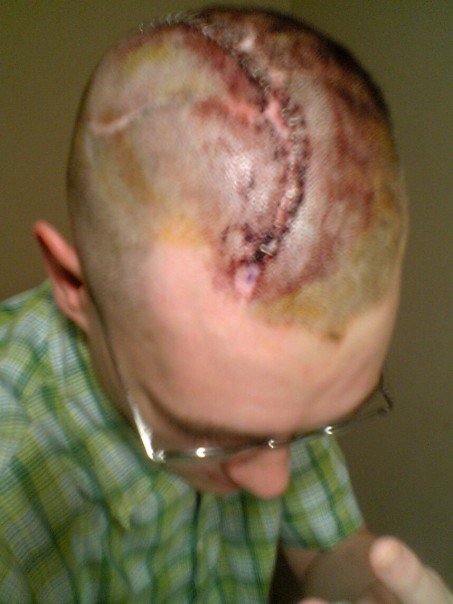 Before the operation, CT scans and
Before the operation, CT scans and
 The earliest cranioplasty operation is dated to 3000 BC in the Pre-columbian Peruvian civilisation, where precious metals, gourds, and shells were found next to trepanned skulls in graveyards, suggesting that cranioplasty had been performed. In the Paracas region of present-day
The earliest cranioplasty operation is dated to 3000 BC in the Pre-columbian Peruvian civilisation, where precious metals, gourds, and shells were found next to trepanned skulls in graveyards, suggesting that cranioplasty had been performed. In the Paracas region of present-day

surgical operation
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
on the repairing of cranial
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
defects caused by previous injuries
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or ...
or operations, such as decompressive craniectomy
Decompressive craniectomy ('' crani-'' + '' -ectomy'') is a neurosurgical procedure in which part of the skull is removed to allow a swelling brain room to expand without being squeezed. It is performed on victims of traumatic brain injury, str ...
. It is performed by filling the defective area with a range of materials, usually a bone piece from the patient or a synthetic material. Cranioplasty is carried out by incision and reflection of the scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.
Structure
The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:
* S: The ski ...
after applying anaesthetics and antibiotics to the patient. The temporalis muscle
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomati ...
is reflected, and all surrounding soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
s are removed, thus completely exposing the cranial defect. The cranioplasty flap is placed and secured on the cranial defect. The wound is then sealed.
Cranioplasty was closely related to trephination
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drill ...
and the earliest operation is dated to 3000 BC. Currently, the procedure is performed for both cosmetic and functional purposes. Cranioplasty can restore the normal shape of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
and prevent other complications caused by a sunken scalp, such as the "syndrome of the trephined". Cranioplasty is a risky operation, with potential risks such as bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of ...
and bone flap resorption.
Etymology
The word cranioplasty can be broken down into two parts: cranio- and -plasty. Cranio- originates from the AncientGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word κρανίον, meaning "cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
", while -plasty comes from the Ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word πλαστός, meaning "moulded" or "fashioned".
Medical uses
The operation has its cosmetic value as the normal shape of the cranium of patients is restored instead of the presence of a sunken skin flap, which may affect the confidence of patients. It also has its therapeutic value as the operation provides structure to the skull and protection to the brain from physical damage. The surgery restores regular cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and cerebral blood flow dynamics, along with normalintracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 Millimeter of mercury, mmHg ...
. Cranioplasty may improve neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal ...
function in some individuals. Furthermore, it can reduce the occurrence of headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
s caused by injury or previous surgery.
The optimal timing of cranioplasty is controversial among literature. Some literature stated that the time between a craniectomy
Decompressive craniectomy ('' crani-'' + '' -ectomy'') is a neurosurgical procedure in which part of the skull is removed to allow a swelling brain room to expand without being squeezed. It is performed on victims of traumatic brain injury, st ...
and a cranioplasty is usually between 6 months to a year, while others stated that the two operations should be more than a year apart.
The timing of cranioplasty is affected by multiple factors. Sufficient time is required for the recovery of the incision from the previous operation, as well as to clear any infections (both systemic and cranial). Some findings showed that a greater infection rate is associated with early cranioplasty due to interruption of wound healing, as well as an increased incidence of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor ...
. Contrarily, there is evidence of early cranioplasty limiting complications caused by "syndrome of the trephined", including changes in cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arterie ...
and abnormal cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the bra ...
hydrodynamics. Other researchers reported no significant difference in infection rate with different operational timings.
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
s are circumstances that indicate the treatment or operation should not be provided due to potential harm. Contraindications for cranioplasty include the presence of bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of ...
, brain swelling, and hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor ...
. Cranioplasty is withheld until all contraindications are cleared.
Procedure
 Before the operation, CT scans and
Before the operation, CT scans and MRIs
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wa ...
are taken to study the cranial defect. The patient is given antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection.
The patient is situated on a foam donut
Foams are materials formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid.
A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the re ...
or a horseshoe head holder
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
for the operation. The patient is then anaesthetised and an incision is made following the incision of the previous operation. The scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.
Structure
The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:
* S: The ski ...
and the temporalis muscle
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomati ...
is reflected to completely reveal the cranial defect. Significant blood loss is observed as new blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s formed in scar tissues are damaged by incision. Any soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
s at the edge of the defect are removed and the defect is cleaned. The cranioplasty material is placed on the defect and is fixed to the surrounding skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
with standard titanium plate and screws. CSF may be drained from the brain to reduce hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the gr ...
tion. Small holes may be drilled on the bone graft or the prosthesis to prevent the accumulation of fluid under the repaired defect. Soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
s, temporalis
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic a ...
, and the scalp are then fixed back in place. Subgaleal drain and dressing are applied to control facial swelling.
After the operation, a CT scan is taken and patients may stay in intensive care for at least a night for better neurological status observation, or be placed in a regular care unit. The subgaleal drain and dressing are removed before the patient is dispatched.
Children
Special considerations to children undergoing cranioplasty are made to accommodate for their growingcranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
. Certain materials are more favoured when compared to adult cranioplasty.
Autologous bone grafts are the most preferred materials for paediatric
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
cranioplasty, as they are accepted by the host and the bone flap can be integrated into the body of the host. However, autologous bone pieces may be unavailable or unsuitable in certain occasions. The body size of children may be not enough to have bone flaps to be stored in their subcutaneous spaces, while cryopreservation
Cryo-preservation or cryo-conservation is a process where Organism, organisms, organelles, cell (biology), cells, Biological tissue, tissues, extracellular matrix, Organ (anatomy), organs, or any other biological constructs susceptible to damage ...
facilities for bone grafts are not widely available. The use of autograft
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek).
The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogene ...
is also associated with a high rate of bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated ...
.
Synthetic materials are used for paediatric cranioplasty when the use of autografts
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek).
The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogene ...
is not available or not recommended. Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. ...
is another option for children cranioplasty as it allows the expansion of cranium for children and its ability to be moulded smoothly. It is less commonly used than autografts due to its brittle nature, high infection rate, and poor ability to integrate with the human cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
.
Bilateral cranioplasties are more prone to complications compared to unilateral cranioplasties in children. This may be explained by its larger scalp wound area, a higher volume of blood loss, and the higher complexity and duration of the operation.
Risks
Cranioplasty is an operation with a complication risk ranging from 15 to 41%. The cause for such a high risk of complication compared to otherneurosurgical
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peri ...
operations is unclear. Male patients and older patients are groups with higher rates of complication.
Complications occurring after cranioplasty include bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of ...
, bone flap resorption, wound dehiscence
Wound dehiscence is a surgical complication in which a wound ruptures along a surgical incision. Risk factors include age, collagen disorder such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, diabetes, obesity, poor knotting or grabbing of stitches, and trauma ...
, hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillary, capillaries. A he ...
, seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or neural oscillation, synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much o ...
, hygroma, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage.
The risk of bacterial infections in performing cranioplasty ranges from 5 to 12.8%. Multiple factors are affecting the risk of infection, one being the materials used for the operation. Using titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, whether being custom-made or using a mesh
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands.
Types
* A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, ex ...
, is associated with a lower infection rate; on the other hand, materials such as methyl methacrylate
Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA ...
and autologous bone is associated with a higher infection rate. Another risk factor for bacterial infection is the location of the operation. Bifrontal cranioplasties are associated with significantly higher infection rates and higher rates for reoperation. Other risk factors for infection include previous infections, contact between sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
and operation site, devascularized scalp (loss of blood supply in the scalp), previous operations, and type of injury.
Bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated ...
is another complication of cranioplasty with a complication rate of 0.7-17.4%. Bone resorption occurs when the autologous graft does not have blood supply due to devitalisation, or when scar tissues or soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
s remain on the edge of the cranial defect during cranioplasty. Paediatric
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
patients have a higher risk of resorption, with a resorption rate up to 50%. Bone resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood.
The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated ...
is more likely to occur in this group of patients when their cranioplasty is carried out over 6 weeks from their previous operation. Fragmented bone flaps, as well as large bone flaps (>70 cm2), are associated with a higher resorption rate.
History
Ancient history
 The earliest cranioplasty operation is dated to 3000 BC in the Pre-columbian Peruvian civilisation, where precious metals, gourds, and shells were found next to trepanned skulls in graveyards, suggesting that cranioplasty had been performed. In the Paracas region of present-day
The earliest cranioplasty operation is dated to 3000 BC in the Pre-columbian Peruvian civilisation, where precious metals, gourds, and shells were found next to trepanned skulls in graveyards, suggesting that cranioplasty had been performed. In the Paracas region of present-day Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
, a skull from 2000 BC with a thin plate of gold covering a cranial defect was found. Moreover, defective skulls were found covered with coconut shells or palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
leaves in ancient tribes of the Polynesian Islands
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
. Sanan and Haines stated that the materials being used for cranioplasty were associated with the status of the patient.
Modern history
Research on cranioplasty was not emphasised among early surgical authors in ancientAsia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, although there were research and practice on trephination
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drill ...
in ancient Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. More emphasis was placed on developing skills in applying dressing on an open wound.
The earliest modern description of cranioplasty was written by surgeon Ibrahim bin Abdullah of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, in his surgical book '' Alâim-i Cerrâhîn'' in 1505. The book mentioned the use of xenografts
Xenotransplantation (''xenos-'' from the Greek meaning "foreign" or strange), or heterologous transplant, is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another. Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenograft ...
from Kangal dogs or goats as materials for cranioplasty. Such materials were used due to the accessibility of these animals near battlefields, where the procedure is likely to be performed.
The first true description of cranioplasty in Europe was made by Fallopius
Gabriele Falloppio (also Gabrielle Falloppia) (1522/23 – 9 October 1562) was an Italian anatomist often known by his Latin name Fallopius. He was one of the most important anatomists and physicians of the sixteenth century, giving his name to ...
in the 16th century, stating that the fractured cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
should be removed and be reinserted with a gold plate if the dura was damaged. This was questioned by other practitioners at his time, concerning that surgeons may keep the gold instead of using it for surgery. The first cranioplasty was reported by the Dutch surgeon Job Janszoon van Meekeren. The report described the use of a segment of a canine cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
as a material for cranioplasty on a nobleman
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
. The operation was successful, however, the use of canine bone in the operation was not accepted by the church and the man was forced to leave Russia.
Since the first operation, bones from more animal species were used as xenografts for cranioplasty. These include dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Do ...
s, ape
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and as well as Europe in prehistory), which together with its sister g ...
s, geese
A goose (plural, : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family (biology), family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera ''Anser (bird), Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some o ...
, rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit speci ...
s, calves, eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
s, oxen, and buffalos. In 1917, William Wayne Babcock reported the use of "soup bone", a piece of cooked and perforated
A perforation is a small hole in a thin material or web. There is usually more than one perforation in an organized fashion, where all of the holes collectively are called a ''perforation''. The process of creating perforations is called perfor ...
animal bone as a xenograft.
Development of modern materials
The prevalence ofhead injuries
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
increased in the 20th century with the advancement of armaments, particularly the use of hand grenades
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade ge ...
in trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became a ...
during World War I (WWI). Along with a decreased mortality from suffering such injuries due to the development of cell debris removal, wound closing, and the use of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s, cranioplasty techniques were therefore improved. Autografts
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek).
The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogene ...
, allografts and synthetic materials are the main types of materials used for cranioplasty.

Autografts
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek).
The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogene ...
, or autologous grafts, are body tissues taken from the patient. The first successful cranioplasty using an autograft was recorded in 1821, with the bone piece being reinserted into the cranium. The operation achieved partial healing. Subsequently, more studies and operations were carried out with autografts. A successful case of reimplantation of cranial bone was reported by Sir William Macewen
Sir William Macewen, (; 22 June 1848 – 22 March 1924) was a Scottish surgeon. He was a pioneer in modern brain surgery, considered the ''father of neurosurgery'' and contributed to the development of bone graft surgery, the surgical trea ...
in 1885, popularising autografts to be material for cranioplasty. Succeeding operations involved autografts taken from different parts of the patient's body, such as the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
(leg bone), scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
(shoulder blade), ilium (hip bone), sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sh ...
(chest bone), along with fat tissues and fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. ...
.
Allografts are tissues from another individual of the same species. The first use of allografts was reported in 1915 with cadaver
A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Stud ...
cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck an ...
by Morestin. Subsequently, another 32 cases of cranioplasties performed with cadaver cartilage were reported by Gosset in 1916. The use of cadaver
A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Stud ...
cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck an ...
was favoured during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
due to its malleability
Ductility is a List of materials properties, mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to Drawing (manufacturing), drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a materia ...
and resistance to infection. Its use declined because of its lack of significant calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Mat ...
and strength. Cadaver
A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Stud ...
skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
was another type of allograft reported to be used as a cranioplasty material multiple times by Sicard and Dambrin from 1917 to 1919. The material was not favoured due to the high infection rate with its use. In the 1980s, the use of cadaver allograft disc for filling in small holes received a satisfactory result, and there was a resurgence of the use of cadaver
A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Stud ...
bone. However, cadaver bones and allografts, in general, are not the preferred materials in modern operations.
The use of methyl methacrylate (PMMA) for cranioplasty was being developed since World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and the material is used extensively since 1954, when there is a high demand for cranioplasty due to a large number of injuries. It becomes malleable when an exothermic reaction
In thermochemistry, an exothermic reaction is a "reaction for which the overall standard enthalpy change Δ''H''⚬ is negative." Exothermic reactions usually release heat. The term is often confused with exergonic reaction, which IUPAC defines ...
occurs between its powder form and benzoyl peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide is a chemical compound (specifically, an organic peroxide) with structural formula , often abbreviated as (BzO)2. In terms of its structure, the molecule can be described as two benzoyl (, Bz) groups connected by a peroxide () ...
, allowing it to be moulded to the cranial defect. Advantages of using PMMA is its malleability, low cost, high strength and high durability. Its disadvantages include being vulnerable to infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
as bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
may adhere to its fibrous
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a #Natural fibers, natural or Fiber#Artificial fibers, artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The stronge ...
layer, as well as its brittle nature and having no growth potential.
Other common synthetic materials for cranioplasty include titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
and hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. ...
. Titanium was first used for cranioplasty in 1965. It can be used as a plate, a mesh, and be 3D printed as a porous form. Titanium is non-ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials ...
and non-corrosive
A corrosive substance is one that will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact by means of a chemical reaction.
Etymology
The word ''corrosive'' is derived from the Latin verb ''corrodere'', which means ''to gnaw'', ...
, making the host free from inflammatory reactions. It is also robust, thus preventing patients from trauma. The use of titanium is associated with a lower infection rate. Disadvantages of using titanium include its high cost, poor malleability, and disruption to CT scan images.
Hydroxyapatite is a compound of calcium phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white ...
being arranged in a hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexa ...
al structure. It bonds well chemically with bones and inflicts little inflammatory reaction by the host, and has good osteointegration. It can be expanded and is used in paediatric
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
cranioplasty. It can be moulded smoothly and has appealing cosmetic results. However, the material is brittle and has low tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
, and is only suitable to be used for small cranial defects. Its use is also associated with a high infection rate. Hydroxyapatite is often used with a titanium mesh to prevent fractures and for better osteointegration.
See also
*Human cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
* Craniotomy
A craniotomy is a surgical operation in which a bone flap is temporarily removed from the skull to access the brain. Craniotomies are often critical operations, performed on patients who are suffering from brain lesions, such as tumors, blood clot ...
* Decompressive craniectomy
Decompressive craniectomy ('' crani-'' + '' -ectomy'') is a neurosurgical procedure in which part of the skull is removed to allow a swelling brain room to expand without being squeezed. It is performed on victims of traumatic brain injury, str ...
* Oral and maxillofacial surgery
* Plastic surgery
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofa ...
* Craniofacial surgery
Craniofacial surgery is a surgical subspecialty that deals with congenital disorder, congenital and acquired deformity, deformities of the human head, head, human skull, skull, face, neck, jaws and associated structures. Although craniofacial treat ...
References
{{Central nervous system tests and procedures Neurosurgical procedures Body modification Oral and maxillofacial surgery