|
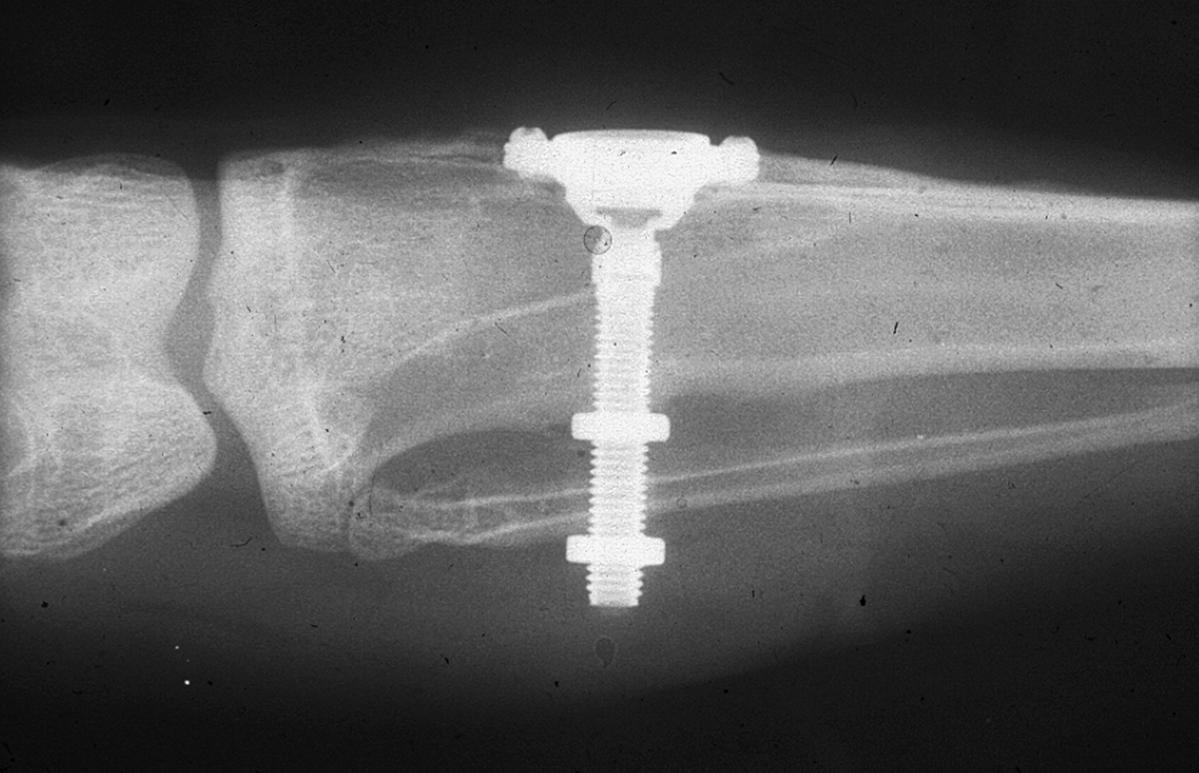
Osteointegration
Osseointegration (from Latin ''osseus'' " bony" and ''integrare'' "to make whole") is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing artificial implant ("load-bearing" as defined by Albrektsson et al. in 1981). A more recent definition (by Schroeder et al.) defines osseointegration as "functional ankylosis (bone adherence)", where new bone is laid down directly on the implant surface and the implant exhibits mechanical stability (i.e., resistance to destabilization by mechanical agitation or shear forces). Osseointegration has enhanced the science of medical bone and joint replacement techniques as well as dental implants and improving prosthetics for amputees. Definitions Osseointegration is also defined as: "the formation of a direct interface between an implant and bone, without intervening soft tissue". An osseointegrated implant is a type of implant defined as "an endosteal implant containing pores into which osteo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osseoincorporation
Osseoincorporation refers to the healing potential of bone onto an implant surface and into an implant structure. Three-dimensional, porous implantable materials used in the orthopedic and dental implant industries offer the potential for ingrowth as well as ongrowth or osseoincorporation. Comparison to osseointegration Conventional textured or coated implant surfaces are designed to achieve bone-to-implant contact, which is called ''ongrowth''. Per-Ingvar Brånemark defined this ongrowth phenomenon, osseointegration, as "the direct structural and functional connection between ordered, living bone and the surface of a load-carrying implant." In the case of dental implants, they osseointegrate. Porous implantable materials are designed for bone to grow not only onto the material but also into its pores, and in some cases interconnecting within the material’s structure, in a process called ''osseoincorporation''. Complications In some cases, the patient has periodontal defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthesis
In medicine, a prosthesis (plural: prostheses; from grc, πρόσθεσις, prósthesis, addition, application, attachment), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (congenital disorder). Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools. Types A person's prosthesis should be designed and assembled according to the person's appearance and functional needs. For instance, a person may need a transra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percutaneous
{{More citations needed, date=January 2021 In surgery, a percutaneous procedurei.e. Granger et al., 2012 is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using an "open" approach where inner organs or tissue are exposed (typically with the use of a scalpel). The percutaneous approach is commonly used in vascular procedures such as angioplasty and stenting. This involves a needle catheter getting access to a blood vessel, followed by the introduction of a wire through the lumen (pathway) of the needle. It is over this wire that other catheters can be placed into the blood vessel. This technique is known as the modified Seldinger technique. More generally, "percutaneous", via its Latin roots means, 'by way of the skin'. An example would be percutaneous drug absorption from topical medications. More often, percutaneous is typically used in reference to placement of medical devices using a need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munjed Al Muderis
Professor Munjed Al Muderis (born 1972) is an Australian Adjunct Clinical Professor in orthopaedic surgery, author and human rights activist. He has done pioneering work on prosthetics, especially on titanium devices. Al Muderis was born in Iraq and became a surgeon under the regime of Saddam Hussein. He was a medical student in Basra at the start of the Gulf War in August 1990. As a junior surgeon, he fled from Iraq following an incident in which he refused to mutilate the ears of army deserters. He traveled through Indonesia and Malaysia and reached Australia where he was kept in at an immigration detention centre near Derby, Western Australia. He was released after 10 months and carried on his career in medicine, eventually specialising in osseointegration surgery. Al Muderis wrote the book ''Walking Free'' on his experiences in Iraq, in the Australian immigration detention system, and on his career in Australia. Early life Munjed Al Muderis was born under the regime of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bofors
AB Bofors ( , , ) is a former Swedish arms manufacturer which today is part of the British arms concern BAE Systems. The name has been associated with the iron industry and artillery manufacturing for more than 350 years. History Located in Karlskoga, Sweden, the company originates from the hammer mill "Boofors", which was founded as a royal state-owned company in 1646. The modern corporate structure was created in 1873 with the foundation of Aktiebolaget (AB) Bofors-Gullspång. The Bofors Works was acquired by Johan Eberhard Geijer in 1762. It was then acquired by the latter's brother, Emanuel af Geijerstam. A leading Swedish steel producer by the early 1870s, when steel began to be used for gun manufacture in Sweden, Bofors initially sold cast and forged steel produced by the Siemens-Martin process to Finspång gun works, but soon started to expand into weapons manufacture. The company's first cannon workshop was opened in 1884. Bofors' most famous owner was Alfred Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatal Obturator
{{no footnotes, date=February 2017 The Latham Device Post Latham Nasal Alveolar Molding Device Post Insertion A palatal obturator is a prosthesis that totally occludes an opening such as an oronasal fistula (in the roof of the mouth). They are similar to dental retainers, but without the front wire. Palatal obturators are typically short-term prosthetics used to close defects of the hard/soft palate that may affect speech production or cause nasal regurgitation during feeding. Following surgery, there may remain a residual orinasal opening on the palate, alveolar ridge, or vestibule of the larynx. A palatal obturator may be used to compensate for hypernasality and to aid in speech therapy targeting correction of compensatory articulation caused by the cleft palate. In simpler terms, a palatal obturator covers any fistulas (or "holes") in the roof of the mouth that lead to the nasal cavity, providing the wearer with a plastic/acrylic, removable roof of the mouth, which aids in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Implants
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown. Success or failure of implants depends on the health of the person receiving the treatment, drugs which affect the chances of osseointegration, and the health of the tissues in the mouth. The amount of stress that will be put on the impla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Gothenburg
The University of Gothenburg ( sv, Göteborgs universitet) is a university in Sweden's second largest city, Gothenburg. Founded in 1891, the university is the third-oldest of the current Swedish universities and with 37,000 students and 6000 staff members it is one of the largest universities in the Nordic countries. About With its eight faculties and 38 departments, the University of Gothenburg is one of the most wide-ranging and versatile universities in Sweden. Its eight faculties offer training in the Creative Arts, Social Sciences, Natural Sciences, Humanities, Education, Information Technology, Business, Economics and Law, and Health Sciences. The University of Gothenburg has the highest number of applicants per study place in many of its subjects and courses, making it one of the most popular universities in Sweden. History The University of Gothenburg was founded as ''Göteborgs högskola'' (Gothenburg University College) in 1891. In 1907 it was granted the same s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist. The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine which have gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and diseases) for which reas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Per-Ingvar Brånemark
Per-Ingvar Brånemark (May 3, 1929 – December 20, 2014) was a Swedish physician and research professor, acknowledged as the "father of modern dental implantology". The ''Brånemark Osseointegration Center'' (BOC), named after its founder, was founded in 1989 in Gothenburg, Sweden. Biography After studying at Lund University in Sweden, Brånemark became professor of Anatomy at Gothenburg University in 1969. Brånemark has been awarded many prizes for his work, including the coveted Swedish Society of Medicine's Soederberg Prize in 1992—often referred to as the 'mini- Nobel'—and the Swedish Engineering Academy's equally prestigious medal for technical innovation. Brånemark has also been honored with the Harvard School of Dental Medicine Medal for his work on dental implants in the United States and holds more than 30 honorary positions throughout Europe and North America, including the Honorary Fellowship of the Royal Society of Medicine in the UK. In 2003, he received an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osseointegration Histology
Osseointegration (from Latin ''osseus'' "bone, bony" and ''integrare'' "to make whole") is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing Implant (medicine), artificial implant ("load-bearing" as defined by Tomas Albrektsson, Albrektsson et al. in 1981). A more recent definition (by André Schroeder, Schroeder et al.) defines osseointegration as "functional ankylosis (bone adherence)", where new bone is laid down directly on the implant surface and the implant exhibits Mechanical properties of biomaterials, mechanical stability (i.e., resistance to destabilization by mechanical agitation or shear forces). Osseointegration has enhanced the science of medicine, medical bone and Replacement joint, joint replacement techniques as well as dental implants and improving Prosthesis, prosthetics for amputees. Definitions Osseointegration is also defined as: "the formation of a direct interface between an implant and bone, without int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |