Coronavirus Envelope Protein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The envelope (E) protein is the smallest and least well-characterized of the four major
 The E protein consists of a short
The E protein consists of a short
 The E protein is found in assembled virions where it forms protein-protein interactions with the
The E protein is found in assembled virions where it forms protein-protein interactions with the
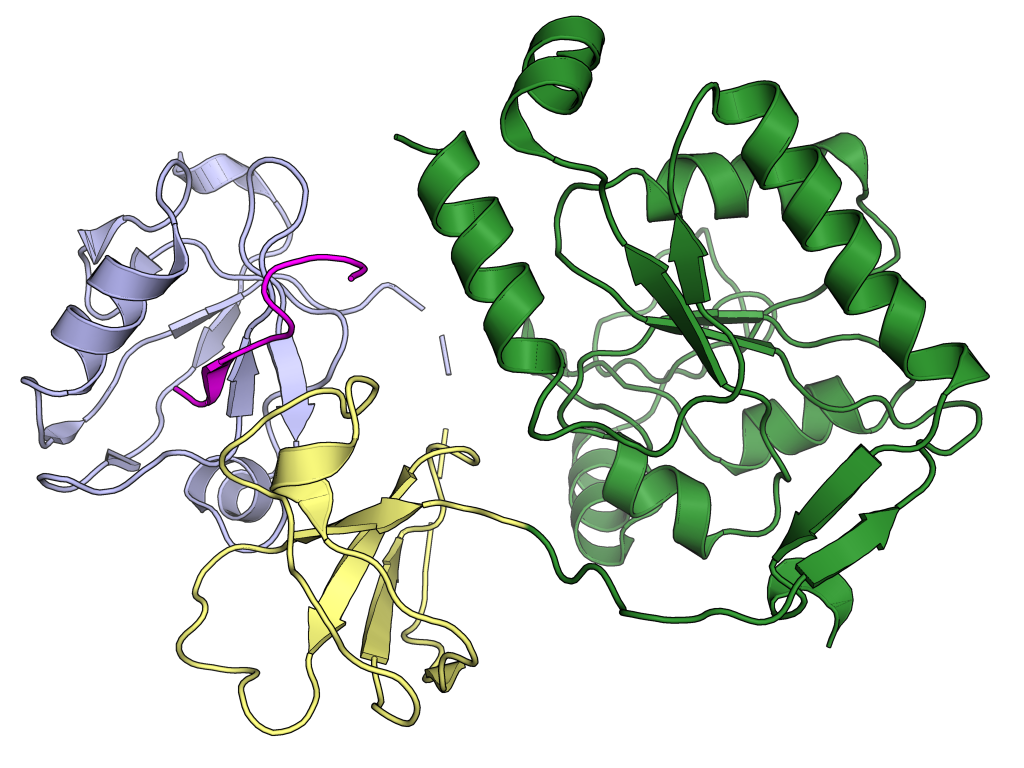 Protein-protein interactions between E and proteins in the host cell are best described in SARS-CoV and occur via the C-terminal
Protein-protein interactions between E and proteins in the host cell are best described in SARS-CoV and occur via the C-terminal
structural protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respond ...
s found in coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the com ...
virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
s. It is an integral membrane protein
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All ''transmembrane proteins'' are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a signi ...
less than 110 amino acid residues long; in SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a ...
, the causative agent of Covid-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, the E protein is 75 residues long. Although it is not necessarily essential for viral replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome an ...
, absence of the E protein may produce abnormally assembled viral capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
s or reduced replication. E is a multifunctional protein and, in addition to its role as a structural protein in the viral capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
, it is thought to be involved in viral assembly, likely functions as a viroporin
Viroporins are small and usually hydrophobic multifunctional viral proteins that modify cellular membranes, thereby facilitating virus release from infected cells. Viroporins are capable of assembling into oligomeric ion channels or pores in the h ...
, and is involved in viral pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
.
Structure
 The E protein consists of a short
The E protein consists of a short hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are no ...
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
region, a hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
helical
Helical may refer to:
* Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape
* Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive
* Helical spring, a coilspring
* Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock
* Helicoil
A t ...
transmembrane domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bil ...
, and a somewhat hydrophilic C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
region. In SARS-CoV
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for ...
and SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a ...
, the C-terminal region contains a PDZ domain
The PDZ domain is a common structural domain of 80-90 amino-acids found in the signaling proteins of bacteria, yeast, plants, viruses and animals. Proteins containing PDZ domains play a key role in anchoring receptor proteins in the membrane to ...
binding motif (PBM). This feature appears to be conserved only in the alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whic ...
and beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiod ...
coronavirus groups, but not gamma
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter re ...
. In the beta and gamma groups, a conserved proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
residue is found in the C-terminal region likely involved in targeting the protein to the Golgi.
The transmembrane helices of the E proteins of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 can oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
ize and have been shown ''in vitro'' to form pentameric structures with central pores that serve as cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
-selective ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
s. Both viruses' E protein pentamer
A pentamer is an entity composed of five sub-units.
In chemistry, it applies to molecules made of five monomers.
In biochemistry, it applies to macromolecules, in particular to pentameric proteins, made of five proteic sub-units.
In microbiol ...
s have been structurally characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic fiel ...
.
The membrane topology
Topology of a transmembrane protein refers to locations of N- and C-termini of membrane-spanning polypeptide chain with respect to the inner or outer sides of the biological membrane occupied by the protein.
Several databases provide experimenta ...
of the E protein has been studied in a number of coronaviruses with inconsistent results; the protein's orientation in the membrane may be variable. The balance of evidence suggests the most common orientation has the C-terminus oriented toward the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
. Studies of SARS-CoV-2 E protein are consistent with this orientation.
Post-translational modifications
In some, but not all, coronaviruses, the E protein ispost-translationally modified
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzyme, enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by r ...
by palmitoylation
Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine (''S''-palmitoylation) and less frequently to serine and threonine (''O''-palmitoylation) residues of proteins, which are typically lipid bilayer, memb ...
on conserved cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
residues. In the SARS-CoV E protein, one glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not al ...
site has been observed, which may influence membrane topology; however, the functional significance of E glycosylation is unclear. Ubiquitination
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
of SARS-CoV E has also been described, though its functional significance is also not known.
Expression and localization
The E protein is expressed at high abundance in infected cells. However, only a small amount of the total E protein produced is found in assembledvirion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
s. E protein is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
, Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ins ...
, and endoplasmic-reticulum–Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), the intracellular compartment that gives rise to the coronavirus viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes.
Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encase ...
.
Function
Essentiality
Studies in different coronaviruses have reached different conclusions about whether E is essential to viral replication. In some coronaviruses, includingMERS-CoV
''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (''MERS-CoV''), or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. Th ...
, E has been reported to be essential. In others, including mouse coronavirus and SARS-CoV, E is not essential, though its absence reduces viral titer, in some cases by introducing propagation defects or causing abnormal capsid morphology.
Virions and viral assembly
 The E protein is found in assembled virions where it forms protein-protein interactions with the
The E protein is found in assembled virions where it forms protein-protein interactions with the coronavirus membrane protein
The membrane (M) protein (previously called E1, sometimes also matrix protein) is an integral membrane protein that is the most abundant of the four major structural proteins found in coronaviruses. The M protein organizes the assembly of corona ...
(M), the most abundant of the four structural protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respond ...
s contained in the viral capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
. The interaction between E and M occurs through their respective C-termini on the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
ic side of the membrane. In most coronaviruses, E and M are sufficient to form virus-like particle
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are molecules that closely resemble viruses, but are non-infectious because they contain no viral genetic material. They can be naturally occurring or synthesized through the individual expression of viral structural pro ...
s, though SARS-CoV has been reported to depend on N as well. There is good evidence that E is involved in inducing membrane curvature Membrane curvature is the geometrical measure or characterization of the curvature of membranes.
The membranes can be naturally occurring or man-made (synthetic). An example of naturally occurring membrane is the lipid bilayer of cells, also known a ...
to create the typical spherical coronavirus virion. It is likely that E is involved in viral budding
Viral shedding is the expulsion and release of virus progeny following successful reproduction during a host (biology), host cell (biology), cell infection. Once replication has been completed and the host cell is exhausted of all resources in ma ...
or scission, although its role in this process has not been well characterized.
Viroporin
In itspentamer
A pentamer is an entity composed of five sub-units.
In chemistry, it applies to molecules made of five monomers.
In biochemistry, it applies to macromolecules, in particular to pentameric proteins, made of five proteic sub-units.
In microbiol ...
ic state, E forms cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
-selective ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
s and likely functions as a viroporin
Viroporins are small and usually hydrophobic multifunctional viral proteins that modify cellular membranes, thereby facilitating virus release from infected cells. Viroporins are capable of assembling into oligomeric ion channels or pores in the h ...
. This may disrupt ion homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
, alter membrane permeability
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
, and modulate pH in the host cell, which may facilitate viral release. The E protein's role as a viroporin appears to be involved in pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
and may be related to activation of the inflammasome
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein oligomers of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes proteolytic cleavage, maturation and secretion of pro-in ...
. In SARS-CoV, mutations that disrupt E's ion channel function result in attenuated pathogenesis in animal model
An animal model (short for animal disease model) is a living, non-human, often genetic-engineered animal used during the research and investigation of human disease, for the purpose of better understanding the disease process without the risk of ha ...
s despite little effect on viral growth.
Interactions with host proteins
 Protein-protein interactions between E and proteins in the host cell are best described in SARS-CoV and occur via the C-terminal
Protein-protein interactions between E and proteins in the host cell are best described in SARS-CoV and occur via the C-terminal PDZ domain
The PDZ domain is a common structural domain of 80-90 amino-acids found in the signaling proteins of bacteria, yeast, plants, viruses and animals. Proteins containing PDZ domains play a key role in anchoring receptor proteins in the membrane to ...
binding motif. The SARS-CoV E protein has been reported to interact with five host cell proteins: Bcl-xL
B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL), encoded by the BCL2-like 1 gene, is a transmembrane molecule in the mitochondria. It is a member of the Bcl-2 family of proteins, and acts as an anti-apoptotic protein by preventing the release of mitochondr ...
, PALS1, syntenin, sodium/potassium (Na+/K+) ATPase α-1 subunit, and stomatin
Stomatin also known as human erythrocyte integral membrane protein band 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STOM gene.
Clinical significance
Stomatin is a 31 kDa integral membrane protein, named after the rare human haemolytic ana ...
. The interaction with PALS1 may be related to pathogenesis via the resulting disruption in tight junction
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
s. This interaction has also been identified in SARS-CoV-2.
Evolution and conservation
The sequence of the E protein is not well conserved across coronavirus genera, with sequence identities reaching under 30%. In laboratory experiments onmouse hepatitis virus
Murine coronavirus (M-CoV) is a virus in the genus ''Betacoronavirus'' that infects mice. Belonging to the subgenus ''Embecovirus'', murine coronavirus strains are enterotropic or polytropic. Enterotropic strains include mouse hepatitis virus (M ...
, substitution of E proteins from different coronaviruses, even from different groups, could produce viable viruses, suggesting that significant sequence diversity can be tolerated in functional E proteins. The SARS-CoV-2 E protein is very similar to that of SARS-CoV, with three substitutions and one deletion. A study of SARS-CoV-2 sequences suggests that the E protein is evolving relatively slowly compared to other structural proteins. The conserved nature of the envelope protein among SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 variants has led it to be researched as a potential target for universal coronavirus vaccine
A universal coronavirus vaccine, also known as a pan coronavirus vaccine, is a theoretical coronavirus vaccine that would be effective against all coronavirus strains. A universal vaccine would provide protection against coronavirus strains that ...
development.
References
{{Viral proteins Coronavirus proteins Viral protein class Viral structural proteins